
The Survey of Big Data Problems in the Video Surveillance System
Xin Wang, Zheng Xu and Jie Dai*
The Third Research Institute of the Ministry of Public Security, Shanghai, China
Keywords: Big data, Video intelligent analysis, Video structured description, Repository database, Cloud computing.
Abstract: Video surveillance has become the main tool due to its rich, intuitive and accurate information. However,
with the large-scale construction of video surveillance systems all over the world, problems such as “useful
information and clues cannot be found immediately with video big data” decrease detecting efficiency
during crime prediction and public security governance. This paper examines the current techniques
including video intelligent analysis and video structured description (VSD), knowledge discovery in
database, and cloud computing including virtualization, distributed computing and storage, and proposes a
framework of the next generation video surveillance system to explain how to discovery knowledge from
video big data, organize and manage massive heterogeneous resources, and provide operating environment
and resources for tasks, for the purpose of supporting police to predict crime quickly and efficiently.
1 INTRODUCTION
1
Recently, the worldwide terrorist incidents and
crime events occur frequently, and it is urgent for
governments and police to pay serious attention to
the public security governance, the traffic accidents,
criminal prediction and other incidents. With the
help of cloud computing (Liu et al., 2010; Liu et al.,
2011), internet of things (Hu et al., 2014; Luo et al.,
2011), and Big Data (Xu et al., 2014; Xu et al.,
2015), video surveillance has become the main tool
due to its rich, intuitive and accurate information. A
great amount of video surveillance systems have
been built all over the world. China has built more
than 23 million video surveillance cameras till 2013,
of which 3 million are utilized by police, and the
video surveillance are entering the big data era with
its 4V properties. That is, the video data has very
huge volume, taking one city for example, thousands
of cameras are built of which each collects high-
definition video over 24 to 48GB every day with the
rapidly growth; secondly, data collected includes
variety of formats involving multimedia, images and
other unstructured data; furthermore the valuable
information contains in only a few frames called key
frames of massive video data; and the last problem
caused is how to improve the processing velocity of
a large amount of original video with computers, so
1
* The corresponding author: Jie Dai
as to enhance the crime prediction and detection
effectiveness of police and users.
To solve those problems, technologies such as
knowledge mining and deduction, pattern
recognition and cloud computing are widely utilized
in the next generation video surveillance system, to
assist police to discover valuable information and
predict crime from large amount data. China
National Laboratory of Pattern Recognition (NLPR)
has developed the distributed video surveillance
system (Zh et al., 2012), which is applied to discover
unusual behaviour and traffic violations with pattern
recognition. The Industrial Technology Research
Institute of Taiwan set up the Surveillance Video
Analysis Center and built the ” Cloud Intelligent
Video Analysis and Retrieval System”, which
provides video retrieval and other video analysis
services to aid police to discover crime efficiently.
Pacific Northwest National Laboratory (PNNL)
founded National Visualization and visual analysis
techniques and tools Analytics Center (NVAC)
providing sorts of video analysis tools
(http://vis.pnnl.gov/). British ADVISOR project
(Annotated Digital Video for Intelligent Surveillance
and Optimized Retrieval) could estimate crowd
density, analyse human behaviour in and around
subway and predict potential danger and crime early.
IBM has developed a “Smart Vision Suite” with the
ability of automatic event detection, and distributed
technology is used to large-scale system deployment
and internet business.
126
126
Dai J., Xu Z. and Wang X.
The Survey of Big Data Problems in the Video Surveillance System.
DOI: 10.5220/0006020301260129
In Proceedings of the Information Science and Management Engineering III (ISME 2015), pages 126-129
ISBN: 978-989-758-163-2
Copyright
c
2015 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
Based on the research above, this paper proposes
a framework including video intelligent analysis and
video structured description (VSD) (
Zh
et al., 2010),
knowledge discovery in database, and cloud
computing, and discusses how to analyse, organize,
manage and store video big data. The rest of the
paper is arranged as follows. Section 2 introduces
the problems. The architecture is detailed in section
3. In section 4, recent work and research are given.
In the end, some conclusions are drawn and future
work is given in section 5.
2 PROBLEMS DESCRIPTION
Surveillance video data has the 4V properties of big
volume, variety of data format, low value and slow
processing velocity, resulting in several problems in
application especially in crime detection and public
security management for police:
(1) Little video analysis technology is utilized to
recognize vehicle information (license-plate, logo,
and colour etc.) and simple applications, however
crime prediction and clue discovery from massive
video data are most rely on human detection, and it
is still hard to discover deep information and
complex content by computers, also lack of the
standardized description of analysed content.
(2) Due to lack of effective resource
management and organization, a great amount of
computing and storage resources could not be
utilized effectively when analyse and process video
big data.
(3) Without the policing repository database, it is
hard to mine the more complex relationship and
deeper semantics from a great amount of data, also
unnecessary to recommend police available
information, clues, case trend.
3 FRAMEWORK FOR THE NEXT
GENERATION VIDEO
SURVEILLANCE SYSTEM
We propose a new framework to show how to
process, organize, manage and store massive video
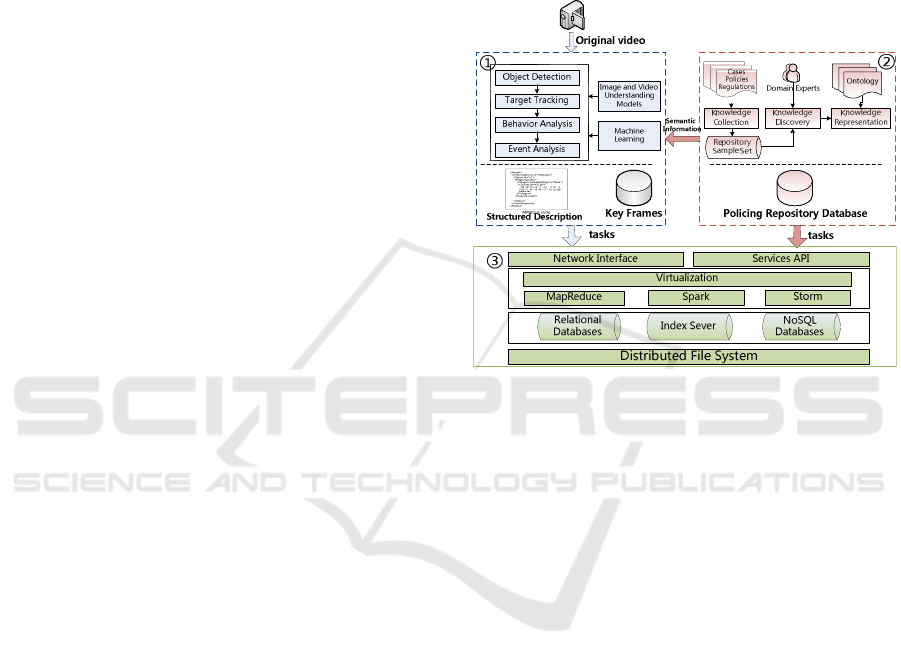
data. As shown in Fig.1.
The framework has three parts: video intelligent
analysis (Object detection, target tracking, behaviour
analysis and event analysis) and video structured
description (VSD) are utilized to mine valuable
information (persons, cars, unusual behaviours etc.)
from large scale video data, which then is expressed
in standard format. The second part is construction
of policing repository database, which is used to data
mining, information describing, moreover
knowledge reasoning as the domain knowledge, and
provide real cases to assist crime prediction.
Furthermore virtualization and cloud computing
provide efficient computing environment for
techniques all above, and storage environment for
various types of structured and unstructured data.
Figure 1: The framework for the next generation video
surveillance system.
3.1 Video Intelligent Analysis and
Video Structured Description
(VSD)
Video intelligent analysis and structured description
are applied to deal with original video, of which the
results are frames containing persons and cars, and
their structured description with standard format.
All the data are packaged with unified standard
format and transferred to the distributed cloud
platform which provides greatly efficient storing and
computing ability. Due to the limited bandwidth, the
“front + back” pattern is adopted, that is: simple
video analysis algorithms are carried out in the
cameras, and results are sent back to “the cloud” to
support more complex computing and applications.
The pattern could avoid network congestion caused
by large-scale video big data.
3.2 Repository Database Construction
Repository database could be constructed as follow
steps: first, knowledge collection, that is collecting
and analyzing existed cases, policies and
regulations, and make them as knowledge repository
The Survey of Big Data Problems in the Video Surveillance System
127
The Survey of Big Data Problems in the Video Surveillance System
127

sample set; secondly is knowledge discovery, that
domain knowledge are mined, clustered and
analyzed from the collected cases and rules, with
machine learning such as support vector machines
(SVM), or expert guidance; thirdly, knowledge
representation, domain knowledge and rules should
be represented with unified form such as RDFS,
OWL and SWRL , and stored in repository database
and model database, from which the information
would be utilized to support training models,
semantic retrieval, reasoning and crime prediction.
3.3 Virtualization, Distributed
Computing and Storage
Technology
For types of tasks such as video content analysis,
semantic modeling and reasoning, Mapreduce,
Spark, Storm and other distributed processing model
are applied to deal with corresponding task. Take
video retrieval for example, Mapreduce would be
used to support the task, of which the key is
represented by the time in video, and video data are
divided into several parts by the key, then all tasks
execute simultaneously.
Moreover, to enhance the efficiency of data
storage, the structured description data, images and
video data during video analyzing, processing, and
retrieval would be classified to optimize the storage
management and satisfy a variety of requests for the
end-users.
Virtualization is adopted to support IT resource
consolidation and optimum use.
4 PREVIOUS WORK
During 2008-2009, the third research institute of
Ministry of Public Security introduced video
structured description technology for the demand in
video surveillance applications, and undertakes a
series national science and technology major
projects including the Ministry of National Science
and Technology Support project, 863 smart city
project and the Core Electronic Devices, High-end
Generic Chips and Basic Software project. Numbers
of public security intelligent video surveillance
systems are carried out successfully, including VSD
based road surveillance video retrieval system in
Shuangliu in Chengdu, Taicang in Jiangsu Province
and so on.
5 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, we propose a novel framework for the
next generation video surveillance system, which
addresses the problems video big data cause during
public security governance and crime predicting. In
this framework, Video intelligent analysis and video
structured description (VSD), knowledge discovery
in database, and cloud computing are introduced,
and video intelligent analysis and VSD discover
targets and express them with standard format.
Knowledge discovery is utilized to repository
database construction, since the repository is the
“material basis” of domain and supports models
training, semantic retrieval, crime prediction and
reasoning. Cloud computing techniques such as
Virtualization, distributed computing and storage
technology provide efficient operating environment,
and optimize the allocation of computing, storage
and network resources for tasks.
The above techniques provide the basic tools
and environment from the point of video big data
mining, organization, and management. However,
some other problems still exist: it still cannot satisfy
the routine detection and application for police. For
example, combining crime prediction results with
visualization methods is necessary for users during
detection. These unsolved problems particularly
merit our further study.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was supported in part by the National
Science and Technology Major Project under Grant
2013ZX01033002-003, in part by the National High
Technology Research and Development Program of
China (863 Program) under Grant 2013AA014601,
in part by the National Science Foundation of China
under Grant 61300028, in part by the Project of the
Ministry of Public Security under Grant
2014JSYJB009.
REFERENCES
Liu,Y., Zhu,Y., Ni, Lionel M., and Xue, G. 2011. A
Reliability-Oriented Transmission Service in Wireless
Sensor Networks. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and
Distributed Systems, 22(12): 2100-2107.
Liu, Y., Zhang, Q., and Ni, Lionel M. 2010. Opportunity-
Based Topology Control in Wireless Sensor Networks.
IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed
Systems, 21(3): 405-416.
ISME 2015 - Information Science and Management Engineering III
128
ISME 2015 - International Conference on Information System and Management Engineering
128

Hu, C., Xu, Z. et al. 2014. Semantic Link Network based
Model for Organizing Multimedia Big Data. IEEE
Transactions on Emerging Topics in Computing,
2(3):376-387.
Luo, X., Xu, Z., Yu, J., and Chen, X. 2011. Building
Association Link Network for Semantic Link on Web
Resources. IEEE transactions on automation science
and engineering, 8(3):482-494.
Xu, Z. et al. 2015. Knowle: a Semantic Link Network
based System for Organizing Large Scale Online
News Events. Future Generation Computer Systems,
43-44:40-50.
Xu, Z., Luo, X., Zhang, S., Wei, X., Mei, L., and Hu, C.
2014. Mining Temporal Explicit and Implicit
Semantic Relations between Entities using Web
Search Engines. Future Generation Computer Systems,
37:468-477.
Zh, H., et al. 2010. Video Structured Description: A Novel
Solution for Visual Surveillance. Lecture Notes in
Computer Science, Volume 6298:629-636.
Zh, T., Liu, S., Xu, C., Lu, H. 2012. Mining Semantic
Context Information for Intelligent Video Surveillance
of Traffic Scenes Industrial Informatics. IEEE
Transactions on Volume:9 , Issue: 1 :149 – 160.
http://vis.pnnl.gov/ .
The Survey of Big Data Problems in the Video Surveillance System
129
The Survey of Big Data Problems in the Video Surveillance System
129
