From a Cloudy View towards a More Structured Approach for
Business Process Related Concepts
Necmettin Ozkan
IT Governance Division, Turkiye Finans Participation Bank, Istanbul, Turkey
Keywords: Business, Process Management, Concept, Model, Structure, Ontology.
Abstract: In today’s information era, one of the greatest areas of confusion is the terminology used to name abstract
business process concepts which are mostly unclear, blurred and ambiguous among people. This study
attempts to remedy the problem of the often-occurring issue of terminology confusion in business process
domain. Following a nested approach, from mission to event, the work firstly defines essential terms used in
the area of research in order to create a common understanding. The paper then formalizes the relations
between the terms represented within a consolidated class diagram. Therefore, the study aims to contribute
the body of knowledge in this area especially for people from practice by consolidating all relevant terms and
providing a meta-model from a consistent point of view.
1 CHALLENGE OF CONCEPTS
In today’s information era, one of the greatest areas
of confusion is the terminology used to name abstract
business process related concepts which can be
unclear, blurred and ambiguous (Alter 2001; Harmon
2007; Jeston and Nelis 2014; Josey 2012; Parry,
Newnes and Huang 2011; Winniforda et asl., 2009).
In an environment where concepts do not imply same
meaning for everyone, expecting people to attach
shared points is meaningless. Furthermore, people
commonly create their own definitions and use them
in their ways. At the end of the day, they are not only
unable to communicate properly but also, even worse,
misunderstand each other. Thus, the concepts which
have blurred relations, and are used in arguable
contexts keep producing imperfect and deficient
results, unable to cover expectations.
All these factors have set off and led to this study.
This study attempts to remedy the problem of the
often-occurring issue of cloudy-defined terminology
in the business process domain. The term "business
process" is used as defined by Sheer, and Nüttgens
(2000) as “a procedure relevant for adding value to an
organization”. Attached to this meaning, following a
nested approach, from mission to event, the work
defines comprehensive and essential terms used in the
area of the research in order to create a vocabulary-
like reference model with enriched contents for a
common understanding. The course of the study starts
with the identifications of the related concepts and
their descriptions, and goes through presenting a
consolidated class diagram for these interdependent,
cascading, and related concepts formalizing the
relations between the terms.
2 RELATED WORK
One of the major goals in every discipline is to define
and categorize terms, concepts, and phenomenon of
the field in order to create a common language and to
advance knowledge in the discipline (Kishore,
Sharman & Ramesh 2004). As a result, there is a
wealth of research providing their definitions on this
subject that points out a part of this study. Some
examples include ArchiMate, BMM, BPMN, CBM,
EBA, ARIS, EPC, and EBMM, listed by Glissman
and Sanz (2009).
The attempt of studies in literatures on business
process area fall into one of the two domains:
information system or business context. Bart, Bontis
and Taggar (2001), Collins and Porras (1996),
Duncan (1999), Gupta, Gollakota and Srinivasan
(2007), Hitt, Ireland and Hoskisson (2013), Johnson
and Scholes (2002), and Thompson and Strickland
(2003) are some examples covering the business side
of this study, while Alter (2001), Kishore, Sharman
Ozkan, N..
From a Cloudy View Towards a More Structured Approach for Business Process Related Concepts.
In Proceedings of the 7th International Joint Conference on Knowledge Discovery, Knowledge Engineering and Knowledge Management (IC3K 2015) - Volume 3: KMIS, pages 315-324
ISBN: 978-989-758-158-8
Copyright
c
2015 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
315
and Ramesh (2004), Pflaeging (2014), Sheer, and
Nüttgens (2000), Weber (1999), and Weske (2007)
examine information system deeply, not at
meaningful or understandable level for business
managers. However, from a strategic business
viewpoint, business process works must be easy to
understand so that they can be used as a platform for
communication with business people (Green and
Rosemann, 2000), for many of the phenomena are
enacted by a human rather than a machine (Curtis,
Kellner and Over, 1992). Different from them, this
work does not hold a purpose of creating a new
process modelling notation or a deep and heavy
weight content. Preferably, the main purpose is to
revisit business process centric terms from a broader
spectrum and refresh the link between information
system or business context. Thus, one of the
distinguishing advantages of this study, over the
others, is to provide a ground to see a comprehensive
list of the related concepts all together in one picture
and their links to each other from a single and
consistent point of view. The other works have a
focus on relatively narrow areas. While this study
discusses 19 concepts, the maximum coverage of the
rest examined is 40% of terms discussed in this study.
Another advantageous side of this study is the
class diagram provided with relevant attributes,
relations and classification of layers. Similarly,
Weske (2007) also defines relatively narrow set of
terms, with the perspective of information system
only and provides a similar usage of class diagrams
but relatively simple with less attributes of class
diagrams notations. The class diagram can be
regarded as ontology, but in a language with limited
expressiveness. The rest of ontology models as a
mean which is over-specified are not preferred in this
study. Instead of defining the entities from scratch,
resulting to add a new proposal to the universe of
business process area, the study rather prefers to focus
on adding clarity to the field. Briefly, this manuscript
does not hold the purpose of finding a new definition
of the terms but the best ones instead.
The study outlines its own scope by process
centric thinking. Among the process, human, and
technology dimensions, only the process dimension
has been examined. The human is the primary impact
on emerging of these concepts. On the other hand, the
human part independently is a separate and huge
study subject. Technology is a means which serves to
provide alternative methods and acceleration for
processes; it does not produce a variation by itself in
this context. What remains is the main subject of this
study: process and its related concepts. This scope is
also regarded as a criterion in selecting for the set of
concepts the paper covers. This process thinking,
which is isolated from people and technology that is
hard to understand for majority of people, is believed
as a way of keeping the study more focused and more
understandable.
3 IDENTIFYING, DEFINING AND
CLARIFYING CONCEPTS
In identifying the concepts, a complete and general
list is targeted. Being general here means free of
sector and size of organizations. Completeness on the
other hand is for covering all relevant and
comprehensive entities of business process field
serving for the objective of this study. It is believed
that a primary list of the business process terms can
be reached from IT related reference models for IT
can be regarded as a kind of representation of real
(business) world in another platform. This relation
also requires and provides a strong link between
business and IT. ITIL (Information Technology
Infrastructure Library) and COBIT (Control
Objectives for Information and Related Technology)
have domination in information technology with its
integrated standards worldwide and are de-facto
frameworks. They deliver a generic process model
that represents all the processes normally found in IT
functions, and provide a common reference model
understandable to IT and business managers. Both
COBIT and ITIL are free of sector, size and integrate
good practices to ensure that any enterprise’s IT
supports the business objectives. Therefore, the list
was achieved by a throughout scanning in ITIL v3
glossary. COBIT v4.1 framework glossary was used
for possible extensions (coloured in a red line in the
figure.1).
The concepts were selected in a nested approach.
Mission statement was selected for the starting point
as organizations should start with setting a mission
first and foremost. All the other including processes
exist to realize it. On these nested links starting from
the concept of mission and going on node by node, if
any new concept is encountered in the description text
of the current concept (node), the next node in the
glossary was selected according to that. By this way,
the nested links were crawled until reaching all dead
nodes that do not include any new term to go further
with. Only one way direction (from-top-to-bottom)
was used to keep the study within reasonable bounds
with a consideration of that there can be many terms
unrelated to the context which contains, let’s say, the
word of process in their descriptions. Thinking
RDBPM 2015 - Special Session on Research and Development on Business Process Management
316
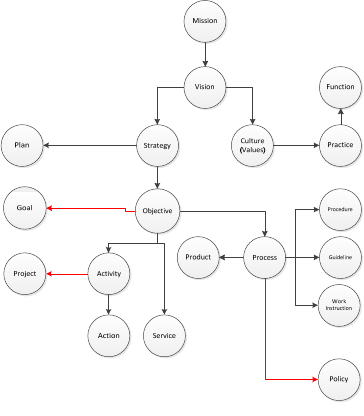
process at the core and adhering to the scope of the
study, the terms related to human/organization side
(such as organization, role, manager, customer and so
on), the terms related to a specific technology (such
as IT infrastructure, configuration management
database, and so on), and the terms related to a
specific method (such as brainstorming, balanced
scorecard and so on) were omitted. The full list of
items excluded by this way includes senior
management, organization, resource, role,
responsibility, customer, team, person, configuration
item, IT infrastructure, requirement, standard, target
and methodology. Instead of devoting a dedicated
title, the terms of target, methodology, requirement
and standard were mentioned in proper places of the
corresponding titles. The final map of targeted
concepts was reached as the following:
Figure 1: Map of the concepts.
In the description phase of the concepts, to reach
proper and common definitions, additional to COBIT
and ITIL resources, a literature review was performed
for possible extensions. Thus, a systematic literature
review was used as the method for getting the
complete spectrum of available definitions. The
fruitful resources obtained were scanned by a single,
holistic and integrated point of view of the researcher
until a consensus of resources for the particular term
was reached. And the best and proper descriptions
according to the researcher’s point of view were
selected and used in the study. Thus the descriptions
were clarified, intensified, and enriched. Moreover,
various methods were applied in order to make the
content more understandable. One of the methods
used is the aspect of “who”, “what”, “where”,
“when”, “why” and “how” questions to helps us
understand and properly define the concepts. “Why”,
“what” and “how” questions are used to determine the
positions and precedence of the concepts. As another
method, various analogies related to the human were
made, for the human is the creator of all these
concepts as he causes to emerge them in
organizations. And all creators bestow their own
essence to what they create, and make them similar to
themselves. The most typical example of this is
technology. Technology is indeed a regeneration
process of the human. Products created are getting
more similar to the human. Technologic products
which can speak, reason, understand, see, and be
touched as the human does are just like a copy of the
human behaviours. Organizations created by the
human similarly behave like a human: grow, evolve,
change, and become deformed and complicated. This
indeed feeds both the problem addressed in this study
and a solution to it. Using the solution side, the study
goes to the origin of the subject and aims to bring the
content up to a more familiar and coherent level.
3.1 Mission
Let’s go back to the beginning when the organization
desires to exist to produce the values necessary to
answer its demands and needs (which are listed by
Maslow (1943) and expanded later on by other
researchers). The mission statement addresses this
reason of existing (Gupta et al. 2007). Dictionaries
state that, “mission relates to that aspect for which an
individual has been or seems to have been sent into
the world”. For organizations, a mission statement
explains why an organization exists by the description
of the overall purpose and intentions of the
organization (Office of Government Commerce
2007).
The purpose mentioned sits at the core of
organizations; that is it inspires and stimulates
changes and progress on the way. When it stops
existing, moving also stops. This is why mission sits
near and next to the organization and is for yesterday,
today and tomorrow, different from vision which is
for tomorrow only. The concept of purpose, itself, is
not a target position or a destination point for the
future or a course to be taken. Whereas an
organization might reach a goal or achieve a strategy,
it pursues but does not reach a purpose which makes
a mission like a guiding star on the horizon (Collins
and Porras, 1996) lasting at least long years with no
change. If a mission shows an end, it creates a point
at which the organization may complete its mission.
This means to determine a point to finish its doing of
business. However, weirdly this result may be
From a Cloudy View Towards a More Structured Approach for Business Process Related Concepts
317
intended, because the needs which produce the
mission may have a limited life. Determining a
limited life to the mission may enable many
organizations to pull out of the market before
bankruptcy or at a good point on the curve.
A well-conceived mission statement provides a
basis for many other features of the organization.
Different from vision, mission considers social
matters and its social oriented dimension divulges the
intention of organization for the society in terms of
products and services (Gupta et al., 2007). These
products and services provide an input for
determination of processes and functions of the
organization. Mission also establishes individuality
of organizations (Duncan, 1999) by reflecting
corporate identity and image of organization (Gupta
et al., 2007). This side of mission statement serves for
business definitions of organizations that specify the
customers to serve, the business area and the scope in
which the organization intends to compete (Ireland
and Hitt, 1992). And it reflects corporate philosophy
and character (Gupta et al. 2007). Similarly,
philosophy and character, in this context, provide a
baseline for core values of organization. Besides,
mission statements influence organization’s policies
by this way.
The mission statement gives some clue about the
scope of business, core functions to operate,
customers, products and technology, but not a direct
answer for the question of “what a particular
organization is”. Business definition must clearly
define identity of organizations as a part of it.
Furthermore, it defines what an organization stands
for, its business area, its scope, and its targeted
customers, by defining two features: (1) Focus of
business which is defined in terms of the type of core
functions the organization performs (2) Features that
specifies how the organization differentiates itself
from others (Hitt et al., 2013).
3.2 Vision
The mission statement answers the question of “why”
(the organization exists), and business definition
defines “what it is” and its environment.
Nevertheless, they are not enough to make an
organization move without a vision. A vision
statement clearly illuminates the direction in which
the organization is headed (Gupta et al., 2007),
provides guidance about what the organization
aspires to become, to achieve, and to create in the
distant future (Thompson and Strickland, 2003) for its
mission. Whereas it may seem unreal to actually
attain it even in the long term; yet, it provides a
direction and aspiration to move and energy to strive
and exert to achieve it (Gupta et al., 2007). By
articulating the future position of an organization, it
points the destination and creates a voltage difference
between today and tomorrow. However, it does not
draw the course to be taken. Therefore, it is away
from addressing the questions of “how” or the
implementation details. Instead, vision influences
strategic planning in this way. While vision states
“where” (want to be), strategy, at some level, defines
“how” (to head there) in the current environment.
3.3 Core Values
Some resources (such as by Thompson and Strickland
(2003), Collins and Porras, (1996)) include core
values into vision. Yet, vision puts the organization
into motion by addressing the destination it aims to
be in the future. Core values, on the other hand, do
not function as an impulsion, but a static reference
point. So, core values are discussed as a different
subject in this study.
By definition, core values are organization’s
timeless character (Collins and Porras, 1996). It is
derived from mission statement and aids in
differentiating the organization from others (Gupta et
al., 2007). Core values are determined according to
the value the organization attributes both to customers
and its own personnel. It includes guidance on
expected behavior, business principles, ethics and
deeply held values of organization (Gupta et al.
2007). It defines organization culture. They are basic,
essential, central, enduring, steady, often un-stated
tenets and serves as standards to weigh actions and
decisions (Gupta et al., 2007). While an organization
must continually adapt to its environment, and its
practices and strategies should change continually,
core values should remain fixed (Collins and Porras,
1996). It is a need to develop policies to ensure that
the organization’s values are accepted and penetrated
to the heart and mind of each employee (Hitt et al.,
2013).
3.4 Goal and Objective
Goal and objective both are about moving forward.
However they are different in the meaning and usage.
First of all, for their meaning, think of a touchable
"object" for objective and “go” for goal. Goal has the
power of defining a destination, changing the
direction to move toward this destination, changing
the mindset to adjust to and support the new direction
(InvestorWords, 2014). It provides a big picture for
actions toward the achievement of the organization’s
RDBPM 2015 - Special Session on Research and Development on Business Process Management
318
mission and vision (Gupta et al., 2007). This usually
makes goal at strategic level and general, not easily
obtainable in the short term, which creates the
necessity to develop specific tactics that break big
goals down to a series of specific action steps. In this
case, setting objectives and linking them with goals
to accomplish them is a must. It is like a divide-and-
conquer strategy aiding in delineating goals.
Objectives are a series of smaller and specific targets
that need to be hit in order to achieve a goal. As a
result, objectives are positioned at tactical and
operational levels, and in short-terms in their nature.
Objectives must be supported by well-designed plans
(Gupta et al., 2007), and thus objectives become
something that can be planned to achieve.
A plan specifies results to achieve, resources to
obtain it, within a time frame, as objectives should do
the same. This time-based, concrete, and specific
attributes of objectives make them measurable
parameters for monitoring and evaluating
performance. Objectives can thus apply to system,
process, activity, project, product, or service.
Through this way, all these form a hierarchy. It begins
with broad statement of mission and vision, takes
form in goals, and ends with specific objectives at the
lower level (Gupta et al., 2007). Processes, plans and
projects run for these objectives to reach.
3.5 Strategy
Together, vision, mission and business definition
provide the foundation organizations need to choose
and implement one or more strategies (Hitt et al.
2013). Organizations must create a strategy intended
to achieve the vision and thus to fulfil the
organization’s mission. By definition, strategy is an
overall plan for deploying resources to establish a
favourable position (Thompson and Strickland, 2003)
and to set a direction for the organization towards the
overall vision. Besides this internal dimension,
strategy has an environmental dimension as
Thompson, and Strickland (2003) pointed out: “A
company’s strategy consists of the combination of
competitive moves and business approaches that
managers employ to please customers and compete
successfully and achieve organizational objectives.”
From this point of view strategy is a game plan and
an organization is not alone in this game. Johnson and
Scholes (2002 merge these two aspects of strategy as:
“… the direction and scope of an organization over
the long-term: which achieves advantage for the
organization through its configuration of resources
within a challenging environment, to meet the needs
of markets and to fulfil stakeholder expectations”.
After defining the strategy, it must be supported
by adequate processes. Somewhat, choosing a
strategy means making tradeoffs between different
activities and creating a preference among these
activities (Thompson and Strickland, 2003). Besides
the strategy, goals and objectives should be aligned
with vision and mission (Bart et al., 2001) for judging
the progress and success towards defined mission,
vision and strategy.
3.6 Policy
Business policy is a vital part of organizations to
ensure that organization’s mission, vision, and values
are accepted and supported by interested parties
(Pearce and Doh, 2005). Policies record decided upon
business rules, guiding principle or course of action
intended to influence and determine decisions,
actions, and other matters to ensure consistency and
compliance with the company’s strategic direction
(IT Governance Institute, 2007).
Policies address what the policy is and its
classification, who is responsible for the execution
and enforcement of the policy, and why the policy is
required (Kcggroup, 2014). In addition to policy
content, policies need to describe the consequences of
failing to comply with the policy, the means for
handling exceptions, and the manner in which
compliance with the policy will be checked and
measured (IT Governance Institute, 2007). Policies
engrave on every part of organizations. Among them,
processes/procedures are governed by policies that
ensure consistent and appropriate development and
implementation of processes, standards, roles (a set of
responsibilities), activities etc. (Office of
Government Commerce 2007).
3.7 Practice
In this hierarchy, none of vision, mission strategy,
policy, goal, and objective is a manner of action. Yet,
an organization is expected to take actions by which
it exercises its practices. A practice is a way of
working or a way in which work must be done to fulfil
needs and requirements and can include activities,
actions, processes, functions, and guidelines (Office
of Government Commerce 2007).
3.8 Function
Functions are core activities supporting
organization’s existence. In other words, a function is
a discrete activity organization wants to pay attention
(e.g. by putting energy into, structurally committing
From a Cloudy View Towards a More Structured Approach for Business Process Related Concepts
319
resources to) in order to meet its business objectives
(Josey, 2012). A business function can therefore be
positioned as a grouping of internal behaviour based
on a certain criteria like location, communication,
required skills, shared resources and shared
knowledge (Josey, 2012). So, a department within an
enterprise is not a function rather a function is core of
business activities carried out by a certain
department.
A function is internal and limited with the
boundary based dimension in the organization. To
deliver a value to customer, it must break away
conventional wisdom and the constraints of
organizational boundaries and should be broad and
cross functional in scope (Hammer, 1990). Function
also means to view from top to down. In this
direction, there are specialization, narrowing,
deepening, and an end which is static and
unchanging. Yet the customer is not on this side. S/he
waits at the end of horizontal way. So, the process
provides value to the customer by intersecting with
the functions vertically and using different functions
on the horizontal. This means that, processes are built
according to concern of creating value with elastic
limits.
3.9 Process
A business process is a way delivering a service or
product to a customer, or partial products or partial
services that are used as part of a service or product
for a customer (Josey, 2012). It does this by relating
activities. It takes inputs from a number of sources,
including other processes, manipulates the inputs, and
produces outputs. Processes may cross functional
areas to connect those points, probably, of different
departments.
Processes have clear business reasons for existing
(IT Governance Institute, 2007). Processes should be
a function of strategy, vision and mission by
producing sustainable success. By doing this, goals
and objectives of organizations are elaborated in
process by defining what value processes create, in
what quality and performance. Validation of the
creation of this value shall be performed in a way
production of the value throughout the organization is
assured.
As a complex dynamic system, business process
represents an organic view because of the human
factors as a part of it. This human factor is the weakest
link for ensuring the sustainability of the process.
People are involved in decisions. Leaving the
decisions up to the people involved may have
unsustainable consequences. It is likely that in the
absence of clear guidelines, the decisions taken by
different people will be different. This will create
inconsistent experiences for the customers and bring
down quality. That is why there are policies and
procedures (methods and rules) built according to the
policies. Procedure comes to ensure process activities
are delivered in an effective, efficient and consistent
manner serving for the common objectives.
The process, in general sense, is an element which
answers the question “how”, not in detail, by relating
activities to produce a service or a product for
customers. When it comes to each activity in a
process, procedure comes in to detail the “how”, by
providing practical information for the execution.
Yet, the “who” in a process/procedure should be a
role, not a specific person. It means there is still a
need of specifying the “who” to a person. A business
role can be assigned to a business actor by tasks
therefore the practice becomes actually an applicable
form.
3.10 Procedure, Work Instruction, and
Guidance
A process is abstract, and the power of it comes from
its abstraction. It describes the essentials of the
purpose, structure, rationale, roles and timing, leaving
plenty of implementation freedom (Bart et al., 2001),
enabling a wide range of its applications to be tailored
by procedures. A process tells “what” is necessary to
be done and the “how” part of it can be tailored and
elaborated in one or more procedures that describe the
means (formed by using method, methodology and
mechanism) of what is needed to be done, when and
by whom (Muller, 2011).
Even though procedures are part of processes, the
“why” in a procedure has often disappeared, replaced
by practical information for the execution (Muller,
2011). However, without understanding of the
thinking behind the procedure (the “why” part),
procedures can be meaningless. The process should
convey this rationale behind to procedures (Muller,
2011).
Similar concepts to procedures are workflow,
work instruction and guidance. Weske (2007) defines
workflow well as “the automation of a business
process, in whole or in part, during which documents,
information, or tasks are passed from one participant
to another for action, according to a set of procedural
rules”. Work instruction is created if very detailed
instructions are needed (Office of Government
Commerce 2007). It includes detailed instructions
that specify exactly what steps to follow with more
detail than a procedure (Office of Government
RDBPM 2015 - Special Session on Research and Development on Business Process Management
320

Commerce 2007). Guidance, on the other hand,
recommends describing best practices of what should
be done. Different from procedures and work
instructions, compliance to a guideline is not
normally enforced (Office of Government Commerce
2007). With a combination of underlying procedures,
work instructions, and guidance, the process will
become more controlled and consistent. The common
point of them is that they assure the standard way of
doing. It is likely that in the absence of them, the
decisions taken by different people will be different.
In the light of this view, one of the good example
delineating relations between policy, process and
procedure are provided by Kcggroup. com (2010) as
below:
Figure 2: Relations between policy, process and procedure.
3.11 Service and Product
A business service represents the added value to
customers by facilitating outcomes customers want to
achieve without the ownership of specific costs and
risks (Office of Government Commerce 2007; Josey
2012). While business functions and business
processes describe the inner way of working, a
business service hides implementation details and
describes the parts of business processes and
functions that are externally visible and usable (Josey,
2012). A service is realized by one or more business
functions or processes and a business function can
realize multiple business services (Josey, 2012).
From the customer point of view, it is enough to know
a certain service is being offered and how the
consumer must use the service (Josey, 2012).
While the thinking has shifted from a pure service
or pure product focus to a combination or product-
service system (Parry et al., 2011), the difference
whether the outputs of the process are a service or a
product shall change the approach to the
corresponding process. As stated by Parry et al.
(2011), service is an act rather than a thing, products
are tangible but service is not and value of experience
of customer is more significant for a service than a
product. For example, the gaps between expectation
and the perception of the service and product may
vary significantly. To exemplify, imagine two people
who can easily have different perceptions for same
service (Bowen and Ford, 2002). Different from
products, even the same person may have different
opinions about the service experience at different
times (Bowen and Ford, 2002). With all these aspects,
the differences between products and services should
affect process approach and design.
3.12 Activity
Activity is a set of actions designed to achieve a
particular result and usually defined as part of
processes or plans, and documented in procedures
(Office of Government Commerce, 2007). Every
activity is part of a business function (Josey, 2012). A
process combines a chain of activities each of which
is part of business functions (Josey, 2012). A single
process will not always belong to a single business
function: a business function will almost always
consist of multiple activities and process steps and a
process will often be realized by multiple business
functions (Josey, 2012).
3.13 Action
Activity consists of actions and events. Whereas an
activity is like a movie, event is like a picture in it. In
contrast to activity, event/action is in a form atomic
and non-decomposable granulation meaning that it
cannot be interrupted (Dennis et al., 2005). From a
practical perspective, events take zero time. The main
difference between event and action is that an event
is an occurrence at information level without a
sentient force causing it to occur. An action, on the
other hand, is an occurrence caused by a sentient
force with knowledge at DIKW (data, information,
knowledge, and wisdom) Pyramid. While an event is
usually stationary, an action is regarded as an event
requiring a reaction.
3.14 Plan
Plan is an intended future course of action which
describes, prioritizes and schedules various activities
From a Cloudy View Towards a More Structured Approach for Business Process Related Concepts
321

and resource allocation aimed at achieving specific
goal(s) or objective(s) within a specific timeframe
(Business Dictionary, 2014; Gupta et al., 2007). It
explains in detail what needs to be done, how, when,
and by whom (Business Dictionary, 2014). Plan
consists of tasks that are feasibly the smallest unit of
work into which the activity can be broken down.
3.15 Project
Projects include a structured set of activities, a
temporary organization, with people and other assets
required to achieve an objective or other outcome
based on an agreed-upon schedule and budget (IT
Governance Institute, 2007). A project is a set of
certain changes (delta) that are designated to change
as-is capabilities of people, processes or technology
of an organization. Program, on the other hand,
consists of a number of projects and activities that are
planned and managed together to achieve an overall
set of related objectives and other outcomes (Office
of Government Commerce, 2007).
4 CLASS DIAGRAM OF THE
CONCEPTS
After the detailed description of each concept, this
class diagram presents the big picture to illustrate
these interdependent, cascading, and related
concepts. Each class has an attribute list, the
classification of strategic, tactical and operational
level, information of abstraction (boxes in italic text)
or whether being in executable form and its relations
with other concepts in terms of name of relations and
the numbers of possible objects that can be related.
All attributes and relations can be driven from the
definition part of the terms mentioned above. The
remaining is the number representation on the
connections such 1-1 and n-1. All notation of classic
class diagram is not fully used, kept at appropriate
level for this study.
Because of the nature of this structure, concepts
change less frequently and in fewer amounts upward.
From top to bottom, it follows a more concrete, more
specific, more applicable, more changeable, and more
granular way; which at the bottom takes an atomic
form.
Strategic, tactic and operational hierarchy is not
only a positioning effort but also an elaboration
method. For instance, an operational act is expected
to serve for a strategic target and vice versa a strategy
must be elaborated and supported at operational level.
Figure 3: Class diagram of the concept.
This expectation necessitates such a mechanism
in which each element at the operational level
(procedure, work instruction, tasks etc.) must either
include “what”, “when”, “where”, “how”, “who”,
optional but critically better “why” dimensions or
acquire them by inheritance from an upper level in
order to be comprehensive. Hence, the first question
to ask before everything is “why”. While all other
questions feed the information and knowledge, the
“why” question feeds the conscious. If someone in the
bottom knows the answer of the question “why” then
s/he becomes conscious. Consciousness increases the
urge to embrace. This way, different and probably
better ways to serve can be captured at the point
where “the subject is best known by the person who
performs it.” Although having information/
knowledge to apply work seems enough,
consciousness enables a person to pass from reactive
to proactive position. Otherwise, this distinction
between “thinker” (who strategize, steer, control,
decide, and thus who has the “why”) and “doer” (who
execute, obey, follow) (Pflaeging, 2014) adds a layer
producing a disconnection between the parts of
diagram.
Achieving to manage effects of a change across
the diagram up and down which occurs in any part of
the diagram as a result of the dynamism of time and
how to penetrate the change through the elements of
the diagram is an important issue.
In this structure effectiveness and efficiency are
distributed to different levels. In the picture,
effectiveness shall be pursued in the levels which
RDBPM 2015 - Special Session on Research and Development on Business Process Management
322
directly include the question “why” and efficiency
shall be pursued in the objects which answer the
question “how.” The conscious which designs and
assesses the quality of results is at upper levels. For
this reason, innovation in goals and strategy may
produce effectiveness. On the other hand, let us say a
change in a project or process, may improve only
efficiency as the right thing in “doing the right thing”
has already set before. The remaining part for the
process or project is doing things right.
5 CONCLUSIONS, LIMITATIONS
AND FUTURE WORK
Despite the fact that it is not easy to reach a
commonly accepted reference model in this field and
this study eventually is another suggestion, the
contribution of the study should be sought in the
method of thinking to make things simple especially
for practice, in the aim connecting the two interrelated
parts (business and information system) and in the
class diagram illustrating the outcomes of the work in
a comprehensive and simply manner.
In order to assess the value of the work, expert
judgment and evaluation of practitioners who suffer
from the addressed problems may consider clarity,
amount of value, coverage, completeness,
effectiveness and consistency of content in the study
as criteria.
In any structure, the whole is greater or smaller
than sum of parts of the whole because of the human
factor. While conducting exercises, one must
therefore have a people view. However, the human
part of this whole that produces and uses all these
concepts, is complex, unpredictable, exhibits
uncertainty, and live and change with many
parameters, remains, on its own, as a huge further
study area.
REFERENCES
Alter, S. (2001). Are the Fundamental Concepts of
Information Systems Mostly About Work Systems?
Communications of the Association for Information
Systems, 5 (11), pp.1-67.
Bart, C., Bontis, N., and Taggar, S. (2001). A model of the
impact of mission statements on firm performance.
Management Decision, 39, pp.19-35.
Bowen, J., and Ford, R. (2002). Managing Service
Organizations: Does Having a "Thing" Make a
Difference? Journal of Management, 28, pp.447-469.
Business Dictionary. [online] Available at http://www.
businessdictionary.com [Accessed 16 Oct. 2014].
Collins, J. C., and Porras, J. I. (1996). Building Your
Company’s Vision. Harvard Business Review, 74 (5),
pp.65–77.
Curtis, B., Kellner, M.I., and Over, J. (1992). Process
modeling. Communications of the ACM, 35(9), pp.75-90.
Dennis, A., Wixom, B., and Tegarden, D. (2005). Systems
Analysis and Design with UML, Wiley.Hoboken, 2
nd
edition.
Duncan, W. (1999). Management, Oxford University Press.
New York.
Glissman, S. (2009). A Comparative Review of Business
Architecture. IBM Research Report. San Jose, CA:
IBM.
Green, P., and Rosemann, M. (2000). Integrated Process
Modelling: an ontological evaluation. Information
Systems, 25 (2), pp.73-87.
Gupta, V., Gollakota, K., and Srinivasan, R. (2007).
Business Policy and Strategic Management, PHI
Learning Pvt. Ltd. New Delhi.
Hammer M. (1990). Reenginering Work: Dont Automate
Oblitetaye. Harvard Business Review, 90(4), pp.104-
112.
Harmon, P. (2007). Business Process Change, The
MK/OMG Press. Burlington, MA, USA.
Hitt, M., Ireland, R., and Hoskisson, R. (2013). Strategic
Management, Cengage South-Western. Mason, OH.
Investorwords.com. Goals vs. Objectives – What’s the
Difference? [online] Available at: http://www.investor
words.com/article/goals-vs-objectives.html [Accessed
16 Oct. 2014].
Ireland. R., and Hitt, A. (1992). Mission Statements:
Importance, Challenge, and Recommendations for
Development. Business Horizons, 35(3), pp.34–42.
IT Governance Institute (2007). COBIT 4.1: Control
Objectives for Information and Related Technology,
Rolling Meadows. IL.
Jeston, J., and Nelis, J. (2014). Business Process
Management, Routledge. New York.
Johnson, G., and Scholes, K. (2002). Exploring corporate
strategy, Financial Times Prentice Hall. Harlow.
Josey, A. (2012). ArchiMate 2.0, Van Haren Publishing.
Zaltbommel.
Kcggroup.com, (2010). Policy, Process, and Procedure -
What is the Difference? | KCG. [online] Available at:
http://kcggroup.com/PoliciesProcessesProcedureDiffer
ences [Accessed 21 Dec. 2014].
Kishore, R., Sharman, R., and Ramesh, R. (2004).
Computational Ontologies and Information Systems: I.
Foundations. Communications of the Association for
Information Systems, vol 14, pp.158-183.
Maslow, A. (1943). A theory of human motivation.
Psychological Review, 50(4), pp.370-396.
Muller, G. (2011). Systems Architecting, CRC Press.
Boca.Raton,.FL.
Office of Government Commerce (2007). ITIL v3:
Information Technology Infrastructure Library, TSO.
London.
From a Cloudy View Towards a More Structured Approach for Business Process Related Concepts
323
Parry, G., Newnes, L. and Huang, X. (2011). Goods,
Products and Services. In: M. Macintyre, P. Parry and
J. Angelis, ed., Service Design and Delivery. Service
Science: Research and Innovations in the Service
Economy 2011. New York: Springer US, pp.19-29.
Pearce, J., and Doh, J. (2005). The High Impact of
Collaborative Social Initiatives. MIT Sloan
Management Review, 46(3), pp.30–39.
Pflaeging, N. (2014). Organize for Complexity, BetaCodex
Publishing. New York.
Sheer, A.W., and Nüttgens, M. (2000). ARIS Architecture
and Reference Models for Business Process
Management. In: W. Van der Aalst, J. Desel, A.
Oberweis. ed., Process Management. LNCS, vol. 1806.
Heidelberg: Springer, pp. 376-389,
Thompson, A., and Strickland, A. (2003). Strategic
management, McGraw-Hill/Irwin. Boston.
Weber, R. (1997). Ontological Foundations of Information
Systems, Coopers & Lybrand. Queensland, Australia.
Weber, R. (1999). The Information Systems Discipline:
The need for and nature of a Foundationa. In: Proc
Core. of the IS Foundations Workshop. Macquarie
University.
Weske, M. (2007). Business Process Management,
Springer. Heidelberg.
Winniforda, M., Congerb S., and Harris L.E. (2009).
Confusion in the Ranks: IT Service Management
Practice and Terminology. Information Systems
Management, 26(2), pp.153-163.
RDBPM 2015 - Special Session on Research and Development on Business Process Management
324
