
Simulation-Based Evaluation of Recommendation Algorithms Assisting
Business Process Modeling
Adam Styperek, Michal Ciesielczyk, Pawel Misiorek and Andrzej Szwabe
Institute of Control and Information Technology, Poznan University of Technology
Piotrowo 3, 60-965 Poznan, Poland
{adam.styperek, michal.ciesielczyk, pawel.misiorek, andrzej.szwabe}@put.poznan.pl
Keywords:
BPMN, recommendation systems, process modeling support, usability of process design tools.
Abstract:
In this paper, we propose a methodology for objective and repeatable simulation-based evaluation of recom-
mendation algorithms supporting the process of designing of a BPMN model. According to the methodology,
an evaluation of the usability of recommendations is done entirely with the use of the dedicated software cou-
pled by a predefined test set. In order to confirm the reliability of the methodology, an additional evaluation
based on the user study has been performed.
1 INTRODUCTION
Business process modeling (BPM) is considered as
an error-prone and time-consuming task (Hornung
et al., 2009; Smirnov et al., 2010). Moreover, despite
rapid development of BPM technology its users in-
clude mostly large companies or organizations. This
is due to the fact that, for small and medium enter-
prises (SMEs), the development of their own systems
business process management is still considered too
expensive. As a result, there is often a lack of docu-
mentation of existing business processes within SME,
and even although employees acquire this knowledge,
it is not properly formalized.
Modeling a business process may be easier – and
thus less expensive – when the user is provided with
a tool able to recommend the subsequent step of the
process being modeled. For that reason, in the last
few years scientists have conducted research on rec-
ommendation systems used in business process mod-
eling (Hornung et al., 2009; Koschmider et al., 2011;
Hornung et al., 2008). The main purpose of this ef-
fort is to provide the user with a tool, that makes the
modeling process less error-prone, as a result of using
the recommendations of Business Process Model and
Notation (BPMN) components based on a repository
of already approved BPMN processes. The applica-
tion of a recommendation system should also make
the modeling process less time laborious, thanks to
the ability of reusing the parts of the existing business
processes in the repository
In this paper, we propose a methodology aimed
at providing means for a quantitative and unambigu-
ous evaluation of the usability of recommendation al-
gorithms enhancing software for the visual design of
business processes. We are focused at taking into ac-
count the specific purpose of a tool supporting the de-
sign of BPMN models. In particular we have evalu-
ated to what extent a recommendation system is able
to support human BPMN modelers at the syntactic
level, and how the provided recommendations may
be trusted. Thus, the usefulness has been measured in
terms of the actual human effort savings, rather than
the recommendation quality measures that are typi-
cally referred to in the literature on recommendation
systems (Herlocker et al., 2004). This is motivated by
the fact that reducing the labor costs could contribute
to the spread of BPM technologies among SMEs and,
by imposing established design patterns, help to im-
prove the overall quality of the business processes
modeled by inexperienced modelers.
Although our evaluation methodology uses the
number of human-computer interactions as a basis
of a performance measure, it also contains the indi-
rect measurement of the quality of recommendation
algorithms supporting the design of BPMN models
in terms of modeller decision support. If the rec-
ommendation of the BPMN component is syntacti-
231
Styperek A., Ciesielczyk M., Misiorek P. and Szwabe A.
Simulation-Based Evaluation of Recommendation Algorithms Assisting Business Process Modeling.
DOI: 10.5220/0005887602310240
In Proceedings of the Fifth International Symposium on Business Modeling and Software Design (BMSD 2015), pages 231-240
ISBN: 978-989-758-111-3
Copyright
c
2015 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

cally correct but incorrect from the perspective of the
model semantics, such a recommendation is classi-
fied as a wrong one (i.e., as rejected by a modeller).
In this scenario, the proposed evaluation methodol-
ogy assumes that the user has to add manually the
correct BPMN component without the help of rec-
ommendations what leads to the increase of the inter-
actions number (e.g., mouse clicks and keystrokes).
In other words, as it is usually done in each eval-
uation methodology, in the phase of testing recom-
mendations’ correctness, we used only these mod-
els, which have been approved by experts. In such
a way, the measure that we proposed also reflects the
issues of modeling semantic correctness. However,
it has to be stressed that our main motivation is to
provide the quantitative measure which directly ad-
dresses the issues of human effort reduction crucial
from the perspective of SMEs. Our goal is to provide
the simulation-based evaluation methodology which
takes into account the features of the modelling tool,
and this way is more reliable than the methodologies
based on the measures typically used in the literature
on recommendation systems.
The usability-centric evaluation introduced in this
paper corresponds to the usability definition formu-
lated in System and Software Quality Requirements
and Evaluation (ISO/IEC, 2011) in terms of effec-
tiveness of achieving the specified goals by a user.
Specifically, we assume that, by reducing the re-
quired amount of human-computer interactions, it is
possible to influence the system characteristics such
as learnabillity, operability, user error protection and
user interface aesthetics which are subcharacteristics
of usability defined in (ISO/IEC, 2011). However, it
should be noted that, in contrast to (ISO/IEC, 2011),
the introduced evaluation does not involve the analy-
sis of opinions about the evaluated system collected
from the users. Instead, we propose a strictly defined
measure based on user-computer interactions saved as
a result of the recommendation system application.
Finally, the proposed evaluation methodology al-
lowed us to formulate two hypotheses:
Hypothesis 1. The use of recommendations reduces
the number of actions performed by a user design-
ing the BPMN model in the shortest possible (i.e., the
least laborious) way.
Hypothesis 2. Real users provided with recommen-
dations are able to reduce the number of actions that
are necessary to complete the preparation of a BPMN
model.
In order to verify these hypotheses we have con-
ducted a series of experiments in which a dedicated
software system has been used to simulate the usage
of a BPMN modeler by a human editor.
In Section 2 we present the state of the art in
the area of BPMN recommendation systems. Section
3 introduces evaluation methodology, and includes a
short description of recommendation system (Subsec-
tion 3.3) and data set used in the presented evaluation
(Subsection 3.4). In Section 4 we show the results of
our experiments. The critical discussion concerning
the effectiveness of recommendations in the case of a
BPMN modeling task has been provided in Section 5.
Section 6 concludes the paper contribution.
2 RELATED WORK
Recommendation-based techniques are becoming
more and more important in the area of research
on business process modeling support methods
(Koschmider et al., 2011; Li et al., 2014; Kluza et al.,
2013). Authors of (Koschmider et al., 2011) has in-
troduced the business process modeling support so-
lution as a recommendation system and described it
as a hybrid recommendation system having features
both of content-based recommendation (as a result
of processing the data about components’ descrip-
tions) and collaborative-based recommendation (as
a result of processing the already developed models
stored in the repository, which serve as a knowledge
base). At the same time, according to (Koschmider
et al., 2011; Chan et al., 2011; Zhang and Xu, 2009)
the recommendation-based techniques for the busi-
ness process modeling may be regarded as context-
based recommendation systems for which the mod-
eling context is defined by process elements that are
already inserted in the workspace.
A few articles presenting recommendation-
based techniques for Business Process Modeling
(BPM) provide the performance evaluation results
(Koschmider et al., 2011) (see Table 1 for compari-
son). On the other hand, the state-of-the-art solutions
use a variety of approaches involving recommen-
dations such as the recommendation of process
fragments and process auto-completion (Koschmider
et al., 2011; Born et al., 2009; Wieloch et al., 2011),
recommendation of subsequent BPM elements during
the modeling process (Zhang and Xu, 2009; Zeng
et al., 2011) (the approach investigated in this paper),
as well as the recommendation of entire processes
and component labels (Leopold et al., 2011). Due to
variety of recommendation approaches used in this
area, the need for defining the common user-centric
performance evaluation methodology enabling the
fair comparison of proposed solutions appears as
even more evident.
Some attempts to adopt information retrieval mea-
Fifth International Symposium on Business Modeling and Software Design
232

sures (such as precision and recall) to business pro-
cess modeling have been made (Dijkman et al., 2011)
but they have been limited to the task of process simi-
larity discovery. In the case of the most advanced rec-
ommendation solutions (Koschmider et al., 2011; Li
et al., 2014; Hornung et al., 2008; Cao et al., 2012;
Zhang and Xu, 2009) the set of more user-centric
measures has been used, including the number of rec-
ommendations used by the modeller, the recommen-
dation accuracy and the reduction of modelling time.
However, these measures do not cover all the issues
regarded as crucial from the perspective of the sys-
tem usability. Particularly, they do not reflect the re-
duction of the number of user-system interactions that
are necessary to build the entire model, including the
necessary mouse clicks and keystrokes.
From the perspective of user interface usability
the research of (Nielsen and Molich, 1990; Wharton
et al., 1994) has to be mentioned. In particular, in
(Nielsen and Molich, 1990) the authors discuss the
major assumptions of user interface design and eval-
uation process whereas in (Wharton et al., 1994) the
interface usability measurement principles are anal-
ysed. In contrast, in our paper we do not evaluate
the user interface – our goal is to measure the reduc-
tion of time and necessary human-computer interac-
tions, when user applies the recommendation system
in modeling process.
Table 1 summarizes the comparison of state-
of-the-art approaches to providing recommendations
supporting business process modeling from the per-
spective of types of similarity between processes used
by recommendation engines, conducting experiments
aimed at recommendation quality evaluation, and the
use of the ontology-based support for the semantic en-
hancement of process representations.
Most of the articles referred to in Table 1 contains
a recommendation quality evaluation section. In (Li
et al., 2014) and (Zhang and Xu, 2009) the systems
are evaluated by measuring the computational effec-
tiveness and the accuracy of recommendations for ev-
ery flow node. The authors of (Dijkman et al., 2011)
measure the precision and recall of provided recom-
mendations and compare them with explicit human
assessments. In (Minor et al., 2007) the users selected
10 processes from a train set that best match the pro-
cesses from test set, and subsequently – by compar-
ison with corresponding recommendation lists – the
precision was calculated. In (Koschmider et al., 2011)
the authors performed experiments in which the users
had to model a business process based on its textual
description. The semantics, syntactic, structural and
labeling correctness of the modeled processes was
then verified. Koschmider et al. admit that they did
not evaluate yet on how to suggest such recommen-
dations to modelers that would allow them to finish
modeling faster. In particular, it has been pointed out
– along with integrating the results from the domain
of human-computer interaction – as a potential direc-
tion for further studies. This paper follows these find-
ings and additionally contributes them by proposing
an evaluation methodology enabling to measure the
reduction of human-computer interactions while not
requiring the participation of real users.
3 EVALUATION
METHODOLOGY
The experiments have been performed in both the sce-
narios: with and without the use of a recommendation
system. In each of the experiments the simulator has
been used to gradually ‘design’ a given process model
(known a priori to the simulator and unknown to the
recommendation system) and, in parallel, to evaluate
recommendations received after adding each element
of the BPMN model being constructed during the ex-
periments. Subsequently, we have performed an addi-
tional user study in order to verify the real-world reli-
ability of the automatic evaluation results. It is worth
noting that, despite the fact that the verification step
required the participation of human users (which may
be a potential source of bias or unrepeatability), the
methodology may still be considered as objective, as
it does not rely on users’ opinions but solely on inde-
pendently measured experimental outcomes.
3.1 Assumptions and Measures
According to the proposed evaluation methodology
the usability of the recommendation system is mea-
sured by estimating the amount of actions a user has
to perform in order to place a new BPMN element on
the model diagram. Such an amount of actions is es-
timated by calculating the number of unit operations
(see Definition 1) performed by the user. The percent-
age of operations that the user does not need to per-
form thanks to the use of recommendations, is used
as the quantitative usability measure. Subsequently,
the individual scores corresponding to the addition of
the BPMN elements are averaged to obtain the over-
all usability seen from the perspective of designing
the entire BPMN model.
Definition 1. The unit operation is assumed to in-
clude mouse cursor movements and mouse clicks, re-
quired by the BPMN editor to modify the newly added
BPMN component (e.g., to change its name or type).
Simulation-Based Evaluation of Recommendation Algorithms Assisting Business Process Modeling
233

Table 1: Comparison of solutions aimed at supporting BPM edition.
Similarity Evaluation Ontologies
labels structures behavioral support
Minor et al. (Minor et al., 2007) no yes no yes no
Li et al. (Li et al., 2008) no yes no no no
Van der Aalst et al. (van der Aalst et al., 2006) yes no yes no yes
Smirnov et al. (Smirnov et al., 2009) yes yes no no no
Koschmider et al. (Koschmider et al., 2011) yes yes no yes yes
Madhusudan et al. (Madhusudan et al., 2004) yes yes no no yes
Dijkman et al. (Dijkman et al., 2011) yes yes yes yes no
Li et al. (Li et al., 2014) no yes yes yes no
Zhang et al. (Zhang and Xu, 2009) no yes no yes no
The number of unit operations (defined as above)
required to add each element to the model is equal to
1 when it has to be modified, or 0 when no change is
needed.
In order to estimate the effort necessary to type the
component name, the additional assumption enabling
calculation of the number of keystrokes in terms of
unit operations is needed. In (Card et al., 1980),
the authors presented a study on the time needed by
the users to perform basic actions such as typing and
mouse cursor movements or clicks. Based on the pre-
sented analysis it has been concluded that, in aver-
age, at the same time as performing a unit operation
(as defined in Definition 1) the user is able to type in
4, 2, or 1 character, depending on the user’s typing
skills (135, 90, or 55 keys per minute, respectively).
We follow these findings, and we additionally assume
that nowadays a typical computer user is able to stroke
135 keys per minute. In other words, we assume that
an average user of the evaluated system is able to type
in 4 characters and perform a unit operation during a
similar unit of time.
Finally, we assume that the usability r
i
of the rec-
ommendations provided for each element i is calcu-
lated using the following formula:
r
i
= 1 −
a +
b
w
a +
n
i
w
=
n
i
− b
wa + n
i
, (1)
where:
• a indicates whether a user had to perform a unit
operation (a = 1) or not (a = 0),
• b denotes the number of keystrokes performed by
the user during entering the element name,
• n
i
denotes the number of characters in the name
of i-th element of the model (we assume that n
i
is
greater that 0 and b ≤ n
i
),
• w is the weight which denotes the number of char-
acters that user can type during the same time as
one unit operation (in the presented evaluation re-
sults we use the weight w = 4).
The goal of Eq. 1 is to calculate what part of the op-
erations necessary to add a new component is saved
(i.e., does not need to be done manually) as a result of
using the recommendation results.
The usability r of the recommendation system ex-
perienced by the user designing a given business pro-
cess model is calculated in accordance with the fol-
lowing formula:
r =
∑
n
i=1
r
i
n
, (2)
where n is the number of elements contained in the
model. Specifically, sequentially for each element
from the test set a corresponding recommendation list
is evaluated. Such a list is generated by the recom-
mendation system, based on the elements that were
previously added to the currently designed BPMN
model and they descriptions. If the provided recom-
mendations include the currently evaluated BPMN el-
ement, values of a and b are set to 0. Thus, accord-
ing to Eq. 2, it is assumed that the effectiveness of
the recommendation system r
i
is equal to 1. Other-
wise, the number of mouse-related unit operations a
is set to 1, and the number of keystrokes b is set to be
equal to the number of different characters between
the name of the current element and the name of the
recommended element having the same type. If the
recommendation list does not contain even a partially
matched element, b is set to be equal n
i
. In such a
case, r
i
is equal to 0, and thus it is also considered as
a recommendation system miss. Finally, the BPMN
element is added to the current model, and the next
element is tested. If the element is the end event, the
evaluation is stopped (as there are no more elements
to add), and the next BPMN model from the reposi-
tory is taken for the evaluation.
The evaluation presented herein has been per-
Fifth International Symposium on Business Modeling and Software Design
234
formed using a leave-one-out method – which is well
known in the Information Retrieval domain, where
for each individual test case one of the models is re-
moved from the repository. The remaining models in
the repository are then used as a training set for the
recommendation system, while the elements from the
removed model are used as a test set. Under such con-
ditions, the experiment is performed for each model in
the repository.
It has to be stressed that the proposed evaluation
methodology does not take into account all the effort
saved by the BPMN editor in order to decide which
component should be used.
3.2 User Study Methodology
In order to verify whether the results of the proposed
evaluation are accurate we have proposed to perform a
corresponding user study. Such an evaluation, besides
the participation of users, requires a BPMN modeler
software with an integrated recommendation system.
In our study we have used the Activiti Modeler (Ac-
tiviti, 2014). However, basically any BPMN editor
that could be integrated with a recommendation sys-
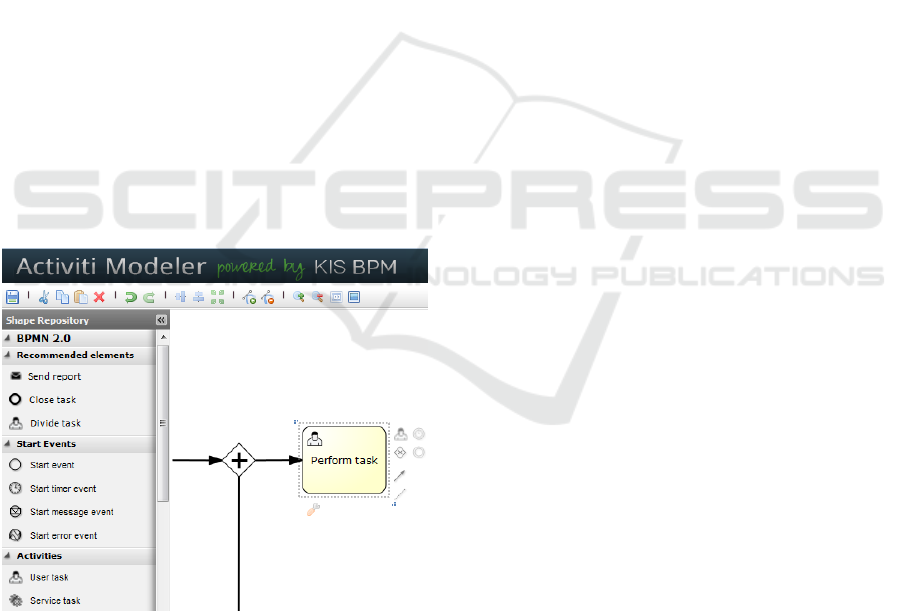
tem might be used as well. Figure 1 presents the user
interface – the recommendation module is integrated
with the BPMN 2.0 shapes repository located on the
left side of the screen.
Figure 1: The user interface of the BPMN editor (with the
recommendation module on the left).
In order to quantitatively estimate the usability im-
provement achieved by the employment of a recom-
mendation module into a BPMN editor, we have con-
ducted a randomized experiment with two variants,
which are identical except for one variation that might
affect a user’s behavior. The first variant is a control
one and includes an unmodified BPMN editor. The
second variant in the controlled experiment involves
the additional use of the recommendation system as-
sisting the user. Using such an approach enables to
perform a two-sample hypothesis testing.
3.2.1 Preliminary Assumptions
The proposed methodology for the user study is based
on the following preliminary assumptions:
• The number of tests involving the usage of each
of the two variants has to be equal so that the two
groups are equally represented. In other words,
half of the tests should be performed with the use
of the recommendation module, and half of the
tests should be performed without it.
• Every user should perform the same number of
experiments that involve and do not involve the
use of the recommendation module. In such a way
we minimize the bias caused by inevitably differ-
ent modelling abilities of the users.
• The order of the individual experiments for each
user must be confirmed to be random. The users,
especially those inexperienced ones, may improve
their skills during the experiment. Thus, setting
up the individual tests in a specific order could po-
tentially favor the experiments performed latterly.
• The business processes to be modelled in the ex-
periment should be equally distributed between
the users in order to avoid, as much as possible,
the bias introduced by a different level of diffi-
culty of each model.
• Every experiment should be unmoderated.
Specifically, the users should have complete
freedom on how to perform the assigned tasks.
Specifically, the testing scenario assumes that
each user receives a printed diagram of the BPMN
process (approved as a correct one by experts) to be
modeled using the provided editor. The procedure as-
sumes, that the user has to model exactly the same
process as in the printed diagram. Thus, the semantic
quality of the process to be modeled is ensured – the
user has the knowledge of a correct business process,
and the modelling is finished when such a process is
obtained. Subsequently, the usability of the recom-
mendation system is estimated using the Eq. 2 – the
same as in the case of the simulator described pre-
viously. Additionally, we also evaluate other factors
important from the perspective of user interface us-
ability such as:
• The time spent on modeling each process,
• The total number of keystrokes, and
Simulation-Based Evaluation of Recommendation Algorithms Assisting Business Process Modeling
235
• The total number of mouse clicks.
These components have been identified as actions
inspected in a formal action analysis in (Holzinger,
2005).
3.2.2 Results Interpretation
The final usability result of the recommendation sys-
tem (in the range < 0, 1 > – the higher, the better)
is calculated as the arithmetic average of results ob-
tained for each element. Particularly, if the result is
equal to 1 the user made a whole model only with the
use of the elements from the recommendation panel
and did not have to enter the names (or any other at-
tributes) of the elements. Conversely, if the result is
equal to 0 the user either did not use any of the recom-
mended elements or used some but have to changed
the whole names of all of them.
3.3 Recommendation System
We implemented a recommendation system that sup-
ports the user in the usage of a graphical BPMN edi-
tor – Activiti (Activiti, 2014). Each query submitted
to the recommendation system contains the currently
designed business process model and an information
about the currently selected element. As a result, the
system returns a list of recommendations containing
new BPMN elements which semantically match to the
current model, and could be effectively added by the
user to the diagram. The length of the recommen-
dation list has been set to three elements by default
(however, it can be changed by the user).
In order to generate a useful list of recommen-
dations, the system analyses both reference business
process models (originating from a process reposi-
tory) and behavioral patterns (collected during the op-
eration of the system). Both structural information
concerning the process flows, BPMN types taxonomy
and textual artifacts are used by the recommendation
algorithm to provide relevant feedback to the user. All
of the information is stored in a common Resource
Description Framework (RDF) format compliant with
a specifically designed ontology describing BPMN ar-
tifacts. Such an approach enables to store heteroge-
neous data and jointly process it.
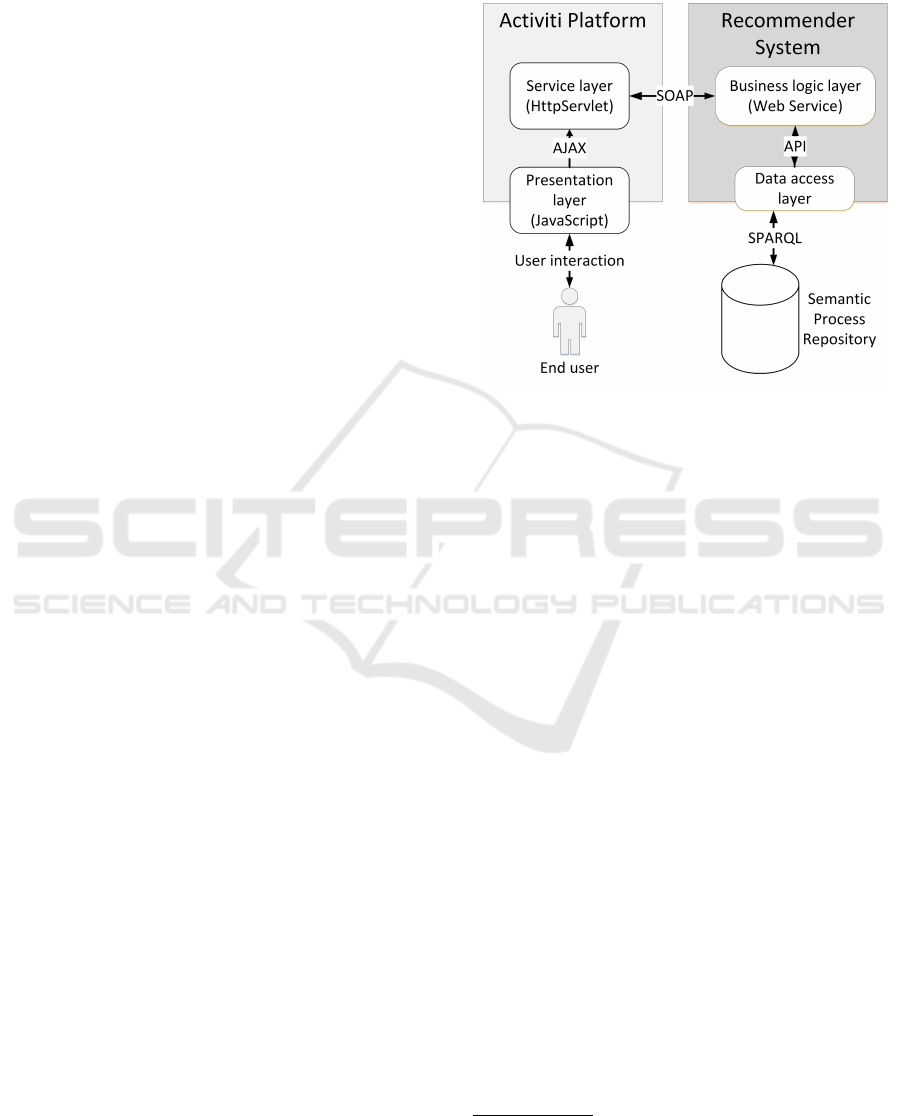
Figure 2 presents a conceptual view of the system
components. The presentation layer, built within the
Activiti, is responsible for capturing all of the relevant
user actions and for asynchronous displaying the re-
ceived recommendations. The service layer module
communicates with the recommendation system and
acts as a data converter. Specifically, it transforms the
data collected by the presentation layer into seman-
tic RDF documents and conversely – the RDF docu-
ments received from the recommendation system into
the JSON format used natively by Activiti.
Figure 2: Conceptual view of system’s components.
A more detailed description of the implemented
software used is clearly out of the scope of the paper,
since it is not focused neither on introducing novel
recommendation techniques nor on the evaluation of
the specific algorithm.
3.4 Data Set
The data set used in the experiments presented in
this paper has been created as one of the outcomes
of the Prosecco project
1
that are not publicly avail-
able. This data set includes BPMN models of pro-
cesses from the field of small and medium enterprises
only, what makes it a rather untypical BPM repos-
itory. As a result of focusing on this quite specific
market sector, the data set is relatively small: it con-
tains only 78 BPMN models and contain 625 distinct
elements. The set of models taken into the evalua-
tion includes 858 elements, what gives the average
of 11 elements per model (sequence flows were not
taken into account). It is worth to note that in most
cases, the repository contained no elements from the
test set, what made any proper recommendation im-
possible. This issue has been caused by the insuffi-
cient number of similar models stored in the reposi-
tory. In general, only in the case of 172 recommen-
dation queries (about 2.2 per model) the system had a
chance of providing a correct recommendation since
1
http://geist.agh.edu.pl/pub:projects:
prosecco:start
Fifth International Symposium on Business Modeling and Software Design
236
for the remaining queries the element needed by the
user was not even present in the training set.
4 EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS
We performed a series of experiments - each exe-
cuted in accordance with the evaluation methodology
described in Section 3.1. The results of the exper-
iments realized by means of the dedicated software
system (logging all of the required parameters), are
presented in Table 2. The ‘average gain’ denotes the
average of recommendation usability for all models,
calculated as a mean of recommendation usability of
each model based on the Eq. 2. The average num-
ber of possible recommendations per model is equal
to the number of correctly recommended elements di-
vided by the number of elements that could be rec-
ommended. The recommendation engine under test
has properly recommended 68 elements (what gives
the average equal to 0.87 per model). A recommen-
dation is considered as a proper one if and only if the
user does not have to change anything in the element,
i.e., the recommended element is identical to required
element.
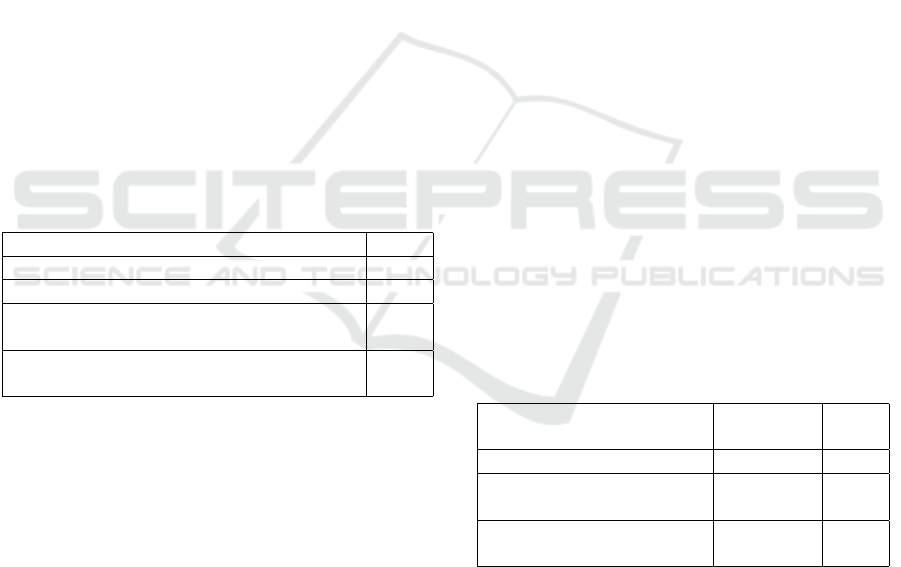
Table 2: Evaluation results.
Measure Value
Average gain from recommendation 0.10
Correctly recommended elements 68
Average correctly recommended elements
per model
0.87
Average gain from recommendation, when
recommendation was possible
0,4
The conducted evaluation led to the result of 0.10
recommendation usability calculated according to the
Eq. 2 what confirms Hypothesis 1. The difference
between this score and the value of properly recom-
mended elements per model (equal to 0.87) is a re-
sult of the fact that (in accordance with the Eq. 1) the
positive values of usability are calculated also for rec-
ommended elements that were not identical but only
similar to the reference element – i.e., for elements
of the proper type, for which the user did not have to
delete or type more characters to correct the recom-
mended element name, than in the case of typing the
name from the beginning.
It should be noted that, for comparison purposes,
we have also evaluated an algorithm yielding random
recommendations. Not surprisingly, due to respec-
tively high diversity of BPMN elements in the data
set, such an algorithm has not provided any measur-
able benefit in our experiments – both in terms of the
usability and accuracy. Thus, we omit its detailed
analysis in our evaluation results.
4.1 User Study Results
In parallel to the evaluation done with the use of ded-
icated simulation software, in order to verify method-
ology correctness, we have conducted a user study
done using the Activiti Modeller tool. The user
study consisted of 48 tests. 24 tests have been per-
formed with the support of the recommendation sys-
tem, whereas the remaining 24 tests without this sup-
port. The half of the participating users have been
qualified as expert users (with the previous experi-
ence in BPMN modelling) when the remaining group
as non-expert users (without any or with a very little
experience in BPMN). The models taken to this study
have been selected on the basis of the results of the
evaluation performed with the use of the simulator:
the models with the highest values of the recommen-
dation usability have been chosen for the user study in
order to enable a more detailed evaluation of recom-
mendation operation, i.e., in order to demonstrate the
methodology correctness in the case of applying rec-
ommendations. For the models for which the system
was not able to suggest the correct recommendation,
both the simulation-based and user-performed evalu-
ation provided the same result indicating no reduction
of the number of interactions. Table 3 illustrates the
results collected during the user study.
Table 3: Average recommendation usability in a test per-
formed on 8 selected models.
Measure Simulation User
study
Recommendation gain 0.33 0.27
Correctly recommended
elements
22 18
Correctly recommended
elements per model
2.75 2.25
For the purposes of the user study, only 8 business
process models (out of 78) have been used. Partic-
ularly, due to extremely high data sparsity, we have
chosen those models for which the tested recommen-
dation system was able to generate the most useful
recommendations (thus the average gain resulted in
the higher value). By that means we were able to
meaningfully measure usability of the recommenda-
tion system. Obviously, if the system was not able
to provide any useful recommendations due to no
Simulation-Based Evaluation of Recommendation Algorithms Assisting Business Process Modeling
237

relevant data in the training set, such an experiment
would be negligible. In order to make the results of
our experiments comparable, we also provide the test
results of a simulation performed using exactly the
same 8 business process models. It should be also
stressed that the simulator tool may be considered as
an ideal business process designer performing the op-
timal number of steps required to build a given busi-
ness process. Thus, as presented in Table 3, the real
users, despite the fact that they were in average pro-
vided with 22 correct recommendations, used only
18 of them. Nevertheless, this observation confirms
that Hypothesis 2 is true. Nonetheless, we may state
that our evaluation methodology enables to provide
approximately the same result as an analogical user
study, without the cost of engaging multiple human
testers.
Based on the results from the user study we can
also conclude that the tested recommendation system
decreases the average number of interactions between
the user and a computer. Specifically, in our study,
the recommendation system enabled to decrease both
the number of mouse clicks by 25% (at a significance
level α = 0.01) and the number of keystrokes by 22%
(at α = 0.01). Although such a result slightly differs
from the usability measured according to Eq. 1, we
may state that the difference between these results is
not significant (α = 0.05). Although the results of
the user study have shown that the recommendation
system allowed to slightly decrease the average time
spent on modeling every process – by about 4%, the
statistical analysis indicated that the difference was
not significant (α = 0.05). In other words, we have
not observed that the recommendation system has any
significant influence on the modeling process time.
5 DISCUSSION
Business process modeling is considered as highly
intellectual work which requires creativity and the
knowledge about the modelled domain. Therefore,
although recommendation-based techniques are be-
coming more and more important in the area of re-
search on business process modeling support methods
(Koschmider et al., 2011; Li et al., 2014; Kluza et al.,
2013), many people have a strong believe that it is not
possible to have really useful recommendation solu-
tion that helps human modelers in this task. Neverthe-
less, since many enterprises (including SMEs) has al-
ready got a set of approved correct business processes
the perspective of reusing their fragments seams to be
promising.
In order to help find the answer to the question
of recommendations’ usability in the area of business
process modeling, in this paper, we have defined the
evaluation methodology, which involves the applica-
tion of a quantitative measure which models the hu-
man effort reduction considered to be crucial from
the perspective of enterprises. Our choice was mo-
tivated by the need of objective evaluation which is
not based on human opinions. Nevertheless, using
such a technical measure may be regarded as not suf-
ficient from the perspective of evaluating the seman-
tic value of recommendations. However, despite the
fact that the proposed quantitative measure is rather
technical, it also indirectly reflects the issues of the
support of human business process modelers at the se-
mantic (pragmatic) level. The reason of this statement
is the fact, the evaluation assumes the application of
correct (and approved by experts) models when test-
ing recommendations correctness. This way, each se-
mantically incorrect recommendation leads to the per-
formance decrease in terms of the proposed measure
based on human-computer interactions. Therefore,
the methodology measure evaluates not only the re-
duction of the number of actions performed by users
but also (indirectly) the semantic value of the recom-
mendations.
Finally, it has to be stressed that the goal of pre-
sented research was not to propose a new the recom-
mendation algorithm but to provide the simulation-
based evaluation methodology which is objective and,
at the same time, reflects the features of a BPMN
modeling tool (we have chosen the Activity Modeler
tool for this purpose).
6 CONCLUSIONS
The realism of any evaluation of a recommendation
system stays in clear conflict with the objectiveness
of the evaluation and with the ability of fully auto-
matic evaluation experiments’ execution. In this pa-
per, we present a methodology that is not based on
users opinions nor on results of experiments involv-
ing human BPMN designers. According to the pro-
posed methodology, an evaluation of the usability of
recommendations assisting the process of designing
of a BPMN model is done entirely with the use of
the dedicated software coupled by a predefined test
set. In order to confirm that the realism of the pro-
posed methodology is not significantly compromised
by the objectiveness and the repeatability of the pro-
posed methodology, we have accompanied the fully
automatic experiments (performed with the use of a
simulator) by analogical experiments involving the
human users’ participation: we have compared the re-
Fifth International Symposium on Business Modeling and Software Design
238

sults of the fully repeatable experiments with the re-
sults of the more realistic experiments. On the basis of
this comparison, we are able to confirm that, at least
as far as the use of the Prosecco project BPMN data
set is assumed, evaluation experiments performed in
accordance with the proposed methodology are both
exactly repeatable and able to provide reasonably re-
liable results.
Based on the comparison of simulation-based
evaluation and the user study, one may conclude that
the presented methodology provides the correct esti-
mation of the level of human-computer interaction re-
duction obtained as a result of applying recommenda-
tions. The evaluation results have showed that the ap-
plication of the recommendation system that was used
in the presented experiments, decreases the number of
human-computer interactions during the BPMN mod-
eling process. Thus, it could reduce the expenses
for documenting and optimizing business processes
of SMEs, which usually do not posses specialized
knowledge of business and information technology
frontier. The user study evaluation results confirmed
that users provided with recommendation system ap-
ply the suggested recommendations, what can im-
prove the reusability of the obtained models or BPMN
elements. The results have also confirmed the correct-
ness of both the hypotheses formulated and investi-
gated in this paper.
This paper motivates several potential directions
of the further research. So far we have focused
on developing a quantitative evaluation methodology.
For future work we plan to investigate, using the
introduced methodology, advanced recommendation
algorithms enabling to process heterogeneous data
(including metadata and semantic data) when their
data structure may not be known in advance. The
most promising solution in this domain are the algo-
rithms based on Statistical Relational Learning meth-
ods, which allow modeling of multi-relational struc-
tures constructed on the basis of heterogeneous input
data and prediction based on these data.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The presented research was partly supported by the
Polish National Center for Research and Develop-
ment under the project no PBS1/B3/14/2012.
REFERENCES
Activiti (2014). Activiti BPM Platform.
http://www.activiti.org/.
Born, M., Brelage, C., Markovic, I., Pfeiffer, D., and
Weber, I. (2009). Auto-completion for executable
business process models. In Ardagna, D., Mecella,
M., and Yang, J., editors, Business Process Man-
agement Workshops, volume 17 of Lecture Notes
in Business Information Processing, pages 510–515.
Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
Cao, B., Yin, J., Deng, S., Wang, D., and Wu, Z. (2012).
Graph-based workflow recommendation: On improv-
ing business process modeling. In Proceedings of
the 21st ACM International Conference on Informa-
tion and Knowledge Management, CIKM ’12, pages
1527–1531, New York, NY, USA. ACM.
Card, S. K., Moran, T. P., and Newell, A. (1980). The
keystroke-level model for user performance time with
interactive systems. Commun. ACM, 23(7):396–410.
Chan, N. N., Gaaloul, W., and Tata, S. (2011). Context-
based service recommendation for assisting business
process design. In Huemer, C. and Setzer, T., edi-
tors, E-Commerce and Web Technologies, volume 85
of Lecture Notes in Business Information Processing,
pages 39–51. Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
Dijkman, R., Dumas, M., van Dongen, B., K
¨
a
¨
arik, R., and
Mendling, J. (2011). Similarity of business process
models: Metrics and evaluation. Information Systems,
36(2):498–516.
Herlocker, J. L., Konstan, J. a., Terveen, L. G., and Riedl,
J. T. (2004). Evaluating collaborative filtering recom-
mender systems. ACM Transactions on Information
Systems, 22(1):5–53.
Holzinger, A. (2005). Usability engineering methods for
software developers. Commun. ACM, 48(1):71–74.
Hornung, T., Koschmider, A., and Lausen, G. (2008).
Recommendation based process modeling support:
Method and user experience. Conceptual Modeling-
ER 2008, pages 265–278.
Hornung, T., Koschmider, A., and Oberweis, A. (2009). A
Recommender System for Business Process Models.
17th Annual Workshop on Information Technologies
& Systems (WITS).
ISO/IEC (2011). ISO/IEC 25010 - Systems and software
engineering - Systems and software Quality Require-
ments and Evaluation (SQuaRE) - System and soft-
ware quality models. Technical report.
Kluza, K., Baran, M., Bobek, S., and Nalepa, G. J. (2013).
Overview of recommendation techniques in business
process modeling. In Nalepa, G. J. and Baumeister,
J., editors, Proceedings of 9th Workshop on Knowl-
edge Engineering and Software Engineering (KESE) ,
Koblenz, Germany.
Koschmider, A., Hornung, T., and Oberweis, A. (2011).
Recommendation-based editor for business process
modeling. Data Knowl. Eng., 70(6):483–503.
Leopold, H., Mendling, J., and Reijers, H. (2011). On the
automatic labeling of process models. In Mouratidis,
H. and Rolland, C., editors, Advanced Information
Systems Engineering, volume 6741 of Lecture Notes
in Computer Science, pages 512–520. Springer Berlin
Heidelberg.
Simulation-Based Evaluation of Recommendation Algorithms Assisting Business Process Modeling
239

Li, C., Reichert, M., and Wombacher, A. (2008). On mea-
suring process model similarity based on high-level
change operations. In Li, Q., Spaccapietra, S., Yu,
E., and Oliv, A., editors, Conceptual Modeling - ER
2008, volume 5231 of Lecture Notes in Computer Sci-
ence, pages 248–264. Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
Li, Y., Cao, B., Xu, L., Yin, J., Deng, S., Yin, Y., and Wu,
Z. (2014). An efficient recommendation method for
improving business process modeling. Industrial In-
formatics, IEEE Transactions on, 10(1):502–513.
Madhusudan, T., Zhao, J., and Marshall, B. (2004). A case-
based reasoning framework for workflow model man-
agement. Data & Knowledge Engineering, 50(1):87–
115.
Minor, M., Tartakovski, A., and Bergmann, R. (2007). Rep-
resentation and structure-based similarity assessment
for agile workflows. In Weber, R. and Richter, M.,
editors, Case-Based Reasoning Research and Devel-
opment, volume 4626 of Lecture Notes in Computer
Science, pages 224–238. Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
Nielsen, J. and Molich, R. (1990). Heuristic evaluation of
user interfaces. In Proceedings of the SIGCHI confer-
ence on Human factors in computing systems, pages
249–256. ACM.
Smirnov, S., Weidlich, M., and Mendling, J. (2010). Busi-
ness process model abstraction based on behavioral
profiles. 6470:1–16.
Smirnov, S., Weidlich, M., Mendling, J., and Weske, M.
(2009). Action patterns in business process models. In
Baresi, L., Chi, C.-H., and Suzuki, J., editors, Service-
Oriented Computing, volume 5900 of Lecture Notes
in Computer Science, pages 115–129. Springer Berlin
Heidelberg.
van der Aalst, W., de Medeiros, A., and Weijters, A. (2006).
Process equivalence: Comparing two process models
based on observed behavior. In Dustdar, S., Fiadeiro,
J., and Sheth, A., editors, Business Process Manage-
ment, volume 4102 of Lecture Notes in Computer Sci-
ence, pages 129–144. Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
Wharton, C., Rieman, J., Lewis, C., and Polson, P. (1994).
Usability inspection methods. chapter The Cognitive
Walkthrough Method: A Practitioner’s Guide, pages
105–140. John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York, NY,
USA.
Wieloch, K., Filipowska, A., and Kaczmarek, M. (2011).
Autocompletion for business process modelling. In
Abramowicz, W., Maciaszek, L., and Wcel, K., ed-
itors, Business Information Systems Workshops, vol-
ume 97 of Lecture Notes in Business Information Pro-
cessing, pages 30–40. Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
Zeng, R., He, X., and van der Aalst, W. (2011). A method to
mine workflows from provenance for assisting scien-
tific workflow composition. In Services (SERVICES),
2011 IEEE World Congress on, pages 169–175.
Zhang, J., L. Q. and Xu, K. (2009). Flowrecommender:
A workflow recommendation technique for process
provenance. In Kennedy P. J., O. K. and P., C., editors,
Australasian Data Mining Conference (AusDM’09),
volume 101 of CRPIT, pages 55–62, Melbourne, Aus-
tralia. ACS.
Fifth International Symposium on Business Modeling and Software Design
240
