
Fine-Grained Prediction of Cognitive Workload in a Modern Working
Environment by Utilizing Short-Term Physiological Parameters
Timm H
¨
ormann, Marc Hesse, Peter Christ, Michael Adams, Christian Menßen and Ulrich R
¨
uckert
Cognitronics and Sensor Systems Group, CITEC, Bielefeld University, Bielefeld, Germany
Keywords:
Fine-Grained, Cognitive Workload, Stress, Heart Rate, Electrodermal Activity, Tablet Computer, Human
Machine Interaction, Industry 4.0.
Abstract:
In this paper we present a method to predict cognitive workload during the interaction with a tablet computer.
To set up a predictor that estimates the reflected self-reported cognitive workload we analyzed the information
gain of heart rate, electrodermal activity and user input (touch) based features. From the derived optimal
feature set we present a Gaussian Process based learner that enables fine-grained and short term detection of
cognitive workload. Average inter-subject accuracy in 10-fold cross validation is 74.1 % for the fine-grained
5-class problem and 96.0 % for the binary class problem.
1 INTRODUCTION
Today’s modern working environments are increas-
ingly challenging for the employees. As one example
the concept of ”Industry 4.0” sketches the design of
new flexible working environments, in which employ-
ees are constantly confronted with new requirements.
This implies manufacturing processes with very small
lot sizes, which will result in a higher diversity of
working processes. It forces the employees to be
highly flexible and to adapt rapidly to changing work
tasks. For instance, the employees will have to mem-
orize and apply new knowledge more often (Botthof
and Hartmann, 2015). Therefore, adaptive Human-
Machine-Interaction (HMI) becomes more important.
Especially by means of the implementation and uti-
lization of adaptive assistive systems, which shall be
used to guide an employee through a new and unfa-
miliar task (Wallhoff et al., 2007). With the ability
to balance the cognitive workload (CW) of a specific
task, the ergonomic design of working tasks could be
improved. This makes the prediction of CW a key
factor towards human centric design, concerning the
development of adaptive HMI and adaptive assistant
systems. (Rouse et al., 1993) (Wallhoff et al., 2007)
To fulfill the requirement of adaptability, an as-
sistive system needs to know the human users’ cog-
nitive capacity. Therefore, in order to adjust corre-
spondingly to the user’s needs, it is important to pre-
cisely model the user’s perceived CW. The goal is to
balance the complexity of a given task. This is be-
cause, on the one hand, if the user is not sufficiently
assisted, it might lead to mistakes. But on the other
hand, if the user feels unchallenged, it might decrease
his attention (Young and Stanton, 2002). Because
both lead to frustration, the prediction of CW has to
be as precisely and therefore as fine-grained as pos-
sible. To prevent such situations, an adaptive assis-
tive system, as an example, could increase or decrease
the amount of supporting information provided or the
general working speed correspondingly.
We present a tablet computer interaction study,
during which different levels of CW are induced. The
proposed experiment abstracts and emulates typical
tasks employees have to fulfill in modern working en-
vironments. In total, 15 subjects participated in the
experiment. To predict the CW, we evaluated the heart
rate (HR), the heart rate variability (HRV), the elec-
trodermal activity (EDA) and the tablet computer’s
touch features (duration and pressure). A sparse fea-
ture subset was identified and tested by comparing the
accuracy of multiple machine learners.
The work is structured as follows: In section 1
we introduce the theoretical background of CW and
summarize related work. An overview of the used
hardware and the conducted experiment is given in
section 2. Furthermore, the applied machine learn-
ing methods are described. In section 3 the results
of our feature selection and classification are shown.
Subsequently, in section 4 follows a discussion of the
results. Finally, we summarize our work in section 5
and give prospect on our future work.
42
Hörmann, T., Hesse, M., Christ, P., Adams, M., Menßen, C. and Rückert, U.
Fine-Grained Prediction of Cognitive Workload in a Modern Working Environment by Utilizing Short-Term Physiological Parameters.
DOI: 10.5220/0005665000420051
In Proceedings of the 9th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies (BIOSTEC 2016) - Volume 4: BIOSIGNALS, pages 42-51
ISBN: 978-989-758-170-0
Copyright
c
2016 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

1.1 Background
Up to now, there is no universal definition of men-
tal or cognitive workload. (Cain, 2007) summarized
mental workload as the capabilities and effort of the
operators in the context of a specific situation. Hence,
CW is not an univariate, but a ”multifaceted” entity.
A comprehensible definition states CW to be: ”an all-
encompassing term that includes any variable reflect-
ing the amount or difficulty of one’s work” (Bowling
and Kirkendall, 2012). We will follow that definition
within this work.
The measurement of CW is as divergent as its def-
inition. CW can either be measured subjectively (self-
reported) via performance measures (primary or sec-
ondary task e.g. error rate, or time-on-task) or by uti-
lizing psycho-physiological measures (Cain, 2007).
Psycho-physiological measures are thereby based
on the physiological responses of the human body,
resulting from a psychological strain (e.g. cognitive
workload). These physiological responses are con-
trolled by the autonomic nervous system, which con-
sists of the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous
system. Both systems regulate body functions accord-
ingly to environmental conditions (e.g. increase alert-
ness in challenging situations). Well known measure-
ments to quantify these body functions and therefore
to predict CW are based on the heart rate (HR) or
heart rate variability (HRV) (Jorna, 1992), as well as
on the electrodermal activity (EDA; or galvanic skin
response - GSR) (Isshiki and Yamamoto, 1994).
1.2 Related Work
The possibility of predicting psychological strain has
frequently been presented in recent research. Physio-
logical strain is thereby often referred to as mental or
cognitive workload or more generally as stress
1
.
For instance (Choi and Gutierrez-Osuna, 2009)
demonstrated the effectiveness of heart rate monitors
in detecting mental stress. They highlighted the im-
portance of an unobtrusive design to obtain high user
acceptance rates. With their approach they were able
to distinguish between stressed and non-stressed men-
tal states with an accuracy of 69 %.
Within the work of (Wijsman et al., 2011) and
(Choi et al., 2012) it was shown that the combina-
tion of the heart rate and additional predictors (e.g.
respiration rate and EDA) improves the prediction ac-
curacy (79 % and 81 %).
Most recent work also emphasizes the problem of
detecting CW (or stress) by considering physical ac-
1
In some applications, e.g. the automotive industry, re-
lated parameters like arousal or fatigue are considered.
tivity as an additional predictor. (Karthikeyan et al.,
2013) used physical activity information in order to
prevent it from becoming a confounding factor. Their
approach resulted in a prediction with an accuracy of
up to 92.4 %.
Additionally, (Sun et al., 2012) focused on short
term signal processing, which enables the detection of
short term stress events. They presented remarkable
results with a classification accuracy of up to 95 %.
Yet, the topic of fine-grained stress or CW prediction
has gained limited attention and is not individually ad-
dressed. Nevertheless, (Healey and Picard, 2005) pre-
dicted the perceived stress of drivers in three distinct
gradations with accuracy up to 97 %.
In this work we focus on both, short-term signal
processing of multiple parameters and fine-grained
prediction of CW. Both are mandatory requirements
in order to implement CW prediction into adaptive as-
sistive technology.
2 METHODS
The following section starts with an overview of the
used sensory equipment (subsection 2.1). Detailed
explanation of the conducted experiment (subsec-
tion 2.2) and the definition of ground truth (subsec-
tion 2.3) is provided afterwards. Finally, we outline
mandatory signal processing steps (subsection 2.4)
and refer the feature selection (subsection 2.5) and
machine learning methods used within this work (sub-
section 2.6).
2.1 Hardware
The hardware setup is based on the Google Nexus
10 tablet computer(Nexus 10, 2012), which has suffi-
cient computing power for the desired task and allows
an easy integration of the external sensors.
The EDA was captured by using the Mindfield
eSense Skin Response system(eSense Skin Response,
2015), which is a portable solution designed for tablet
computers and smartphones. Its microphone jack is
connected to the tablet computer and the two finger
(hook and loop) electrodes are placed around the sub-
ject’s index- and middle finger.
The Mindfield system was compared to a Brain-
products EDA sensor connected to a appertaining
QuickAmp Amplifier(QuickAmp, 2015) as a refer-
ence system. Although both systems produced dif-
ferent outputs in terms of absolute value, their signals
showed close agreement (Pearson’s r > 0.8). There-
fore, we used the mobile and inexpensive Mindfield
system.
Fine-Grained Prediction of Cognitive Workload in a Modern Working Environment by Utilizing Short-Term Physiological Parameters
43

The heart rate was captured by two redundant sys-
tems. Firstly, we used an ECG based Polar H6 heart
rate sensor(Polar H6, 2012), which is attached to a
chest strap. Secondly the photoplethysmogram (PPG)
based Mio Alpha watch(MIO Alpha, 2013) was used,
which is worn around the wrist. Both heart rate sen-
sors communicate wirelessly with the tablet computer
via Bluetooth Low Energy. Measurement readings
from both devices were comparable (mean deviation
3.85 %). However, we noted that the Mio Alpha
smooths the measured values. For this reason, we
only use data obtained from the Polar module in the
following.
2.2 Experiment
We conducted an experiment to induce varying levels
of CW during the interaction with a tablet computer.
In total, 15 subjects volunteered to participate in the
experiment. Subjects were mainly male students (14
male, 1 female, mean age 25.9 ±2.1). All subjects
were aware about the design of the experiment and
gave their informed consent.
The total experiment lasted approximately 20 to
25 minutes for each participant and was repeated af-
ter a short break. During the break, the sensors
were reapplied to increase robustness in terms of
repeatability concerning the various sensors’ attach-
ment. Each pass of the experiment was divided into
five phases:
1. Relaxation video (2 minutes)
2. Memorize items (3 to 4 minutes)
3. Stroop test (3 to 4 minutes)
4. Recall items (4 to 5 minutes)
5. Memory and reaction test (3 to 4 minutes)
The experiment started with a resting phase in
which a relaxation video was presented to the subject
(phase 1, video duration 90 s). This was done in order
to prevent possible effects resulting from the excite-
ment of the ongoing experiment.
Afterwards, a memory test was initiated (phase 2).
During this phase, 12 items of learning content were
provided to the subject. The learning content con-
sisted of demographic and economic data of the
United States (first pass) and the Czech Republic (sec-
ond pass). For each item, the time to memorize the
provided information was limited to 10 s.
Before the memorized content had to be recalled
(phase 4) by the subject a Stroop test was carried out
(phase 3, (Stroop, 1935)). During the Stroop test the
user had to touch the button with the color that is iden-
tical to the color of a shown text on the screen (fig-
ure 1). The background color, the number of possible
Figure 1: Example of the Stroop test in phase 3 of our
tablet based experiment. Here, the user is asked to touch
the magenta-colored button.
Figure 2: Checker board used to recall the color sequences
in phase 5 of our tablet based experiment.
solutions (buttons) and the available time to answer
was altered randomly. Hence, the Stroop test chal-
lenged the user with varying intensity levels. Over-
all, the subject was asked to reply to 90 Stroop items
during 6 repetitions (15 items each). A short break
preceded every repetition.
Afterwards, the subject was asked to recall the
learning content from phase 2. This was done in a
multiple-choice way, whereas 7 questions were com-
posed into 3 blocks of varying difficulties. To increase
the CW for the multiple-choice test in each block, the
available time to answer was reduced (7 s, 6 s and 5 s,
respectively). Additionally, in the last block, only in-
valid answers were provided.
Finally, the subject had to perform a mixed mem-
ory and reaction test (phase 5). For this test, colored
circles were consecutively drawn on the screen. The
subject’s task was to memorize the color sequence and
immediately recall it afterwards. The difficulty was
altered by changing the count and duration of the cir-
cles shown (3 to 7 circle were shown for a duration of
700 to 500 ms each). Moreover, the number of used
colors was changed randomly (3 to 7). To recall the
color sequence, a checker board was presented to the
subject (figure 2). The checker board was sparsely
filled with colored circles (randomly distributed). The
BIOSIGNALS 2016 - 9th International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
44

subject was asked to recall the color sequence, which
was shown beforehand, by touching the correspond-
ing circles.
The proposed experiment covers typical tasks
workers are faced with in an abstract way. The ab-
straction focuses on the tasks to memorize and recall
various working steps, e.g. while assembling a work
piece or wiring a cable harness at the production line
(mixed reaction and recall test, phase 5). The worker
has to recall a new working process under time pres-
sure. Another example is performing and following
a diagnostic sequence. In this case the worker has to
memorize facts and later on recall and compare the
results (memory test: phase 2 and 4).
2.3 Ground Truth
During the experiment, we simulated short-term
stress events with varying intensities. Each event was
assigned with an estimated or demanded CW by the
experimenter. The annotation scale reached from 1 to
5. Yet, it is unclear if the subjects’ perceived CW cor-
responds to the demanded CW. Therefore, in order to
obtain ground truth data, all participants were asked
to self-report their perceived CW on a scale from 1 to
5. The self-report was enquired directly after a spe-
cific task was finished. Thereby, during each pass of
the experiment, the subject was asked 17 times to give
self-report of the perceived CW. This self-report was
then assigned as ground truth (target label) for the pre-
viously performed task.
2.4 Preprocessing and Feature
Extraction
The utilized Polar H6 provides the heart rate and the
RR-interval for each recognized heart beat. There-
fore, the data stream is recorded in non-uniform time
intervals. To enable a common frequency based
analysis the data is re-sampled to 4 Hz as suggested
by (Singh et al., 2004). For the transformation into
the frequency domain Welch’s method in combina-
tion with a Hamming window is used. Prior to the
feature extraction, the RR-interval is normalized and
detrended as demonstrated by (Tarvainen et al., 2002).
Furthermore, heart rate for each subject is min-max
normalized to increase inter-subject comparability.
The EDA is captured with a sample rate of 10 Hz.
In order to remove outliers, we applied a low pass fil-
ter with a cut-off frequency of 0.5 Hz. The raw EDA
signal is decomposed into the skin conductance level
(SCL) and skin conductance response (SCR), as de-
scribed by (Choi et al., 2012). Their method is based
on the approach from (Tarvainen et al., 2002), which
was also used to detrend the RR-interval beforehand.
Statistical data (minimum, maximum, mean, stan-
dard deviation) is calculated from HR, RR-interval,
EDA, SCR and SCL. In addition, amplitude, dura-
tion, area and frequency of the EDA and SCR signals
are computed and commonly known features based
on heart rate variability are used (Malik et al., 1996).
As the experiment was carried out using a tablet com-
puter, we additionally record mean pressure, mean
duration and total count of touch events on the touch
screen display during the experiment. A comprehen-
sive overview of all extracted features is given in sec-
tion 3.2.
Because the extracted features are not all com-
mensurate, min-max scaling (equation 1) or z-
transformation (equation 2) is used.
Min-Max(X) =
X −min(X)
max(X) −min(X)
(1)
Z-Trans.(X ) =
X −
¯
X
σ(X)
(2)
σ(X) =
s
1
n −1
n
∑
i=1
(x
i
−
¯
X)
2
and
¯
X =
1
n
n
∑
i=1
x
i
2.5 Feature Selection
To identify the optimal window size and overlap, we
derive multiple feature subsets based on the corre-
sponding sensory element (HR, EDA, Touch). Then,
we empirically explore the predictive performance for
each combination of subset, window size and overlap.
For this purpose, we refer to the mean accuracy from
stratified 10-fold cross-validated Decision-Trees. Af-
terwards, we reduce the feature space to avoid redun-
dancies. Therefore, all features are ranked by their
information gain, utilizing Weka 3 data mining soft-
ware (Witten and Frank, 2005).
2.6 Classification
With a comparative analysis we want to identify the
potential of the derived feature set for the fine-grained
and short-term prediction of CW. Therefore, we train
multiple fine-grained supervised classification mod-
els with the optimal feature set and window size that
was evaluated beforehand (section 3.2). We com-
pare various well-known classifiers, using the cor-
respondent MATLAB Toolbox(MATLAB, 2015) im-
plementations. Evaluated methods are: Na
¨
ıve Bayes,
Fine-Grained Prediction of Cognitive Workload in a Modern Working Environment by Utilizing Short-Term Physiological Parameters
45

Decision-Tree, k-Nearest Neighbor and Support Vec-
tor Machine. Additionally, we set up a Gaussian Pro-
cess Regression model utilizing the GMPML MAT-
LAB Toolbox (Rasmussen and Nickisch, 2010).
The Na
¨
ıve Bayes classifier provides a generative
model of the feature space. It is used to estimate the
probability distribution of the feature space given a
specific class label. Thereby, the estimate is based
on the (na
¨
ıve) assumption that, given a certain class
label, the corresponding predictors are conditionally
independent to each other. (Webb, 2010)
The Decision-Tree classifier follows the devide-
and-conquer approach, meaning that multiple deci-
sion rules are created and arranged in a tree like
structure. Thus, Decision-Trees allow non-parametric
modeling, which at the same time, however, can lead
to over-fitting. (F
¨
urnkranz, 2010)
The k-Nearest Neighbor classifier belongs to the
group of lazy or instance-based learners. The classifi-
cation is based on querying the similarity (or distance)
of a new observation to the known observations from
the training set. Typically, a Euclidean distance mea-
sure is used. Each new observation is then classified
by majority vote in respect to its k nearest neighbors.
(Keogh, 2010)
The Support Vector Machine is a kernel-based
discriminative classifier. Utilizing the kernel trick
(Bishop, 2006) the Support Vector Machine con-
structs a hyperplane that allows non-linear separation
of the feature space. Often polynomial, Gaussian or
radial-basis functions are used as kernel functions. In
order to enable multiclass classification with Support
Vector Machine, we make use of the MATLAB Error-
Correcting Output Codes implementation (Dietterich
and Bakiri, 1995).
Lastly, we train a Gaussian Processes Regression
(also known as Kriging), which is a non-parametric
kernel-based model. In the Gaussian Process Regres-
sion, the observations of the training set are seen as
random samples from a multivariate Gaussian distri-
bution. The prediction is based on a Gaussian process,
which is defined by a mean and a covariance function.
To attain class labels, we round the output values of
the regression. (Bishop, 2006)
To compare predictive performance, we refer to
accuracy (equation 3), sensitivity (true positive rate,
equation 4), specificity (true negative rate, equa-
tion 5) and precision (positive predictive value, equa-
tion 6). To prevent overfitting and assure validity of
the classifier, we make use of stratified 10-fold cross-
validation.
Accuracy =
T P + T N
T P + FP + T N + FN
(3)
Sensitivity =
T P
T P + FN
(4)
Specificity =
T N
T N + FP
(5)
Precision =
T P
T P + FP
(6)
TP - True Positive FP - False Positive
TN - True Negative FN - False Negative
3 RESULTS
In this section, we present findings from the experi-
ment (section 3.1) and reveal the selected feature sub-
set (section 3.2). Finally, we compare results of the
trained classifiers (section 3.3).
3.1 Experiment
To verify that the subjects were adequately challenged
during the experiment we compare the demanded CW
with the self-reported CW (ground truth). In di-
rect comparison, the demanded CW level of the ex-
periment mostly coincided with the subjects’ self-
reported CW level (figure 3). However, while the
subjects were performing tasks with demanded CW
level of 4 and 5 no significant difference between the
self-reported CW levels were found (1-way ANOVA,
p = 0.27). We conclude, that the subjects were
equally challenged during both tasks. Furthermore,
the tasks with a demanded CW level 3 were experi-
enced equally or even less challenging than the tasks
with a demanded CW level 2 by the majority of the
subjects. This could be explained through the effect
of habituation during the experiment. The demanded
CW could have been overestimated by the subjects,
thus the expectation may additionally confounded the
self-reported CW (Harris et al., 1993). Nevertheless,
Demanded CW level (1 - low, 5 - high)
Self reported CW level
1 2 3 4 5
1
2
3
4
5
1st pass
1 2 3 4 5
2nd pass
Figure 3: Distribution of the self-reported CW level dur-
ing the 1st and 2nd pass of the experiment, grouped by the
demanded CW level.
BIOSIGNALS 2016 - 9th International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
46
the self-reported CW with 5 distinct levels is used, be-
cause 14 subjects (93 %) self-reported 4 or 5 different
CW levels during the experiment. Only one subject
reported CW with just three different levels (1 to 3).
Additionally, we verified repeatability of the ex-
periment by comparing the first and the second pass
of the experiment. We found similar mean and vari-
ance concerning the self-reported CW levels during
the different experimental phases (figure 3). With
paired t-test the null hypothesis that the self-reported
CW between first and second pass are equal could not
be rejected (p = 0.14). Thus, we conclude there was
no significant difference in the perceived stress level
during both passes of the experiment.
3.2 Feature Selection
We extracted a total of 49 features (table 1) from the
different sensor elements (HR, EDA, touch)
2
.
Table 1: Overview of all extracted features.
Source Feature
HR
mean, standard deviation, min., max.
RR
mean, standard deviation, min., max.,
pRR50, RMSSD, SD1, SD2, SD1/2,
skew, kurtosis, VLF, LF, nLF, nHF,
LF/HF
SCL
mean, standard deviation, min., max.,
EDA, SCR
mean, standard deviation, min., max.,
peak count, peak prominence, max.
peak prominence, mean peak promi-
nence, median peak prominence, peak
duration, peak area
Touch
mean duration, mean pressure, count
To determine an appropriate window size for the
feature extraction, we defined multiple feature sub-
sets. For every subset we extracted features and var-
ied the length of the time window from 10 to 60 s in
5 s steps. We additionally altered the time window
overlap. To generate overlapping windows the signal
window is shifted by 25 %, 50 %, 75 % or 100 % (no
overlap) of the length of the time window. To pre-
estimate the usability and to determine the optimal
window size and overlap, we evaluated the accuracy
of 10-fold cross-validated Decision-Trees for each of
the 308 possible feature sets (table 2).
For all tested combinations of window length,
overlap, optimal accuracy for each feature subset was
2
Detailed information can be found in table 5 located in
the appendix.
Table 2: Best classification accuracy for each feature subset
in respect to window size and overlap.
Subset Length Overlap Accuracy
ALL 35 s 75 % 62.22 %
HR 60 s 75 % 51.54 %
EDA 30 s 75 % 50.50 %
TOUCH 45 s 75 % 46.01 %
HR & EDA 25 s 75 % 60.16 %
HR & TOUCH 50 s 75 % 58.21 %
TOUCH & EDA 35 s 75 % 55.89 %
found with 75 % overlap. With regard to the window
length, the results were not equally consistent. Except
for the heart rate feature set (Pearson’s r = 0.9503,
p < 0.05), we found no significant trend or correlation
between the classifier’s performance and the length
of the time windows. We conclude that there is no
all-encompassing optimal window size or overlap, but
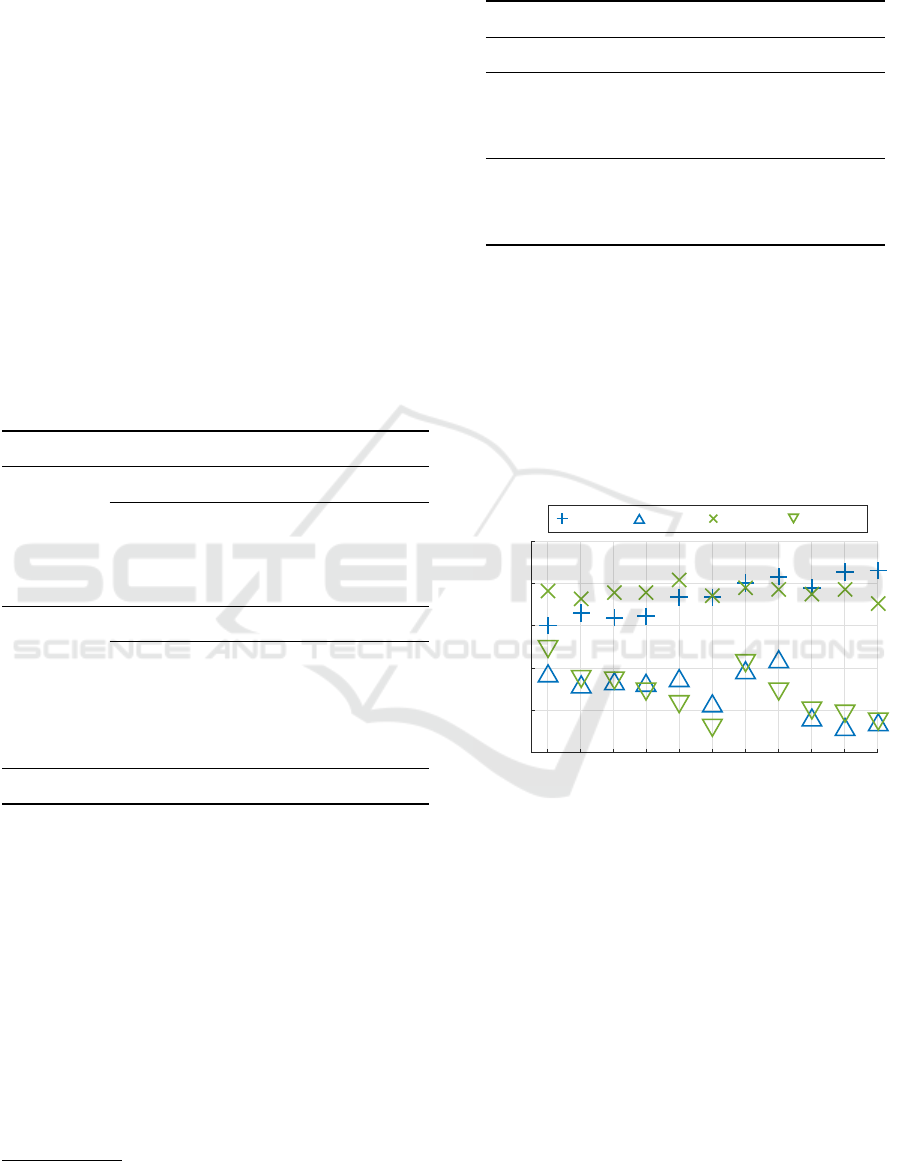
each subset has its own optimum (figure 4).
10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60
Window size [s]
0.3
0.35
0.4
0.45
0.5
0.55
Accuracy [%]
HR; 75% HR; 0% EDA; 75%
EDA; 0%
Figure 4: Mean accuracy from 10-fold cross-validated
Decision-Tree trained on the heart rate and EDA feature
subsets. Features were extracted on time windows with
length of 10 to 60 s in 5 s steps. For the sake of clarity only
75 % and 0 % overlap are depicted.
Following the objective to set up a short-term pre-
diction of CW, the window size needs to be as short as
possible. On the other hand, we need to keep a min-
imal length in order to obtain reliable features, e.g.
from the heart rate sensor. We found that a 40 s win-
dow resulted in a good predictive performance con-
cerning the heart rate features as well as the EDA fea-
tures (figure 4). Hence, for further analysis, we chose
a window size of 40 s with an overlap of 75 %. With
this compromise, we fit with the classification accura-
cies and keep the window size short at the same time.
Nevertheless, due to the overlap, we obtain a new esti-
Fine-Grained Prediction of Cognitive Workload in a Modern Working Environment by Utilizing Short-Term Physiological Parameters
47

mate every 10 s. The chosen window length is by 20 s
smaller compared to related work from (Sun et al.,
2012) or (Karthikeyan et al., 2013).
Next, we select an optimal feature subset. From
the first test, we found maximum accuracy by using
the full feature set. However, to reduce interdepen-
dencies and redundancies within the full feature set
we want to identify the most valuable features and de-
duce a sparse feature subset. Therefore, we ranked all
features by their information gain (table 3).
Table 3: Average information gain and standard deviation
for the top 12 ranked features. Selected features for the
sparse feature subset are printed bold.
Feature Information Gain
Minimum EDA 0.486 ±0.006
Average SCL 0.451 ±0.004
Average EDA 0.451 ±0.004
Maximum EDA 0.416 ±0.003
Average touch duration 0.361 ±0.004
Average touch pressure 0.333 ±0.003
Minimum heart rate 0.323 ±0.020
Maximum heart rate 0.228 ±0.012
Average heart rate 0.199 ±0.004
standard deviation SCR 0.151 ±0.003
Average RR 0.116 ±0.003
Maximum GSR peak promi-
nence
0.098 ±0.002
Using information gain, we found EDA features
to be most important. Although the touch fea-
tures showed worst predictive performance before-
hand (Decision-Tree, table 2), they were ranked sec-
ond most important after the EDA features. With fur-
ther analysis, we have to assume that this result is due
to spurious relationship within the experimental de-
sign. We must note that the expected count of touch
events was not evenly distributed among the different
phases of the experiment or the demanded CW levels.
Furthermore, there was no control setting for touch
pressure or duration, between the touch intensive and
challenging phases (phase 3 and 5) and those phases
that required only few or no touch inputs (phase 1, 2,
4). For this reason, we withdraw touch features from
further analysis.
To reduce the total complexity of the feature
space, the maximum prominence peak feature (de-
rived from the EDA signal) was also withdrawn. The
resulting sparse feature set contains the 9 most valu-
able features (regarding information gain), which in-
clude 5 features based on EDA and 4 heart rate based
features (table 3).
3.3 Predictive Performance
To evaluate the quality of the selected feature subset,
we tested multiple classifiers and compared their ac-
curacy (table 4).
Lowest accuracy resulted from Na
¨
ıve Bayes clas-
sifier (45.09 ±2.08 %). We tested normal distribu-
tions as well as multiple kernel smoothing density
estimates for the probability density. Regardless of
the configuration, no perceptibly difference in the ac-
curacy could be found. One explanation for the low
accuracy is the lack of independence concerning the
feature set. However, a thorough investigation of the
cause is not part of this work.
For the Decision-Tree based classifier an average
accuracy of 60.13 ±4.05 % was achieved. In order
to avoid over-fitting, we chose a limit of 100 splits
per tree. Maximum average sensitivity is found on
level 1 (80.49 ±7.56 %). However, the mean sen-
sitivity considering levels 2, 3 and 4 reached only
56.75 ±9.45 %. Thus, the misclassifications (or in-
accuracy) mainly resulted from the confusions on the
CW levels 2, 3 and 4. Comparable results are found
with the classifier’s specificity.
The usage of k-Nearest Neighbor resulted in an
enhanced accuracy and overall sensitivity. Again,
the highest sensitivity is found with level 1
(82.14 ±5.35 %). Compared to the Decision-Tree
based classifier, the critical confusion on self-reported
CW levels 2, 3 and 4 is reduced (sensitivity:
65.38 ±6.75 %). However, we noticed a continu-
ous drop of the accuracy with a growing neighbor-
hood. Best results were found with k = 1, which
could suggest an over-fitted model. For instance if
the neighborhood is set to k = 10, accuracy declines
to 58.96 ±2.05 %.
Using Support Vector Machine we were able to
further reduce confusion in the mid-levels (sensiti-
vity: 69.10 ±7.74 %) and therefore increase the over-
all accuracy to 71.00 ±3.36 %. Best results were
archived with radial-basis kernel, although usage of
Gaussian or polynomial kernel did only slightly affect
the predictive performance.
In consideration of the observed confusion in the
mid-levels of the CW prediction, we infer both the
target values (self-reported CW) and the predictors
(EDA, HR) to be noisy. Taking the assumption of
noisy predictors and target values into account, we
chose Gaussian Process Regression as an additional
learner for the comparison. Gaussian Process Regres-
sion is well known to act as a linear smoother and
therefore generally provide good predictive power in
noisy settings (Quadrianto et al., 2010). Indeed, the
Gaussian Process based classification outperformed
the other methods with an accuracy of 74.05 % (fig-
BIOSIGNALS 2016 - 9th International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
48

Table 4: Comparison of different classifiers based on the sparse feature subset in descending order of 5-class accuracy. All
tests are 10-fold cross validated. Standard deviation during the cross correlation is given with the mean accuracy.
Classifier Normalization Settings Accuracy, 5-class Accuracy, 2-class
Gaussian Process min-max Mat
´
ern kernel 74.05 ±3.11 % 96.03 ±1.47 %
Support Vector Machine z radial-basis kernel 71.00 ±3.36 % 91.43 ±1.51 %
k-Nearest Neighbor z euclidean distance 67.90 ±3.98 % 92.10 ±2.34 %
Decision-Tree min-max pruned; 100 split limit 60.13 ±4.05 % 90.85 ±1.76 %
Na
¨
ıve Bayes min-max Gaussian kernel 45.09 ±2.08 % 84.37 ±3.20 %
True class
1 2 3 4 5
Predicted class
1
2
3
4
5
42
17.5 %
7
2.9 %
0
0.0 %
0
0.0 %
0
0.0 %
85.7 %
(14.3 %)
2
0.8 %
41
17.1 %
16
6.7 %
1
0.4 %
0
0.0 %
68.3 %
(31.7 %)
0
0.0 %
9
3.8 %
52
21.7 %
7
2.9 %
0
0.0 %
76.5 %
(23.5 %)
0
0.0 %
1
0.4 %
8
3.3 %
44
18.3 %
0
0.0 %
83.0 %
(17.0 %)
0
0.0 %
0
0.0 %
0
0.0 %
4
1.7 %
6
2.5 %
60.0 %
(40.0 %)
95.5 %
(4.5 %)
70.7 %
(29.3 %)
68.4 %
(31.6 %)
78.6 %
(21.4 %)
100.0 %
(0.0 %)
77.1 %
(22.9 %)
Figure 5: Confusion matrix for the best Gaussian Pro-
cess based CW prediction (during 10-fold cross-validation).
Last row contains sensitivity together with false negative
rate (bracketed). The last column contains precision to-
gether with false discovery rate (bracketed).
ure 5). Additionally, the mean sensitivity concern-
ing predicted CW level 2, 3 and 4 was enhanced
(72.95 ±8.10 %).
Still, not all uncertainties are covered by the Gaus-
sian Process. This can easily be seen by shrinking the
classification task to a binary problem. In this case
self-reported CW level 1 is interpreted as no CW. All
remaining levels are taken as present CW. By reduc-
ing the machine learning task to this binary problem,
the average accuracy for the Gaussian Process reaches
up to 96.03 ±1.47 %. For the binary classification
task, the ranking of the predictive power (accuracy) of
the other tested classifiers remains mainly unchanged.
In contrast to the fine-grained tasks, the Na
¨
ıve Bayes
classifier also provided an acceptable classification
rate.
4 DISCUSSION
Within this work, we successfully demonstrated a
fine-grained prediction of CW. By focusing on a fine-
grained prediction based on short-term signals, we ex-
tended the complexity of the classification task. Ad-
ditionally, we reached the accuracy of today’s state of
the art publications for the binary classification task.
In comparison, the fine-grained classification resulted
in a lower overall accuracy. This was explained by a
low sensitivity regarding mid-level CW levels. This
observed variation in the self-reported CW levels is
partly explained due to the subjective perception of
CW. In future work the usage of more detailed self-
reports (e.g. based on NASA- Task Load Index (Hart
and Staveland, 1988)) could overcome this issue. Ad-
ditionally, performance measures like error rate or
time-on-task could further clarify the level of sub-
jectively perceived CW. Nevertheless, regarding the
Gaussian Process model, misclassification rarely ex-
ceeded more than one class (or level). Therefore, de-
spite the lower overall accuracy, the fine-grained pre-
diction should be favorable, because it facilitates a de-
tailed specification of the perceived CW.
Although Gaussian Process showed best accu-
racy, Support Vector Machine yielded comparable
accuracy. As Support Vector Machines are more
widespread and computationally efficient implemen-
tations are commonly available, they might be used
preferentially.
Ranking of the extracted features revealed EDA
features to contain maximum information content, di-
rectly followed by the heart rate features. As empha-
sized by (Sun et al., 2012) care has to be taken if heart
rate is chosen as a predictor, because it is possibly in-
fluenced by means of physical activity. However, dur-
ing our experiment the subjects were monitored by the
experimenter, thus we can exclude physical activity as
confounding factor. Nevertheless, the observed con-
founding influence of the touch features has to be con-
sidered in future tablet computer based experiments.
Yet, we found that even a narrow short-term fea-
ture subset is sufficient to precisely estimate a per-
Fine-Grained Prediction of Cognitive Workload in a Modern Working Environment by Utilizing Short-Term Physiological Parameters
49

son’s cognitive workload. This is a mandatory re-
quirement in order to set up an adaptive assistive sys-
tem, which is capable of balancing a given tasks’
complexity accordingly to the users cognitive capac-
ity.
5 SUMMARY AND CONCLUSION
We were able to achieve a fine-grained prediction of
cognitive workload (stress), which exceeds the com-
plexity of the ordinary binary classification task. Ad-
ditionally, short-term feature were utilized. To re-
produce a realistic setting, modern working environ-
ments were simulated in the presented experimen-
tal setup. The subjects self-reported their perceived
CW directly after each task. After the preprocessing
we were able to extract a total of 49 features. The
most significant features and their ideal window size
and overlap were determined with an initial estimate
based on 10-fold cross-validated Decision-Trees. The
identified sparse feature subset contains 9 features,
which include 5 features based on EDA and 4 heart
rate based features. The feature subset was then eval-
uated, by comparing the accuracy of multiple well es-
tablished machine learning methods.
In conclusion, we achieved a classification accu-
racy of 96.03 % for the binary CW prediction task and
an accuracy of 74.05 % for the fine-grained predictive
model. This is likely to enable the development of
more advanced assistive technology that can precisely
adjust to the user’s requirement in modern working
environments.
In future work we plan to integrate the utilized
sensors into a wearable and hands-free system. This
will allow field studies in real working environments
including skilled manual work. Additionally, the us-
age of more detailed self-reports is planned. Further-
more, we want to investigate how our fine-grained
prediction of CW can be used to adapt the complexity
of a task to the user’s needs.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This research was supported by the DFG CoE 277:
Cognitive Interaction Technology (CITEC), the Ger-
man Federal Ministry of Education and Research
(BMBF) within the Leading-Edge Cluster ”Intelligent
Technical Systems OstWestfalenLippe” (it’s OWL),
managed by the Project Management Agency Karl-
sruhe (PTKA), the BMBF project ALUBAR, and the
PhD program ”Design of Flexible Work Environ-
ments - Human-Centric Use of Cyber-Physical Sys-
tems in Industry 4.0” supported by the North Rhine-
Westphalian funding scheme ”Fortschrittskolleg”.
The authors are responsible for the contents of this
publication.
The authors would like to thank Mindfield for pro-
viding the API for their eSense Skin Response sys-
tem.
REFERENCES
Bishop, C. M. (2006). Pattern Recognition and Machine
Learning (Information Science and Statistics), chapter
Kernel Methods, pages 291–323. Springer New York.
Botthof, A. and Hartmann, E. (2015). Zukunft der Arbeit in
Industrie 4.0 - Neue Perspektiven und offene Fragen.
In Botthof, A. and Hartmann, E. A., editors, Zukunft
der Arbeit in Industrie 4.0, pages 161–163. Springer
Berlin Heidelberg.
Bowling, N. A. and Kirkendall, C. (2012). Workload: A
Review of Causes, Consequences, and Potential Inter-
ventions, pages 221–238. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Cain, B. (2007). A review of the mental workload liter-
ature. In RTO-TR-HFM-121-Part-II. NATO Science
and Technology Organization.
Choi, J., Ahmed, B., and Gutierrez-Osuna, R. (2012). De-
velopment and evaluation of an ambulatory stress
monitor based on wearable sensors. IEEE Trans-
actions on Information Technology in Biomedicine,
16(2):279–286.
Choi, J. and Gutierrez-Osuna, R. (2009). Using heart rate
monitors to detect mental stress. In Sixth International
Workshop on Wearable and Implantable Body Sensor
Networks, pages 219–223.
Dietterich, T. G. and Bakiri, G. (1995). Solving multiclass
learning problems via error-correcting output codes.
Journal of artificial intelligence research, pages 263–
286.
eSense Skin Response (2015). Biofeedback system. Mind-
field Biosystems Ltd., Berlin, Germany.
F
¨
urnkranz, J. (2010). Decision tree. In Sammut, C. and
Webb, G., editors, Encyclopedia of Machine Learn-
ing, pages 263–267. Springer US.
Harris, W., Hancock, P., and Arthur, E. (1993). The effect of
taskload projection on automation use, performance,
and workload. In Proceedings of the Seventh Interna-
tional Symposium on Aviation Psychology.
Hart, S. G. and Staveland, L. E. (1988). Development of
NASA-TLX (task load index): Results of empirical
and theoretical research. In Human Mental Workload,
volume 52, pages 139–183. North-Holland.
Healey, J. and Picard, R. (2005). Detecting stress during
real-world driving tasks using physiological sensors.
IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Sys-
tems, 6(2):156–166.
Isshiki, H. and Yamamoto, Y. (1994). Instrument for mon-
itoring arousal level using electrodermal activity. In
BIOSIGNALS 2016 - 9th International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
50

Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on In-
strumentation and Measurement Technology, pages
975–978. IEEE.
Jorna, P. G. (1992). Spectral analysis of heart rate and psy-
chological state: a review of its validity as a workload
index. Biological psychology, 34(2-3):237–257.
Karthikeyan, P., Murugappan, M., and Yaacob, S. (2013).
Detection of human stress using short-term ECG and
HRV signals. Journal of Mechanics in Medicine and
Biology, 13(02):1350038.
Keogh, E. (2010). Nearest neighbor. In Sammut, C. and
Webb, G., editors, Encyclopedia of Machine Learn-
ing, pages 714–715. Springer US.
Malik, M., Bigger, J. T., Camm, A. J., Kleiger, R. E.,
Malliani, A., Moss, A. J., and Schwartz, P. J. (1996).
Heart rate variability. European Heart Journal,
17(3):354–381.
MATLAB (2015). Version 8.5.0 (R2015a). The MathWorks
Inc., Natick, Massachusetts.
MIO Alpha (2013). Heart rate watch. Physical Enterprises
Inc. (Mio Global), Canada, Vancouver.
Nexus 10 (2012). GT-P8110. Google Inc.; Samsung Elec-
tronics.
Polar H6 (2012). Model: X9. Polar Electro Oy, Finland,
Kempele.
Quadrianto, N., Kersting, K., and Xu, Z. (2010). Gaus-
sian process. In Sammut, C. and Webb, G., editors,
Encyclopedia of Machine Learning, pages 428–439.
Springer US.
QuickAmp (2015). Biofeedbacksystem. Brain Products
GmbH, Gilching, Germany.
Rasmussen, C. E. and Nickisch, H. (2010). Gaussian pro-
cesses for machine learning (GPML) toolbox. Journal
of Machine Learning Research, 11:3011–3015.
Rouse, W., Edwards, S., and Hammer, J. M. (1993). Model-
ing the dynamics of mental workload and human per-
formance in complex systems. IEEE Transactions on
Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, 23(6):1662–1671.
Singh, D., Vinod, K., and Saxena, S. (2004). Sampling
frequency of the RR interval time series for spectral
analysis of heart rate variability. Journal of medical
engineering & technology, 28(6):263–272.
Stroop, J. R. (1935). Studies of interference in serial ver-
bal reactions. Journal of Experimental Psychology,
18(6):643–662.
Sun, F.-T., Kuo, C., Cheng, H.-T., Buthpitiya, S., Collins,
P., and Griss, M. (2012). Activity-aware mental stress
detection using physiological sensors. In Gris, M. and
Yang, G., editors, Mobile Computing, Applications,
and Services, volume 76, pages 211–230. Springer
Berlin Heidelberg.
Tarvainen, M., Ranta-aho, P., and Karjalainen, P. (2002).
An advanced detrending method with application to
HRV analysis. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical En-
gineering, 49(2):172–175.
Wallhoff, F., Ablassmeier, M., Bannat, A., Buchta, S.,
Rauschert, A., Rigoll, G., and Wiesbeck, M. (2007).
Adaptive human-machine interfaces in cognitive pro-
duction environments. In Proceedings of IEEE Inter-
national Conference on Multimedia and Expo, pages
2246–2249.
Webb, G. (2010). Na
¨
ıve bayes. In Sammut, C. and Webb,
G., editors, Encyclopedia of Machine Learning, pages
713–714. Springer US.
Wijsman, J., Grundlehner, B., Liu, H., Hermens, H., and
Penders, J. (2011). Towards mental stress detection
using wearable physiological sensors. In Proceedings
of IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society,
pages 1798–1801.
Witten, I. H. and Frank, E. (2005). Data Mining: Practi-
cal Machine Learning Tools and Techniques. Morgan
Kaufmann Publishers Inc., San Francisco, CA, USA,
second edition.
Young, M. S. and Stanton, N. A. (2002). Attention and au-
tomation: New perspectives on mental underload and
performance. Theoretical Issues in Ergonomics Sci-
ence, 3(2):178–194.
APPENDIX
Table 5: Selected methods used for feature calculation.
categorie function definition
time mean µ =
1
n
∑
n
i=1
x
i
standard
deviation
σ =
q
1
n−1
∑
n
i=1
(x
i
−µ)
2
statistical skew
1
/n
∑
n
i=1
(x
i
−µ)
3
kurtosis
1
/n
∑
n
i=1
(x
i
−µ)
4
heart rate
variability
NN50
∑
n−1
i=1
(x
i
−x
i+1
> .05)
RMSSD
q
1
/n
∑
n
i=1
(x
i
−x
i+1
)
2
SDSD σ((x
1
−x
2
)... (x
n−1
−x
n
))
SD1
√
.5 ·SDSD
2
SD2
p
(2 ·SDSD
2
) −(.5 ·σ
2
(x))
SD12
SD1
/SD2
(spectral) VLF energy 0.00 to 0.04 Hz
LF energy 0.04 to 0.15 Hz
HF energy 0.15 to 0.40 Hz
nLF normalized energy (
LF
/LF+HF )
nHF normalized energy (
HF
/LF+HF )
LF/HF
LF
/HF
geometric
(peak)
count number of peaks
prominence distance between to successive
peaks
width distance between the two mini-
mums surrounding a peak
area integral between the two mini-
mums surrounding a peak
Fine-Grained Prediction of Cognitive Workload in a Modern Working Environment by Utilizing Short-Term Physiological Parameters
51
