Reliability and External Validity of Tensiomyography Measurements
Following Strength Exercise
Rauno Álvaro de Paula Simola
1
, Christian Raeder
1
, Michael Kellmann
2,3
, Tim Meyer
4
,
Mark Pfeiffer
5
and Alexander Ferrauti
1
1
Department of Training and Exercise Science, Faculty of Sports Science, Ruhr-University Bochum, Bochum, Germany
2
Department of Sport Psychology, Faculty of Sports Science, Ruhr-University Bochum, Bochum, Germany
3
School of Human Movement Studies and School of Psychology, The University of Queensland, Brisbane, Australia
4
Institute of Sports and Preventive Medicine, Saarland University, Saarbruecken, Germany
5
Institute of Sports Science, Johannes-Gutenberg University, Mainz, Germany
Keywords: Tensiomyography, Reliability, Validity, Strength Exercise.
Abstract: Tensiomyography (TMG) reliability and external validity using maximal voluntary isometric contraction
(MVIC) following different strength training protocols (STP) were analysed. Twenty healthy male were
tested two times over one week and TMG reliability was analysed in the muscles Rectus Femoris (RF),
Biceps Femoris (BF), and Gastrocnemius Lateralis (GL), after an individual maximal and submaximal
electrical stimulation. Moreover, TMG external validity was assessed through Pearson correlation between
changes in TMG muscle mechanical properties in RF and changes in MVIC in squat exercise after five
different lower-limb STPs. Maximal electrical stimulation showed the highest ICC scores for TMG muscle
properties reliability in all muscles investigated. Significant Pearson correlation coefficients were found
between changes in TMG mechanical properties and changes in MVIC after STPs characterized by high
intensity, time under tension and eccentric overload. TMG is a valid and reliable method to assess muscle
mechanical properties especially under maximal condition.
1 INTRODUCTION
Different methods and techniques have been used to
assess neuromuscular function, such as torque
recordings during voluntary or evoked contractions,
mechanical power, surface electromyography,
magnetic resonance imaging and ultrasound (Tous-
Fajardo et al., 2010). In this context, a novel
technique, tensiomyography (TMG), may have an
additional advantage. TMG measures can be carried
out quickly, are not producing additional fatigue and
do not depend on voluntary motivation. It allows a
non-invasive muscular function analysis, through the
assessment of different specific muscle mechanical
properties (Dahmane et al., 2001; García-Manso et
al., 2012). Although the reliability of TMG was
already reported (Rey et al., 2012), it is still unclear
its reliability from submaximal electrical stimuli.
Despite many existing techniques to evaluate
neuromuscular function, muscle force has been
considered the best indicator of the ability of the
muscle to perform (Jackman et al., 2010). Effective
strength training programs can be performed with
different ranges of load intensity, repetition number
and rest period between sets, type of muscle action
and time under tension (Kraemer and Ratamess,
2004). As far as we know, no study has correlated
the acute strength performance changes with
changes in TMG muscle properties after the
execution of different strength training protocols
used in the applied field.
Therefore, the purpose of the present study was to
analyse the TMG reliability and external validity
using maximal voluntary isometric contraction
(MVIC). The reliability values were investigated
within maximal and submaximal electrical stimuli.
Changes in MVIC were assessed after five different
lower-body strength training protocols. We
hypothesized that TMG is a reliable method to
assess muscular function within submaximal and
maximal electrical stimuli and that changes in TMG
muscle mechanical properties correlate with changes
in MVIC values after different strength training
protocols.
174
Simola, R., Raeder, C., Kellmann, M., Meyer, T., Pfeiffer, M. and Ferrauti, A..
Reliability and External Validity of Tensiomyography Measurements Following Strength Exercise.
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Congress on Sport Sciences Research and Technology Support (icSPORTS 2015), pages 174-178
ISBN: 978-989-758-159-5
Copyright
c
2015 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
2 METHODS
2.1 Experimental Design
The current study was organized in two different
parts. In the first part of the study, it was analysed
the reliability of the TMG mechanical properties.
Twenty healthy male (age: 26.5 ± 6.7 years; body
mass: 78.5 ± 6.8 kg; height: 181.0 ± 5.5 cm) were
tested two times over one week period. Muscles
analysed were rectus femoris (RF), biceps femoris
(BF) and gastrocnemius lateralis (GL) left and right
sides, after an individual maximal and a submaximal
electrical stimulation (40 mA). Absolute reliability
was assessed by the standard error of measurement
(SEM) whereas the relative reliability by the
intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC).
In the second part of the study, external validity
of the most appropriate TMG mechanical properties
verified in the first part of the current study from left
and right muscle rectus femoris (RF) were assessed
after the execution of five different lower-body
strength training protocols in a randomized cross-over
design with multiple repeated measures. Fourteen
healthy male (age: 23.0 ± 1.9 years; body mass: 76.6
± 7.8 kg; height: 179.4 ± 6.8 cm), experienced in
strength training participated in this part of the study.
All participants attended a familiarization session to
introduce the testing and training procedures to
minimize any learning effect. Average baseline
values were collected on two occasions interspaced
by one week including measures of body
composition, TMG mechanical properties, one
repetition maximum (1RM), and maximal voluntary
isometric contraction (MVIC) for the parallel squat.
The five different squat training protocols were
randomly assigned for each participant and
performed once per week, separated by six days in
between, within 1.5 - 2 hours at the same time of the
day throughout the study. It was told to the subjects
not to exercise at the day before training, and to
consume their last meal (caffeine-free) at least 2
hours before training and testing. TMG followed by
MVIC measurements were conducted up to 0.5 hours
after the end of each training protocol (post-train).
Subjects were informed about all details of the
experimental procedures and the associated risks
and discomforts. All participants gave their written
consent to participate in the study and were free to
withdraw from the study at any time. The
experimental protocol followed the world medical
association’s declaration of Helsinki on research with
humans and was approved by the local Ethics
Committee of the Ruhr-University Bochum.
2.2 Training Protocols
Multiple Sets (MS): A smith rack machine with a
guided barbell was used for training (TechnoGym
Multipower, Italy). The protocol consisted of 4 sets
of 6RM (i.e., 85% 1RM) parallel squats (knees are
flexed until the inguinal fold is in a straight
horizontal line with the top of the knee
musculature), intended explosive during the concen-
tric phase and 2 seconds in eccentric phase,
approximately 72 seconds of time under tension
(TUT), and 3 minutes rest between sets (Drinkwater
et al., 2005). A laser imager and an acoustic stimulus
were used to standardize the range of motion (ROM)
of approximately 110-120°.
Drop Sets (DS): Subjects performed DS with the
same barbell machine and ROM as described for
MS. 1 set of 6RM (i.e., 85% 1RM), 4 seconds in
eccentric and 2 seconds in concentric phase
respectively, and approximately 130-150 seconds
TUT was conducted (Skurvydas et al., 2010).
Immediately after the first set, the load was reduced
for the next three sets (70%, 55% and 40% 1RM,
respectively), so that the subjects continued to train
until concentric failure for each load, which was
defined as the point when the muscles involved can
no longer produce force enough to sustain the given
load (Yarrow et al., 2007).
Eccentric Overload (EO): This protocol
combined concentric with enhanced eccentric
muscle actions (Yarrow et al., 2007) with the same
barbell machine and ROM as the two protocols
described before. 4 sets of 6 repetitions at a load of
70% concentric and 100% eccentric of their
individual 1RM, 3 minutes rest between sets, were
performed during approximately 4 seconds each
repetition (i.e., 2 seconds eccentric, 1 second
isometric, and intended explosive in concentric
phase), and approximately 96 seconds TUT. Two
helpers organized the weight changes during the
upright and lower position.
Flywheel (FW): A YoYo squat flywheel machine
was used for training (YoYo Technology, Stockholm,
Sweden). Subjects performed 4 sets of 6 maximal
rep- etitions, approximately 96 seconds TUT, 3
minutes rest between sets. Besides 6 intended
maximal repetitions, 2 previous repetitions were
selected for initial movement acceleration. The squat
movement was executed with a ROM of about 95-
105°, starting the concentric action at approximately
60-70° until about 165° of internal knee angle,
carefully controlled by an experienced supervisor
(Norrbrand, 2010). Subjects were asked to perform
each repetition with a maximum effort, accelerating
Reliability and External Validity of Tensiomyography Measurements Following Strength Exercise
175
the wheel in the concentric action and upon
completion, decelerating the wheel by means of an
eccentric action.
Plyometrics (PL): Subjects performed 4 sets of
15 drop jumps from a 60 cm-jump box, with 5
seconds rest between repetitions, and 3 minutes rest
between sets (de Villarreal et al., 2009). The study
participants were asked to land until the knees are
flexed of about 90° followed by a simultaneous
explosive knee extension and arms swing for
maximum vertical jump height.
2.3 Measurements
Tensiomyography (TMG): TMG measurements were
conducted using a specific electrical stimulator
(TMG-S2), the TMG-OK 3.0 software, as well as a
displacement sensor tip with a prefixed tension of
0.17 N m-1, which was positioned perpendicular to
the selected muscle belly (TMG-BMC, Ljubljana,
Slovenia). Mechanical properties under submaximal
(40 mA) and individual maximal conditions were
obtained after a single 1 ms electrical stimuli.
Maximal electrical stimulation and maximal muscle
belly displacement were found by progressively
increasing the electric current by 20 mA for each
stimuli. An average from two consecutive stimuli
from both legs was taken and a rest period of 10 s
was interspersed between the measurements. The
measuring point for each muscle was carefully
determined as a point of maximal muscle belly
displacement during voluntary contraction. The
measurements were performed in the lower limbs in
a supine position and a knee joint angle of 120°
was kept by using supporting pads. The electrodes
(5 x 5 cm) were placed five cm distally and five
cm proximally to the sensor. The positions of
electrodes and sensor were marked and kept
constant during the complete experimental period.
All the measurement procedures were accomplished
according Rey et al. (2012). Maximal radial muscle
displacement (Dm), time contraction (Tc),
determined from 10% to 90% Dm, delay time (Td),
determined from onset of electrical stimulus to 10%
Dm, sustain time (Ts), determined as time between
50% Dm during muscle contraction and relaxation,
relaxation time (Tr), determined from time of fall
from 90% to 50% Dm, mean contraction velocity
until 10% Dm (V
10
) and mean contraction velocity
until 90% Dm (V
90
) were analysed.
One Repetition Maximum (1RM): The
hypothetical one repetition maximum (1RM) for
each participant in a smith rack machine
(TechnoGym Multipower, Italy) was assessed by the
formula proposed by Brzycki (1993). Subjects were
instructed to position into a shoulder bride stand and
the barbell was placed on the trapezius muscle and
posterior deltoid muscle. In the parallel squat, the
knees are flexed until the inguinal fold is in a straight
horizontal line with the top of the knee musculature.
A laser imager and an acoustic stimulus served to
standardize the ROM of approximately 105-110°.
Subjects started with two warm-up sets consisting of
five repetitions with an intensity of 50% of the
individual body weight with two minutes pause.
After that, a work set including five repetitions with
an intensity of 80 to 85% of the individual body
weight was performed. Finally, after five minutes,
the test supervisor asked to increase the weight for
estimating the 1RM. The test was stopped when
subjects were unable to raise the barbell with a
proper technique or without the help of the
supervisor. If subjects exceeded the limit of ten
repetitions, the supervisor stopped the test and the
intensity was increased. The test ended when
subjects achieved five to ten maximum repetitions
and the 1RM was estimated in kg.
Maximal Voluntary Isometric Contraction
(MVIC): MVIC was measured in a half squat
isometric exercise using a Multitrainer 7812-000
(Kettler Profiline, Germany) and analogous user
software (DigiMax Version 7.X). The subjects were
directed to position under the shoulder upholstery
into a shoulder bride stand. Subsequently the subject
was set up into a testing position up to a knee-joint
angle of 90° using a custom made goniometer.
Without moving explosively, but low rate of force
development they were asked to produce a maximal
voluntary isometric contraction over a 3 second time
interval, as recommended by Blazevich et al. (2002).
All subjects performed two MVICs with 2 min rest in
between and the mean of both attempts was
recorded.
2.4 Statistical Analyses
Data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation
(SD). These data were analysed using the Statistical
Package for the Social Sciences 18.0 Software
(SPSS Inc., USA). The Kolmogorov-Smirnov test
was used to check the normality of the data
distribution. In the first part of the study, absolute
reliability was assessed by the standard error of
measurement (SEM) whereas the relative reliability
by the intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC). After
the calculation of the changes in TMG parameters
and MVIC from each protocol from baseline to post-
train, Pearson correlation coefficient between those
icSPORTS 2015 - International Congress on Sport Sciences Research and Technology Support
176
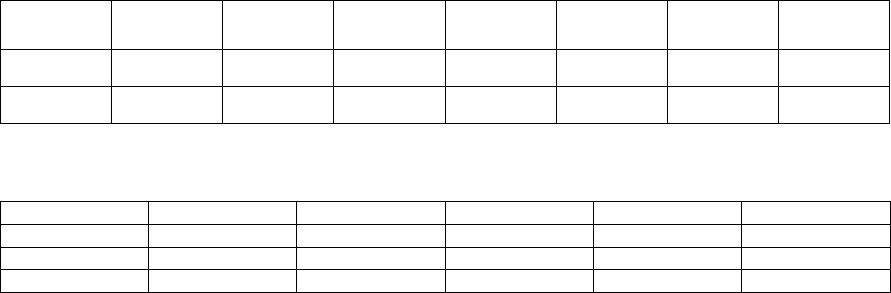
Table 1: Intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) and standard error of measure (SEM) for TMG parameters under
maximal stimulation for the muscles RF, BF and GL (* p
<
0.01).
Tc
(ms)
Td
(ms)
Tr
(ms)
Dm
(mm)
Ts
(ms)
V
10
(mm.s
-1
)
V
90
(mm.s
-1
)
ICC
0.91*-0.94* 0.87*-0.92*
0.70*-0.93* 0.92*-0.95* 0.85*-0.88* 0.92*-0.94*
0.92*-0.95*
SEM
1.9-6.8
0.8-1.3
8.1-26.9
0.9-1.0
13.3-29.0
3.2-4.0
10.1-17.9
Table 2: Pearson correlation coefficients for changes from baseline to post-train, between Dm, V
10
, V
90
, and MVIC (*
p < 0.05; **p < 0.01).
MS
DS
EO FW PL
Dm
0.21 0.61* 0.72** 0.17 0.14
V
10
0.25 0.62* 0.76** 0.18 0.04
V
90
0.25 0.63* 0.66** 0.08 -0.04
changes was used to establish TMG external validity.
Moreover, it was established at baseline the
correlation between TMG parameters. Statistical
significance was set at p < 0.05.
3 RESULTS
Maximal electrical stimulation showed the highest
ICC significant values for TMG reliability in all the
muscles investigated (Table 1). Regarding
submaximal condition, not all TMG muscle
properties exhibited sufficient reliability. Tc, Td,
Dm, V
10
, and V
90
showed significant ICC scores
(0.66-0.92; 0.65-0.92; 0.81-0.96; 0.85-0.94; 0.85-0.93)
in the different muscles respec
tively.
It was found a high significant Pearson
correlation (r > 0.9; p < 0.001) between TMG
muscle properties Dm, V
10
, and V
90
. Pearson
correlation coefficients from each protocol between
MVIC changes and respective changes of Dm, V
10
,
and V
90
, are presented in Table 2.
4 DISCUSSION
Maximal electrical stimulation has demonstrated
higher reliability in comparison with submaximal
condition. In some muscles, under submaximal
stimuli, Tr and Ts have not been repeatable. As the
higher reliability scores were found after maximal
stimulation and not all TMG muscle properties were
repeatable, in the second part of the study, maximal
stimuli and muscle properties Dm, V
10
, and V
90
were used.
Dm has been considered as a measure of muscle
belly radial stiffness, and an increasing in such
variable indicates smaller muscle belly radial stiffness,
whereas its decreasing means greater muscle belly
radial stiffness (García-Manso et al., 2012; Hunter et
al., 2012; Rey et al., 2012). However, because of a
high positive Pearson correlation coefficients found
between the TMG muscle properties Dm, V
10
, and
V
90
(r > 0.90; p < 0.001), Dm might also indicate
the capacity to perform fast muscle contractions,
under the conditions of the present study.
It was observed a significant correlation between
changes in Dm, muscle contraction velocities, and
changes in MVIC after the execution of DS and EO (r
range between 0.61 and 0.76). These results are in
accordance with Hunter al. (2012), which
demonstrated a positive correlation between changes
in strength performance and changes in TMG
muscle properties after eccentric muscle actions. The
association between changes in TMG muscle
properties and changes in MVIC might be explained
by some specific characteristics of DS and EO,
possibly related to fatigue. The number of
repetitions at a high workload performed in DS led
to the highest TUT, compared to the other protocols.
Moreover, it has been shown greater fatigue levels
after drop-set strength protocols (Willardson, 2007),
as additional higher threshold motor units are
recruited and subsequently fatigued. Regarding EO,
because of a greater eccentric muscle acti
vation and
higher exercise-induced muscle damage (Norrbrand,
2010; Schoenfeld,
2012), this protocol may have a
special effect on fatigue. Eccentric muscle actions
have been shown to produce a greater amount of
force than isometric or concentric actions despite a
decreased motor units recruitment (Tesch et al.,
2004). The result is a higher tension produced per
cross-bridge and progressive sarcomere over-
stretching, predisposing to destruction of contractile
proteins and damage in cellular structures (Proske
Reliability and External Validity of Tensiomyography Measurements Following Strength Exercise
177
and Allen, 2005; Tesch et al., 2004).
TMG is a valid and reliable method to assess
muscle mechanical properties especially under
maximal conditions. Based on our results, we advise
researches that analyse the relationship between
TMG muscle properties and muscle fatigue after the
execution of strength training exercises.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The present study was initiated and funded by the
German Federal Institute of Sport Science. Rauno
Simola gratefully acknowledges CAPES for finan-
cial support. The authors disclose no conflicts of
interest.
REFERENCES
Blazevich, A. J., Gill, N., and Newton, R. U. Reliability
and validity of two isometric squat tests. J Strength
Cond Res 16: 298–304, 2002.
Brzycki, M. Strength testing: predicting a one-rep max
from repetitions to fatigue. J Physical Education 64:
88–90, 1993.
Dahmane, R, Valencic, V, and Erzen, NK. Evaluation of
the ability to make non- invasive estimation of muscle
contractile properties on the basis of the muscle belly
response. Med Biol Eng Comput 39: 51–55, 2001.
Drinkwater, EJ, Lawton, TW, Lindsell, RP, Pyne, D,
Hunt, PH, and McKenna, MJ. Training leading to
repetition failure enhances bench press strength gains
in elite junior athletes. J Strength Cond Res 19: 382–
388, 2005.
García-Manso, J. M., Rodríguez-Matoso, D., Sarmiento,
S., de Saa, Y., Vaamonde, D., and Rodríguez-Ruiz, D.
Effect of high-load and high-volume resistance
exercise on the tensiomyographic twitch response of
biceps brachii. J Electromyogr Kinesiol 22: 612–619,
2012.
Hunter, A. M, Galloway, S. D., Smith, I. J., Tallent, J.,
Ditroilo, M., and Fairweather, M. M. Assessment of
eccentric exercise-induced muscle damage of the
elbow flexors by tensiomyography. J Elektromyogr
Kinesiol 22: 334–341, 2012.
Jackman, S. R., Witard, O. C., Jeukendrup, A. E., and
Tipton, K. D. Branched-chain amino acid ingestion
can ameliorate soreness from eccentric exercise. Med
Sci Sports Exerc 42: 962–970, 2010.
Kraemer, W. J., and Ratamess, N. A. Fundamentals of
resistance training: progression and exercise
prescription. Med Sci Sports Exerc 36: 674–688, 2004.
Norrbrand, L. P. Flywheel resistance training calls for
greater eccentric muscle activation than weight
training. Eur J Appl Physio 110: 997–1005, 2010.
Proske, U, and Allen, T. J. Damage to skeletal muscle
from eccentric exercise. Exerc Sport Sci Rev 33: 98–
104, 2005.
Rey, E., Lago-Pen˜as, C., and Lago-Ballesteros, J.
Tensiomyography of selected lower-limb muscles in
professional soccer players. J Electromyogr Kinesiol
22: 866–872, 2012.
Schoenfeld, B. Does exercise-induced muscle damage
play a role in skeletal muscle hypertrophy? J Strength
Cond Research 26: 1441–1453, 2012.
Skurvydas, A, Streckis, V, Brazaitis, M, and Rudas, E.
The effect of plyometric training on central and
peripheral fatigue in boys. Int J Sports Med 31: 1–7,
2010.
Tesch, PA, Ekberg, A, Lindquist, DM, and Trieschmann,
JT. Muscle hypertrophy following 5-week resistance
training using a nongravity-dependent exercise system.
Acta Physiol Scand 180: 89–98, 2004.
Tous-Fajardo, J., Moras, G., Rodriguez-Jimenez, S.,
Usach, R., Doutres, D. M., Maffiuletti, N. A. Inter-
rater reliability of muscle contractile property
measurements using non-invasive tensiomyography. J
Electromyogr Kinesiol 20: 761–766, 2010.
de Villarreal, E. S., Kellis, E., Kraemer, W. J., and
Izquierdo, M. Determining variables of plyometric
training for improving vertical jump height
performance: a meta- analysis. J Strength Cond Res
23: 495–506, 2009.
Willardson, J. M. The application of training to failure in
periodized multiple-set resistance exercise programs. J
Strength Cond Res 21: 628–631, 2007.
Yarrow, J. F., Borsa, P. A., Borst, S. E., Sitren, H. S.,
Stevens, B. R., and White, L. J. Neu- roendocrine
responses to an acute bout of eccentric-enhanced
resistance exercise. Med Sci Sports Exerc 39: 941–
972, 2007.
icSPORTS 2015 - International Congress on Sport Sciences Research and Technology Support
178
