Pseudo Relevance Feedback Technique and Semantic Similarity for
Corpus-based Expansion
Masnizah Mohd
1
, Jaffar Atwan
2
and Kiyoaki Shirai
1
1
Japan Advanced Institute of Science and Technology, 1-1 Asahidai, Nomi, Ishikawa, 923-1292, Japan
2
Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia, 43600, Bangi, Selangor, Malaysia
Keywords: Query Expansion, Pseudo Relevance Feedback, Semantic, Information Retrieval, Arabic.
Abstract: The adaptation of a Query Expansion (QE) approach for Arabic documents may produce the worst rankings
or irrelevant results. Therefore, we have introduced a technique, which is to utilise the Arabic WordNet in the
corpus and query expansion level. A Point-wise Mutual Information (PMI) corpus-based measure is used to
semantically select synonyms from the WordNet. In addition, Automatic Query Expansion (AQE) and Pseudo
Relevance Feedback (PRF) methods were also explored to improve the performance of the Arabic information
retrieval (AIR) system. The experimental results of our proposed techniques for AIR shows that the use of
Arabic WordNet in the corpus and query level together with AQE, and the adaptation of PMI in the expansion
process have successfully reduced the level of ambiguity as these techniques select the most appropriate
synonym. It enhanced knowledge discovery by taking care of the relevancy aspect. The techniques also
demonstrated an improvement in Mean Average Precision by 49%, with an increase of 7.3% in recall in
comparison to the baseline.
1 INTRODUCTION
Ambiguity is the foremost challenge in Query
Expansion (QE) for the Arabic language. It is not
uncommon for different possible translations of a
word to have very different meanings, and because of
its rich and complex morphology, Arabic is notorious
for its morphological ambiguity (Attia, 2007). In light
of the foregoing, it is clear that the developers of
Arabic information retrieval systems need to consider
the issues associated with QE. One of the main
problems faced by web search engines in the Middle
East is that there are very few Arabic Web pages with
valuable information; this can clearly be seen in the
case of the free encyclopedia (Wikipedia), which
enables Internet users to create and edit different
articles, where the Arab contribution does not even
exceed 1%, at best (Al-Kabi et al., 2012).
Furthermore, from their evaluation of Google queries
based on language preferences (Al-Eroud et al.,
2011), it can be concluded that, if an Arabic query is
submitted in Arabic, and if there are many relevant
popular pages in English, it is not justifiable for
Google to retrieve such popular pages, even if they
are in English and the query is in Arabic.
Furthermore, Arabic users prefer to use English terms
instead of Arabic ones in their queries. Although there
is no QE technique that fully meets human requirements
in finding a quick and efficient query, use of the
expansion technique has become an urgent necessity due
to the differences between the languages spoken in the
world’s communities and the vast developments that
have occurred in the World Wide Web since each
technique demonstrates its own advantages and
disadvantages.
In this work, a technique for query result
expansion is introduced in which the query results,
rather than the query, are expanded. In our proposed
method, a query is submitted and the system retrieves
a set of expanded related documents. For the queries,
we used the TREC-2001 Arabic dataset corpus and its
25 queries. We expanded the relevant documents
using an Arabic WordNet (AWN) (Al Ameed et al.,
2006). We also used a Pointwise Mutual Information
(PMI) method, using data collected via Information
Retrieval (PMI-IR) as a corpus-based measure of the
semantic similarity of words (Turney, 2011).
Therefore, the contributions of this work are:
i. The proposal of an automatic corpus-based
expansion technique. This technique uses a
PRF expansion technique and the Arabic
WordNet based on available synsets of terms
Mohd, M., Atwan, J. and Shirai, K..
Pseudo Relevance Feedback Technique and Semantic Similarity for Corpus-based Expansion.
In Proceedings of the 7th International Joint Conference on Knowledge Discovery, Knowledge Engineering and Knowledge Management (IC3K 2015) - Volume 1: KDIR, pages 445-450
ISBN: 978-989-758-158-8
Copyright
c
2015 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reser ved
445
as a semantic resource to select expansion
terms.
ii. The development of an effective approach that
applies a PMI-IR semantic similarity measure
with an automatic corpus-based expansion
technique to select the most appropriate
expansion terms in order to disambiguate
word senses. The proposed Corpus-based
Expansion using the Pseudo Relevance
Feedback and Semantic Similarity
(CEPRFSS) approach has improved the
performance of the AIR framework.
The rest of the paper is organised as follows:
Section 2 highlights the related work; Section 3
explains the methodology; Section 4 discusses the
result; and finally, Section 5 concludes this study.
2 RELATED WORK
Previously mentioned methods in literature did not
fully consider the semantic relations between terms
and expanded terms in query, which has led to the
failure of improving retrieval effectiveness (Hoseini,
2011; Jarrar, 2011) However methods involving
automatic relevance feedback query expansion
successfully improved retrieval effectiveness (Liu et
al., 2004). Thus, we have proposed an approach to
build and find the best co-occurrence relationship
between terms.
In light of the foregoing, it is clear that QE can be
and in fact has been addressed using a variety of
different approaches. Here, the focus has been on the
application of these approaches in AIR problems,
taking special note of how these approaches might be
suitable in dealing with specific features of the Arabic
language. At the moment, the TREC 2001 corpus is
the most popular in terms of Arabic text IR and is
adequate enough to be considered for system
evaluation. However, researchers face problems with
stop-word lists in the pre-processing process since
there is no standard one. So, researchers have resorted
to creating their own lists. Text normalisation is
another problem that affects AIR because there are no
standard steps for researchers to follow; therefore,
researchers create and follow their own normalisation
steps.
The stemming process is very important for highly
morphological languages such as the Arabic language
because it impacts AIR in terms of removing
inappropriate affixes (Attar & Fraenkel, 1977). Here
too, there is no standardisation as researchers use
different set of affixes with different lengths. As we
have seen in this study, different approaches and
different challenges have led researchers to seek to
achieve different sets of objectives, making it difficult
to perform comparisons in many cases. However,
difficulties in comparisons are also real in many of
the studies. Most researchers’ evaluations focus on
the expansion of their own collected texts. There is
very little work on the expansion of standard corpora,
particularly those that describe much of the
information found on the Internet, where expansion is
in demand (Menai & Alsaeedan, 2012; Otair et al.,
2013). Usually, researchers test their expansion
techniques using recall, precision, average recall,
average precision, mean average precision, and the f-
measure, which are evaluation measures commonly
used in the research and development of IR
technology. Query expansion techniques were tested
as well (Mitra et al., 1998). All these processes were
combined and incorporated into the different phases
of the standard IR framework and the additional
phases to support Arabic text retrieval were also taken
into account in the enhanced framework. We used
TREC 2001 corpus and queries based on previous
researches (Larkey et al., 2002; Taghya et al., 2005).
3 METHODOLOGY
We used one Arabic test corpus, the Arabic Newswire
from the Linguistic Data Consortium (LDC), which
has also been used in recent TREC experiments. This
corpus is composed of articles from the Agence
France Presse (AFP) Arabic Newswire service. The
source material was tagged using a TIPSTER style
SGML and was transcoded to Unicode (UTF-8). The
corpus includes articles from 13 May 1994 to 20
December 2000. The data is stored in 2337
compressed Arabic text data files. There are 209
Mbytes of compressed data (869 Mbytes
uncompressed) consisting of 383 872 documents
containing 76 million tokens of over approximately
666 094 unique words. The query set associated with
the LDC corpus was created for TREC 2001. There
are 25 topics with relevance judgements [14],
available in Arabic, French and English, with Title,
Description, and Narrative fields. We used the Arabic
titles and descriptions as queries in our monolingual
experiment. Queries, which are also called “topics" in
the TREC 2001, have special SGML mark-up tags. A
total of 25 queries were defined as part of the TREC
2001.
We applied a corpus-based expansion method
using the PRF technique and semantic similarity
using WordNet. The enhancement of the initial
retrieved result is an important step in retrieving more
KDIR 2015 - 7th International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Information Retrieval
446
of the documents that did not appear in the initial
result. The query expansion technique is an important
approach that is used to enhance the performance of
any retrieval system. An automatic query expansion
(i.e., without user interaction) was also used. The
expansion technique consists of two stages.
A. First Stage: Corpus-based Expansion using PRF
(CEPRF)
The first stage is based on the PRF technique and is
applied to the initial retrieved document result from
the initial query submission. The first stage is called
the Corpus-based Expansion using Pseudo Relevance
Feedback (CEPRF) technique. The general procedure
of this step is:
• Step 1: The terms are selected from the top n-
ranked document after the query ‘Q’ is submitted
for the first time.
• Step 2: The synonym(s) for all the terms from the
top n documents are selected from WordNet.
• Step 3: The new query of the selected synonyms
from step 2, Q’, is constructed.
• Step 4: The difference between the retrieved
documents of Q’ and the result of the original Q
are added to the final result.
B. Second Stage: Corpus-based Expansion using
PRF and Semantic Similarity (CEPRFSS)
The second stage is a modified version of stage one,
which is based on the PRF technique, the Arabic
WordNet, and the semantic similarity measure. It is
called CEPRFSS. The general procedure is:
• Step 1: The terms are selected from the top n
ranked document after the query ‘Q’ is submitted
for the first time.
• Step 2: The synonym(s) for all terms from the top
n documents is (are) selected from WordNet.
• Step 3: The PMI_IR scores between each term
and its corresponding synonym(s) are calculated.
• Step 4: The synonym of the highest PMI-IR score
i.e., the highest semantic relationship is selected.
• Step 5: The new query of selected synonyms
from step 4, Q’, is constructed.
• Step 6: The difference between the retrieved
documents of Q’ and the result of the original Q
are added to the final result.
The goal of this approach is to retrieve more
relevant documents for the user query. To achieve
this, the system provides an approach to deal with
expansion terms. After checking the semantic
similarity between the documents’ terms and their
corresponding synonyms, only the highest similarity
is accepted.
The current release of AWN contains 11 270
Arabic synsets (vs. 115 000 synsets for English
WordNet) and 23 496 Arabic words (vs. 200 000
words for English WN). It also contains entries that
are named entities (1142 synsets and 1648 words).
The AWN ontology contains different relations
between its items such as hyperonymy/hyponymy
(supertypes/subtypes relations), synonymy,
meronymy/holonymy part/whole relations), etc. Our
semantic expansion approach uses synonyms. The
idea of this research is to apply our semantic
expansion process to acquire new documents related
to the top-ranked documents. Then, we add these
documents to the documents’ retrieved result to store
data relevant to the user query. In this study, we built
a stem-semantic relationship via the following steps:
Step 1: After normalisation and tokenisation, the
tokenised, non-stop-word words from each document
are sent to WordNet so the corresponding synonym(s)
can be searched. Simultaneously, the same word is
sent to the stemmer for stemming. If any synonym(s)
is available for this word in WordNet, we save the
synonym(s) in a database, as shown in Table 1.
Table 1: Sample of document terms’ stem with the available
synonym(s) from WordNet.
Document Name Term Synonym
19980923_AFP_ARB
.0118.txt
(strange) (odd/typical)
19980923_AFP_ARB
.0118.txt
19980923_AFP_ARB
.0118.txt
(foreign)
19980923_AFP_ARB
.0118.txt
(wondrous)
19980923_AFP_ARB
.0118.txt
(slave) (odalisque)
19980923_AFP_ARB
.0118.txt
(servant)
Step 2: To select the most appropriate semantically-
related synonym for the document term, we used a
semantic similarity measure to find the value of
similarity between each term, followed by a corpus-
based semantic similarity measure to find the
corresponding synonym. Turney (2011) suggested
using the Pointwise Mutual Information with data
collected via Information Retrieval (PMI-IR), as an
unsupervised measure for the evaluation of the
semantic similarity of words (i.e., the semantic
similarity between the term and the corresponding
synonym). These data are based on word co-
occurrence using the counts collected over a large
Pseudo Relevance Feedback Technique and Semantic Similarity for Corpus-based Expansion
447
corpora (e.g., the Web). The semantic similarity
measure between the term and the corresponding
synonym scores are computed as follows:
• Given two words w1 and w2, their PMI-IR is
measured as:
PMI-IR(
;
) log
p
(
&
)
p
(
)*p(
)
(1)
where w1 is the term, w2 is the corresponding
synonym, and p(w1) is the number of times the term
(w1) appears in the corpus. p(w2) is the number of
times the synonym (w2) appears in the TREC.
p(w1&w2) is the number of times both (term,
synonym) appear together in the TREC-2001.
• After the PMI-IR is calculated for each term and
its corresponding synonym(s), the synonym of
the highest PMI-IR score is selected. Table 2
shows the synonyms of the terms that have the
highest PMI-IR score, previously presented in
Table 1.
Table 2: Example of
PMI-IR score for Arabic terms and its
synonym.
Term (w1) Synonym (w2) PMI-IR
4.969
0.512
The Arabic WordNet was used to provide the
semantic relationship between the terms in the
expansion process.
4 RESULTS
In the experiment, the retrieval result of a typical
baseline IR system (Atwan et al., 2014) is compared
against the retrieval achieved by stemming, and after
expansion. Four experiments were executed. Based
on previous work (Atwan et al., 2014), two runs were
carried out: Baseline without stemming (Baseline);
and Baseline with a Light10 stemmer with a
combined stop-words list (LCS). The other two runs
that were executed were the Corpus-based Expansion
using Pseudo Relevance Feedback (CEPRF); and the
Corpus-based Expansion using Pseudo Relevance
Feedback and Semantic Similarity (CEPRFSS) runs.
The CEPRFSS used PMI-IR as the semantic
similarity measure whereas the CEPRF did not.
Recall and precision measures were used to evaluate
all four runs. The retrieval results were analysed by
calculating the differences between the different runs
using the Mean Average Precision (MAP) and F-
measure techniques.
Method based on automatic query expansion
Pseudo-Relevance Feedback technique and word
sense disambiguation using WordNet was applied. In
this case, we did not expand the original query itself;
we expanded the retrieved documents instead. The
concept behind this step is to automatically find more
relevant data for the user query without user
intervention.
The results demonstrate the usefulness of the
integration of the expansion technique with the AIR.
The output results obtained from the experiments
consisted of recall and precision measurements.
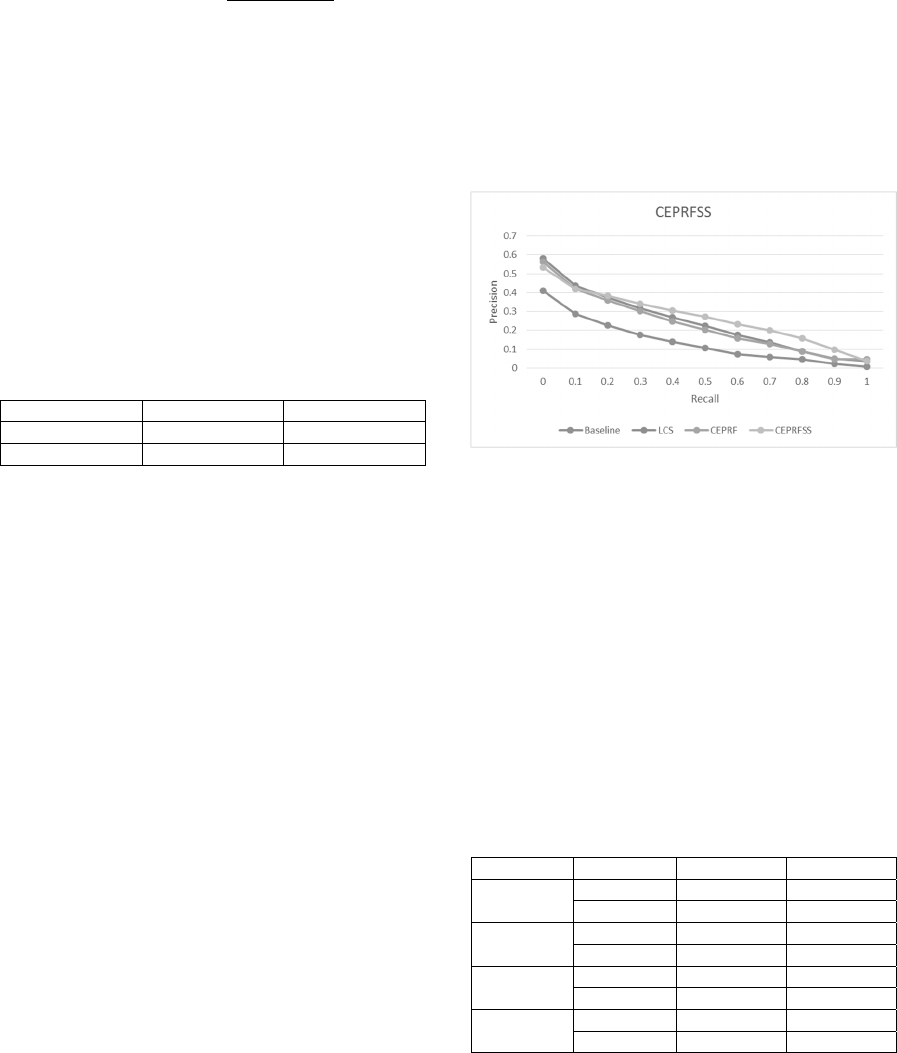
Figure 1 shows the 11-point precision graph for
Baseline, LCS, CEPRF, and CEPRFSS.
Figure 1: 11-point precision graph for Baseline, LCS,
CEPRF, and CEPRFSS.
In the evaluation phase, four runs were tested.
Based on previous work, a total of four runs were
performed, namely, (1) baseline without stemming;
(2) LCS; (3) CEPRF; and (4) CEPRFSS. Our
expansion technique was used with a PMI-IR
measure for synonym selection. The results obtained
from the system are then used to achieve recall and
precision. The retrieval results were analysed using
MAP, which calculates the differences between the
four runs as shown in Table 3. The best results were
obtained when the semantic similarity measure was
used to select the best synonym.
Table 3: Four runs with a Light10 stemmer.
Runs Metrics Value F-Measure
Baseline
MAP 0.162
Recall 0.468 0.241
LCS
MAP 0.255
Recall 0.488 0.335
CEPRF
MAP 0.249
Recall 0.498 0.332
CEPRFSS
MAP 0.293
Recall 0.502 0.370
KDIR 2015 - 7th International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Information Retrieval
448
The performances of the F1 measure for LCS and
CEPRF were quite similar. The reasons for these
results are because: (1) the expansion is recall-
oriented and the CEPRF directly uses AWN
synonyms in the expansion process, which may bring
about uncertainty. For example, the term ‘’, which
means ‘sort’ has many synonyms such as ‘’, which
means ‘universe’ and ‘format’. Because of this, the
expansion terms will affect the number of retrieved
documents (it will be increased) but the similarity to
the queries will be low. So the new related documents
to the queries will have low similarity; (2) the
elimination of stop-words improves the precision,
which reduces the appearance of the most frequent
words and the ones that do not have meaning.
The best results were obtained when the semantic
similarity measure was used to select the best
synonym
. The results show that our proposed
approach is effective in expanding the results and
disambiguating word senses. This automatic
expansion technique (CEPRFSS) based on PRF and
semantic similarity measure using AWN achieved the
best result in comparison to the other two systems i.e.,
LCS and CEPRF.
Building the Stem-Semantic relationship process
based on the terms in the TREC-2001 and the
synonyms in the Arabic WordNet with a semantic
similarity measure has improved AIR performance.
The use of the Arabic WordNet and the semantic
expansion is in line with the work of other
researchers. However, this improvement in expansion
is limited to the available synonyms of the terms in
the TREC-2001 and are further restricted to the small
size of the Arabic WordNet relations. Experiments
that have used the expansion technique showed that
the overall results exhibited improvement in retrieval
effectiveness in terms of MAP by 49% and without
degradation in recall compared to the baseline. In
addition, the result in terms of recall was also
improved by 7.3%.
5 CONCLUSIONS
This work presents two proposed approaches as
automatic expansion techniques. The first approach is
based on corpus and the PRF technique using the
Arabic WordNet to select the expansion terms, in
which the relationship among the candidate
expansion terms and the corresponding synonyms are
identified using corpus-based semantic similarity
measurements that are based on their co-occurrence
distributions. The second approach is that of
automatic query expansion, for which we jointly use
the Arabic WordNet and the PRF technique with
semantic similarity measurement to confirm the
newly expanded query terms. To overcome the
limitation of the semantic synonym selection from
WordNet, a corpus-based semantic similarity
measurement is also used. The expansion approach
has an important function in this system; it is the heart
of this retrieval system, utilising knowledge regarding
the synonyms from the Arabic WordNet based on
available synsets of terms as a semantic resource to
select expansion terms and expanded terms so as to
add suitable and relevant documents for the user
query. The CEPRFSS is an effective approach that
applies the PMI-IR semantic similarity measure with
the automatic corpus-based expansion technique to
select the most appropriate expansion terms to
disambiguate word senses. Overall, this approach has
improved the AIR performance.
REFERENCES
Al Ameed, H. K., Al Ketbi, S. O., Al Kaabi, A. A., Al
Shebli, K. S., Al Shamsi, N. F., Al Nuaimi, N. H. & Al
Muhairi, S. S. 2006. Arabic Search Engines
Improvement: A New Approach Using Search Key
Expansion Derived from Arabic Synonyms Structure.
6th International Conference on Innovations in
Information Technology, pp. 944-951.
Al-Eroud, A. F., Al-Ramahi, M. A., Al-Kabi, M. N.,
Alsmadi, I. M. & Al-Shawakfa, E. M. 2011. Evaluating
Google Queries Based on Language Preferences.
Journal of Information Science, vol. 37, pp. 282-292.
Al-Kabi, M., Wahsheh, H., Alsmadi, I., Al-Shawakfa, E.,
Wahbeh, A. & Al-Hmoud, A. 2012. Content-Based
Analysis to Detect Arabic Web Spam. Journal of
Information Science. vol. 38, pp. 284-296.
Attar, R. & Fraenkel, A. S. 1997. Local Feedback in Full-
Text Retrieval Systems. Journal of the ACM (JACM),
vol. 24, pp. 397-417.
Attia, M. A. 2007. Arabic tokenization system. Proceedings
of the 2007 Workshop on Computational Approaches
to Semitic Languages: Common Issues and Resources.
Prague, Czech Republic: Association for
Computational Linguistics, pp. 65-72.
Atwan, J., Mohd, M., Kanaan, G., Bsoul, Q. 2014. Impact
of stemmer on arabic text retrieval. The Tenth Asia
Information Retrieval Societies Conference (AIRS
2014). Sarawak, Malaysia, pp. 314-326.
Hoseini Ma-S. 2011. Modeling the arabic language through
verb based ontology. International Journal of
Academic Research; 3(3): 67-74.
Jarrar M. 2011. Building a formal arabic ontology
methodology and progress. In: Experts meeting on
Arabic Ontologies and Semantic Networks, 2011,
Alecso, Arab League, Tunis, pp. 497-503.
Pseudo Relevance Feedback Technique and Semantic Similarity for Corpus-based Expansion
449
Larkey L. S., Ballesteros L. and Connell M. E. 2002.
Improving stemming for arabic information retrieval:
light stemming and co-occurrence analysis. In: 25th
Annual International ACM SIGIR Conference on
Research and development in information retrieval,
Tampere, Finland, 11-15 Aug 2002, pp. 275-282.
Liu, S., Liu, F., Yu, C. & Meng, W. 2004. An effective
approach to document retrieval via utilizing WordNet
and recognizing phrases." Proceedings of the 27th
annual international ACM SIGIR conference on
Research and development in information retrieval.
ACM, pp. 266-272.
Menai, M. E. B. & Alsaeedan, W. 2012. Genetic Algorithm
for Arabic Word Sense Disambiguation. International
Conference on Software Engineering, Artificial
Intelligence, Networking and Parallel & Distributed
Computing (SNPD), 13th ACIS, pp. 195-200.
Mitra, M., Singhal, A. & Buckley, C. 1998. Improving
Automatic Query Expansion. Proceedings of the 21st
annual international ACM SIGIR conference on
Research and development in information retrieval, pp.
206-214.
Otair, M., Kanaan, G. & Kanaan, R. 2013. Optimizing an
Arabic Query Using Comprehensive Query Expansion
Techniques. International Journal of Computer
Applications, vol. 71, pp. 42-49.
Taghva K., Elkhoury R. and Coombs J. 2005. Arabic
stemming without a root dictionary. In: International
Conference on Information Technology: Coding and
Computing (ITCC), Las Vegas, USA, 4-6 April 2005,
pp. 152-157.
Turney, P. 2001. Mining the web for synonyms: PMI-IR
Versus LSA on TOEFL. Proceedings of the Twelfth
European Conference on Machine Learning, Freiburg,
Germany, Springer, pp. 491-502.
KDIR 2015 - 7th International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Information Retrieval
450
