
Si elegans: A Computational Model of C. elegans Muscle Response
to Light
Alicia Costalago Meruelo, Pedro Machado, Kofi Appiah and T. M. McGinnity
School of Science and Technology, Nottingham Trent University, Nottingham, U.K.
Keywords: Si elegans, Phototaxis, Modelling, Muscle, Sensory Neurons C. elegans, Izhikevich Neuron Model.
Abstract: It has long been the goal of computational neuroscientists to understand animal nervous systems, but their
vast complexity has made it very difficult to fully understand even basic functions such as movement. The C.
elegans nematode offers the opportunity to study a fully described connectome and link neural network to
behaviour. In this paper a model of the responses of the body wall muscle in C. elegans to a random light
stimulus is presented. An algorithm has been developed that tracks synapses in the nematode nervous system
from the stimulus in the phototaxis sensory neurons to the muscles cells. A linear second order model was
used to calculate the isometric force in each of the C. elegans body wall muscle cells. The isometric force
calculated resembles that of previous investigations in muscle modelling.
1 INTRODUCTION
Using computational neuroscience models, one can
simulate the nervous system by simplifying brain
models into neural circuits to attempt to understand
behaviour. There have been huge advances in
understanding the operations of neurons at a cellular
and sub-cellular level, as well as the operations of
large scale neural networks (Boyle and Cohen, 2007).
However, typically artificial neural networks are
highly simplified models of the individual neurons
they represent and do not have any neural structure in
mind or refer to the nervous systems of any particular
species (Cangelosi, 1997).
In this paper, we present a neural model of the
muscle cells in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans
(C. elegans). C. elegans (Fig. 1) is a small soil
nematode, with a simple anatomy comprising of
about 1000 cells, 302 neurons, 135 muscle cells and
about 8000 synapses (Altun and Hall, 2009a). The
anatomical description of the whole animal has been
completed at the electron microscopy level, making
the worm an important model for research in many
fields (Brenner, 1973; Wood, 1988). The adult
hermaphrodite consists of a mere 302 neurons, with
their connectivity already well described, making it a
model system for advancing the connectome program
(Varshney et al., 2011). Unfortunately, far less
information is available on the properties of these
neurons (Boyle and Cohen, 2007).
Figure 1: C. elegans anatomy, including the head, intestine
and tail (Altun and Hall, 2009a).
The C. elegans nervous system is sufficiently rich
to generate a large set of behaviours, including
locomotion (Gjorgjieva et al., 2014), touch response
Chalfie et al., 1985), detection of chemicals,
temperature and light gradients (Dunn et al. 2004;
Rankin, 2002; Ward et al., 2008) even memory has
been observed (Lin and Rankin, 2010).
Movement, or locomotion, in the worm typically
consists of periods of forward motion interspersed
with short periods of backward motion and turns,
controlled by a subset of its nervous system (Boyle
and Cohen, 2007). A number of models have been
developed for the C. elegans locomotion, yet it is still
partially understood and remains significantly
challenging to modellers and experimentalists
(Bryden, 2004; Suzuki et al., 2005).
The worm also exhibits escape responses to
external stimuli. A gentle touch with a fine hair
around the head area will cause the worm to move
backwards and a touch in the tail causes the worm to
Tail
Head
Intestine
Meruelo, A., Machado, P., Appiah, K. and McGinnity, T..
Si elegans: A Computational Model of C. elegans Muscle Response to Light.
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Congress on Neurotechnology, Electronics and Informatics (NEUROTECHNIX 2015), pages 121-126
ISBN: 978-989-758-161-8
Copyright
c
2015 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
121

move forward (Chalfie et al., 1985). The worm has
the ability to orient in response to gradients of
chemical concentration also referred to as chemotaxis
(Bargmann and Horvitz, 1991). Chemotaxis is used to
locate food and males use it to locate hermaphrodites.
This has been studied by establishing a two-
dimensional gradient chemical concentration,
demonstrating that chemotaxis behaviour in the worm
is consistent with true orientation of the chemical
gradient (Morse et al., 1998). Other behaviour
exhibited by the worm is the ability to move into
regions with constant or gradient temperatures. The
worm is known to migrate to regions with desirable
temperatures and deviates from undesirable
temperatures by sudden switches in direction
(Hedgecock and Russell, 1975).
Another behaviour recently observed in C.
elegans is phototaxis, which is the ability to sense and
react to light. A series of sensory neurons located in
the worm’s head are able to detect light stimuli and
they elicit a robust avoidance response (Ward et al.,
2008). The worm is known to lack specialised light-
sensing organs and lives in dark soil, yet it possesses
a simple way of detecting light which induces
avoidance behaviour mediated by a group of
chemoreceptive neurons (Ward et al., 2008). Light
stimuli evoke negative responses in the worm and
drive it back to a dark environment. If exposed to light
when moving forward, it would stop and then initiate
reversal. Similarly, the worm stops moving
backwards when exposed to light and starts moving
forward. This behaviour serves as a survival
mechanism in the soil.
In this paper we provide an initial model of the
responses to light of the C. elegans. It is being
developed as a test bed for the European Si elegans
project. The European Si elegans project intends to
provide an open-access and user-friendly framework
for the accurate emulation of the C. elegans nervous
system (Blau et al., 2014). It will provide a
sophisticated emulation environment with an
advanced design environment where users can design
their own custom neuron models, or use models from
a model library, run and visualise the emulation
results on a unique 3D virtual arena. The emulation
will run on a hardware parallel architecture based on
field programmable gate arrays (Machado et al.,
2015).
2 METHODS
2.1 Network Pathway
Light stimulates a series of sensory neurons situated
in the head of the nematode, which in turn excite a
series of interneurons and motor neurons, creating a
neural network. Some of these motor neurons
innervate 95 body wall muscles that run along the
body of the C. elegans (Fig. 2) (Hresko et al., 1994;
Varshney et al., 2011; White et al., 1986). When a
light source is focussed on the worm’s head, the
sensory neurons trigger a burst of neuronal activity
that results in muscle contractions and relaxations
which guide the nematode away from the light source.
This network then produces the light-induced head
avoidance response known as negative phototaxis
(Ward et al., 2008).
Figure 2: Body wall muscles of the C. elegans, divided into
four quadrants, from head to tail. Adapted from Altun &
Hall (2009).
We have elavorated a Matlab
®
algorithm that
follows the synapses from the sensory neurons
stimulated by light to each of the motor neuron
connected to body wall muscles. Through this
algorithm the neural pathways to each of the 95 body
wall muscles have been calculated, providing a
representation of a network that reflects the actual
neural connections of the worm, including the
weights of such connections. The connections and
weights between individual neurons in the C. elegans
have already been described (Hresko et al., 1994;
NeBICA 2015 - Symposium on Neuro-Bio-Inspired Computation and Architectures
122
Varshney et al., 2011), and the algorithm is able to
use this information and track the synapses from the
sensory neurons to the interneurons and motor
neurons. From all possible pathways calculated, only
those targeting specific motor neurons that innervate
the body wall muscles are selected.
The algorithm also allows the selection of the
depth in the network to observe either direct pathways
between sensory to motor neurons, networks with one
layer of interneurons or larger networks. Further
details about the neurons and muscles models are
given in the next two sections.
2.2 Neuron Model
To model the sensory neurons, interneurons and
motor neurons, an Izhikevich spiking neural model is
implemented (Izhikevich, 2003). In this particular
case, we are making the assumption that all neurons
behave equally (i.e. all share the same model), even
though C. elegans is thought to have no spiking
neurons (Lockery and Goodman, 2009).
The Izhikevich neural model combines the
biologically plausibility of Hodgkin-Huxley type
dynamics and the computational efficiency of
integrate-and-fire neurons (Izhikevich, 2003). It
follows a system of differential equations of the form:
=0.04
+5+140−+
=(−)
If ≥30 mV, then
←
←+
(1a)
(1b)
(1c)
In these equations, the variables and represent
the membrane potential and the recovery variable
respectively, I is the injected dc current, is the time
scale of the recovery variable, is the sensitivity of
the recovery variable, is the after-spike reset value
of the membrane potential caused by high-threshold
potassium conductance and is the after-spike reset
value of the membrane potential caused by low-
threshold potassium conductance.
The parameters were set to typical values: =
0.02 , b =0.2, =−65 mV, =2 (Izhikevich,
2003). In order to consider both excitatory and
inhibitory motor neurons responses, the inhibition has
been simplified to a negative current of the same
amplitude as its excitatory counterpart.
2.3 Muscle Model
To model the muscle responses to motor neuron
inputs, an isometric model has been chosen. Isometric
models calculate the force of contraction of a muscle
when no output movement is produced (Windmaier
et al., 2003).
A second order linear model (Bobet et al., 1993)
was used to model the isometric force, since linear
models are attractive due to their simplicity and ease
of analysis. However, they have to be considered
carefully, as they may lead to loss of information and
might not provide a good description of muscle force
(Bobet et al., 2005).
(
)
+
(
)
+
(
)
=
(
)
(2)
Where
(
)
is the muscle force as a function of
time,
are the model parameters and () is the
input spike train coming from the motor neurons. For
this particular test, the values chosen are
= 0.004,
=0.26 and
= 0.023, based on the model fitted
to an invertebrate muscle response (Wilson et al.,
2012), since no data is available to fit the model to the
C. elegans.
3 RESULTS
3.1 Phototaxis Network Pathway
The pathways from the sensory neurons receiving
phototaxis to the motor neurons that innervate the
body wall muscles have been calculated using the
algorithm developed.
To provide an example, the connections to the
muscle MDR05 (Muscle Dorsal Right number 05), at
the neck of the worm, are described. In this particular
case, there are four sensory neurons (AWBR, ASKR,
ASHL, ASHR) that synapse directly with the muscle
motor neurons (RMGR, RIML). By increasing the
depth and adding connections through interneurons,
there are connections to 20 interneurons from all the
14 sensory neurons excited by light. These
interneurons synapse to five motor neurons that
innervate the muscle, producing a total of 100
different pathways (Fig. 3). Adding a second layer of
interneurons would form a four layer network, with a
total of 1848 pathways and 98 different neurons
involved.
As the number of layers increases, so does the
number of connections and neurons involved,
increasing the complexity of the network. For this
analysis, the number of layers is restricted to three,
analysing a network with a single interneuron.
In the case of the network to innervate muscle
MDR05, most of the connections are found in the
neck and head of the nematode, with a few exceptions
in the rest of the body (Fig. 3)
Si elegans: A Computational Model of C. elegans Muscle Response to Light
123

Figure 3: a) Representation of the C. elegans nematode including the positions of the sensory neurons, interneuron and motor
neurons in the example calculated from phototaxis sensory neurons to the muscle MDR05 with a single interneuron layer. b)
Network pathway example calculated to the muscle MDR05.
Figure 4: Number of synapses from motor neuron to each
of the body wall muscles, where MDL stands for Muscle
Dorsal Left, MDR for Muscle Dorsal Right, MVL for
Muscle Ventral Left and MVR for Muscle Ventral Right.
The fact that most neurons and pathways are near the
head of the nematode is not limited to the network of
muscle MDR05. The muscles in the head and neck
and on the top half of the body are the ones which
received most inputs from the sensory neurons (Fig.
4). Considering that the phototaxis sensitive neurons
are situated near the head, it is possible that this dense
interconnectivity in the top half is due to network
optimisation to minimise wiring cost (Chen et al.,
2006).
3.2 Responses of Body Wall Muscles to
Light
Using the pathway calculated for each body wall
muscle, an artificial neural network has been created
using the Izhikevich neural model (Izhikevich, 2003).
The random stimulus in the sensory neurons is
transmitted through the network to the motor neurons,
where the input spike train to the muscle is created.
Using the linear model described in Section 2.3,
the isometric force produced by each of the 95 body
wall muscles is calculated. Following the previous
example, the response of muscle MDR05 to a random
stimulus is as shown in Figure 5.
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
123456789101112131415161718192021222324
Head Neck Body
Number of input synapses
Muscle cell
MDL
MDR
MVL
MVR
Average
Intestine
Phar
y
nx
Tail
Mouth
a
b
Sensor
y
Neurons
Motor Neurons
Muscle
Interneurons
NeBICA 2015 - Symposium on Neuro-Bio-Inspired Computation and Architectures
124
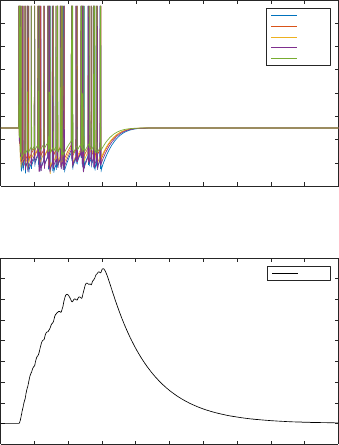
Figure 5: Spike train from the motor neurons and isometric
force calculated for the example muscle MDR05.
The force calculated in the body wall muscles can
be translated into muscle contraction and,
furthermore, into movement. Many investigators
have provided different models to achieved this
(Boyle et al., 2012; Bryden and Cohen, 2008; Bryden,
2004), however, in this particular piece of work, the
translation has not been performed.
4 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
WORK
In this paper we have presented an algorithm and a
cascade of models to simulate the force produced in
the C. elegans body wall muscles in response to a
random light stimulus.
The algorithm developed is able to read the
information on the connections for each neuron and
follow those connections to the motor neurons
connected to the body wall muscles. This way we
have created a representation of the network that
reflects the actual neural connections of the worm.
This pathway was effectively used in producing an
Artificial Neural Network, using Izhikevich neural
models, which transmitted the random stimulus to the
muscle cell.
The isometric force calculated with the stimulus
transmitted through the network provides an
approximation of the behaviour of the body wall
muscles that could be translated into locomotion.
Due to the lack of neuromuscular recordings and
since the simulation of locomotion has not yet been
performed, it is difficult to assess the accuracy of the
force obtained. The shape of the isometric force is
however comparable to that of other works simulating
C. elegans body wall muscle (Boyle and Cohen,
2008), other animals (Wilson et al., 2012) and even
human muscle force (Hunt et al., 1998).
This paper presents an early stage investigation.
Future work in this system includes that of the model
of phototaxis sensitive sensory neurons responding to
specific light amplitudes and frequencies (Ward et al.,
2008). Furthermore, the artificial neural network used
standard Izhikevich spiking neural models
(Izhikevich, 2003) for all neurons involved in the
network. Specific models for each of the neurons will
be implemented in future work approximating more
accurately the behaviour of the neurons involved in
this system in the C. elegans.
An implementation of this system into the Si
elegans framework to simulate the output movement
in response to light among other behaviours has
already started. This implementation would provide
an answer to whether the models presented here are
accurate enough to produce simulated C. elegans
avoidance in the presence of light. Therefore, the
models will need to be implemented into the
hardware framework forming the Si elegans project.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The research leading to these results has been
supported by the Si elegans project, which has
received funding from the European Community’s
7th Framework Programme under the Neuro
BioInspired Systems Project Grant agreement
601215.
REFERENCES
Altun, Z.F., Hall, D.H., 2009a. Introduction [WWW
Document]. WormAtlas. URL www.wormatlas.org
(accessed 9.2.15).
Altun, Z.F., Hall, D.H., 2009b. Muscle System, somatic
muscle [WWW Document]. WormAtlas. URL
www.wormatlas.org (accessed 9.2.15).
Bargmann, C.I., Horvitz, H.R., 1991. Chemosensory
neurons with overlapping functions direct chemotaxis
to multiple chemicals in C. elegans. Neuron 7, 729–742.
Time [s]
0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 1.2 1.4 1.6 1.8 2
Spike voltage (mV)
-120
-100
-80
-60
-40
-20
0
20
40
Input spikes
RIML
RMGR
SMDDL
RMDR
AS01
Time [s]
0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 1.2 1.4 1.6 1.8 2
Isometric force (%)
-0.1
0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
MDR05
b)
Si elegans: A Computational Model of C. elegans Muscle Response to Light
125
Blau, A., Callaly, F., Cawley, S., Coffey, A., De Mauro, A.,
Epelde, G., Ferrara, L., Krewer, F., Liberale, C.,
Machado, P., Maclair, G., McGinnity, T.-M., Morgan,
F., Mujika, A., Petrushin, A., Robin, G., Wade, J., 2014.
The Si elegans Project – The Challenges and Prospects
of Emulating Caenorhabditis elegans. In: Duff, A.,
Lepora, N., Mura, A., Prescott, T., Verschure, P.M.J.
(Eds.), Biomimetic and Biohybrid Systems SE - 54,
Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Springer
International Publishing, pp. 436–438.
Bobet, J., Gossen, E.R., Stein, R.B., 2005. A comparison of
models of force production during stimulated isometric
ankle dorsiflexion in humans. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst.
Rehabil. Eng. 13, 444–451.
Bobet, J., Stein, R.B., Oguztoreli, M.N., 1993. A Linear
Time-Varying Model of Force Generation in Skeletal-
Muscle. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 40, 1000–1006.
Boyle, J.H., Berri, S., Cohen, N., 2012. Gait Modulation in
C. elegans: An Integrated Neuromechanical Model.
Front. Comput. Neurosci. 6.
Boyle, J.H., Cohen, N., 2007. The role of body wall muscles
in C. elegans locomotion. In: BioSystems. p. 363.
Boyle, J.H., Cohen, N., 2008. Caenorhabditis elegans body
wall muscles are simple actuators. BioSystems 94, 170–
181.
Brenner, S., 1973. The genetics of behaviour. Br. Med. Bull.
29, 269–271.
Bryden, J., Cohen, N., 2008. Neural control of
Caenorhabditis elegans forward locomotion: The role
of sensory feedback. Biol. Cybern. 98, 339–351.
Bryden, J.A., 2004. A simulation model of the locomotion
controllers for the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans.
Cangelosi, A., 1997. A neural network model of
caenorhabditis elegans: the circuit of touch sensitivity.
Neural Process. Lett. 6, 91–98.
Chalfie, M., Sulston, J.E., White, J.G., Southgate, E.,
Thomson, J.N., Brenner, S., 1985. The neural circuit for
touch sensitivity in Caenorhabditis elegans. J. Neurosci.
5, 956–964.
Chen, B.L., Hall, D.H., Chklovskii, D.B., 2006. Wiring
optimization can relate neuronal structure and function.
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 103, 4723–4728.
Dunn, N.A., Lockery, S.R., Pierce-Shimomura, J.T.,
Conery, J.S., 2004. A neural network model of
chemotaxis predicts functions of synaptic connections
in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. J. Comput.
Neurosci. 17, 137–147.
Gjorgjieva, J., Biron, D., Haspel, G., 2014. Neurobiology
of caenorhabditis elegans locomotion: Where do we
stand? Bioscience 64, 476–486.
Hedgecock, E.M., Russell, R.L., 1975. Normal and mutant
thermotaxis in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans.
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 72, 4061–4065.
Hresko, M.C., Williams, B.D., Waterston, R.H., 1994.
Assembly of body wall muscle and muscle cell
attachment structures in Caenorhabditis elegans. J. Cell
Biol. 124, 491–506.
Hunt, K.J., Munih, M., Donaldson, N., Barr, F.M.D., 1998.
Investigation of Hammertein Hypothesis in the
Modelling of Electrically Stimulated Muscle. IEEE
Trans. Biomed. Enginering 45.
Izhikevich, E.M., 2003. Simple model of spiking neurons.
IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 14, 1569–72.
Lin, C.H., Rankin, C.H., 2010. Nematode learning and
memory: neuroethology, Encyclopedia of Animal
Behavior. Elsevier.
Lockery, S.R., Goodman, M.B., 2009. The quest for action
potentials in C. elegans neurons hits a plateau. Nat.
Neurosci. 12, 377–8.
Machado, P., Wade, J.J., Appiah, K., McGinnity, T.M.,
2015. Si elegans: Hardware Architecture
and Communications Protocol. In: The 2015
International Joint Conference on Neural Networks.
IEEE, pp. 3473–3479.
Morse, T.M., Lockery, S.R., Ferree, T.C., 1998. Robust
Spatial Navigation in a Robot Inspired by Chemotaxis
in Caenorhabditis elegans. Adapt. Behav. 6, 393–410.
Rankin, C.H., 2002. From gene to identified neuron to
behaviour in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nat. Rev. Genet.
3, 622–30.
Suzuki, M., Tsuji, T., Ohtake, H., 2005. A model of motor
control of the nematode C. elegans with neuronal
circuits. Artif. Intell. Med. 35, 75–86.
Varshney, L.R., Chen, B.L., Paniagua, E., Hall, D.H.,
Chklovskii, D.B., 2011. Structural properties of the
Caenorhabditis elegans neuronal network. PLoS
Comput. Biol. 7, e1001066.
Ward, A., Liu, J., Feng, Z., Xu, X.Z.S., 2008. Light-
sensitive neurons and channels mediate phototaxis in C.
elegans. Nat. Neurosci. 11, 916–922.
White, J.G., Southgate, E., Thomson, J.N., Brenner, S.,
1986. The Mind of a Worm. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B
Biol. Sci. 314, 1–340.
Wilson, E., Rustighi, E., Newland, P.L., Mace, B.R., 2012.
A comparison of models of the isometric force of locust
skeletal muscle in response to pulse train inputs.
Biomech. Model. Mechanobiol. 11, 519–532.
Windmaier, E., Raff, H., Strang, K., 2003. Human
Physiology: The Mechanisms of Body Functions. The
McGraw−Hill Companies.
Wood, W.B., 1988. Introduction to C. elegans Biology. The
Nematode Caenorhabditis elegans 1–16.
NeBICA 2015 - Symposium on Neuro-Bio-Inspired Computation and Architectures
126
