
BioMed Wizard
An Approach for Gathering Personal Risk Factor Data
Mohammad Shafahi, Hamideh Afsarmanesh and Stefan Paap
Informatics Institute, Faculty of Science, University of Amsterdam, Science Park 904, Amsterdam, The Netherlands
Keywords:
BioMed Wizard, Personal Data, Privacy, Risk Factors, Survey, Data Collection, Socio-economical Aspects.
Abstract:
People can be at risk of developing some serious diseases without being aware of it. Such diseases either do
not present symptoms in early stages or have simple symptoms that are ignored or not properly identified by
patients, due to their lack of medical know-how. On the other hand, in order to provide patients with early
indications of their risk level on developing such diseases, specially for chronic diseases such as diabetes type
2, it is necessary to collect substantial amount of personal data about risk factors related to the disease. A
smart wizard software applying the approach developed in our study, which brings awareness about some
socio-economical concerns of patients, can increase patients’ engagement in providing their personal data.
The case study focuses on the diabetes type 2 and some socio-economical concerns of patients, including
privacy invasion, time, and cost. In this research, the willingness of a sample group of more than 100 people
is surveyed, in providing their personal data, for three different scenarios and related to nine main risk factors.
The results collected in this survey is then applied to develop four user-specific data collection flow models,
to be implemented in a smart wizard software.
1 INTRODUCTION AND
RESEARCH APPROACH
For a number of diseases, people can be at risk of
developing them, without being aware. Such dis-
eases do not present symptoms in early stages or have
symptoms that are typically ignored or not properly
identified by patients due to their lack of medical
know-how in identifying symptoms. However, it is
very important to recognize diseases in their early
stages of development, in order to reduce the chance
of life threatening situations. An example of a disease
that can develop without alarming with early symp-
toms, is diabetes mellitus type 2. This is a chronic
disease that causes high levels of glucose in the blood.
Diabetes can result in serious complications such as
heart disease and stroke, obesity, high blood pressure,
blindness, kidney disease, nervous system related dis-
eases and more (Zhang and Zhao, 2013).
According to the World Health Organization, in
2012, 1.5 million deaths were directly caused by dia-
betes (World Health Organization, 2014) demonstrat-
ing the importance of detecting the risk of diabetes for
the general public in an early stage. Diabetes type 2
can be developed during any stage of ones life. Sev-
eral risk factors are known to be associated to this dis-
ease, which vary from someones lifestyle that can in-
fluence the risk of developing diabetes type 2, but also
inheritance (i.e DNA) can be of influence. Therefore,
people are not always aware of being in risk of devel-
oping diabetes. Although lack of exercising and con-
suming unhealthy food might not have a direct (neg-
ative) influence on someone, but it increases his/her
chance of developing the disease. Early detection
can reduce the burden of complications of diabetes, if
treated on time (Knowler et al., 2002). As such bring-
ing awareness and insight of the possible risk level of
developing diabetes, based on information provided
about current personal habits and status (i.e risk fac-
tors), will definitely help with this illness. Although
many researchers have designed prediction models
for risk of developing type 2 diabetes(Abbasi et al.,
2012), the current process of assessing the risk of de-
veloping a disease entails setting appointments with
general practitioners or specialists as a starting point,
followed by conducting a blood test. This can be a
time consuming and costly process for diagnosing the
risks at the early stages. To reduce the time and cost
of such process, and in order to have a more extensive
coverage of the assessment process, one would like to
only perform such a process when necessary and after
an initial screening and diagnosis process.
298
Shafahi, M., Afsarmanesh, H. and Paap, S.
BioMed Wizard - An Approach for Gathering Personal Risk Factor Data.
DOI: 10.5220/0005701102980305
In Proceedings of the 9th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies (BIOSTEC 2016) - Volume 5: HEALTHINF, pages 298-305
ISBN: 978-989-758-170-0
Copyright
c
2016 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

There are online software wizards that provide
users with information about diabetes, but these are
often only based on a limited number of risk factors
(e.g. only asking about the gender). For example after
a gender selection option, the online wizard provides
all risk factors and symptoms specific for that specific
gender. Although this could be helpful, it still very
much leaves the assessment of the risk level to the pa-
tients, and depends on the proper identification of the
symptoms by them. However, the indication of the
patients risk level can be further clarified and can be
made more precise if more risk factors are measured
or identified from the user. For example tools such as
the Diabetes Risk Score (Lindstr
¨
om and Tuomilehto,
2003) use information about certain risk factors such
as age, BMI and diet to calculate a score that indicates
the risk level of developing diabetes type 2.
In this research we aim to develop an approach
for user specific data collection that can be developed
within a smart wizard software to provide users with
an indication of their current risk level, with the con-
sideration of socio-economical aspects in the collec-
tion process. A smart wizard software automatically
adapts future data collection based on the data that
the user has provided up to that stage. By doing so,
the software creates a user specific flow for entering
data, helping the user to traverse through the process,
making it easier, faster, and more efficient in a user
centric manner. In the case of this research the fo-
cus is more on what, how, in which order, and how
frequently to collect risk factor data. Next to focus-
ing on these, we focus on factors such as cost, time,
and the needed effort, since these are also factors that
play important roles on the willingness of someone to
share data. Therefore, socio-economical aspects are
also taken into consideration. The goal here is to get
insight on what data can be realistically gathered and
from where, and how it can be gathered for different
types of scenarios when considering diffident phases
of screening for diabetes as an example disease. As
such in this research we try to answer the following
research question:
How can personal data be collected from users
when considering socio-economic barriers?
In order to address this research question a five-
phase research approach has been designed, consist-
ing of the following phases: 1) Identification of Main
Risk Factors and Relevant Bio-markers, 2) Design of
the Survey, 3) Evaluation of the Survey, 4) Conduct-
ing the Survey, and 5) Analysis of Results and Design
of User Specific Data Collection Flow Models.
2 RELATED WORK
With the introduction of electronic medical files, cre-
ated and stored in digital systems, it became more
easy to share medical information. Later with the in-
troduction of electronic health records (EHRs), elec-
tronically sharing medical information about patients
with third parties became feasible and trivial for hos-
pitals upon the request of patients. This provided pa-
tients with more control over the availability of their
medical information.
Although research in 2009 (Jha et al., 2009) shows
that US hospitals still struggle to implement the elec-
tronic forms of health records (9.1% make use of a
basic EHR system), a study in 2014 (Adler-Milstein
et al., 2014) showed that at least 50% of the US hospi-
tals make use of a basic EHR system. This adoption is
not limited to hospitals, but also other medical profes-
sions, such as physicians, show an increasing trend of
using EHR systems (Xierali et al., 2013). These stud-
ies show that EHR systems are becoming more pop-
ular and the use of them will continue to rise in the
coming years. Since these electronic health records
contain medical data about the patient, information
about risk factors are likely to be found in these files.
A study in 2009 (Hivert et al., 2009) used informa-
tion stored in electronic health records to find pat-
terns that identify patients with metabolic syndrome
that would put them at larger risk of becoming obese
and develop diabetes. This study demonstrated that
electronic health records can play an import role as
data sources in identifying patients with a risk of de-
veloping diseases.
Although such sources of data look promising one
must investigate the level of willingness and the situ-
ation in which people are willing to provide access
to their electronic health records. Studies have inves-
tigated the willingness of users to share information
in general for a certain cause. A study (Teixeira et al.,
2011) has investigated the willingness of HIV patients
to share personal health information with others. The
founding of the study suggests that the vast major-
ity (84%) are willing to share this data electronically,
but the individuals who would receive the shared data
have to be involved in the direct care of the patient.
Fewer patients (39%) are willing to share it with non-
carers electronically. Another study (Beckjord et al.,
2011) has looked into the willingness of cancer pa-
tients to exchange personal related information elec-
tronically. They have compared participants who are
diagnosed with cancer against participants who are
not diagnosed, and have found that people who are di-
agnosed are much more willing to share this informa-
tion to help others. A research done in 2014 (Pickard
and Swan, 2014) has concluded that there is a strong
BioMed Wizard - An Approach for Gathering Personal Risk Factor Data
299

willingness of people to share personal data in order
to enable next generation health care services, ulti-
mately leading to improved health outcomes for all.
These findings suggest that people are willing to
share personal information electronically, which is
also an important requirement for a smart wizard soft-
ware, but these studies also suggest that the amount of
information shared differ depending on the amount of
engagement the patient has in a specific disease and
how the share of this information directly influences
their health conditions. In this research we further
investigate the willingness of people in sharing per-
sonal information in a more fine grained manner (i.e
bio-markers’ level) while taking into account the in-
fluence of their profile (i.e demographics and engage-
ment with disease) and will investigate the possibility
of adjusting data collection based on the users profile
and level of engagement.
3 IDENTIFICATION OF RISK
FACTORS AND RELEVANT
BIO-MARKERS
There are many studies on individual risk factors re-
lated to diabetes mellitus type 2, such as obesity
(Tirosh et al., 2011), diet (Montonen et al., 2004)
and ethnicity (Harris, 2001) but Mayo Clinic (Mayo
Clinic, 2015) and the Dutch National Institute for
Public Health and Environment (Rijksinstituut voor
Volksgezondheid en Milieu, 2013), have provided an
extensive collection of the main risk factors including:
age, obesity, ethnicity, family history, genetic factors,
diet, smoking behavior, pre-diabetes, gestational dia-
betes (pregnancy diabetes) and (in)activity. But in or-
der to assess the risk level of developing diabetes type
2, we are interested in collecting bio-markers related
to risk factors. Bio-markers are aspects of the body
that can be measured in order to understand the cur-
rent condition of the risk factors. As an example, for
the risk factor obesity, BMI (Body Mass Index) can
be considered as a bio-marker and can be calculated
based on two other measurable bio-markers being the
height and weight of the patient. The same applies
in the case of genome factors, where the genome se-
quence is considered, so that research can focus on the
specific parts needed to determine the genome factors
regarding diabetes.
Although most risk factors can easily be mapped
to a bio-marker and are easily perceived, there are oth-
ers that are perceived differently by different people
such as being active or not (Shephard, 2003). This
makes the measurement of these risk factors unreli-
able (Prince et al., 2008). Such risk factors have not
been incorporated in this research as covering all pos-
sible perspectives of such risk factors (e.g. cycling as
a perspective to measure activity) is not feasible and
would cause misinterpretation of the results of this re-
search.
Based on the above for the proof of concept, only
9 main risk factors/bio-markers have been selected in
order to be incorporated into the survey, including:
age, weight, height, ethnicity, family history, genome
sequence, diet, smoking behavior and pre-/pregnancy
diabetes. This is also due to the fact that in this re-
search we are not focused on identifying all possible
risk factors or providing the best possible risk pre-
diction model, rather investigating the feasibility of
a personalized data collection experience to reduce
socio-economical barriers.
4 DESIGN OF THE SURVEY
In order to measure the willingness of people to share
information about risk factors, a survey has been con-
ducted. The guidelines suggested by the literature
(Fink, 2012; D
¨
ornyei and Taguchi, 2010) have been
followed to ensure the validity and quality of the re-
sults and the conclusions. The survey is designed
in a manner which: i) provides confidence that the
questions are answered with appropriate awareness,
ii) the engagement of the participants in the survey
is maximized, and iii) false responses, due to privacy
concerns or boredom, is minimized. To achieve the
above a set of rules have been designed, that the sur-
vey should comply to: 1) The time needed to an-
swer all questions should be approximately 5 minutes;
2) The questionnaire should not contain more than 30
questions; 3) The questionnaire should be available
in the language of the majority of the sample popu-
lation (Dutch) and in English; 4) Only complete sub-
missions are acceptable, as such, partially filled ques-
tionnaires are not acceptable; 5) The survey should
be conducted in a completely anonymous manner;
6) The minimum age of the participants should be 18;
The questionnaire of the survey has been designed in
a manner that for each bio-marker, the participants
will be asked to respond to four types of questions:
Situation Questions. As we are interested in con-
sidering diffident phases of screening, four different
scenarios with an increasing level of confidentially
have been designed: 1) Social chatting 2) (General)
research 3) Family related 4) Diagnosed
Each scenario has been fitted with an appropriate
image to visually attach the participant to the scenario
and a lines of text representing the situation. For each
HEALTHINF 2016 - 9th International Conference on Health Informatics
300

bio-marker, participant are asked to select in what sit-
uation(s)/scenario(s) they would provide information
regarding that specific bio-marker. Participants can
select none, one or more options. If one or more
options are selected, follow-up questions will be pre-
sented to them regarding that specific bio-marker oth-
erwise they can proceed to the question(s) about an-
other bio-marker.
Means of Providing Information. If the partici-
pant selects one or more scenarios, he/she is asked
about the means of which he/she prefers providing
information about the specific bio-marker in the spe-
cific scenario(s). All bio-markers are provided with
the option to manually provide information as well
as through an electronic health record (EHR). We
have assumed that if EHR is chosen as a means of
providing bio-marker information, then this informa-
tion in definitely available in the EHR of the partici-
pant. Besides these two options, several bio-markers
have other option. Age can also be shared through
social networks. The same accounts for family his-
tory. Although it is very unlikely to find informa-
tion about diabetes of other family members on their
social network, relationships between them can be
extracted from these networks. By questioning the
users about diabetes in their families, a more de-
tailed profile can be created of the user: a parent is
of larger influence than a far relative. Finally, in-
formation about pregnancy diabetes can be shared
through social networks. If, for example, informa-
tion about pregnancy is found on the user’s network,
by analyzing their posts, a more specific question
about their pregnancy can be asked. As for weight,
another mean of providing information is presented:
a smart scaling device. These devices, such as the
Fitbit
1
https://www.fitbit.com/aria Aria and Withings
smart body analyser
2
, are able to measure someones
weight and wirelessly transmit it to an external ap-
plication. Over all, depending on the scenario and
bio-marker a sub-set of the following means of pro-
viding information, that are applicable, is presented:
1) Manually providing the data through an online
form 2) Through Social Media 3) Through your Elec-
tronic Health Record (EHR) 4) Through smart de-
vices In this type of question multiple options could
be selected and a minimum of one option is required.
Frequency of Providing Information. For certain
questions another follow-up question is the frequency
1
https://www.fitbit.com/aria
2
http://www.withings.com/eu/en/products/smart-body-
analyzer
of providing information. Certain risk factors, such
as weight, diet & smoking behavior can frequently
change and therefore have an important influence on
the current risk of developing diabetes. So the fre-
quency of sharing the information by the participants
is also an important factor that should be measured
in order to get a more detailed insight. For each mean
of providing information question, a separate question
for the frequency of sharing information might also be
asked. So for example if both manually filling in an
online form and through a smart scaling device are se-
lected, two extra questions appeared: one question for
each. This is done due to the fact that there could be
a large difference between filling in an online form
or transmit data automatically with a smart scaling
device with regards to effort as well as cost. Man-
ually providing the information requires more time
than stepping on a scale that automatically transmits
the data to the application, but the purchasing price
of such a scaling device is also a factor to consider.
Therefore, the participants are given the flexibility to
accurately indicate this. Not every means of provid-
ing information question have a follow-up question
for frequency. For example, length (as an adult), eth-
nicity and genome sequence are factors that do not
change over time. Over all, depending on the means
of providing information, scenario and bio-marker a
sub-set of the following frequencies of proving in-
formation, that are applicable, is presented: 1) Only
once, 2) Monthly, 3) Weekly, 4) Daily, 5) Whenever
I feel like, and 6) Permanent Access. In this type of
question multiple options could be selected.
Demographics. Questions related to each of the
nine risk factors of diabetes used for this research and
the associated questions are located in separate pages
of the questionnaire. Besides these pages, two other
pages are placed before these questions. The first
page contained demographic questions, such as what
is your sex, what is your age group and do you know
someone with diabetes in order to investigate possi-
ble differences between demographic groups. For ex-
ample the willingness to share information for dia-
betic research in people that know someone close to
them diagnosed with diabetes compared to others is
higher as they know how it is like to live with diabetes
(Beckjord et al., 2011). The ages groups are divided
into three groups: youth (18-24 years), adult (25-64
years) and senior (65+ years), based on the Canadian
age classification standard. No option has been pro-
vided for ages less than 18 as the minimum age of 18
is set as a rule for the questionnaire, in order for the
participant him/her-self be able to decide on sharing
personal information.
BioMed Wizard - An Approach for Gathering Personal Risk Factor Data
301

5 EVALUATION OF THE SURVEY
In order to develop a solid and sound questionnaire
and in order to evaluate the compliance of the sur-
vey with the set rules discussed in section 4 an up-
date cycle is used to improve the questionnaire. After
each round of the cycle, the updated questionnaire’s
compliance to the rules are re-verified. In the first
step the questionnaire is tested by three experts. The
purpose is to test if the setup is correct (e.g. to ver-
ify the questions, the question formulation, availabil-
ity of answers ) and to test the initial fitness to the
set rules. Then a small pilot group of 10 participants
are invited to participate in the questionnaire.The pur-
poses of this phase is to verify the understandability of
the questionnaire for a broader audience and to mea-
sure the required time to answer the questionnaires.
The later is needed in order to verify if the question-
naire satisfied the set rules. The results indicate that
in average the time needed to answer the question-
naire is 6 minutes, 19 seconds and the median is 5
minutes, 21 seconds. After further investigation it be-
comes clear that two participants took almost twice
as long as the others due to external interruptions (e.g
phone call), making the average time longer than pro-
jected. After removing the outliers, the time needed
to complete the questionnaire is satisfying (5 minutes,
42 seconds). Finally, every member of the pilot group
is contacted and asked for feedback. Each question
is discussed as well as the setup of the questionnaire.
The feedback of the participants are then applied to
the questionnaire. For example, it has been noted that
the term genome sequence is not very clear, as well
as pre-diabetes and pregnancy diabetes. In order to
clarify the risk factors/bio-markers additional links to
external web-pages are added with more information
about genome sequences, pre-diabetes and pregnancy
diabetes. Also the images of the scenarios are up-
graded to better quality images. After these and other
changes are applied, the questionnaire is then tested
again.
6 CONDUCTING THE SURVEY
The survey is implemented using LimeSurvey
3
, an
open source software for implementing complex sur-
veys. LimeSurvey provides several features such as
exportable paper-based version of the online ques-
tionnaire, follow up questions, multilingual support,
and time-tracking. The PHP web application is in-
stalled on a private web server and made available. To
3
https://www.limesurvey.org
ensure the privacy of the participant, secure connec-
tions are established using the SSL encryption pro-
tocol to prevent unwanted interception between the
private server and the participants web browser. The
start page provides the participant with information
about the context of the questionnaire as well as an es-
timated completion time and information on how their
information will be processed and handled, anony-
mous. Participants can also choose their preferred
language: English or Dutch with the default set to
English. When the participants are finished, they are
presented with a thank you screen with a link to a
page with information on diabetes type 2. This page
is provided in order to create more awareness as well
as inform the participant about diabetes mellitus type
2 and its risk factors. The survey is also advertised
by means of email, social media and physical posters.
The survey is conducted for two consecutive weeks
and then closed. In total 116 responders have partic-
ipated in the survey, 11 of which are incomplete. As
such a total of 105 completed submissions are gath-
ered resulting in a completion rate of 90.5%. The av-
erage answering time is 6 minutes, 46 seconds. This
average response time is longer than projected (5 min-
utes), but further investigation shows some high re-
sponse times (>25 minutes) that could indicate exter-
nal interruptions in the survey process for some par-
ticipants. The median however is 5 minutes and 22
seconds, which is satisfying regarding the rules set.
Four participants out of the 105 complete results have
only selected one scenario for all risk factors , while
the intention is to select all applicable options. Since
these results could act as outliers, they have been ex-
cluded from the analyse, as such reducing the num-
ber of valid responses to 101. Out of the valid re-
sponses, 39 participants are youth (18-24 years), 58
adults (25-64 years) and only 4 seniors (65+ years).
Although the senior population is significantly lower
in the sample group, this will not influence a smart
wizard software for screening diabetes as the seniors
are not in the target group for such a software. On
the other hand 46 of the participants are male and
55 are female, suggesting an acceptable split between
both genders. Although the participant are from 17
different nationalities, 74% of them have a dutch na-
tionality. This is due to the fact the the research is
conducted in the Netherlands. Finally our popula-
tion is quite well distributed between different dis-
ciplines (23 from Computer & Information sciences,
24 from Biological & Health Sciences, 22 from Engi-
neering, Physical & Social sciences and Psychology,
and 32 from other educational backgrounds). While
the level of education has shown not to influence the
understanding of privacy, the field of study has been
HEALTHINF 2016 - 9th International Conference on Health Informatics
302
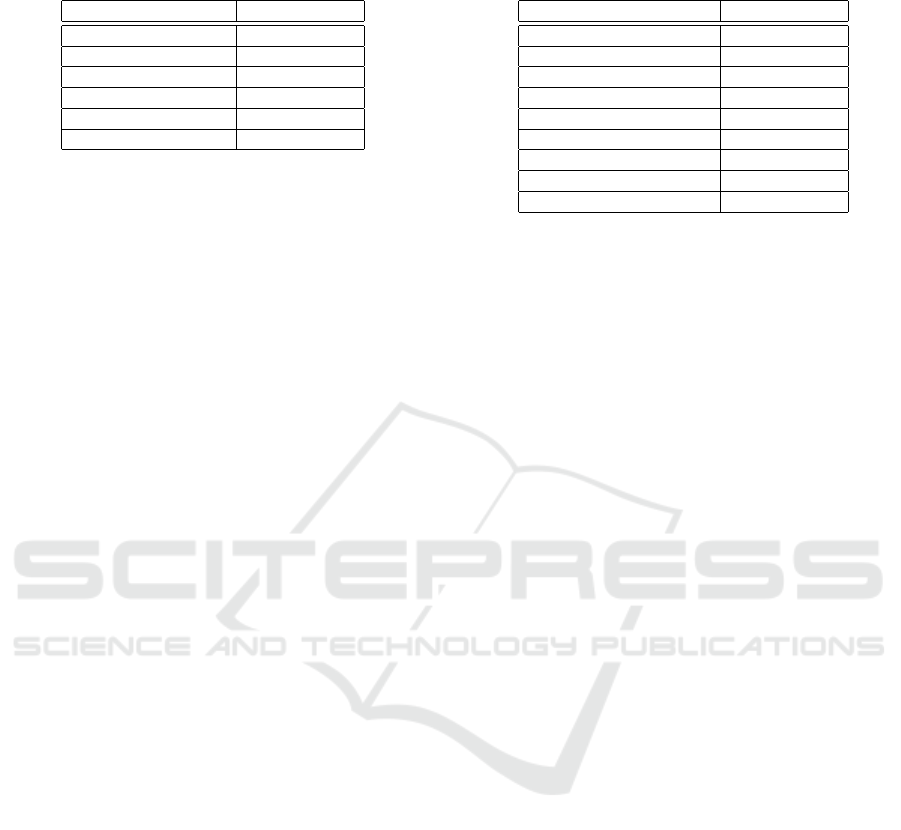
Table 1: Overview of selection rates for frequency of pro-
viding information.
Frequency Selection Rate
Whenever I feel like 38.5%
Only once 19.6%
Monthly 17.6%
Weekly 10.6%
Permanent Access 3.2%
Daily 2.9%
suggested to have such an influence (Ferreira et al.,
2011). Other than this, the understanding of the im-
portance of sharing this data for medical research
might influence participants choice on sharing their
information. The distributed between different disci-
plines in our study prevents biased results due to these
factors.
7 STATISTICAL ANALYSIS AND
USER SPECIFIC DATA
COLLECTION FLOW
The statistical analysis shows that, as expected, an
increasing amount of positive responses can be seen
when the scenarios become more confidential. The
diagnosed scenario is the most selected, with a 94.4%
selection rate, followed by family related situation,
(general) research and social chat scenarios with se-
lection rates of 90.7%, 69.9%, and 53%, respectively.
When looking at the means of providing information,
manual submission of information is by far the most
selected option with a selection rate of 28.9% fol-
lowed by EHR, Smart Devices, Social Network with
selection rates of 10.9%, 7.1%, and 1.9% , respec-
tively. However, when only looking at means of pro-
viding the genome sequence, we can see that the
selection rate for providing through EHR is 30.7%
while manual submission is 29.8%. For all other
risk factors/bio-markers, manual submission has been
chosen substantially more. Finally, the frequency of
providing information when applicable (weight, diet
and smoking) are shown in Table 1. As visible, the
option Whenever I feel like is by far the most selected
frequency. Although for the risk factors weight and
diet the second most selected frequency is Monthly,
and for smoking, the second most selected frequency
is Only once.
Using the above statistical analysis and by finding
significant differences between different demographic
groups, a user specific data collection flow model
is designed using BPMN 2.0 for each scenario, that
represents a smart wizard software for each screen-
ing phase. The significant differences are found used
Table 2: Overview of selection rates for risk factors for the
social chat scenario.
Bio-marker/Risk factor Selection Rate
Age 80%
Smoking 79%
Ethnicity 75%
Height 74%
Diet 58%
Weight 49%
Family history 29%
Pre-/Pregnancy diabetes 24%
Genome sequence 14%
the binary logistic regression method. And if a sig-
nificant difference is found, the Crosstabs method is
used to discover the cause of the difference. A sig-
nificance level of p <0,05 is used to indicate signifi-
cant differences for all methods. In order to demon-
strate how these significant values are used to imple-
ment the model, one of the developed models (i.e so-
cial chat representing the initial screening phase) will
be discussed in detail. Each model consists of three
lanes, two of which are the most important: the soft-
ware lane and the user lane. The software lane repre-
sents the action preformed by the smart wizard soft-
ware, such as asking a question. The user lane on the
other hand represents the action by a participant in the
screening process, such as providing an answer. Fi-
nally, the third lane represent external services that are
invoked to retrieve information. The order in which
the questions are asked in the model is based on the
willingness of people to share their data related to a
bio-marker. Table 2 demonstrates the distribution in
which the respondents are willing to share informa-
tion in social chat context. As visible most of the par-
ticipants are willing to provide their age, while the
least are willing to provide their genome sequence.
This order is used to prevent offending users of the
software, by asking for data that are not likely to be
share by them, and to keep the user engagement with
the wizard to its maximum.
Now that the order in which questions are asked
by the software has been set, the focus lies on what
can and cannot be asked to the users regarding a
higher chance of offending them. To achieve this
as stated in the method, a binary logistic regression
has been conducted. If a significant result was found,
a crosstabs method was used to get insight on what
caused the significant difference. Our findings sug-
gest that women are significantly less likely to pro-
vide information about their age, height and weight
compared to men. On the other hand our finding
also suggest that non-Dutch (minorities) are signif-
icantly less likely to provide information about their
age and height. These significant differences are mod-
elled into the smart wizard software model. There-
BioMed Wizard - An Approach for Gathering Personal Risk Factor Data
303

fore, the software asks the user for his/her sex as well
as nationality first in order to decide what questions
should be presented further. The complete model for
the social chat scenario is illustrated in the BPMN no-
tation
4
. The first two questions ask about the sex and
nationality. After which the age is asked about. How-
ever, due to the identified significances the model is
adjusted. The same approach is followed for height,
weight and pre-/pregnancy diabetes.
Regarding the means of providing information, it
is important to notice that all information have to be
provided manually with the exception of genome se-
quence. Since there is almost no significance differ-
ence between manual submission and EHR the deci-
sion has been made to provide the user with both op-
tions. A XOR statement enables the user to select one
of the options. If the user selects the option to share it
through his/her electronic health record, a request to
an external service is made, i.e. the service that holds
the data of the electronic health record.
Finally, the frequency by which data can be gath-
ered is also implemented in the model. As discussed
before and visible in Table 1, the option to share in-
formation whenever the user feels like is the most se-
lected option. For both diet and weight the second
most selected option is monthly and therefore a re-
minder is modelled for these factors. For these cases
the user is send a monthly reminder via a notification
(e.g phone notification or email), stating that the user
can update its information if he or she feels like doing
so. It is important to state that at each point the user
has the ability to skip every question.
8 DISCUSSION
One should have in mind that people are not always
completely honest when asked about privacy related
matters and in real-life might act differently. This
might jeopardize the results of this research, as such
on one hand, we have tried our best not to reveal
the intention of the questionnaire to reduce any pre-
judgement and perception that might cause this phe-
nomenon and on the other hand, we observe the par-
ticipants tendency to being truthful, by their response
to situation questions addressed in section 7. An-
other possible challenge with our approach rises when
the user is not asked to provide bio-marker informa-
tion for some of risk factors. For example BMI for
obesity in women and non-Dutch users in the model
of the social chat cannot be calculated. However,
BMI is a very important factor to know, since over-
4
Available online http://goo.gl/AUDJ1a
weight is the primary risk factor for diabetes type 2
for both adults (Hartemink et al., 2006) and children
(Wei et al., 2003). This becomes further clear when
looking into a study (Baan et al., 1999) that has in-
vestigated what data is essentially required to identify
patients at a greater risk of developing diabetes type 2.
This study created three risk prediction models. The
first model is based on data gathered in files of a gen-
eral practitioner, such as age, sex and absence of obe-
sity. The second model used additional information
by asking questions about family history and smok-
ing. The third model incorporated medical data, such
as diastolic blood pressure and systolic blood pres-
sure. The study has concluded that while the first
and second models generate similar results, adding
the risk factors in the third model is not useful, and
the extra medical data used in the third model has no
additive predictive value. At the end researchers have
recommend the first model, since it uses less infor-
mation that is usually available in the patient specific
notes of a general practitioner. Even when looking
at the minimal model still obesity, as a risk factor,
plays a critical role and as such the bio-marker BMI
is critical in properly assessing the risk of developing
diabetes type 2. A possible solution can be to esti-
mate critical bio-markers such as BMI for patients us-
ing knowledge-based and learning-based approaches
(Khan et al., 2012) to fill in gaps where information is
missing.
9 CONCLUSION AND FUTURE
WORK
The aim of this research is to achieve a model for user
specific data collection, using a smart wizard software
that would ultimately provide users with an indica-
tion of their current risk level, when also considering
socio-economical aspects. As a first step in this pro-
cess, we have created four models (for different types
of possible software scenarios) that can be used to
create a user specific software wizard to gather data
related to diabetes type 2. A survey is conducted to
measure the willingness of users to share data about
different risk factor. Four scenarios are used to distin-
guish possible differences in the willingness to share
information in different phases of screening for dia-
betes type 2. The users are also asked about the pre-
ferred means of sharing the information and, if appli-
cable, the frequency in which they are willing to share
this information. Future work can use the method
proposed in this research to develop similar data col-
lection models for other diseases. Another further
research can be conducted with larger and more di-
HEALTHINF 2016 - 9th International Conference on Health Informatics
304

verse populations to investigate possible differences
between regions and countries. Also, once the wizard
is developed, evaluation of the approach can be pre-
formed using A/B testing and measuring parameters
such as the dropout rate.
REFERENCES
Abbasi, A., Peelen, L. M., Corpeleijn, E., van der Schouw,
Y. T., Stolk, R. P., Spijkerman, A. M., Moons, K. G.,
Navis, G., Bakker, S. J., Beulens, J. W., et al. (2012).
Prediction models for risk of developing type 2 di-
abetes: systematic literature search and independent
external validation study. Bmj, 345:e5900.
Adler-Milstein, J., DesRoches, C. M., Furukawa, M. F.,
Worzala, C., Charles, D., Kralovec, P., Stalley, S., and
Jha, A. K. (2014). More than half of us hospitals have
at least a basic ehr, but stage 2 criteria remain chal-
lenging for most. Health Affairs, pages 10–1377.
Baan, C. A., Ruige, J. B., Stolk, R. P., Witteman, J., Dekker,
J. M., Heine, R. J., and Feskens, E. (1999). Per-
formance of a predictive model to identify undiag-
nosed diabetes in a health care setting. Diabetes care,
22(2):213–219.
Beckjord, E. B., Rechis, R., Nutt, S., Shulman, L., and
Hesse, B. W. (2011). What do people affected by
cancer think about electronic health information ex-
change? results from the 2010 livestrong electronic
health information exchange survey and the 2008
health information national trends survey. Journal of
Oncology Practice, 7(4):237–241.
D
¨
ornyei, Z. and Taguchi, T. (2010). Questionnaires in sec-
ond language research: Construction, administration,
and processing. Routledge.
Ferreira, A. M., Tziortzios, C., and Shafahi, M. (2011).
Passwords awareness in the academic world. Tech-
nical report, University of Amsterdam.
Fink, A. (2012). How to conduct surveys: A step-by-step
guide. Sage Publications.
Harris, M. I. (2001). Racial and ethnic differences in health
care access and health outcomes for adults with type
2 diabetes. Diabetes care, 24(3):454–459.
Hartemink, N., Boshuizen, H. C., Nagelkerke, N. J., Jacobs,
M. A., and van Houwelingen, H. C. (2006). Com-
bining risk estimates from observational studies with
different exposure cutpoints: a meta-analysis on body
mass index and diabetes type 2. American journal of
epidemiology, 163(11):1042–1052.
Hivert, M.-F., Grant, R. W., Shrader, P., and Meigs, J. B.
(2009). Identifying primary care patients at risk for
future diabetes and cardiovascular disease using elec-
tronic health records. BMC health services research,
9(1):170.
Jha, A. K., DesRoches, C. M., Campbell, E. G., Donelan,
K., Rao, S. R., Ferris, T. G., Shields, A., Rosenbaum,
S., and Blumenthal, D. (2009). Use of electronic
health records in us hospitals. New England Journal
of Medicine, 360(16):1628–1638.
Khan, A., Doucette, J. A., Cohen, R., and Lizotte, D.
(2012). A hybrid design for medical decision support
using data mining to impute missing data.
Knowler, W. C., Barrett-Connor, E., Fowler, S. E., Ham-
man, R. F., Lachin, J. M., Walker, E. A., and Nathan,
D. M. (2002). Reduction in the incidence of type 2
diabetes with lifestyle intervention or metformin. The
New England journal of medicine, 346(6):393.
Lindstr
¨
om, J. and Tuomilehto, J. (2003). The diabetes risk
score a practical tool to predict type 2 diabetes risk.
Diabetes care, 26(3):725–731.
Mayo Clinic (2015). Risk factors type 2 diabetes
risk factors. http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-
conditions/type-2-diabetes/basics/risk-factors/con-
20031902. Accessed: 2015, May 21.
Montonen, J., Knekt, P., J
¨
arvinen, R., and Reunanen, A.
(2004). Dietary antioxidant intake and risk of type 2
diabetes. Diabetes Care, 27(2):362–366.
Pickard, K. T. and Swan, M. (2014). Big desire to share big
health data: A shift in consumer attitudes toward per-
sonal health information. In 2014 AAAI Spring Sym-
posium Series.
Prince, S. A., Adamo, K. B., Hamel, M. E., Hardt, J., Gor-
ber, S. C., and Tremblay, M. (2008). A comparison of
direct versus self-report measures for assessing phys-
ical activity in adults: a systematic review. Interna-
tional Journal of Behavioral Nutrition and Physical
Activity, 5(1):56.
Rijksinstituut voor Volksgezondheid en Milieu (2013).
Welke factoren beinvloeden de kans op diabetes mel-
litus? welke factoren benvloeden de kans op diabetes
mellitus? - nationaal kompas volksgezondheid. http://
www.nationaalkompas.nl/gezondheid-en-ziekte/
ziekten-en-aandoeningen/endocriene-voedings-en-
stofwisselingsziekten-en-immuniteitsstoornissen/
diabetes-mellitus/welke-factoren-beinvloeden-de-
kans-op-diabetes-mellitus. Accessed: 2015, May 21.
Shephard, R. J. (2003). Limits to the measurement of habit-
ual physical activity by questionnaires. British journal
of sports medicine, 37(3):197–206.
Teixeira, P. A., Gordon, P., Camhi, E., and Bakken, S.
(2011). Hiv patients willingness to share personal
health information electronically. Patient education
and counseling, 84(2):e9–e12.
Tirosh, A., Shai, I., Afek, A., Dubnov-Raz, G., Ayalon, N.,
Gordon, B., Derazne, E., Tzur, D., Shamis, A., Vinker,
S., et al. (2011). Adolescent bmi trajectory and risk of
diabetes versus coronary disease. New England Jour-
nal of Medicine, 364(14):1315–1325.
Wei, J.-N., Sung, F.-C., Lin, C.-C., Lin, R.-S., Chiang,
C.-C., and Chuang, L.-M. (2003). National surveil-
lance for type 2 diabetes mellitus in taiwanese chil-
dren. Jama, 290(10):1345–1350.
World Health Organization (2014). Global health estimates:
Deaths by cause, age, sex and country, 2000-2012.
Geneva, WHO.
Xierali, I. M., Hsiao, C.-J., Puffer, J. C., Green, L. A.,
Rinaldo, J. C., Bazemore, A. W., Burke, M. T., and
Phillips, R. L. (2013). The rise of electronic health
record adoption among family physicians. The Annals
of Family Medicine, 11(1):14–19.
Zhang, J. and Zhao, Y. (2013). A user term visualization
analysis based on a social question and answer log.
Information Processing & Management, 49(5):1019–
1048.
BioMed Wizard - An Approach for Gathering Personal Risk Factor Data
305
