
Statistical Characterization, Modelling and Classification of
Morphological Changes in imp Mutant Drosophila Gamma Neurons
A. Razetti
1
, X. Descombes
2
, C. Medioni
3
and F. Besse
3
1
University of Nice Sophia Antipolis, I3S, 2000 Route des Lucioles, Sophia Antipolis, France
2
Inria, CRISAM, 2003 Route des Lucioles, Sophia Antipolis, France
3
Institute of Biology Valrose, University of Nice Sophia Antipolis, Parc Valrose, Nice, France
Keywords: Gamma Neurons, Remodelling, Stochastic Models, Likelihood Analysis.
Abstract: In Drosophila brain, gamma neurons in the mushroom body are involved in higher functions such as olfactory
learning and memory. During metamorphosis, they undergo remodelling after which they adopt their adult
shape. Some mutations alter remodelling and therefore neuronal final morphology, causing behavioural
dysfunctions. The RNA binding protein Imp, for example, was shown to control this remodelling process at
least partly by regulating profilin expression. This work aims at precisely characterizing the morphological
changes observed upon imp knockdown in order to further understand the role of this protein. We develop a
methodological framework that consists in the selection of relevant morphological features, their modelling
and parameter estimation. We thus perform a statistical comparison and a likelihood analysis to quantify
similarities and differences between wild type and mutated neurons. We show that imp mutant neurons can
be classified into two phenotypic groups (called Imp L and Imp Sh) that differ in several morphological
aspects. We also demonstrate that, although Imp L and wild-type neurons show similarities, branch length
distribution is discriminant between these populations. Finally, we study biological samples in which Profilin
was reintroduced in imp mutant neurons, and show that defects in main axon and branch lengths are partially
suppressed.
1 INTRODUCTION
Gamma neurons in Drosophila brain mushroom body
are in charge of high functions such as olfactory
learning and memory (Xie et al., 2013). Mutations
affecting their adult shape cause several behavioural
dysfunctions (Redt-Clouet et al., 2012).
During metamorphosis, gamma neurons go
through a process of pruning –where the main part of
their axons and dendrites is lost– followed by
regrowth, resulting in the establishment of the adult
shape (Williams and Truman, 2005). The
understanding of this process and its main involved
factors is critical to explain why some mutations
cause important changes in the neuron adult
morphology.
This study is focused on the remodelling process,
composed by regrowth and branching after pruning.
The correct development of this process gives rise to
well-formed and functional adult neurons.
Medioni et al. (2014) have shown that the RNA
binding protein Imp is not essential during the initial
axonal growth of gamma neurons, but is necessary
during their remodelling. This work shows that, in
adults, ~50% of imp mutants display shorter axons
than wild types (WT) and fail to reach their target.
Imp mutants also exhibit an overall loss of branch
number and complexity. Molecular and genetic
analysis have further shown that profilin mRNA,
which encodes an actin cytoskeleton regulator
(Verheyen and Cooley, 1994), is a direct and
functional target of Imp and both are key regulators
of the Drosophila gamma neuron axonal remodelling
process, acting on the same molecular pathway.
Interestingly, the overexpression of profilin in imp
mutants partially rescues the main axon length, but
not the branch complexity (
Figure 1). These results
suggest that Imp controls axonal extension during
remodelling by regulating profilin mRNA expression.
However they also suggest that the branching process
may be dependent on the regulation of other Imp
mRNA targets, yet to be identified.
In this paper, we intend to further understand the
role of Imp and the importance of profilin mRNA
Razetti, A., Descombes, X., Medioni, C. and Besse, F.
Statistical Characterization, Modelling and Classification of Morphological Changes in imp Mutant Drosophila Gamma Neurons.
DOI: 10.5220/0005703800630074
In Proceedings of the 9th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies (BIOSTEC 2016) - Volume 3: BIOINFORMATICS, pages 63-74
ISBN: 978-989-758-170-0
Copyright
c
2016 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
63

Figure 1: Representation of the morphology of each one of the groups under study (in order: Wild type, imp mutant and imp
mutant rescued by Profilin). imp mutants are divided into short and long species (named Imp Sh and Imp L respectively) as
both phenotypes are equally observed (Medioni et al., 2014).
expression regulation during remodelling by deeply
analysing the impact of Imp knockdown in neuron
development. To overcome the variability of axonal
projection patterns associated with a given biological
sample, we propose to identify the main features of
adult gamma neuron morphology and quantify their
similarities and differences between WT and mutated
axons using a well-defined statistical framework.
This approach provides both a biological
interpretation and a quantification of resemblance
between biological samples. This framework is
general and can be applied to model and characterize
neuron types.
Because effects of Imp knockdown and rescue
with Profilin can be identified in the main axon as
well as in the branch development or independently,
we consider both structures separately. The four
features we chose are: “main axon length”, “main
axon shape”, “first order branch distribution along the
main axon” and “branch length distribution”. To
measure these features, we segmented a set of images
corresponding to each neuron type to obtain a
numeric tree-shaped skeleton representing the
morphology of each neuron. We then measured the
features values using homemade software. The image
segmentation as well as the measurement of each
feature are described in the following sections.
Neuron morphological automatic classification
has already been addressed in the bibliography. Kong
et al. (2005) proposed an unsupervised clustering of
ganglion cells in the mouse retina by the k-means
algorithm in order to define cell types. They initially
disposed of 26 morphological parameters and found
out that clustering with only three of them was the
most effective way. Guerra et al. (2011) establish the
advantage of applying supervised classification
methods regarding morphological feature based
classification to distinguish between interneurons and
pyramidal cells. They also conclude that reducing the
number of features to an optimal number outperforms
the classical approach of using all the available
information. Lopez-Cruz et al., (2014) built a
consensus Bayesian multinet representing the
opinions of a set of experts regarding the
classification of a pool of neurons. The
morphological parameters chosen by each expert to
make their decisions are not considered. A different
approach was proposed by Mottini et al., (2014)
which consists on classifying different neuron types
by reducing them to trees and calculating a distance,
combining geometrical and topological information.
Nevertheless, the different published approaches
intend to accurately discriminate between different
types of neurons, considering misclassification as a
methodological error and consequently developing
techniques to avoid these cases. However, similarities
between populations are not necessarily to be
excluded as they may reflect the properties of
biological samples and help us in their
characterization. Furthermore, these methods do not
intend to understand which morphological
characteristic is discriminant between different
species. A deeper multi-criteria statistical analysis is
thus required. Our approach thus consists in
developing a probabilistic model for each of the
mentioned features and estimate the associated
parameters. The similarities or dissimilarities
between the populations for each feature are assessed
through statistical tests under null hypothesis and
likelihood classification.
In the next section, we introduce each one of the
features followed by the correspondent model. Next
we present the results of the classification combining
different criteria which allows to finally deduce the
morphological changes induced by the studied
mutations.
BIOINFORMATICS 2016 - 7th International Conference on Bioinformatics Models, Methods and Algorithms
64

2 DATA
2.1 Images
We used 3D images taken with a confocal
microscope. Each set of images show the distal part
of an axonal tree at adult stage (Figure 2). Single
axons are labelled by GFP using the MARCM
technique (Wu and Luo, 2006), which allows to
image a single mutated (or wild type) neuron in a wild
type environment. The database we used for this
study consists of 46 wild type images, 48 imp mutants
and 15 imp mutants rescued by Profilin.
The voxel size varies among the images and is
anisotropic in the Z axis. The voxel length in Z is
between 5 and 12 times its length in X and Y, which
varies from 0.09 to 0.15 µm.
Figure 2: Maximum intensity Z projection showing a wild
type axon (red) and the morphology of the mushroom body
(blue).
2.2 Segmentation
To avoid artificial jumps along the Z axis due to
image anisotropy, we applied a simple quadratic
interpolation algorithm included in FIJI (the open
source image analysis software developed by NIH,
Maryland, USA) (Schindelin et al., 2012).
An automatic segmentation of the images is still
not available in our case due to noisy background and
poorly defined neuron trace. When observing the
images, it can be not trivial even for experts to
determine the correct 3D path followed by main
axons and their branches. Their trajectories can be
very complex as well as non-continuous and difficult
to differentiate from background structures.
Therefore we segmented the images with the open
software Neuromantic (
Myatt et al., 2012
), specially
developed to segment 2 or 3D neurons manually or
semi-automatically. As output we obtain a set of
points along the main axon and branches that we
connect using a Bresenham-inspired 6-connectivity
algorithm. We chose this connectivity to keep further
measurements and models simple. After this process
we obtain a tree-like set of numeric 3D curves that
describe the morphology of each neuron (
Figure 3
).
To ensure all the neurons to be similarly oriented
we rotated the images to align the medial and the
dorsal lobes with the X (horizontal) and Y (vertical)
axis correspondingly. The beginning of each neuron
was considered just before entering the medial lobe.
No further registration was applied to the images, to
avoid axon deformation. Conserved morphology was
preferred rather than more accurate spatial location.
Figure 3: Detail of the Z projected image showed in Figure
2, where the neuron has been segmented (yellow) to obtain
a tree-like set of numeric 3D curves.
2.3 Tree Hierarchy
When studying their morphology it is necessary to
understand how neurons are structured i.e. main axon
and first, second, third (etc.) order branches (the
neuron body and dendrites are not present in the
studied images). To accurately label the paths
forming the tree that represents each neuron, we have
developed an automatic pseudo-recursive algorithm
capable of processing trees of any order. It first takes
the whole tree and labels the selected path as the main
axon, followed by a repeated identical analysis of all
the resulting sub-trees. In each step, the main path is
assigned following the criteria used by experts when
done visually: total length, directionality and sense
coherence. To achieve this, in each step we consider
the points in all the paths between the root and the
leaves of the tree (i.e. the whole axon) or subtree and
calculate their linear regression obtaining a straight
guideline, which will determine directionality and
sense coherence. For each path in the analysed
subtree, a cost function is computed that depends on
the distance between each point in the path and the
guideline (directionality), the parallelism between
them (accounting for the sense coherence) and the
path total length. Finally the path that minimizes this
Statistical Characterization, Modelling and Classification of Morphological Changes in imp Mutant Drosophila Gamma Neurons
65

cost function is selected as main axon in the case of
the whole tree (first step), or main branch in the case
of the different subtrees (Figure 4).
Figure 4: Scheme of the three-hierarchy algorithm. For a
given tree, the guideline is calculated followed by the cost
function for each possible path (1-4). The one that
minimizes it is assigned as main axon (here path 2). The
algorithm is applied recursively to each subtree resulting in
the hierarchy of the entire tree.
3 MODEL DEVELOPMENT
After the segmentation, interpolation in the Z axis and
tree hierarchy algorithm, the neuron skeletons
become a 3D tree made out of unitary segments
described by their round coordinates or pixels. Taking
this simple neuron geometrical description into
account, we define the main features that describe and
discriminate the individuals under study: the main
axon length and sinuosity, as well as the branch
density and length distribution. In the following
sections we describe the probabilistic models for each
feature and compute associated statistical tests under
null hypothesis between the different groups (WT:
wild type neurons that are used as controls, Imp:
neurons with imp knockdown, reported to be
morphologically aberrant in the literature, and Prof
Rescue: imp mutants with an overexpression of
profilin, known to partially suppress the imp
phenotype). Besides, we derive the likelihood of each
model.
3.1 Main Axon Length
The main axon length was measured taking the total
amount of pixels in the corresponding path and
multiplying by the pixel size (µm). The length
distribution was modelled as Gaussian where the
mean and standard deviation for each group (µ
m.a.
,
σ
m.a.
) were calculated from data. We observed the
bimodal behaviour in the Imp group reported by
Medioni et al. (2014) (Figure 5). Therefore, to make
a more accurate modelling of this parameter, we
separated Imp mutant neurons into two groups -
neurons with long axons (Imp L) and neurons with
short axons (Imp Sh)- using the k-means algorithm.
54% of the neurons were assigned to Imp Sh and 46%
to Imp L, consistent with the percentage reported by
Medioni et al. (2014). Figure 5 shows the main axon
length histograms for each group, Imp divided into
Imp L and Imp Sh.
Figure 5: Main axon length distributions for each biological
sample.
To know which groups can be considered to
present significantly different main axon length
measurements, non-parametric Kruskal Wallis tests
were carried out between all the possible pairs of
groups (
Table 1
). We chose this test for the sake of
consistency, as it can be applied to analyse all the
features (independently of each model). For p values
inferior to 5%, we consider that the null hypothesis
that both distributions are the same can be rejected.
Thus, the only pair not presenting a significant
difference is WT and Imp L. It is relevant to highlight
that Prof Rescue distribution lies in between the
distributions for Imp L and Sh and even though more
similar to Imp L, still significantly different.
Table 1: p values from the non-parametric Kruskal Wallis
test comparing the main axon length between the studied
groups.
Imp L Imp Sh Prof Rescue
WT 0.1219 5.0098E-12 0.000144
Imp L 3.2627E-09 0.0013
Imp Sh 2.48E-06
The likelihood of a given neuron n of length
to
belong to a given group is defined by the Normal
probability density function
1
2
3
4
Main axon
First order branches
Second order branches
First order subtrees
Second order subtrees
BIOINFORMATICS 2016 - 7th International Conference on Bioinformatics Models, Methods and Algorithms
66

|∈
|∈
1
.
√
2
.
.
,
(1)
where (
.
,
.
) are the mean and standard
deviation of the main axon length corresponding to
the group X.
3.2 Main Axon Morphology
To define the shape model, we consider as random
variable the unit vector
that accounts for the shift
of the axon tip between t-1 and t. Because we consider
the 6-connectivity and backwards moves are not
allowed, each
can take five different values, as
shown in Figure 6. Assuming the main axon
development follows a second order Markov
property, we have
|
|
,
.
(2)
The morphology model is then completely
defined by the conditional probabilities
|
,
. There are 30 possible
combinations of the two unit vectors [
,
] and
each of these combinations has five possible future
jumps
, giving a total of 150 possible transitions
in t+1, each of them with probability
(conditionally
to [
,
]). The order of the Markov chain was
chosen to combine a discriminative efficiency
between similarly shaped axons and a reasonable
combinatorial to robustly estimate the conditional
probabilities.
Figure 6 presents two basic configurations of a
pair of unit vectors [
,
] and their corresponding
five possible
. The one on the left depicts one of
the six possible cases where the vectors
and
are in line (in this case in the +z direction). The
second configuration exemplifies the 24 cases where
the vectors
and
are not in line.
We estimate the conditional probabilities from
data using the empirical estimator (3), where
#
accounts for the number of times the n
th
configuration of three unit vectors
,
,
]
appears.
#
∑
#
,
1,...,5
0,...,29
(3)
We performed the Kruskal Wallis non-parametric test
between populations for each
,1150. Table
2 shows the amount of parameters
that presents a
p value inferior to 5% between each pair of
populations.
Figure 6: Two examples of three vector (past, present and
future steps) configurations on a 3D 6-connected path. Each
future direction has a probability of occurrence conditioned
by the present and past directions and is numbered from 1
to 150.
Table 2: Number of parameters with p<0.05 for the non-
parametric Kruskal Wallis test.
Imp L Imp Sh Prof Rescue
WT 12 22 28
Imp L 16 19
Imp Sh 14
Regarding the possible two past unit vectors [
,
], the results of the estimation show that all the
groups share the six most frequent configurations,
representing together between 65 and 76% of the
total.
The computation of the Markov chain likelihood
appears to lack of robustness when comparing
populations. This can be explained by the limited
length of the axons in pixels (~1500) and the
combinatorial of the problem (150 conditional
probabilities). Indeed, some of the three vector
configurations, even though with non-zero
probability, may not appear in the learning sample.
When this is the case, if the axon to classify does
present at least one time this configuration the
likelihood becomes zero. This means that the
likelihood is extremely sensible to fluctuations in the
presence of low probable events, which is statistically
inevitable with the size of our data. To overcome this
inconvenience and add robustness to the likelihood
analysis, we consider the 30 probability distributions
|
,
as independent, and define a
multinomial Bernoulli distribution for each possible
value of
given [
,
].
Statistical Characterization, Modelling and Classification of Morphological Changes in imp Mutant Drosophila Gamma Neurons
67
For each neuron n, the likelihood of each group X
according to the shape model of X,
,
,and the
frequencies of appearance of three unit vectors
corresponding to n, #
, is then defined as follows
#
#
|∈
#
#
|∈
|∊X
#
#
#
#
#
#
#
#
#
#
#
#
#
#
#
.
5
1
,
#
(4)
3.3 Branch Density
We propose a model to describe the branching point
distribution independently of the axon length, based
on the biological process of interstitial branch
formation during development. This process can be
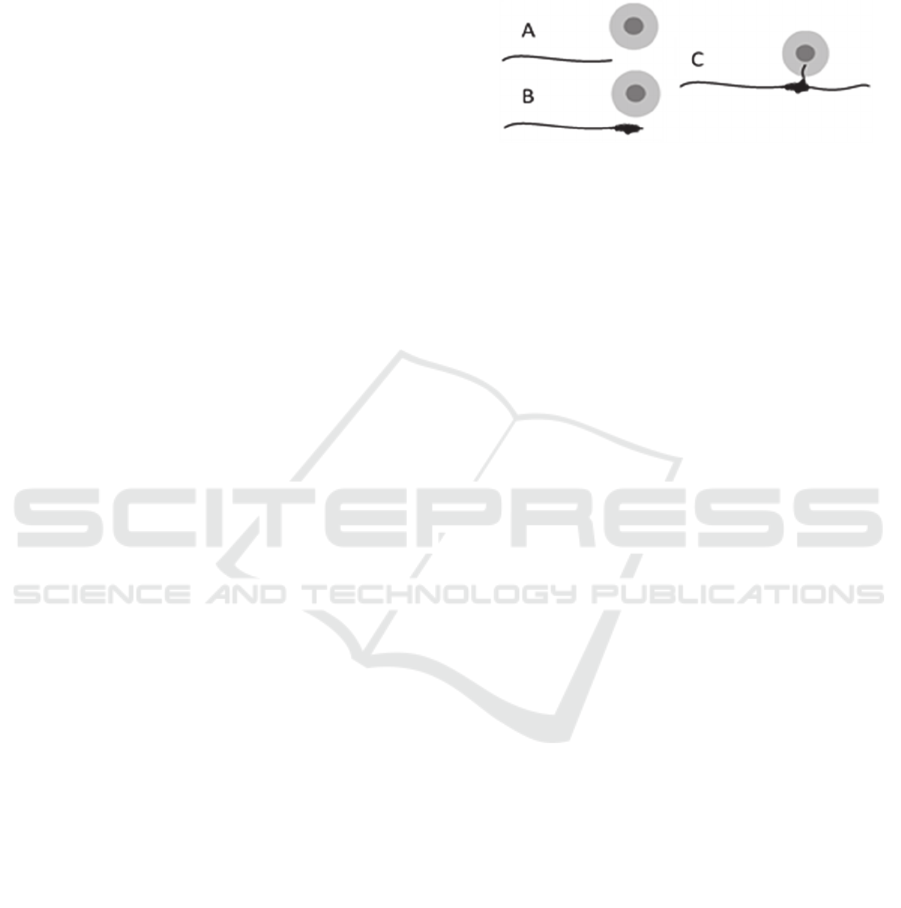
described in three simple steps (Figure 7): A. the main
axon grows following particular external and internal
guiding cues. B. When the growth cone senses
external guiding cues indicating the formation of an
interstitial branch, the main axon decreases its
growing speed until it stops while it accumulates
molecular material in its tip. C. After some time the
main axon continues growing following its particular
cues, leaving the accumulated material in a specific
zone of its shaft. The left material has been organized
into an independent growing tip and starts elongating
an interstitial branch towards its particular target,
different from the one of the main axon (
Szebenyi et
al., 1998
).
In summary, the emergence of an interstitial
branch depends on the presence of specific external
guiding cues that cause the modification of the axon
growing rate, which allows the accumulation of the
molecular material needed for the creation of the new
branch. Modelling this process becomes initially
unreachable as none of this two features (growing
rate, guiding cues presence) can be measured from the
adult stage static images available as data. Regarding
this limitations, we propose a model to mimic this
dynamic process from our static data. We focus our
study on the behaviour of the axon growing rate,
starting with a certain initial speed
and evolving
until 0, when a new branch point appears.
Figure 7: Interstitial branch formation during axonal
development described schematically in three main steps,
adapted from Szebenyi et al. (1998).
We can measure the number k of pixels between
every two successive branching points along the main
axon of a segmented neuron. Then we suppose that
each one of this pixels represents a differential
progress in the axonal growth where, during
development, the axon had a certain growing rate.
Our model assumes random decreases in speed which
we call∆, with a probability of occurrence p. When
a certain number of decreases ∆ occur, the speed
equals zero thus the growing tip stops, allowing the
material needed to form a branch to accumulate. After
some time the process starts again, with initial
speed
.
Because at each one of the k pixels a decrease in
may or not happen, we describe the problem using
a Bernoulli probability distribution (Forbes et al.,
2011) where each success means a differential
decrease in speed. We consider that the growing rate
goes to zero after A+1 steps of speed decreasing. The
probability to reach 0 after k steps is then written
as follows:
1
1
.
(5)
Equation (5) gives the probability of having A
successes in 1 trials and a success in the k
th
trial.
This means the axon tip decreases its speed A times
before stopping completely (which happens in A+1),
or equivalently that the length between two branching
points is k (Figure 8). Thus, our Bernoulli-based,
time-mimicking branching point distribution model
has two parameters, A and p, to be estimated from
data. Knowing the distances k between successive
branching points for every axon in each group, we can
calculate their mean and variance
and
. From
μ
k
1
1
(6)
BIOINFORMATICS 2016 - 7th International Conference on Bioinformatics Models, Methods and Algorithms
68

and
σ
2
k
1
1
μ
k
(7)
it can be shown that μ
k
, and σ
2
k
, have the
simple forms
μ
k
,
,
σ
2
k
,
1
(8)
which allow to easily estimate A and p from data.
Once A and p are estimated, A needs to be rounded as
it has to be an integer. Then p can be recalculated
knowing the value of A as
μ
k
σ
2
k
μ
k
σ
2
k
.
(9)
The number A+1 of needed accumulation of
increments ∆
and p their probability to happen will
define each axonal group regarding their branch
density.
Table 3 and Table 4 present the resulting values
of A and p for each group and the p values from the
non-parametric Kruskal Wallis test of the distances
between two consecutive branches k among neuron
groups, respectively.
While every group has the same value of A, Imp
Sh presents the highest value of p meaning that
∆occurrence is more probable and it takes less time
to reach 0, thus it is the most branched group.
This difference is significant (p<0.05) between Imp
Sh and every other group.
To calculate the likelihood of each neuron n to
belong to the group X regarding this model, we use
the Binomial probability density function considering
the distances between each pair of branches
,
independent between them, obtaining
,
∊X
,
,…,
,
|∊X=
,
∊X
,
1
,
(10)
where M is the total number of pairs of branches.
Figure 8: 2D 4-connected path showing the axonal
trajectory until the formation of a branching point (3D not
shown for simplicity). Pink pixels occur with a probability
p, decreasing the growing rate. When the number of pink
pixels equals A+1,
=0 and a new branching point appears.
Table 3: p values from the non-parametric Kruskal Wallis
test comparing the distances in pixels between consecutive
branches between the studied groups.
Imp L Imp Sh Prof Rescue
WT 0.9398 4.20E-03 0.5704
Imp L 2.16E-02 0.6478
Imp Sh 1.32E-02
Table 4: Value of the parameters A and p describing the
branching points distribution.
A p p for A=1
WT 1.2 0.0087 0.0078
Imp L 1.0 0.0068 0.0067
Imp Sh 0.9 0.008 0.0084
Prof Rescue 1.2 0.0074 0.0068
3.4 Branch Length Distribution
To study the branch length distribution within the
neuron groups, we established four length categories
();
:
0,1
,
:
1,5
,
:
5,10
and
:10,∞
following Tessier and Broadie (2008). The length was
measured in the same way as described for the main
axon, and branches of all levels were taken into
account. For each group of axons we calculated the
mean and standard deviation (µ
bi
, σ
bi
), 1<i<4 of the
relative number of branches corresponding to each
length category per axon b
1
-b
4
(i.e. number of
branches in each length category normalized by the
total number of branches, per axon).
The percentage of branches in each category is
shown in Table 5.
To know between which groups and length
category the differences in the results displayed in
Table 5 are significant we performed the Kruskal
Wallis non-parametric test for the four length groups.
Significant results (p<0.05) are only present in
Statistical Characterization, Modelling and Classification of Morphological Changes in imp Mutant Drosophila Gamma Neurons
69

and
. The p values are shown in Table 6 and
Table 7.
Table 5: Branch length distribution by length and neuron
group (%).
WT 10.6 49.2 11.7 28.5
Imp L 8.4 66.5 10.1 15
Imp Sh 19.8 48.2 14.5 17.5
Prof Rescue 19.5 48.3 10.2 22
Table 6: p values from the non-parametric Kruskal Wallis
test comparing the branch length distribution in
between
the studied groups.
Imp L Imp Sh Prof Rescue
WT 8.92E-05 0.9392 0.7884
Imp L 9.04E-04 0.0014
Imp Sh 0.9134
Table 7: p values from the non-parametric Kruskal Wallis
test comparing the branch length distribution in
between
the studied groups.
Imp L Imp Sh Prof Rescue
WT 3.45E-04 1.29E-04 0.1822
Imp L 0.7383 0.1238
Imp Sh 0.1387
Imp L presents significantly more branches in
than any other group while WT has a bigger
proportion of
branches than Imp L and Sh, but not
Prof Rescue. For further analysis we take the
categories
and
.The distribution modelling the
relative amount of branches within these length
categories and for each group was considered as
Gaussian.
To calculate the likelihood of each neuron n with
each group X regarding the branch length distribution
in
and
-
,
and
,
- we considered a bivariate
Gaussian distribution with mean
,
andΣ
the covariance matrix between
and
.
|∊X
|∊X
1
2
|
Σ
|
,
(11)
where
|
Σ
|
is the determinant of the covariance
matrix Σ
.
4 LIKELIHOOD ANALYSIS
For a neuron n, we calculate the corresponding
features and then compute the likelihood for each
group of neurons X, (X∊WT,Imp,ProfRescue}).
The neuron n is then classified in the group that
maximizes the global likelihood. All the
classifications present in this work were done using
the leave one out technique, which consists in
classifying a sample that has been removed from the
database to perform the learning stage, i.e. the
estimation of the distribution parameters. This
maximum likelihood classification provides some
assessment about the discriminative properties of the
proposed models but is also used to analyse the
mixture of feature values between the populations.
Considering our four features to be independent
from each other, the global likelihood is given as
follows
,#
,
#
,
,
,
∊X
|
∊X
#
,
#
,
∊X
|
∊X
∊X,
(12)
and the maximum likelihood estimation results
∊X
↔X
argmax
,#
,
#
,
,
,
∊X
X
WT,ImpL,ImpSh,Pro
f
Rescue
.
(13)
Equation (13) allows to classify each neuron by
resemblance to each group considering the four
morphological features and their mathematical
models. Table 8 presents the results of the general
resemblance analysis.
Table 8: General likelihood analysis considering the four
features. Imp L and Imp Sh reconsidered separately.
Predicted (%)
WT Imp L Imp Sh
Actual Class
WT 82.6 17.4 0
Imp L 54.5 45.5 0
Imp Sh 19.2 3.9 76.9
This results suggest a relevant difference between
neurons belonging to Imp L and Imp Sh, as well as
between WT and Imp Sh. More than half of Imp L are
likely to be WT while for Imp Sh this propotion is less
than 20%.
BIOINFORMATICS 2016 - 7th International Conference on Bioinformatics Models, Methods and Algorithms
70
To understand how each morphological feature
contributes to the results in Table 8, we carried out
the likelihood analysis regarding each of them
separately. For the main axon length, as expected
from Figure 5, WT neurons are shared between WT
and Imp L; and Imp L is correspondingly mixed with
WT. Imp Sh is completely separated from the rest of
the groups (
Table 9).
Table 9: Likelihood analysis according to main axon length.
L
Predicted (%)
WT Imp L Imp Sh
Actual Class
WT 39.1 54.4 6.5
Imp L 22.7 77.3 0
Imp Sh 0 0 100
According to the main axon shape in Table 10,
WT and Imp L look again similar and, interestingly,
Imp Sh looks more similar to WT than to Imp L.
Table 10: Likelihood analysis according main axon shape.
SH Predicted (%)
WT Imp L Imp Sh
Actual Class
WT 54.3 43.5 2.2
Imp L 50 50 0
Imp Sh
61.5 38.5 0
Table 11 presents the likelihood analysis results
regarding the branch point density. It can be noticed
that every group is mainly classified as Imp Sh, which
our previous analysis revealed as the most branched
group. The reason for this behaviour relies on the
nature of the model. Even though the means of the
distances between branches are different between the
biological groups, axons frequently display one or
more pairs of branches which are close. Because for
close branches the likelihood is maximum for Imp Sh,
with a significant difference from the other groups,
the presence of near branches automatically classifies
a neuron as Imp Sh. Nevertheless, the branch density
coherence is respected for each group as the
resemblance with Imp Sh is maximum for the most
branched group (itself) and is followed in the correct
order: WT and then Imp L.
Finally, according to the branch length
distribution (Table 12) WT, Imp L and Imp Sh show
a higher likelihood to their own groups, suggesting a
significant difference between them regarding this
feature.
Table 11: Likelihood analysis according branching point.
BP
Predicted (%)
WT Imp L Imp Sh
Actual Class
WT 0 13 87
Imp L 13.6 18.2 68.2
Imp Sh 7.7 11.5 80.8
Table 12: Likelihood analysis according branch length
distribution.
BL Predicted (%)
WT Imp L Imp Sh
Actual Class
WT 60.9 23.9 15.2
Imp L 18.2 72.7 9.1
Imp Sh 15.4 30.8 53.8
In order to analyse the morphological changes
induced by profilin recue, we performed the general
likelihood analysis considering either imp mutants
altogether (
Table 13), or split between Imp L and Imp
Sh (
Table 14). We have already shown in the previous
section that Prof Rescue presents i) an histogram in
between that one of Imp L and Imp Sh regarding the
main axon length, ii) no significant difference with
WT nor Imp L (but with Imp Sh) regarding branching
point density and ii) it is the only group to present no
significant differences with WT regarding the
branching length distribution.
Table 13: General likelihood analysis considering the four
features. Prof. Rescue is included.
Predicted (%)
WT Imp
Actual Class
WT 80.4 19.6
Imp 37.5 62.5
Prof Rescue 60 40
Table 14: General likelihood analysis considering the four
features. Imp L and Imp Sh reconsidered separately and
Prof. Rescue is included.
Predicted (%)
WT Imp L Imp Sh
Actual Class
WT 82.6 17.4 0
Imp 35.5 23 41.5
Prof Rescue 40 26.7 33.3
Statistical Characterization, Modelling and Classification of Morphological Changes in imp Mutant Drosophila Gamma Neurons
71

From the analysis in Table 13 we can highlight
that while only 37.5% of imp mutants present a WT
phenotype, the 60% of Profilin rescue neurons exhibit
this behaviour. A deeper study, considering the
subdivision of imp mutants in Imp Sh and Imp L
(Table 14), shows that 40% of neurons in Prof Rescue
present WT phenotype compared to 35% for Imp.
Moreover, it is interesting to analyse how Prof Rescue
is classified regarding Imp L and Imp Sh. The
percentage of neurons classified as Imp Sh decreases
compared to imp mutants from 41 to 33% while the
tendency for Imp L is inversed, with 23% for Imp and
27% for Prof Rescue. We have also performed the
likelihood analysis for Prof Rescue considering each
feature separately, and observed that Prof Rescue
presents 33% of short main axons compared to 54%
in imp mutants, and a likelihood towards WT
regarding the branch length distribution of 33%,
which is around two times that of Imp L and Imp Sh.
Finally a brief comparison can be done regarding
the classification results with those in Mottini et al.
(2013), who analysed wild type as well as imp
mutated gamma neurons. The authors report an 80.4
and 91.7% of accurate classifications for WT and imp
mutants respectively with the ESA curve distance
method and 85 and 79.2% with RTED. It is relevant
to highlight that the goal in their work is to merely
discriminate between populations, thus they privilege
to consider exclusively highly discriminative
parameters. On the contrary, our results -80.4 and
62.5% for WT and Imp respectively- aim to show and
value not only the differences but also the existing
similarities between phenotypes, considering relevant
morphological features and link the conclusions with
biological parameters. Finally, our sample size
doubles the one used in the cited work.
5 DISCUSSION
5.1 Axon Growing Rate and Branch
Formation
The value of A=1 indicates that the axon tip
diminishes its growing speed only two times before
stopping to create a branch, instead of doing it
gradually. The first time can be related to when it
senses the external guiding cues. Then it continues
growing more slowly, which may facilitate other cues
detection, until it finally stops, consequence of the
second and last speed lost. When this happens,
branching material is accumulated and after some
time an interstitial branch is created. An increased
value of p may indicate a higher sensibility to external
cues as well as the presence of aberrantly stronger
internal cues triggering branching. Another
interpretation can be that axons with a defective
growing rate (i.e. slower speed, or high p) are more
susceptible to stop independently from external cues,
and therefore to branch more.
All the groups present the same value of A
indicating this two-step behaviour may be conserved
and therefore independent from Imp. Regarding p,
Imp Sh is significantly more branched than the rest of
the groups, including Imp L, even though they have
the same genotype. We suggest a correlation between
the size of the main axon and the branch density for
imp mutants. More interestingly, Profilin rescue
axons present the same value of p than Imp L. This
suggests that the phenotype presenting an aberrant
branch density is rescued by profilin overexpression
(or, in other words, is back to wild type branch
density).
5.2 Wild Type Neurons Are
Characterized by Their Branch
Length Distribution
The general likelihood analysis results in more than
80% of WT axons to be correctly classified (Table 8,
Table 13 and Table 14). Nevertheless, when looking
at each particular feature it becomes evident that WT
shares most of them with Imp L. Regarding the main
axon length (
Table 9), 54% of WT neurons are likely
to be Imp L and 43% for the main axon shape (Table
10). The analysis following the branching point
density results in 13% of WT neurons likely to be Imp
L, while no WT neuron was correctly classified. This
results are validated by the p values for main axon
length and branch length distribution that do not show
significant differences. We encounter a similar
situation regarding the shape model, as between Imp
L and WT the amount of significantly different
parameters is the minimum of all the group pairs and
it is only 12 in 150.
Regarding the likelihood analysis taking branch
length distribution, WT is well defined (Table 12).
WT and Imp L present both 80% of branches in
and
(Table 5), with the difference that WT
shows statistically more branches in
while Imp L
in
. We can relate our results to those of Tessier and
Broadie (2008) and Medioni et al. (2014). The first
publication reports that a loss of
branches by a late
pruning process occurs in wild type neurons and not
in dFMRP mutants (dFMRP is also a profiling
regulator) and the second one concludes a defective
development of long branches (
) in imp mutants.
BIOINFORMATICS 2016 - 7th International Conference on Bioinformatics Models, Methods and Algorithms
72

The maximal percentage of correct classification
for WT considering the features separately is 60% for
the branch length distribution (Table 12), followed by
54, 39 and even 0% corresponding to main axon
shape, length and branching point distribution (Table
10,
Table 9 and Table 11). Interestingly, the general
classification mixing the four features improves these
percentages up to 80% (Table 8, Table 13 and Table
14). This suggests that WT neurons are well defined
and different from Imp mutants but it is necessary to
consider all the morphological features together. This
highlights the advantages of our method as it goes
beyond a simple statistical analysis, allowing to mix
different features as well as to consider each neuron
independently.
5.3 imp Knockdown Presents Two
Different Phenotypes
It has already been reported by Medioni et al. (2014)
that imp mutants could either present a conserved
main axon length or an aberrant one, with a 50% of
occurrence each. We corroborate this results by
applying the k-means automatic algorithm which
separated our Imp population in Imp L and Imp Sh,
with a 46 vs. 54% of incidence each. This bimodal
behaviour can also be seen in the length distribution
Figure 5. Surprisingly, we have found other relevant
morphological differences between this two groups
that have not been yet reported in the bibliography.
The main one is the branching points distribution, as
Imp Sh is significantly more densely branched than
Imp L (Table 3 and Table 4). Also, the percentage of
branches ranging from 1 to 5 µm, while aberrant in
Imp L, is conserved in Imp Sh (which shows no
differences from WT (Table 6)).
Regarding the general likelihood analysis (Table
8), while less than 20% of Imp Sh neurons can be
considered to have a WT phenotype, 55% of Imp L
do, allowing to conclude that Imp L presents a
generally more wild type phenotype. Finally, we can
conclude that the penetrance of the phenotype is
~63%, following our general likelihood analysis
(Table 13 and Table 14).
5.4 Adding Back Profilin Rescues the
Main Axon Length and the Branch
Length Distribution
The general likelihood analysis (Table 13)
considering Imp altogether shows that Profilin
decreases the percentage of imp mutant phenotype
from 63 to 40%.
Regarding the main axon length, while the
aberrant neurons represent the 54% of the Imp
population, they are reduced to only 33% in Prof
Rescue (in Prof Rescue 67% of neurons present a
conserved length (WT + Imp L) and only 33% do
not). Following the branch length distribution
resemblance analysis, 33% of Prof Rescue neurons
are classified as WT and represent the second
maximum percentage after WT itself (only 18 and
15% correspond to Imp L and Sh, respectively).
Looking at the p values between branch length
categories (Table 6 and Table 7), we can conclude
that Profilin rescues the late pruning showing a
conserved percentage of
branches and also allows
to develop long branches. Even though the percentage
of branches in
is slightly smaller for Prof Rescue
than WT (Table 5), this difference does not come out
as significant in the statistical tests, suggesting a
conserved percentage of long branches in Prof Rescue
which is not seen in Imp Sh nor in Imp L.
Finally, regarding the general likelihood analysis
considering Imp L and Imp Sh separately (Table 14),
we conclude that Profilin rescue diminishes the
general morphological aberration, as it moves the
tendency towards WT and Imp L phenotypes and
diminishing the percentage of neurons with an Imp Sh
phenotype.
6 CONCLUSIONS
In this work we proposed probabilistic models
describing the behaviour of relevant morphological
features (i.e. main axon length and shape as well as
branch length and density) in Drosophila gamma
neurons. This approach allows to accurately describe
as well as differentiate genetically different
Drosophila gamma neurons considering their
morphology. The similarities and differences we are
able to enunciate thanks to this work between wild
type neurons and the studied mutants directly help to
the understanding of the role of Imp and Profilin
during axonal remodelling, particularly on axon
elongation and branch formation.
We propose that this method consisting in feature
selection, model application and likelihood analysis
could be applied to any case of study between species
where similarities are as important as differences. We
can also conclude that the study of individuals is
relevant and more enriching than just population
analysis driven by ordinary statistics.
Statistical Characterization, Modelling and Classification of Morphological Changes in imp Mutant Drosophila Gamma Neurons
73

ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was supported by the French Government
(National Research Agency, ANR) through the «
Investments for the Future » LABEX SIGNALIFE:
program reference # ANR-11-LABX-0028-01.
All the authors are within Morpheme (a joint team
between Inria CRI-SAM, I3S and IBV).
REFERENCES
Forbes, C., Evans, M., Hastings, N., and Peacock, B.,
2011. Statistical distributions, John Wiley & Sons, 4
th
edition.
Guerra, L., McGarry, L. M., Robles, V., Bielza, C.,
Larranaga, P., & Yuste, R., 2011. Comparison between
supervised and unsupervised classifications of neuronal
cell types: a case study. Developmental
neurobiology, 71(1), 71-82.
Keller, M.T. and Trotter, W.T., 2015. Applied
Combinatorics. Georgia Institute of Technology,
Preliminary Edition.
Kemeny, J. G., and Snell, J. L., 1960. Finite markov chains,
vol. 356. van Nostrand, 1
st
edition.
Kong, J. H., Fish, D. R., Rockhill, R. L., and Masland, R.
H., 2005. Diversity of ganglion cells in the mouse
retina: unsupervised morphological classification and
its limits. J. of Comp. Neurology, 489(3), 293-310.
López-Cruz, P. L., Larrañaga, P., DeFelipe, J., and Bielza,
C., 2014. Bayesian network modeling of the consensus
between experts: An application to neuron
classification. Int. J. of Approx. Reasoning, 55(1), 3-22.
Luo, L., 2002. Actin cytoskeleton regulation in neuronal
morphogenesis and structural plasticity. Annual review
of cell and developmental biology, 18(1), 601-635.
Medioni, C., Ramialison, M., Ephrussi, A., and Besse, F.,
2014. Imp promotes axonal remodeling by regulating
profilin mRNA during brain development. Current
Biology, 24(7), 793-800.
Mottini, A., Descombes, X., and Besse, F., 2013. Tree-like
shapes distance using the elastic shape analysis
framework. In British Machine Vision Conference.
Mottini, A., Descombes, X., Besse, F., and Pechersky, E.,
2014. Discrete stochastic model for the generation of
axonal trees. In EMBS, 6814-6817.
Mottini A, Descombes X., and Besse F., 2014. From Curves
to Trees: A Tree-like Shapes Distance Using the Elastic
Shape Analysis Framework. Neuroinformatics, 13,
175–191.
Myatt, D. R., Hadlington, T., Ascoli, G. A., and Nasuto, S.
J., 2012. Neuromantic–from semi-manual to semi-
automatic reconstruction of neuron
morphology. Frontiers in neuroinformatics, 6.
RedtClouet, C et al., 2012. Mushroom body neuronal
remodelling is necessary for shortterm but not for
longterm courtship memory in Drosophila. European
Journal of Neuroscience, 35(11), 1684-1691.
Schindelin, J et al, 2012. Fiji: an open-source platform for
biological-image analysis. Nature meth.9(7), 676-682.
Schlüter, K., Jockusch, B. M., and Rothkegel, M., 1997.
Profilins as regulators of actin dynamics. Biochimica et
Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Molecular Cell
Research, 1359(2), 97-109.
Szebenyi, G., Callaway, J. L., Dent, E. W., and Kalil, K.,
1998. Interstitial branches develop from active regions
of the axon demarcated by the primary growth cone
during pausing behaviours. The Journal of
neuroscience, 18(19), 7930-7940.
Tessier, C. R., and Broadie, K., 2008. Drosophila fragile X
mental retardation protein developmentally regulates
activity-dependent axon pruning. Development, 135(8),
1547-1557.
Verheyen, E. M., and Cooley, L., 1994. Profilin mutations
disrupt multiple actin-dependent processes during
Drosophila development. Development, 120(4), 717-
728.
Williams, D. W., and Truman, J. W., 2005. Remodeling
dendrites during insect metamorphosis. Journal of
neurobiology, 64(1), 24-33.
Wu, J. S., and Luo, L., 2006. A protocol for mosaic analysis
with a repressible cell marker (MARCM) in
Drosophila. Nature protocols, 1(6), 2583-2589.
Xie, Z., Huang, C., Ci, B., Wang, L., and Zhong, Y., 2013.
Requirement of the combination of mushroom body γ
lobe and α/β lobes for the retrieval of both aversive and
appetitive early memories in Drosophila. Learning &
Memory,20(9), 474-481.
BIOINFORMATICS 2016 - 7th International Conference on Bioinformatics Models, Methods and Algorithms
74
