
Fully Automated Image Preprocessing for Feature Extraction from
Knife-edge Scanning Microscopy Image Stacks
Towards a Fully Automated Image Processing Pipeline for Light Microscopic
Images
Shruthi Raghavan and Jaerock Kwon
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering,
Kettering University, 1700 University Ave., 48504, Flint, MI, U.S.A.
Keywords:
KESM, Artifact Removal, Preprocessing, Tissue Extraction, Image Normalization.
Abstract:
Knife-Edge Scanning Microscopy (KESM) stands out as a fast physical sectioning approach for imaging
tissues at sub-micrometer resolution. To implement high-throughput and high-resolution, KESM images a
tissue ribbon on the knife edge as the sample is being sectioned. This simultaneous sectioning and imaging
approach has following benefits: (1) No image registration is required. (2) No manual job is required for
tissue sectioning, placement or microscope imaging. However spurious pixels are present at the left and right
side of the image, since the field of view of the objective is larger than the tissue width. The tissue region
needs to be extracted from these images. Moreover, unwanted artifacts are introduced by KESM’s imaging
mechanism, namely: (1) Vertical stripes caused by unevenly worn knife edge. (2) Horizontal artifacts due
to vibration of the knife while cutting plastic embedded tissue. (3) Uneven intensity within an image due to
knife misalignment. (4) Uneven intensity levels across images due to the variation of cutting speed. This paper
outlines an image processing pipeline for extracting features from KESM images and proposes an algorithm to
extract tissue region from physical sectioning-based light microscope images like KESM data for automating
feature extraction from these data sets.
1 INTRODUCTION
Analysis of biological structures in tissues at sub
micrometer resolution is enabled by techniques like
the Knife Edge Scanning Microscopy (KESM) (May-
erich et al., 2008), Confocal Microscopy (Shot-
ton, 1989), Automatic tape collecting lathe ultra-
microtome (ATLUM) (Hayworth et al., 2006), Se-
rial Block Face Scanning Electron Microscopy (SBF-
SEM) (Denk and Horstmann, 2004) and All Opti-
cal Histology (Tsai et al., 2003). These microscopic
imaging methods are based on either physical or opti-
cal sectioning, or both (ATLUM).
Knife-edge scanning microscopy is the technique
of concurrently slicing and imaging tissue samples at
sub micrometer resolution. This preserves image reg-
istration throughout the depth of the tissue block and
eliminates undesirable events such as back-scattering
of light and bleaching of fluorescent-stained tissue be-
low the knife.
The KESM based high-throughput and high-
resolution tissue scanner has produced multiple
Figure 1: Imaging principles of the KESM.The objective
and the knife is held in place, while the specimen affixed on
the positioning stage moves at the resolution of 20 nm and
travel speed of 1-5, and gets scraped against the diamond
knife (5 mm wide for 10X objective), generating a thin sec-
tion flowing over the knife. Imaging happens at knife-edge.
Direction of movement of light and stage is indicated with
solid arrows. (Adopted from (Choe et al., 2011)).
datasets till date. A diamond knife is used as colli-
mator and also to section the tissue as illustrated in
Raghavan, S. and Kwon, J.
Fully Automated Image Preprocessing for Feature Extraction from Knife-edge Scanning Microscopy Image Stacks - Towards a Fully Automated Image Processing Pipeline for Light Microscopic
Images.
DOI: 10.5220/0005708700930100
In Proceedings of the 9th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies (BIOSTEC 2016) - Volume 2: BIOIMAGING, pages 93-100
ISBN: 978-989-758-170-0
Copyright
c
2016 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
93

Figure 1. The tissue sample being sliced by the knife
is imaged just above the knife edge by a powerful line
scan camera. The image capture mechanism is trig-
gered based on the encoded position of the tissue be-
ing sliced, which ensures that every sectioning results
in an image capture. The KESM can image a 1cm
3
tissue block in approximately 50 hours at a resolution
of 0.6µm × 0.7µm × 1.0µm.
To get information from this data, the KESM im-
ages have to be preprocessed followed by feature ex-
traction and post-processing if necessary. This pa-
per describes the first preprocessing step in an image
processing pipe that is being designed for automat-
ing feature extraction and sharing. A novel method
for extraction of tissue regions is being proposed for
physical sectioning-based light-microscope imaging
data.
2 BACKGROUND
While sectioning and imaging in KESM, width of the
tissue slice is not exactly the field of view of the ob-
jective. Thus, there is additional non-tissue area that
appears as dark regions on either side of the tissue
in every image. The additional region causes signif-
icant increase in the amount of memory required by
applications that process the images. For instance, as-
sume we imaged a tissue sample using KESM. Let the
width of a line scan image be 4096 pixels and a slice
consist of 12000 lines. If pixels are a byte each, the
raw KESM image will occupy 46.875MB. However,
if tissue width is only 2400pixels, only 27.466MB of
memory is actually useful. KESM could collect ter-
abytes of images and 41.41% reduction in image size
will significantly improve the efficiency of feature ex-
traction.
Ideally, the tissue region should be at a fixed lo-
cation in the image. This would make it possible to
crop all images in a given column at the same posi-
tion, given the tissue width. However, this is not al-
ways the case. In case of interruptions in the imaging
process like power outages and clogging in the wa-
ter circulation, the KESM might need to be stopped
for maintenance and the setup might be disturbed. In
such scenarios, after restarting the KESM, the start
of tissue may not be at the same pixel position in the
image as before. In this case, cropping at fixed posi-
tion may cause loss of tissue data. This necessitates
detection of the tissue edge for every image.
Each tissue sample imaged by the KESM can gen-
erate up to around 80,000 images (the tissue is lat-
erally sectioned several times and each column has
around 10,000 images). Thus, to extract tissue region
manually requires a lot of time and effort and is ineffi-
cient. So we need image processing to automate this.
A template matching based method was proposed for
tissue extraction from the KESM image stacks (Kwon
et al., 2011). However, this method suffered from a
high error rate. The novel algorithm for tissue extrac-
tion proposed in this paper has lower error rates and
is more efficient in automation of the process.
Knife chatter and illumination artifacts affect
KESM images as shown in Figure 9. Varying cut-
ting speeds introduced to reduce knife chatter cause
inter-image intensity differences. These artifacts hin-
der visualization and feature extraction. So inter- and
intra- image normalization is also a necessary prepro-
cessing step for KESM stacks.
3 METHOD
This section explains the newly proposed tissue area
detection and extraction algorithm. It focuses on the
reasoning behind the methodology used. We also de-
scribe the method used for intensity normalization al-
gorithm as proposed in (Kwon et al., 2011) for com-
pleteness.
3.1 Tissue Area Detection
The image from the KESM consists of a right and a
left edge of tissue as shown in Figure 2(a). Figure
2(b) shows the seemingly sharp right-edge. However,
Figure 2(c) reveals gradual decay in the intensity pro-
file of the right edge. Moreover, KESM is affected
by multiple artifacts as described earlier. For this rea-
son, we do not use the Sobel (Duda et al., 1973), Pre-
witt (Prewitt, 1970) and similar edge detectors. The
Canny edge detector (Canny, 1986) is robust to noise
(Maini and Aggarwal, 2009) but is complex to com-
pute and gives us additional information about cor-
ners that we do not need. Hence, we take the Gaussian
gradient, which can smooth the image before detect-
ing edge gradients to give us a clear right edge loca-
tion. The Gaussian Gradient applies a filter in the x
and y directions of the two dimensional tissue image
being processed. The equations for first order Gaus-
sian derivatives of Gaussian are as given below:
dG(x, y, σ)
dx
=
−x
2πσ
4
e
−(x
2
+y
2
)
2σ
2
(1)
dG(x, y, σ)
dy
=
−y
2πσ
4
e
−(x
2
+y
2
)
2σ
2
(2)
,where x and y represent the kernel location starting
with zeros at the center and σ represents the standard
BIOIMAGING 2016 - 3rd International Conference on Bioimaging
94
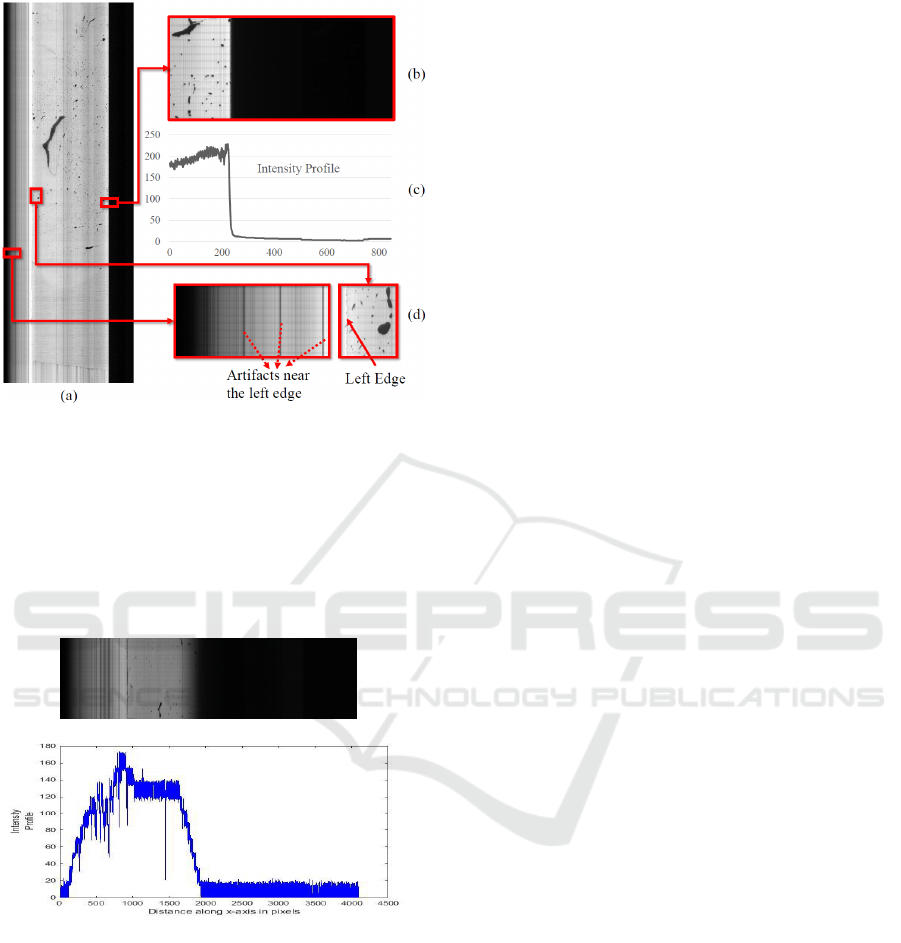
Figure 2: Showing the spurious data and edges of tissue re-
gion in image. (a) One Tissue Slice from KESM microvas-
culature data stack. (b) Right Edge of Tissue expanded
shows sharp demarcation. (c) Intensity Profile along x axis
(distance in pixels from the left side of the image shown
in (b)) shows a gradual gradient that might cause spurious
edge detection by some edge operators. (d) Left edge (the
solid arrow) of tissue expanded shows vertical noise lines
(dotted arrows) that have to be distinguished from the real
left edge.
(a)
(b)
Figure 3: A horizontal section from a KESM image with
no clear right edge necessitating left edge detection. (a)
A small horizontal section of KESM image with occluded
right edge. (b) Intensity profile along the x axis of the image
shown in (a)
deviation of the Gaussian distribution. Smoothing ef-
fect of the Gaussian Kernel, increases as σ increases.
This algorithm does not work with right-occluded
images. Figure 3 shows a horizontal section from a
KESM image with no clear right edge. It is seen that
the edge like profile occurs much before the actual
image edge. In these cases we try to detect the left
edge of tissue to crop the image. It is challenging due
to vertical noise artifacts produced by illumination ir-
regularities in the KESM shown in Figure 2(d).
The technique used to find the left edge relies on
the fact that in KESM images, only the correct left
edge has more horizontal as well as vertical gradients.
To use this information efficiently, we first take the
horizontal followed by the vertical Gaussian gradient
of the image. This leaves us with a strong response at
the left edge. We then use a thresholding to eliminate
the weak responses of vertical noise outside the left
tissue edge. Then, the image is optionally eroded with
a slightly elongated rectangular structuring element to
strengthen edges that remain.
To detect the position of the strong vertical re-
sponse from this image, we use probabilistic hough
line (Galamhos et al., 1999) estimation with one sin-
gle angle (zero) and a decreasing line length starting
from half the height of the entire image. The location
of the longest vertical line found in the left half of the
image is taken to be the index of the left edge.
Rarely, a KESM image is so dark that neither the
left edge nor the right edge of the tissue can be reli-
ably found by the proposed algorithm. Our effort to
make the image processing pipeline fully automated
involved using a best-effort thresholding based tis-
sue region detection algorithm. Minimum cross en-
tropy approach has proven to be a useful segmenta-
tion method in many applications and it has been used
in (Yi-de et al., 2004; Sarkar et al., 2011; Al-Attas
and El-Zaart, 2007) efficiently, which is empirical ev-
idence for effectiveness of this threshold. So in our
algorithm, we used Li threshold (Li and Lee, 1993)
that is based this thresholding. Thus the proposed au-
tomated algorithm will extract the tissue region from
every single image generated by the KESM, with
best-effort cropping for very occluded or dark images.
3.2 Image Intensity Normalization
We implemented the image intensity equalization al-
gorithm previously proposed for KESM image stacks
(Kwon et al., 2011). Briefly, this method normalizes
each pixel in a row or column based on the median
intensity value of that row or column. This procedure
is applied to all rows and columns in the image to
achieve uniform intensity. We also adopt the method
of selective normalization and set a threshold for fore-
ground segmentation when the median intensity is too
low to get a clear distinction between tissue and back-
ground. It alleviates artifacts and translates all images
to a common background intensity level.
Fully Automated Image Preprocessing for Feature Extraction from Knife-edge Scanning Microscopy Image Stacks - Towards a Fully
Automated Image Processing Pipeline for Light Microscopic Images
95
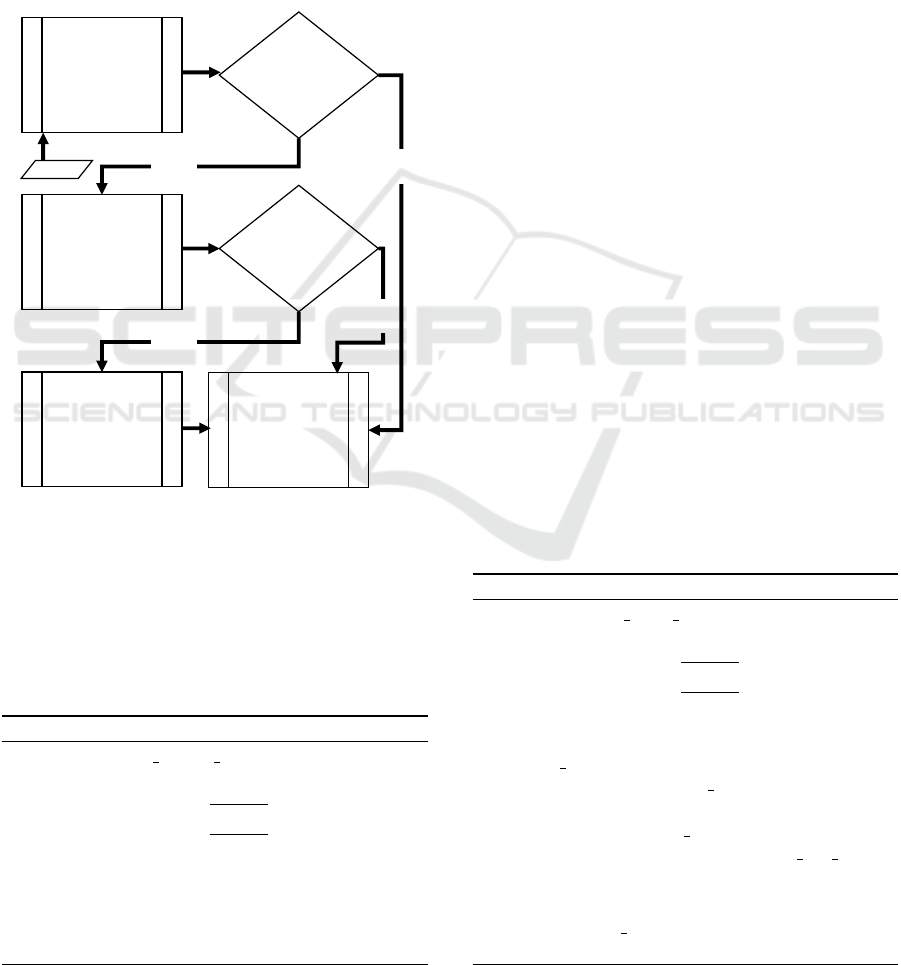
4 IMPLEMENTATION
The algorithm for tissue extraction developed in this
paper consists of three logical divisions - edge detec-
tion, admissibility check and cropping. Edge is de-
tected using one of the two methods explained below
or by thresholding based right edge detection. The
overview of the algorithm flow is shown in Figure 4.
Once the tissue region is extracted from the image,
a normalization algorithm is applied to enable further
processing. The interested reader is referred to (Kwon
et al., 2011) for the implementation details.
Right
Edge
Detection
Admissible
Right Edge?
Left
Edge
Detection
NO
Best Effort
Min. Cross
Entropy
Threshold
Admissible
Left Edge?
Extract
Tissue
Region
NO
YES
YES
Input
Figure 4: Flowchart showing the logical structure of pro-
posed automated cropping algorithm
4.1 Right Edge Detection for Tissue
Extraction
The right edge detection algorithm involves finding
the right edge at the strongest Gaussian gradient re-
Algorithm 1: Right Edge Detection.
1: function FIND RIGHT EDGE
2: init
3: image ← image ∗
dG(x,y,2)
dx
4: image ← image ∗
dG(x,y,2)
dy
5: y,x ← Non-zero Indices from image
6: xo ← (val,occ) in x,sorted by freq. of val
7: x ← xo for 10 highest ”val” in xo
8: index ← val with max(occ) x
9: return index
sponse on the right half of image. The Gaussian gradi-
ent function with sigma of 2 is applied. First, the hor-
izontal derivative of Gaussian is convolved with the
image (convolution is indicated by ∗) and then the re-
sult is convolved with vertical derivative of Gaussian.
Ideally, this gives an image with its last non-zero pixel
along the x-axis at the right edge of tissue in the im-
age. However, to ensure the algorithm is picking the
most well defined edge, the largest non-zero x-index
(val) that corresponds most occurrences (occ) of non-
zero pixels in y is chosen as the result. The pseudo-
code for this procedure is given in Algorithm 1. This
works for any KESM image that has sufficient con-
trast at the right edge. However, if the right edge of
tissue is too dark or blurred to recover due to artifacts
introduced by the imaging mechanism, this will not
give the correct right edge location. The result pro-
vided by this right edge detection function is validated
by an admissibility test based on tissue width (Tis-
sueWidth), sanity checks and image properties near
detected edge. If the result is admissible, it is used
to crop the tissue from [index-TissueWidth,index]. If
not, the left edge detection algorithm, described next,
is used to try and find the index of the left edge of
tissue region.
4.2 Left Edge Detection for Tissue
Extraction
The left edge detection algorithm works by isolat-
ing the edge with greater vertical connectivity and
also maximum horizontal gradients on the left half of
the image. The Gaussian gradient works with lesser
smoothing than for right edge detection. This is to
ensure we do not smooth out the gradient information
we are trying to detect on the left edge. After this edge
Algorithm 2: Left Edge Detection.
1: function FIND LEFT EDGE
2: init
3: image ← image ∗
dG(x,y,1)
dx
4: image ← image ∗
dG(x,y,1)
dy
5: image ← Triangle thresholded image
6: image ← BinaryErode(image)
7: roi lines ← WIDTH - TissueWidth
8: image ← image[0:roi lines]
9: while lines == [ ] and height 6= 0 do
10: lines ← hough lines(image,height)
11: height ← height - predefined dec step
12: if lines == [ ] then
13: return fail
14: index ← x inx of longest line found
15: return index
BIOIMAGING 2016 - 3rd International Conference on Bioimaging
96
detection step, we apply a triangle threshold to bina-
rize the image. This image is then given as an input to
a binary erode filter using a narrow rectangular struc-
turing element. This ensures that only the strongest
vertical lines survive. Then probabilistic hough lines
are found in the y-direction and the highest connected
vertical line which in turn is the tallest line found is
taken as being at the position of the left edge. The
x-index at which this line was found is returned to the
cropping algorithm. The pseudo-code for this proce-
dure is given in Algorithm 2.
If the left edge found is admissible, tissue region
is extracted with the result index value. If not, the
image is cropped with a best effort algorithm based on
minimum cross entropy threshold (Li and Lee, 1993).
The image is first thresholded based on this method.
Then the strongest vertical edge in the image that is
farthest to the right is taken as the right edge of the
tissue region.
5 VALIDATION
Validation with a real data subset is impractical be-
cause we have to manually find the correct tissue
edge in each image. This would be subjective, er-
ror prone and cannot be considered ground truth. So
the proposed algorithm was validated using synthetic
images. The algorithm was run on a computer with
an AMD-64 quad-core processor running at 3.8GHz
with 8GB RAM.
5.1 Testing Proposed Algorithm
The tissue extraction code itself that was explained
in the implementation section was written in Python.
The code for normalization of the data was written in
C++. Synthetic images were generated using a python
script. They mimic the properties of KESM images
and their artifacts. They faithfully reproduce the na-
ture of the edges of tissues in KESM data. An exam-
ple of an image generated by this algorithm is shown
in Figure 5(a). The edge properties are shown in Fig-
ure 5(b) and (c). Thus, we can assume that the results
from the synthetic data are directly representative of
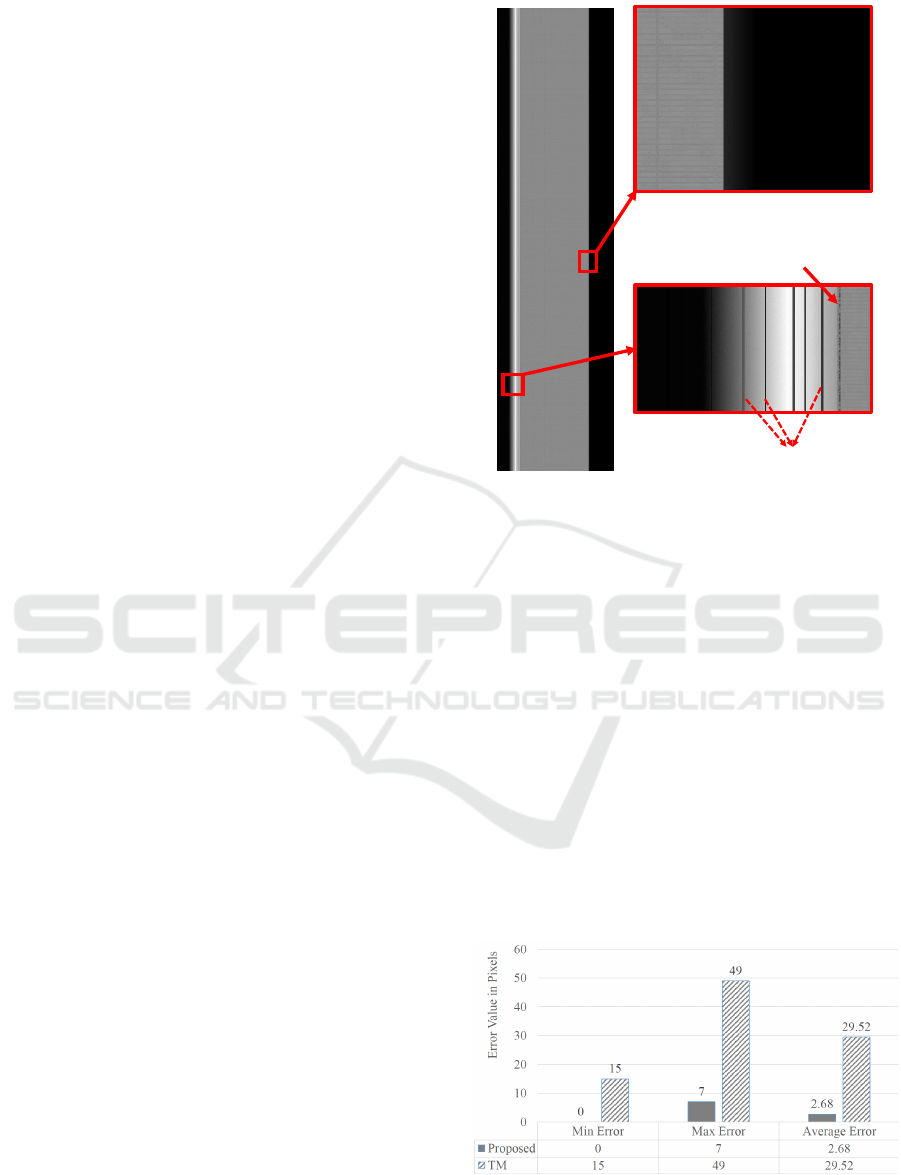
those from KESM data. We tested the proposed crop-
ping algorithm on hundred synthetic images. From
this, the average and maximum errors were found to
be 2.68 pixels and 7 pixels respectively.
(a)
(b)
(c)
Left Edge
Artifacts near the left edge
Figure 5: Synthetic image. It has edge properties that mimic
the real KESM images. These images can thus serve as
ground truth for validation of results from the proposed al-
gorithm. (a) Full synthetic image. (b) Right edge magnified.
(c) Left edge magnified.
5.2 Comparitive Evaluation
We also compared the proposed method to a previ-
ously proposed algorithm for tissue extraction. The
algorithm being compared is the template match-
ing(TM) based cropping algorithm proposed in
(Kwon et al., 2011). Error in the number of pix-
els for both these methods is compared in the chart
shown in Figure 6. From this we infer that the pro-
posed algorithm has improved error rate by 90.92%
compared to the template matching based algorithm.
The minimum error for the template matching based
algorithm for the same set of synthetic images is 15
pixels whereas the proposed algorithm is capable of
Figure 6: Quantitative comparison between the proposed
algorithm for tissue extraction and the template matching
algorithm from (Kwon et al., 2011).
Fully Automated Image Preprocessing for Feature Extraction from Knife-edge Scanning Microscopy Image Stacks - Towards a Fully
Automated Image Processing Pipeline for Light Microscopic Images
97
cropping images with zero error. Figure 7 shows the
result of cropping using the two methods on a syn-
thetic image. Clearly, the proposed algorithm has bet-
ter accuracy in locating the edge of tissue region in
the image.
Error Pixels
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
Figure 7: Comparison of cropping using proposed method
and template matching method on a synthetic image for
qualitative results. (a) A small horizontal portion from a
synthetic image. Right edge location = 3442(x). (b) Output
of template matching algorithm proposed in (Kwon et al.,
2011). (c) Output of proposed algorithm cropped at 3442(x)
with zero error. (d) Magnified result from the rectangle
shown in (b) indicating erroneous pixels near the right edge
after cropping, crop location = 3459(x).
6 REPRESENTATIVE RESULTS
We ran the proposed cropping algorithm on the mouse
brain vasculature data stacks imaged by the KESM.
We could crop the entire image stack and also nor-
malize all the images after cropping. This method was
robust enough to work on very dark, very bright and
images affected by different artifacts that are common
in KESM including illumination artifacts. This can be
seen in Figure 9. Each of the figures show the orig-
inal, cropped and normalized versions of the KESM
images that have been affected by different artifacts.
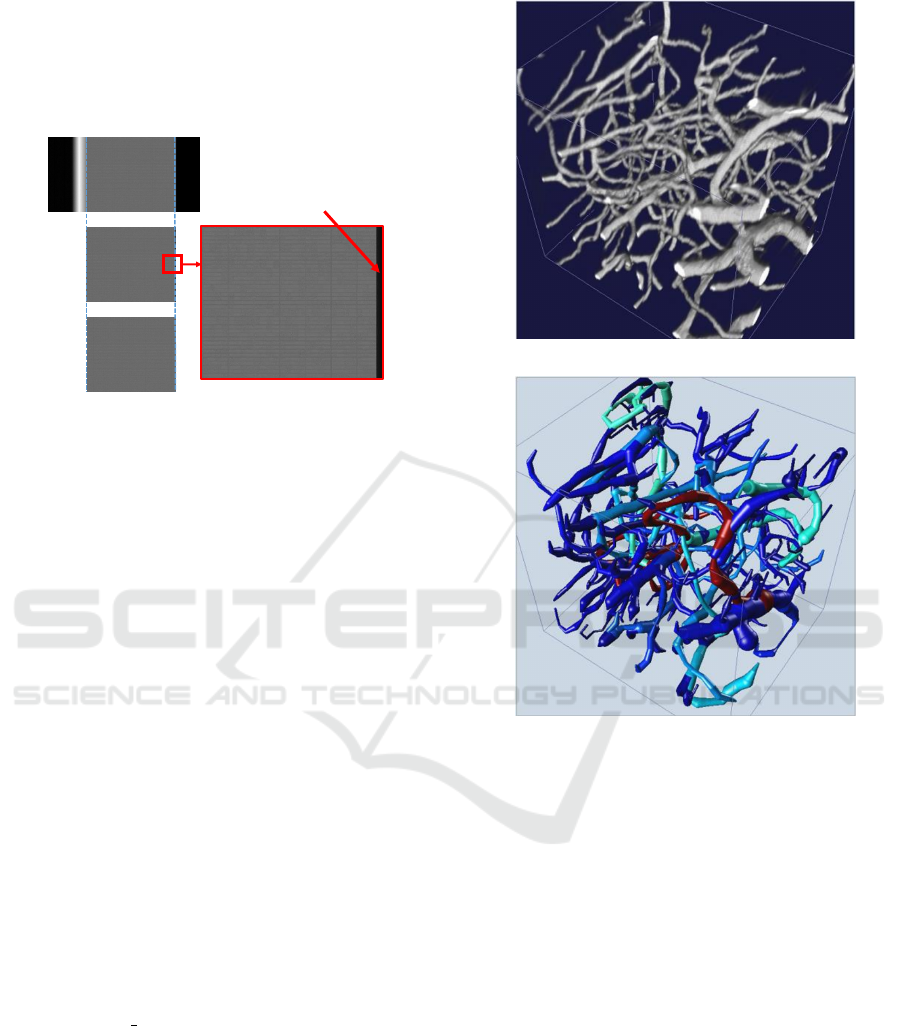
The traced result shown in Figure 8 was gener-
ated using the All Path Pruning 2.0 (APP2) (Xiao and
Peng, 2013) plug-in in Vaa3D (Peng et al., 2010). De-
fault APP2 parameters were used for the trace except
the background threshold that was set to −1. The
KESM image stack was inverted to have a bright fore-
ground tissue area on a dark background.
7 CONCLUSION AND FUTURE
WORK
A new algorithm has been proposed to extract tis-
sue region from physical sectioning based light mi-
(a)
(b)
Figure 8: 3D visualization of the image data. (a) 3D view
of a properly cropped image volume using the proposed al-
gorithm. The dimension of the image is 153 × 179 × 177
scaled by 0.6 × 0.7 × 1.0 ratio (b) A blood vessel trace re-
sult of (a) using the Vaa3D (Peng et al., 2010) plugin based
on the All Path Pruning 2.0 (APP2) algorithm (Xiao and
Peng, 2013).
croscopy image stacks. The algorithm was developed
using the mouse brain vasculature data set generated
by the KESM. The challenges were mainly the vary-
ing nature of KESM images, which the algorithm was
designed to handle. This made it possible to crop
the entire image stack automatically with high ac-
curacy. The average error for the proposed method
was found to be less than 3 pixels from tests on syn-
thetic data. This was compared against a previously
proposed method for tissue extraction and quantita-
tive comparison results have been shown in the paper.
This algorithm along with normalization, is part of
preprocessing.
An image processing pipeline of our design is pro-
posed as shown in Figure 10. The goal is to automat-
BIOIMAGING 2016 - 3rd International Conference on Bioimaging
98
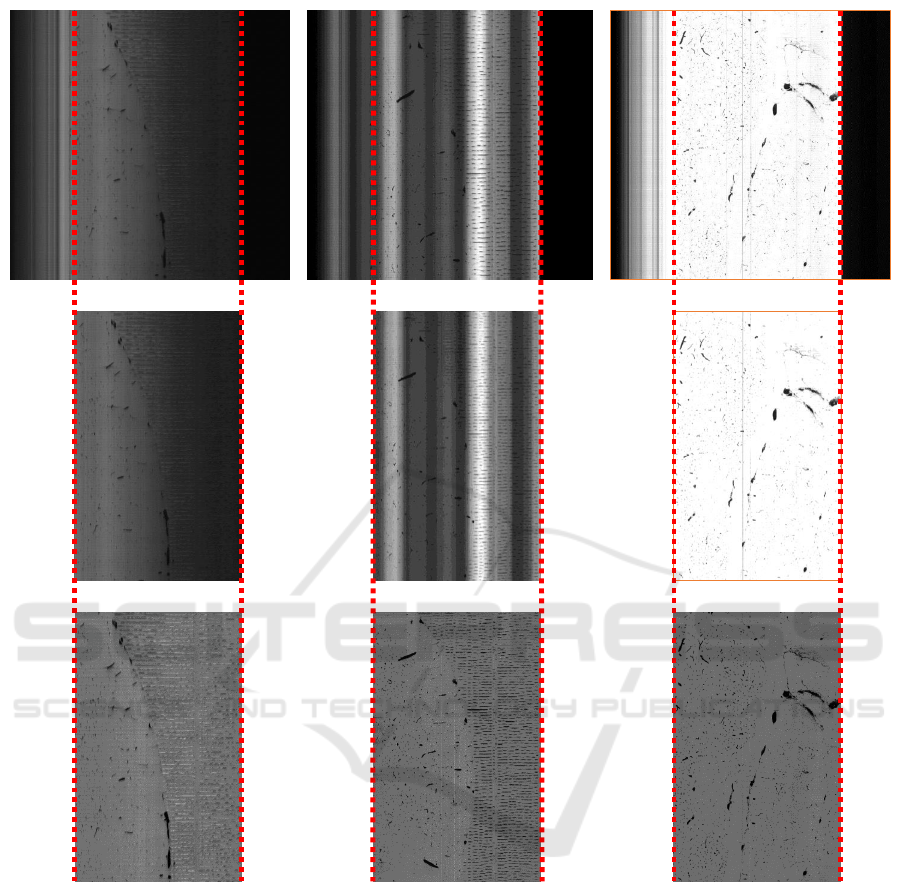
(a) (b) (c)
Figure 9: Results of proposed algorithm to find tissue edge under different conditions and the output of normalization algo-
rithm. A small portion from a sample KESM image (top row). The image cropped using proposed tissue extraction algorithm
(middle row). Image normalized using algorithm adapted from (Kwon et al., 2011) (bottom row). (a) A very dark KESM
image (brightness increased for viewing only), the extracted tissue region and its normalized version. (b) A KESM image
with severe illumination artifacts in the form of vertical bands that could be mistaken for edges, the extracted tissue region
and its normalized version. (c) A very bright KESM image, the extracted tissue region and its normalized version.
ically extract the important biological features from
light microscopy images and also publish it online for
the scientific community to access.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This material is based upon work supported by the
National Science Foundation (NSF) #1337983.
Fully Automated Image Preprocessing for Feature Extraction from Knife-edge Scanning Microscopy Image Stacks - Towards a Fully
Automated Image Processing Pipeline for Light Microscopic Images
99
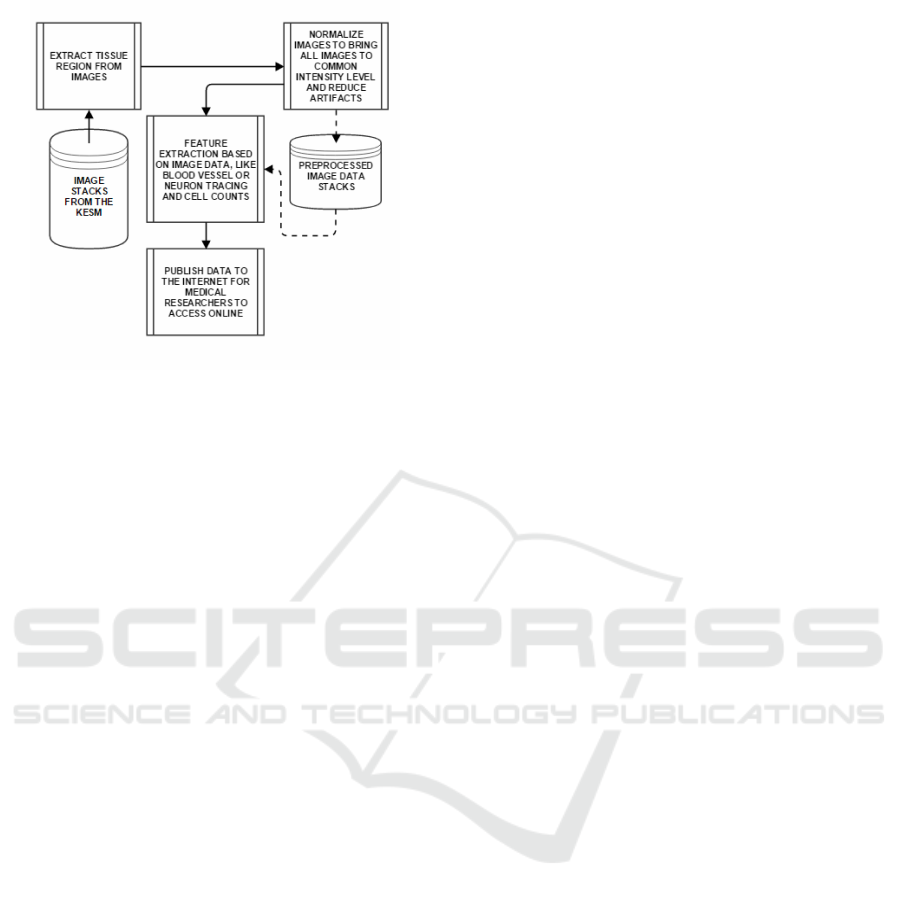
Figure 10: A pipeline to be implemented for information
extraction from the KESM and other physical sectioning-
based microscope image stacks
REFERENCES
Al-Attas, R. and El-Zaart, A. (2007). Thresholding of med-
ical images using minimum cross entropy. In 3rd
Kuala Lumpur International Conference on Biomed-
ical Engineering 2006, pages 296–299. Springer.
Canny, J. (1986). A computational approach to edge detec-
tion. Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, IEEE
Transactions on, (6):679–698.
Choe, Y., Mayerich, D., Kwon, J., Miller, D. E., Sung,
C., Chung, J. R., Huffman, T., Keyser, J., and Ab-
bott, L. C. (2011). Specimen preparation, imaging,
and analysis protocols for knife-edge scanning mi-
croscopy. (58):e3248.
Denk, W. and Horstmann, H. (2004). Serial block-
face scanning electron microscopy to reconstruct
three-dimensional tissue nanostructure. PLoS Biol,
2(11):e329.
Duda, R. O., Hart, P. E., et al. (1973). Pattern classification
and scene analysis. J. Wiley and Sons.
Galamhos, C., Matas, J., and Kittler, J. (1999). Progres-
sive probabilistic hough transform for line detection.
In Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 1999.
IEEE Computer Society Conference on., volume 1.
IEEE.
Hayworth, K., Kasthuri, N., Schalek, R., and Lichtman, J.
(2006). Automating the collection of ultrathin serial
sections for large volume tem reconstructions. Mi-
croscopy and Microanalysis, 12(S02):86–87.
Kwon, J., Mayerich, D., and Choe, Y. (2011). Automated
cropping and artifact removal for knife-edge scanning
microscopy. In Biomedical Imaging: From Nano
to Macro, 2011 IEEE International Symposium on,
pages 1366–1369. IEEE.
Li, C. H. and Lee, C. (1993). Minimum cross entropy
thresholding. Pattern Recognition, 26(4):617–625.
Maini, R. and Aggarwal, H. (2009). Study and comparison
of various image edge detection techniques. Interna-
tional journal of image processing (IJIP), 3(1):1–11.
Mayerich, D., Abbott, L., and McCormick, B. (2008).
Knife-edge scanning microscopy for imaging and re-
construction of three-dimensional anatomical struc-
tures of the mouse brain. Journal of microscopy,
231(1):134–143.
Peng, H., Ruan, Z., Long, F., Simpson, J. H., and Myers,
E. W. (2010). V3d enables real-time 3d visualization
and quantitative analysis of large-scale biological im-
age data sets. Nature biotechnology, 28(4):348–353.
Prewitt, J. M. (1970). Object enhancement and extraction.
Picture processing and Psychopictorics, 10(1):15–19.
Sarkar, S., Patra, G. R., and Das, S. (2011). A differ-
ential evolution based approach for multilevel image
segmentation using minimum cross entropy threshold-
ing. In Swarm, Evolutionary, and Memetic Comput-
ing, pages 51–58. Springer.
Shotton, D. M. (1989). Confocal scanning optical mi-
croscopy and its applications for biological speci-
mens. Journal of Cell Science, 94(2):175–206.
Tsai, P. S., Friedman, B., Ifarraguerri, A. I., Thompson,
B. D., Lev-Ram, V., Schaffer, C. B., Xiong, Q., Tsien,
R. Y., Squier, J. A., and Kleinfeld, D. (2003). All-
optical histology using ultrashort laser pulses. Neuron,
39(1):27–41.
Xiao, H. and Peng, H. (2013). App2: automatic tracing of
3d neuron morphology based on hierarchical pruning
of a gray-weighted image distance-tree. Bioinformat-
ics, 29(11):1448–1454.
Yi-de, M., Qing, L., and Zhi-Bai, Q. (2004). Automated im-
age segmentation using improved pcnn model based
on cross-entropy. In Intelligent Multimedia, Video and
Speech Processing, 2004. Proceedings of 2004 Inter-
national Symposium on, pages 743–746. IEEE.
BIOIMAGING 2016 - 3rd International Conference on Bioimaging
100
