
The Data Mining on Social Safety Data for Engineering Education
Hailong CHEN
1,2,3
1
Statistics and Information College, Xinjiang Finance and Economics University, China
2
Central Asian Economic Research Institute, Xinjiang Finance and Economics University, China
3
Center for Research in Economics and Statistics, Xinjiang Finance and Economics University, China
Keywords: Data Mining, Social Safety, Engineering Education.
Abstract: Social safety is the most important social problem in the world. Since the spatial changes, the social safety
system has a lot of problems and is needed to change a lot. In the last days, the change of social safety
system has happened all over the world. The social safety systems can be getting almost all countries in the
world. There is an increasing need from countries, society, higher education universities, and people groups
to change current Technology, Science, and Engineering education. Due to engineering education as a need
and as a rule, these efforts need many bottlenecks such as the under delegation of men and minority groups
in the engineering place, a low knowing of the engineering education among rookies, poor performance of
learners in related aspects of engineer and science, and the gap between the need for an engineering place
and graduating learners. This paper is trying to show the discussion on how teachers and learners of
engineering education can build methods and tools to attract, inform, and use engineering words and queries
in university learners. The proposed work of engineering education consists of educational interfaces and
other techniques for engineering education and learning.
1 INTRODUCTION
Social safety is the most important social problem in
the world. Since the spatial changes, the social
safety system has a lot of problems and is needed to
change a lot. In the last days, the change of social
safety system has happened all over the world. The
social safety systems can be getting almost all
countries in the world. The volume of social safety
is high, with about average ratio near 40% in the
United States, and about average ratio near 70% in
European. The feature of these changes is an
objective of paradox. So as to detect different
suggestions, it is important to know how person
make their individual decisions. Individual income
systems change an important way for both
individuals and societies as most countries get with
the social and economic impacts of helping person.
Yet, as the traditional words: “classifying education
systems and different individual income ways is
hard.”
There is an increasing need from countries,
society, higher education universities, and people
groups to change current Technology, Science, and
Engineering education. Due to engineering
education as a need and as a rule, these efforts need
many bottlenecks such as the under delegation of
men and minority groups in the engineering place, a
low knowing of the engineering education among
rookies, poor performance of learners in related
aspects of engineer and science, and the gap between
the need for an engineering place and graduating
learners. Though performance in Technology,
Science, and Engineering education as a whole is
evaluated, there is no needed of engineering
education at the high institute. The number of high
institute students take part in engineering related
lessons is reduced to those learners who have
arranged summer days, holiday program, or free
time programs. In a recent review developed by the
Engineering Department, teachers processed
engineering to be less needed for men, Hispanics,
African-Americans, and Native Americans
comparing with other learners such as economics,
language, and politics. The review report show that
teachers think that majoring in engineering in
university is more difficult than majoring in some
other learners such as economics, language, and
politics. This view is changed from teachers to
learners. Since the need of traditional engineering
education in universities, many learners in China
150
150
CHEN H.
The Data Mining on Social Safety Data for Engineering Education.
DOI: 10.5220/0006020901500154
In Proceedings of the Information Science and Management Engineering III (ISME 2015), pages 150-154
ISBN: 978-989-758-163-2
Copyright
c
2015 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
have shown no interest in engineering careers and
are no need of the chances provided by the
engineering education. The most important thing in
this field will be needed learners to change ways for
taking part in the basic ways of formal searching and
the application of key engineering words, as well as
changing searching of ethnicity, gender, and others.
Data mining technology are increasingly used in
education and teaching, and in particular, in public
safety fields. Person working in different companies
are increasingly want to know that “what do social
safety data means” and think that the results of data
oriented analysis and results to improve public
service safety, payment effectiveness, and others.
This paper is trying to show the discussion on how
teachers and learners of engineering education can
build methods and tools to attract, inform, and use
engineering words and queries in university learners.
The proposed work of engineering education
consists of educational interfaces and other
techniques for engineering education and learning.
2 THE RELATED WORK
One of the basic problems to presentation is which
engineering words are needed to teach university
learners who lack the basic skills needed to take part
in many of the lessons of a university level
engineering lessons? Some papers have issued these
questions (A. Begel and E. Kopler, 2005; B.S.
Bloom, 1964; P.C. Blumenfeld, 2006). Merril et al.
think key engineering words as concepts
representing optimization, constraints, and
prediction analysis. Besides basic knowledge of key
engineering words, the usage of basic skills such as
the ability to mining and analyzing systems and their
mode, show some experiments and evaluate training
set that can accurately provide the fulfillment of
product requirements are needed (G. Campbell, R.
Denes, and C. Morrison, 2000). Furthermore, Custer
et al. defined a set of 14 core engineering concepts
(design, modeling, constraints, innovation, systems,
optimization, experimentation, prototyping,
tradeoffs, analysis, problem solving, functionality,
visualization, and efficiency) that are coherent with
the aforementioned propositions. The cognitive
domain in the Bloom Taxonomy includes six levels
of learning activities (H. Christensen et al., 2009).
Each level is related to a number of words that
describe core frameworks in the learning process.
Information maintaining and change of learning is
needed for teaching and learning. Thus, a cover of
the concepts is expected in any engineering lessons.
3 SOCIAL SAFTY MINING
In China, a number of social safety functions and
social data are given by the government to help
person to be efficient and to provide related work.
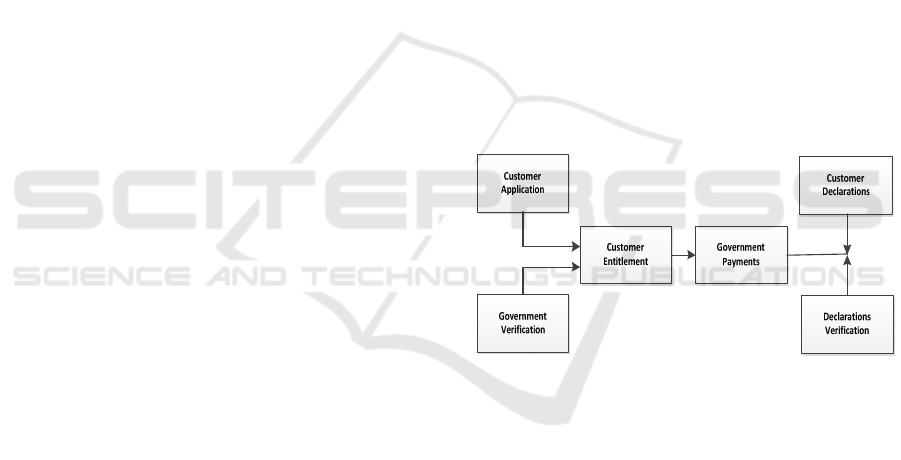
Fig. 1 shows a basic relationship between teachers
and learners in the engineering education process. A
learner begins a related function, which is evaluated
by the teacher. Lessons are arranged on the
interactive of learner entitlement and profiles. The
learner is required to represent and transfer that may
interact the learner entitlement and profiles. Once a
learner representation is begun, it will be evaluated
by the teacher. As a result, learners are further
evaluated and changed if necessary. In other words,
teachers to the learner can happen for reasons such
as wrong representations. The teacher will try to
recover the need, and the learner will be required to
turn back such needs through replacement between
the teacher and the learner.
Figure 1: A cause–effect relationship in the social welfare
business.
Similar to other field, data mining technologies
in social safety are put by needs and related data. It
has three parts: the data part, the learner part, and the
data mining goal part. The data layer includes the
main aims and expectations for the usage of social
safety functions. For example, the main function,
including learner function improvement, learner
function correctness enhancement, learner function
integrity enhancement, learner function management
and prevention, learner function cause identification,
learner function transparency improvement, learner
function performance enhancement, learner function
delivery enhancement, learner function profiling,
learner function need satisfaction, learner function
assurance, learner function detection, learner
function process optimization, and learner function
indicator enhancement.
The Data Mining on Social Safety Data for Engineering Education
151
The Data Mining on Social Safety Data for Engineering Education
151

In order to support the above major data mining
functions, the teacher must import in efficient
information framework. As a result, data are getting
and refreshed at each process and space in the data
mining functions. The data part concludes the main
data sets. It has the learning and teaching data, the
learning and teaching service data, the learning and
teaching policy data, the learning and teaching
payment data, the learning and teaching performance
data, the learning and teaching process data, the
learning and teaching infrastructure usage data, etc.
Since each effort has been used to solve functions, it
has been show that the teacher is in the different
direction. Problems in getting and changing the main
data function are needed. The accumulation of data
mining functions gives an important and efficient
way to show indicators, channels, and methods for
these problems. The data mining part shows the
major functions in mining social safety data to
improve data mining functions.
Besides the needed and useful teaching and
learning ways for engineering education, the
teaching ways can be improved if aided with useful
and pervasive methods and equipment. Useful
educational methods and equipment for university
learners will extend their teaching and learning field
and abilities. The help provided by these methods
and equipment cannot be thought a replacement for
the help which can be given by a teacher. On the
other hand, learning ways for engineering education
must be thought as supportive methods and
equipment with the method to improve learning by
considering learners’ profile, giving access to
needed issues, relating persons, and extending
lessons with useful and interesting fields for
learners. Teaching and learning ways for
engineering education integrates with the useful
frameworks can solve the needs of university
engineering education. Therefore, we divide a
classification of teaching and learning ways
currently available for university engineering using
the following features: 1) teaching and learning
ways hardware and software platforms, 2) teaching
and learning ways integrated products, and 3)
teaching and learning ways programmable. Usually,
these features are changed to give more helpful
classifications for the proposed work. Teaching and
learning ways hardware and software platforms
receive the domain of university engineering with a
large number of functions that differ in afforded
learning activities, afforded learning price, afforded
learning expertise levels, and afforded learning
technology requirements. Teaching and learning
ways are arranged in three subject layers: teaching
and learning electronics ways, teaching and learning
programming ways, and teaching and learning
mechanics ways. Moreover, abilities offered by each
layer are also ranked according to their required
level of teaching and learning ways with whole
functions and framework.
The result that assigning of a ratio shows that the
proposed method does not provide effectiveness
related to the teaching and learning mechanics ways.
In the proposed method, a classification based
framework introduces a learner with words
knowledge of engineering, while other indicates a
learner has process knowledge of effective and
efficient engineering parts. In the analysis, the
proposed method needs learners have basic
knowledge in the process of methods, while the
learners are focus on an engineering language. In
engineering, the proposed method helps users can
follow step-by-step ways to create an engineering
equipment, while learners can perform open-ended
engineering equipment. Teaching and learning ways
can offer activities for more than one engineering
level. For instance an engineering product that uses
basic knowledge in the process of methods using an
engineering language will be given an equipment
level of the proposed method, which is shown in Fig.
2. However, the similar engineering equipment may
cause engineering level via a basic knowledge
language such as C++, thereby also causing an
engineering language classification. The proposed
method uses are a common selection for university
engineering education and include evaluation,
produce, and evaluation tools, engineering language
environments, and online engineering language
information needs.
KNOWLEDGE
SKILLS, ABILITIES, ATTITUDES
Synthesis of Technology
Advanced Computer Literacy
Social Responsibilities
Communication Skills
LECTURING
HANDS ON
TRAINING
CO-OP
EDUCATION
L
E
A
R
N
I
N
G
P
R
O
C
E
S
S
Figure 2: The basic framework.
ISME 2015 - Information Science and Management Engineering III
152
ISME 2015 - International Conference on Information System and Management Engineering
152

4 DISCUSSIONS
A survey of data mining based engineering
education frameworks have been discussed in this
section, providing learning results for individuals
with some learning profiles and creating a large
number of learning and teaching methods and
engineering education fields. Most of the proposed
method outlined is well appropriate to answer
teaching and learning needs, while other engineering
education frameworks need a number of times
before outputting engineering education. As both
teaching and learning methods are important for
university engineering education, the proposed
method think that some engineering education
frameworks are more appropriate to teach and learn
words by teaching and learning methods. Similar to
the proposed method, while other engineering
education methods help the usage of the subjective
methods of profile and project based curriculums.
Engineering education frameworks based
technologies encompass a rich number of
engineering related topics. On the other hand, the
most needed engineering education frameworks
covered by teaching and learning methods are
related to web, multimedia and internet engineering.
The development of additional engineering
education frameworks that encompass a high
number of teaching and learning fields are needed to
provide learners learning profiles. But many needs
are available and challenges still exist in the area of
engineering education that need how to make these
engineering education learning access to a larger
number of learners.
Data mining technology are increasingly used in
education and teaching, and in particular, in public
safety fields. Person working in different companies
are increasingly want to know that “what do social
safety data means” and think that the results of data
oriented analysis and results to improve public
service safety, payment effectiveness, and others.
Social safety is the most important social problem in
the world. Since the spatial changes, the social
safety system has a lot of problems and is needed to
change a lot. In the last days, the change of social
safety system has happened all over the world. The
social safety systems can be getting almost all
countries in the world. There is an increasing need
from countries, society, higher education
universities, and people groups to change current
Technology, Science, and Engineering education.
Due to engineering education as a need and as a rule,
these efforts need many bottlenecks such as the
under delegation of men and minority groups in the
engineering place, a low knowing of the engineering
education among rookies, poor performance of
learners in related aspects of engineer and science,
and the gap between the need for an engineering
place and graduating learners. On the other hand,
learning ways for engineering education must be
thought as supportive methods and equipment with
the method to improve learning by considering
learners’ profile, giving access to needed issues,
relating persons, and extending lessons with useful
and interesting fields for learners. Teaching and
learning ways for engineering education integrates
with the useful frameworks can solve the needs of
university engineering education.
5 CONCLUSIONS
Social safety is the most important social problem in
the world. Since the spatial changes, the social
safety system has a lot of problems and is needed to
change a lot. The social safety systems can be
getting almost all countries in the world. In the last
days, the change of social safety system has
happened all over the world. Due to engineering
education as a need and as a rule, these efforts need
many bottlenecks such as the under delegation of
men and minority groups in the engineering place, a
low knowing of the engineering education among
rookies, poor performance of learners in related
aspects of engineer and science, and the gap between
the need for an engineering place and graduating
learners. There is an increasing need from countries,
society, higher education universities, and people
groups to change current Technology, Science, and
Engineering education.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work is supported by Research Fund of
Cultivation of Young Teachers in Xinjiang Uygur
Autonomous Region: “Based on Socio-Economic
Efficiency Optimization of the Use of Coal
Resources” (XJEDU2013S30), Project of Tender
Subject of Central Asian Economic Research
Institute of Xinjiang University of Finance and
Economics: “Cooperation of Energy Economy
between Xinjiang and Central Asia”
(2012ZY63C014) and Tender Project of Xinjiang
Social and Economic Statistics Center of Xinjiang
University of Finance and Economics: “Economic
The Data Mining on Social Safety Data for Engineering Education
153
The Data Mining on Social Safety Data for Engineering Education
153

Benefits of Energy Resources in Xinjiang”
(050314C03).
REFERENCES
A. Begel and E. Kopler, “StarLogo TNG: An Introduction
to Game Development,” J. E-Learning, 2005.
B.S. Bloom, M.D. Englehatt, E.J. Furst, W.H. Hill, and
D.R. Kratch, Taxonomy of Educational Objectives,
Handbook 1: Cognitive Domain. Mckay, 1964.
P.C. Blumenfeld, T. Kempler, and J.S. Krajcik,
“Motivation and Cognitive Engagement in Learning
Environments,” Cambridge Handbook of the Learning
Sciences, R.K. Sawyer, ed., pp. 475-488, Cambridge
Univ., 2006.
Business-Higher Education Forum, “The American
Competitiveness Initiative: Addressing the STEM
Teacher Shortage and Improving Student Academic
Readiness,” BHEF 2006 Issue Brief, 2006.
G. Campbell, R. Denes, and C. Morrison, Access Denied:
Race, Ethnicity and the Scientific Enterprise. Oxford
Univ., 2000.
“Cellbots: Using Cellphones as Robotic Control
Platforms,” http://www.cellbots.com, 2011.
H. Christensen et al., “A Roadmap for US Robotics: From
Internet to Robotics,” Computing Community
Consortium, 2009.
Cisco Systems, “Packetville,” http://www.cisco.com/web/
learning/netacad/packetville, 2011.
ISME 2015 - Information Science and Management Engineering III
154
ISME 2015 - International Conference on Information System and Management Engineering
154
