
Gene-gene Interaction Analysis by IAC
(Interaction Analysis by Chi-Square)
A Novel Biological Constraint-based Interaction Analysis Framework
Sidney K. Chu
1
, Samuel Guanglin Xu
2
, Feng Xu
3
and Nelson L. S. Tang
1,4,5
1
Department of Chemical Pathology, Faculty of Medicine, The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China
2
Shanghai American School (Pudong), Shanghai, China
3
Department of Biochemistry & Centre of Genomic Science, LKS Faculty of Medicine,
The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China
4
Li Ka Shing Institute of Health Sciences, Faculty of Medicine, The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, China
5
School of Biomedical Sciences, Faculty of Medicine, The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, China
Keywords: Genome Wide Association Study, SNP-SNP Interaction, Genetic Susceptibility, Statistical Modelling.
Abstract: In the recent years of the GWAS era, large-scale genotyping of million polymorphisms (SNPs) among
thousands of patients have identified new disease predisposition loci. However, these conventional
GWAS statistical models only analyse SNPs singularly and cannot detect significant SNP-SNP (gene-
gene) interaction. Studies of interacting genetic variants (SNPs) are useful to elucidate a disease’s
underlying biological pathway. Therefore, a powerful and efficient statistical model to detect SNP-
SNP interaction is urgently needed. We hypothesize that among all the exhaustive model patterns of
interaction (>100), only limited patterns are plausible based on the principle of protein-protein
interaction (in the context of GWAS data analysis). The production of proteins by the process of
translation of DNA predicts that gene-gene interaction resulting in a phenotype should only occur in
classical genetic epistasis models, such as dominant-dominant, and recessive-recessive models. We
developed a statistical analysis model, IAC (Interaction Analysis by Chi-Square), to examine such
interactions. We then exhausted different population and statistical parameters, upon a total of 532
simulated case-control experiments to study the effects of these parameters on statistical power and
type I error of using an interaction vs. singular SNP analysis. Our method has also detected potential
pairwise interactions associated with Parkinson's disease that were previously undetected in
conventional methods. We showed that the detection of SNP-SNP interaction is actually feasible using
typical sample sizes found in common GWAS studies. This approach may be applied in
complimentarily with other models in two-stage association tests to efficiently detect candidate SNPs
for further study.
1 INTRODUCTION
1.1 Recent Progress in GWAS
Advances in Genome-Wide Association Studies
(GWAS) have been successful in identifying genetic
variation carrying predisposition to diseases.
Prostate cancer, breast cancer, ovarian cancer,
colorectal cancer and many other diseases have all
shown to have predisposition loci by GWAS
(Musani et al., 2007). Polymorphic sites are present
every 2000 to 3000 bp in the human genome. In the
past five years, studies have detected many disease
associated SNPs and genes which enhanced our
understanding of cancer-related genetic variants
(Visscher et al., 2012). For example, single
nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) of more than 50
genes are related to cancer susceptibility (Stadler et
al., 2010). This era of GWAS and Haplotype
analysis have helped researches to understand
contribution of genetic variation in predisposition of
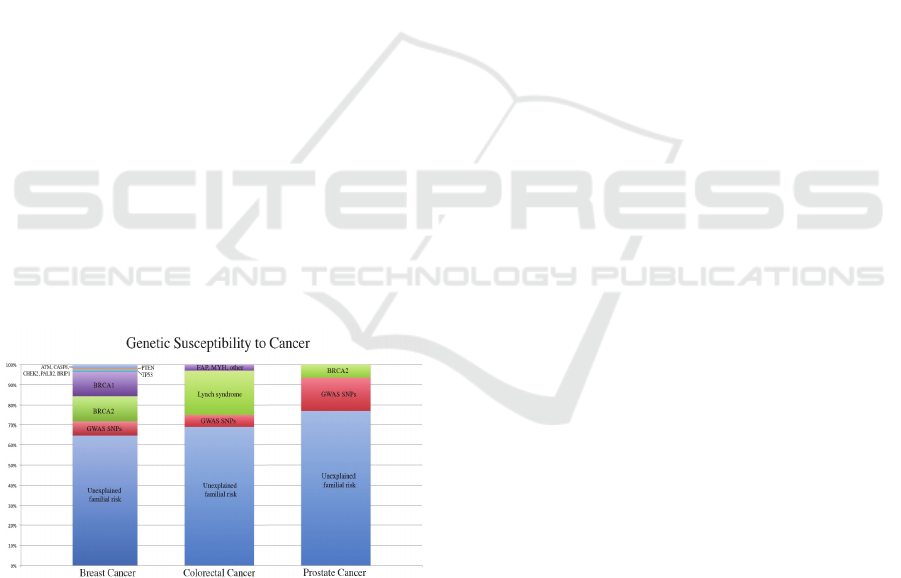
most cancers (such as breast cancer) (Figure 1).
GWAS greatly contribute to our understanding of
disease predisposition.
142
Chu, S., Xu, S., Xu, F. and Tang, N.
Gene-gene Interaction Analysis by IAC (Interaction Analysis by Chi-Square) - A Novel Biological Constraint-based Interaction Analysis Framework.
DOI: 10.5220/0005654601420150
In Proceedings of the 9th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies (BIOSTEC 2016) - Volume 3: BIOINFORMATICS, pages 142-150
ISBN: 978-989-758-170-0
Copyright
c
2016 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
1.2 Current Limitations in GWAS
While GWAS was successful to find thousands of
predisposition SNPs, a large portion of heritability is
still unexplained and this problem of missing
heritability has generated a large interest within the
scientific community. Little progress in both
analysis method of interaction and outcomes has
been made so far. Interaction among genes and
variants may account for this unexplained
heritability, hence it may yield new insights into the
details of complex traits.
So far, less than 30% of heritability in breast
cancer, colorectal cancer, and prostate cancer can be
explained by predisposition genes and SNPs that
have been discovered (Stadler et al., 2010)
(Figure
1). Although conventional single SNP analyses can
be preformed quickly nowadays (Purcell et al.,
2007), it is not designed to detect interactions
between variants (Wan et al., 2010). As a result,
researchers solely rely on increasing sample size (up
to tens of thousands) to increase statistical power
(Manolio et al., 2009). On the other hand, an
efficient and universally acceptable statistical model
would make detecting SNP-SNP interaction a more
efficient and reliable process. Researchers had
proposed a stage-wise approach, by accurately
selecting subsets of SNPs during the first stage of an
association test, such SNPs may be linked to higher
order interactions or may further understand the
phenotypic variance of cancer subsets and other
diseases (Musani et al., 2007).
Figure 1: [Data from: “Genome-Wide Association Studies
of Cancer by Zsofia K. Stadler et al. 2010”] This is a
representation of discovered genes and their affect on the
genetic susceptibility of different cancer subsets. GWAS
SNPs found with contribution to the predisposition of the
respective cancer subset is marked in red.
Even with SNP-SNP interaction analysis (in 3x3x2
contingency table), of a typical GWAS microarray
of 500,000 SNPs, a large number of 2-SNP pairs
(125 billion tests) will be generated from the
genotyping array; this large number of analyses
makes the detection process over-exhaustive
(Schüpbach et al., 2010). Currently all these analysis
approaches, exhaustively exploit all possible
interaction pattern enumerations in each of the 3x3
genotype interaction table.
In short, the search space for interaction is too
large and will result in reduced statistical power,
leading to an increased false positive rate (type I
error). Although potential statistical solutions to
exhaust all these models have been proposed (Wan
et al., 2010) it may not be the most efficient and
appropriate analytical approach. The need for an
appropriate analysis method is exacerbated by
failure to replicate results from other association
studies.
1.3 Our Solution
Here, based on the biological principles of Protein-
Protein Interaction (PPI), we propose that 8
interaction patterns (4 dominant-dominant, 4
recessive-recessive) (Figure 3) are plausible in it's
biological context; this contrasts to the exhaustive
models from exhaustive enumerations, many of
which have their biological plausibility questioned
(Figure 8). Ultimately, these unnecessary and
biologically implausible exhaustive searches would
increase computational burdens and would
subsequently be counterproductive
(Li and Reich,
2000).
Studies of model organisms (saccharomyces
cerevisiae) have shown that interactions occur
frequently and have strong effects on certain
phenotypes (Raval and Ray, 2013). These studies
have shown the presence of dominant-dominant and
recessive-recessive interactions (Segrè et al., 2005)
(Venturi et al., 2000) from PPI analysis through the
two-hybrid screening. The presence of underlying
biological epistasis in model organisms suggests a
need to base statistical analysis on biological
constraints of protein interactions (Emily et al.,
2009).
Interaction Analysis by Chi-Square (IAC)
applies classical epistasis models (dominant-
dominant, recessive-recessive) as biological
constraints to reduce search space and computational
intensity commonly associated with interaction
testing in GWAS. Apart from applying our
framework on 532 case-control simulations, we were
also able to detect one pair of interacting SNPs
associated with Parkinson's disease that was
previously undetected with conventional analysis.
Using a reduced dimension chi-square test, we have
Gene-gene Interaction Analysis by IAC (Interaction Analysis by Chi-Square) - A Novel Biological Constraint-based Interaction Analysis
Framework
143

found interaction patterns and parameters that
present strong SNP-SNP interaction which
conventional single SNP analyses fail to detect. For
the simulations, we used parameters that are realistic
and similar to those of GWAS and have studied
statistical power in the computational analysis. The
results have demonstrated benefits of analysing the
generated datasets with IAC along with focused
searches amongst plausible interaction patterns in
light of PPI. Statistical power was determined by
using 60,000 emulated case-control datasets under
varying sample sizes and parameters. This chi-
square test with reduced dimensions may be useful
for the identification of SNP-SNP interaction in
GWAS.
2 MODELS AND METHODS
2.1 Biological Plausibility of
Interaction Model
Great deals of research efforts in the past have
attempted to screen for all possible interaction
patterns in GWAS. In order to be exhaustive,
investigators enumerated all possible patterns of
interaction that is feasible in a 3x3x2 (Genotype A x
Genotype B x Case-control) contingency table.
Under such exhaustive searches, 100+ non-
redundant patterns have been defined. Our insight
into this problem suggests that a majority of these
investigation patterns are not biologically plausible.
We base our hypothesis on the central dogma of
biology in which the gene translation and protein-
protein interactions occur in one of the recognized
patterns implemented directly to its statistical
augmentation.
Protein-protein interactions occur either as
ligand-receptor pair or as polymeric subunits of a
protein complex, which must have corresponding
biochemical characteristics in order to interact (it is
also applicable to a ligand and receptor pair)
(Jones and Thornton, 2009) (Figure 2).
Wet-laboratory experiments support the notion
of limited ways of interaction between proteins.
Studies in the past have shown that protein inter-
allelic complementation has the ability to produce
enough biochemical activity to express or regulate a
multi-protein complex (Steingrimson et al., 2003).
The physical interaction of mutated protein subunits
(Figure 2) only occurs under certain circumstances
(for example facilitated by the particular allele of a
polymorphism) due to biochemical constraints. To
show this, Bondos et al. (2004) used the yeast two-
hybrid assay to assess which proteins interact with a
Hox protein and found that only a few out of the
Figure 2: (opposite page). This shows the flow of information from the central dogma to statistical augmentation in the 3x3
genotypic interaction table. Uniform transcription leads to a number of possible random interactions (depending on if the
protein is a monomer or dimer) at the subunit level. In this case, the "healthy" subunit pair is assigned at random (recessive-
recessive) depending on its role in the multi-protein complex. Biological action scores(~) are then calculated by the
probability a interaction will yield the assigned "healthy" protein by the specific genotype.
BIOINFORMATICS 2016 - 7th International Conference on Bioinformatics Models, Methods and Algorithms
144

many proteins tested were able to physically interact
with each other. Conformational epistasis (Ortlund
et al., 2009) describes the theory that proteins may
interact in many possible ways, but only a few
biochemical pathways are functionally plausible as
there are many constraints due to evolutionary
recourses.
The models are based on the assumption that the
constraints of PPI are based on three biochemical
principles:
(I) Protein A (encoded by gene A with 2 alleles
A or a) and protein B (encoded gene B with allele B
or b) interacts as subunits of a protein complex or a
ligand and receptor pair.
(II) Uniform transcriptions of both copies of the
gene (both paternal and maternal copies)
(III) Random pairing of subunits from translated
products of the two copies.
We confined the statistical analysis of interaction
to biologically plausible model patterns that is 4
dominant-dominant and 4 recessive-recessive
configurations.
Figure 3: Eight biologically plausible interaction patterns.
Supported by studies from Dummer et al. (2015),
Phillips (2008) and Emily et al. (2009), we are
convinced that these constraints based on biological
epistasis are essential; however, very few existing
algorithms have taken them into account.
2.2 Reduced Dimension Chi-Square
Test for Interaction
We used 266 simulation settings that are based on
the simulated genotype counts of the bi-allelic 3x3x2
contingency table. Conventional univariate analysis,
such as the ones used in PLINK (Purcell et al.,
2007), are often unable to detect interacting SNP
pairs; hence, specific analyses for modelling
interaction needs to be preformed. The power to
detect interaction by our method is characterized by
the simulated counts within the table for detecting
SNP-SNP interaction. A chi-square test is done by
pooling high-risk interaction counts (dominant-
dominant) and low risk (recessive-recessive)
interaction counts to calculate the genotype
frequency distributions. It efficiently reduces a
3x3x2 table to a series of 2x2 tables (Figure 4). This
statistical approach is shown to be a balanced
solution for data sparsity and computational burdens
(Schwarz et al., 2010).
Figure 4: In this illustration, a model of dominant-
dominant interactions is shown; the four genotype
interactions (aa-bb, Aa-bb, aa-Bb, Aa-BB) are considered
to have many similar biological activities, hence they are
combined and collapsed as the high-risk interactions in the
2x2 table. The four other recessive-recessive interactions
are combined in the same fashion as the low risk
interaction. In conventional interaction analyses, each cell
is considered separated.
2.3 Dataset Generation
We generate a genotype distribution for a population
of a given sample size to generate 60,000 datasets
(studies) with genotype counts of assigned
parameters (sample size, MAF, odds ratio) for
different simulations. Based on the Hardy-Weinberg
principle, we first generate genotype frequencies of
2 SNPs based on 2 given MAF’s. Then,
combinations of given Minor Allele Frequency
(MAF) of SNP A and SNP B, disease relative risk,
one of the eight biologically plausible interaction
patterns, sample sizes, proportions and counts may
be generated in each of the cells in the 3x3x2 table
using a multinomial distribution.
IAC converts GWAS data from 9 genotype
counts into high risk and low risk counts (2 counts)
(along with reducing the observed 3x3x2 into 2x2
contingency table). This allows for clear illustrations
in interaction pattern, improving our assessment of
the model's biological plausibility.
2.4 IAC Dataset Analysis
From each collection of simulation datasets of
different population parameters and settings, the
constraints were applied when determining statistical
Gene-gene Interaction Analysis by IAC (Interaction Analysis by Chi-Square) - A Novel Biological Constraint-based Interaction Analysis
Framework
145

power of the interaction analysis and marginal
singular SNP analysis. The Bonferroni correction
was used to correct for multiple testing.
We approached all the analyses conservatively
by placing the Bonferroni corrected P-value for false
discovery rates at a global level of 0.05,which
ensures that the probability of having false positives
does not exceed the nominal significance level.
While calculating the power and type I error with
IAC, a conventional single SNP analysis is also run
for the same dataset. In the results, the average type
I errors for the conventional method analysis results
barely reached the nominal false positive
significance level of global 5%, thus deeming the
setup for the conventional method to be accurate and
conservative as well. The same datasets are
spontaneously converted using the same genotype
distributions and probabilities to fit two
conventional 2x3 single SNP association tests for
determining the statistical significance if the Single
SNP analysis is applied. To handle possible data
sparsity, the observed and expected values for the
modified setup are calculated once again for
statistical power. In order to ensure fairness in
comparison of the two models, both models are
analysed by their p-values using the same
significance filters and other SPC. Our
supplementary data (included in the website)
includes the records for all the simulations and the
analysis setup.
3 RESULTS
3.1 Simulation Results
We have exhausted many parameter configurations
and have arrived at several important conclusions:
We have focused the search amongst the 8
interaction patterns instead of the exhaustive search
of over 100 interaction patterns commonly used
nowadays in various algorithms) and have shown
that the IAC analysis is more efficient in detecting
interaction than conventional single SNP analyses.
We are certain that on top of these 8 pathologically
feasible patterns other patterns may exist and have
not been investigated. However, these 8 models
should be most representative of the biological
nature of gene-gene interaction.
Both IAC and the conventional single SNP
analysis show that type I error levels do not (or
barely) exceed the nominal significance number for
false positives. As the management of false positives
is a common factor in computational burdens
(Visscher et al., 2012) our controlled type I error
rates suggested our approach is conservative. As we
approach the data conservatively, we deem all power
percentages >80% to have enough power to detect
underlying significant SNP-SNP interaction. The
simulation analysis is comprised of many
population-based variables such as Odds Ratio,
Sample Size, disease distribution pattern and Minor
Allele Frequency. The prevalence of the disease
does not affect the statistical power since it does not
affect the population proportions or genotype
frequencies. Below we summarize the effects of
sample size, MAFs and interaction patterns on the
ability to detect significant interaction in GWAS.
We exhaustively analyse our method under many
parameter settings (table 1). The 532 mass-
simulation comparisons (266 by IAC, 266 by Single
SNP analysis) have contained the empirical power
and type I error for 60,000 simulations each.
Table 1: The exhaustive simulations in this study used
these parameters interchangeably for different
investigations. Please note that this table only depicts the
types of parameters we have tested (not the quantity of the
simulations); many of these settings were repeated with
other parameters for other specific investigations.
3.2 Effect of Sample Size
As the sample size (n) increases, the p-value
decreases accordingly (Spencer et al., 2009). A large
sample size, though preferred, is extremely difficult
to acquire in GWAS databases for the detection of
statistically significant interactions
(Bush and Moore,
2012). Using the results from our simulation, our
method clearly shows a dramatic improvement of
power (along with conservative type I error rates)
compared to the 2x3 single SNP analysis. IAC not
only requires less sample size to detect interaction,
but it is also has greater power to detect interactions
with recessive-recessive patterns (Figure 5). By
setting the MAF of both SNPs at 0.5 (the best-case
scenario), the dominant-dominant patterns are able
to detect interaction at only 4000 individuals with
IAC, while the conventional method requires
approximately 8000 individuals. IAC is able to
BIOINFORMATICS 2016 - 7th International Conference on Bioinformatics Models, Methods and Algorithms
146

detect recessive low-risk patterns at about 14000
individuals, while the conventional method requires
unrealistic sample sizes (more than 20,000).
Figure 5: The results from using IAC (top graph) and the
conventional single SNP analysis (bottom graph) with
sample sizes ranging from 2000-15000. The MAF (SNP
A=0.5, SNP B=0.5), odds ratio and all other simulation
parameter settings (besides sample size) remained the
same throughout. The statistical power for SNP A and
SNP B for the single SNP analysis was averaged for the
trend line.
As all the plausible dominant and recessive patterns
exhibit extremely similar trends in statistical power,
we have decided to use only one of each to simplify
the graphs for viewing (Figure 5). Our results
conclude that significant interaction may be detected
using the sample sizes commonly implemented
amongst current GWAS studies.
3.3 Odds Ratio
A disease’s odds ratio can significantly impact the
genotype frequencies observed in patients and thus
Figure 6: The results from using IAC and the conventional
single SNP analysis with varying odds ratios. The
interaction pattern (dominant-dominant), sample size
(4000) and SNP A MAF (0.1) remained constant
throughout.
greatly influence the power of statistical tests. We
based our primary analysis on two common disease
odds ratios of 1.5 and 2 and to compare the power of
both methods. In this scenario (Figure 6), it is clear
that IAC may detect significant interaction as long
as the MAF is above 0.2.
3.4 Minor Allele Frequency (MAF)
Like the odds ratio, the MAF greatly affects the
power of the analysis (Lettre et al., 2007). Though
most of the trends exhibit constant or exponential-
like growth of power with increasing MAF.
Sometimes, unexpected power curves may still
occur when using MAF as a variable. Computing the
genotypic distributions on the interaction table
allows us to use the population disease
characteristics to consider behaviours of interacting
proteins (Moore and Williams, 2005), which
conventional methods may not detect.
Figure 7: A relationship between Minor Allele
Frequencies and statistical power is shown with dominant-
dominant interaction patterns at a sample size of 4000.
MAF of SNP A remains at 0.5.
3.5 Parkinson's Disease Dataset
Analysis
Parkinson's disease is a neurodegenerative disorder
that affects an estimated seven to 10 million people
worldwide. Fung et al. (2006) genotyped 408,803
unique SNPs for 267 Parkinson's disease patients
and 270 neurologically normal controls. In their
analysis of the data, they did not identify any
significant associations using the single SNP
analysis. Different Bayesian models, such as the
ones implemented in Tang et al. (2009), were also
not able to detect any interaction effect. After
running the dataset with IAC, we were able to
replicate and confirm one dominant-dominant
Gene-gene Interaction Analysis by IAC (Interaction Analysis by Chi-Square) - A Novel Biological Constraint-based Interaction Analysis
Framework
147

interaction between SNPs rs849523 (chromosome 2)
and rs10519435 (chromosome 5) with a raw p-value
of 1.79x10
-3
. Although it did not reach a genome-
wide level of statistical significance, it serves here as
a demonstration of feasibility of our approach. The
SNPs are located in the NRP2 and LVRN genes
respectively. NRP2 is related to axon degeneration
and LVRN has been associated with level of very
long chain fatty acid. Both of them are relevant to
neuronal function. However, more experiment and
validation are needed to confirm this preliminary
finding.
4 DISCUSSION
The results indicated better efficiency of the IAC
analysis approach compared to conventional analysis
in many aspects, including; the detection of
interaction under plausible interaction patterns, the
detection of interaction under a given sample size or
relative risk and the detection of interaction under
unexpected power fluctuations. We believe that this
is an ideal search approach for future interaction
studies to increase efficiency when selecting subsets
of SNPs for further validation. Our results have
shown that most trends are biologically multivariate
(Turner and Bush, 2011) and thus IAC does not
require any multiplicative model to conduct high
capacity genome wide scans. Two-stage association
tests are becoming increasingly popular for
interaction analysis, in which the first stage is crucial
for selecting interactions with high power for in-
depth analysis (Feng et al., 2007).
For datasets with genetic interaction, which
results in no main marginal effect, univariate tests
are not able to exhibit power in conventional single
SNP analysis (Goodman et al., 2006). Several
univariate models such as FastEpistasis (Schüpbach
et al., 2010), TEAM (Zhang et al., 2010)and
EPIBLASTER (Kam-Thong et al., 2011) can be
computationally intensive when handling datasets
with complicated interaction patterns and difficult
sample sizes
(Moore and Williams 2005). In fact,
parametric models such as linear and logistic
regression fail to perform well when population
characteristics cannot be known a priori (Moore et
al., 2006). With Bayesian models, the process is too
computationally intensive. Furthermore, the
computationally efficient model BOOST (Wan et
al., 2010) has no consideration of biological
assumptions. IAC can work complementarily with
network-based approaches (Emily et al., 2009). By
filtering potential SNP pairs associated with certain
known protein-protein interactions, the biological
plausibility of the test for statistical epistasis will
substantially improve.
The advantage of IAC is that biologically
redundant patterns are excluded, reducing search
space and enhancing power, also promoting lower
false positive rates. Biologically plausible
interactions rarely exhibit univariate and/or linear
trends in statistical power (Boulesteix et al., 2012),
and have biochemical constraints in PPI (Emily et
al., 2009), hence more studies need to transverse the
disunity between the biological principles of
association and pure statistical reasoning to increase
productivity in exploiting SNP-SNP interactions.
Our results not only showed the efficiency of our
statistical distributions (using IAC) but have also
proposed evidence that detecting significant SNP-
SNP interaction should be feasible in the common
settings of GWAS studies. We have also shown
those scenarios in which the detection of SNP-SNP
interaction is not possible due to lack of statistical
power (eg. extremely low power in recessive-
recessive interaction patterns).
5 CONCLUSIONS
This investigation shows that by using biological
principles of PPI to constrain statistical analysis,
interaction tests become more effective. Once we are
able to understand the behaviour of biochemical
interactions, we may further enhance the practicality
of computational genetic analysis. Thornton-wells et
al., (2004) also believed that “the real power of
existing and yet-to-be-developed methods lies in our
ability to marry them into a comprehensive approach
to genetic analysis, so that their relative strengths
and weaknesses can be balanced and few alternative
hypotheses are left uninvestigated”. Through this
experiment, we were also able to detect two-locus
interaction in GWAS.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
NLST received grant support from Health and
Medical Research Fund 14130282 of the HKSAR
Government.
BIOINFORMATICS 2016 - 7th International Conference on Bioinformatics Models, Methods and Algorithms
148

SUPPLEMENTARY
INFORMATION
Additional materials can be found at our website:
www.interactionanalysisbychisquare.com
REFERENCES
Bondos SE, Catanese DJ, Tan X-X, et al. Hox
transcription factor ultrabithorax Ib physically and
genetically interacts with disconnected interacting
protein 1, a double-stranded RNA-binding protein. J
Biol Chem. 2004;279(25):26433-26444.
doi:10.1074/jbc.M312842200.
Boulesteix A-L, Janitza S, Kruppa J, König IR. Overview
of random forest methodology and practical guidance
with emphasis on computational biology and
bioinformatics. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Data Min Knowl
Discov. 2012;2(6):493-507.
Bush WS, Moore JH. Chapter 11: Genome-wide
association studies. PLoS Comput Biol.
2012;8(12):e1002822.
Dummer PD, Limou S, Rosenberg AZ, et al. APOL1
Kidney Disease Risk Variants: An Evolving
Landscape. Semin Nephrol. 2015;35(3):222-236.
Emily M, Mailund T, Hein J, Schauser L, Schierup MH.
Using biological networks to search for interacting
loci in genome-wide association studies. Eur J Hum
Genet. 2009;17(10):1231-1240.
Evans DM, Marchini J, Morris AP, Cardon LR. Two-stage
two-locus models in genome-wide association. PLoS
Genet. 2006;2(9):e157.
Feng T, Zhang S, Sha Q. Two-stage association tests for
genome-wide association studies based on family data
with arbitrary family structure. Eur J Hum Genet.
2007;15(11):1169-1175.
Fung H-C, Scholz S, Matarin M, et al. Genome-wide
genotyping in Parkinson’s disease and neurologically
normal controls: first stage analysis and public release
of data. Lancet Neurol. 2006;5(11):911-916.
Goodman JE, Mechanic LE, Luke BT, Ambs S, Chanock
S, Harris CC. Exploring SNP-SNP interactions and
colon cancer risk using polymorphism interaction
analysis. Int J Cancer. 2006;118(7):1790-1797.
Jones S, Thornton J.M, Encyclopedia of Life Sciences,
John Wiley & Sons Ltd, 2011.
Kam-Thong T, Czamara D, Tsuda K, et al.
EPIBLASTER-fast exhaustive two-locus epistasis
detection strategy using graphical processing units.
Eur J Hum Genet. 2011;19(4):465-471.
Lettre G, Lange C, Hirschhorn JN. Genetic model testing
and statistical power in population-based association
studies of quantitative traits. Genet Epidemiol.
2007;31(4):358-362.
Li W, Reich J. A complete enumeration and classification
of two-locus disease models. Hum Hered.
2000;50(6):334-349.
Manolio TA, Collins FS, Cox NJ, et al. Finding the
missing heritability of complex diseases. Nature.
2009;461(7265):747-753.
Moore JH, Gilbert JC, Tsai C-T, et al. A flexible
computational framework for detecting,
characterizing, and interpreting statistical patterns of
epistasis in genetic studies of human disease
susceptibility. J Theor Biol. 2006;241(2):252-261.
Moore JH, Williams SM. Traversing the conceptual divide
between biological and statistical epistasis: systems
biology and a more modern synthesis. Bioessays.
2005;27(6):637-646.
Musani SK, Shriner D, Liu N, et al. Detection of gene x
gene interactions in genome-wide association studies
of human population data. Hum Hered. 2007;63(2):67-
84. doi:10.1159/000099179.
Ortlund EA, Bridgham JT, Redinbo MR, Thornton JW.
Crystal structure of an ancient protein: evolution by
conformational epistasis. Science.
2007;317(5844):1544-1548.
Phillips PC. Epistasis-the essential role of gene
interactions in the structure and evolution of genetic
systems. Nat Rev Genet. 2008;9:855-867.
Purcell S, Neale B, Todd-Brown K, et al. PLINK: a tool
set for whole-genome association and population-
based linkage analyses. Am J Hum Genet.
2007;81(3):559-575.
Raval A, Ray A. Introduction to Biological Networks.
CRC Press; 2013.
Schüpbach T, Xenarios I, Bergmann S, Kapur K.
FastEpistasis: a high performance computing solution
for quantitative trait epistasis. Bioinformatics.
2010;26(11):1468-1469.
Schwarz DF, König IR, Ziegler A. On safari to Random
Jungle: a fast implementation of Random Forests for
high-dimensional data. Bioinformatics.
2010;26(14):1752-1758.
Segrè D, Deluna A, Church GM, Kishony R. Modular
epistasis in yeast metabolism. Nat Genet.
2005;37(1):77-83.
Spencer CCA, Su Z, Donnelly P, Marchini J. Designing
genome-wide association studies: sample size, power,
imputation, and the choice of genotyping chip. PLoS
Genet. 2009;5(5):e1000477.
Stadler ZK, Thom P, Robson ME, et al. Genome-wide
association studies of cancer. J Clin Oncol.
2010;28(27):4255-4267.
Steingrimsson E, Arnheiter H, Hallsson JH, Lamoreux
ML, Copeland NG, Jenkins NA. Interallelic
Complementation at the Mouse Mitf Locus. Genetics.
2003;163(1):267-276.
Tang W, Wu X, Jiang R, Li Y. Epistatic module detection
for case-control studies: a Bayesian model with a
Gibbs sampling strategy. PLoS Genet.
2009;5(5):e1000464.
Thornton-Wells TA, Moore JH, Haines JL. Genetics,
statistics and human disease: analytical retooling for
complexity. Trends Genet. 2004;20(12):640-647.
Turner SD, Bush WS. Multivariate analysis of regulatory
SNPs: empowering personal genomics by considering
Gene-gene Interaction Analysis by IAC (Interaction Analysis by Chi-Square) - A Novel Biological Constraint-based Interaction Analysis
Framework
149

cis-epistasis and heterogeneity. Pac Symp Biocomput.
January 2011:276-287.
Venturi GM, Bloecher A, Williams-Hart T, Tatchell K.
Genetic Interactions Between GLC7, PPZ1 and PPZ2
in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics.
2000;155(1):69-83.
Visscher PM, Brown MA, et al. Five years of GWAS
discovery. Am J Hum Genet. 2012;90(1):7-24.
Wan X, Yang C, Yang Q, et al. BOOST: A fast approach
to detecting gene-gene interactions in genome-wide
case-control studies. Am J Hum Genet.
2010;87(3):325-340.
Zhang X, Huang S, Zou F, Wang W. TEAM: efficient
two-locus epistasis tests in human genome-wide
association study. Bioinformatics. 2010;26:i217.
BIOINFORMATICS 2016 - 7th International Conference on Bioinformatics Models, Methods and Algorithms
150
