
What Changes Need to be Made within the LNHS for Ehealth
Systems to be Successfully Implemented?
Mansour Ahwidy
1,2
and Lyn Pemberton
1
1
University of Brighton, School of Computing, Engineering and Mathematics, Mithras housey, Lewes road, Brighton, U.K.
2
Keywords: Technology Readiness Assessment, Ehealth, Patient Electronic Health Records, Electronic Prescription.
Abstract: This piece of work provides an assessment of the readiness levels within both urban and rural hospitals and
clinics in Libya for the implementation of Ehealth systems. This then enabled the construction of a
framework for Ehealth implementation in the Libyan National Health Service (LNHS). The study assessed
how medications were prescribed, patients were referred, information communication technology (ICT) was
utilised in recording patient records, how healthcare staff were trained to use ICT and the ways in which
consultations were carried out by healthcare staff. The research was done in five rural healthcare institutions
and five urban healthcare institutions and focused on the readiness levels of the technology, social attitudes,
engagement levels and any other needs that were apparent (Jennett et al., 2010; Hasanain et al., 2014).
Collection of the data was carried out using a mixed method approach with qualitative interviews and
quantitative questionnaires (Molina et al., 2010; Creswell and Plano, 2010; Mason, 2006; Cathain, 2009;
Cathain et al. 2008). The study indicated that any IT equipment present was not being utilised for clinical
purposes and there was no evidence of any Ehealth technologies being employed. This implies that the
maturity level of the healthcare institutions studied was zero.
1 INTRODUCTION
When Ehealth systems are incorporated in
healthcare systems they can support them in
addressing the healthcare problems that are now
facing most countries within the developing world
(Kwankam, 2004; Ludwick and Doucette, 2009; Lau
et al., 2011). However, in order to introduce Ehealth
systems in developing countries there needs to be an
overhaul of the ICT systems being used there at
present and these calls for examinations of the
infrastructure, organisation and political situations in
these countries (Hossein, 2012). The research
carried out on transforming the LNHS has indicated
that a majority of Libyans do not have enough
access to the basics required for healthcare and most
people receive medical attention purely from the
LNHS. The LNHS has invested large amounts of
money in both urban and rural healthcare institutions
and services, along with ICT, in order that the
provision of healthcare services are improved by
healthcare staff having more efficient work
processes (Hamroush, 2014). However, although
there had been a large financial has been invested,
many healthcare staff have not benefitted from
improved ICT. This study looks at how Ehealth
systems can lead to healthcare professionals carrying
out their jobs more effectively and efficiently in the
LNHS. For achieving this, the researcher conducted
a study of urban and rural healthcare institutions in
order to assess their Ehealth readiness and to be able
to create an Ehealth framework for improving the
job processes of healthcare staff. The study looked at
ways in which Ehealth systems could be utilised for
improving the keeping of patient healthcare records,
making consultations, carrying out training, making
referrals and prescribing medication (Bilbey and
Lalani, 2013; Yellowlees, 2005; Broens et al., 2007;
Khoja et al., 2007). This study has lead to the
compilation of an Ehealth framework formulated
from the research data and it has formulated a list of
recommendations that can be utilised for the
transition from the present ICT levels in the LNHS
to a more complex and developed one where Ehealth
solutions can be integrated.
Ahwidy, M. and Pemberton, L.
What Changes Need to be Made within the LNHS for Ehealth Systems to be Successfully Implemented?.
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Information and Communication Technologies for Ageing Well and e-Health (ICT4AWE 2016), pages 71-79
ISBN: 978-989-758-180-9
Copyright
c
2016 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
71

2 THE THEORY OF Ehealth
READINESS ASSESSMENTS
The theory of Ehealth Readiness Assessments was
carried out to define Ehealth systems, how they
might benefit a populace in a developing country
and how the readiness of that country might be
evaluated. There are many factors determining the
readiness of a country for the implementation of
Ehealth systems (Khoja et al., 2007; Jennett et al.,
2004), so it was a rewarding task to investigate the
findings of previous research. Using the Brighton
University data base, Science Direct, Google
Scholar, various Libyan data bases and existing
reports from hospitals in Libya, searches were made
for relevant articles about the implementation of
Ehealth systems in developing countries. Though
there were already assessments made of several
countries, none had yet been carried out in Libya.
This literature review will give some examples of
relevant research discovered during this search and
then expand on how these frameworks will be
utilised in this assessment on the readiness of Libya
for the implementation of Ehealth systems. There
was though a limited amount of formal articles on
this subject pertaining to developing countries, so a
search was made on many databases to find any
recent research carried out on assessing the readiness
of developing countries for Ehealth implementation.
Blaya et al, 2010 made a review of Ehealth
system that had been implemented in developing
nations. They found that if a system improved
communications between the healthcare institutions,
assisted in the management and ordering of
medications and helped in monitoring patients that
might abandon their care plan, then it could be
considered as ‘promising’. They found the systems
were effective at evaluating personal electronic
assistants and mobile apparatus as they improved the
collection of data in regards to quality and time
taken.
A majority of studies carried out to evaluate
Ehealth systems are made once the system has been
implemented, as seen in the example of
Ammenwerth et al. 2001. Alexander, 2007 points
out the importance of such studies for evaluating the
success of an Ehealth system, though Brender, 2006
points out the need for evaluations to take place
before the implementation of an Ehealth system in,
order to allow decisions to have a better sense of
direction. It is the advice of Brender, 2006 that the
researcher has heeded in the formulation of the
research question, tending toward the theory that a
readiness evaluation framework is needed before
implementing Ehealth systems (Yellowlees, 2005;
Broens et al., 2007; Khoja et al., 2007).
Li et al, 2010 cite four main areas to evaluate in a
study to assess readiness for implementing an
Ehealth system. Those areas are: if it is feasible;
does the organisation possess the necessary
resources, the risks involved; an assessment needs to
be made of what external factors might threaten the
project’s success, areas where problems may arise;
to identify weaknesses in the solution where risks
may occur and an assessment of how complete and
consistent the solution is.
3 METHODS
A mixed method approach was employed for
carrying out this research on healthcare institutions,
in both rural and urban areas of Libya (Figure 1)
(Molina et al., 2010; Creswell and Plano, 2010;
Mason, 2006; Cathain, 2009; Cathain et al. 2008),
employing both questionnaires and group
interviews. The data from the multi-case study was
analysed using the Cresswell framework (2007)
(Lynna et al., 2009). The formulation of the
interview questions and questionnaires was carried
out to make sure there was not anything missing by
seeing what was needed from the literature review
and the Chan framework (2010). The selection of the
healthcare institutions was done so that all the major
population centres of Libya were covered in five
primary areas.
3.1 Research Methods and Sample Size
For the purposes of this study the participants were
found in hospitals and clinics within the professions
of nursing, hospital administration, ward attendants
and doctors. The sample size (see Figure 1) of this
study was 165, with 138 of these returning a
questionnaire; as a percentage that worked out at
83.6%. Because 58 of the questionnaires were
excluded from the final total because they were
filled out incorrectly or superfluous, the final
number for analysis was 80 (N=80).
The questionnaire was divided into two sections,
with one set of questions aimed at general medical
staff, the other aimed at administration staff. The
questions for the medical staff were designed in
order to better understand of the work processes
involved in recording the healthcare data of patients,
carrying out referrals, consultations and
prescriptions. The questions for the administrative
staff were formulated in order to better understand
ICT4AWE 2016 - 2nd International Conference on Information and Communication Technologies for Ageing Well and e-Health
72

Figure 1: Sample size.
Table 1: Semi-structured interviews.
categories of
participants
Healthcare institution
Tripoli
Medical Centre
Al Razi Clinic
Benghazi
Medical Centre
Quiche Clinic
Sabha Medical
Centre
Al-Manshia
Clinic
Ibn Sina
Medical centre
Al- hyat Clinic
Zawia Medical
Centre
Al Bassatein
Clinic
Administrators 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 10
Doctors 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 10
Nurses 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 10
Ward assistants 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 10
Total of participants
40
of the present ICT infrastructure in the healthcare
institutions, the background history of the healthcare
institutions and the settings of the healthcare
institutions. The formulation of each question was
done using the Li et al, 2010 framework for
assessing Ehealth readiness.
Semi-structured interviews: A total of 40
individual actors (doctors, ward assistants,
administrators and nurses) were interviewed in
Arabic using semi-structured interview techniques
(Table 1). The durations of the interviews varied
between 20 and 40 minutes and averaged out at 30
minutes for each interview. The total time taken for
all the interviews was about 20 hours and the details
of these interviews are shown below in Table 1.
The reason for interviewing the staff at the
healthcare institutions was to find out what their
perceptions of Ehealth technologies were and how
useful and beneficial they would be if implemented
in the healthcare institutions where they worked.
4 RESULTS
The results of the data were separated into separate
sections based upon the Cresswell framework
(2007).
What Changes Need to be Made within the LNHS for Ehealth Systems to be Successfully Implemented?
73

4.1 Results of the Questionnaire
4.1.1 Healthcare Staff Availability within
Urban and Rural Healthcare
Institutions
The results of the research showed that there was a
lack of doctors available to work in rural healthcare
institutions. The results indicated that the lack of
doctors in rural healthcare institutions meant that
doctors have much less time to spend treating
patients and often patients had more severe
symptoms as they had further to travel to receive
treatment and had consequently waited until their
condition worsened, whereas patients in urban areas
would seek treatment earlier as they lived closer to
healthcare institutions and had better transport
options available.
4.1.2 ICT Access in Urban and Rural
Healthcare Institutions
The study indicated that urban healthcare institutions
had more ICT equipment and more reliable internet
connections than those in rural areas. The rural
healthcare institutions had their internet connections
affected by bad phone lines and electrical power
supplies that were unreliable. Though the urban
healthcare institutions had more computers per
doctor than their rural counterparts, this was
academic as there were no computers present in the
rooms utilised by doctors for their consultations in
both rural and urban healthcare institutions,
indicating that doctors were not employing
computers to carry out consultations. Rather than
being used for medical purposes, it was ascertained
in the study that the computers in the healthcare
institutions were being utilised for administration
purposes. Though the study indicated that rural
medical staff were using computers more often than
in urban areas, this was only for personal use and
was not being carried out during their work time at
the healthcare institutions where they worked.
4.2 Results of the Group Interviews
Results of the group interviews were conducted by
using qualitative data analysis program called
NVIVO (Bazeley, 2007; Hamed and Alabri, 2013;
Ishak and Abu Bakar, 2012).
4.2.1 Access to Ehealth Solutions in Urban
and Rural Healthcare Institutions
The results of comparing access to Ehealth
solutions, in both rural and urban healthcare
institutions, indicated that there were not any
Ehealth solutions in any of the healthcare institutions
used in the case studies. The participants returned
positive feedback regarding the possible future
implementation of Ehealth solutions in the
healthcare institutions where they worked. It was felt
that the implementation of Ehealth technology
would improve the recording of patient healthcare
records, the treating of patients and the diagnosis of
patient's ailments. The results indicated that the
participants thought that the use of electronic patient
healthcare record systems would greatly improve the
service offered to patients and make the job easier
for staff and it would stop patients that attended
multiple healthcare institutions in order to get repeat
prescriptions of medication, therefore stopping fraud
occurring and saving the LNHS valuable resources.
Presently patient referrals are carried out by giving a
patient a handwritten referral on paper to take with
them to the healthcare institution to which they have
been referred. This meant referral letters were
getting lost or patients did not attend. Respondents
felt that this task being carried out electronically
would eliminate many of these problems.
5 DISCUSSION
5.1 Availability of Medical Staff in
Urban and Rural Healthcare
Institutions
The issue of physician shortages is far more pressing
in rural healthcare institutions than in urban
hospitals, though urban clinics do also experience
shortages.
The World Bank (2008), Jennett et al. (2005),
Campbell et al. (2001) , Blaya and Fraser (2010)
indicate that there are many challenges to providing
healthcare services in rural areas because of the
distances between populations that are dispersed and
isolated. Because of these challenges, in rural areas
there have often been problems in the recruitment of
staff and of them leaving to urban healthcare
institutions. In the LNHS, most of the skilled
healthcare staff choose to work in urban areas
(8280), whereas in rural areas staff are more
reluctant to relocate for work (3043) (Hamroush,
2014). A lot of rural areas do not have any
healthcare staff to provide healthcare to those that
require it, so the inhabitants have to travel long
distances to seek medical attention, particularly as
Libya is so big, yet so sparsely populated.
ICT4AWE 2016 - 2nd International Conference on Information and Communication Technologies for Ageing Well and e-Health
74

The lack of healthcare staff in rural healthcare
institutions has to be the driving force for attracting
more money being invested in Ehealth solutions to
help healthcare staff to provide improved healthcare
using localised Ehealth frameworks that are
appropriate like the framework offered in this
research study. Hamroush (2014) compares the
availability of physicians in urban and rural
healthcare institutions in Libya.
Tables in Hamroush (2014) summarise the
average number of physicians that worked in the
rural healthcare institutions that were surveyed. The
Tables show that on average, there are
approximately 73% of physicians in Libya working
in urban healthcare institutions, compared to 26 %
physicians working in rural hospitals. Those
percentages indicate there are 20 physicians for
every ten thousand local inhabitants in Libya. The
following section will focus on how available and
accessible ICT technology is within the healthcare
institutions chosen for this study.
5.2 The Availability of ICT in Urban
and Rural Healthcare Institutions
The study outcomes showed that the availability of
ICT and internet connections in both rural and urban
healthcare institutions was insufficient for the
implementation of Ehealth solutions. In order to
function efficiently the ICT systems at each
healthcare institution need to be expanded and
integrated with other healthcare institutions.
Figure 2: Phases of Ehealth Maturity Curve.
6 EHEALTH MATURITY
DIAGRAM (EMD)
The study outcomes showed that when placed on an
Ehealth Maturity Curve (Van de Wetering and
Batenburg, 2009) the healthcare institutions in both
rural and urban areas were at level 0, as can be seen
below in Figure 2.
Figure 2 above shows that the urban and rural
healthcare institutions Ehealth solution levels are at
level 0. The healthcare institutions are able to send
emails to a central data storage facility for the
purpose of administration, but do not appear to use
this facility for medical purposes. Despite the
existence of some ICT in the healthcare institutions,
these systems are not used for contacting other
healthcare institutions. This is because of a lack of
equipment sometimes or bad internet connections
and electrical supplies, but is primarily due to the
technophobic attitudes of staff who feel unwilling to
embrace new forms of technology (Bain, and Rice,
2006-2007). Therefore, it is essential if these
healthcare institutions are to rise above level 0, a
Provincial Ehealth framework be formulated using
these findings to facilitate a plan for the future in
order for the healthcare institutions to move to level
2 on the Ehealth maturity curve. Because of this the
Provincial Ehealth framework was formulated, as
can be seen below in Figure 3.
The Provincial Ehealth framework architecture
highlights the need for the services offered in the
healthcare institutions to be integrated online by
using an Ehealth service hub that supports the whole
of the LNHS and for data to be stored electronically
rather than by using paper records as at present.
7 STRATEGY FOR EHEALTH IN
THE LNHS
In order for the LNHS to raise its maturity levels for
the implementation of Ehealth technology, it needs
to persuade LNHS staff and patients to adopt
Ehealth technologies. This can be carried out at a
local level throughout the LNHS, though this will
need to be orchestrated at a national level through
training, education and programmes to encourage
compliance and providing incentives.
The drive to raise the maturity levels for the
implementation of Ehealth technology throughout
the LNHS needs to focus in several areas. This is a
non exhaustive list of some of those:
1. LNHS users need to be made aware of what is
available to them through use of Ehealth in the
LNHS through media and other sources and be
shown the advantages of accessing their
individual healthcare records. Public support
for Ehealth developments will encourage
politicians to invest in developing ICT
What Changes Need to be Made within the LNHS for Ehealth Systems to be Successfully Implemented?
75
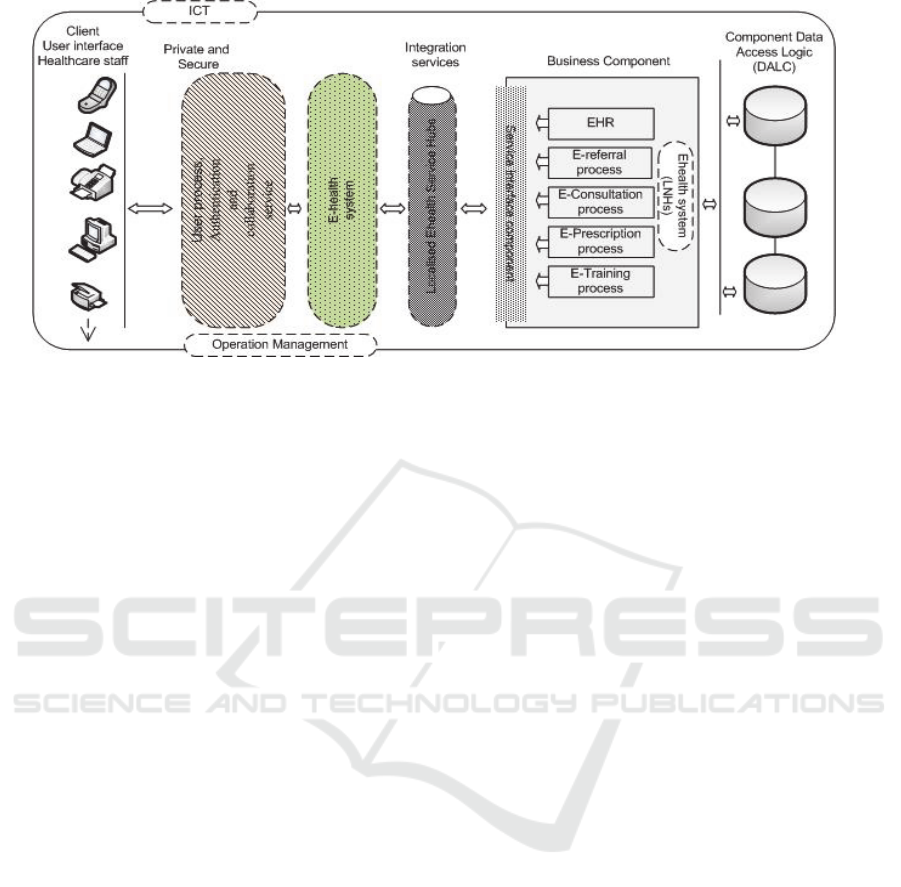
Figure 3: Provincial Ehealth framework.
infrastructures and to ensure that broadband
speeds are sufficient and telephone connections
are reliable.
2. Healthcare institutions need to be given
financial aid with implementing Ehealth
systems to encourage their widespread usage.
There needs to be a direct link between usage
of Ehealth technology and funding.
3. It is of great importance for a healthcare system
utilising Ehealth technologies to ensure that
sufficient numbers of healthcare staff have
been trained to high enough standards to
operate the technology effectively. Staff also
need to be convinced of the need for Ehealth
technologies and be enthusiastic about the
prospect of being able to utilise it in order to
offer improved healthcare services
4. Researches carried out in other countries have
shown the Ehealth solutions that need to be
prioritised: sources of healthcare data, tools for
the delivery of services and the sharing of
electronic information.
5. The establishment of the foundation required
for exchanging data electronically throughout
the LNHS. This development is essential
because if it is not possible to exchange
healthcare data in a secure manner within the
LNHS there will be no Ehealth capabilities in
the LNHS.
6. Making sure that the LNHS Ehealth adoption
program is effectively coordinated, lead and
overseen. This will help establish the necessary
structures and mechanisms for governing
Ehealth solutions in the LNHS.
7. There needs to be a lot of money spent on
updating the IT infrastructure throughout the
LNHS as lack investment, coupled with
widespread civil war and looting, has left the
LNHS in short supply of basic computer
equipment.
8. Ehealth information stored by the LNHS needs
to be standardised throughout the LNHS in
order that information can be exchanged
effectively. This can be carried out through
central planning establishing implementation
procedures along with Ehealth implementation.
9. It is essential that the LNHS protects sensitive
healthcare data so that it remains private. In
order for this to succeed there needs to be a
robust and secure security system implemented
throughout the LNHS.
10. Healthcare information requires a regime for
identifying and authenticating information as
quickly as the LNHS can manage so that it can
be accessed and shared securely.
11. Facilitating healthcare institutions in the
establishment of ICT that are appropriate for
their individual needs.
12. Coordinating healthcare institutions to create
ICT infrastructures that are sustainable.
13. Supporting healthcare institutions to connect to
a nationwide fibre optic network for sharing
data and connecting to other healthcare
institutions.
14. Implementing policies for the exchange of
information between healthcare institutions that
do not contravene any privacy laws.
ICT4AWE 2016 - 2nd International Conference on Information and Communication Technologies for Ageing Well and e-Health
76

15. Implementing E-learning for improving
education levels.
16. The construction of the Ehealth capabilities of
the LNHS incrementally and pragmatically,
while initially investing in Ehealth
technologies that will afford the most benefits
to users of the LNHS.
17. Provide help to those areas of the LNHS that
require it, but not at the expensive of those that
would like to develop at a faster pace.
18. Creating processes for EHRs, E-consultations,
E-prescriptions, E-referrals and E-training
systems;
8 THE STUDY’S LIMITATIONS
The largest challenge in carrying out this case study
for the researcher was not just the large distances
between healthcare institutions that were travelled,
in order to create as balanced a reflection as possible
of opinions in the LNHS, but the state of warfare
that existed in the country at the time between rival
tribal factions.
The other limitation in this study is that the
framework has not been used in practice to see
where it does not work, so that it can be improved.
This is because it would require a lot of money to
test it that is not currently available in Libya, though
when the researcher presented his findings to experts
in Libya it was received positively.
A lot of the limitations inherent in the research
technique and methodology have already been
covered in the writings above. Further factors
affecting the efficiency of the research were the time
limitations imposed by the LNHS and the Libyan
culture itself. The reason for employing the methods
of questionnaire and interview in this study was to
enhance the level of confidentiality that the
participants would enjoy. That a high level of
privacy was maintained was of utmost importance.
Another hurdle placed in the researcher’s way in
carrying out the interviews was that of gender.
Because of the restrictions within Libyan culture
regarding the mixing of males and females, the
researcher being male needed to employ females to
carry out such tasks. It was expected that by placing
guarantees of anonymity the participants would
therefore feel more relaxed and deliver answers that
were more accurate, confidential and honest. Time
presented a serious limitation to the researcher due
to healthcare institutions allowing interviews to be
for no longer than 25 minutes. This was because the
LNHS authorities did not want the medical staff’s
private time intruded upon, hence limiting interview
time to that reserved for giving lectures, thus placing
a limitation upon the quantity of variables that could
be harvested.
The fact that the participant’s confidential details
were self reported creates yet another limitation to
the study. This is because it may create inaccuracies,
thus information that is technologically, socially,
culturally or medically influenced, may need to be
considered as differing somewhat to reality when
medical ISs are being planned.
9 CONCLUSIONS
After having reviewed the available literature on
Ehealth technology, assessing the healthcare
institutions selected for Ehealth readiness and
analysing the results, this paper will now set out the
conclusions reached by the researcher, namely that:
all the healthcare institutions were at level 0 on the
Ehealth maturity curve and their ICT infrastructures
would need integrating so that medical staff could
communicate within their healthcare institutions and
with other healthcare institutions, therefore
benefitting from Ehealth solutions that might be
implemented at some future date. The researcher
therefore concludes that, for the successful
implementation of Ehealth systems into the LNHS,
the ICT infrastructures within the healthcare
institutions of the LNHS need to be interconnected
so that E-consultations can be carried out to aid
medical staff in treating patients more efficiently
when they do not have the training for a specific
condition, but can source this information from a
colleague in another healthcare institution. The
researcher also came to the conclusion that all the
various systems and patient healthcare data need to
become interoperable and brought together into an
efficient and effective system. To conclude, this
paper has laid out a provisional Ehealth framework
that, if followed, will lead to the healthcare
institutions of the LNHS moving from level 0 on the
Ehealth maturity curve to a level 2, thus enabling
healthcare staff to provide improved levels of
healthcare to their patients.
REFERENCES
Ammenwerth E., Eichstadter R., Haux R., Pohl U., Rebel
S. and Ziegler S. (2001). A randomized evaluation
of a computer-based nursing documentation
What Changes Need to be Made within the LNHS for Ehealth Systems to be Successfully Implemented?
77

system, Methods Inf Med 40, pp. 61–68.
Alexander H. (2007). Health service evaluations: Should
we expect the results to change practice? Evaluation,
9(4), 405-414.
Bain, C.D., and Rice, M.L. (2006-2007). The Influence of
Gender on Attitudes, Perception, and use of
Technology. Journal of Research on Technologyin
Education, 39(2), 119- 132.
Bazeley, P. (2007). Qualitative data analysis with NVivo.
(p6-15) London: Sage Publications Ltd.
Bilbey, N. and Lalani, S. (2013). Canadian Health Care:
A Focus on Rural Medicine. aVancouver Fraser
Medical Program 2013, UBC Faculty of Medicine,
Vancouver, BC. UBCMJ. issue 2(2).
Blaya, J. and Fraser, H. F. (2010). Implementing Medical
Information Systems in Developing Countries, What
Works and What Doesn’t. AMIA 2010 Symposium
Proceedings Page – 232.
Brender J. (2006). Evaluation Methods for Health
Informatics. Elsevier Inc. London, UK.
Bryman, A. (2006). Integrating Quantitative and
Qualitative Research: How is it Done?, Qualitative
Research, Vol. 6, pp 97-113.
Bryman, A. (2007). Barriers to Integrating Quantitative
and Qualitative Research, Journal of Mixed Methods
Research, Vol. 1, pp 8-22.
Broens, T., Huis in’t Veld, R.M.H.A., Vollenbroek-
Hutten, M.M.R., Hermens, H.J., Van Halteren,
A.T. & Niewenhuis, L.J.M. (2007). Determinants of
successful telemedicine implementations, Journal of
Telemedicine and Telecare, 6(13), 303- 309.
Cathain, A. (2009). Mixed Methods Research in the
Health Sciences. A Quiet Revolution, Journal of
Mixed Methods Research, Vol. 3, pp 3-6.
Cathain, A., Murphy, E. and Nicholl, J. (2008). The
Quality of mixed Methods Studies in Health Services
research, Journal of Health Services Research &
Policy, Vol 13, No 2, 2008: 92–98: The Royal Society
of Medicine Press Ltd 2008.
Campbell J.D., Harris K.D. and Hodge R. (2001).
Introducing telemedicine technology to Rural
Physicians and settings, J Fam Pract; 50:419-24.
Creswell, J. and Plano Clark, V. (2010). Designing and
Conducting Mixed Methods Research, 2nd Edition,
Sage, Thousand Oaks.
Connie V. Chan , David R. Kaufman (2010) A technology
Selection Framework for Supporting Delivery of
Patient-Oriented Health Interventions in Developing
Countries. Journal of Biomedical Informatics 43
(2010) 300–306.
Hasanain, R., Vallmuur, K., and Clark, M. (2014).
Progress and Challengesin the implementation of
electronic medical records in Saudi Arabia: A
systematic review. Health Informatics- An
International Journal (HIIJ) Vol.3, No.2, May 2014.
Hamed, H. AlY. and Alabri, S. (2013). Using NVIVO for
Data Analysis in Qualitative Research. Ministry of
Education, Sultanate of Oman. International
Interdisciplinary Journal of Education – January
2013, Volume 2, Issue 2.
Hamroush, F. (2014). Medical Studies & Training:
Challenges and Opportunities. Minister Of Health in
the Transitional Libyan Government, Libya Higher
Education Forum 2014, London.
Hossein, S. M. (2012). Consideration the Relationship
between ICT and Ehealth. International Institute for
Science, Technology & Education. Vol 2, No 8.
Ishak, N. M. and Abu Bakar, A. Y. (2012). Qualitative
Data Management and Analysis uSing NVivo:An
approach used to Examine Leadership Qualities
Among Student Leaders. Education Research Journal
Vol 2.(3) pp. 94-103, March 2012, International
Research Journals.
Jennett P., Yeo M., Pauls M. and Graham J. (2004).
Organizational readiness for telemedicine:
implications for success and failure. J Telemed
Telecare. 9 Suppl 2: S27-30.
Jennett P., Jackson A., Ho K., Healy T., Kazanjian A.,
Woollard R. et al. (2005). The Essence of Telehealth
Readiness in Rural Communities: an Organizational
Perspective. Telemed J E Health: 11:137-45.
Jennett, P., Gagnon, M. & Brandstadt, H. (2010).
Readiness Models for Rural Telehealth, Journal of
Postgraduate Medicine, 51(4), 279-283.
Khoja S., Scott R., Ishaq A. and Mohsin M. (2007).
Testing Reliability of eHealth Readiness Assessment
Tools For Developing Countries. ehealth international
journal, Volume 3(1).
Khoja, S., Scott, R., Casebeer, A., Mohsin, M., Ishaq, A.
& Gilani, S. (2007). e-Health readiness assessment
tools for healthcare institutions in developing
countries, Telemedicine and e-Health, 13(4), 425-432.
Kwankam, S. (2004). What e-Health can offer?, World
Health Organization: Bulletin of the World Health
Organization, 82(10): 800-802.
Lau, F., Price, M. and Keshavjee, K. (2011). From Benefit
Evaluation to Clinical Adoption: making Sense of
Health Information System Success in Canada.
Electronic Healthcare, Vol. 9, No.4.
Li, J. (2010). E-health readiness framework from
electronic health records perspective. Australia.
Ludwick, DA., Doucette, J. (2009). Adopting Electronic
Medical Records in Primary Care: Lessons Learned
from Health Information Systems Implementation
experience in seven countries. Int J Med Inform 78:
22–31.
Lynna, J., Martens, J. , Washington, E., Steele, D. and
Washburn, E. ( 2009). A cross Case Analysis of
Gender issues in Desktop Virtual Reality Learning
environment. Volume 46. Number 3. Oklahoma State
University.
Mason, J. (2006). Mixing Methods in a Qualitatively
Driven Way, Qualitative Research, Vol. 6, pp 9-25.
Molina Azorín,J, M and Cameron, R. (2010). The
Application of Mixed Methods in Organisational
Research: A Literature Review. The Electronic
Journal of Business Research Methods, Volume 8,
Issue 2 2010 (pp.95-105).
Niglas, K. (2004). The Combined Use of Qualitative and
Quantitative Methods in Educational Research
Tallinn
ICT4AWE 2016 - 2nd International Conference on Information and Communication Technologies for Ageing Well and e-Health
78

Pedagogical University Press, Tallinn.
Nouh, M. H. and Jagannadha, R. P. (2013). Post-operative
Antibiotic Usage at Benghazi Medical Center, Libya
between 2009 and 2012. IOSR Journal of Pharmacy
and Biological Sciences (IOSR-JPBS). Volume 8,
Issue 4, PP 57-60.
Van de Wetering, R. & Batenburg, R. (2009). A PACS
maturity model: A systematic meta-analytic review on
maturation and evolvability of PACS in the hospital
enterprise, International Journal of Medical
Informatics, 78, 127-140.
Yellowlees, P. (2005). Successfully developing a
telemedicine system, Journal of Telemedicine and
Telecare, 11(7), 331-336.
Wong, L. P. (2008). Data Analysis in Qualitative
Research: a Brief Guide to Using Nvivo. Malaysian
Family Physician 3(1).
World Health Organization (WHO). (2008). Developing
Health Management Information Systems: A Practical
Guide for Developing Countries. Geneva: World
Health Organization.
What Changes Need to be Made within the LNHS for Ehealth Systems to be Successfully Implemented?
79
