
Internet of Smart Things
A Study on Embedding Agents and Information in a Device
Leo van Moergestel
1
, Melvin van den Berg
1
, Marco Knol
1
, Rick van der Paauw
1
, Kasper van Voorst
1
,
Erik Puik
1
, Dani
¨
el Telgen
1
and John-Jules Meyer
2
1
Institute of ICT, HU University of Applied Sciences, Utrecht, Netherlands
2
Information and Computing Sciences, Utrecht University, Utrecht, Netherlands
Keywords:
Agent-based IoT, Device Information, Life Cycle Dependent Information.
Abstract:
The term Internet of Things (IoT) is used for situations where one or more devices are connected to a network
or possibly the Internet. Most studies focus on the possibilities that arise when a device is capable to share its
data with other devices or humans. In this study, the focus is on the device itself and what kind of possibilities
an Internet connection gives to the device and its owner or user. Also the data the device needs to participate
in a smart way in the IoT are part of this study. Agent technology is the enabling technology for the ideas
introduced here. A proof of concept is given, where some concepts proposed in the paper are put into practice.
1 INTRODUCTION
Nowadays, many devices are connected to a network,
be it the Internet or another implementation of net-
work connectivity. The connectivity may be based on
wireless technology like Bluetooth or WiFi, but wired
solutions are also possible. The connectivity is used
by a device to share or exchange data with other de-
vices or humans. This so-called Internet of Things
(IoT) (Ashton, 2009) is considered to be the next step
in the direction of a world where everything is con-
nected. Most devices are offering data or accepting
data to operate in a certain environment. In this paper
the focus will be on using agent technology as a basis
for devices operating in the IoT.
The rest of this paper is organised as follows: Sec-
tion 2 is dedicated to IoT. Several classifications and
implementations are presented as well as the added
value that is offered by IoT. In Section 3, after a short
introduction of agent technology, the classes of IoT
devices where agent technology can be applied are
discussed. The reason why agent technology fits in
the IoT model is also explained in Section 3. The
roles of agents and the data a device needs to operate
in the IoT depending on the phase of the life cycle are
the subjects of Section 4. The use phase of the life cy-
cle of the product will be the phase that will have the
main focus, but the roles of the agents in other phases
are mentioned as well. In this section the technical
possibilities are also discussed.
The implementation is the subject of section 5.
Here the device to be produced is introduced and the
parts it consists of. This will lead to a device descrip-
tion format that is both computer- as well as human-
readable. This device description will be enhanced
by assembling instructions that will be the basis of
the information about the manufacturing. Next the
implementation of some ideas proposed in Section 4
will be explained. Section 6 discusses related work.
A conclusion and a bibliography will end the paper.
2 IoT
This section will discuss IoT. First, classifications of
IoT devices are presented followed by a short motiva-
tion what the merits are by connecting devices to the
Internet.
2.1 Classifications of IoT Devices
Three types of classification will be presented here:
1. classification based on administration;
2. classification based on connectivity;
3. classification based on the soft- and hardware ca-
pabilities of the device.
A possible way to classify IoT devices is looking at
their administration. By this is meant the way the de-
vices know each other and what they are expected to
102
Moergestel, L., Berg, M., Knol, M., Paauw, R., Voorst, K., Puik, E., Telgen, D. and Meyer, J-J.
Internet of Smart Things - A Study on Embedding Agents and Information in a Device.
DOI: 10.5220/0005659801020109
In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART 2016) - Volume 1, pages 102-109
ISBN: 978-989-758-172-4
Copyright
c
2016 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

do in the IoT environment. Five different classes of
IoT systems are presented here.
1. Fully static systems. All the devices in the sys-
tem are pre-configured to communicate and inter-
act with each other. An example is an industrial
sensor network like WirelessHART (Song et al.,
2008).
2. Centrally administrated systems with a single ad-
ministration unit. In this case the devices are pre-
configured to interact with a central unit - This is
the registration step. Each device can query the
central unit to identify other devices that it needs
to interact with. Devices can communicate with
each other directly or they can communicate via
the central unit. An example of this class of IoT
devices are devices in smart homes with capabili-
ties for coordinating power usage, adapting to en-
vironmental conditions, ensuring security of the
home, etcetera.
3. Centrally administered systems with multiple ad-
ministrative units where the administrative units
are centrally coordinated. These systems are typ-
ically widely distributed, hence several admin-
istrative units are used at different geographi-
cal locations. The devices are pre-configured to
locate/interact with nearby administrative units.
The administrative units keep track of all the de-
vices and ensure that each device is aware of the
other devices that it may need to interact with.
An example is an infrastructure system for auto-
mated guided vehicles (AGV) in a wide geograph-
ical area.
4. Centrally administered systems with multiple ad-
ministrative units where the administrative units
form a decentralized system. The administrative
units are mobile systems. These systems cooper-
ate with each other to identify and track all the de-
vices. The devices are made aware by the nearest
administrative unit of the other devices they may
need to interact with. Devices can communicate
with each other directly or they can communicate
via the administrative units. Devices themselves
are typically mobile units. An example for this
class of IoT are systems that keep track of chil-
dren and old people to ensure their safety.
5. Fully autonomous decentralized systems. In this
case each device is an independent unit that has
capabilities to identify other units and coordinate
with them. Devices communicate with each other
directly. Devices can be fixed or mobile units -
The autonomy is used to minimize the interaction
time while ensuring requisite coordination and co-
operation with other units. An example in this
case are avionic systems: each aircraft can au-
tonomously identify nearby aircrafts and coordi-
nate its motion in order to prevent accidents.
Another way to classify IoT devices is to look how
they are connected to the Internet, resulting in three
different classes.
1. A device can be part of a special network, wired
or wireless that is connected by a special net-
work device that will be the gateway to the In-
ternet. This situation occurs in the so-called sen-
sor networks, where simple devices use a dedi-
cated network technology to connect with each
other or the gateway. Examples of such networks
are WirelessHART (Song et al., 2008) and Zig-
Bee (Ian Akyildiz et al., 2002).
2. A device can have its own Internet address but is
only capable to reply to requests received from the
network to send data.
3. A device can have its own Internet address and be-
ing capable to communicate directly and actively
with other devices on the Internet.
The third classification that will presented here is
based on the computing capabilities of the device it-
self. Two classes are important for our discussion.
1. A device has only a single thread of execution to
make it work as an IoT device. Normally there
is not much storage capability in this type of de-
vice. An example is a sensor or actuator that is
connected to a network.
2. A device is capable to execute multiple threads,
resulting in a system that has more than one pro-
cess running. This type of device can even be ca-
pable to run an operating system and use some
local storage.
2.2 Benefits of IoT
By connecting devices to the Internet, the following
two possibilities arise:
1. Data collecting: data can be collected and anal-
ysed giving insight in all kind of situations where
the IoT devices are involved.
2. Control: because a device is connected, it can be
controlled. This results is three possibilities:
(a) Communication: this is an extension of data
collecting because the kind of data can be se-
lected.
(b) Interaction: remote control, updates and adjust-
ments are possible.
(c) Automation: a device can learn, but not in a
stand-alone situation, but in the situation where
Internet of Smart Things - A Study on Embedding Agents and Information in a Device
103

resources and other devices on the network can
support the learning system.
To see where agent technology fits in the aforemen-
tioned classifications we will give a short introduction
to agent technology and a definition of what an agent
is as used in this paper.
3 AGENT TECHNOLOGY
This section will start with a short introduction to
agents and the way they can be embedded in a device.
The section will continue with a motivation for using
agent technology. Finally, the types of IoT devices
as introduced in the classification, where the agent
model can be used are discussed.
3.1 Embedding Agents
An agent is an autonomous software system that is de-
signed to play its role and to achieve one or more of its
goals. Agents are autonomous entities that can be em-
bedded in a device under the condition that the device
itself contains a processor and memory to store the
agent code as well as to execute this code. In practice
this means that the device should be capable to run
a kind of operating system. Two important solutions
for embedding an agent in a device exist:
1. The agents can be a part of the device software
infrastructure. Without the agent the device can-
not operate properly. This situation applies when
the agent is developed in combination with the de-
vice software and the device infrastructure itself is
agent-based.
2. The agent can be a software system that oper-
ates separately from the device infrastructure it-
self. In this situation, the device will operate prop-
erly without the agent. An advantage is that the
agent can be added at any time and the agent can
even run in cyberspace. In the latter case a con-
nectivity with the device is compulsory.
3.2 Why Agent Technology?
The main reason for using agent technology is the
fact that an agent can operate without human inter-
vention. It is autonomous in a sense. Intelligence can
be a property of an agent as well as mobility. A mo-
bile agent can move from one workspace to another
opening the possibility to embed it in a product when
the product is made, let the agent move to cyberspace
when needed and let the agent go to another device.
Agents can communicate, thus exchange information
So if a mobile agent is not possible in certain situ-
ations, a newly created agent can take over valuable
information from another agent.
3.3 IoT Device Types
As stated already, the device should have the capa-
bilities to run the agent. This means that it must be
capable to run multiple threads or even better pro-
cesses. The device should be connected directly to the
Internet, because when the device is hidden behind a
gateway, as in the situation of some implementations
of sensor networks, standard software techniques can-
not be used to communicate with the agent embedded
in the device. It depends on the situation if the de-
vice operates actively or just waits for requests. In
regard to the administration, agents can be used in all
five types mentioned. However, in practice fully static
systems (the first type in the list) require human inter-
vention in configuring. This approach conflicts with
the idea that the system should work and configure
itself autonomously.
4 AGENT ROLES IN IoT
In this section the focus will be on generic roles that
an agent can play in a device. The roles depend on the
phase in the life cycle of a product. First these phases
will be introduced including the possible roles for a
product agent. Next, for every role in every phase,
the data or knowledge of the device is summarized.
A more thorough discussion of agents roles in the life
cycle of a product can be found in (Moergestel et al.,
2010).
4.1 Phases in the Life Cycle of a Product
A device starts its life during manufacturing. Mo-
ergestel et al. (Moergestel et al., 2011) describes a
production system where a product starts its life as a
software agent that is responsible for the manufactur-
ing of a single possibly unique product. This so-called
product agent contains the blueprint of the product to
be manufactured and is the basis for the concept of the
IoT in other phases of the life cycle of the product it is
embedded in. In Figure 1 the life cycle of an arbitrary
product is shown. After the design, the product is pro-
duced in the manufacturing phase. After manufactur-
ing, the product is distributed. Next comes a very im-
portant phase, being the use of the product and finally
the phase where the product should be recycled. In all
of these phases, the product agent can play a role that
will be globally described in the next subsections. For
ICAART 2016 - 8th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
104

every phase and associated role, an overview of infor-
mation acquired or used is given. A more extended
discussion can be found in (Moergestel et al., 2014).
We remark that in the literature the term product life
Design Manufacturing Distribution Use Recycling
Figure 1: Life cycle of a product.
cycle (PLC) is commonly used to denote a concept
that is different from what we call the life cycle of a
product. The product life cycle can be defined as the
process wherein a product is introduced to a market,
grows in popularity, and is then removed as demand
drops gradually to zero (Lilien et al., 2003).
4.1.1 Design and Manufacturing
A trend in modern manufacturing is that the de-
sign of a product will be greatly influenced by the
individual end-user requirements. Nowadays cost-
effective small scale manufacturing will become more
and more important. This trend is enabled by Inter-
net technology and new developments in manufactur-
ing like 3D printing opening possibilities to adapt a
manufacturing system to individual end user require-
ments. In (Moergestel et al., 2015) an implementation
of manufacturing as a service (MaaS) is described. In
this MaaS system the product agent is created. Im-
portant is the fact that the product agent is responsi-
ble for the manufacturing of the product as well as
for collecting relevant production information of this
product. This concept is the basis for the roles of the
product agent in later phases of the life cycle. The
product agent carries the product design as well as
the production data and can be viewed as the software
entity that represents the product in cyberspace. The
information available should open the possibility for
a the device to clone itself.
4.1.2 Distribution
In (Burmeister et al., 1997) a logistic application
based on a multiagent system is described. Agent-
based logistic applications have transport from source
to destination as the main goal. However, other
important data can be information about product
handling and external conditions, like temperature,
shocks etcetera. These data can be measured by cheap
possibly wireless sensors and collected by the product
agent in its role of guidance agent during the transport
or after arrival at the destination. The handling and
external conditions during transport can be important
for the other coming cycles in the life phase, because
they influence product quality thus having impact on
maintenance and repair. The information available
gives an overview in time of the physical and condi-
tional data. The main problem related to this phase is
powering the device during transport. That is the rea-
son that in most cases it is better to collect the trans-
port information at arrival, when de device is powered
on. Low power battery-operated sensors already exist
that can collect and store information during trans-
port. These devices will collect the needed informa-
tion and can be read by the product agent when it pow-
ered on.
4.1.3 Use
In the use phase, the product agent can perform ac-
tions that will help and support the end-user by keep-
ing valuable information at hand, offering a user man-
ual or preventing or minimizing the effects of mis-
use. By giving feedback about the usage and prob-
lems that occur during usage it can also help the man-
ufacturer to improve its products. Finally in the re-
cycling phase, the information collected during usage
can be very helpful.
In the next paragraphs several topics of usage of
the product agent are discussed.
Collecting Information. A product agent will col-
lect information about the use of the product as well
as the use of the subparts of the product. Testing the
health of the product and its subsystems or subparts
can also be done by the agent. These actions should
be transparent for the end-user. To perform these ac-
tions, the product agent should be connected to sen-
sors and software subsystems in the product.
Advising and Control. The information collected
by the product agent gives a clue about the product
use and the use of the subsystems. An agent can sug-
gest maintenance or replacement of parts. The agent
can advice a user about the usage of a product, this
can be done directly but also automatically without
direct user intervention. An example of the latter is:
If a product needs resources like electric power, an
agent can suggest a product to wait for operation un-
til the cost of electric power is low i.e. during the
night. It depends of course on the type of device if
this should be implemented.
Maintenance and Repair. An agent can identify a
broken or malfunctioning part or subsystem. This
could be achieved by continuous monitoring, mon-
itoring at certain intervals or a power-on self test
(POST). Condition monitoring is the process of con-
trolling the functioning of parts of a device or of the
Internet of Smart Things - A Study on Embedding Agents and Information in a Device
105

device itself. It is an important possibility to pre-
vent malfunctioning. Three types of information play
an important role: the manufacturing information,
the transport information and the usage information.
This is exactly the information that is collected by the
product agent. Repairing a product is easier if infor-
mation about its construction is available. Issues dur-
ing transport have an influence on the quality as well
as the way a product has been used.
Other Possibilities. Some possibilities that could
be achieved by using a product agent are:
• Transparency of the status of a product after main-
tenance by a third party. The agent can report to
the end-user what happened during repair so there
is a possibility to check claimed repairs. Of course
the agent should be isolated from the system dur-
ing repair to prevent tampering with it.
• Recovery and tracing in case of theft or loss
are also possible by using the embedded product
agent technique.
• Advising the end-user who wants to replace a cer-
tain device by a new one. The product agent can
give advice about the properties the replacing de-
vice should have, based on what the product agent
has learned during the use phase.
4.1.4 Recycling
In Moergestel et al. (Moergestel et al., 2014) the role
of the product agent in the reuse of subsystems and
components is mentioned as well as in locating ex-
pensive or rare material.
Another advantage of having a product agent at
hand in case of recycling is the fact that the prod-
uct agent has the information how a product is con-
structed. This is helpful when a product must be taken
apart. For certain steps a kind of undo-steps should be
carried out to dismantle a product. These undo-steps,
if they exist, can be incorporated at the moment the
product is assembled.
4.2 Embedded Knowledge for Different
Phases
The whole design including the user preferences that
are taken into account form the basis of the knowl-
edge or information of the product agent. The prod-
uct agent will use this knowledge to guide the prod-
uct to be made during manufacturing. This concept is
treated in (Moergestel et al., 2010). The design will
lead to sequences of production steps. In the man-
ufacturing phase itself other knowledge is added to
the knowledge base, especially the information about
how the manufacturing has been carried out for all the
production steps and what parameters where used. In
the distribution phase, all kind of conditions met dur-
ing transport can be collected. The transport route
itself could also be of interest and can be enabled by
the use of a global position system (GPS). This might
be helpful to trace a device to its end-user. However,
as mentioned before the device should be capable to
operate during transport. In the use phase, user pref-
erences during use and usage of subparts are interest-
ing data to be collected. In the recycling phase, data
about the whole manufacturing process is available.
The information about the condition of parts or com-
ponents is also known. This will help to identify parts
that might be available for further use. In this case,
the device should be operating. If that is not possi-
ble, the component where the agent is stored should
be reachable so the information is available. Making
backups in cyberspace during the use phase can be a
solution for situations where the embedded agent is
completely lost.
5 IMPLEMENTATION
To illustrate the concepts mentioned in the previous
sections a device has been chosen that is capable to
play Internet audio streams. For the end-user it will
look like a radio device also know as an Internet radio.
The goal of the work presented here is to embed a
product agent together with the knowledge collected
during manufacturing. The product agent will play
its role in the use phase. It will collect information,
advise the user and display information that can be
helpful in case of repair or maintenance.
5.1 The Internet Radio
The Internet radio adheres to the requirements given
in section 3. It is connected to the Internet, it has com-
puting power available for extra processes and it con-
sists of different components that can be monitored
during use phase, making it a good test case to imple-
ment ideas mentioned in Section 4. The end-user can
also give his or her preferences in the design phase. In
Figure 2, the prototype of the Internet radio is shown.
A block schematic is given in Figure 3. The device
consists of a BeagleBone computerboard, a display,
an audio subsystem connected to an USB-port, speak-
ers and a casing. The main electronic parts are shown
in Figure 4.
ICAART 2016 - 8th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
106
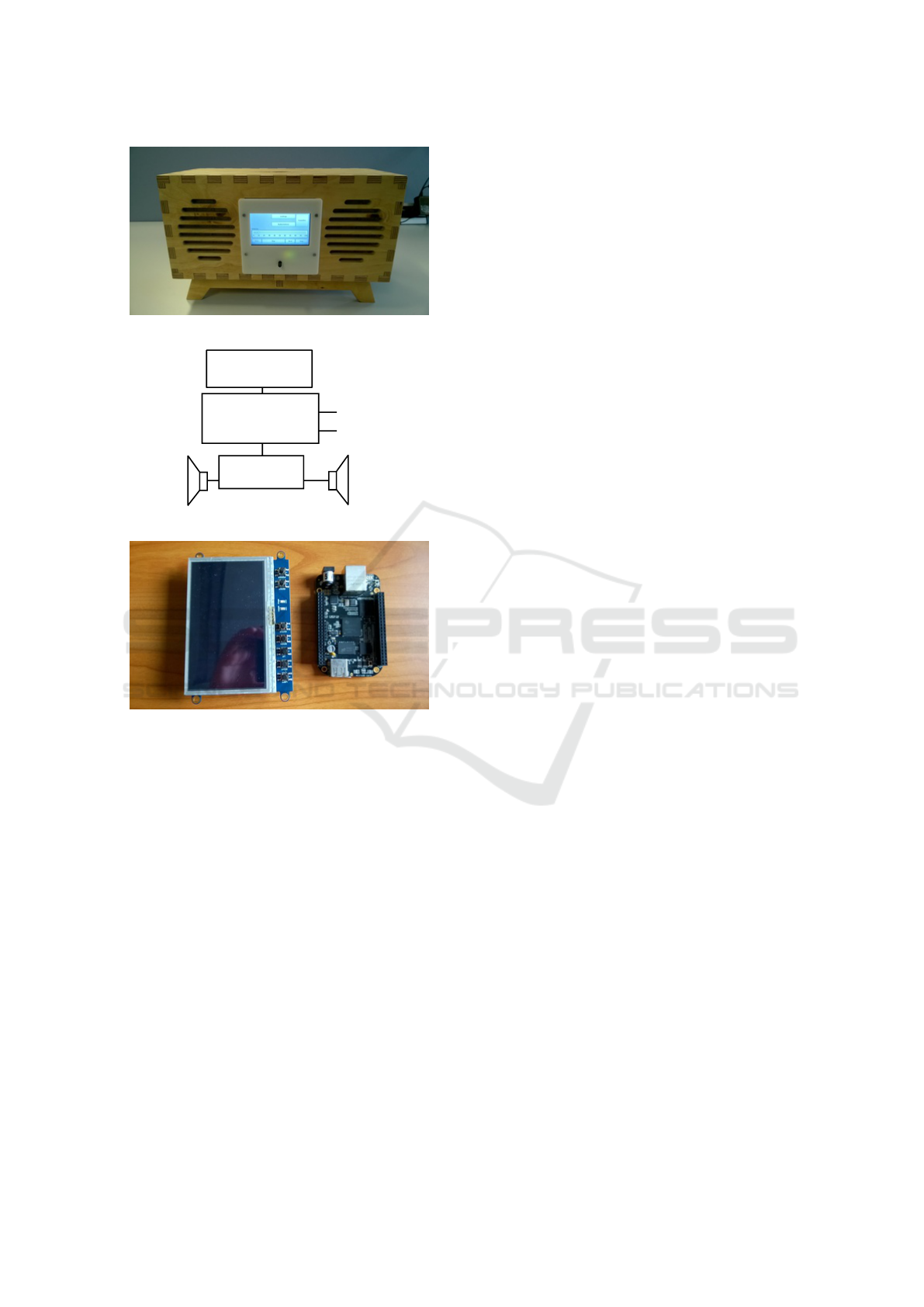
Figure 2: Radio.
Main board
(Beaglebone)
USB-Sound
System
power
Internet
Touch-Screen
Figure 3: Radio.
Figure 4: Main electronic parts of the radio.
5.2 XML Description
All information is stored in XML-format. The main
reason for using XML is that it is a widely accepted
open standard. A lot of libraries for many program-
ming environments exist. An alternative could have
been JSON. Some examples of information storage
will be presented in this section. In the design phase a
top-down composition of the radio is given. The radio
consists of six panels (front, back, top, bottom, left
and right) with zero or more attachments. The end-
user can select a shape, resulting in these six panels.
This results in a toplevel XML-file where the radio is
defined to consist of a these six panels in combination
with actions describing how to assemble the radio us-
ing these panels.
<Radio>
<Source>
six panels
</Source>
<Actions>
assembly instructions
</Actions>
</Radio>
Details of the panels themselves should be added.
A small abbreviated part of the XML-file describing
the front panel of the radio looks like:
<Front>
<Source>
<Panel>
info about panel
</Panel>
<Attachments>
<Speakers>
info about position and type
</Speakers>
<Display>
info about display position
</Display>
</Attachments>
</Source>
<Actions>
info about construction
</Actions>
</Front>
The panel info part contains the file used by the
water jet cutter device that was used to construct the
panel and also the material used. An instruction video
or instruction list can be part of the information in the
Actions-section. The components that are attached
to the panel are also included in the Attachments-
section. Again a video instruction or instruction list
in the Actions-section can help to construct the com-
plete part.
What is now available in this file is information
about the parts, the way they are made, the way they
should be combined, in fact the production steps. Af-
ter the manufacturing phase an extended XML-file is
created containing information when it was actually
constructed including the production feedback. The
manufacturing phase consists of a sequence of pro-
duction steps. Every step is carried out by produc-
tion equipment or by human workers. The results of
the steps are collected by the product agent in the ex-
tended XML-file. In the last step the product agent
will be embedded in the product together with all the
information collected so far. At this stage is is also
possible to add information about reversing the pro-
duction steps if possible at all. This information can
be helpful to disassemble the device at the end of its
life cycle or for repair or maintenance.
There are two types of user-specified properties
that will be added to the knowledge base of the prod-
uct agent being the XML-file. The properties that the
Internet of Smart Things - A Study on Embedding Agents and Information in a Device
107
user selected when the design of the radio was made
and the properties the user specifies during its use.
The first type of properties are mostly fixed if it con-
cerns hardware properties, while the second type may
change during use. The shape and colour of the case is
fixed, but settings and preferences controlled by soft-
ware can change. An example of the user preferences
made during design that might alter during usage, is
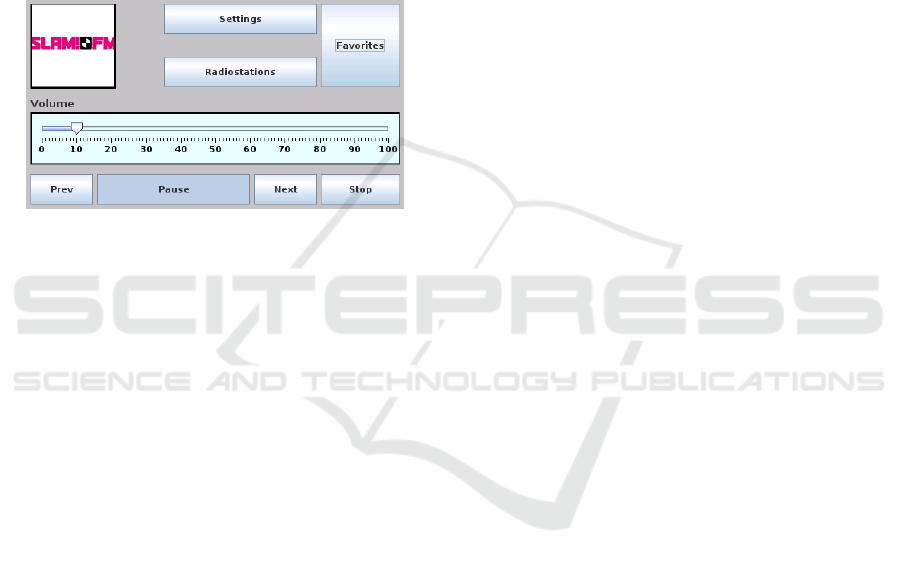
the layout of the control display. In Figure 5 an exam-
ple is given how the display arrangement can be made
by the end-user using a web-interface and generating
an XML-layout file to be used by the GUI software.
This information is also included in the XML-file.
Figure 5: Display and touchscreen.
5.3 Embedding the Product Agent
In the prototype an existing agent platform has been
used. The platform Jade (Bordini et al., 2005) was
chosen for the following reasons:
• Jade is Java-based. Java is a versatile, widely sup-
ported and powerful programming language;
• Because Jade is Java-based it also has a low learn-
ing curve for Java programmers;
• Jade offers possibilities for agents to negotiate. If
we need extra capabilities, the Jade platform can
easily be upgraded to an environment that is es-
pecially designed for BDI agents like 2APL (Das-
tani, 2008) or Jadex (Bordini et al., 2006). Both
2APL as well as Jadex are based on Jade but have
a more steep learning curve for Java developers;
• The Jade runtime environment implements
message-based communication between agents
running on different platforms connected by a
network.
• In Jade, agents can migrate, terminate or new
agents can appear. This feature is important for
the implementation described here.
When information is embedded, the question
arises how much detail should the information give.
In the example of the radio, the electronic heart of the
system is a BeagleBone single board computer. This
computer will be considered as a building block with-
out details about its components like chips, capacitors
and other electronic parts. This could be included in
a separate product agent belonging to the board itself.
If such an agent exists a method of contacting it is the
only thing needed. If there is no such agent available,
the information should be accessible by using Inter-
net technologies in another way. This method can be
used for mass-produced components and prevents the
situation where all this information is replicated.
So far, the radio contains the design and manu-
facturing information as well as the information col-
lected during usage. The list of preferences is ad-
justed to the usage of the device by the end-user. The
information is available to the Internet and can be in-
spected using a web-interface.
6 RELATED WORK
This work started by investigating new manufac-
turing methods as described in (Moergestel et al.,
2011). The agent-based manufacturing opened the
method to preserve the manufacturing information per
product. Agent-based manufacturing has been de-
scribed and developed by Bussmann. In the work
of Bussmann a work-piece agent resembles the prod-
uct agent proposed in our paper. An important dif-
ference is that the work-piece agent ceases to ex-
ist when the product has been made. Among other
work that focusses on agent-based manufacturing, the
work of Paolucci should be mentioned here (Paolucci
and Sacile, 2005), because this work gives a good
overview of the possibilities that arise by using agent
technology. The possibilities of using the agents
in the whole life cycle of the product are described
in (Moergestel et al., 2010). In (Moergestel et al.,
2013) a system is presented that embeds a product
agent in an already complete product that supports re-
pair and reuse of material.
An example of energy saving using multiagent
technology is described by Ruta e.a. (Ruta et al.,
2012). This work has the focus on domotics and
agents play a role in negotiating to lower the energy
usage in a domotic environment. In this case the
agents are not part of the devices themselves as de-
scribed in our paper, but they represent energy con-
suming devices.
7 CONCLUSION
This paper described the possibilities of Internet-
connected devices, when agent technology is added
ICAART 2016 - 8th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
108

to make the device a powerful and also versatile com-
ponent in the IoT. Embedding and collecting infor-
mation enables possibilities that will benefit the end-
user as well as the manufacturer and the environment.
It makes the task of data mining more reachable be-
cause the agent can select interesting data and it helps
to improve products. Storing data can be done in
cyberspace as well as in the device itself depending
on the circumstances like internal storage capabilities
and continuous network connection. In the prototype
presented in this paper only a few possibilities are
implemented. In future research, other possibilities
mentioned in this paper should be implemented.
REFERENCES
Ashton, K. (2009). That ’the internet of things’ thing. RFID
Journal, (22 july).
Bordini, N., Dastani, M., Dix, J., and Seghrouchni, A. E. F.
(2005). Multi-Agent Programming. Springer.
Bordini, R., Braubach, L., Dastani, M., Seghrouchni, A.,
and Gomez-Sanz, J. (2006). A survey of programming
languages and platforms for multi-agent systems. The
Free Library.
Burmeister, B., Haddadi, A., and Matylis, G. (1997). Appli-
cation of multi-agent systems in traffic and transporta-
tion. IEEE Proceedings on Software Engineering 144
(1), pages 51-60.
Dastani, M. (2008). 2apl: a practical agent programming
language. Autonomous Agents and Multi-Agent Sys-
tems, 16(3):214–248.
Ian Akyildiz, I., Su, W., Sankarasubramanian, Y., and
Cayirci, E. (2002). A survey on sensor network. IEEE
Communications Magazines, August.
Lilien, G., Kotler, P., and Sridhar Moorthy, K. (2003). Mar-
keting models. Prentice-Hall of India.
Moergestel, L. v., Meyer, J. J. C., Puik, E., and Telgen, D.
(2010). The role of agents in the lifecycle of a product.
CMD 2010 proceedings, pages 28–32.
Moergestel, L. v., Meyer, J. J. C., Puik, E., and Telgen,
D. (2011). Decentralized autonomous-agent-based
infrastructure for agile multiparallel manufacturing.
ISADS 2011 proceedings, pages 281–288.
Moergestel, L. v., Meyer, J. J. C., Puik, E., and Telgen,
D. (2013). Embedded autonomous agents in products
supporting repair and recycling. Proceedings of the
International Symposium on Autonomous Distributed
Systems (ISADS 2013) Mexico City, pages 67–74.
Moergestel, L. v., Meyer, J. J. C., Puik, E., and Telgen, D.
(2015). Implementing manufacturing as a service: A
pull-driven agent-based manufacturing grid. Proceed-
ings of the International Conference on ICT in Edu-
cation, Research and Industrial Applications (ICTERI
2015) Lviv Ukraine, pages 172–187.
Moergestel, L. v., Puik, E., Telgen, D., Folmer, H., Grn-
bauer, M., Proost, R., Veringa, H., and Meyer, J. J. C.
(2014). Enhancing Products by Embedding Agents:
Adding an Agent to a Robot for Monitoring, Mainte-
nance and Disaster Prevention, volume 449 of Com-
munications in Computer and Information Science.
Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
Paolucci, M. and Sacile, R. (2005). Agent-based manufac-
turing and control systems : new agile manufacturing
solutions for achieving peak performance. CRC Press,
Boca Raton, Fla.
Ruta, M., Scioscia, F., Loseto, G., and Di Sciascio, E.
(2012). An agent framework for knowledge-based
homes. Third International Workshop on Agent Tech-
nologies for Energy Systems (ATES 2012). A work-
shop of the Eleventh International Conference on
Autonomous Agents an Multiagent Systems (AAMAS
2012).
Song, J., Song, H., Mok, A., and Chen, D. (2008). Wire-
lesshart: Applying wireless technology in real-time
industrial process control. Symposium on Real-Time
and Embedded Technology and Applications, pages
377–386.
Internet of Smart Things - A Study on Embedding Agents and Information in a Device
109
