
Multiple People Tracking in Smart Camera Networks by Greedy
Joint-Likelihood Maximization
Nyan Bo Bo, Francis Deboeverie, Peter Veelaert and Wilfried Philips
Ghent University/iMinds, TELIN, Image Processing and Interpretation
Sint-Pietersnieuwstraat 41, Ghent 9000, Belgium
Keywords:
Multi-camera Tracking, Decentralized System, Joint-likelihood Maximization.
Abstract:
This paper presents a new method to track multiple people reliably using a network of calibrated smart cam-
eras. The task of tracking multiple persons is very difficult due to non-rigid nature of the human body, oc-
clusions and environmental changes. Our proposed method recursively updates the positions of all persons
based on the observed foreground images from all smart cameras and the previously known location of each
person. The performance of our proposed method is evaluated on indoor video sequences containing person–
person/object–person occlusions and sudden illumination changes. The results show that our method performs
well with Multiple Object Tracking Accuracy as high as 100% and Multiple Object Tracking Precision as high
as 86%. Performance comparison to a state of the art tracking system shows that our method outperforms.
1 INTRODUCTION
Nowadays, many computer vision-based applica-
tions, such as automatic surveillance, smart meeting
rooms/homes and human behavior/activity analysis,
require robust tracking of multiple people in indoor
or outdoor environment. However, the task of reliably
tacking multiple non-rigid targets such as humans is
in fact very challenging because the appearance of a
person easily changes by body movement, pose and
orientation changes with respect to the camera view.
Moreover, the appearance of the target may also be al-
tered by changes in the environment, such as lighting,
which makes the tracking even more difficult.
Since multiple people may be moving about in the
scene, a person can be fully/partially occluded by an-
other person(s) or other object(s) in the scene. This
occlusion problem makes the tracking task even more
challenging and is very difficult to address in single
camera methods. Over the past fifteen years, many
trackers for camera networks with overlapping views
have been introduced. These trackers use informa-
tion from different view points to handle the occlusion
problem. Additionally, joint estimation of a person’s
position from multiple views is usually more precise
than estimation from a single view point.
In this paper, we propose a new method to track
multiple people in real time using a network of smart
cameras. Our proposed method follows a decen-
tralized architecture, i.e., all image processing tasks
can be executed on smart cameras and only num-
bers are exchanged between nodes rather than im-
ages/frames.
1
Our tracker recursively estimates the
current positions of all persons by maximizing the
likelihood of the current observations of all cameras.
The estimate is recursive because the aforementioned
likelihood is determined by the previous positions.
In our method, the observations are binary images
obtained by foreground/background estimation on all
camera views. Moreover in our method these images
remain in private memory within each smart camera
and are never transmitted; this is one of the contribu-
tions of our method. In practice, observations clearly
depend on the positions of all persons in the scene.
Therefore in this paper observations are not tied to in-
dividual persons, but to camera views. Since the like-
lihood maximization takes into account the positions
of all persons, our tracker does not need to perform an
explicit occlusion detection and handling.
Another contribution of this paper is the real-time
maximization of the likelihood of an observations
from all cameras, given the positions of all persons,
using a greedy search. The search space is defined
by the known positions of all persons at previous time
instance and the physical limitation that a person can-
not move very far between two consecutive frames.
1
In this paper, the smart cameras are simulated on a
computer.
604
Bo, N., Deboeverie, F., Veelaert, P. and Philips, W.
Multiple People Tracking in Smart Camera Networks by Greedy Joint-Likelihood Maximization.
DOI: 10.5220/0005716206020609
In Proceedings of the 11th Joint Conference on Computer Vision, Imaging and Computer Graphics Theory and Applications (VISIGRAPP 2016) - Volume 3: VISAPP, pages 604-611
ISBN: 978-989-758-175-5
Copyright
c
2016 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

These known positions at earlier time instance comes
from a person detector or from the previous estima-
tions of the tracker itself. We use the integral image in
the algorithm’s implementation to achieve high com-
putational efficiency.
We evaluate our method on three multi-camera
video sequences, each of which contains different
scenarios such as people having meeting, walking a
round under steady and varying lighting, captured
in an indoor meeting room environment. The re-
sults confirm that our method achieves high accuracy
and precision on video sequences containing frequent
person–person and object–person occlusions. The
performance comparison to a publicly available state
of the art tracker shows that our method outperforms.
2 RELATED WORK
Over the last decade, many techniques have been pro-
posed for robust tracking of multiple people using a
single-camera as well as networks of cameras. Many
trackers (Yang et al., 2009), (Henriques et al., 2011),
(Yun et al., 2012) (single-camera trackers) (Bredereck
et al., 2012), (Gruenwedel et al., 2014), (Bo Bo et al.,
2014) (multi-camera trackers) recursively update the
position of each person based on priors from previ-
ous frames and the observations in the current frame,
such as appearance models based on color/texture,
foreground blobs, person detector responses, and so
on. These trackers are usually relying on extracting
observations of individual persons from all the input
images. Most of these methods then process the “per-
son observations” independently, e.g. feeding them to
a recursive state estimator (Kalman filter, Particle fil-
ter, . . . ) for that person. As such, persons are tracked
independently after their observations have been sep-
arated.
Some trackers (Zhang et al., 2008), (Bredereck
et al., 2012), (Andriyenko and Schindler, 2010)
(Berclaz et al., 2011) adopt a tracking-by-detection
strategy, i.e., people are firstly detected in multiple
video frames and then detections are linked across
time. These systems usually need input of the en-
tire video or a batch of frames. Additionally, to our
knowledge the computation of occupancy maps or
detection of humans takes a relatively large potion
of allowed computation time for real-time tracking.
These factors limit the feasibility for real-time track-
ing. However, these methods have the advantage of
having information from future video frames, while
estimating the person’s positions. Therefore, by ex-
ploiting information from future video frames, these
methods can potentially perform better in terms of ac-
curacy.
Recently, several methods (Andriyenko and
Schindler, 2011), (Milan et al., 2013) have been intro-
duced to improve the trajectories produced by base-
line trackers (Wojek et al., 2010), (Pirsiavash et al.,
2011). The approach of Andriyenko et al. (An-
driyenko and Schindler, 2011) formulates an energy
function from human detector’s detections, object dy-
namics, collision avoidance and object persistence
together with a regularization term for each trajec-
tory produced by a baseline tracker. Then the energy
is minimized by growing/shrinking, splitting/merging
or adding/removing the trajectories. The work of Mi-
lan et al. follows a similar approach but using a dif-
ferent energy formulation and optimization. The re-
ported optimization time for these approaches is 1 to
2 second per frames excluding the time for generat-
ing baseline trajectories and person detections. There-
fore, they are not feasible for real-time applications.
3 PROPOSED TRACKER
Our tracking system uses a decentralized architec-
ture, i.e., the computational load is distributed over
C calibrated cameras and a greedy likelihood maxi-
mization node. Each smart camera captures and pro-
cesses its video on board. Thus, only meta-data, such
as positions and likelihoods, are exchanged between
nodes rather than images. This reduces network band-
width requirements, thus increasing scalability, i.e.,
additional smart cameras may be added to the system
without concerning too much about the communica-
tion bottleneck. Fig. 1 shows the building blocks of
the proposed tracker and the data exchange between
nodes.
One analysis cycle of processing a single video
frame from all cameras is as follows. At time t, each
smart camera c captures image and computes a fore-
ground image from it. In our tracker, we use the same
texture-based foreground detection method as in our
previous work (Bo Bo et al., 2015). The likelihood
maximizer node then requests the likelihood of ob-
serving foreground image in each camera view given
the hypothesized positions of all persons. All smart
cameras compute the requested likelihood and send
back to the likelihood maximizer. This likelihood re-
quest and response process is repeated until the like-
lihood maximizer finds the positions of all persons
which give the highest likelihood. Finally, the like-
lihood maximizer then outputs the jointly estimated
positions of all persons and begins a new cycle to esti-
mate the positions of all persons at next time instance
t + 1. The following subsections describe the details
Multiple People Tracking in Smart Camera Networks by Greedy Joint-Likelihood Maximization
605

of each component of our tracker.
3.1 The Proposed Likelihood Model
We extend the single camera likelihood model that we
have previously proposed in (Bo Bo et al., 2015) to a
multi-camera likelihood model. We model a person
m at position s
m
as a fixed size cuboid placed at s
m
.
Thus, the observation model of a person m at s
m
from
a smart camera c is in fact the projection of the cuboid
at s
m
. A more accurate model would be to represent
persons by detailed 3D shapes, better approximating
to the shape of the human body. However, projecting
a cuboid on the image plane is computationally more
efficient than projecting more complex 3D shapes and
allows speedups using integral images. Also, com-
plex 3D shapes with more parameters, require these
parameters to be optimized as part of tracking. Fi-
nally, the foreground observations are imperfect any-
way and the there is little benefit in employing an
“perfect model.” For this reason, we also further ap-
proximate the projected cuboid by its bounding box
ω
c
(s
m
).
Consider a particular smart camera c, we have
a foreground image F
t,c
as an observation at time t.
Given the positions of M persons s
1
t
,. ..s
M
t
, we would
like to compute the likelihood
p
c
(F
t,c
|s
1
t
,. ..s
M
t
) = l
c
(s
1
t
,. ..s
M
t
). (1)
of the observed image F
t,c
. Since there are M per-
sons in the scene, there will be M rectangles on the
image plane, some of which may be intersecting each
other. For simplicity, let S
t
4
= [s
1
t
,. ..s
M
t
] be the ma-
trix whose columns are the M person positions and
let Ω
c
(S
t
)
4
=
S
M
m=1
ω
c
(s
m
t
) be the union of all rectan-
gles in the image. Ideally, when S
t
is equal to the true
positions of all M persons, Ω
c
(S
t
) must contain all
foreground pixels, and all background pixels must be
outside of Ω
c
(S
t
). However, this ideal situation can
never be reached since the cuboid model is far from
the actual 3D shape of the human body. Moreover, a
true foreground pixel can accidentally be detected as a
background pixel and vice versa due to noise. There-
fore, we formulate a likelihood function based on a
noisy binary channel model.
Let us denote the probability that a true fore-
ground pixel is wrongly detected as background as
ε
f
and the probability that a true background pixel
is wrongly detected as foreground as ε
b
. Obviously,
the values of ε
f
and ε
b
highly depend on the perfor-
mance of the foreground detection method. Here, we
make an assumption that conditioned on S
t
, all pixels
of F
t,c
are statistically independent. Then the condi-
tional probability p
c
(F
c
t
|S
t
) becomes a binomial dis-
tribution and the likelihood l
c
of M person(s) at S
t
,
given the observation F
t,c
from a smart camera c can
be computed as:
l
c
(S
t
) =
∏
r∈Ω
c
(S
t
)
(1 − ε
f
)
F
t,c
(r)
ε
1−F
t,c
(r)
f
·
∏
r/∈Ω
c
(S
t
)
(1 − ε
b
)
1−F
t,c
(r)
ε
F
t,c
(r)
b
(2)
The first factor of Eq. (2) evaluates how well the
pixels inside Ω
c
(S
t
) agree with the hypothesis that
S
t
is correct, while the second factor evaluates how
well the pixels outside of Ω
c
(S
t
) agree with the same
hypothesis. In many heuristic methods for “template
matching” in literature, the second factor is not taken
into account, but it is required according to the pro-
posed likelihood model and plays an important role.
To simplify the computation, taking the logarithm of
Eq. (2) gives
ll
c
(S
t
) =k + λ|Ω
c
(S
t
)| + λ
f
∑
r∈Ω
c
(S
t
)
F
t,c
(r)
+ λ
b
∑
r/∈Ω
c
(S
t
)
(1 − F
t,c
(r)),
(3)
where |R| is the area of an image region R, λ
f
4
=
ln
1−ε
f
ε
f
, λ
b
4
= ln
1−ε
b
ε
b
, λ
4
= ln
ε
f
ε
b
, and k
4
=
|I
c
|ln(ε
b
) is a constant independent of S
t
.
The interpretation of Eq. (3) is simplest when
ε
f
= ε
b
, i.e., the chance of a true foreground pixel
accidentally detected as background and the change
of a true background pixel accidentally detected as
foreground are equally likely. This simplification is
reasonable in practice since parameters of foreground
detection can be tuned to meet this condition. Thus
λ = 0 and Eq. (4) becomes
ll
c
(S
t
) =k + λ
f
∑
r∈Ω
c
(S
t
)
F
t,c
(r)
+ λ
b
∑
r/∈Ω
c
(S
t
)
(1 − F
t,c
(r)).
(4)
This shows that log-likelihood increases when more
foreground pixels are in Ω(S
t
) and fewer foreground
pixels are outside of Ω(S
t
).
To compute the likelihood of jointly observ-
ing F
t,1
,F
t,2
,. ..F
t,C
in camera 1,2,...C respectively,
given the positions of all persons S
t
, we assume that
the observations F
t,c
of different cameras are statisti-
cally independent, when conditioned on S
t
. the joint
likelihood l of all camera observations is then
p(F
t,1
,F
t,2
,. ..F
t,C
|S
t
) =
C
∏
c=1
l
c
(S
t
)
(5)
and
ll(S
t
) =
C
∑
c=1
ll
c
(S
t
). (6)
VISAPP 2016 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
606
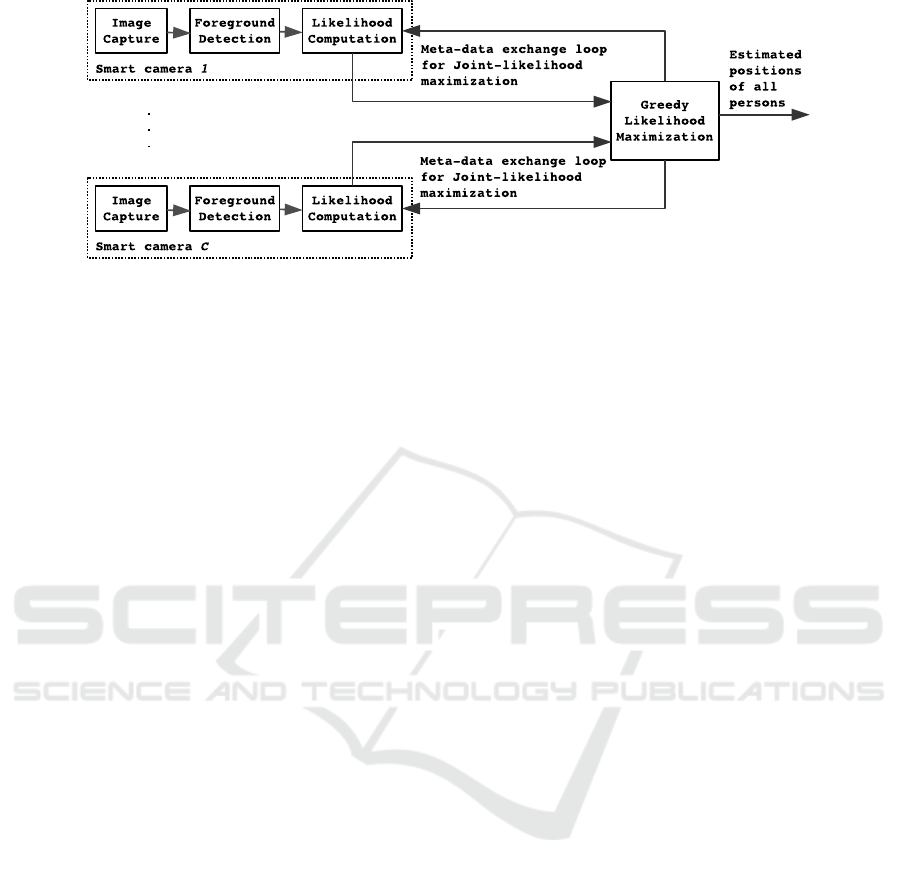
Figure 1: Block diagram showing the essential components and information flow of proposed decentralized multi-camera
tracker.
3.2 Real-time Likelihood Maximization
Our tracker maximizes the product of the likeli-
hood p(F
t,1
,F
t,2
,. ..F
t,C
|S
t
) and the motion model
p(S
t
|S
t−1
). The motion model expresses the probabil-
ity of persons moving from one position to the another
over the course of one time unit. We assume that all
persons move independently of each other. This as-
sumption is reasonable when people are far apart, but
not when they get closer together. In the latter case,
our assumption e.g., allows that people move to ex-
actly the same position, which is physically impossi-
ble. However, this assumption makes the likelihood
computation computationally tractable and some of
the possible inconsistencies can be detected and cor-
rected using post-processing.
Because of the assumption, the motion model be-
comes:
p(S
t
|S
t−1
) = p(s
1
t
|s
1
t−1
),. .. p(s
M
t
|s
M
t−1
).
(7)
Due to physical limitation, a person can move up to
a particular distance limit d
max
over the course of one
time unit. For our tracker, we assume that all motion
within a distance less than d
max
is equally likely, i.e.,
we adopt a uniform motion model. We believe that
this model is more robust to sudden motion changes
than more traditional Gaussian models. The latter fa-
vors slow motion over fast motion, but the uniform
model allows sudden motion changes. In the motion
model, we also do not take into account people’s ve-
locities and motion directions at time t − 1, as would
be done in popular Kalman models. Many Kalman
models in literature employ unrealistic assumptions,
i.e., they favor continuous or even constant velocity or
acceleration, which increases the probability of track-
ing loss. On the other hand, modeling discontinu-
ous motion is quite difficult. Therefore, we prefer the
“non-informative” uniform motion model.
A brute force search for S
t
= {s
1
t
,..., s
M
t
} that gives
the highest likelihood ll(S
t
) in a discretized search
space is a very time consuming task because it re-
quires the computation of likelihood using Eq. (6) for
all possible combinations of discretized people’s posi-
tions on the ground plane. Fortunately, because of the
constrained uniform motion model, the search space
is already greatly reduced: each person position can
only be in a circular region with radius d
max
around
the last known position of each person. Even in this
constrained search space, the computation time for
brute force likelihood maximization increases expo-
nentially with the number of persons M and with the
discretization accuracy.
However, by using the greedy likelihood maxi-
mization as shown in the pseudo code in Algorithm
1, we can make the computation time increases lin-
early with the number of persons M. The inputs of
the algorithm are the positions of all persons at time
t −1 sorted in descending order of
∑
C
c=1
Ω
c
(s
t−1
), i.e.,
the sum of the area of projected cuboids in all views
for a person at position s
t−1
. The reason behind this
sorting is that a larger projected cuboid contributes
more in likelihood computation. Thus it is desirable
to start the greedy maximization from a person’s posi-
tion which contributes the most to the joint likelihood
computation.
In Algorithm 1, we initialize S
t
with all previously
known positions in S
t−1
. Then, each position in S
t
is
optimized one at a time. The following steps are re-
peated until all positions in S
t
are updated. At each
iteration, a previously known location at the m
th
col-
umn is selected as s
m
t−1
. We define H as a set of all
discretized positions that fall within the circle with ra-
dius d
max
, which center is at s
m
t−1
. Then, an exhaustive
search is performed for each position in H as s
m
t
,
which gives the highest likelihood while keeping the
positions of the remaining person(s) fixed. The pre-
viously known position at the m
th
column in S
t
is re-
placed by s
m
t
. The iteration in Algorithm 1 can be
repeated until a stable solution is reached. However,
we experimentally found that terminating the iteration
when all the positions in S
t
are updated gives the op-
Multiple People Tracking in Smart Camera Networks by Greedy Joint-Likelihood Maximization
607

Algorithm 1: Greedy likelihood maximization.
1: Initialize S
t
4
= [s
1
t
,. ..s
M
t
] with [s
1
t−1
,. ..s
M
t−1
]
2: for m = 1 to M step 1 do
3: s
m
t
= the m
th
column of S
t
4: H
m
= the set of points s with ks − s
m
t
k ≤
d
max
.
5:
ˆ
s
m
t
= max
s∈H
m
ll([s
1
t
,. ..s
m
t
,s, s
m+1
t
,. ..s
M
t
])
6: Update S
t
by replacing its m
th
column by
ˆ
s
m
t
.
7: end for
timal trade-off between the accuracy and the compu-
tational time.
3.3 Decentralized Processing
This subsection describes how decentralized process-
ing is done in Algorithm 1 as well as the meta-data
exchanges between nodes. At each iteration of the
loop in the algorithm, all smart cameras compute
ll
c
([s
1
t
,. ..s
m
t
,s, s
m+1
t
,. ..s
M
t
]) : ∀s ∈ H
m
using Eq. 4 lo-
cally and send computed likelihoods (a set of num-
bers) to the likelihood maximizer. This meta-data
exchange is the most significant amount of data ex-
change between smart cameras and the likelihood
maximizer. The numbers of likelihoods to be sent
depends on the grid size of the discretized ground
plane and d
max
. The detailed analysis on commu-
nication bandwidth between nodes will be discussed
in Section 5. Once required likelihoods are received
from all cameras, the likelihood maximizer computes
ll([s
1
t
,. ..s
m
t
,s, s
m+1
t
,. ..s
M
t
]) using Eq. 6 and proceeds
to the remaining steps in the algorithm.
4 EVALUATION
4.1 Test Videos
To evaluate the performance of our tracker, we use
video sequences captured in a room of 8.8×9.2 m
2
.
Each sequence has a total duration of approximately
six minutes and is captured using four calibrated cam-
eras with overlapping views. There are a table and
chairs at the center of the meeting room. All videos
are captured at 20 fps with a resolution of 780×580
pixels. Up to four people are walking in the scene
and they are often occluded by other persons or furni-
ture. During the video capturing of the last sequences,
lights are switched on and off a couple of times to cre-
ate a scenario of rapid illumination changes. Ground
plane positions for each person are manually anno-
tated every 20 frames.
Walking Sequence: The purpose of this sequence
is to measure the performance of the tracker when
people are just walking around in the scene. In this
sequence, four people come into the meeting room
one after another, greet each other, walk around in the
room and finally leave the room. Most of the existing
publicly available datasets focus on tracking people
over a short period of time. For example, tracking a
person passing through the scene which may last for
a minute or two. In contrast, the same people walk
around in the room for about five minutes in this se-
quence.
Meeting Sequence: The majority of publicly
available dataset for people tracking are made in a
scenario in which people are moving around in the
scene. We are interested in evaluating our tracker in
a scenario in which people walk, sit down and walk
again. Thus, we capture this video sequence in a
meeting room scenario. In this video, four people
come into the room, greet each other and sit around
the table. During the meeting, a person sometimes
leave the chair to give a presentation.
Unsteady Lighting Sequence: To evaluate the
performance of our tracker when there are rapid il-
lumination changes, we capture the video sequence
of people walking while the illumination of the scene
is deliberately changed suddenly several times. The
scenario of this sequence is the same as Walking se-
quence except for the lighting in the room which is de-
liberately reduced to half and then completely turned
off several times. Note that although the lights are
switched off in the room, there is still dimmed light
coming from outside of the room.
4.2 Evaluation and Comparison
The performance of our tracker is evaluated on three
aforementioned video sequences. The same set of pa-
rameters is used for processing all sequences. We
experimentally select the parameters, i.e., brute force
search for a parameters combination, which gives the
optimal performance on all video sequences. The pa-
rameters of foreground extraction are set as follows:
the sliding window size k = 9, the correlation coeffi-
cient threshold ρ
min
= 0.98. For likelihood maximiza-
tion, the ground plane is discretized with 10 cm × 10
cm grid. The other parameters are set ε
f
= ε
b
= 0.001
and the maximum distance that a person can move be-
tween two consecutive frames d
max
= 50 cm. Using
aforementioned ground truth, we compute the most
widely used systematic evaluation metrics (Bernardin
and Stiefelhagen, 2008); the Multiple Object Track-
ing Accuracy (MOTA) and the Multiple Object Track-
ing Precision (MOTP) of the resulting trajectories.
VISAPP 2016 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
608

We use the same hit/miss threshold 100 cm as in
(Bredereck et al., 2012), (Andriyenko and Schindler,
2011), (Milan et al., 2013). For both metrics, higher
value indicates better performance.
Moreover, we compare the performance of our
tracker to the publicly available state of the art tracker
of Berclaz et al. (Berclaz et al., 2011) in terms of
both MOTA and MOTP. Their approach computes the
Probabilistic Occupancy Map (POM) on the ground
plane using the results of foreground detection from
all camera views. Their POM computation only con-
siders information from the current frames of all cam-
eras, but not the positions estimated in the previous
frame. However, in the data association step, K-
Shortest Path (KSP) optimization is used to find the
optimal trajectory of a person by enforcing tempo-
ral continuity constraints over POMs computed from
both past and future frames. In this paper, we will
refer to their tracker as POM-KSP.
For fair comparison, we use the same foreground
detection method as well as the same set of param-
eters for the POM-KSP tracker. As in our tracker,
we also set 10 cm ×10 cm grids for the POM-KSP
tracker. Since we set d
max
= 50 cm for our tracker, we
also set maximum distance traveled between consec-
utive frames for POM-KSP to be 5 grid locations.
5 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Our tracker achieves a MOTA value of 100% for
Walking sequence with a MOTP value as high as
86%. In the Meeting sequence, the MOTA value
drops slightly to 98% with MOTP of 77%, which is
still showing quite good performance for such chal-
lenging sequence. Performance comparison to pub-
licly available state of the art tracker shows that our
tracker outperforms.
In our tracker, we just approximate the volumet-
ric model of an upright standing human as a cuboid
with fixed width and height. The model fits well to
the observation as long as a person is standing. How-
ever, when a person sits down, the height of a person
is just a bit over an half of the standing height and
the actual observed foreground shape is far from the
shape of the projected model. Moreover, lower body
parts are occluded by both table and chair when a per-
son sits down and foreground detection fails to detect
occluded body parts. These are the main reasons for
small drop in MOTA and relatively high decrement in
MOTP. The example tracking results from our tracker
for both the Walking and the Meeting sequences are
shown in Fig. 2. The bounding box around each per-
son is in fact the Ω
c
(s
m
t
) and a different box color
shows different identity. The tailing dots of the bound
box, which has the same color as the box, is the pro-
jection of the positions estimates from the past 80
frames.
The evaluation of the Unsteady Lighting sequence
shows that our tracker is robust to sudden illumination
changes. Even in such difficult scenario, our tracker
achieves a MOTA value of 97% and a MOTP value
of 84%. The drop in MOTA is mainly caused by
false positive trajectories due to the presence of false
positive foreground blobs. These false positive fore-
ground blobs appear every time the light of the room
is completely off, i.e., the captured image tends to be
very noisy when illumination in the scene is very low.
The example frames for all four views of the Unsteady
Lighting sequence is shown in Fig. 3.
The projected cuboid to all views Ω
c
(s
m
t
) and the
projected points of 80 previously estimated positions
are shown as in Fig. 2. The first row of Fig.3 shows
the scene under under usual illumination. The second
row shows the frame after five seconds (100 frames),
where the lighting in the room is completely off.
Within a five seconds interval, the lighting in the room
is firstly reduced to half and then fully off. Despite the
presence of sudden illumination changes, we can see
that our tracker is still able to track all persons cor-
rectly.
As aforementioned, we compare the performance
of our tracker to the state of the art tracker of Berclaz
et al. (POM-KSP) as shown in Table 1. The compari-
son shows that our tracker outperforms in all three se-
quences. The POM-KSP performs well in sequences
containing only upright walking persons, i.e., the
Walking and the Meeting sequences. However, the
POM-KSP performs poorly in the Meeting sequence.
The reason could be that their tracker is not designed
to track sitting persons as there is reported results in
their paper (Berclaz et al., 2011) are only for upright
moving people. Moreover, Berclaz et al. (Berclaz
et al., 2011) reported that their POM-KSP tracker is
sensitive to false detections and missing ones. In the
Unsteady Lighting sequence, the sudden illumination
changes cause foreground detection to produce false
positive blobs which leads to false detection in POM
thus lower accuracy in tracking. However, for our
tracker, these false positive blobs cause only 3% drop
in MOTA. This shows that our tracker is less sensitive
to false positive detections.
In each iteration of greedy likelihood algorithm
(Algorithm 1), each smart camera sends 81 likelihood
values (numbers) to the likelihood maximizer when
using 10 cm ×10 cm grids and d
max
= 50 cm. Since
the number of iteration is the number of person being
tracked, each smart camera sends 81 ×m numbers per
Multiple People Tracking in Smart Camera Networks by Greedy Joint-Likelihood Maximization
609

Cam 1 Cam 2 Cam 3 Cam 4
Figure 2: Example tracking results obtained by our tracker. The first row shows the example trajectories in four views of
the Walking Sequence and the second row shows the Metting Sequence. Different bounding box colors indicates different
identities.
Cam 1 Cam 2 Cam 3 Cam 4
Figure 3: Example tracking results obtained by our proposed tracker in the Unsteady Lighting sequence. Different bounding
box colors indicates different identities.
frame, i.e., the amount of data exchange increases lin-
early with the number of person being tracked. This
shows that our tracker is more communication effi-
cient than those follows centralized architecture.
6 CONCLUSION
In this paper, we present a novel method for tracking
multiple people simultaneously within a smart camera
network by maximizing the likelihood of observed
foreground image in all camera views given the posi-
tions of all persons. The evaluation results show that
our tracker achieves MOTA value as high as 100%
and MOTP value as high as 86%. We also show that
our tracker is able to track people reliably even when
they are sitting down. This is a desirable advantage
in several applications, such as smart meeting room,
since people are sitting in the scene most of the time.
Moreover, our tracker is robust to sudden illumination
changes.
When we compare to publicly available state of
the art tracker (POM-KSP), our tracker outperforms.
Currently, our prototype tracker is implemented on
an ordinary computer as a single thread C++ pro-
gram, which processes all four camera views sequen-
tially. Without code optimization, the average pro-
cessing time of our tracker is 200 milliseconds per
frame, approximately 50 milliseconds per frame per
camera view, on a single core of Intel Core2Quad @
2.66 GHz with 8 GB of memory. Therefore, we be-
lieve that our tracker can reach the processing speed
VISAPP 2016 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
610
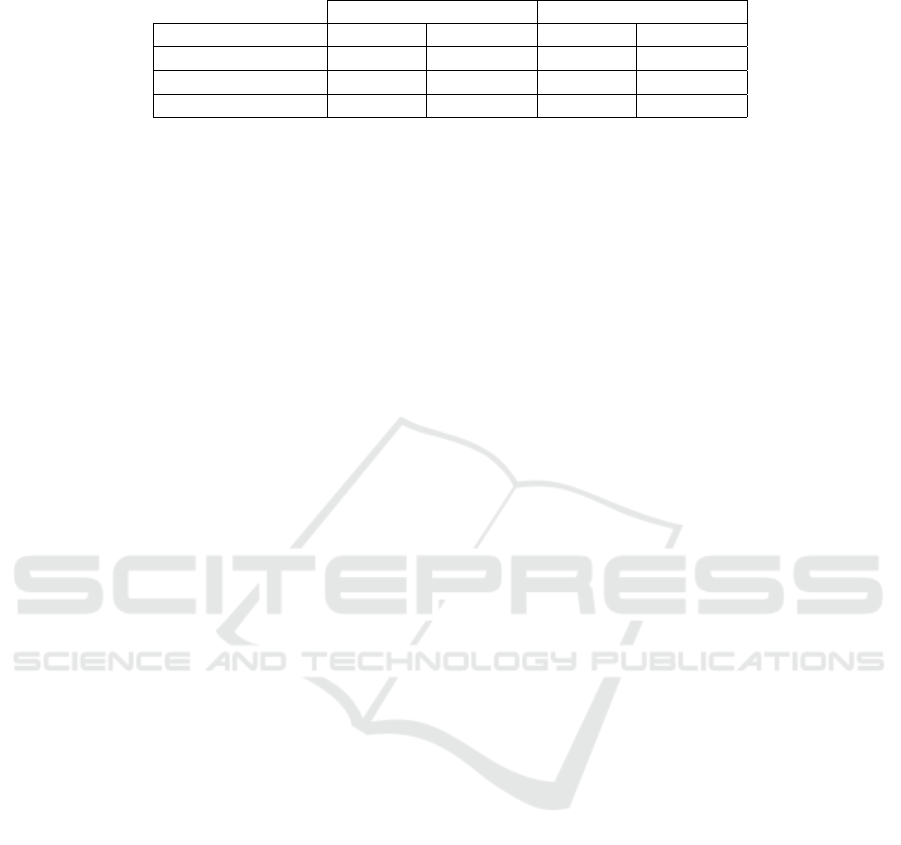
Table 1: MOTA and MOTP comparison.
MOTA MOTP
Sequence Proposed POM-KSP Proposed POM-KSP
Walking 100% 93% 86% 83%
Meeting 98% 54% 77% 75%
Unsteady Lighting 97% 83% 86% 84%
of 20 frames per second if the processing is paral-
lelized in a distributed architecture, i.e., processing
for each camera is implemented as a separate thread
or on a smart camera.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The work was financially supported by FWO through
the project G.0.398.11.N.10 “Multi-camera human
behavior monitoring and unusual event detection”.
REFERENCES
Andriyenko, A. and Schindler, K. (2010). Globally optimal
multi-target tracking on a hexagonal lattice. In Pro-
ceedings of the 11th European Conference on Com-
puter Vision: Part I, ECCV’10, pages 466–479.
Andriyenko, A. and Schindler, K. (2011). Multi-target
tracking by continuous energy minimization. In Com-
puter Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2011
IEEE Conference on, pages 1265–1272.
Berclaz, J., Fleuret, F., Turetken, E., and Fua, P. (2011).
Multiple object tracking using k-shortest paths opti-
mization. IEEE Trans. on Pattern Analysis and Ma-
chine Intelligence, 33(9):1806–1819.
Bernardin, K. and Stiefelhagen, R. (2008). Evaluating mul-
tiple object tracking performance: The clear mot met-
rics. J. Image Video Process., 2008:1–10.
Bo Bo, N., Deboeverie, F., Eldib, M., Guan, J., Xie, X.,
Nio, J., Van Haerenborgh, D., Slembrouck, M., Van de
Velde, S., Steendam, H., Veelaert, P., Kleihorst, R.,
Aghajan, H., and Philips, W. (2014). Human mobility
monitoring in very low resolution visual sensor net-
work. Sensors, 14(11):20800–20824.
Bo Bo, N., Deboeverie, F., Veelaert, P., and Philips, W.
(2015). Real-time multi-people tracking by greedy
likelihood maximization. In International Conference
on Distributed Smart Cameras (ICDSC2015), Seville,
Spain.
Bredereck, M., Jiang, X., Korner, M., and Denzler, J.
(2012). Data association for multi-object tracking-by-
detection in multi-camera networks. In Distributed
Smart Cameras (ICDSC), 2012 Sixth International
Conference on, pages 1–6.
Gruenwedel, S., Jela
˘
ca, V., Ni
˜
no Casta
˜
neda, J., Van Hese,
P., Van Cauwelaert, D., Van Haerenborgh, D., Vee-
laert, P., and Philips, W. (2014). Low-complexity
scalable distributed multi-camera tracking of humans.
ACM Transactions on Sensor Networks, 10(2).
Henriques, J. F., Caseiro, R., and Batista, J. (2011). Glob-
ally optimal solution to multi-object tracking with
merged measurements. In IEEE International Con-
ference on Computer Vision, ICCV 2011, Barcelona,
Spain, November 6-13, 2011, pages 2470–2477.
Milan, A., Schindler, K., and Roth, S. (2013). Detection-
and trajectory-level exclusion in multiple object track-
ing. In Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition
(CVPR), 2013 IEEE Conference on, pages 3682–
3689.
Pirsiavash, H., Ramanan, D., and Fowlkes, C. C. (2011).
Globally-optimal greedy algorithms for tracking a
variable number of objects. In Proceedings of the
2011 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pat-
tern Recognition, CVPR ’11, pages 1201–1208.
Wojek, C., Roth, S., Schindler, K., and Schiele, B. (2010).
Monocular 3d scene modeling and inference: Under-
standing multi-object traffic scenes. In Proceedings of
the 11th European Conference on Computer Vision:
Part IV, ECCV’10, pages 467–481.
Yang, J., Vela, P. A., Shi, Z., and Teizer, J. (2009). Proba-
bilistic multiple people tracking through complex sit-
uations. In 11th IEEE International Workshop on
PETS, pages 79–86.
Yun, Y., Gu, I.-H., and Aghajan, H. (2012). Maximum-
likelihood object tracking from multi-view video by
combining homography and epipolar constraints. In
The 2012 Sixth International Conference on Dis-
tributed Smart Cameras (ICDSC).
Zhang, L., Li, Y., and Nevatia, R. (2008). Global data asso-
ciation for multi-object tracking using network flows.
In Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2008.
CVPR 2008. IEEE Conference on.
Multiple People Tracking in Smart Camera Networks by Greedy Joint-Likelihood Maximization
611
