The Vantage Point Bees Algorithm
Sultan Zeybek and Ebubekir Koç
Department of Computer Engineering, Fatih Sultan Mehmet Vakif University, Beyoglu, İstanbul, Turkey
Keywords: Bees Algorithm, Swarm Intelligence, Artificial Intelligence, Combinatorial Optimization, Local Search,
Vantage Point Trees, Nearest Neighbourhood Search.
Abstract: In this paper, an implementation of vantage point local search procedure for the Bees Algorithm (BA) in
combinatorial domains is presented. In its basic version, the BA employs a local search combined with
random search for both continuous and combinatorial domains. In this paper, a more robust local searching
strategy namely, vantage point procedure is exploited along with random search to deal with complex
combinatorial problems. This paper proposes a hybridization technique which involves the Bee Algorithm
(BA) and a local search technique based on Vantage Point Tree (VPTs) construction. Following a
description of the Vantage Point Bees Algorithm (VPBA), the paper presents the results obtained for several
local search strategies for BA, demonstrating efficiency and robustness of the VPBA.
1 INTRODUCTION
Many real-world engineering problems require the
searching of a system of variables in order to
optimize performance of a product and/or process.
They involve large number of finite solutions that
are encoded in real-valued variables or discrete
variables (Blum et al., 2003). A class of optimization
problems with discrete values called Combinatorial
Optimization Problems which can be defined as NP-
hard and many of them can not be solved exactly
within polynomially bounded computation times
(Pham et al., 2005).
Researchers have implemented different
strategies to deal with complex optimization
problems. Nature-inspired and population-based
metaheuristics often rely on stochastic search
methods based on swarm intelligence. They have
two major components namely: selection of the
fittest solutions and randomness (Yang, 2010).
The Bees Algorithm (BA) is one of the examples
of a nature inspired algorithm which mimics the
food foraging behaviour of honey bees. In its basic
version, the algorithm proposed a well-balanced
neighbourhood search combined with random
explorative search (Pham et al., 2005). The BA can
be used in order to solve optimization problems and
it is implemented for both continuous domains and
combinatorial domains. But research mainly focused
on continuous domains with many succesfull
applications and implementations (Pham, 2009).
There is major diffirence between these two domains
in terms of mathematical definition of distance (Koç,
2010). There are some studies present several
different local search strategies for the BA.
In this paper, an efficient and robust local search
algorithm with vantage point strategy is proposed to
increase the efficiency of the original algorithm for
combinatorial domains called the Vantage Point
Bees Algorithm (VPBA). Vantage point is a
selection procedure of a pivot element or vantage
point from metric space elements (combinatorial
search space elements) and the VPBA returns
pointer to the root of an optimized vantage point tree
algorithm with median calculations that satisfied the
local optimum value.
The paper gives brief description of bees in
nature, the BA and its local search strategy in
section 2. Section 3, gives the details of vantage
point approach in mathematical terms and presents
the VPBA with details and the advantages of using
Vantage Point Trees structures is explained. Problem
definition and experimental results presented in
section 3 and 4. The paper concluded with further
discussions in section 5.
340
Zeybek, S. and Koç, E..
The Vantage Point Bees Algorithm.
In Proceedings of the 7th International Joint Conference on Computational Intelligence (IJCCI 2015) - Volume 1: ECTA, pages 340-345
ISBN: 978-989-758-157-1
Copyright
c
2015 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

2 THE BEES ALGORITHM
2.1 Bees in Nature and Foraging
Process
Honey bees have many different behaviours to
organise the complex structure of their colony in
nature. There are several examples of these
behaviours such as waggle dance. It is basically a
language that tells the bees direction and distance of
flower patches, along with their the quality ratings
(Frisch, 1967).
One of their most complex and efficient
behaviour is foraging for food. Scout bees search
randomly from one flower patch to another for
decent nectar sources when the foraging process
begins. After scout bees turns back to hive, they
perform the waggle dance on crowded parts of hive
(namely, the dance floor) to share the information
regarding directions, distances and quality ratings of
nectar sources.
2.2 The Bees Algorithm
The BA performs a kind of local search combined
with random. It has six parameters to set; number of
scout bees (n), number of selected sites (m), number
of top-ranking (elite) sites among the m selected
sites (e), number of bees recruited for each non-elite
site (nsp), number of bees recruited for each elite
site (nep), and neighbourhood size (ngh) and the
stopping criterion. The pseudo code of the BA is
shown in Figure 1, and the main algorithm
parameters are given in Table 1.
The algorithm starts with the n scout bees
randomly sample a solution space and, via fitness
function scout bees report the quality of visited
locations. This is the part of global search procedure
where scout bees explore the solution space
randomly and increase their chance to escape from
local optima.
Step 1: Initialise population with random solutions.
Step 2: Evaluate fitness of the population.
Step 3: While (stopping criterion not met) //Forming new
population.
Step 4: Select sites for neighbourhood search.
Step 5: Recruit bees for selected sites (more bees for best
e sites) and evaluate fitnesses.
Step 6: Select the fittest bee from each patch.
Step 7: Assign remaining bees to search randomly and
evaluate their fitnesses.
Step 8: End While.
Figure 1: Pseudo code of the basic bees algorithm (Pham
et al., 2005).
The algorithm then selects best bees with fittest
results from the solution space. Then it recruits
predefined number of bees around the selected sites
for local search. Again, fittest bees from each site
selected for further exploitation of the site (Pham et
al., 2005)
These steps are repeated until a stopping
criterion is met. At the end of each iteration,
population is updated and new population of the bee
colony is formed out representatives from each
selected patch and other scout bees assigned to
conduct random searches. New population generated
from neighbourhood search and global search phase
(Pham et al., 2005)
Table 1: Basic Parameters of the BA.
n number of scout bees
m number of selected sites
e number of elite sites out of m sites
nep recruited bees for elite sites
nsp number of bees recruited for the other
(m-e) selected sites
ngh neighbourhood size
3 THE VANTAGE POINT
NEIGHBOURHOOD SEARCH
FOR THE BEES ALGORITHM
3.1 Vantage Point Trees (VPTs)
In this section, details of the Vantage Point Tree
(VPTs) construction is presented. Searching in a
metric space includes several forms of vantage point
trees. (Yianilos, 1993). As a part of Nearest
Neihgbourhoud Search literature it is a data structure
and the algorithm that is used to search in metric
space with a distance function that satisfies the
triangle inequality (Chávez, 2001).
A metric space is defined as a pair of M =
(,d) where the set denotes domain or search
space (universe) of valid objects (points, elements)
of the metric space sometimes called database,
dictionary or simply set of objects or elements. The
distance function
: → (1)
satisfies the following axioms:
i∀u
,u
∈ d
u
,u
0positiveness,
ii∀u
,u
∈ d
u
,u
d
u
,u
symmetry,
iii∀u ∈
d
u, u
0reflexivity,
iv∀u
,u
,u
∈ d
u
,u
d
u
,u
d
u
,u
triangleinequality,
The Vantage Point Bees Algorithm
341
then the pair (,d) is called a metric space. When the
elements of the metric space (,d) are n-tuples of
real numbers then the pair is called a finite-
dimensional vector space, if the elements are
identified with k real-valued coordinates (
,…,
the vector space is called k-dimensional vector
space. There are a number of options for the distance
function for instance the most commonly used is the
family of
distances, defined as
,…,
,
,…,
=
∑
|
|
/
(2)
As an example
is the block or Manhattan
distance,
is the well known Euclidean distance
and
corresponds to taking the limit of the
when s goes to infinity. The vantage point bees
algorithm with neighbourhood search procedure, we
used k = 2, we have a 2-dimensional search space
and the distance between two elements with standard
Euclidean metric.
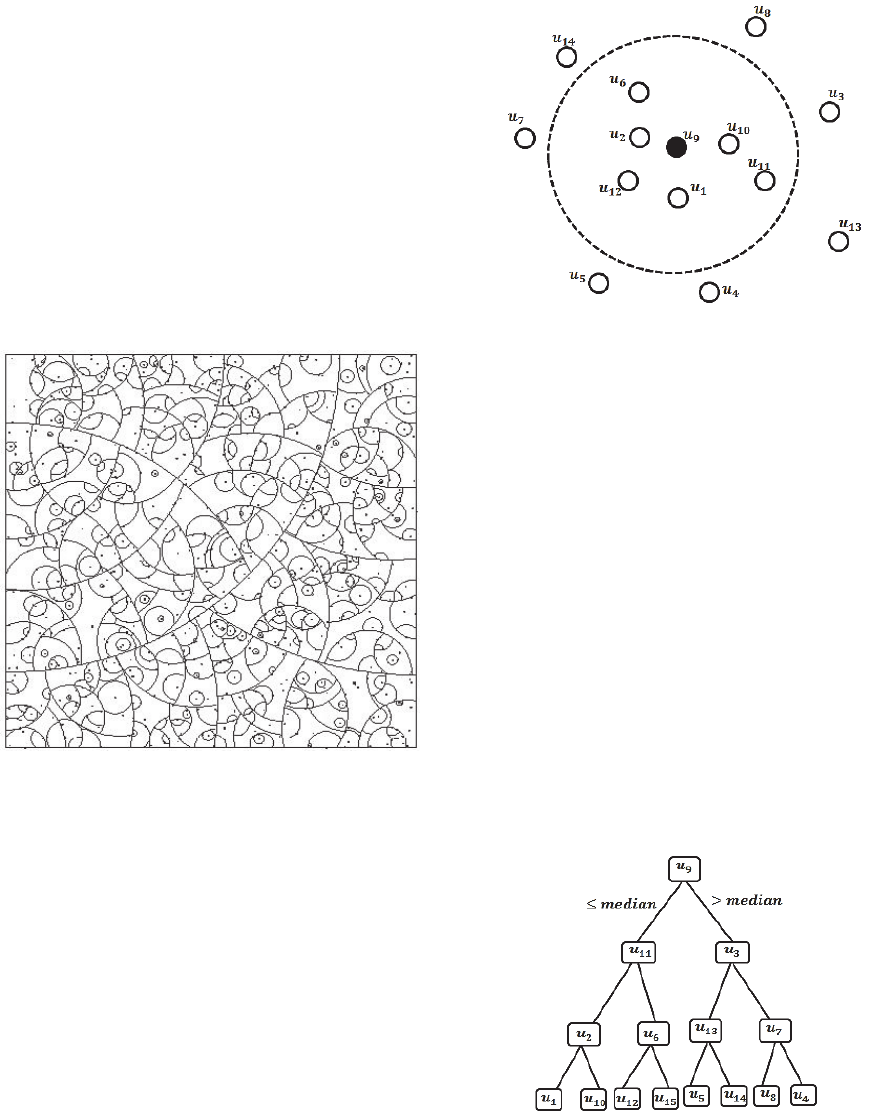
Figure 2: Vantage point decomposition (Yianilos, 1993).
The measure of distance between objects, for
example in the VPBA it denotes the measure of
distance between two sites. The distance function is
Euclidean metric. In this work, q is selected as a
pivot element sometimes called center or vantage
point that cuts/divide the entire space to form a
vantage point tree. Each element of metric space
distances to every other element formed a
perspective on the entire space.
The similarity-based queries commonly search
for all elements (points or sites) within some
spicified distance from a given query object and
require retrieval of the nearest neighbours of the
vantage point. For a given vantage point q, as the
selected site and vantage point tree basically
partitions the search space into spherical fields
around a chosen vantage point at each level which is
similar to first method in Burkhard and Keller
(1973) (Uhlmann, 1991).
Figure 3: Selecting vantage point
and plot the radius M
used for the root
(Chávez, 2001).
The median is found and the sites are partitoned into
two groups. The left side group containes the sites
whose distances to the vantage point are less then or
equal to median distance, the right side group
contains the sites whose distances are larger than the
madian distance.
Thus the structure of a binary vantage-point tree
is (q,m,
,
, where q is the vantage point, m is
the median distance among the distances of all the
sites (from q) indexed below that node, and
is the
left branch of node,
is the right branch of node
(Bozkaya, 1999).
Vantage Point Trees (VPTs) formed by simplest
algorithm. Its distinguished vantage point then splits
the space into left and right space. This may be
defined as building a binary tree recursively, taking
any element p as the root (vantage point) and taking
the median of the set of all distances.
M =
,
|
∈
(3)
Figure 4: Example of VPTs with root
(Chávez, 2001).
ECTA 2015 - 7th International Conference on Evolutionary Computation Theory and Applications
342

The left space or left subtree contains the elements
u, which satisfied , and right subtree
contains the elements u, which satisfied,
. This subtrees with a selected vantage point
element is constructed by the algorithm randomly.
The VPTs takes O(n) space and is built in
O(nlogn) worst case time, since it is balanced.
(Chávez, 2001), the query complexity is argued to
be O(logn) (Yianilos, 1993) for small search radius.
3.2 The Vantage Point Bees Algorithm
The Vantage Point Bees Algorithm (VPBA)
proposed a hybridization technique which involves
the Bees Algorithm and a local search technique
based on Vantage Point Trees (VPTs).
Since the similarity criterion is a distance
function which satisfies the triangle inequality the
vantage point tree splits sites using absolute distance
from a single selected sites. The triangle inequality
which is used to find the upper and lower bounds of
the list of sites that are within our chosen distance
and only calculate the distance for those selected
sites, so it is reduced the number of distance
evaluations. Another advantages of VPTs structure
is that is although it is designed for the continuous
domains it can be used for discrete domains with
virtually no modifications (Chávez, 2001).Hence the
BA with VPTs local search procedure can be used
both for continuous and combinatorial domains
without a different approach of local search
strategies when it comes to a mathematical definiton
of the distance.
Step 1: Recurse the following steps until all sites are
chosen.
Step 2: Select a vantage point p
(pivot site) randomly
from the all sites.
Step 3: Add vantage point to the solution list; // i.e hist
list
Step 4: Calculate median of the set of all distances,
// return a list hist of the distances from the item to each
vantage point.
M =
,
|
∈
.
Step 5: Splits site list into two list L and R. Take only left
site list (L) for optimal solution.
for (site=1; site allSites; site ++)
if (,
median) add site to L,
Step 6: Select new vantage point from the L randomly.
Add pivot site to the solution list and delete selected site
from all sites.
Step 7: Go to step 3, and repeat until convergence or
termination conditions are met.
Step 8: Return solution site list for evaluating fitness.
Figure 5: The Pseudo code of vantage point recruitment
phase.
The VPBA has the same six parameters, namely;
n, m, e, nsp, nep, ngh. Initially, a number of bees (n)
is sent randomly to the search space. Each bee is
associated with one solution. The solutions
representing the fitness of individual bees were then
ranked in descending order. The top m solutions
were regarded as selected sites. Out of m sites, a
number of top e site(s) is considered as elite one(s).
Each of non-elite (m-e) and elite (e) sites
respectively receives nsp and nep forager bees to
exploit the discovered food source.
The Pseudo code of vantage point recruitment
phase is given in Figure 5 and the pseudo code of the
VPBA is shown in Figure 6.
Step 1:Initial population with n random solution.
Step 2: Evaluate fitness of the population.
Step 3: While (stopping criterion not met)
Step 4: Select sites (m) for neighbourhood search.
Step 5: Recruit bees for selected sites, evaluate fitnesses,
select the fittest bee from each site.
for (k=l ; k=e ; k++)
// More bees for best e sites
for (Bee=l ; Bee= nep ; Bee++)
// Vantage Point Tree Recruitment Phase Start
BeesPositionlnNgh=GenerateVPTs(Bee(i),allsites)
// Evalute the fitnees of recruited Bee(i)
Evaluate Fitness = Bee(i);
If (Bee(i) is better then Bee(i-l))
RepresentativeBee = Bee(i);
// Other selected sites(m-e)
for (k=e ; k=m ; k++)
// Less Bees for Other Selected Sites (m-e)
for (Bee=l ; Bee= nsp ; Bee++)
BeesPositionlnNgh=GenerateVPTs(Bee(i),all sites),
// Evalute the fitnees of recruited Bee(i)
Evaluate Fitness = Bee(i);
Step 6: If (Bee(i) is better then Bee(i-l))
RepresentativeBee = Bee(i);
Step 7: Assign remaining bees to search randomly and
evaluate their fitnesses.
// (n-m) assigned to search randomly into whole solution
space.
Step 8: End While
Figure 6: Pseudo code of VPBA.
4 THE TRAVELLING SALESMAN
PROBLEM (TSP)
4.1 Symmetric Travelling Salesman
Problem
The Travelling Salesman Problem (TSP) can be
defined as finding a Hamiltonian path with
minimum cost. The salesman starts his tour from a
The Vantage Point Bees Algorithm
343
city and returns back to his starting city while
determining a minimum distance passing through
each city once and only once. It is a easy to describe
but difficult to solve problem, which is why it draws
so much attention from the scientific community.
This problem is a mathematical NP-hard problem
(Laporte, 1992) and it is important for many
different industries.
In this paper, the metric TSP deployed since
many other optimization models prefers to do so as a
standard. Let V is a set of m cities,
,…,
}.
Metric TSP is satisfy the triangle inequality, see
Figure 7, and since the distance
,
) =
,
for every
,
∈, the problem is a symmetric TSP
and we find the optimal tour after each iteration of
VPTs recruitment phase.
Figure 7: Triangularity in a road network. The distance
from A to B is determined by the shortest route
,
,
,
for every X (Hetland, 2009).
4.2 Experimental Results
In this section, the performance of the VPBA is
evaluated. First, the efficiency of the algorithm is
presented in Table 2. The algorithm with new local
search strategy is run with several different data sets.
It proves that the VPBA is an efficient and robust
algorithm and it can converge local optima.
Table 2: Performance of VPBA for selected benchmark
problems in TSPLIB.
Problem
[Cities/evaluation]
VPBA
Best
Result
VPBA
Average
Iterations
Best
Known
Results
att48 [48/500] 10628 10823 10628
eil51[51/500] 426 436 426
eil76 [76/500] 538 565 538
kroa100[100/500] 22631
23511
21282
Eil101 [101/500] 668 681.96 629
d198 [198/500] 16752 17811 15780
Secondly the performance of the VPBA
compared with the BA results with several local
search strategies. The VPBA is significantly fast in
finding the optimal value of tested benchmark
function. The Vantage point local search procedure
improves the local search efficiency of the
algorithm.
The performance of the VPBA is investigated by
applying the algorithm to TSP taken from TSPLIB.
As an instance we choose Eil51, that is a 51-city
TSP problem and we compare the test result with the
performance of the BA with several local search
operators including simple (2 point) swap, double (4
point) swap, insert, 3 point swap, 2-Opt and 3-Opt.
The experiments were performed using the
VPBA to evolve its own parameter values. It was
run 100 times for each parameter setting on eil51
benchmark problem.
The computing platform used to perform the
experiments was a 2.50 GHz Intel(R) Core(TM) i5-
2450M CPU PC with 4 GB of RAM. The
experimental programs were coded in the Java
language and compiled with Eclipse IDE. Each
problem instance was run across 100 random seeds.
The parameters of Vantage Point Bees Algorithm for
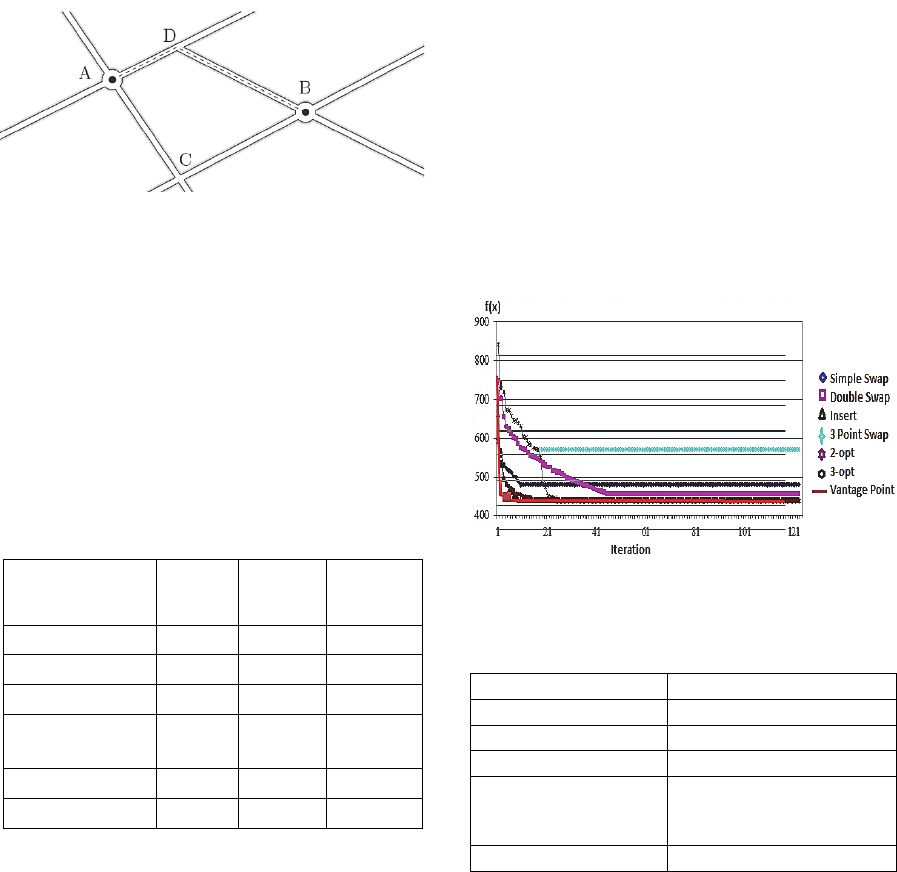
Eil51 TSP shown in Table 3. Figure 8 summarizes
the results of the Bees Algorithm with (2 point)
swap, double (4 point) swap, insert, 3 point swap, 2-
Opt and 3-Opt operator on Eil51 TSP (Koç, 2010).
Figure 8: Benchmark results of the VPBA for a 51 city
TSP.
Table 3: The parameters of VPBA for experiments.
n = 80 number of scout bees
m = 40 number of selected sites
e = 5 number of elite sites
nep = 80 recruited bees for elite sites
nsp = 40
number of bees recruited
for the other
(m-e) selected sites
100 Number of iterations
ECTA 2015 - 7th International Conference on Evolutionary Computation Theory and Applications
344
The Eil51 problem was tested 100 independent
runs. From the experimental results the best tour
length and average tour length is selected. Standard
deviation of experiments is used to measure the
performance of benchmarked strategies. For each
data set the proposed algorithm can find the best tour
in almost each trial and the error rate is only 0.02%
away from the optimal. Standard deviation over 100
runs is 1,08358.
5 CONCLUSIONS
An improved version of the BA is presented with a
new local search strategy which is called the
Vantage Point Bees Algorithm (VPBA). The
performance of the VPBA was significantly fast in
finding the optimal optimum of tested benchmark
function.
The performance of the VPBA was evaluated
using 51-city TSP and the results were compared
with The Bees Algorithm with several local search
operators including simple (2 point) swap, double (4
point) swap, insert, 3 point swap, 2-Opt and 3-Opt.
Results shows that the VPBA outperformed the BA
with several other local search strategies.
REFERENCES
Bonabeau, E., Dorigo, M., and Theraulaz, G. 1999. Swarm
intelligence: From Natural to Artificial Systems.
Oxford University Press, Oxford.
Blum, C., Roli, A., 2003. Metaheuristics in combinatorial
optimization: Overview and conceptual comparison.
ACM Computing Surveys. pp. 268–308.
Bozkaya, T., Ozsoylu, M., 1999. Indexing Large Metric
Spaces for Similarity Search Queries. ACM
Transactions on Database Systems (TODS).
Burkhard, W., Keller, R., 1973. Some approaches to best-
matching file searching. Comm. of the ACM.
Chávez, E., Navarro, G., Baeza-Yates, R., and Marroquín,
J., L., 2001. Searching in metric spaces. ACM
computing surveys (CSUR).
Frisch, K., 1967. The Dance Language and Orientation of
Bees. Cambridge, Mass, The Belknap Press of Harvard
University Press.
Hetland, M., L.,2009. The Basic Principles of Metric
Indexing.
Johnson, D., S., and McGeoch, L., A., 1997. The traveling
salesman problem: A case study in local optimization.
Laporte, G., 1992. The traveling salesman problem: An
overview of exact and approximate algorithms.
European Journal of Operational Research, vol. 59, no.
2, pp. 231-247.
Pham, D., T., Ghanbarzadeh A., Koç, E., Otri, S., Rahim,
S. and Zaidi, M., 2005. The Bees Algorithm. Technical
Note, Manufacturing Engineering Centre, Cardiff
University, UK.
Pham, D., T., Ghanbarzadeh, A., Koç, E., Otri, S., Rahim,
S. and Zaidi, M. 2006. The Bees Algorithm - A Novel
Tool for Complex Optimisation Problems. In
Proceedings of the Second International Virtual
Conference on Intelligent production machines and
systems, Elsevier, Oxford, 2006, pp. 454–459.
Pham, D., T., Castellani, M., 2009. The bees algorithm:
Modelling foraging behaviour to solve continuous
optimization problems. Proceedings of the Institution
of Mechanical Engineers, Part C: Journal of
Mechanical Engineering Science 223(12), pp. 2919-
2938.
Kelly, J., K., 1955. General Topology. New York: D. Van
Nostrand.
Kennedy, J., Eberhart, R., Shi, Y., 2001. Swarm
Intelligence. Academic Press, London.
Koç, E., 2010. The Bees Algorithm Theory , Improvements
and Applications, PhD. Manufacturing Engineering
Centre School of Engineering University of Wales,
Cardiff, United Kingdom.
Liu, Y. and Passino, K., M., 2000. Swarm Intelligence:
Literature Overview. Dept. of Electrical Engineering,
The Ohio State University.
Seeley, T., D., 1996. The wisdom of the hive: The social
physiology of honey bee colonies. Cambridge,
Massachusetts: Harvard University Press.
Uhlmann, J., K., 1991. Satisfying General
Proximity/Similarity Queries with Metric Trees.
Information Processing Letters.
Uhlmann, J., K., 1991. Metric Trees. Applied Mathematics
Letters, vol. 4, no. 5.
Yang, X., S., 2008. Nature-inspired Metaheuristic
Algorithm. Bristol UK: Luniver Press.
Yang, X., S., 2010. Engineering Optimization: An
Introduction with Metaheuristic Applications. Wiley,
Chichester.
Yianilos, P., N., 1993. Data structures and algorithms for
nearest neighbor search in general metric spaces. In
Proceedings of the fourth annual ACM-SIAM
Symposium on Discrete algorithms, PA, USA, Society
for Industrial and Applied Mathematics.
The Vantage Point Bees Algorithm
345
