
An Interactive Digital Platform for Teaching Auditory Physiology
using Two Classes of Electronic Basilare Membrane Models
Gregor Hohenberg
1
, Gebhard Reiss
2
and Thomas Ostermann
3
1
Centre for IT, Media and Knowledge Management, University of Applied Sciences Hamm,
Marker Allee 76-78, 59063, Hamm, Germany
2
Chair and Institute for Anatomy and Clinical Morphology, University of Witten/Herdecke,
Alfred-Herrhausen-str. 50, D-58448, Witten, Germany
3
Chair of Research Methodology and Statistics in Psychology, Witten/Herdecke University,
58313, Herdecke, Germany
Keywords: Digital Learning, Basilar Membrane Model, Software, Education.
Abstract: Teaching and understanding the principles of physiology is one of the most important and complex fields in
medical education. This article describes the development of a digital learning platform for hearing
physiology with computer experiments demonstrating the perceptual masking properties of the human ear.
The basis for the development of this platform were two different hearing models: the sequential electronic
model of the inner ear described by David in 1972 and the parallel Gammatone model by Patterson from
1988. The platform was evaluated from 44 undergraduate students of audiology. On a Likert Scale from 1=
absolutely agree to 5=do not agree at all, students found the learning platform helpful for understanding
“audiological physics” (2.10 ±0.67). After working on the learning module, the physiological hearing
processes also became more evident to the students (2.24 ±0.69). They also were able to use the learning
platform independently without relevant technical problems (1.93 ±0.80). As a conclusion, the usage of such
interactive digital platforms might also lead to more efficient learning pathways which interconnect
knowledge acquisition, skill development and life experience at the same time.
1 INTRODUCTION
Teaching and understanding the principles of
physiology is one of the most important and complex
fields in medical education. Already in 1863
Helmholtz brought out his pathbreaking work “On the
Sensations of Tone as a Physiological Basis for the
Theory of Music”, which in it’s origin german
language was titled “Die Lehre von den
Tonempfindungen”, which clearly emphasized the
educational aspect (stressed by the word “Lehre”) of
his work (Helmholtz and Ellis, 2009).
What can also be seen on this historical example
is that, depending on the respective context,
physiolgical teaching implies the availability of
knowledge of a variety of related medical sciences
most of all anatomy, cell biology or biophysics. From
that knowledge base, normal physiological processes
can be explained, which is necessary to develop
students’ knowledge of disordered
pathophysiological functioning. Therefore besides of
a huge amount of background knowledge, thinking in
structural relationships is one of the essentials for
understanding physiological working principles.
As pointed out by Beard et al., (2003) the use of
electrical engineering and computer science for
creating models of physiological pathways has led to
a deeper understanding of physiological frameworks
in the last decades e. g. in modeling the blood flow
(Wong et al., 1991; Mabotuwana et al., 2007) or
human motor behavior (Lemos et al. 2004; Tagliabue
et al., 2007) to mention some examples. This line of
reasoning was taken up and refined by (Modell, 2006)
who argues, that a “view from the inside” might also
help students to develop model oriented learning
strategies focusing on causal relationships in
physiology. Thus, integration of such models into
computer-based educational strategies offer
promising new perspectives. To be efficient for
students, models should be integrated into an easy to
handle learning platform to manage the underlying
mathematical algorithms. Today such e-learning
Hohenberg, G., Reiss, G. and Ostermann, T.
An Interactive Digital Platform for Teaching Auditory Physiology using Two Classes of Electronic Basilare Membrane Models.
DOI: 10.5220/0005656901890193
In Proceedings of the 9th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies (BIOSTEC 2016) - Volume 5: HEALTHINF, pages 189-193
ISBN: 978-989-758-170-0
Copyright
c
2016 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
189
applications using physiological models already do
exist, e. g. simulation models to teach respiratory
mechanics (Kuebler et al., 2007) or integrative
mathematical model for circulatory physiology
(Abram et al., 2007).
This article describes the development of a special
learning platform for hearing physiology with
computer experiments demonstrating the perceptual
masking properties of the human ear. It gives some
examples on human voice processing are how they
are described using auditory imaging and presents the
results of a student evaluation of this tool. Finally
future prospects for this platform are discussed with a
special focus on web-based learning strategies.
2 MATERIAL AND METHODS
The basis for the development of our learning
platforms were two different hearing models: the
mechanico-electronical model of the inner ear
described by David (1972) and the Gammatone
model by Patterson (1987). Despite of the fact, that
these models date back more than 20 years, they both
still represent classes of current models which are
used in scientific studies. Such is the approach of
David one of the first models which used a low pass
filterbank to describe the cochlea function. It consists
of a series of 64 low pass filters with descending cut-
off-frequency with one entrance and two exits in each
filter. One exit transmits the oscillations to the next
element, while the second exit transmits the signals to
the query system and is further processed according
to the neural auditory pathway (Figure 1).
Figure 1: The functional elements of the hearing model of
David (from David, 1972).
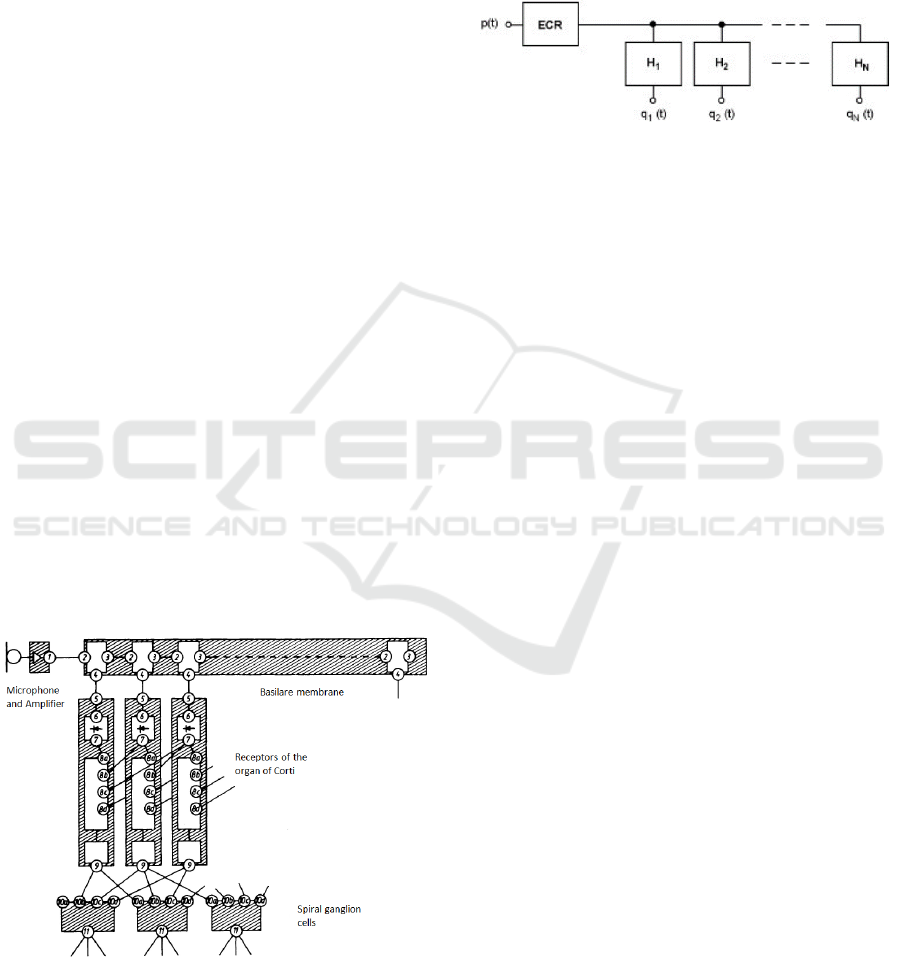
In contrast to this approach, the gammatone model
represents the basilar membrane as a chain of parallel
switched band pass filters. The band pass filters allow
to pass sound within a certain frequency band and so
influences the spectrum of the input signal. Thus, in
contrast to the low-pass-model of David which is a
nonlinear serial appoach, sound in this class of
models is processed linear and parallely through the
filters and then processed further (Figure 2).
Figure 2: The canal model of the sound transference in the
peripheral auditive system. p(t):Input signal; ECR: Ear
Canal Resonances; H1-H2: Transference functions of the
single auditive filters; N: Number of the parallel filters;
q
1
(t)-q
N
(t): Source signals.
To create a basis for the development of learning
platforms based on these two hearing models, both
model classes were realized with MatLAB Version
6.5.1. On that basis the model of David and the
gammatone model were implemented as independent
PC-programs. To show the performance of the
models the technique of auditory imaging of the
basilar membrane movement over time was used for
both models.
Finally, evaluation of the didactic qualities of this
platform was carried out by a questionnaire survey of
29 undergraduate students of medical engeneering.
Following the evaluation program of the
Coordination Center Homburg eLearning in medicine
(Graf et al., 2007), we gave the students six
statements about the learning platform which had to
be judged on a five-point Likert scale from 1=
absolutely agree to 5=do not agree at all.
3 RESULTS
To show the validity of the implemented models we
first carried out simulations with pure sinus tones of
2ms and a pitch level of 500, 1000, 2000 and 5000
Hz. As can be seen in the model of David (1972), high
frequencies are presented in the upper channels
representing the region of the round window and low
frequencies can be associated with the region of the
Helicotrema. Both models also showed a very good
correspondence in their auditory images of basilar
membran movement in conjunction with the applied
signal (e.g. spoken vocal e).
Next, to introduce normal and pathological
hearing to medical students, we showed how acoustic
HEALTHINF 2016 - 9th International Conference on Health Informatics
190
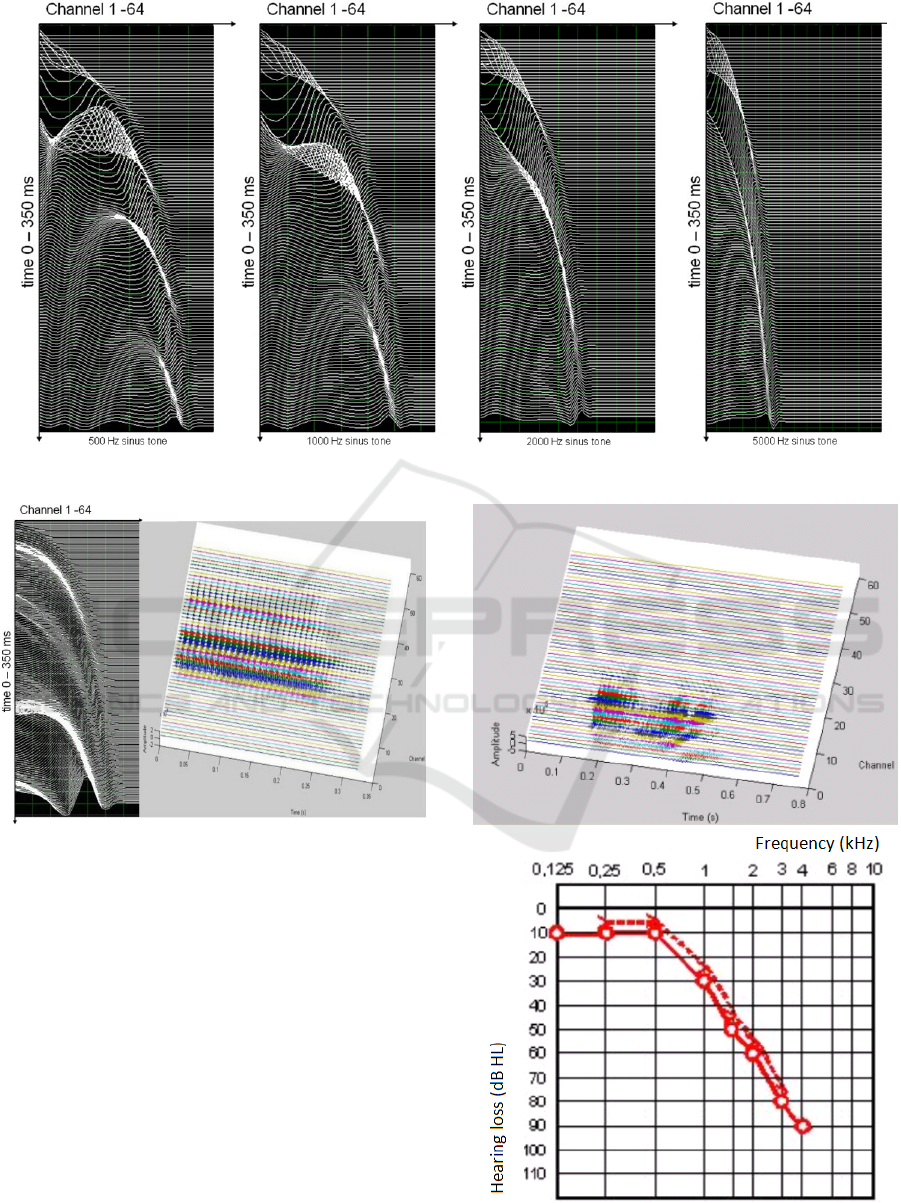
Figure 3: Basilar membrane of hearing model of David (with a 0.5 kHz to 5 kHz sinus tone).
Figure 4: Comparison hearing model of David vs.
Gammatone model for the vocal ‘e’.
signals (e.g. spoken words) are processed by hearing
impaired person. First with the gammatone model.
According to the impairments we adapted the filters
to the pathological situation and compared the results
of the basilar membran movement with a
conventional threshold audiogram (Figure 5).
Due to the more physiological approach we
therefore used the David-model for auditory imaging
of hearing impairments. (Figure 6).
For evaluation purposes, we offered our learning
platform to 29 undergraduate students of audiology.
They tested the benefit of this digital platform in their
learning process. The following statements were
judged on a five-point Likert scale from 1= absolutely
agree to 5 =do not agree at all:
Figure 5: Comparison of the Gammatone model with a
threshold audiogram.
An Interactive Digital Platform for Teaching Auditory Physiology using Two Classes of Electronic Basilare Membrane Models
191

Figure 6: Comparison of the David model with a threshold
audiogram.
1. The learning platform was helpful for the
understanding of the lesson “audiological
physics”.
2. I was able to use the learning platform
independently without relevant technical
problems.
3. After working on the learning module, the
physiological hearing processes became evident
to me.
4. I would like further instruction for a more
intensive use of the platform.
5. Would you prefer to use additional carrying-on
learning platforms?
6. Did the learning module also help you to improve
your practical competences in audiology?
Figure 7 reports the judgements of the 44 students.
Figure 7: Judgements of 44 students on a five-point Likert
scale from 1= absolutely agree to 5 =do not agree at all.
A total of 34 students found that the learning
platform was helpful for the understanding of the
lesson “audiological physics” (Mean ± StDev: 2.20 ±
0.82). 35 Students were able to use the learning
platform independently without relevant technical
problems (Mean ± StDev: 2.07 ± 0.93). 32 students
reported that after working on the learning module,
the physiological hearing processes became evident
to them (Mean ± StDev: 2.23 ± 0.80). However, also
34 students claimed that further instruction for a more
intensive use of the platform would have been helpful
to them (Mean ± StDev: 2.02 ± 0.90). This goes
alongside with the fact that 36 students would prefer
to use additional carrying-on learning platforms
(Mean ± StDev: 1.75 ± 1.33). With respect to
practical skills only 22 students reported that this
digital platform also helped to improve their practical
competences in audiology (Mean ± StDev: 2.52 ±
1.02).
4 CONCLUSIONS
For more than 20 years teaching in the medical
program at Witten/Herdecke Private University has
followed the goal of introducing students to the
reality of patient care by a practical approach
(Mitzkat et al., 2007). Therefore several aspects like
problem based learning have been introduced into a
integrated curriculum. Alongside of these innovative
didactical approaches, e-learning is one of the future
prospects of medical teaching. As one component in
the teaching-framework this article describes a
learning platform for hearing physiology based on
computational models of the cochlea.
After proving the validity of our model, we
showed how our simulation can be used as a e-
learning device for undergraduate medical students
and used our simulation to demonstrate the
relationship between a tone threshold audiogram and
the basilar membrane displacement. With this
approach, students are enabled to construct a causal
relationship between the threshold audiograms and
the tone allocation on the basilar membrane. By
interfacing of different types of media, students not
only get technical informations but also impressions
how hearing pathologies restrict the processing of
auditory informations in hearing disabled persons.
The usage of such interactive learning programs
might also lead to more efficient learning pathways
which interconnect knowledge acquisition, skill
development and life experience at the same time.
Our program therefore can easily be embedded into
practical training in physiology or linked to larger e-
learning environments e.g. in interactive casebooks
on imaging systems in otorhinolaryngology
described by Grunewald et al., (2005) or virtual
HEALTHINF 2016 - 9th International Conference on Health Informatics
192

models of the human temporal bone developed by
Wang et al., (2006).
Online availability of such a platform might also
lead to an indenpendent teaching and learning of
audiology from time and place, which can be enriched
by direct care of the professional lecturer. Thus, the
integration of learning platforms like ours into
medical education can catalyze the shift toward
applying learning strategies, where teachers will no
longer serve mainly as the distributors of content, but
will become more involved as facilitators of learning
and assessors of competency.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
This article is dedicated to Eduard David’s 80
th
birthday. His model of the cochlea inspired us to start
our research and we are grateful for his engagement
and support.
REFERENCES
Abram, S. R., Hodnett, B. L., Summers, R. L., Coleman,
T.G., Hester, R.L., 2007. Quantitative Circulatory
Physiology: an integrative mathematical model of
human physiology for medical education. Adv Physiol
Educ. 2007; 31(2):202-10.
Beard, D. A., Bassingthwaighte, J. B., Greene, A. S., 2005.
Computational modeling of physiological systems.
Physiol Genomics 23: 1–3.
David, E., 1972. Elektronisches Analogmodell der
Verarbeitung akustischer Information in Organismen.
Habil.-Schrift, University of Erlangen.
Graf, N., Hohenberg, G., Igel, C., Herrmann, M., 2008. E-
Learning in der Medizin: Nachfrageorientiert statt
angebotsbasiert. Dtsch Arztebl. 105(21): A-1127.
Grunewald, M., Zenk, J., Alibek, S., Knickenberg, I.,
Ketelsen, D., Iro, H., Bautz, W.A., Greess, H., 2005.
HNORAD - Eine interdisziplinäre interaktive
Fallsammlung zu bildgebenden Verfahren in der Hals-
Nasen-Ohren-Heilkunde im Internet. HNO 53(4):337-
345.
Helmholtz, H. L. F., Ellis, A. J., 2009. On the Sensations of
Tone as a Physiological Basis for the Theory of Music.
Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Kuebler, W. M., Mertens, M., Pries, A. R., 2007. A two-
component simulation model to teach respiratory
mechanics. Adv Physiol Educ. 31(2):218-22.
Lemos, R. R., Epstein, M., Herzog, W., Wyvill, B., 2004.
A framework for structured modeling of skeletal
muscle. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin.7(6):
305-17.
Mabotuwana, T. D., Cheng, L. K., Pullan, A. J., 2007. A
model of blood flow in the mesenteric arterial system.
Biomed Eng Online. 6:17.
Mitzkat, A., Schulz, C., Kasenda, B., Langer, T., Schnell,
M. W., 2006. „Physician in the full spectrum": The
integrated curricula as a part of medical education at the
University Witten/Herdecke - looking back on six years
of teaching in view of practical and theoretical
requirements. GMS Z Med Ausbild 23(4):Doc66.
Modell, H. I., 2007. Helping students make sense of
physiological mechanisms: the "view from the inside".
Adv Physiol Educ. 31(2):186-92.
Nicholson, D. T., Chalk, C., Funnell, W. R., Daniel, S. J.,
2006. Can virtual reality improve anatomy education?
A randomised controlled study of a computer-generated
three-dimensional anatomical ear model. Med Educ.
40(11):1081-7.
Patterson, R. D., Nimmo-Smith, I., Holdsworth, J., Rice,
P., 1987. An efficient auditory filterbank based on the
gammatone function. In Meeting of the IOC Speech
Group on Auditory Modelling at RSRE (Vol. 2, No. 7).
1987.
Song, Y., Spanias, A., Atti, V., Berisha, V. 2005.
Interactive JAVA Modules for the MPEG-1
Psychoacoustic model. Proc. IEEE ICASSP-05
Philadelphia, Vol. 5: 581-584.
Tagliabue, M., Pedrocchi, A., Pozzo, T., Ferrigno, G., 2007.
A mathematical tool to generate complex whole body
motor tasks and test hypotheses on underlying motor
planning. Med Biol Eng Comput. 46(1):11-22.
Tan G. M., Ti, L. K., Suresh, S., Ho, B. S., Lee, T. L., 2002.
Teaching First-Year Medical Students Physiology:
Does the Human Patient Simulator Allow for More
Effective Teaching? Singapore Med J 43(5) : 238-242.
Wang, H., Northrop, C., Burgess, B., Liberman, M.C.,
Merchant, S.N., 2006. Three-dimensional virtual model
of the human temporal bone: a stand-alone,
downloadable teaching tool. Otol Neurotol. 27(4):452-
457.
Wong, P. K., Johnston, K. W., Ethier, C. R., Cobbold, R.
S., 1991. Computer simulation of blood flow patterns in
arteries of various geometries. J Vasc Surg. 14(5): 658-
67.
Ziv, A., Wolpe, P. R., Small, S. D., Glick, S., 2003.
Simulation-Based Medical Education: An Ethical
Imperative. Academic Medicine 78(8): 783-8.
An Interactive Digital Platform for Teaching Auditory Physiology using Two Classes of Electronic Basilare Membrane Models
193
