
Comparison of a Sensorized Garment and Activity Trackers with a
Mobile Ergospirometry System Concerning Energy Expenditure
Sven Feilner
1
, Andreas Huber
1
, Christian Sauter
1
, Dirk Weish
¨
aupl
2
, Michael Hettchen
2
,
Wolfgang Kemmler
2
, Christian Weigand
1
and Christian Hofmann
1
1
Fraunhofer Institute for Integrated Circuits IIS, Erlangen, Germany
2
Institute of Medical Physics IMP, Friedrich-Alexander-University Erlangen-Nuremberg, Erlangen, Germany
Keywords:
Energy Expenditure, Ergospirometry, Wearable Sensors, Activity Tracking, Heart Rate, Respiration Rate,
Accelerometry.
Abstract:
Energy expenditure is an important parameter during the performance of physical activity. An algorithm
is presented calculating the burnt calories by three given parameters: heart rate, respiration rate and move-
ment. These three vital parameters are provided by the FitnessSHIRT system which was developed by the
Fraunhofer IIS. A study was performed to compare the calculated values of the energy expenditure with a
reference system based on ergospirometry, an on-body monitoring system and two commercially available
activity trackers. Compared to the reference system the developed algorithm, based on the parameters derived
by the FitnessSHIRT, reaches a deviation of 18.0 % during running and 18.9 % during cycling.
1 MOTIVATION
Obesity and overweight are a big challenge for fu-
ture’s society and the resulting consequences con-
cerning health (WHO, 2015). For affected people
the knowledge about their actual energy expenditure
(EE), indicated in kcal/h is a significant parameter.
Moreover this is what people motivates to quantify
themself (Nißen, 2013).
The measurement of a person’s physical effort is
often performed by using lookup tables (Kent, 1997).
Based on these tables athletes are able to estimate
their energy expenditure on the basis of parameters
like body height, body weight and their performed ac-
tivity. As only a few parameters are considered, the
lookup table just provides a rough estimation of the
EE by a specific athlete. Another disadvantage is the
increased demand for memory space.
The gold standard for the measurement of EE is
the doubly labelled water method based on the carbon
metabolism in the human body (Mueller et al., 2010).
This method is, due to its complexity, often not ap-
plicable in practice, e.g. in the field of exercise phys-
iology. Therefore, the most widespread method for
measuring the EE is the ergospirometry (ESM) based
on the indirect calorimetry (Mueller et al., 2010).
Thereby, the breathing gases of athletes are analyzed
for the estimation of the EE by applying a breathing
mask. Hence the ESM is nowadays mobile applica-
ble, the uncomfortable mask and the high costs make
it unattractive for the usage in mass sports. However,
ESM was used in this study as the reference method.
Several in the market available fitness trackers
promise a reliable measurement of the EE. Most of
these devices are either worn on the wrist or on the
hip whereby an integrated accelerometer detects the
movement of the user. Some of them also measure
the heart rate (HR) by an optical sensor and additional
personal information like age, gender, body weight
and height of the user has to be entered. Out of all
these parameters an estimation of the EE is calculated,
e.g. after a training session.
The FitnessSHIRT system is a development of the
Fraunhofer Institute for Integrated Circuits IIS (Hof-
mann, 2015). It provides a comfortable, longterm
and accurate measurement of heart activity, respira-
tion and movement of the user.
In this work an algorithm for the calculation of
the EE, based on the parameters measured with the
FitnessSHIRT, was developed. The quality of the al-
gorithm has been evaluated by comparison to the EE
values gained by the ESM and commercially available
fitness trackers.
232
Feilner, S., Huber, A., Sauter, C., Weishäupl, D., Hettchen, M., Kemmler, W., Weigand, C. and Hofmann, C.
Comparison of a Sensorized Garment and Activity Trackers with a Mobile Ergospirometr y System Concerning Energy Expenditure.
DOI: 10.5220/0005707502320238
In Proceedings of the 9th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies (BIOSTEC 2016) - Volume 4: BIOSIGNALS, pages 232-238
ISBN: 978-989-758-170-0
Copyright
c
2016 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
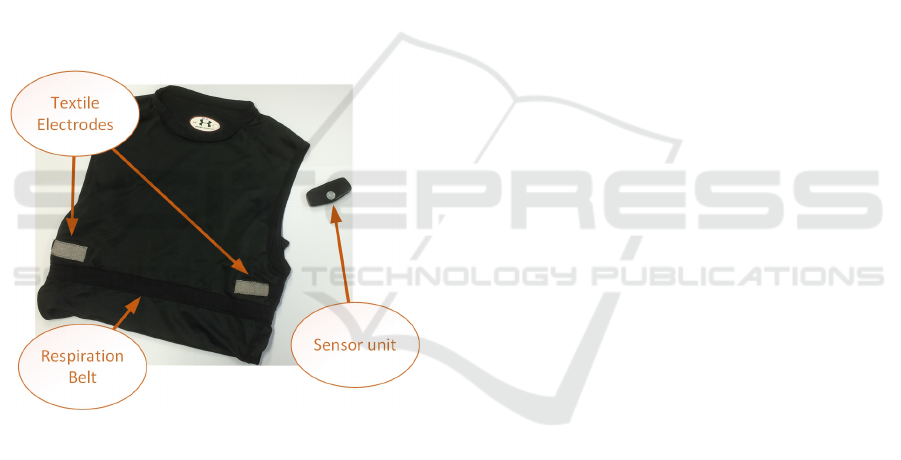

2 SYSTEMS
2.1 Fraunhofer FitnessSHIRT
The FitnessSHIRT, a development by the Fraunhofer
IIS, is a textile with unobtrusive integrated sensors for
measuring a 1-channel ECG and the thoracic move-
ment of the chest to determine the respiration fre-
quency (Figure 1). Therefore, two conductive textile
electrodes and a flexible respiration belt were inte-
grated into a compression shirt. An attachable sensor
unit, either applied in the chest region or between the
shoulders, gathers the sensors raw data. Based on this
raw data reliable and stable algorithms calculate sec-
ondary parameters like heart rate (HR), heart rate vari-
ability (HRV) and respiration rate (RR). Additionally,
an integrated accelerometer records the movement of
the wearer. By means of the acceleration data an im-
plemented algorithm detects movement patterns like
walking or running as well as the person’s posture.
Figure 1: Fraunhofer FitnessSHIRT.
2.2 CareFusion Oxycon Mobile
The mobile ergospirometry, a diagnostic method to
measure the composition of the breathing gases dur-
ing physical strain, is enabled by the Oxycon Mo-
bile (CareFusion, 2015). The behaviour of the cardio-
vascular system, heart activity, breathing performance
and metabolism as well as cardiopulmonary capabil-
ity is analyzed in a qualitative and quantitative man-
ner. As this method is classified as a gold standard for
measuring EE it provides the reference data.
The entire system consists of a shoulder belt with
applied O
2
/CO
2
analyzers and a transmitter, a teleme-
try unit (receiver) with calibration module, a breath-
ing mask with TripleV-Sensor and a chest sensor strap
to measure the heart rate.
With the aid of the associated software application
the acquired data can be depicted instantly and saved
for a more detailed post analysis.
2.3 BodyMedia SenseWear
The SenseWear MF armband by BodyMedia (Body-
Media, 2015) is applied to the left upper arm, so
that the electrodes are directly applied on the wear-
ers skin. By means of the integrated sensors motion,
steps, galvanic skin response, skin temperature and
heat flux is detected. Based on the gained data and
an integrated algorithm the system calculates the EE
(kcal/min) over a given time.
2.4 FitBit Flex and FitBit One
The FitBit Flex and the FitBit One are two activity
trackers to monitor and record the all-day activity by
tracking steps and estimating the burned calories (Fit-
Bit, 2015). Therefore, both trackers have an inte-
grated 3-axis accelerometer. Additionally the FitBit
One provides an altimeter to calculate the taken steps
or stairclimbs.
3 METHODS
In total 13 male test persons aged between 19 and 51
years participated in the trial (see Table 2). The group
had a mean age of 33.9 years (standard deviation σ
= 9.9 years), an average body height of 181.0 cm (σ
= 6.0 cm) and a mean weight of 83.9 kg (σ = 11.1
kg). The body mass index (BMI) was calculated with
25.5 kg/m
2
(σ = 2.5 kg/m
2
) with an average body fat
percentage of 16.5 % (σ = 6.3 %).
In order to generate valid data packages the 13
subjects had to perform the following test run. The
first step was to analyze the body composition with
the aid of the InBody 770 body composition analyzer
(InBody, 2015). The measurement systems were ap-
plied to the subjects in the following order:
• Heart rate sensor strap Polar H7 (heart rate data
used by Oxycon Mobile)
• FitnessSHIRT with correct size to achieve good
skin contact
• Activity tracking modules FitBit Flex (wrist) and
FitBit One (collar of shirt)
• SenseWear MF armband (left upper arm)
• CareFusion Oxycon Mobile
The complete application of the systems can be
seen in Figure 2.
Comparison of a Sensorized Garment and Activity Trackers with a Mobile Ergospirometry System Concerning Energy Expenditure
233
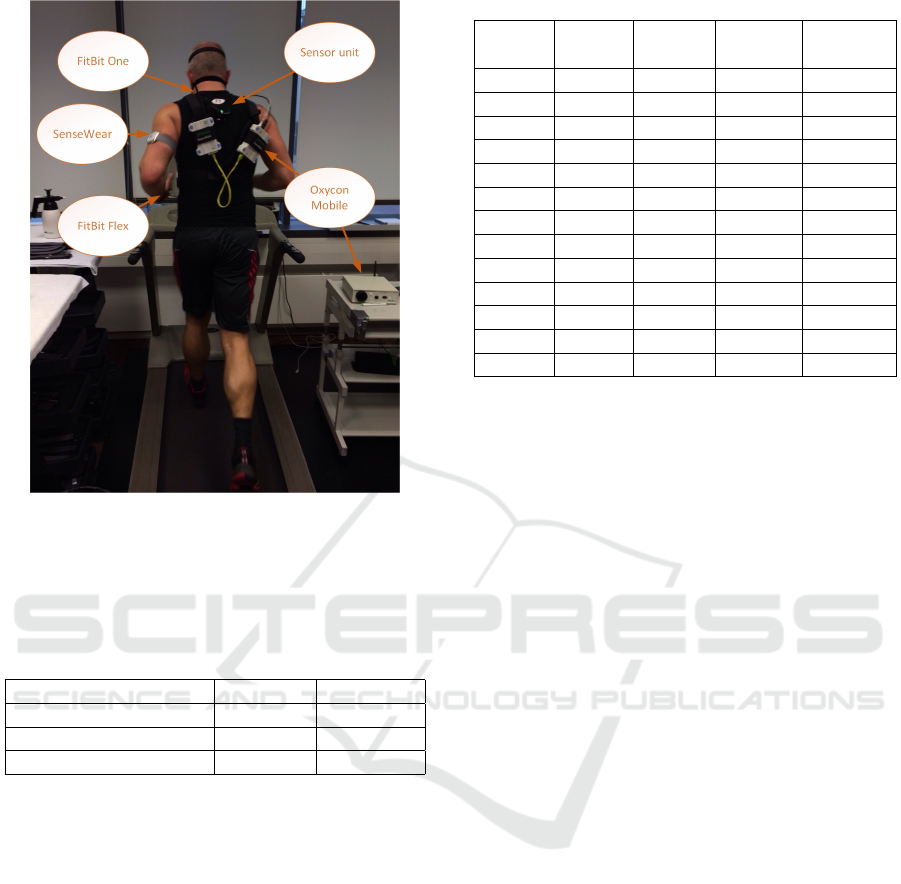
Figure 2: Overview of all applied systems used in the trial.
Two test scenarios had to be fulfilled during the
trial by each subject, one incremental step test on the
treadmill and one on the cycle ergometer. The given
test protocols are presented in Table 1.
Table 1: Procedure of incremental step tests.
Treadmill Ergometer
Starting load 10 km/h 130 Watt
Duration of first period 5 min 3 min
Increase (every 3 min) 1 km/h 30 Watt
The test run starts at 10 km/h (treadmill) and 130
Watt (ergometer), respectively. In contrast to the
treadmill with a starting interval of 5 minutes the first
period on the cycle ergometer takes 3 minutes. Sub-
sequently, every 3 minutes the load was increased by
1 km/h on the treadmill and by 30 Watt on the cy-
cle ergometer. The pedal frequency was defined to 70
1/min constantly throughout the whole test.
Each data sample was stored in pseudonymous
form to assure the security of the personal data of the
subjects.
4 ALGORITHM DEVELOPMENT
4.1 Idea
The main idea of the algorithm was to show an im-
provement by using three measured parameters com-
Table 2: Overview test group.
Age Height Weight BMI Body fat
[years] [cm] [kg] [kg/m
2
] [%]
37 177 76.7 24.5 17.0
51 177 73.4 23.4 13.9
34 190 98.5 27.3 23.0
37 194 96.8 25.7 20.3
46 177 90.2 28.8 28.3
19 182 65.6 19.8 8.1
19 180 84.1 26.0 10.1
26 173 72.5 24.2 9.9
27 180 82.4 25.4 12.9
33 181 93.8 28.6 24.7
46 186 98.0 28.3 19.6
36 181 85.3 26.0 14.8
30 175 72.8 23.9 11.6
pared to standard methods measuring only one pa-
rameter. Since our system is able to record respira-
tion, heart activity (ECG) and movement (accelera-
tion), which are all related to the energy usage of the
body, an algorithm considering all these parameters
was developed. This results in several advantages: If
one parameter does not provide reliable data (e.g. no
data at all or implausible data), a backup is still given
and can use the other two parameters. The different
parameters can also be weighted based on the plausi-
bility.
4.2 Preprocessing
Based on these ideas the raw data of three sensors as
well as a reference system are used to develop the fol-
lowing algorithm using MATLAB.
4.2.1 Interval of Energy Values
The reference system gives one energy value per
minute. Therefore this frequency is the reference for
the estimated energy values.
4.2.2 Electrocardiogram
A complete ECG is recorded. In a first step the RR
intervals are detected and this data is used to calculate
the heart rate (Tantinger et al., 2012). Then the data
set is divided in parts with a duration of one minute.
Each part is sorted and the highest 20 % and the low-
est 20 % of the values are removed to ensure that no
extreme values are influencing out results. An aver-
age of the remaining 60 % is used as a representative
value for each minute. This representative value is
used for further calculations.
BIOSIGNALS 2016 - 9th International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
234

4.2.3 Respiration
Again raw data is available representing a complete
curve. In a first step the respiration rate is detected and
after that the same ideas as described above for the
ECG will be used: Divide the data into one-minute-
blocks, remove extreme values and average the re-
maining 60 % for getting a representative value. This
representative respiration rate value is used for further
calculations.
4.2.4 Movement
The sensor records three axis of acceleration. An
intensity-value was calculated, which represents how
much movement and accelerations influenced the sig-
nal. Since only one axe had a relevant correlation
of 0.48 with the reference values, this axe was used.
Again a representative value was gained by averaging
with a FIR-Filter and extracting one value per minute
from the filtered signal.
4.3 Calculating Energy Values
There are three values for each minute: An average
heart rate, an average respiration rate and a movement
intensity representative. The heart rate and the res-
piration rate can both be used as an important input
value for energy estimation. Both formulas are based
on the same idea to transport oxygen by breathing into
the lungs and this oxygen will be transported by the
blood through the body. Depending on the amount of
used energy, the oxygen usage of the body changes
which also results in a change of respiration rate and
heart rate. An additional effect was considered, about
the body using the oxygen more efficient if higher
amounts of oxygen are needed.
Therefore the formula for both parameters is
based on the same core formulas:
EE = O
2
· EF ·
E
O
2
(1)
EE: estimated energy [kcal]
O
2
: amount of oxygen transported through the
body calculated in the following formulas [ml]
EF: efficiency-factor based on heart rate
E
O
2
: energy per oxygen can be calculated from
chemical formulas [kcal/ml]
Now we distinguished between respiration and
the heart rate to get two values for the used oxygen.
Based on the respiration rate we get the following for-
mula:
O
2
= O
2IN
− O
2OUT
= RR · LV · ∆O
2%
(2)
O
2
: oxygen used by the body [ml]
O
2IN
: oxygen in the air coming into the body
[ml]
O
2OUT
: oxygen in the air coming out of the
body [ml]
RR: respiration rate [1/min]
LV: lung volume [ml]
∆O
2%
: difference between the amount of
oxygen, when breathing in and out. Usually
the difference is 5 % (the amount of oxygen is
reduced from 21 % to 16 % when breathing)
The formula for the heart rate is similar:
O
2
= B ·
O
2
B
= HR · HBV ·
O
2
B
(3)
O
2
: oxygen used by the body [ml]
B: amount of blood transported through the
body [ml]
O
2
B
: amount of oxygen that can be transported
in the blood [ml/ml]
HR: number of heart beats [1/min]
HBV: heart beat volume, the amount of blood
that is transported with each beat [ml]
In a first approach, the following assumptions
were made:
• The HBV was assumed constant as well as the LV
(both were calibrated with a subset of data). A
further idea for later approaches might be to con-
sider age, sex, height, weight or similar aspects
for calculating each volume.
• The amount of used oxygen (∆O
2%
) was set to 5
%. This value was used from literature (Mueller,
2001).
• The efficiency-factor was described in literature
for two heart-rate-values. Therefore all values
above and below were kept constant, all values
between were linear interpolated.
These formulas were used to get two estimates for
the used energy.
The simple approach for the movement was not
sufficient enough to calculate a value only based on
the movement signal, but it was sufficient to esti-
mate a difference. Therefore the actual value of the
movement representative was compared with the pre-
vious one. Then this relation was used to estimate the
change in the energy consumption:
EE
mov(t)
= EE
(t-1)
·
mov(t)
mov(t − 1)
(4)
t, t-1: time points (actual, previous)
EE(t-1): previous estimated energy consump-
tion (of all parameters)
mov(t): movement-intensity representative for
the time point t
This approach is surely not optimal, especially it
ignores the fact that there is a basal metabolic rate.
Comparison of a Sensorized Garment and Activity Trackers with a Mobile Ergospirometry System Concerning Energy Expenditure
235
But it still gives an estimate for energy consumption,
especially under strong movement.
4.4 Plausibility
Now it is necessary to combine these three estimated
values to more reliable estimated value. The trivial
idea just to average them has a major disadvantage:
If just one value is erroneous the complete average is
corrupted, e.g. if one value is not measured, what will
result in a zero-value, the average will be 33 % too
small. Therefore it is obvious that some checking of
the plausibility of these values is necessary. In this
approach the plausibility
1
was not binary, but values
from 0 to 10 were given. This values based on the
following checks:
• Difference between the actual value and the pre-
vious value. The higher the difference, the lower
the plausibility.
• Threshold values were used to check if the value
itself was plausible. Especially if a very low en-
ergy consumption (below basal metabolic rate) or
a very high energy consumption was detected, the
value of plausibility was set to 0.
• The similarity of the estimated energy values. If
two values are similar and the third one is differ-
ent, it is assumed that the similar ones are more
plausible. This idea is not yet implemented in our
first approach.
Because the values derived from movement had
less direct connection to the energy consumption (e.g.
the correlation was below 0.5, the basal metabolic
rate was not considered in the formula), the maximum
plausibility was set to 5, the values derived from heart
rate and respiration rate had, as mentioned above, a
maximum of ten.
And since some values could not be calculated for
the first value, we started the calculation as follows:
EE
(1)
=
EE
HR(1)
+ EE
BR(1)
2
(5)
And then for t ≥ 2:
EE
(t)
=
EE
HR(t)
· P
HR(t)
+ EE
BR(t)
· P
BR(t)
P
HR(t)
+ P
BR(t)
+ P
MOV(t)
+ 0.01
+
+
EE
MOV(t)
· P
MOV(t)
+ EE
(t-1)
· 0.01
P
HR(t)
+ P
BR(t)
+ P
MOV(t)
+ 0.01
(6)
Therefore a weighted average of the energy esti-
mates is calculated. The last part of the sum ensures
1
We later were informed that our concept of plausibility
has similarities to the Dempster-Shafer theory(Shafer et al.,
1976). During the development of the algorithm we did
not consider those findings but will check if they help to
improve further versions
that the formula still result in reliable values if all
other plausibility values are 0. In this case the previ-
ous value is used, in other cases the small plausibility
has almost no influence. If this value should be shown
on a display or at least a warning should be added de-
pending on the use case.
5 RESULTS
Based on the developed algorithm the energy expen-
diture was calculated for the FitnessSHIRT system.
The calculated EE values of all measurement systems
were compared to the reference ergospirometry sys-
tem. The results are presented as percentage devia-
tion to the reference in Table 3. In the first two lines
the EE were calculated by taking either only the heart
rate (FS HR) or only the respiration rate (FS RR) into
account. The result using all three measured param-
eters (heart rate, respiration rate, movement data) is
given in line three with FS Comb (highlighted green).
As the calculation of the EE is not supported by the
FitBit systems during cycling the stress test for the
ergometer was not feasible.
Table 3: Percentage deviation of the systems from reference
(ergospirometry).
Treadmill Ergometer
FS HR 24.6 % 19.6 %
FS BR 47.7 % 45.1 %
FS Comb 18.0 % 18.6 %
SenseWear 21.6 % 28.1 %
FitBit One 18.1 % n/a
FitBit Flex 21.9 % n/a
Wahoo 37.2 % 21.8 %
With a deviation of 18.0 % (treadmill) and 18.6 %
(cycle ergometer) the FitnessSHIRT system in combi-
nation with the presented algorithm achieves the most
accurate proposition by combination of heart rate, res-
piration rate and movement data. Hence, it is clearly
visible that a calculation only based on a single pa-
rameter is not applicable with the developed algo-
rithm. The calculation based on the respiration rate
has the highest deviation of all applied systems with
a value of of 47.7 % (treadmill) and 45.1 % (cycle
ergometer).
In Figure 3 the comparison of the ergospirometry
system to the FitnessSHIRT system is represented for
only one data set. The calculated EE values for the
treadmill stress test of proband 11 are visualized over
a period of 15 minutes.
BIOSIGNALS 2016 - 9th International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
236
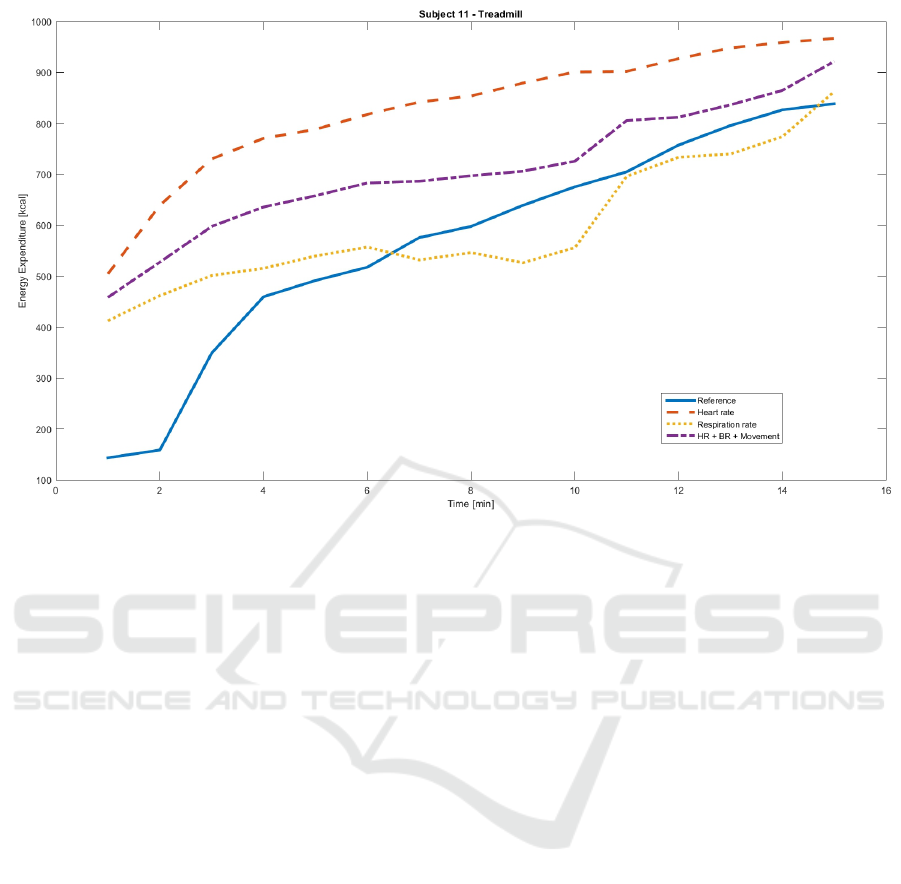
Figure 3: Reference data compared with calculated FitnessSHIRT data concerning energy expenditure.
6 CONCLUSION AND OUTLOOK
An algorithm to calculate the energy expenditure with
the Fraunhofer FitnessSHIRT system is presented.
The acquired data comprises heart rate, respiration
rate and movement data on which the calculation is
based. In a first trial with 13 subjects the basic func-
tionality of the algorithm was verified.
Although the basic algorithm showed good re-
sults, several improvements can be realized in future
research: As mentioned above, a further considera-
tion of the movement data would lead to a more accu-
rate value of the EE. In addition there are possibilities
to calculate a more detailed plausibility value, some
options are already mentioned in this paper. Also the
considerations about some data of the patient should
be taken into account. Right now the algorithm as-
sumes that each person has the same blood volume
transported during each heart beat and the same air
volume used during respiration. Considering age,
height and weight in the algorithm should improve the
quality of output. A personal calibration might result
in reliable values, but this process is more complex
and might not be applicable in all use cases.
Another approach will be a more extensive trial
with a larger number of subjects. Therefore, it would
be possible to divide the complete test sample into
several groups. Different parameters, e.g. age, body
mass index (BMI) or body fat percentage, can be eval-
uated more specific and it could be examined if those
parameters differ concerning the calculation of the en-
ergy expenditure.
In this trial only male participants were tested as
there is no FitnessSHIRT for women developed at the
moment. Consequently we have to realize a sensor
shirt in order to address this target and user group.
Hereby particular attention has to be paid to the
anatomical differences of the chest. It is mandatory
to have enough pressure on the electrodes to guaran-
tee continuous skin contact for high signal quality.
In conclusion, the presented system gives the user
an easy-to-use and accurate value of the burnt calo-
ries during exercises compared to the used reference.
Based on the promising results, the presented method
offers a reliable measurement of the physical effort
without the need of cost-intensive reference systems.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors would like to thank all the subjects who
accepted to participate as volunteers to the test.
REFERENCES
BodyMedia (2015). The sensewear armband.
Comparison of a Sensorized Garment and Activity Trackers with a Mobile Ergospirometry System Concerning Energy Expenditure
237

CareFusion (2015). Oxycon mobile device.
FitBit (2015). Fitbit activity tracker.
Hofmann, C. (2015). Fitnessshirt: Improving safety
through telemonitoring.
InBody (2015). Inbody770.
Kent, M. (1997). Food and Fitness: A Dictionary of Diet
and Exercise. Oxford University Press, 1st edition.
Mueller, C., Winter, C., and Rosenbaum, D. (2010). Current
objective techniques for physical activity assessment
in comparison with subjective methods. In Deutsche
Zeitschrift fuer Sportmedizin.
Mueller, R. (2001). Atmung, stoffwechsel und blutkreis-
lauf. Praxis der Naturwissenschaften - Physik in der
Schule, pages 23–26.
Nißen, M. (2013). Quantified Self - An Exploratory Study
on the Profiles and Motivations of Self-Tracking. Karl-
sruhe Institute of Technology (KIT).
Shafer, G. et al. (1976). A mathematical theory of evidence,
volume 1. Princeton university press Princeton.
Tantinger, D., Feilner, S., Schmitz, D., and Weigand, C.
(2012). Evaluation of qrs detection algorithm imple-
mented for mobile applications based on ecg data ac-
quired from sensorized garments. In Biomedical Engi-
neering / Biomedizinische Technik Band 57, Heft SI-1
Track-F.
WHO (2015). Obesity and overweight. Fact sheet No. 311.
BIOSIGNALS 2016 - 9th International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
238
