
3D Descriptor for an Oriented-human Classification from Complete
Point Cloud
Kyis Essmaeel, Cyrille Migniot and Albert Dipanda
LE2I-CNRS, University of Burgundy, Dijon, France
Keywords:
Human Classification, Histogramm of Oriented Normals, 3D Point Cloud.
Abstract:
In this paper we present a new 3D descriptor for the human classication. It is applied over a complete point
cloud (i.e 360
◦
view) acquired with a multi-kinect system. The proposed descriptor is derived from the His-
togram of Oriented Gradient (HOG) descriptor : surface normal vectors are employed instead of gradients,
3D poins are expressed on a cylindrical space and 3D orientation quantization are computed by projecting
the normal vectors on a regular polyhedron. Our descriptor is utilized through a Support Vector Machine
(SVM) classifier. The SVM classifier is trained using an original database composed of data acquired by
our multi-kinect system. The evaluation of the proposed 3D descriptor over a set of candidates shows very
promising results. The descriptor can efficiently discriminate human from non-human candidates and pro-
vides the frontal direction of the human with a high precision. The comparison with a well known descriptor
demonstrates significant improvements of results.
1 INTRODUCTION
Human detection has been an important research sub-
ject in computer vision for many years. It is used in
a wide variety of applications including health mon-
itoring, driving assistance, video games and behav-
ior analysis. It is particularly a challenging prob-
lem for many reasons. Pose, color and texture sig-
nificantly vary from one person to another, besides
the complexity of the working environment represents
another challenge to overcome. While most of the ap-
proaches for human detection rely on color-image, the
recent advances in depth sensor technology provided
additional solutions. The introduction of affordable
and reliable depth sensors like the kinect from Mi-
crosoft has dramatically increased the interest of these
technologies and is leading to a huge number of ap-
plications using such sensors. Human detection was
one of the first domains to use this new technology
and exploit its benefits. Depth information is most of
the time used to reduce the computation cost. How-
ever the descriptiveness of the 3D shape of the human
envelop was never really exploited.
There are two main categories of methods for human
detection: descriptor/classifier (Figure 1) and match-
ing templates. In the first category, HOG (Histogram
of Oriented Gradients ) (Dalal and Triggs, 2005) is
considered as one of the most successful descriptor
for 2D image human detection. It is used most of the
time with SVM as a classifier. The HOD (Histogram
of Oriented Depths) (Spinello and Arras, 2011; Choi
et al., 2013) is a well-known adaptation of the HOG
which is applied on depth images. HOD locally en-
codes the direction of depth changes and relies on a
depth-informed scale-space search. In fact it uses the
depth array as a 2D image to apply the HOG pro-
cess. Hence 3D data are not exploited in their first
forms, which makes them difficult to apply in scenar-
ios where multiple sources of information are com-
bined to produce the 3D data like in a multi-sensor
system. The Relational Depth Similarity Features
(RDSF) (Ikemura and Fujiyoshi, 2011) arise the same
problem as before. The RDSF calculate the degrees
of similarity between all of the combinations of rect-
angular regions inside a detection window in a sin-
gle depth image only. The second category of meth-
ods rely on matching one or many templates of cer-
tain body-parts in 2D data (images) or 3D data (point
clouds). The Ω-shape of the head and shoulders of a
human body are an example of descriptive templates
(Tian et al., 2013). To compare it to the data, Xia (Xia
et al., 2011) uses chamfer distance and Choi (Choi
et al., 2011) uses the Hamming distance.
In this paper we propose a human classification
method that operates on point clouds and exploits
uniquely the 3D features of the human without using
Essmaeel, K., Migniot, C. and Dipanda, A.
3D Descriptor for an Oriented-human Classification from Complete Point Cloud.
DOI: 10.5220/0005679803530360
In Proceedings of the 11th Joint Conference on Computer Vision, Imaging and Computer Graphics Theory and Applications (VISIGRAPP 2016) - Volume 4: VISAPP, pages 353-360
ISBN: 978-989-758-175-5
Copyright
c
2016 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
353
color information. The proposed 3D descriptor can be
considered as a generalization of the HOG descriptor.
The calculation of the descriptor starts by dividing the
3D cloud into 3D blocks. The 3D descriptor is then
obtained by computing the histogram of orientations
of the normals on the points in each block similarly to
(Tang et al., 2012). Song (Song and Xiao, 2014) uses
also the normals to describe 3D object. For his learn-
ing, he renders each example from different view an-
gles. In our method we set an orientation for the learn-
ing. Hence we increase the descriptivity of our model
and we can estimate the orientation of the frontal di-
rection. Finally we use a SVM classifier to determine
whether the 3D descriptor represents a human or not.
Moreover, the descriptor provides additional informa-
tion about the frontal orientation of the human. Such
information is important for numerous applications
namely tracking initialization, human-machine inter-
action and behavior analysis.
For optimal performance the proposed method is ap-
plied on a Complete Point Cloud (CPC). Indeed the
isotropic property of the CPCs (i.e 360
◦
view) allows
the estimation of the frontal orientation contrary to
other types of data. In our case we employ a multi-
kinect platform to capture the CPC. Building a multi-
kinect system requires dealing with several challenges
like calibration, interference and noise removing (Es-
smaeel et al., 2012). The platform covers the entire
working environment and thus the complete 3D shape
of the subject is reconstructed. Exploiting 3D data
Figure 1: Overview of the descriptor/classifier framework.
The descriptor transforms the data into a more descriptive
space. A classifier is built from the database of positives and
negatives examples.The classifier computes for each candi-
date a classification score.
has recently become easier after the arrival of reliable
and affordable depth sensors like the kinect. In ad-
dition, the flexibility of these sensors allows building
3D acquisition systems that combine multiple units.
Such 3D acquisition systems can provide now accu-
rate and reliable measurements. These systems can
be used even for high level applications like medi-
cal applications that require a complete view of per-
sons in a controlled environment. In a complete 3D
view it is guaranteed to capture more valuable infor-
mation about the studied subjects. For example in a
3D model of a person the side view is less descriptive
than the front view, this information can be helpful
to determine the frontal direction of a person. Also
In classification applications fewer training examples
are required since a complete 3D training model can
capture more variation of the targeted class at once.
The paper is organized as follows. Section 2 presents
our framework for human classification, in this we de-
tail our acquisition system, the new descriptor we pro-
pose and the classification process. Section 3 gives
the experimental results that validates our method.
Comparison with single view processes is performed.
Section 4 draws the conclusions.
2 HUMAN CLASSIFICATION
The proposed method for an oriented human classi-
fication follows the descriptor/classifier approach. It
requires a complete 3D point cloud. A descriptor is
computed from a point cloud to transfer the raw data
into more descriptive information, then a classifica-
tion model is built using the SVM machine learning
algorithm.
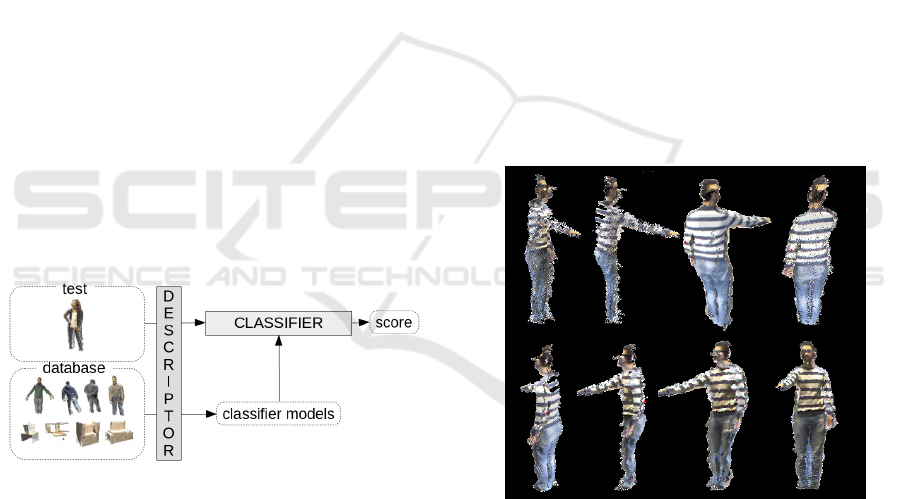
Figure 2: An example of a CPC from different points of
view.
2.1 Acquisition System
The 3D descriptor is computed from a CPC i.e a 360
◦
view (Figure 2). In order to achieve this complete
coverage of the scene a multi-kinect platform is con-
structed. The platform consists of three kinects posi-
tioned so that two consecutive kinects share an over-
lapping field of view. The multi-kinect system is then
calibrated to obtain the extrinsic and the intrinsic pa-
rameters for each kinect.
The intrinsic parameter are required to transfer the 2D
VISAPP 2016 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
354

depth image into a 3D point cloud while the extrin-
sic parameters allows the transformation of the point
clouds from each kinect to a commune coordinate
system. There are many efficient methods to com-
pute these parameters (Deveaux et al., 2013; Raposo
et al., 2013). The kinect calculates the depth image
via structured light imaging technology. For this, the
kinect uses an infra-red light projector to project a pat-
tern on the scene. The kinect captures the projected
pattern via its inferred camera. Then the disparity d is
calculated from this pattern and a pre-registered one
at known distance. The depth is then computed as the
inverse of the disparity using the following equation:
z =
1
c
v
× d +c
u
(1)
where c
u
and c
v
are the image central point coordi-
nates.
The depth camera follows a pin-hole camera model.
From this the 3D world points are projected on image
plane according to the equation:
u
v
1
= K ×
x
z
y
z
1
with K =
f
u
0 c
u
0 f
v
c
v
0 0 1
(2)
where K is the matrix of the intrinsic parameters of the
camera, f
u
and f
v
are the focal length. So we have:
x = z
u − c
u
f
u
and y = z
v − c
v
f
v
(3)
The extrinsic parameters are the rotation R
i,o
and
translation T
i,o
matrices between each kinect frame F
i
and a reference frame F
o
(which is usually overposed
on one of the kinects). Hence, the point cloud pc
i
captured by any kinect is transformed to the reference
frame by means of its rotation and translation matri-
ces. Finally the complete point cloud PC is obtained
as follows:
PC =
[
i∈[1,N]
R
i,o
× pc
i
+ T
i,o
(4)
where N is the number of kinects in the platform.
The applications that will exploit our methods take
place mainly in an indoor environment that contains
large planar surfaces (ground, walls). Thus a modi-
fied RANSAC algorithm (Fischler and Bolles, 1981)
is applied to the acquired CPC to remove these sur-
faces. An euclidian clustering is applied to the rest
of the cloud that geometrically separates it into sub-
clouds. RANSAC is used again to check the valid-
ity of each sub-cloud, if the sub-cloud is composed
mainly of planer surfaces then it is removed. Hence,
the remaining of CPC contains only the set of candi-
dates to be used as input for classifier.
Figure 3: Example of surface normals shown at randomly
chosen points from a CPC.
2.2 Descriptor Construction
The proposed 3D descriptor transposes the HOG into
3D point clouds. In HOG a window is densely subdi-
vided into a uniform grid of blocks. In each block the
gradient orientations over the pixels are computed and
collected in a 1D histogram. In the 3D point cloud the
gradient is meaningless. So it is replaced by the sur-
face normal at each point (Figure 3). The local surface
normal is estimated for each point p using the least-
mean square plane fitting (Holz et al., 2012). The
method works by fitting a plane to the set of neigh-
bouring points of p, and the normal of the plane is
assigned to point p. The point clouds acquired by the
kinect could contain some artifacts and noise. This
does not affect the surface normal estimation process
as the used method can provide good results even with
the presence of noise.
The 3D space is divided into sub-areas (blocks). We
use a cylindrical subdivision similar to the one pro-
posed by Gond (Gond et al., 2008) for his work on
pose recognition from voxel reconstruction. Hence
we respect the axial symmetry of the human class.
The point cloud is included inside a cylinder perpen-
dicular with the ground plane and divided as follows:
• First a radial cut divides the cylinder (Figure 4a).
• Second an azimuth cut divides the cylinder into
sectors (Figure 4b).
• Third an axial cut across the cylinder main axis
subdivides the cylinder into sections (Figure 4c).
The resulting block is a shell sector as represented
in (Figure 4d). Figure 5 shows an illustration of this
process over a point cloud. Each block contains a cer-
tain number of 3D points and then the histogram of
oriented normal is computed.
Since a normal is a 3D vector it can not be associated
to a 1D histogram. To solve this problem we used
the generic 3D orientation quantization proposed by
3D Descriptor for an Oriented-human Classification from Complete Point Cloud
355

Figure 4: Cylindric subdivision into blocks: a radial cut (a),
an azimuth cut (b) and an axial cut (c). The resulting block
(d).
Kl
¨
aser (Klaser et al., 2008).
The normal vector is placed inside a regular polyhe-
dron (Figure 6) and then projected onto the faces of
the polyhedron. Each face of the polyhedron corre-
sponds to a bin of the histogram. The projection of
the normal vector on a face is computed by:
p(
−→
n , f ) =
−→
n .
−→
n
f
, if
−→
n .
−→
n
f
> 0
0 otherwise
(5)
where
−→
n is the normal vector and
−→
n
f
is the vector
from the center of the polyhedron to the center of the
face f (Figure 7).
Then the histogram related to the block b is com-
puted by:
Figure 5: Dividing a candidate into blocks, where each
block is represented by a different color.
H
b
( f ) =
h
b
( f )
∑
f
0
h
b
( f
0
)
(6)
h
b
( f ) =
∑
−→
n ∈C
b
p(
−→
n , f ) (7)
where C
b
is the set of normal vectors on points inside
of block b.
The concatenation of all the histograms provides the
descriptor.
D = H
1
·H
2
·...·H
N
b
(8)
where N
b
is the number of blocks.
Figure 6: The five regular polyhedrons.
Figure 7: Projection of normal vector for 3D orientation
quantization.
2.3 Classification
As mentioned previously, the proposed method works
on a complete 3D point cloud which is acquired in
an indoor environment. To our knowledge, there
is no training database that provides such types of
data. For this purpose we have decided to build an
original database of CPCs. The database comprises
two types of examples: positives (Human) and neg-
atives (random objects that can be found in an in-
door environment) (Figure 8). The positive part of
the database dedicated to human subjects contains
600 point clouds. This part was constructed from
17 different persons with various poses, shapes and
clothing. The negative part of the database contains
the non-human examples, and it consists of approxi-
matively 600 point clouds. It contains elements that
could appear in an indoor scene: furniture, stacks of
cartons, computer equipment, etc. Objects that has
similar dimension to human body shape (for exam-
ple clothes rack where we are put clothes) are formed
to make challenging experimental tests. When con-
structing the database, only one subject is placed in
the middle of the scene. The frontal direction infor-
mation of each human subject is saved while perform-
ing different positions. The information about the di-
rection will be used in the learning step and also in
the testing step as a ground truth.
A Support Vector Machine (SVM) classifier (Chang
and Lin, 2011) was chosen to train a classification
VISAPP 2016 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
356

Figure 8: Examples of CPC of human (left) and non-human subjects (right).
model. The SVM uses for this task the descriptors
calculated from the set of positive and negative ex-
amples. The classification model will also allow the
determination of the frontal orientation of the per-
son. This is achieved with the help of the informa-
tion about the frontal direction vector of each posi-
tive example in the database. When testing a human
candidate we choose an arbitrary direction vector and
then rotate it several times. Hence, each rotation of
the direction vector will result in a different descrip-
tor. These descriptors are tested by the classifica-
tion model and the descriptor with the highest positive
score provides the orientation of the human.
3 EXPERIMENTS
In this section we present the evaluation of our clas-
sification method. The first round of experiments was
conducted to assess the efficiency of our descriptor.
We show the results of testing our method on data set
of positives and negatives CPC examples. In the sec-
ond set of experiments, we performed two types of
comparisons. First, we compare the results of CPC
with those obtained by using single point clouds. Dif-
ferent scenarios are presented. In the second com-
parison stage, we performed a comparison between
the proposed 3D descriptor and the one introduced
in (Munaro et al., 2012). Finally, the last experiments
were conducted experiments in order to validate the
orientation estimation.
3.1 Efficiency
Since there is no similar database in the literature
we created two sets of examples to evaluate the
classification and to optimize the different required
parameters of the method. Each set contains 64
positive and 64 negative examples. The two sets were
acquired using our multi-kinect platform similarly
to the training data. The examples in each set were
then tested by the classification model. The trained
classification model returns a score that corresponds
to the probability that the point cloud is a human.
The first set was more challenging and the results
obtained from this set are presented in the following
sections. The second set provides absolutely perfect
results.
There are several parameters used to compute the
3D descriptor (Table 1). We repeat the classification
test several times with different combinations of de-
scriptor parameters. Figure 9 and Figure10 show the
results obtained from different values for the cylinder
radius and polyhedron parameters respectively.
Table 1 shows the best value for each parameter.
With the best configuration of parameters, we obtain
a precision of 0.97 and a recall of 0.97, which gives a
F
measure
of 0.97. These excellent results validate the
efficiency of our method.
A descriptor is computed in about 30ms with a
non-optimized C++ implementation running on a
3GHz processor. With further optimization the
descriptor can be used in applications that require
real-time performance such as patient surveillance
and gait assessment.
3D Descriptor for an Oriented-human Classification from Complete Point Cloud
357

Figure 9: ROC curves obtained with different values of
cylinder radius.
Figure 10: ROC curves obtained with different types of
polyhedrons.
Table 1: Descriptor parameters.
Parameter Value
Cylinder Height 2 meter
Cylinder Radius 0.5 meter
Polyhedron octahedron
Cylinder Radial Cut 5 circles
Cylinder Azimuth Cut 8 sectors
Cylinder Axial Cut 8 sections
3.2 Complete vs Single Point Cloud
To illustrate the benefits of using a CPC from a multi-
kinect system we repeat the process of classification
in two different scenarios. In the first scenario we
assume that the kinects are working independently
and we compute the descriptors from the Single Point
Cloud (SPC) that come from each kinect separately.
In the second scenario we consider that the kinects are
working together but the output of this multi-kinect
system is a set of SPCs, and of course the number
of these SPCs is equivalent to number of the kinects
in the system. In this scenario we take only the SPC
with the maximum classification result (Max-SPC).
Figure 11 shows the ROC curves for the three exper-
iments. We notice that using a single camera signifi-
cantly decreases the classification performances. This
shows the advantages of using multi-kinect platform
over single sensors approaches. On the other hand,
the CPC curve is above the Max-SPC one which also
confirms that working with a CPC is better that using
separated point clouds independently.
Figure 11: ROC curves obtained from our complete point
cloud (CPC) and with the point cloud of each kinect taken
individually (SPC) or combined (Max-SPC). A single view
decreases significantly the performances and our CPC out-
performs the combination of single point cloud.
3.3 Comparison with HOG
We have compared our method with HOG descriptor
for 3D camera developed in (Munaro et al., 2012).
The methods works by selecting a set of candidates
clusters from the point clouds and then apply HOG
classification method on the corresponding 2D color
image of these clusters. For comparison we used a
dataset of 80 complex scenes. Each scene represents
an indoor location with different objects and only one
person. There are five different persons in this data
set, each of them performing various poses. For each
scene we obtained the CPC and also the separate sin-
gle point clouds from each kinect. We applied our
method on the CPC and the method of (Munaro et al.,
2012) is applied separately on each of the other sin-
gle point clouds. The obtained results are shown on
Table 2. HOG-SC (Single Image) corresponds to the
classification result of (Munaro et al., 2012) from a
single kinect. In HOG-CC (Combined Camera) a
cluster provides a detection if it was detected from
at least one kinect with (Munaro et al., 2012). Once
again, a single point of view provides low perfor-
mances. Our method outperforms the combination of
(Munaro et al., 2012) processed on the three kinects
especially with the recall criterion.
VISAPP 2016 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
358

Table 2: Classification performances of our method com-
pared with HOG applied on a single color image (HOG-
SC) then applied on the color images acquired by the all
cameras (a person is detected if he is detected at least in one
of the color image) (HOG-CC). We notice that our method
provides the best results.
Method Precision Recall F
measure
our method 0.99 0.86 0.92
HOG-SC 0.93 0.22 0.36
HOG-CC 0.91 0.51 0.66
In Figure 12 some examples where HOG process
is failed are shown while our descriptor shows very
good robustness.
Figure 12: Examples of scenes where a simple HOG pro-
cess is failed and our method succeeds. Green lines corre-
spond to true detections and red lines correspond to false
detections.
3.4 Orientation Estimation
In order to evaluate the orientation estimation, we
tested for each positive example several hypothetical
frontal orientations. We choose an arbitrary direction
and rotate it around the subject’s vertical axis. In our
case we performed the rotation 4 times (i.e we in-
crease the rotation angle by 90
◦
), and at each rotation
we computed the descriptor using the corresponding
orientation vector. For each positive example from
the test dataset, we compared the orientation of de-
scriptor with the highest score with the ground-truth
orientation. The orientation was correctly estimated
for a vast majority of examples in the datase (90%),
except for some situations (8%) where the back is es-
timated as the frontal orientation resulting in a 180
◦
error. This is due to the fact that when a person’s arms
are parallel to its torso, the 3D surface of the front and
back views are very similar. The orientation for the
reaming 2% were estimated with 90
◦
error from the
ground truth.
4 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper we proposed a new 3D descriptor for the
human classification which estimates the orientation
of the human. The proposed descriptor uses complete
3D point clouds provided by a multi-kinect system.
To validate it, we built an original database. The clas-
sification performs with an excellent precision. Two
main contributions can be highlighted: first the use of
the surface normal orientation and cylindrical space
division to compute a human descriptor and second
the set-up of a multi-kinect platform to acquire com-
plete point cloud. We have proved that this acquisi-
tion framework improves significantly the detection
performance.
In this paper, we focused on the classification of iso-
lated subjects. Future work includes the complete de-
tection process by a dense scan of the scene. For this
purpose, we will work with scenarios where several
persons are present in the scene. The cylinder will
scan across the scene at all positions and conventional
non-maximum suppression will be run on the output
to detect human instances.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors gratefully acknowledge the support of
R
´
egion de Bourgogne for this work.
REFERENCES
Chang, C. C. and Lin, C. J. (2011). Random sample consen-
sus: A paradigm for model fitting with applications to
image analysis and automated cartography. Transac-
tions on Intelligent Systems and Technology, 27:1–27.
Choi, B., Mericli, C., Biswas, J., and Veloso, M. (2013).
Fast human detection for indoor mobile robots using
depth images. International Conference on Robotics
and Automation, pages 1108–1113.
Choi, B., Pantofaru, C., and Savarese, S. (2011). Detecting
and tracking people using an rgb-d camera via multi-
ple detector fusion. Conference on Computer Vision
Workshops, pages 6–13.
3D Descriptor for an Oriented-human Classification from Complete Point Cloud
359

Dalal, N. and Triggs, B. (2005). Histograms of oriented
gradients for human detection. Computer Vision and
Pattern Recognition, I:886–893.
Deveaux, J. C., Hadj-Abdelkader, H., and Colle, E. (2013).
A multi-sensor calibration toolbox for kinect : Appli-
cation to kinect and laser range finder fusion. Interna-
tional Conference on Advanced Robotics.
Essmaeel, K., Gallo, L., Damiani, E., De Pietro, G., and
Dipanda, A. (2012). Multiple structured light-based
depth sensors for human motion analysis: A review.
Ambient Assisted Living and Home Care, 7657:240–
247.
Fischler, M. A. and Bolles, R. C. (1981). Random sample
consensus: A paradigm for model fitting with appli-
cations to image analysis and automated cartography.
Commun. ACM, 24:381–395.
Gond, L., Sayd, P., Chateau, T., and Dhome, M. (2008). A
3d shape descriptor for human pose recovery. Lecture
Notes in Computer Science, 5098:370–379.
Holz, D., Holzer, S., Rusu, R. B., and Benke, S. (2012).
Real-time plane segmentation using rgb-d cameras.
Lecture Notes in Computer Science, pages 306–317.
Ikemura, S. and Fujiyoshi, H. (2011). Real-time human
detection using relational depth similarity features.
Asian Conference on Computer Vision, pages 25–38.
Klaser, A., Marszalek, M., and Schmid, C. (2008). A spatio-
temporal descriptor based on 3d-gradients. British
Machine Vision Conference, pages 275:1–10.
Munaro, M., Basso, F., and Menegatti, E. (2012). Tracking
people within groups with rgb-d data. International
Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, pages
2101–2107.
Raposo, C., Barreto, J. P., and Nunes, U. (2013). Fast and
accurate calibration of a kinect sensor. International
Conference on 3D Vision, pages 342–349.
Song, S. and Xiao, J. (2014). Sliding shapes for 3d object
detection in depth images. European Conference on
Computer Vision.
Spinello, L. and Arras, K. O. (2011). People detection in
rgb-d data. pages 3838–3843.
Tang, S., Wang, X., Lv, X., Han, T. X., Keller, J., He,
Z., Skubic, M., and Lao, S. (2012). Histogram of
oriented normal vectors for object recognition with a
depth sensor. Asian Conference on Computer Vision,
7725:525–538.
Tian, Q., Zhou, B., Zhao, W., Wei, Y., and Fei, W. (2013).
Human detection using hog features of head and
shoulder based on depth map. Journal of Software,
8:2223–2230.
Xia, L., Chen, C., and Aggarwal, J. K. (2011). Human de-
tection using depth information by kinect. Computer
Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, pages 15–
22.
VISAPP 2016 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
360
