
Continuous Real-time Heart Rate Monitoring from Face Images
Tatsuya Mori, Daisuke Uchida, Masato Sakata, Takuro Oya, Yasuyuki Nakata, Kazuho Maeda,
Yoshinori Yaginuma and Akihiro Inomata
Fujitsu Laboratories Ltd., Kanagawa, Japan
Keywords: Heart Rate, Pulse Wave, Face Image, Real-time Remote Monitoring.
Abstract: A real-time monitoring method of heart rate (HR) from face images using Real-time Pulse Extraction
Method (RPEM) is described and corroborated for the theoretical efficacy by investigating fundamental
mechanisms through three kinds of experiments; (i) measurement of light reflection from face covered by
copper film, (ii) spectroscopy measurement and (iii) simultaneous measurement of face images and laser
speckle images. The investigation indicated the main causes of brightness change are both the green light
absorption variation by the blood volume changes and the face surface reflection variation by pulsatory face
movements. RPEM removes the motion noise from the green light absorption variation and the
effectiveness is ensured by comparing with the pulse wave of the ear photoplethysmography. We also
applied RPEM to continuous real-time HR monitoring of seven participants during office work under non-
controlled condition, and achieved HR measured rate of 44 % to the number of referential ECG beats while
face is detected, with RMSE = 6.7 bpm as an average result of five days.
1 INTRODUCTION
Recently there has been a growing attention on ICT-
enabled personal health services which utilize
information on personal health record (PHR) via
ubiquitous devices, wireless network and cloud. By
continuously monitoring vital signs and activities
related to person’s health condition, personalized
services such as health promotion and disease
prevention are expected to be provided. Therefore,
the continuous data acquisition in daily life has
become an active area of research (Pantelopoulos
and Bourbakis, 2010; Inomata and Yaginuma, 2014;
Uchida et al., 2015). Especially, heart rate (HR) has
been utilized widely as a vital sign to keep one’s
health in good shape by monitoring load of exercise
or work. Long-term and detailed HR monitoring is
also expected to be useful for prognostic observation
in relation to diseases (Dyer et al., 1980; Jensen et
al., 2013). However, a typical way using contact
sensor device onto subject’s skin is not suitable for
HR monitoring in daily life because it makes them
uncomfortable and inconvenient. For that reason, a
non-contact measurement method is preferred.
Recently, methods using face images were reported
(Takano and Ohta, 2007; Poh et al., 2010; Poh et al.,
2011; Kwon et al., 2012; Balakrishnan et al., 2013;
Li et al., 2014). Balakrishnan et al., directly detected
small head moving amount caused by the blood
circulation for measuring HR. Others detected face
colour or brightness changes which is also related to
blood circulation. In these reports, high accuracy
results were obtained under well-controlled
conditions. However these methods do not satisfy
continuous HR monitoring in daily life. People
frequently have various large and small movements,
and it makes the extraction of pulse waves from
brightness change difficult. Therefore methods
which need to accumulate data, such as independent
component analysis (ICA) are not suitable because
accumulation of data is often interrupted by large
motion in daily life, and the method with shorter
measurement time is required. In 2013, we
demonstrated continuous HR monitoring in daily life
by the Real-time Pulse Extraction Method (RPEM)
(Sakata et al., 2013). In this paper, we describe
RPEM and we corroborate the theoretical efficacy of
RPEM by the investigation of brightness change on
face images with three fundamental experiments.
Continuous real-time HR monitoring with RPEM in
office is also performed as an example of
applications.
52
Mori, T., Uchida, D., Sakata, M., Oya, T., Nakata, Y., Maeda, K., Yaginuma, Y. and Inomata, A.
Continuous Real-time Heart Rate Monitoring from Face Images.
DOI: 10.5220/0005682400520056
In Proceedings of the 9th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies (BIOSTEC 2016) - Volume 4: BIOSIGNALS, pages 52-56
ISBN: 978-989-758-170-0
Copyright
c
2016 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

2 REALTIME METHOD
In this section, the framework to measure HR from
face images in real time is explained. It has 5 steps.
(1) Face images are captured by a RGB camera
(webcam) and (2) face detection is performed in
each frame. (3) Averaged red, green and blue signals
are calculated from region of interest of face images,
respectively. (4) Filtering process is performed in
order to extract pulse waves due to the blood
circulation. (5) Calculation of HR is performed.
In this 4th step of the framework, we focus on
the green signal, which is assumed to include pulse
components, and remove the noise caused by face
movements to obtain the pulse signal. Our method
assumes that small head movement affects reflection
light from face only in the brightness and not in the
colour. Therefore, the intensity ratio between green
and red/blue signals stays constant in all frequency
range except at the frequency of pulse. We defined
the intensity ratio as , and red and green signals in
pulse frequency as
and
, respectively.
We calculate the ratio in the lower frequency
range than the pulse frequency, then we estimate the
noise included in green signal
by the
multiplication of the ratio and the red signal
.
We obtain the pulse signal
by subtracting the
estimated noise
from the green signal
as shown in (1).
(1)
With the described method, the noise derived from
the large movement cannot be removed. Thus we
also use the confidence indicator with the
autocorrelation and remove the HR with small
indicator value. The calculation of HR is performed
by averaging signals for consecutive 4, 8 or 15 beats
with confidence indicators larger than a threshold.
With this method, the HR can be measured in
several seconds, which is much shorter time than
that of conventional HR extraction method such as
Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT) method.
3 FUNDAMENTAL MECHANISM
In our method in the section 2, we assumed that
green signal has stronger pulsatory component than
other colours (hypothesis 1). Also, we assumed that
the ratio between green and red signals stays
constant in all frequency range except at the pulse
frequency (hypothesis 2). In this section, we
experimentally validate these hypothesises by
clarifying the contribution of surface reflection and
light absorption caused by blood circulation to
brightness change of the face images.
Firstly, the effect of the surface reflection from
the face was investigated. The face images (video)
were captured and two regions at right and left
cheeks were compared. The right cheek was covered
with a thin copper film (Figure 1). The frequency
characteristics of the red, green and blue signals
obtained by fast Fourier transform (FFT) from the
copper surface and skin surface are shown in Figure
2 (a) and (b), respectively. In Figure 2, there are
peaks around 75 cycles per minute (cpm) in both of
(a) and (b). Note that this peak value is the same as
the finger pulse rate of 75 bpm simultaneously
measured by photoplethysmography (PPG).
Figure 1: The region of interests (ROIs). ROI 1 is at a
copper film attached on the surface of right cheek.
Figure 2: RGB spectra of face images at (a) ROI 1 and at
(b) ROI 2. Frequencies are shown as cycles per minute
(cpm).
Since complete light reflection from the copper
surface and no reflection from face skin surface are
0.2
0.1
0.0
FFT Amplitude (a.u.)
200150100500
Frequency (cpm)
Red
Green
Blue
(a)
0.2
0.1
0.0
FFT Amplitude (a.u.)
200150100500
Frequency (cpm)
Red
Green
Blue
(b)
Continuous Real-time Heart Rate Monitoring from Face Images
53

expected in Figure 2 (a), this peak indicates the
contribution of pulsatory movement of the head at
75 cpm caused by the blood circulation. These
reflection peaks and profiles in all frequency range
are very similar for all RGB signals in (a). On the
other hand, the green signal at the peak frequency is
stronger than red and blue signals in Figure 2 (b).
In order to clarify the colour dependency of the
signal from skin surface, a spectroscopy experiment
was performed. To create similar circumstance with
the RGB camera measurement, the distance between
a spectroscope and subject’s face is about 50 cm and
the face was exposed by the intense light using an
incandescent lamp. The raw spectra were divided by
the incandescent light spectrum. Characteristic peaks
were observed around 540 nm and 570 nm. These
peaks are consistent with the peaks of oxy-
haemoglobin absorption at around 540 nm and 570
nm (Steknke and Shephered, 1992). Since the
wavelength of the green light is around 500 nm –
570 nm, the strong peak for green signal in Figure 2
(b) is contributed by the absorption by the oxy-
haemoglobin under the face skin. Therefore, it is
assumed that the absorption variation by pulsatory
blood volume change is causing the strong peak for
green signal in Figure 2 (b).
We also carried out a simultaneous measurement
of face images by RGB camera and blood flow
images by laser speckle imager (Forrester et al.,
2004). Laser speckle imager detects the mobility of
red blood cells in a measurement area, and the
phases of blood flow wave and time differential
green signal wave are expected to match.
Figure 3: A comparison of the differential green wave
with the blood flow wave obtained by a laser speckle
imager.
Figure 3 shows a time differential green wave
and blood flow wave obtained simultaneously by
averaging signals at the centre area of the face. The
phase of differential green wave is in agreement
with that of the blood flow wave.
From these experiments and results, the causes of
the brightness change on face are combined effects
of the oxy-haemoglobin absorption variation by
pulsatory blood volume change and the surface
reflection variation caused by pulsatory movements.
These results validates the hypothesises of our
method by the facts that the absorption rate in green
is higher than red or blue by the spectroscopy
experiment (hypothesis 1), and the influence of
movements have no dependence on colour channel
in any frequency as shown in Figure 2 (a)
(hypothesis 2). Therefore RPEM extracts pulse
waves due to the blood volume changes from green
light by cancelling the effect of head movements.
4 WAVES UNDER MOTION
Figure 4 shows a comparison of waveforms when
the face is moving. In Figure 4 (a), raw red, green
and blue (RGB) signals averaged in the region of
interest (ROI) are shown. The ROI is determined by
choosing a centre part of face detected area. Motions
almost equally affect all RGB signals.
Figure 4: A comparison of waveforms when the face is
moving: (a) raw RGB signals from face images, and (b)
RPEM, filtered green, PPG wave.
In Figure 4 (b), an extracted pulse wave by
RPEM, filtered green wave and ear PPG wave are
shown. The filtered green wave is extracted by a
conventional method of infinite impulse response
(IIR) filter applied on green signal at frequencies
between 50 and 150 bpm. The filtered green wave is
13.5
13.0
12.5
12.0
11.5
Blood Flow Amplitude (a.u.)
1086420
Time (s)
80
60
40
20
0
-20
-40
Differential Green Amplitude (a.u.)
Blood flow wave
Differential green wave
180
170
160
150
140
130
120
Average Image
Brightness (a.u.)
Red
Green
Blue
(a)
-0.6
-0.4
-0.2
0.0
0.2
0.4
0.6
Pulse Wave Amplitude (a.u.)
4442403836
Time (s)
460
440
420
400
380
360
Photoelectric Pulse
Wave Amplitude (a.u.)
RPEM
Filtered green
Photoplethysmography
(b)
BIOSIGNALS 2016 - 9th International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
54
largely affected by the motions and the waveform is
distorted. On the other hand, the extracted pulse
waveform by RPEM is similar to the ear PPG wave
without major distortion.
From these results, the effectiveness of RPEM
for HR measurement is corroborated especially
when the filtered green waveform is affected by
motions
.
5 CONTINUOUS MONITORING
We applied RPEM to continuous monitoring of HR
during daily office work under non-controlled
conditions. In the experiment, seven participants (A,
B, C, D, E, F and G) aged from 24 to 55 years old
were monitored. Commercially available web
cameras were attached on top of the computer
display on their desk to capture their face during
desk work. Also, an electrocardiograph (ECG)
device was on their chest as a reference. All of them
were requested to do their work as usual for five
days. Face image data for approximately 133 hours
was obtained in total for seven participants.
Figure 5 shows the HR trend calculated from the
results of RPEM for the participant D. The trend of
HR in one day is in good agreement with the HR
from ECG. The data missing period around noon is
because the participant left his desk for lunch, and
the large change after the lunch break is due to the
effects of running during the break.
Figure 5: HR trend during office work compared with HR
calculated from ECG (reference).
During the continuous measurements, the face
detection is frequently chopped because people
frequently move their face to execute their tasks,
such as phone calls, conversation with colleagues, or
leaving for lunch or breaks. In one case as an
example, only 33 % of the sum of the face detection
time is for the continuous detections with more than
30 seconds, and about 90 % is for the detections
with more than 4 seconds. Therefore the shorter
measurement time is required to increase the
chances to measure HR.
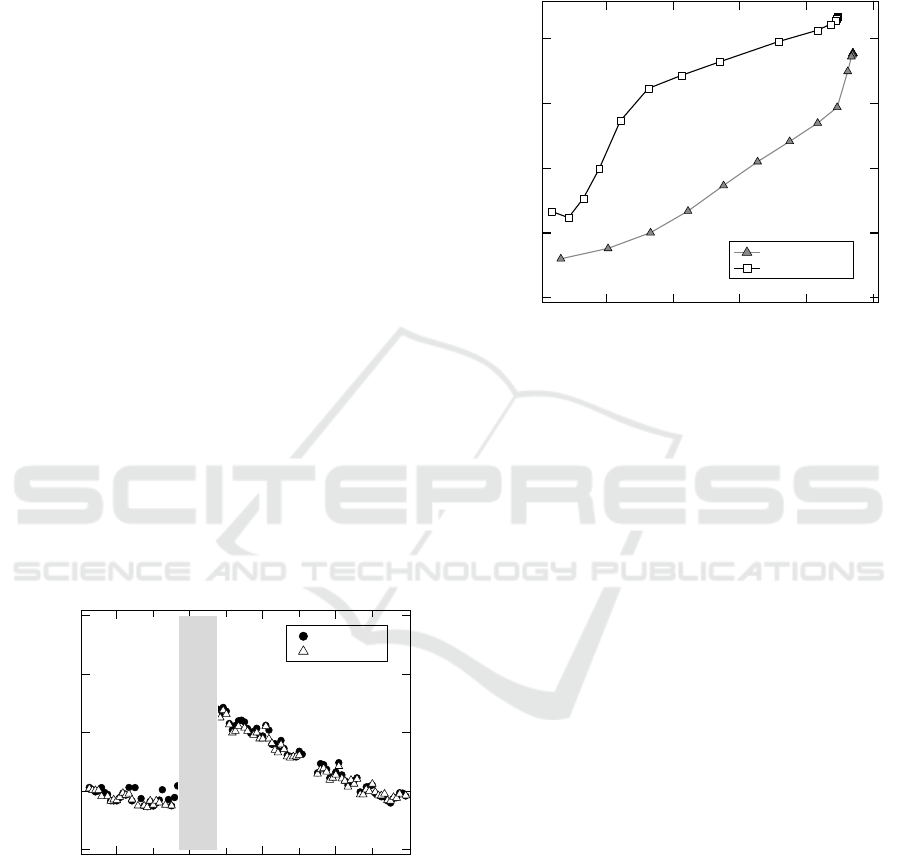
Figure 6: The trade-off relationship between the HR
measured rate and RMSE for RPEM and filtered green.
The result of HR measured rate and root mean
squared error (RMSE) is shown in Figure 6. The
result is an average for seven participants and the
signal averaging is for 4 beats. The HR measured
rate is defined as a ratio of the number of beats
measured from face images to the number of
referential ECG beats while face is detected. The
rate can be controlled by changing the threshold of
the confidence indicator with autocorrelation.
Smaller RMSE are found at lower HR measured
rate, and there is a trade-off relationship. Our
method achieves both higher measured rate of HR
and higher accuracy than filtered green method. HR
measured rate = 44 % at the confidence indicator =
0.6 with RMSE = 6.7 bpm are obtained as the mean
result of seven participants for five days.
The results of each participant are shown in
Table 1. The RPEM result shows 1.5 - 6.7 times
higher HR measured rate with almost equal or
higher accuracy than filtered green in 4 averaging
beats. By increasing the averaging beats from 4 to 8
or 15, the RMSE improves although HR measured
rate decreases.
6 CONCLUSIONS
We propose a real-time pulse extraction method for
continuous heart rate monitoring from face images.
120
100
80
60
40
Heart Rate (bpm)
10:00 12:00 14:00 16:00
Time (HH:MM)
Reference
RPEM
20
15
10
5
0
Root Mean Squared Error (bpm)
10080604020
HR Measured Rate (%)
RPEM
Filtered green
Continuous Real-time Heart Rate Monitoring from Face Images
55

Table 1: HR Measured rate and RMSE for seven participants. RPEM is compared with filtered green for different averaging
beats.
Paticipants
HR measured rate (%) RMSE
Filtered Green RPEM Filtered Green RPEM
4 beats 4 beats 8 beats 15 beats 4 beats 4 beats 8 beats 15 beats
A 6 40 24 15 11.1 7.2 3.5 2.1
B 19 50 30 16 6.4 4.9 1.9 0.8
C 13 49 30 17 7.9 5.9 2.3 1.7
D 15 45 24 13 18.8 6.7 2.9 1.5
E 9 33 15 7 12.1 9.0 3.3 1.8
F 38 58 40 26 5.1 5.4 3.3 2.8
G 20 37 16 7 7.3 7.6 2.4 0.7
The investigation of fundamental mechanisms
experimentally revealed that the main cause of the
brightness change of the face image is both the light
absorption variation due to the blood volume
changes and the face surface reflection generated by
pulsatory movements.
Our method enables to extract the differences
between red and green absorption derived from oxy-
haemoglobin absorption characteristics by
cancelling the effect of head movement. The
comparison of RPEM with ear PPG under motion
ensured the effectiveness of RPEM. We also applied
RPEM to HR monitoring in office under non-
controlled condition. The HR trend obtained by
RPEM is in agreement with the reference ECG
result. Our method achieves HR measured rate =
44 % with RMSE = 6.7 bpm even in 4 averaging
beats measurement. These results indicate that
RPEM enables HR monitoring in daily life with high
accuracy without losing much data even under non-
controlled conditions.
REFERENCES
Pantelopoulos, A., Bourbakis, N. G., 2010, “A Survey on
Wearable Sensor-Based Systems for Health
Monitoring and Prognosis”, IEEE Trans. Syst., Man,
Cybern.-Part C: Applications and Reviews, 40 (1), pp.
1-12.
Inomata, A., Yaginuma, Y., 2014, “Hassle-free Sensing
Technologies for Monitoring Daily Health Changes”,
Fujitsu Sci. Tech. J., 50 (1), pp. 78-83.
Uchida, D., Nakata, Y., Inomata, A., Shiotsu, S.,
Yaginuma, Y., 2015, “Hassle-free Sensing
Technologies for Human Health Monitoring”,
Proceedings of the IEICE general conference / the
Institute of Electronics, Information and
Communication Engineers, S-16.
Dyer, A. R., Persky, V., Stamler, J., Paul, O., Shekelle, R.
B., Berkson, D. M., Lepper, M., Schoenberger, J. A.,
Lindberg H. A., 1980, “Heart rate as a prognostic
factor for coronary heart disease and mortality:
findings in three Chicago epidemiologic studies”, Am.
J. Epidemio., 112, pp. 736-49.
Jensen, M. T., Suadicani, P., Hein, H. O., Gyntelberg, F.,
2013, “Elevated resting heart rate, physical fitness and
all-cause mortality: a 16-year follow-up in the
Copenhagen Male Study”, Heart, 99 (12), pp. 882-
887.
Takano, C., Ohta, Y., 2007, “Heart rate measurement
based on a time-lapse image”. Medical Engineering
and Physics, 29, pp. 853-857.
Poh, MZ., McDuff, D. J., Picard, R. W., 2010, “Non-
contact, automated cardiac pulse measurements using
video imaging and blind source separation.”, OPTICS
EXPRESS, 18 (10), pp. 10762-10774.
Poh, MZ., McDuff, D. J., Picard, R. W., 2011,
“Advancements in Noncontact, Multiparameter
Physiological Measurements Using a Webcam”, IEEE
Trans. Biomed. Engineering, 58 (1), pp. 7-11.
Kwon, S., Kim, H., Park, S., 2012, “Validation of heart
rate extraction using video imaging on a built-in
camera system of a smartphone”, Proceedings of the
Ann. Intl Conf. of the IEEE Eng. in Medicine and
Biology Soc. (EMBC), pp. 2174-2177.
Balakrishnan, G., Durand, F., Guttag, J., 2013, “Detecting
Pulse from Head Motions in Video”, Proceedings of
the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern
Recognition (CVPR), pp. 3430-3437.
Li, X., Chen, J., Zhao, G., Pietikainen, M., 2014, “Remote
Heart Rate Measurement From Face Videos Under
Realistic Situations”, Proceedings of the IEEE
Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern
Recognition (CVPR), pp. 4321-4328.
Sakata, M., Uchida, D., Inomata, A., Yaginuma, Y., 2013,
“Continuous Non-contact Heart Rate Measurement
Using Face Imaging”, Proceedings of the IEICE
general conference / the Institute of Electronics,
Information and Communication Engineers, 1 (73).
Steknke, J. M., Shephered, A. P., 1992, “Effects of
Temperature on Optical Absorbance Spectra of Oxy-,
Carboxy-, and Deoxyhemoglobin”, Clin. Chem., 38
(7), pp. 1360-1364.
Forrester, K. R., Tulip, J., Leonard, C., Stewart, C., Bray,
R. C., 2004, “A Laser Speckle Imaging Technique for
Measuring Tissue Perfusion”, IEEE Trans. Biomed.
Engineering
, 51 (11), pp. 2074-2084.
BIOSIGNALS 2016 - 9th International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
56
