
Sparse Physics-based Gaussian Process for Multi-output Regression
using Variational Inference
Ankit Chiplunkar
1,3
, Emmanuel Rachelson
2
, Michele Colombo
1
and Joseph Morlier
3
1
Airbus Operations S.A.S., 316 route de Bayonne 31060, Toulouse Cedex 09, France
2
Universit
´
e de Toulouse, ISAE, DISC, 10 Avenue Edouard Belin, 31055 Toulouse Cedex 4, France
3
Universit
´
e de Toulouse, CNRS, ISAE-SUPAERO, Institut Cl
´
ement Ader (ICA), 31077 Toulouse Cedex 4, France
Keywords:
Gaussian Process, Kernel Methods, Variational Inference, Multi-output Regression, Flight-test data.
Abstract:
In this paper a sparse approximation of inference for multi-output Gaussian Process models based on a Vari-
ational Inference approach is presented. In Gaussian Processes a multi-output kernel is a covariance function
over correlated outputs. Using a general framework for constructing auto- and cross-covariance functions that
are consistent with the physical laws, physical relationships among several outputs can be imposed. One major
issue with Gaussian Processes is efficient inference, when scaling up-to large datasets. The issue of scaling
becomes even more important when dealing with multiple outputs, since the cost of inference increases rapidly
with the number of outputs. In this paper we combine the use of variational inference for efficient inference
with multi-output kernels enforcing relationships between outputs. Results of the proposed methodology for
synthetic data and real world applications are presented. The main contribution of this paper is the applica-
tion and validation of our methodology on a dataset of real aircraft flight tests, while imposing knowledge of
aircraft physics into the model.
1 INTRODUCTION
In this work we consider the problem of modelling
multiple output Gaussian Process (GP) regression
(Rasmussen and Williams, 2005) correlated through
physical laws of the system, while in presence of
large number of inputs. In the literature inference
on multiple output data is also known as co-kriging
(Stein, 1999) or multi-kriging (Boyle and Frean,
2005). Modelling multi-output kernels is particularly
difficult because we need to construct auto- and cross-
covariance functions between different outputs. We
turn to a general framework (Constantinescu and An-
itescu, 2013) to calculate these covariance functions
while imposing prior information of the physical pro-
cesses. While a joint model developed using corre-
lated covariance functions gives better predictions, it
incurs a huge cost on memory occupied and computa-
tional time. The main contribution of this paper is to
apply variational inference on these models of large
datasets (of the order O(10
5
))and reduce the heavy
computational costs incurred.
Let us start by defining a P dimensional input
space and a D dimensional output space. Such that
{(x
j
i
, y
j
i
)} for j ∈ [1;n
i
] are the training datasets for
the i
th
output. Here n
i
is the number of measure-
ment points for the i
th
output, while x
j
i
∈ R
P
and
y
j
i
∈ R. We next define x
i
= {x
1
i
;x
2
i
;. . . ;x
n
i
i
} and y
i
=
{y
1
i
;y
2
i
;. . . ;y
n
i
i
} as the full matrices containing all the
training points for the i
th
output such that x
i
∈ R
n
i
×P
and y
i
∈ R
n
i
. Henceforth we define the joint output
vector Y = [y
1
;y
2
;y
3
;. . . ;y
D
] such that all the output
values are stacked one after the other. Similarly, we
define the joint input matrix as X = [x
1
, x
2
, x
3
, . . . , x
D
].
If Σn
i
= N for i ∈ [1, D]. Hence N represents the to-
tal number of training points for all the outputs com-
bined. Then Y ∈ R
N
and X ∈ R
N×P
.
For simplicity take the case of an explicit relation-
ship between two outputs y
1
and y
2
. Suppose we mea-
sure two outputs with some error, while the true phys-
ical process is defined by latent variables f
1
and f
2
.
Then the relation between the output function, mea-
surement error and true physical process can be writ-
ten as follows.
y
1
= f
1
+ ε
n1
y
2
= f
2
+ ε
n2
(1)
Where, ε
n1
and ε
n2
are measurement error sam-
pled from a white noise gaussian N (0, σ
n1
) and
Chiplunkar, A., Rachelson, E., Colombo, M. and Morlier, J.
Sparse Physics-based Gaussian Process for Multi-output Regression using Variational Inference.
DOI: 10.5220/0005700504370445
In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods (ICPRAM 2016), pages 437-445
ISBN: 978-989-758-173-1
Copyright
c
2016 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
437

N (0, σ
n2
). While the physics based relation can be
expressed as,
f
1
= g ( f
2
, x
1
) (2)
Here g is an operator defining the relation between
f
1
and an independent latent output f
2
. A GP prior in
such a setting with 2 output variables is:
y
1
y
2
∼ GP
m
1
m
2
,
K
11
+ σ
2
n1
K
12
K
21
K
22
+ σ
2
n2
(3)
K
12
and K
21
are cross-covariances between the two
inputs x
1
and x
2
. K
22
is the covariance function of
independent output, σ
2
n1
and σ
2
n2
are the variance of
measurement error, while K
11
is the auto-covariance
of the dependent output variable. m
1
and m
2
are the
mean of the prior for outputs 1 and 2. The full covari-
ance matrix is also called the joint kernel, henceforth
we will denote the joint-kernel as K
XX
.
K
XX
=
K
11
K
12
K
21
K
22
(4)
while the joint error matrix will be denoted by Σ;
Σ =
σ
2
n1
0
0 σ
2
n2
(5)
Full joint-kernel of a multi-output GP has huge
memory and computational costs. For a multi-output
GP as defined earlier the covariance matrix is of
size N, needing O
N
3
calculations for inference
and O
N
2
for storage. (Snelson and Ghahramani,
2006) introduced “Fully independent training condi-
tional” (FITC) and (Quionero-candela et al., 2005) in-
troduced and “Partially Independent Training Condi-
tional” (PITC) approximations on inference of a GP
using inducing inputs. Later (Alvarez and Lawrence,
2009) extended the application of FITC and PITC to
approximate the inference of multi-output GP’s con-
structed through convolution processes. One prob-
lem with FITC and PITC approximation is their ten-
dency to over-fit. In this work we extend the use
of a variational approach (Titsias, 2009) to approxi-
mate the inference in a joint-kernel for both linear and
non-linear relationships. We observe that the current
approximation reduces the computational complexity
to O
N(MD)
2
and storage to O (NMD), where M
denotes the number of inducing points in the input
space.
In Section 2, we start with an introduction to
multi-output GP and later derive the multi-output GP
regression in presence of correlated covariances. In
Section 3 we discuss various methods of approximat-
ing inference of a GP and later derive application of
variational inference on the problem of multi-output
kernels. Finally, in Section 4 we demonstrate the ap-
proach on both theoretical and flight-test data.
2 MULTI-OUTPUT GAUSSIAN
PROCESS
Choosing covariance kernels for GP regression with
multiple outputs can be roughly classified in three cat-
egories. In the first case, the outputs are known to be
mutually independent, and thus the system can be de-
coupled and solved separately as two or more unre-
lated problems. In the second case, we assume that
the processes are correlated, but we have no infor-
mation about the correlation function. In this case, a
model can be proposed, or nonparametric inferences
can be carried out. In the third situation, we assume
that the outputs have a known relationship among
them, such as equation 2. The last point forms the
scope of this section.
2.1 Related Work
Earlier work developing such joint covariance func-
tions (Bonilla et al., 2008) have focused on build-
ing different outputs as a combination of a set of la-
tent functions. GP priors are placed independently
over all the latent functions thereby inducing a cor-
related covariance function. More recently (Alvarez
et al., 2009) have shown how convolution processes
(Boyle and Frean, 2005) can be used to develop
joint-covariance functions for differential equations.
In a convolution process framework output functions
are generated by convolving several latent functions
with a smoothing kernel function. In the current
paper we assume one output function to be inde-
pendent and evaluate the remaining auto- and cross-
covariance functions exactly if the physical relation
between them is linear (Solak et al., 2003) or use
approximate joint-covariance for non-linear physics-
based relationships between the outputs (Constanti-
nescu and Anitescu, 2013).
2.2 Multi-output Joint-covariance
Kernels
If the two outputs y
1
and y
2
satisfy a physical relation-
ship given by equation 2 with g (.) ∈ C
2
, and known
covariance matrix K
22
. Then the joint-covariance ma-
trix for a linear operator g(.) can be derived analyti-
cally as (Stein, 1999):
K
XX
=
g(g(K
22
, x
2
), x
1
) g(K
22
, x
1
)
g(K
22
, x
2
) K
22
(6)
Since a non-linear operation on a GP does not re-
sult in a GP, for the case of non-linear g (.) the above
joint-covariance matrix as derived in equation 6 is not
ICPRAM 2016 - International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods
438

positive semi-definite. Therefore we will use an ap-
proximate joint-covariance as developed by (Constan-
tinescu and Anitescu, 2013) for imposing non-linear
relations:
K
XX
=
LK
22
L
T
LK
22
K
22
L
T
K
22
+ O
δy
3
2
(7)
Where L =
∂g
∂y
y
2
= ¯y
2
is the Jacobian matrix of g (.)
evaluated at the mean of independent output y
2
. δy
2
is
the amplitude of small variations of y
2
, introduced by
the Taylor series expansion of g(K
XX
) with respect to
y
2
.
The above kernel takes a parametric form that de-
pends on the mean value process of the independent
variable. Equation 7 is basically a Taylor series ex-
pansion for approximating related kernels. Since a
Taylor series expansion is constructed from deriva-
tives of a function which are linear operations the re-
sulting approximated joint kernel is a gaussian kernel
with the non-gaussian part as the error. Higher-order
closures can be derived with higher order derivatives
of the relation g(.). For simplicity we will restrict
ourselves to first order approximation of the auto- and
cross-covariance functions leading to an error of the
order O
δy
3
2
. (Constantinescu and Anitescu, 2013)
provide a more detailed derivation of equation 7.
2.3 GP Regression using
Joint-covariance
We start with defining a zero-mean prior for our ob-
servations and make predictions for y
1
(x
∗
) = y
∗1
and
y
2
(x
∗
) = y
∗2
. The corresponding prior according to
equation 3 and 4 will be:
Y (X))
Y (X
∗
))
= GP
0
0
,
K
XX
+ Σ K
XX
∗
K
X
∗
X
K
X
∗
X
∗
+ Σ
(8)
The predictive distribution is then given as a nor-
mal distribution with expectation and covariance ma-
trix given by (Rasmussen and Williams, 2005)
Y
∗
| X , X
∗
, Y = K
X
∗
X
(K
XX
)
−1
Y (9)
Cov (Y
∗
| X, X
∗
, Y ) = K
X
∗
X
∗
− K
X
∗
X
(K
XX
)
−1
K
XX
∗
(10)
Here, the elements K
XX
, K
X
∗
X
and K
X
∗
X
∗
are block
covariances derived from equations 6 or 7.
The joint-covariance matrix depends on several
hyperparameters θ. They define a basic shape of the
GP prior. To end up with good predictions it is impor-
tant to start with a good GP prior. We minimize the
negative log-marginal likelihood to find a set of good
hyperparameters. This leads to an optimization prob-
lem where the objective function is given by equation
11
log(P(y | X, θ)) = log[GP(Y |0, K
XX
+ Σ)] (11)
With its gradient given by equation 12
∂
∂θ
log(P(y | X, θ)) =
1
2
Y
T
K
−1
XX
∂K
XX
∂θ
K
−1
XX
Y
−
1
2
tr(K
−1
XX
∂K
XX
∂θ
) (12)
Here the hyperparameters of the prior are θ =
l
2
, σ
2
2
, σ
2
n1
, σ
2
n2
. These correspond to the hyperpa-
rameters of the independent covariance function K
22
and errors in the measurements σ
2
n1
and σ
2
n2
. Calculat-
ing the negative log-marginal likelihood involves in-
verting the matrix K
XX
+ Σ. The size of the K
XX
+ Σ
matrix depends on total number of input points N,
hence inverting the matrix becomes intractable for
large number of input points.
In the next section we describe how to solve the
problem of inverting huge K
XX
+ Σ matrices using
sparse GP regression. We also elaborate on how varia-
tional approximation overcomes the problem of over-
fitting by providing a distance measure between two
approximate models.
3 SPARSE GP REGRESSION
The above GP approach is intractable for large
datasets. For a multi-output GP as defined in sec-
tion 2.2 the covariance matrix is of size N, where
O
N
3
time is needed for inference and O
N
2
mem-
ory for storage. Thus, we need to consider approx-
imate methods in order to deal with large datasets.
Sparse methods use a small set of m function points
as support or inducing variables.
Suppose we use m inducing variables to construct
our sparse GP. The inducing variables are the latent
function values evaluated at inputs x
M
. Learning x
M
and the hyperparameters θ is the problem we need
to solve in order to obtain a sparse GP method. An
approximation to the true log marginal likelihood in
equation 11 can allow us to infer these quantities.
3.1 Related Work
Before explaining variational inference method, we
review FITC method proposed by (Snelson and
Ghahramani, 2006). The approximate log-marginal
likelihoods have the form
F = log[GP(y|0, Q
nn
+ Σ)] (13)
Sparse Physics-based Gaussian Process for Multi-output Regression using Variational Inference
439

where Q
nn
is an approximation to the true covariance
K
nn
. In FITC approach, the Q
nn
takes the form,
Q
nn
= diag[K
nn
− K
nm
K
−1
mm
K
mn
] + K
nm
K
−1
mm
K
mn
(14)
Here, K
mm
is a m × m covariance matrix on inducing
points x
m
, K
nm
is a n × m cross-covariance matrix be-
tween the training and inducing points.
Hence the position of x
M
now defines the approx-
imated marginal likelihood. The maximization of the
marginal likelihood in equation 13 with respect to
(x
M
; θ), is prone to over-fitting especially when the
number of variables in x
M
is large. Fitting a modi-
fied sparse GP model implies that the full GP model
is not approximated in a systematic way since there is
no distance measure between the two models that is
minimized.
3.2 Variational Approximation
During variational approximation, we seek to apply
an approximate variational inference procedure where
we introduce a variational distribution q(x) to approx-
imate the true posterior distribution p(x|y). We take
the variational distribution to have a factorized Gaus-
sian form as given in equation 15
q(x) = N (x|µ, A) (15)
Here, µ and A are parameters of the variational distri-
bution. Using this variational distribution we can ex-
press a Jensens lower bound on the logP(y) that takes
the form:
F(q) =
Z
q(x)log
p(y|x)p(x)
q(x)
dx
=
Z
q(x)logp(y|x)dx −
Z
q(x)log
q(x)
p(x)
dx
=
¯
F
q
− KL(q||p) (16)
Where the second term is the negative Kullback
Leibler divergence between the variational posterior
distribution q(x) and the prior distribution p(x). To
determine the variational quantities (x
M
, θ), we mini-
mize the KL divergence KL(q||p). This minimization
is equivalently expressed as the maximization of the
variational lower bound of the true log marginal like-
lihood
F
V
= log(N [y|0, σ
2
I + Q
nn
]) −
1
2σ
2
Tr(
˜
K) (17)
where Q
nn
= K
nm
K
−1
mm
K
mn
and
˜
K = K
nn
−
K
nm
K
−1
mm
K
mn
. The novelty of the above objec-
tive function is that it contains a regularization
trace term: −
1
2σ
2
Tr(
˜
K). Thus, F
V
attempts to
maximize the log likelihood Q
nn
and simultaneously
minimize the trace Tr(
˜
K). Tr(
˜
K) represents the
total variance of the conditional prior. When Tr(
˜
K)
= 0, K
nn
= K
mp
K
−1
mm
K
mn
, which means that the
inducing variables can exactly reproduce the full GP
prediction.
3.3 Variational Approximation on
Multi-output GP
(
´
Alvarez et al., 2010) derived a variational approxi-
mation to inference of multi-output regression using
convolution processes. They introduce the concept of
variational inducing kernels that allows them to effi-
ciently sparsify multi-output GP models having white
noise latent functions. White noise latent functions
are needed while modelling partial differential equa-
tions. These variational inducing kernels are later
used to parametrize the variational posterior q(X).
For our expression of the joint kernel, the auto-
and cross-covariance functions are dependent on the
independent covariance function K
22
. Hence the in-
dependent output function in our case behaves like a
latent function for the case of (
´
Alvarez et al., 2010).
Moreover, the latent function or independent output
is a physical process and hence will almost never be
white noise. Henceforth we will place the inducing
points on the input space. We now extend the varia-
tional inference method to deal with multiple outputs.
We try to approximate the joint-posterior distribu-
tion p(X|Y ) by introducing a variational distribution
q(X). In the case of varying number of inputs for
different outputs, we place the inducing points over
the input space and extend the derivation of (Titsias,
2009) to multi-output case.
q(X) = N (X|µ, A) (18)
Here µ and A are parameters of the variational dis-
tribution. We follow the derivation provided in sec-
tion 3.2 and obtain the lower bound of true marginal
likelihood.
F
V
= log(N [Y |0, σ
2
I + Q
XX
]) −
1
2σ
2
Tr(
˜
K) (19)
where Q
XX
= K
XX
M
K
−1
X
M
X
M
K
X
M
X
and
˜
K = K
XX
−
K
XX
M
K
−1
X
M
X
M
K
X
M
X
. K
XX
is the joint-covariance matrix
derived using equation 6 or 7 using the input vector
X defined in section 1. K
X
M
X
M
is the joint covari-
ance function on the inducing points X
M
, such that
X
M
= [x
M1
, x
M2
, ..., x
M2
]. We assume that the induc-
ing points x
Mi
will be same for all the outputs, hence
ICPRAM 2016 - International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods
440

x
M1
= x
M2
= ... = x
M2
= x
M
. While K
XX
M
is the cross-
covariance matrix between X and X
M
.
Note that this bound consists of two parts. The
first part is the log of a GP prior with the only differ-
ence that now the covariance matrix has a lower rank
of MD. This form allows the inversion of the covari-
ance matrix to take place in O
N(MD)
2
time. The
second part as discussed above can be seen as a pe-
nalization term that regularizes the estimation of the
parameters.
The bound can be maximized with respect to all
parameters of the covariance function; both model hy-
perparameters and variational parameters. The opti-
mization parameters are the inducing inputs x
M
, the
hyperparameters θ of the independent covariance ma-
trix K
22
and the error while measuring the outputs
Σ. There is a trade-off between quality of the es-
timate and amount of time taken for the estimation
process. On the one hand the number of inducing
points determine the value of optimized negative log-
marginal likelihood and hence the quality of the es-
timate. While, on the other hand there is a computa-
tional load of O
N(MD)
2
for inference. We increase
the number of inducing points until the difference be-
tween two successive likelihoods is below a prede-
fined quantity.
4 NUMERICAL RESULTS
In this section we provide numerical illustration to
the theoretical derivations in the earlier sections. We
start with a synthetic problem where we try to learn
the model over derivative and quadratic relationships.
We compare the error values for the variational ap-
proximation with respect to the full GP approach. Fi-
nally we look at the results in presence of a real world
dataset related to flight loads estimation.
The basic toolbox used for this paper is GPML
provided with (Rasmussen and Williams, 2005), we
generate covariance functions to handle relationships
as described in equations 6 and 7 using the ”Sym-
bolic Math Toolbox” in MATLAB 2014b. Since vari-
ational approximation was not coded in GPML we
have wrapped the variational inference provided in
gpStuff (Vanhatalo et al., 2013) in the GPML tool-
box. All experiments were performed on an Intel
quad-core processor with 4Gb RAM.
4.1 Numerical Results on Theoretical
Data
We begin by considering the relationship between two
latent output functions as described in equation 2.
Such that
f
2
∼ GP[0, K
SE
(0.1, 1)]
σ
n2
∼ N [0, 0.2]
σ
n1
∼ N [0, 2] (20)
K
SE
(0.1, 1) means squared exponential kernel
with length scale 0.1 and variance as 1.
4.1.1 Differential Relationship
We take the case of a differential relationship g(.),
such that g( f , x) =
∂ f
∂x
. Since the differential relation-
ship g(.) is linear in nature we use the equation 6 to
calculate the auto- and cross-covariance functions as
shown in table 1.
Table 1: Auto- and cross-covariance functions for a differ-
ential relationship.
Initial Covariance K
22
σ
2
exp(
−1
2
d
2
l
2
)
Cross-Covariance K
12
σ
2
d
l
2
exp(
−1
2
d
2
l
2
)
Auto-covariance K
11
σ
2
d
2
−l
2
l
4
exp(
−1
2
d
2
l
2
)
To generate data a single function is drawn from
f
2
as described in equation 20 which then is used to
calculate y
1
and y
2
. 10,000 training points are gener-
ated for both the outputs. Values of y
2
for x ∈ [0, 0.3]
are removed from the training points. Next we opti-
mize the lower bound of log-marginal likelihood us-
ing variational inference, for independent GP’s on y
1
and y
2
as described in 3.2. Later we optimize the same
lower bound but with a joint-covariance approach as
described in section 3.3 using y
1
, y
2
and g(.). As
explained in section 3.3 we settled on using 100 in-
ducing points for this experiment because there was
negligible increase in lower bound F
V
of log-marginal
likelihood upon increasing the inducing points.
In figure 1(a) we show the independent (blue
shade) and joint fit (red shade) of two GP for the dif-
ferential relationship. The GP model with joint co-
variance gives better prediction even in absence of
data of y
2
for x ∈ [0, 0.3] because transfer of infor-
mation is happening from observations of y
1
present
at those locations. Nonetheless we see an increase
in variance at masked ’x’ values even for joint-
covariance kernel. The distribution of inducing points
may look even in the diagram but are uneven at places
where we have removed the data from y
2
.
Sparse Physics-based Gaussian Process for Multi-output Regression using Variational Inference
441
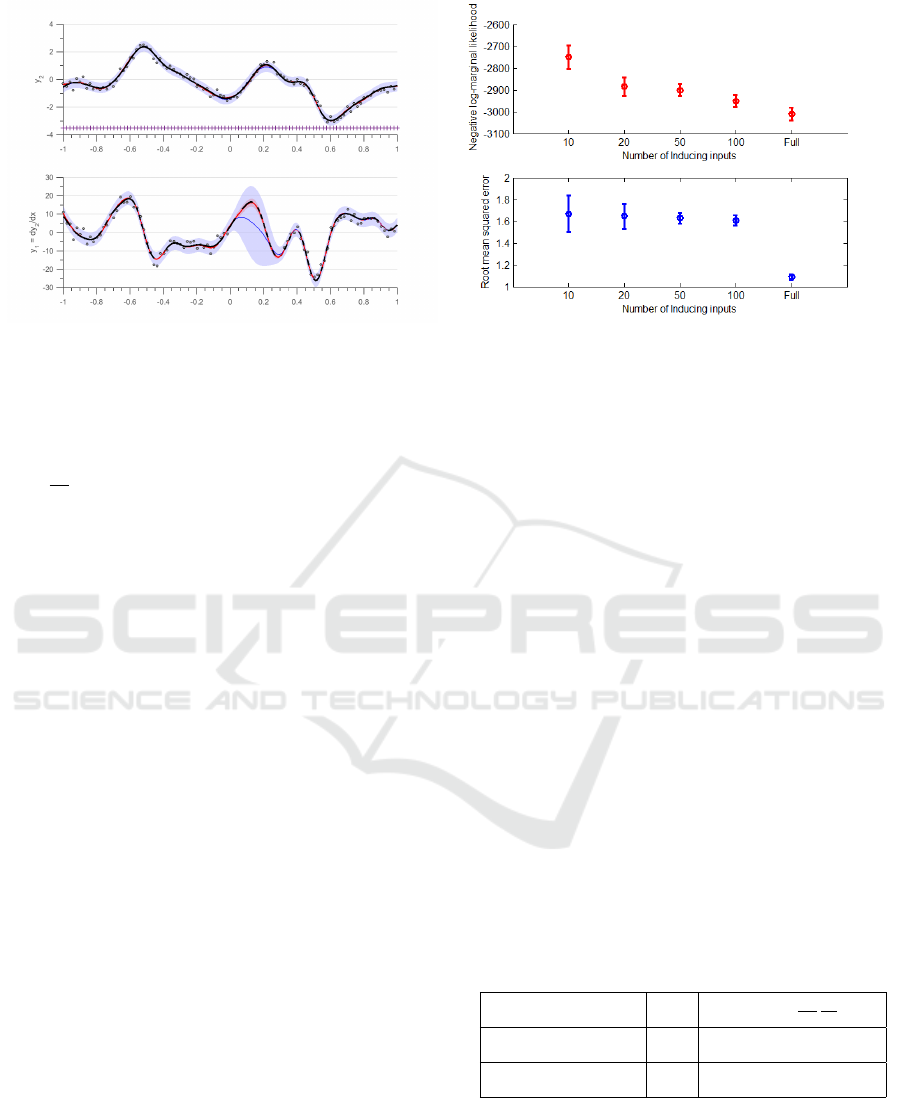
(a) Independent fit for two GP’s in blue variance is repre-
sented by light blue region and mean is represented by solid
blue line. Variance and mean of the dependent are repre-
sented in red region and solid red line. The dashed black
line represents the true latent function values; noisy data is
denoted by circles. Experiment was run on 10,000 points but
only 100 data points are plotted to increase readibility.Here
f
1
=
∂ f
2
∂x
, y
1
= f
1
+ σ
n1
and y
2
= f
2
+ σ
n2
. The + points
refer to the location of the inducing points in the inference.
(b) The figure shows progression of different measures upon
increasing number of inducing points from 10, 20, 50 to 100
and finally full Multi-output physics based GP. The top fig-
ure in red shows the value of mean and variance of nega-
tive log-marginal likelihood, while the bottom figure in blue
shows the mean and variance of root mean squared error. 10
sets of experiments were run on 75% of the data as training
set and 25% of the data as the test set, the training and test
sets were chosen randomly.
Figure 1: Experimental results for differential relationship with approximate inference using variational approximation.
For the second experiment we generate 1000
points and compare the Root Mean Squared Error
(RMSE) and log-marginal likelihood between full re-
lationship kernel as described in section 2.3 and vari-
ational inference relationship kernel as described in
section 3.3, using 10, 20, 50 and 100 inducing points.
10 sets of experiments were run on 75% of the data
as training set and 25% of the data as the test set, the
training and test sets were chosen randomly. We learn
the optimal values of hyper-parameters and inducing
points for all the 10 sets of experiments of training
data. Finally, RMSE values are evaluated with respect
to the test set and negative log-marginal likelihood are
evaluated for each learned model. The RMSE values
are calculated for only the dependent output y
1
and
then plotted in the figures below.
In figure 1(b) the mean and variance of negative
log-marginal likelihood for 10 sets of experiments are
calculated with varying number of inducing inputs
at the top in red. As expected upon increasing the
number of inducing points we see that the values of
mean negative log-marginal likelihood tends to be-
come an asymptote reaching the value of mean nega-
tive log-marginal likelihood of a full multi-output GP.
In the bottom figure we have the mean and variance
of RMSE for 10 sets of experiments. We see that the
mean value of RMSE does not vary drastically upon
increasing the inducing points but the value of vari-
ance gets reduced. One can observe an almost con-
stant RMSE in figure 1(b) with a sudden decrease for
a full GP (as M tends to N). Although this behaviour
was expected, providing an explanation for the slow
decrease with low values of M requires further inves-
tigation.
4.1.2 Quadratic Relationship
Now we take the case of a quadratic relationship g(.),
such that g( f , x) = f
2
. Since the quadratic relation-
ship g(.) is non-linear in nature we use the equation 7
to calculate the auto- and cross-covariance functions
as shown in table 2. The Jacobin L for this case be-
comes 2
¯
f
2
(x). Here the value of
¯
f
2
(x) is the mean
value of the latent-independent output function f
2
cal-
culated at the input point x.
Table 2: Auto- and cross-covariance functions for a
quadratic relationship.
Initial Covariance K
22
σ
2
exp(
−1
2
d
2
l
2
)
Cross-Covariance K
12
2
¯
f
2
(x)K
22
Auto-covariance K
11
4(
¯
f
2
(x)
2
K
22
+ 2K
2
22
)
As stated in the earlier section 4.1.1 the output
data was generated using the same draw of f
2
as ex-
plained in equation 20. 10,000 training points are gen-
erated for both the outputs. Values of y
2
for x ∈ [0, 0.3]
are removed from the training points. Note that the
above calculated auto- and cross-covariances are third
ICPRAM 2016 - International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods
442

(a) Independent fit for two GP in blue variance is rep-
resented by light blue region and mean is represented
by solid blue line. Variance and mean of the depen-
dent are represented in red region and solid red line.
The dashed black line represents the true latent function
values; noisy data is denoted by circles only 100 data
points are plotted to increase readibility. Here f
1
= f
2
2
,
y
1
= f
1
+ σ
n1
and y
2
= f
2
+ σ
n2
. The + points refer to
the location of the inducing points in the inference.
(b) The figure shows progression of different measures
upon increasing number of inducing points from 10, 20,
50 to 100 and finally full Multi-output physics based GP.
The top figure in red shows the value of mean and vari-
ance of negative log-marginal likelihood, while the bot-
tom figure in blue shows the mean and variance of root
mean squared error. 10 sets of experiments were run on
75% of the data as training set and 25% of the data as the
test set, the training and test sets were chosen randomly.
Figure 2: Experimental results for quadratic relationship with approximate inference using variational approximation.
order Taylor series approximations as presented in
equation 7.
Calculating the Jacobin
¯
f
2
(x) at the inducing and
input points was a requirement of the algorithm.
Moreover, during the optimization process the value
of x
m
keeps on changing, since the
¯
f
2
(x
m
) depends
on the value of x
m
. Many a times we don’t have
value of latent independent output function at these
new points. To solve this problem we first learn an in-
dependent model of the output y
2
recover an estimate
of
¯
f
2
(x) and use this value to calculate the required
auto- and cross-covariances.
In figure 2(a) we show the independent and joint
fit of two GP for the quadratic relationship. Even
in the presence of the error the joint-covariance GP
model gives better prediction because of transfer of
information. The GP model with joint covariance
gives better prediction even in absence of data of y
2
for x ∈ [0, 0.3] because transfer of information is hap-
pening from the observations of y
1
present at those
locations.
Upon performing the second experiment as de-
scribed in section 4.1.1 we get the figure 2(b). The
top part in the figure is the mean and variance of neg-
ative log-marginal likelihood for varying number of
inducing points. We see that the value mean nega-
tive log-marginal likelihood reaches the value of full
negative log-marginal likelihood. In the lower figure
we have mean and variance of RMSE of the depen-
dent output y
1
. As seen in the earlier experiment we
observe high amount of variance for lower inducing
points due to the approximate nature.
4.2 Numerical Results on Flight Test
Data
Figure 3: Wing Load Diagram.
In this section we conduct experiments, applying our
approach on the flight loads data recovered during
flight test campaigns at Airbus. We look at normal-
ized data of a simple longitudinal maneuver. The two
outputs in our case are shear load T
z
and bending mo-
ment M
x
as described in figure 3. The input space is
2-dimensional space with wing span η or point of ac-
tion of forces as he first input variable and angle of
attack α as the second input variable. The maneuver
is quasi-static which means that airplane is in equi-
librium at all time and there are no dynamic effects
observed by the aircraft. The relation between T
z
and
Sparse Physics-based Gaussian Process for Multi-output Regression using Variational Inference
443
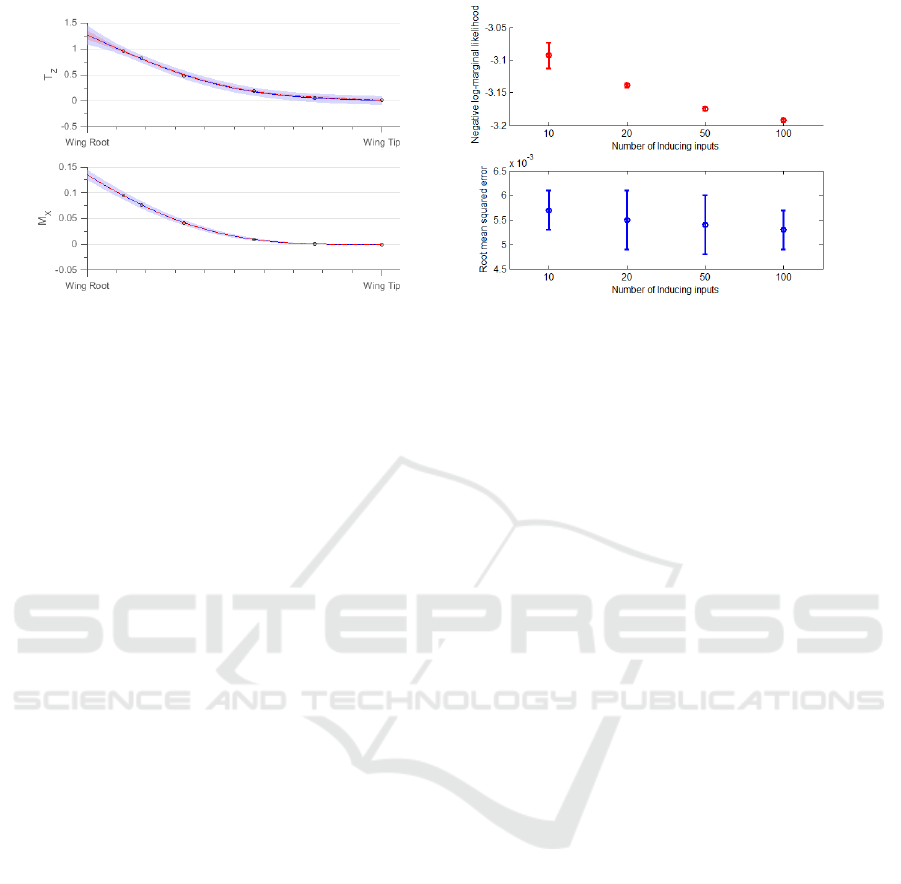
(a) Independent fit for two GP in blue variance is rep-
resented by light blue region and mean is represented
by solid blue line. Variance and mean of the depen-
dent are represented in red region and solid red line. The
dashed black line represents the true latent function val-
ues; noisy data is denoted by circles only 1 α step is
plotted.
(b) The figure shows progression of different measures
upon increasing number of inducing points from 10, 20,
50 to 100. The top figure in red shows the value of mean
and variance of negative log-marginal likelihood, while
the bottom figure in blue shows the mean and variance
of root mean squared error.
Figure 4: Experimental results for aircraft flight loads data with approximate inference using variational approximation.
M
x
can be written as:
M
x
(η, α) =
Z
η
edge
η
T
Z
(x, α)(x − η)dx. (21)
Note that the above equation is calculated only
on the η axis. Here, η
edge
denotes the edge of the
wing span. The above equation is linear in nature
and hence we will use equation 6 to calculate the
auto- and cross-covariance functions. The forces are
measured at 5 points on the wing span and at 8800
points in the second axis. We follow the procedure
described in earlier experiments where we compare
plots of relationship-imposed multioutput GP and in-
dependent GP. Secondly, we compare the measures of
negative-log marginal likelihood and RMSE for vary-
ing number of inducing points.
In figure 4(a) we see the plot of independent and
dependent T
Z
at the top with the dependent plot in red
and independent plot in blue. In the bottom part of
figure we show the plot for M
X
. Only one α is plot-
ted here for better viewing. 100 inducing points in
the input space are used to learn and plot the figure.
We see that the region in red, has a tighter variance
than the one in blue confirming the improvement by
our method. The relationship in equation 21 is acting
as extra information in tightening the error margins of
the loads estimation. This becomes very useful when
we need to identify faulty data because the relation-
ship will impose a tighter bound on the variance and
push faulty points out of the confidence interval.
In figure 4(b) we see how the negative log-
marginal likelihood and RMSE plots improve upon
increasing number of inducing points. As expected
the likelihood and RMSE improves with more induc-
ing points because of the improvement in the approx-
imate inference. We settle on choosing 100 inducing
points for figure 21 because there is not much im-
provement in RMSE and likelihood upon increasing
the inducing points.
5 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
WORK
We have presented a sparse approximation for
physics-based multiple output GP’s, reducing the
computational load and memory requirements for in-
ference. We extend the variational inference as de-
rived by (Titsias, 2009) and reduce the computational
load for inference from O
N
3
to O
N(MD)
2
and
load on memory from O
N
2
to O (NMD).
We have demonstrated our strategy to work on
both linear and non-linear relationships, in presence
of large amount of data. The strategy of imposing re-
lationships is one way of introducing domain knowl-
edge into the GP regression process. We conclude
that due to the support of added information provided
by the physical relationship we have a tighter confi-
dence interval for the joint-GP approach, eventually
leading to better estimates. Additionally, the results
in identification of measurements incoherent with the
physics of the system and a more accurate estimation
of the latent function, which is crusial in aircraft de-
sign and modeling. The approach can be extended to
ICPRAM 2016 - International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods
444

larger number of related outputs giving a richer GP
model.
Aircraft flight domain can be divided into various
cluster of maneuvers. Each cluster of maneuvers has
a specific set of features and mathematically mod-
elled behaviour, which can also be seen as domain
knowledge. Recent advancements in approximate in-
ference of GP such as “Distributed Gaussian Process”
(Deisenroth and Ng, 2015) distribute the input do-
main into several clusters. Such kind of approximate
inference technique should be explored in the future
for our kind of dataset. Future work deals with han-
dling clustered input space with individual features.
REFERENCES
Alvarez, M. and Lawrence, N. D. (2009). Sparse convolved
gaussian processes for multi-output regression. In
Koller, D., Schuurmans, D., Bengio, Y., and Bottou,
L., editors, Advances in Neural Information Process-
ing Systems 21, pages 57–64. Curran Associates, Inc.
Alvarez, M. A., Luengo, D., and Lawrence, N. D. (2009).
Latent force models. In Dyk, D. A. V. and Welling,
M., editors, AISTATS, volume 5 of JMLR Proceed-
ings, pages 9–16. JMLR.org.
´
Alvarez, M. A., Luengo, D., Titsias, M. K., and Lawrence,
N. D. (2010). Efficient multioutput gaussian processes
through variational inducing kernels. In Teh, Y. W.
and Titterington, D. M., editors, AISTATS, volume 9
of JMLR Proceedings, pages 25–32. JMLR.org.
Bonilla, E., Chai, K. M., and Williams, C. (2008). Multi-
task gaussian process prediction. In Platt, J., Koller,
D., Singer, Y., and Roweis, S., editors, Advances
in Neural Information Processing Systems 20, pages
153–160. MIT Press, Cambridge, MA.
Boyle, P. and Frean, M. (2005). Dependent gaussian pro-
cesses. In In Advances in Neural Information Pro-
cessing Systems 17, pages 217–224. MIT Press.
Constantinescu, E. M. and Anitescu, M. (2013). Physics-
based covariance models for gaussian processes with
multiple outputs. International Journal for Uncer-
tainty Quantification, 3.
Deisenroth, M. P. and Ng, J. W. (2015). Distributed gaus-
sian processes. In Proceedings of the 32nd Interna-
tional Conference on Machine Learning, ICML 2015,
Lille, France, 6-11 July 2015, pages 1481–1490.
Quionero-candela, J., Rasmussen, C. E., and Herbrich, R.
(2005). A unifying view of sparse approximate gaus-
sian process regression. Journal of Machine Learning
Research, 6:2005.
Rasmussen, C. E. and Williams, C. K. I. (2005). Gaussian
Processes for Machine Learning (Adaptive Computa-
tion and Machine Learning). The MIT Press.
Snelson, E. and Ghahramani, Z. (2006). Sparse gaussian
processes using pseudo-inputs. In ADVANCES IN
NEURAL INFORMATION PROCESSING SYSTEMS,
pages 1257–1264. MIT press.
Solak, E., Murray-smith, R., Leithead, W. E., Leith, D. J.,
and Rasmussen, C. E. (2003). Derivative observations
in gaussian process models of dynamic systems. In
Becker, S., Thrun, S., and Obermayer, K., editors, Ad-
vances in Neural Information Processing Systems 15,
pages 1057–1064. MIT Press.
Stein, M. L. (1999). Interpolation of Spatial Data: Some
Theory for Kriging. Springer, New York.
Titsias, M. K. (2009). Variational learning of inducing vari-
ables in sparse gaussian processes. In In Artificial In-
telligence and Statistics 12, pages 567–574.
Vanhatalo, J., Riihim
¨
aki, J., Hartikainen, J., Jyl
¨
anki, P.,
Tolvanen, V., and Vehtari, A. (2013). Gpstuff:
Bayesian modeling with gaussian processes. J. Mach.
Learn. Res., 14(1):1175–1179.
Sparse Physics-based Gaussian Process for Multi-output Regression using Variational Inference
445
