
The Construction on “Green Commuting” Three-dimensional Public
Transportation Governance System for Chinese Cities
Renbao Liu
1
and Jingxia Zou
2
1
School of Public Administration, Shandong Institute of Business and Technology, P.R. China
2
Modern Education Technology Centre, Shandong Institute of Business and Technology, P.R. China
Keywords: Public Transportation, Congestion, Green Commuting, City Management.
Abstract: By using the method of comparative analysis and quantitative analysis with qualitative analysis, studies on
the favourable measures, characteristics and experience and achievements in the development of city green
public transportation of the world typical countries and cities. In an attempt to provide reference for the
large and medium-sized cities of China to construct the "five one" "green commuting" three-dimensional
governance system that includes urban bus, rail transportation, taxi, bicycle and pedestrian, then can
effectively solve the problem of traffic jams. The new and original in this paper is solving practical
problems from the angle of effective demand by using the methods of comprehensive analysis and
comparison.
1 INTRODUCTION
In recent years, with the development of social
economy, the number of China domestic private cars
are also increasing, thus also causes of urban road
traffic congestion and traffic difficult. To solve the
traffic congestion, ensure the traffic smooth, become
an important issue that should be solved in the city's
economic and social development.
2 THE PRESENT SITUATION OF
CHINESE CITY TRAFFIC JAM
At present, many large and medium-sized cities in
China are exposed to different levels of traffic jams
and congestion problems, especially in Beijing,
Shanghai, Wuhan, Xi'an, Guangzhou, Chongqing
and other big cities, traffic congestion is becoming
more and more serious. Motor vehicle average speed
of mega cities in China is already down to 12 km
now by the past 20 km, in some big cities central
area, the mean vehicle speed has fallen to 8 - 12 km.
In the 31 national cities whose population over 1
million mega , the majority of traffic load is close to
saturation, while some of the central area of the city
traffic has close to half paralyzed. The car runs 100
km outside the city only needs about an hour or so,
while in the central area of the city 10 km mileage
may consume more than an hour, the serious traffic
jam time can last 2-3 hours, which brings great
inconvenience to people's traffic, and directly affect
the people's work and life (Daqing Zhang, Zhihong
Zhang, 2002).
3 THE MAIN REASON FOR THE
CITY TRAFFIC JAM
Throughout Chinese domestic city traffic situation,
we can find that the main reason leading to the city
traffic congestion can be attributed to the following:
3.1 Motor Vehicle Especially Private
Car Ownership Increased Rapidly
Taking Beijing as an example, according to
statistics, as of 2013, the number of motor vehicle
has reached more than 5.371 million vehicles (Tab.
1). According to the survey of Beijing City
Transportation Research Centre, if not to limit, the
largest car ownership in Beijing is about for 5.5
million. If in accordance with the principle of
“traffic restrictions based on the last digit of license
plate numbers” from Monday to Friday, the largest
number of cars ownership in Beijing is about for 6.7
million (Fig. 1).(Yanyan Sun, Zhijian Lv, 2013)
397
Zou J. and Liu R.
The Construction on â
˘
AIJGreen Commutingâ
˘
A
˙
I Three-dimensional Public Transportation Governance System for Chinese Cities.
DOI: 10.5220/0006027203970401
In Proceedings of the Information Science and Management Engineering III (ISME 2015), pages 397-401
ISBN: 978-989-758-163-2
Copyright
c
2015 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
397
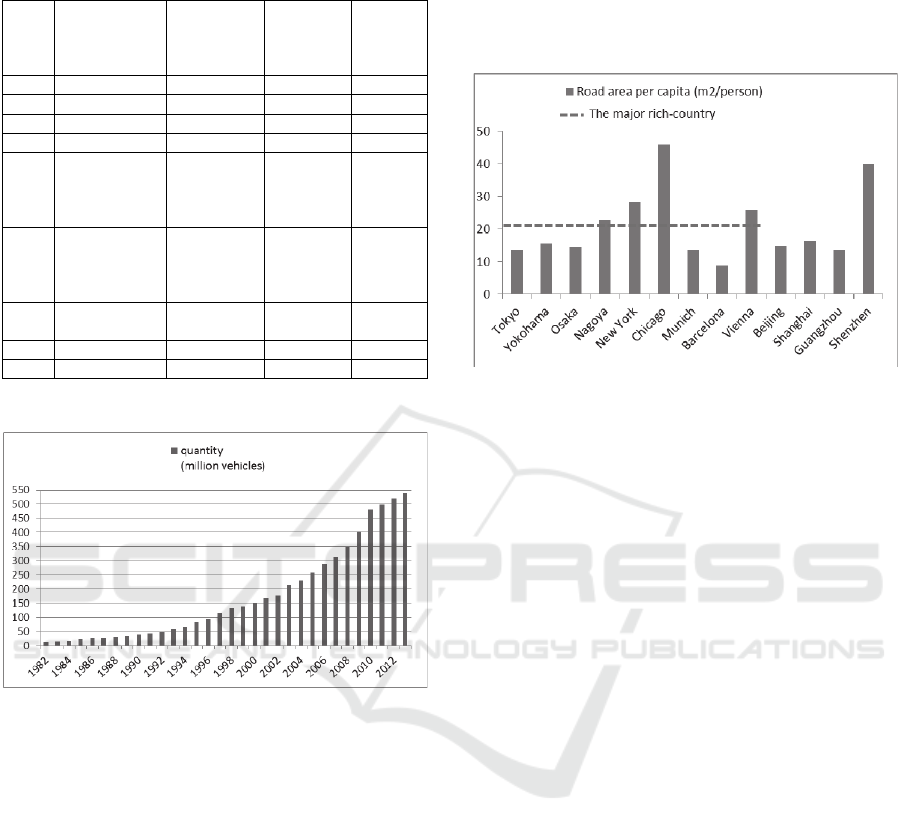
Table 1: Beijing motor vehicle quantities important
change cycle TAB.
NO.
Motor
vehicle
quantities
(million)
Increasing
number
(million)
Date
Time
spent
1 5.371 0.171 2013.12 1year
2 5.200 0.216 2012.12 1year
3 4.984 0.175 2011.12 1year*
4 4.809 0.790 2010.12 1year
5 4.019 1.019 2009.12
2 years
and
seven
months
6 3.00 1.000 2007.5
3 years
and
nine
months
7 2.00 1.000 2003.8
6.5
years
8 1.00 0.9977 1997.2 48 years
9 0.0023 founding
*Since 2011, the car lottery purchase policy has been taken in
Beijing.
Figure 1: Beijing motor vehicle quantities variations in
1982-2013.
3.2 The Number and Speed of Road
Construction Can’t Meet the Needs
of the Rapid Growth of Motor
Vehicle
Taking Beijing as an example, each a net increase of
1 million cars, it needs to increase the capacity of
network 2.82 million cars km. This’s equivalent to
the entire Beijing third ring Road Network Capacity
or 30% road network capacity within fifth ring
(Qingheng An, 2014). Road construction, both in
terms of quantity, or in terms of speed, the
construction period is relatively long, can’t meet the
needs of the rapid growth of motor vehicle parc.
3.3 Not Set up the City Effective
Expressway and Roads, Secondary
Roads, Branch Supporting
Transport Network
Figure 2: The per capita road area comparison of some
main cities of domestic and foreign.
At present, during the road network construction,
most of China city often only pay attention to the
planning and construction of expressways and trunk
road, but didn’t pay full attention to secondary road
and branch. Because city secondary road and branch
outdate facilities, poor road conditions, vehicle
speed is significantly lower than expect, the
efficiency of road network composed of city main
line, trunk, branch is low. Motor vehicles are racing
to the city expressway and arterial road, resulting in
peak hour traffic flow is too concentrated, thus
causes congestion (Fig. 2) (Yifan Wang,2009).
3.4 Traffic Management Is
Incompetence
The planning and design (set) of Line, intersection,
signal lamp is not perfect, such as cross road
entrance layout, traffic signal lights transform set
etc.
3.5 Public Transportation Does Not
Play Its Due Role
City bus number is less, poor condition, no point,
slow speed, more crowded, poor comfort, site less or
unreasonable setting, compared to private car, the
city bus lacks of great superiority, so the public is
not willing to choice for city bus.
ISME 2015 - Information Science and Management Engineering III
398
ISME 2015 - International Conference on Information System and Management Engineering
398

4 THE PRACTICE TO SOLVE
THE PROBLEM OF ROAD
CONGESTION IN LARGE AND
MEDIUM-SIZED CITIES OF
DOMESTIC AND FOREIGN
In the process of promoting the economic
development and the process of the city, a number of
large and medium-sized cities of domestic and
foreign have met road congestion, many cities have
taken many measures suit one's measures to local
conditions, and received good results. In this
process, vigorously develop the city public
transportation, open Easy Access, implement green
commuting, become a common practice of large and
medium-sized cities of domestic and foreign.
4.1 Implement of Public Transport
Priority Policy, Vigorously Develop
the City Public Transportation
The public transportation development of Brazil
Curitiba city can be said to be the model of the
world. Through more than thirty years of
development and perfection, the public transport
system in Curitiba city has become the efficient,
convenient, comfortable, advanced public
transportation system of the world, and regard as the
"Surface Subway". Its success lies in establishing the
systematic and perfect integrated public transport
system, implementing a series of perfect and
facilities public transport priority policy.
4.1.1 The Systematic and Improved
Integrated Transport System in
Curitiba
There is an integrated public transport system
composed of a perfect line and adequate vehicle in
Curitiba city, passenger traffic volume of up to 1.9
million people every day. Bus lines covered all the
urban roads, among them the bus lane is 60 km, bus
daily mileage of 38000 km. The roads in Curitiba
city are mainly composed of fast line, feedback line,
interregional contact line, station express line,
conventional integrate radiate line and city centre
circle line.
4.1.2 The Perfect and Matching Bus Priority
Policy in Curitiba City
In Curitiba city, a series of perfect and matching
public transportation priority policy have been
implemented. Such as in the use of the land, priority
must be given to the traffic, during the city planning,
should give priority to the development of public
traffic system. The design of traffic system on the
vehicle speed, convenient mounting problems, the
overall structure of the system have made detailed
provisions, attract customers by the convenient and
fast public transport system. To build the bicycle
lane, even at the cost of occupancy vehicle lane, put
the public traffic and pedestrian (not the private car
and the vehicle) on the top priority. Using the
management system of integrate public traffic
system that separates government functions from
enterprise management, separates operation and
system of ticket. The government uses a variety of
economic policies that favourable to the social
development to encourage people to use public
transport, such as free purchase tickets for more than
65 years of age for the elderly and children under the
age of 5, subsidies by the government if someone
spends more than 6% excess wage for public
transport, the poor in poor areas can exchange for a
bus ticket by using for sweeping garbage etc. Traffic
management departments of the government adopts
a series of traffic management measures to ensure
the priority development of public transport, such as
through the reasonable countermeasures to reduce
parking on road, reduce the taxi driving no
passenger, the taxi must be docked at the taxi stand,
prevent intersection clogging by delimiting no
parking sign at the junction, give priority to bus
through the intersection, etc., ensure public traffic
unblocked. (Liren Duan, 2001)
4.2 Efficient Taxi Traffic System
As the representative of taxi operation in Singapore,
taxi plays the almost equally important role as
subway. Singapore subway daily passenger capacity
is slightly higher than the 1 million passengers, and
taxi passenger capacity has nearly 1 million
passengers daily, while taxies in Singapore are only
18000 cars. The main reason is that one is the fare is
reasonable, in Singapore, the taxi first km traffic
cost is 2.4 Singapore dollars, within 10 km per 240
meters 10 cents, above 10 km is 10 cents per 225
meters, second is the booking very convenient, GPS
equipment with universal Singapore taxi, the control
centre tracks vehicle through the GPS system,
people can at any time convenient appointments to
the taxi, the whole process is fully automatic,
manual operation is not needed extra.
The Construction on “Green Commuting” Three-dimensional Public Transportation Governance System for Chinese
Cities
399
The Construction on â
˘
AIJGreen Commutingâ
˘
A
˙
I Three-dimensional Public Transportation Governance System for Chinese Cities
399
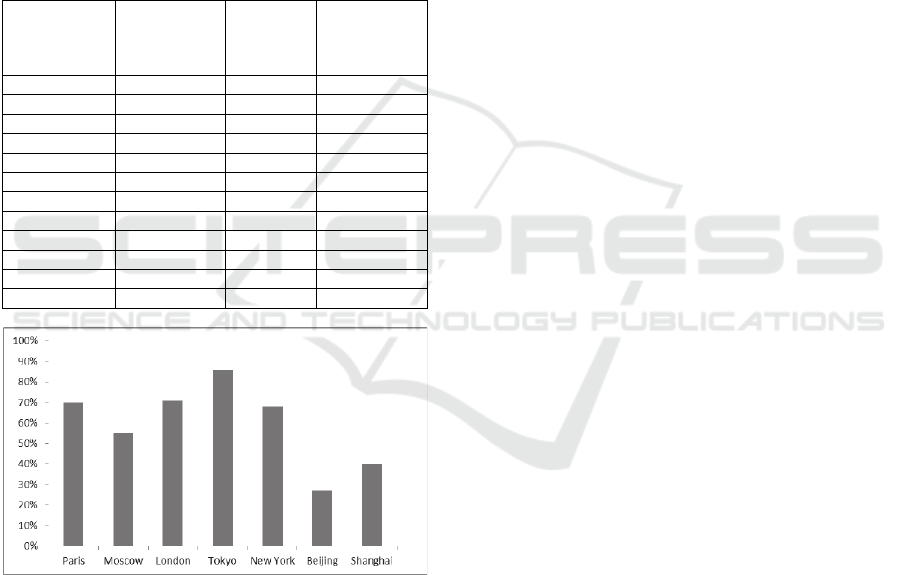
4.3 Stable and Time-sensitive Rail
Transit
The subway construction in Moscow, New York,
Paris, London, Tokyo, Berlin city is developed, the
line length is more than 100 km, passenger traffic
volume is more than 1 million passengers daily
average also. The subway in Beijing, Shanghai,
Guangzhou, Tianjin, Wuhan, Dalian and other cities
of China has also achieved good results on rail
transit such as subway, light rail, streetcar, single
track, city expressway (Tab. 2, Fig. 3) (Jin Luo,
2009).
Table 2: The subway construction of part of the world
cities.
City
Urban
population
(Million)
Line
(km)
Passenger
traffic
(Million
people/daily)
Moscow 8.50 234 7.00
Barcelona 2.70 61.8 0.91
Berlin 3.12 138.4 1.07
Chicago
2.85 155 0.40
Hamburg 2.65 89 0.60
Mexico City 9.20 62 2.80
Tokyo 11.70 218 3.80
Rotterdam 1.05 40 10.13
Rome 2.90 25.5 0.28
New York 9.00 438 2.85
Paris 10.00 294 3.08
London 4.00 387.9 2.50
Figure 3: The orbit traffic carrier ratio of part of the world
cities.
4.4 Convenient Trips Done by Bike
Now, more and more countries and cities vigorously
promote and implement of bicycle, some countries
and cities have even established public bicycle
system.
4.4.1 The European Third Generation
Public Bicycle System
Since the late 1990s, after the first generation and
the second generation of public bicycle system,
France Paris, Germany Lyon, Spain Barcelona and
other countries and cities of European have
researched and development of a new generation of
public bicycle system which using modern
electronic, information integration, wireless
communication and Internet technology. The biggest
characteristic of this kind of system is able to know
who is in the use of bicycles, which brought the
fundamental change of the mode of management
system, provide a convenient and fast and healthy
way to traffic for people, reduce the city air
pollution, but also effectively solve the management
issues such as bicycle is easy to be stolen, damaged
and lost and etc., thus improve the utilization rate of
resources, enhance the image of the city (Xue Xiao,
Zhiian Lv, 2013).
4.4.2 "With the Bicycle as a Fundamental"
Low Carbon, Green Transportation
Policy
Holland, Denmark, South Korea and other countries
implement the "With the bicycle as a fundamental"
low carbon, green transportation policy. Holland
nation has about 16 million people, but has about 18
million bicycles, bicycle per capita ranks first in the
world. In Holland, more than 30% of the traffic is by
riding a bicycle to complete. In recent 20 years.
Holland has completed up to 120 items about the
bicycle traffic scientific research projects, and the
Treasury provides substantial financial support each
year. In Holland law, during the city planning, road
facilities should not truncate main bike lanes, city
construction should not cause inconvenience to the
bicycle traffic.
The Danish population is about 5.3 million, but
bikes are about more than 3 million vehicles. In
Copenhagen's, 1/3 of commuters ride bicycles,
including officials, wealthy and celebrities, the
British newspaper "Independent" reported that
Copenhagen is be worthy of the name of the city of
bicycle. At present, in the city of Copenhagen, 37%
of people riding bicycles, 28% by bus and train, 31%
drive, walk 4%, in 2015, 50% of the people in
Copenhagen will go to work and school by bike
ways.
In recent years, the South Korea government
vigorously promote green commuting by bike. In
order to encourage people to ride a bicycle green
ISME 2015 - Information Science and Management Engineering III
400
ISME 2015 - International Conference on Information System and Management Engineering
400

commuting, the South Korea government introduced
a number of policies, such as the formulation of
"2010 bicycle policy promotion plan", established
the "bicycle day" to promote the national bicycle
road network construction. Government invests to
construct bicycle demonstration city, bicycle
demonstration zone and bicycle using demonstration
school, subsidies and buys insurance for bike
commuters. Launches the "green plus P shop",
cyclists can buy cheaper goods from the "green plus
P shop" than conventional store. The newly revised
"Road traffic law" provisions that it should must to
establish bicycle lanes and must to provide space for
bicycle parking during new city construction.
4.5 Effective Traffic Demand
Management
As a representative office in Hong Kong, although
there are many people and little land, high rises, it is
congenitally deficient for development of traffic
conditions, but we rarely see traffic congestion in
common like other metropolis. This is largely due to
the organic combination between the construction
planning and the public traffic system of Hong
Kong. In Hong Kong, the public transport service is
variety and unique, the public can choose their right
traffic according to the fast, comfortable and
convenient, such as railway (including subway),
tram, bus, minibus (small bus), taxi and ferry. The
government of Hong Kong is committed to the
development of public transport, not to encourage
the attitude of private cars. The private cars
operation cost is higher: The first is difficult to park,
most office buildings do not have their own parking
spaces, foreign visitors can’t park in the master's
home, and the special parking position is less, and
fees is higher; secondly, parking is expensive; third
is the oil prices is high; the last is all kinds of fees
for per vehicle per year are not little also, and have a
limit to apply for a licence. (Ming Wu, 2011)
5 CONCLUSIONS
Throughout the various approaches to solve the
problems of road congestion of the large and
medium-sized cities of domestic and foreign, we
found that develop the public transport, open up the
green channel, construct the "five one" "green
commuting" three-dimensional system of social
management that includes urban bus, rail
transportation, taxi, bicycle and pedestrian, this can
be the effective way to relieve the congestion
problems in large and medium-sized cities in china.
In the actual operation of the process, the city
managers should suit one's measures to local
conditions, deep analysis and argumentation, good
planning, to formulate a scientific program, then can
receive good effect.
REFERENCES
Daqing Zhang, Zhihong Zhang, 2002. Urban road traffic
problems and solutions. Chongqing Traffic University
Journal (social science edition), 2(2), pp. 20-25. (in
Chinese).
Yanyan Sun, Zhijian Lv, 2013. Development of the public
bicycle countermeasures for Beijing city. City
Management and Science and Technology, (05), pp.
28-30. (in Chinese).
Qingheng An, 2014. The consideration of auto purchase
limit in Beijing. Automobile Aspect, (03), pp. 20-22.
(in Chinese).
Yifan Wang, 2009. The main problems and suggestions
for development of city road system at present stage.
Gansu Science and Technology, (17), pp. 7-9. (in
Chinese).
Liren Duan, 2001. A city traffic international model-The
integrated transport system in Brazil curitiba. City
Vehicles, (1), pp. 11-14. (in Chinese).
Jin Luo, 2009. Building-up of urban rail transit system
development present situation. Traffic Technology,
(2), pp. 59-61. (in Chinese).
Xue Xiao, Zhiian Lv, 2013. Paris's policies on sustainable
transport development and its significance for Bejng.
Global Science Technology and Economy Outlook,
28(9), pp. 70-76. (in Chinese).
Ming Wu, 2011. Hong Kong why not "block" than
Beijing. Yiling, (04), pp. 25. (in Chinese).
The Construction on “Green Commuting” Three-dimensional Public Transportation Governance System for Chinese
Cities
401
The Construction on â
˘
AIJGreen Commutingâ
˘
A
˙
I Three-dimensional Public Transportation Governance System for Chinese Cities
401
