
A Turntable-based Approach for Ground Truth Tracking Data
Generation
Zolt
´
an Pusztai
1,2
and Levente Hajder
1
1
Distributed Events Analysis Laboratory, MTA SZTAKI, Kende utca 13-17. H-1111, Budapest, Hungary
2
E
¨
otv
¨
os Lor
´
and University, Budapest, Hungary
Keywords:
Ground Truth Dataset, Ground Truth Dataset, 3D Scanner, 3D Reconstruction.
Abstract:
Quantitative evaluation of feature trackers can lead significant improvements in accuracy. There are widely
used ground truth databases in the field. One of the most popular datasets is the Middlebury database to
compare optical flow algorithms. However, the database does not contain rotating 3D objects. This paper
proposes a turntable-based approach that fills this gap. The key challenge here is to calibrate very accurately
the applied camera, projector, and turntable. We show here that this is possible, even if just a simple chessboard
plane is used for the calibration. The proposed approach is validated on 3D reconstruction and ground truth
tracking data generation of real-world objects.
1 INTRODUCTION
Developing a realistic 3D approach for feature tracker
evaluation is very challenging since realistic moving
3D objects can simultaneously rotate and translate,
moreover, occlusion can also appear in the images.
It is not easy to implement a system that can generate
ground truth (GT) data for real-world 3D objects. The
aim of this paper is to present a novel structured-light
reconstruction system that can produce extremely ac-
curate feature points of rotating spatial objects.
The Middlebury database
1
is considered as the
state-of-the-art GT feature point generator. The
database itself consists of several datasets that had
been continuously developed since 2002. In the
first period, they generated corresponding feature
points of real-world objects (Scharstein and Szeliski,
2002). The first Middlebury dataset can be used for
the comparison of feature matchers. Later on, this
stereo database was extended with novel datasets us-
ing structured-light (Scharstein and Szeliski, 2003) or
conditional random fields (Pal et al., 2012). Even sub-
pixel accuracy can be achieved in this way as it is dis-
cussed in (Scharstein et al., 2014).
However, our goal is to generate tracking data via
multiple frames, the stereo setup is too strict limita-
tion for us.
1
http://vision.middlebury.edu/
The description of the optical flow datasets of
Middlebury database was published in (Baker et al.,
2011). It was developed in order to make the optical
flow methods comparable. The latest version contains
four kinds of video sequences:
1. Fluorescent Images: Nonrigid motion is taken by
a color and a UV-camera. Dense ground truth
flow is obtained using hidden fluorescent texture
painted on the scene. The scenes are moved
slowly, at each point capturing separate test im-
ages in visible light, and ground truth images with
trackable texture in UV light.
2. Synthesized Database: Realistic images are gen-
erated by an image syntheses method. The tracked
data can be computed by this system as every
parameters of the cameras and the 3D scene are
known.
3. Imagery for Frame Interpolation: GT data is com-
puted by interpolating the frames. Therefore the
data is computed by a prediction from the mea-
sured frames.
4. Stereo Images of Rigid Scenes: Structured light
scanning is applied first to obtain stereo recon-
struction. (Scharstein and Szeliski 2003). The
optical flow is computed from ground truth stereo
data.
The main limitation of the Middlebury optical
flow database is that the objects move approximately
500
Pusztai, Z. and Hajder, L.
A Turntable-based Approach for Ground Truth Tracking Data Generation.
DOI: 10.5220/0005719404980509
In Proceedings of the 11th Joint Conference on Computer Vision, Imaging and Computer Graphics Theory and Applications (VISIGRAPP 2016) - Volume 3: VISAPP, pages 500-511
ISBN: 978-989-758-175-5
Copyright
c
2016 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

linearly, there is no rotating object in the datasets.
This is a very strict limitation as tracking is a chal-
lenging task mainly when the same texture is seen
from different viewpoint.
It is interesting that the Middlebury multi-view
database (Seitz et al., 2006) contains ground truth 3D
reconstruction of two objects, however, the ground
truth tracking data were not generated for these se-
quences. Another limitation of the dataset is that only
two low-textured objects are used.
It is obvious that tracking data can also be gen-
erated by a depth camera (Sturm et al., 2012) such
as Microsoft Kinect, but its accuracy is very limited.
There are other interesting GT generators for planar
objects such as the work proposed in (Gauglitz et al.,
2011), however, we would like to obtain the tracked
feature points of real spatial objects.
Due to these limitations, we decided to build a
special hardware in order to generate ground truth
data. Our approach is based on a turntable, a cam-
era, and a projector. They are not too costly, however,
the whole setup is extremely accurate as it is shown
here.
Accurate Calibration of Turntable-based 3D Scan-
ners. The application of structured-light scanner is
a relatively cheap and accurate possibility to build a
real 3D scanner as it is discussed in the latest work
of (Moreno and Taubin, 2012). Another possibility
for a very accurate 3D reconstruction is laser scan-
ning (Bradley et al., 1991), however, the accurate cal-
ibration of the turntable is not possible using a laser
stripe since it can only reconstruct a 2D curve at a mo-
ment. For turntable calibration, the reconstruction of
2D objects is a requirement since the axis of the rota-
tion can be computed by registrating the point clouds
of the same rotating object.
Moreover, the calibration of the camera and pro-
jector intrinsic and extrinsic parameters is also cru-
cial. While the camera calibration can be accurately
carried out by the well-known calibration method
of (Zhang, 2000), the projector calibration is a more
challenging task. The projector itself can be consid-
ered as an inverse camera: while the camera projects
the 3D world to the 2D image, the projector projects
the planar image onto the 3D world. For this rea-
son, the corresponding points of the 3D world and
the projector image cannot be matched. Therefore,
firstly the pixel-pixel correspondences have to be de-
tected between the camera and the projector. The
application of structured light was developed in or-
der to efficiently realize this correspondence detec-
tion (Scharstein and Szeliski, 2003).
Many projector calibration methods exist in the
field. The first popular class of existing solu-
tions (Sadlo et al., 2005; Liao and Cai, 2008; Ya-
mauchi et al., 2008) is to (i) use a calibrated camera
to determine the world coordinate, (ii) then a pattern
is projected onto the calibration plane, the corners are
detected and locations are estimated in 3D, (iii) then
the 3D → 2D correspondences are given by running
the (Zhang, 2000) calibration. The drawback of this
kind of approaches is that its accuracy is relatively
low since the projected 3D corner locations are esti-
mated, and these estimated data are used for the final
calculation.
Another possible solution is to ask the user to
move the projector at different positions (Anwar et al.,
2012; Jamil Drar
´
eni, 2009). It is not possible for our
approach as the projector is fixed. Moreover, the ac-
curacy of these kind of approaches is also very low.
There are algorithms where both projected and
printed pattern are used (Audet, 2009; Martynov
et al., 2011). The main idea here is that if the pro-
jected pattern is iteratively adjusted until it fully over-
laps the printed pattern, then the projector parameters
can be estimated. Color patterns can also be applied
for this purpose (Park and Park, 2010). However, we
found that this quite complicated method is not re-
quired to calibrate the camera-projector system.
Our calibration methods for both the camera and
projector use a simply chessboard plane. Our al-
gorithms are very similar to those of (Moreno and
Taubin, 2012). As it is shown here later, we cali-
brate the camera first by the method of (Zhang, 2000).
Then the point correspondences between camera and
projector pixels are determined by robustly estimating
the local homography close to the chessboard corners.
Then the intrinsic projector parameters can be com-
puted by (Zhang, 2000) as well. The extrinsic param-
eters (relative translation and orientation between the
camera and the projector) can given by a stereo cal-
ibration problem. For this purpose, there are several
solutions as it is discussed in (Hartley and Zisserman,
2003) in detail. However, we found that the accuracy
of stereo calibration is not accurate, therefore we pro-
poses a more sophisticated estimation here.
Contribution of this Study. The main novelty of
this paper is that we show here that very accurate GT
feature data can be generated for rotating object if a
camera-projector system is applied with turntable. To
the best of our knowledge, our approach is the first
system that can yield such accurate GT tracking data.
The usage of a turntable for 3D reconstruction itself is
not a novel idea, but its application for GT data gen-
eration it is.
The calibration algorithms within the system have
a minor and a major improvements:
• The camera-projector correspondence estimation
A Turntable-based Approach for Ground Truth Tracking Data Generation
501

Turntable
Projector
Object
Camera
Figure 1: Hardware components of structured light scanner. Left: schematic figure. Right: Realized scanner.
is based on a robust (RANSAC-based) homogra-
phy estimation.
• The turntable calibration is totally new: while
usual turntable calibrators (Kazo and Hajder,
2012) compute the axis by performing a usual
chessboard-based calibration method (Zhang,
2000) for the rotating chessboard plane, and the
axis of the rotation is computed from the extrin-
sic camera parameters, we propose a novel opti-
mization problem that minimizes the reprojection
for the corners of the rotating chessboard. We
found the accuracy of this novel algorithm is sig-
nificantly better. During the turnable calibration,
the extrinsic parameters of the camera and projec-
tor are also obtained.
2 PROPOSED EQUIPMENT AND
ALGORITHMS
Our 3D scanner consists of 3 main parts. It is visu-
alized in Fig. 1. The left plot is the schematic setup,
while the right one shows the realization of the scan-
ner. The main components of the equipment are the
camera, the projector, and the turntable. Each of the
above needs to be calibrated correctly to reach high
accuracy in 3D scanning. The camera and the pro-
jector are fixed to their arms, but the turntable can
move
2
: it is able to rotate the object to be recon-
structed.
The bottleneck of the proposed approach is the
calibration of the components. In this section, it is
overviewed how the camera, the projector, and the
axis of the rotating table can be accurately calibrated.
2
These arms are also moving, but their calibration is not
considered here, it is a possible future work.
The paper is organized as follows. The software
components are overviewed in Figure 2. The cam-
era, projector and turntable calibration is described in
Section 2.1, 2.1, and 2.3, respectively. Sec. 3 shows
how accurate GT data can be generated by the devel-
oped equipment. Finally, Sec. 6 concludes the work
and discusses the limitations. calibration,
2.1 Camera Calibration
For describing the camera we choose the pinhole
model with radial distortion. Assuming that the coor-
dinate system is aligned to the camera, the projection
of the point X ∈ R
3
to the camera plane is u ∈ R
2
,
which can be described by the equation:
u = K
c
˜u,
K
C
=
f
x
γ p
x
0 f
y
p
y
0 0 1
,
˜u =
u
x
[1 + k
1
r
2
+ k
2
r
4
]
u
y
[1 + k
1
r
2
+ k
2
r
4
]
,
r
2
= u
2
x
+ u
2
y
,
where K
C
stands for the camera matrix, f
x
and f
y
are
the focal length, (p
x
, p
y
) is the principal point, and γ is
the shear. In our case we only used radial distortion,
which can be described by two parameters: (k
1
,k
2
).
The camera matrix and the distortion parameters are
together called the intrinsic parameters of the camera.
A black and white chessboard is held in sight of
the camera at arbitrary positions. Images were taken
and the chessboard corners were found on the images,
and they refined to reach sub-pixel precision. Then we
can compute the intrinsic parameters of the camera by
the method of (Zhang, 2000).
VISAPP 2016 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
502

parameters
parameters
calibration
Camera
calibration
Projector
Basic Calibration
calibration images
calibration images
illuminated by projector
Turntable Calibration
in Chessboard Plane
Axis Point Estimation
camera extrinsic
parameters
projector extrinsic
parameters
camera intrinsic
projector intrinsic
turntable axis
using PnP Method
with/without illumination of projector
Images of rotating chessboard
Axis Direction Estimation
Figure 2: Software components of the whole calibration pipeline.
2.2 Projector Calibration
Since the projector can be viewed as an inverse cam-
era, it can be described by the same model applied for
the camera before. However, finding the right pro-
jector pixels, which through the chessboard corners
are seen from the viewpoint of the projector is not
so obvious. To overcome this problem, a structured
light sequence is projected to the scene. It precisely
encodes the pixel coordinates in the projector image.
For each scene point, the projected codes has to be
decoded. From this point, the chessboard must be
placed in a position that can be viewed from both the
camera and projector.
The structured light we used for the calibration is
based on the binary Gray code since it is the most
accurate coding for structured light scanning as it is
discussed in (Scharstein and Szeliski, 2003). In addi-
tion, we project inverse images after every single one,
meaning that every pixel on the images is reversed.
But before structured light utilized, full black and
white images are projected for easier object recogni-
tion, and for easier decoding of the structured light.
Since the resolution of our projector is 1024×768,
the number of the projected images are 42 for each
chessboard orientation. The projected sequence con-
sists of 2 pure black and white images, 10 images for
encoding the horizontal, and 10 for encoding the ver-
tical coordinates of each projector pixel. Addition-
ally, the inverse images have to be inserted into the
sequence as well. These images are taken from one
viewpoint, and they are called as the image set.
After all the images are taken, one can begin
the decoding of the structured light. First of all, we
calculate the direct and indirect intensity of the light,
pixel by pixel for each image set. The full method is
described in (Nayar et al., 2006). Then the minimum
and maximum intensities are determined per pixel
and then the direct and indirect values are given by
the equations as follows:
L
D
=
L
max
− L
min
1 − B
L
I
=
2(L
min
− B ∗ L
max
)
1 − B
2
Where B is the amount of light emitted by a
turned-off projector pixel. We needed to separate
these 2 components from each other, because we are
only interested in the direct intensities lit by the pro-
jector.
Then we need to classify the pixels on each image
pair, consisting the image given by the structured light
and its inverse. There are 3 clusters to classify into:
1. The pixel is lit on the first image.
2. The pixel is not lit on the first image.
3. Cannot be determined.
The classification rules are as follows:
• L
D
< M =⇒ the pixel is in the 3. class,
• L
d
> L
I
∧ P
1
> P
2
=⇒ the pixel is lit,
• L
d
> L
I
∧ P
1
< P
2
=⇒ the pixel is not lit,
• P
1
< L
D
∧ P
2
> L
I
=⇒ the pixel is not lit,
• P
1
> L
I
∧ P
2
< L
I
=⇒ the pixel is lit,
• otherwise it cannot be determined.
The pixel intensity in the first and inverse images are
denoted by P
1
, and P
2
, respectively, while M is a user-
defined threshold: M = 5 is set in our approach. If the
difference between P
1
and P
2
is greater than M, then
the pixel is discarded.
For further reading about the classification, we
recommend to read the study of (Xu and Aliaga,
2007).
Since the chessboard consists of alternating black
and white squares, decoding near the chessboard cor-
ners can resolve errors. To avoid these errors, we cal-
culate local homographies around the corners. We use
A Turntable-based Approach for Ground Truth Tracking Data Generation
503

11 pixel-wide kernel window and every successfully
decoded projector pixel is in consideration. For the
homography estimation, a RANSAC-based (Fischler
and Bolles, 1981) DLT homography estimator is ap-
plied in contrast to the work of (Moreno and Taubin,
2012) where robustification is not dealt with. We
found that the accuracy is increased when RANSAC-
scheme is applied. After the homography is com-
puted among the camera and projector pixels, we use
this homography to transform the camera pixels to the
projector image. In this way we get the exact projec-
tor pixels we needed, so we can use the method of
(Zhang, 2000) to calibrate the projector. Remark that
the extrinsic projector calibration will be refined later,
but the intrinsic parameters will not.
2.3 Turntable Calibration
The aim of the turntable calibration is to compute the
axis of the turntable. It is represented by a point and
a direction. Therefore, the degree of freedom of a
general axis estimation is four (2 DoFs: position of a
plane; other 2 DoFs: direction) .
Fortunately, the current problem is constrained.
We know that the axis is perpendicular to the plane
of the turntable. Thus, the direction is given, only
the position should be calculated within the turntable
plane.
The turntable is calibrated if we know the center-
line which the table is turning around. Two methods
was used to calculate this 3D line. First we place the
chessboard on the turntable, and start rotating it. Im-
ages are taken between the rotations, and the extrinsic
parameters can be computed for each image since the
camera is already calibrated. This motion is equiv-
alent with the motion of a steady chessboard and a
moving camera. The circle that the camera follows
has the same centerline as the turntable. Thus fitting a
circle to the camera points estimates the centerline of
the turntable (Kazo and Hajder, 2012).
However, we found that this method is not accu-
rate enough. Therefore, we developed a novel algo-
rithm that is overviewed in the rest of this section.
2.3.1 Problem Statement of Turntable Axis
Calibration
Given a chessboard with known size, for which the
corners can be easily detected by widely used pat-
tern recognition algorithms, the goal is to estimate
the axis of the turntable. This is part of the calibra-
tion of a complex structured-light 3D reconstruction
system that consists of one camera, one projector, and
one turntable. The latter one is driven by a stepping
motor, the angle of the rotation can be very accurately
set. The camera and projector intrinsic parameters are
also known, in other words, they are calibrated.
The input data for axis calibration comes from de-
tected chessboard corners. The chessboard are placed
on the turntable. Then it is rotated and images are
taken with different rotational axis. The corners are
detected on all of these images. Then the chessboard
is placed in a higher position on the turntable, but the
new plane orientation is also parallel to the turntable.
Then the chessboard are rotated, and the corners are
detected as well. (The chessboard can be placed in
arbitrary altitudes. We only use two different values,
but the proposed calibration method can work with
arbitrary number of positions.)
If we consider the case when the planes of the
chessboard and the turntable are parallel, the distance
between them is h, then the chessboard corners can be
written as
X
Y
= (1)
cosα − sin α
sinα cosα
x − o
x
y − o
y
+
o
x
o
y
=
cosαx − sin αy + o
x
(1 − cos α) + o
y
sinα
sinαx + cos αy − o
x
cosα + o
y
(1 − cos α)
where α denotes the current angle of the rotation.
Note that altitude h does not influence the relation-
ship. Also remark that capital X and Y denote spatial
coordinates, while their lowercase letters (x and y) are
2D coordinates in image space.
2.3.2 Proposed Algorithm
The proposed axis calibration consists of two main
steps:
1. Determination of the axis center [o
x
,o
y
]
T
on
chessboard plane, and
2. computation of the camera and projector extrinsic
parameters.
Axis Center [o
x
,o
y
]
T
Estimation on Chessboard
Plane. The goal of the axis center estimation is
to calculate the location [o
x
,o
y
]
T
. We propose an
alternation-type method with two substeps:
Homography-step. The plane-plane homography
is estimated for each image. The 2D locations
of the corners in the images are known. The 2D
coordinates can be determined in the chessboard
plane by Eq. 1. If the homogenous coordinates are
used, the relationship becomes
VISAPP 2016 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
504

u
v
1
∼
H
cosαx − sin αy + o
x
(1 − cos α) + o
y
sinα
sinαx + cos αy − o
x
cosα + o
y
(1 − cos α)
1
.
(2)
We apply the standard normalized direct linear
transformation (normalized DLT) with a numerical
refinement step (Hartley and Zisserman, 2003) in or-
der to estimate the homography. It solves the lin-
earized version of Eq. 2:
E (α,x,y,o
x
,o
y
) = E
1
(α,x,y,o
x
,o
y
)+E
2
(α,x,y,o
x
,o
y
)
where
E
1
(α,x,y,o
x
,o
y
) =
uh
31
(cosαx − sin αy + o
x
(1 − cos α) + o
y
sinα) +
uh
32
(sinαx + cos αy + −o
x
cosα + o
y
(1 − cos α)) +
uh
33
−
h
11
(cosαx − sin αy + o
x
(1 − cos α) + o
y
sinα) −
h
12
(sinαx + cos αy + −o
x
cosα + o
y
(1 − cos α)) −
h
13
and
E
2
(α,x,y,o
x
,o
y
) =
vh
31
(cosαx − sin αy + o
x
(1 − cos α) + o
y
sinα) +
vh
32
(sinαx + cos αy + −o
x
cosα + o
y
(1 − cos α)) +
vh
33
−
h
21
(cosαx − sin αy + o
x
(1 − cos α) + o
y
sinα) −
h
22
(sinαx + cos αy + −o
x
cosα + o
y
(1 − cos α)) −
h
13
This is a linear problem. The center and the scale of
the applied coordinate system can be arbitrary chosen.
As it is discussed in (Hartley and Zisserman, 2003),
the mass center and quasi-uniform scale is the most
accurate choice. The error function E (α,x,y, o
x
,o
y
)
can be written for every chessboard corner point for
every rotational angle. Therefore, the minimization
problem is formulated as
argmin
H
G
x
∑
i=1
G
y
∑
j=1
N
∑
k=1
E (α
k
,x
i,α
,y
j,α
,o
x,α
,o
y,α
).
where a
k
∈ [0,2π], x
i
∈ [0,G
x
], and y
i
∈ [0,G
y
],
and G
x
,G
y
are the dimensions of chessboard cor-
ners, respectively. (Possible values for (x
i
,y
j
) are
(1,1),(1,2),(2,1),...etc. ) This problem remains an
over-constrained homogeneous linear one that can be
optimally solved.
Axis-step. Its goal is to estimate the axis location
[o
x
,o
y
]
T
. The above two equations are linear with re-
spect to the center coordinates. Therefore, the equa-
tions form a homogeneous linear system of equations
A[o
x
,o
y
]
T
= b, where
A =
a
11
a
12
a
21
a
22
where
a
11
= h
11
− h
11
cosα − h
12
sinα −
u(h
31
− h
31
cosα − h
32
sinα),
a
12
= h
11
sinα + h
12
− h
12
cosα −
u(h
31
sinα + h
32
− h
32
cosα),
a
21
= h
21
− h
21
cosα − h
22
sinα −
v(h
31
− h
31
cosα − h
32
sinα),
a
22
= h
21
sinα + h
22
− h
22
cosα −
v(h
31
sinα + h
32
− h
32
cosα),
and
b =
b
11
− b
12
b
21
− b
22
where
b
11
= h
13
+
h
11
(x cosα − y sin α) + h
12
(ycosα + x sin α),
b
12
= h
33
) +
u(h
31
(x cosα − y sin α) + h
32
(ycosα + x sin α),
b
21
= h
23
+
h
21
(x cosα − y sin α) + h
22
(ycosα + x sin α),
b
22
= h
33
+
v(h
31
(x cosα − y sin α) + h
32
(ycosα + x sin α)).
The above equations can be written for all corners
of the chessboard for all rotated positions. There-
fore, both the homography- and the axis-steps are ex-
tremely over-constrained. Thus, the parameters can
be very accurately estimated. It is interesting that
the homography and the axis location estimations
are homogeneous, and inhomogeneous linear prob-
lems, respectively. They can also solved for the over-
determined case as it is well-known (Bj
¨
orck, 1996).
The two substeps have to be run one after the
other. Both steps minimize the same algebraic error,
therefore the method converges to the closest (local)
minimum. Unfortunately, global optimum cannot be
theoretically guaranteed. But we found that the algo-
rithm converges to the correct solution. The speed of
A Turntable-based Approach for Ground Truth Tracking Data Generation
505

the convergence is relatively fast, to our experiments,
20 − 30 iterations are required to reach the minimum.
Parameter Initialization. The proposed alternation
method requires initial values for o
x
and o
y
. It has
been found that the algorithm is not too sensitive to
the locations of the initial values. The center of the
chessboard is an appropriate solution for o
x
and o
y
.
Moreover, we have tried more sophisticated methods.
If the camera centers are estimated by a Perspective
n Point (PnP) algorithm such as (Lepetit et al., 2009),
then the camera centers for the rotating sequence form
a circle (Kazo and Hajder, 2012) as it is mentioned in
the first part of this section. The center of this circle is
also a good initial value. However, we found that the
correct solution is reached as well if the initial center
is an arbitrary point within the chessboard region.
2.3.3 Axis Center Estimation in the Global
System
The first algorithm estimates the center of the axis
in the coordinate system of the chessboard. But the
chessboard are placed in different positions with dif-
ferent altitudes. The purpose of the algorithm dis-
cussed in this section is to place the rotated chess-
board in the global coordinate system and to deter-
mine the extrinsic parameters (location and orienta-
tion) of the projector. The global system is fixed to
the camera, therefore, the camera extrinsic parame-
ters have not to be estimated.
In our calibration setup, only two chessboard se-
quences are taken. The extrinsic position can be eas-
ily determined. If the 3D coordinates of the plane are
known, the 2D locations are detected, then the esti-
mation of the projective parameters is called the PnP
problem. Mathematically, the PnP optimization can
be written as
argmin
R,t
G
x
∑
i=1
G
y
∑
j=1
N
∑
k=1
Rep
R,t,
u
i,α
v
j,α
,
x
0
i,α
h
where the definition of the function Rep is as fol-
lows:
Rep
R,t,
u
i
v
j
,
x
0
i
y
0
j
h
=
DeHom
R
x
0
i
y
0
j
h
+t
−
u
i
v
j
2
2
.
The applied comma (’) means that the origin
of the coordinate system for chessboard corners
are placed at [o
x
,o
y
]
T
.Function DeHom gives
the dehomogeneous 2D vector of a spatial vector
as DeHom([X,Y, Z]
T
) = [X/Z,Y /Z]
T
.
There are solutions that can cope with planar
points. We used the EPnP (Lepetit et al., 2009) al-
gorithm for our approach. At this point, the rel-
ative transformation between the chessboard planes
and the camera can be calculated. They are denoted
by [R
1
,t
1
], and [R
2
,t
2
]. The altitude of the chessboard
can be measured. Without loss of generalization, al-
titude of the first plane can be set to zero: h
1
= 0.
(The simplest way is to set the first chessboard to the
turntable. Then the altitude of the second chessboard
can be easily measured with respect to the turntable.)
The estimation of one parameter is relatively sim-
ple. We solve it by exhaustive search. The best value
is given by the rotation for which the reprojection er-
ror of the PnP problem is minimal:
argmin
R,t
G
x
∑
i=1
G
y
∑
j=1
N
∑
k=1
Rep
1
+ Rep
2
where
Rep
1
= Rep
R
1
,t
1
,
u
i,α
k
v
j,α
k
,
x
0
i,α
k
y
0
j,α
k
0
Rep
2
= Rep
R
2
,t
2
,
u
i,k
v
i,k
,
x
0
i,α+α
k
y
0
j,α+α
k
h
where the upper index denotes the number of the
chessboard. The relationship between the left and
right terms are that the spatial points have to rotated
with the same angle, but a fix angular offset ∆α has to
be added to each rotation for the second chessboard
plane with respect to the first one. (The setup is vi-
sualized in Fig. 3.) The impact of ∆α for the second
rotation matrix is written as follows:
R
2
=
cos∆α − sin ∆α 0
sin∆α cos∆α 0
0 0 1
R
1
(3)
The minimization problem is also a PnP one,
therefore it can be efficiently solved by (Lepetit et al.,
2009). The estimation of ∆α is obtained by an ex-
haustive search.
Finally, the extrinsic parameters of the projector
are computed by running the PnP algorithm again for
the corners detected in the projector images. The ob-
tained projector parameters have to be transformed by
the inverse of the camera extrinsic parameters since
our global coordinate system is fixed to the camera.
VISAPP 2016 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
506

Figure 3: Visualized chessboard planed in the first position.
The edged are not parallel, therefore the relative angle ∆α
has to be estimated.
2.4 Object Reconstruction
The object reconstruction looks very similar to the
projector calibration. In this case, an object is placed
on the turntable instead of the chessboard. Structured
light is projected onto it, images are taken, then the
object is rotated. This procedure is repeated until
the object returns to the starting position. Then we
decode the projector pixels back from the structured
light projected in each image set. After it is done,
we use the Hartley-Strum triangulation (Hartley and
Sturm, 1997) for corresponding camera-projector pix-
els due to its accuracy to determine the object points
from one viewpoint. We calculate these for each
viewpoint, and then we can combine the point sets
together, which results a 3D points et of the full ob-
ject.
3 RESULTS
The main advantage of our method is that the whole
GT data generation is totally automatic. Therefore,
arbitrary number of objects can be reconstructed. We
show here four typical objects that have well trackable
feature points. They are as follows:
• Dinosaur. A typical researcher enjoys the recon-
struction of dinosaurs as it is shown in several sci-
entific papers, e.g (”Fitzgibbon et al., 1998). For-
tunately, kids also like it, and one of the authors’
sons has a plastic dinosaurs that could be recon-
structed. Therefore, we inserted a dino to our test-
ing dataset.
• Flacon. The Plastic holder is a good test case
since at least one well-textured label is fixed on
the surface of a usual flacon.
• Plush Dog. The tracking of the feature point of a
soft toy is a challenging task as it does not have a
flat surface. For this reason, we include a plush
dog into the testing database.
• Poster. The last sequence of our dataset is a rotat-
ing newspaper page. It is useful since it is a simple
textured plane. The efficiency of the trackers can
be checked in this example due to two reasons: (i)
there is no occlusion, and (ii) the feature tracking
is the determination of a plane-plane homography.
During the test, the objects were rotated by the
turntable, the difference of the degree of two subse-
quent was set to 3
◦
. Our GT tracking data generator
has two modes. (i) The first version regularly gener-
ates the feature points in the first image. The feature
points are located across a regular grid in the valid re-
gion of the camera image. (ii) The points in the first
image is determined by a feature generator. We use
the SIFT features (Lowe, 1999) in our testing exam-
ples, but arbitrary feature generators can be included.
Then the generated feature points were recon-
structed in the first image using the structured light.
Then these 3D reconstructed point coordinates were
rotated around the turntable axis with the known ro-
tating axis, and projected to the next image. This pro-
cedure was repeated for all the images of the test se-
quence. The 2D feature coordinates after projection
give the final GT for quantitative feature tracker com-
parison.
The input images of the sequences are visualized
in Figs. 4– 7. The 3D model of the reconstructed ob-
jects are also visualized in these Figures except the
Poster as it is a planar paper and its 3D model is not
interesting. The 3D models are represented by col-
ored point clouds, however, the color itself does not
influence the reconstruction. It is only painted due to
its spectacularity.
The computed ground truth data for the four ex-
amined sequences are pictured in Figs. 8– 11. The
first row shows the tracked points when the points are
selected across a grid. The second rows of Figs. 8– 7
consist of images with the tracked GT SIFT feature
points (yellow dots). We also applied an automatic
feature tracker (BruteForceMatcher of OpenCV) and
the estimated feature points are drawn in the images
with red color. However, the comparison of feature
vectors is out of the scope of this paper, we only want
to demonstrate that this comparison can be easily car-
ried out.
The obtained ground truth data were visually
checked by us and we have not found any inaccu-
racy on it. We think that the accuracy is below
pixel, in other word, subpixel accuracy was reached.
This is extremely low as the camera resolution is
2592 × 1936 (5 Mpixel).
A Turntable-based Approach for Ground Truth Tracking Data Generation
507

Figure 4: Two images of the ’Dino’ sequence and the reconstructed 3D point cloud from three viewpoints.
Figure 5: Two images of the ’Plush Dog’ sequence and the reconstructed 3D point cloud from three viewpoints.
Figure 6: Two images of the ’Flacon’ sequence and the reconstructed 3D point cloud from three viewpoints.
Figure 7: Two images from the ’Poster’ sequence.
4 COMPARISON OF
WELL-KNOWN FEATURE
TRACKERS
Thought this paper does not concentrate on the com-
parison of feature trackers, we run the most popu-
lar trackers implemented in the OpenCV library
3
.
Each tracker consists of separated methods in order
to generate, describe, and finally track good features.
However, the generation and description is given by
the same algorithms in our examples. The tracking
(matching) is different, we selected the most accurate
tracker for the generators based on our tests.
The applied feature generators are as follows:
1. Scale Invariant Feature Transform (SIFT) (Lowe,
1999)
2. Speeded Up Robust Features (SURF) (Bay et al.,
2008)
3. KAZE (Alcantarilla et al., 2012)
3
http://opencv.org
4. Accelerate KAZE (AKAZE) (Alcantarilla et al.,
2013)
5. Binary Robust Invariant Scalable Keypoints
(BRISK) (Leutenegger et al., 2011)
6. ORB (Oriented FAST and Rotated BRIEF)
(Rublee et al., 2011)
Several matchers have been tested for the selected
feature detectors/descriptors. OpenCV supports a
brute-force based matchers as well as the Flann (Fast
Approximate Nearest Neighbor) matcher (Muja and
Lowe, 2009). In the case of the brute-force based
matchers, all descriptors on the first image are com-
pared with all descriptors on the second image and
the best match, when the distance of the descriptors
is the lowest, is chosen. In Fig 12, ’BF L1’ means
that the brute-force matcher is used with the L
1
norm,
while ’BF H1’ means that the brute-force matcher is
used with the Hamming distance. L
2
norm is used for
algorithms ’BF L2’ and ’BF H2’.
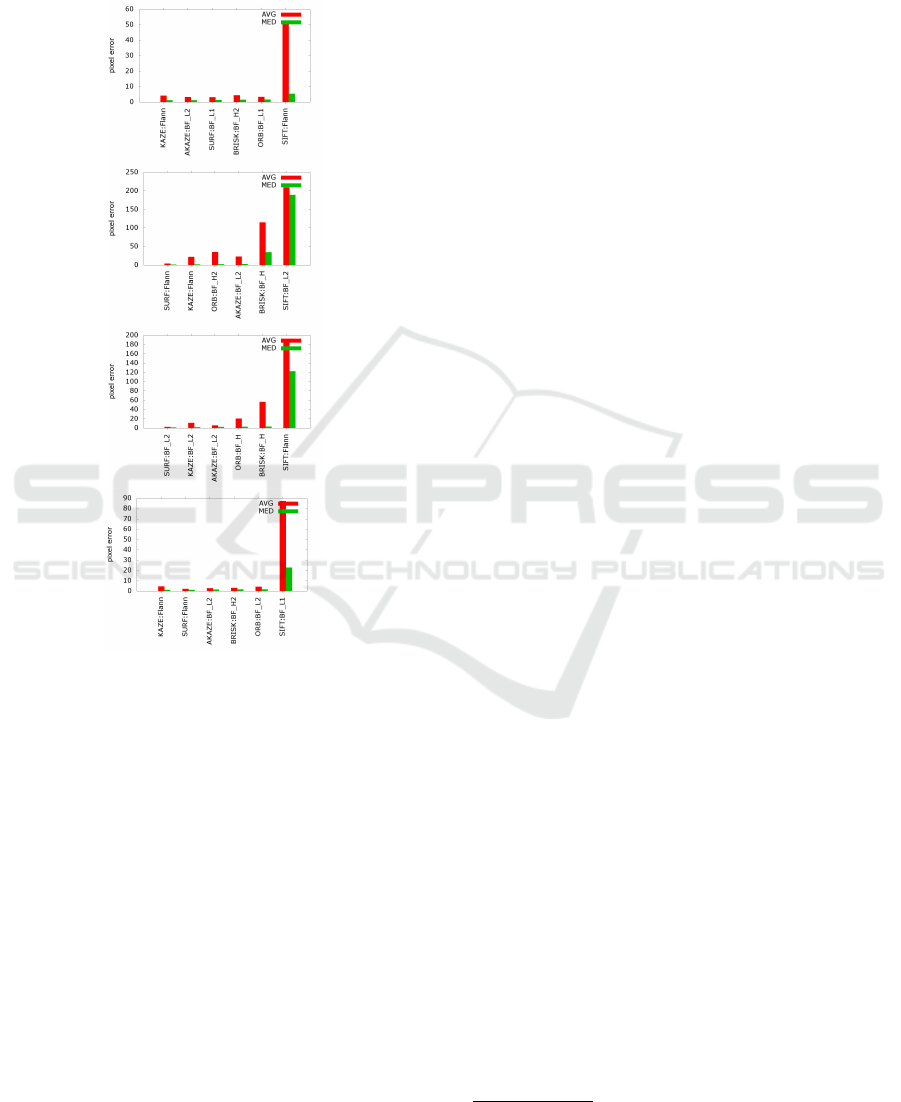
The rival trackers are compared on every test se-
quence. The error of the feature tracking is defined
as the difference between the tracked and GT coor-
dinates. The averages are calculated for each frame,
and this mean values is the error for the examined fea-
ture. Then the error of all feature errors are computed
as well. The median of the feature errors is also cal-
culated. These mean and median values of the rival
trackers are visualized in the plots of Fig. 12.
The detailed description of the feature detectors
and the evaluation of the test results are out of the
VISAPP 2016 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
508

Figure 8: The visualized ground truth tracking data drawn on images of the ’Flacon’ sequence. Top row: features generated
by a grid within valid image region. Bottom row: features generated by SIFT method.
Figure 9: The visualized ground truth tracking data drawn on images of the ’Dino’ sequence. Top row: features generated by
a grid within valid image region. Bottom row: features generated by SIFT method.
Figure 10: The visualized ground truth tracking data drawn on images of the ’Plush Dog’ sequence. Top row: features
generated by a grid within valid image region. Bottom row: features generated by SIFT method.
Figure 11: The visualized ground truth tracking data drawn on images of the ’Poster’ sequence. Top row: features generated
by a grid within valid image region. Bottom row: features generated by SIFT method.
A Turntable-based Approach for Ground Truth Tracking Data Generation
509
scope of this paper. We know that more informa-
tion are required to compare the methods, this short
description only wants to demonstrate that quantita-
tive comparison is possible by our equipment. A deep
comparison will be published very soon.
Figure 12: Tracking error for test sequences. Avg: mean,
Med: median. From top to bottom: Results for ’Flacon’,
’Dino’, Plush Dog’, and ’Poster’ testing objects.
5 LIMITATIONS & FUTURE
WORK
The main goal of the approach proposed here is to
be able to generate ground truth tracking data of
real-world rotating objects. Therefore, the turntable-
based equipment is unable to simulate moving cam-
eras. However, other databases (e.g. the famous Mid-
dlebury one) can do that, thus our approach should
be unified with existing datasets. Nevertheless, our
equipment contains two moving arms for both the
camera and projector, therefore novel viewpoints can
be added to the system. It is possible if the arms are
very accurately calibrated. This is a possible feature
work of our GT generation project.
Another disadvantage of the current system is that
part of the objects can be self-occluded due to the ob-
ject rotation. This cannot be detected by the hard-
ware, therefore surface reconstruction is required to
detect if the part of the scanned 3D object is occluded
by another part. To avoid this problem, we plan to de-
velop a continuous surface reconstruction method for
free-form spatial objects. If their quality is reliable,
it will help to detect the self-occlusion of the moving
objects.
6 CONCLUSIONS
We have proposed a novel GT tracking data genera-
tor here that can automatically produce very accurate
tracking data of rotating real-world spatial objects.
The main novelty of our approach is that it consists
of a turntable, and we showed how this turntable can
be accurately calibrated. Finally, the validation of our
equipment was shown. It was justified that the pro-
posed structured-light 3D scanner can produce accu-
rate tracking data as well as realistic 3D point clouds.
The GT tracking data are public, they are available at
our web page
4
.
REFERENCES
Alcantarilla, P. F., Bartoli, A., and Davison, A. J. (2012).
Kaze features. In ECCV (6), pages 214–227.
Alcantarilla, P. F., Nuevo, J., and Bartoli, A. (2013). Fast
explicit diffusion for accelerated features in nonlin-
ear scale spaces. In British Machine Vision Conf.
(BMVC).
Anwar, H., Din, I., and Park, K. (2012). Projector calibra-
tion for 3d scanning using virtual target images. Inter-
national Journal of Precision Engineering and Manu-
facturing, 13(1):125–131.
Audet, S.and Okutomi, M. (2009). A user-friendly method
to geometrically calibrate projector-camera systems.
In Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Work-
shops, pages 47 – 54.
Baker, S., Scharstein, D., Lewis, J., Roth, S., Black, M.,
and Szeliski, R. (2011). A database and evaluation
methodology for optical flow. International Journal
of Computer Vision, 92(1):1–31.
Bay, H., Ess, A., Tuytelaars, T., and Van Gool, L. (2008).
Speeded-up robust features (surf). Computer Vision
and Image Understanding, 110(3):346–359.
Bj
¨
orck,
˚
A. (1996). Numerical Methods for Least Squares
Problems. Siam.
Bradley, C., Vickers, G., and Tlusty, J. (1991). Automated
rapid prototyping utilizing laser scanning and free-
4
http://web.eee.sztaki.hu
VISAPP 2016 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
510

form machining. CIRP Annals – Manufacturing Tech-
nology, 41(1):437–440.
Fischler, M. and Bolles, R. (1981). RANdom SAmpling
Consensus: a paradigm for model fitting with appli-
cation to image analysis and automated cartography.
Commun. Assoc. Comp. Mach., 24:358–367.
”Fitzgibbon, A. W., Cross, G., and Zisserman, A. (”1998”).
”automatic 3D model construction for turn-table se-
quences”. In ”3D Structure from Multiple Images of
Large-Scale Environments, LNCS 1506”, pages ”155–
170”.
Gauglitz, S., H
¨
ollerer, T., and Turk, M. (2011). Evaluation
of interest point detectors and feature descriptors for
visual tracking. International Journal of Computer
Vision, 94(3):335–360.
Hartley, R. I. and Sturm, P. (1997). Triangulation. Computer
Vision and Image Understanding: CVIU, 68(2):146–
157.
Hartley, R. I. and Zisserman, A. (2003). Multiple View Ge-
ometry in Computer Vision. Cambridge University
Press.
Jamil Drar
´
eni, S
´
ebastien Roy, P. S. (2009). Geometric
video projector auto-calibration. In Proceedings of the
IEEE International Workshop on Projector-Camera
Systems, pages 39–46.
Kazo, C. and Hajder, L. (2012). High-quality structured-
light scanning of 3D objects using turntable. In IEEE
3rd International Conference on Cognitive Infocom-
munications (CogInfoCom) , pages 553–557.
Lepetit, V., F.Moreno-Noguer, and P.Fua (2009). Epnp: An
accurate o(n) solution to the pnp problem. Interna-
tional Journal Computer Vision, 81(2):155–166.
Leutenegger, S., Chli, M., and Siegwart, R. Y. (2011).
Brisk: Binary robust invariant scalable keypoints. In
Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on
Computer Vision, pages 2548–2555.
Liao, J. and Cai, L. (2008). A calibration method for un-
coupling projector and camera of a structured light
system. In IEEE/ASME International Conference on
Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics, pages 770 – 774.
Lowe, D. G. (1999). Object recognition from local scale-
invariant features. In Proceedings of the International
Conference on Computer Vision, ICCV ’99, pages
1150–1157.
Martynov, I., Kamarainen, J.-K., and Lensu, L. (2011). Pro-
jector calibration by ”inverse camera calibration”. In
SCIA, volume 6688 of Lecture Notes in Computer Sci-
ence, pages 536–544.
Moreno, D. and Taubin, G. (2012). Simple, accurate, and
robust projector-camera calibration. In 2012 Second
International Conference on 3D Imaging, Modeling,
Processing, Visualization & Transmission, Zurich,
Switzerland, October 13-15, 2012, pages 464–471.
Muja, M. and Lowe, D. G. (2009). Fast approximate near-
est neighbors with automatic algorithm configuration.
In In VISAPP International Conference on Computer
Vision Theory and Applications, pages 331–340.
Nayar, S. K., Krishnan, G., Grossberg, M. D., and Raskar,
R. (2006). Fast separation of direct and global com-
ponents of a scene using high frequency illumination.
ACM Trans. Graph., 25(3):935–944.
Pal, C. J., Weinman, J. J., Tran, L. C., and Scharstein, D.
(2012). On learning conditional random fields for
stereo - exploring model structures and approximate
inference. International Journal of Computer Vision,
99(3):319–337.
Park, S.-Y. and Park, G. G. (2010). Active calibration of
camera-projector systems based on planar homogra-
phy. In ICPR, pages 320–323.
Rublee, E., Rabaud, V., Konolige, K., and Bradski, G.
(2011). Orb: An efficient alternative to sift or surf.
In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference
on Computer Vision, ICCV ’11, pages 2564–2571.
Sadlo, F., Weyrich, T., Peikert, R., and Gross, M. H.
(2005). A practical structured light acquisition sys-
tem for point-based geometry and texture. In Sympo-
sium on Point Based Graphics, Stony Brook, NY, USA,
2005. Proceedings, pages 89–98.
Scharstein, D., Hirschm
¨
uller, H., Kitajima, Y., Krathwohl,
G., Nesic, N., Wang, X., and Westling, P. (2014).
High-resolution stereo datasets with subpixel-accurate
ground truth. In Pattern Recognition - 36th German
Conference, GCPR 2014, M
¨
unster, Germany, Septem-
ber 2-5, 2014, Proceedings, pages 31–42.
Scharstein, D. and Szeliski, R. (2002). A Taxonomy and
Evaluation of Dense Two-Frame Stereo Correspon-
dence Algorithms. International Journal of Computer
Vision, 47:7–42.
Scharstein, D. and Szeliski, R. (2003). High-accuracy
stereo depth maps using structured light. In CVPR
(1), pages 195–202.
Seitz, S. M., Curless, B., Diebel, J., Scharstein, D., and
Szeliski, R. (2006). A comparison and evaluation of
multi-view stereo reconstruction algorithms. In 2006
IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vi-
sion and Pattern Recognition (CVPR 2006), 17-22
June 2006, New York, NY, USA, pages 519–528.
Sturm, J., Engelhard, N., Endres, F., Burgard, W., and Cre-
mers, D. (”2012”). ”a benchmark for the evaluation
of rgb-d slam systems”. In ”Proc. of the International
Conference on Intelligent Robot Systems (IROS)”.
Xu, Y. and Aliaga, D. G. (2007). Robust pixel classification
for 3d modeling with structured light. In Proceedings
of the Graphics Interface 2007 Conference, May 28-
30, 2007, Montreal, Canada, pages 233–240.
Yamauchi, K., Saito, H., and Sato, Y. (2008). Calibration
of a structured light system by observing planar ob-
ject from unknown viewpoints. In 19th International
Conference on Pattern Recognition, pages 1–4.
Zhang, Z. (2000). A flexible new technique for camera cal-
ibration. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and
Machine Intelligence, 22(11):1330–1334.
A Turntable-based Approach for Ground Truth Tracking Data Generation
511
