
Virtual Correction of Eyesight using Visual Illusions
Midori Aoki, Fumihiko Sakaue and Jun Sato
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Nagoya Institute of Technology,
Gokiso, Showa, Nagoya 466-8555, Japan
Keywords:
Eyesight Correction, Visual Illusion, Lateral Inhibition, High Resolution, Deconvolution.
Abstract:
Degradation of eyesight is a serious problem, and the number of weak-sighted people is increasing rapidly in
recent years because of the spread of tablets and smart phones. The weak-sighted people often wear glasses and
contact lenses for recovering their eyesight. However, these rectification devises are painful for weak-sighted
people. Thus, in this paper, we propose a novel method for displaying visual information for weak-sighted
people to see rectified images on displays. In particular, we show that visual illusions in human vision system
can be used efficiently for correcting the eyesight. By using our method, weak-sighted people can see clear
images on the display without wearing glasses and contact lenses. The efficiency of the proposed method is
tested by using synthetic signals and real images.
1 INTRODUCTION
In recent years, many people suffer from eyesight
problems. Young people often have nearsightedness
because of reading textbooks, tablets etc., and old
people have farsightedness because of aging. Once
we have eyesight problems, we usually wear eye
glasses or contact lenses. However, these glasses and
contact lenses are painful, and they also cause stress
to weak-sighted people.
Thus, we in this paper propose a method for cor-
recting the eyesight of weak-sighted people virtually
by showing modified images on displays. The near-
sightedness and farsightedness cause depth blurs on
the retina, and these depth blurs can be described by
the convolution of a point spread function (PSF) with
the original image.
For correcting the weak-sightedness, Alonso and
Barreto (Alonso and Barreto, 2003) proposed a
method for displaying deconvolution images with the
PSF of weak-sightedness. However, the dynamic
range of the deconvolution images becomes much
larger than that of the standard displays, and thus we
need to reduce the contrast of the deconvolution im-
ages, or cut out the over range signals which causes
errors in eyesight correction. For showing clear
images without reducing image contrast, Huang et
al. (Huang et al., 2012; Wetzstein et al., 2012; Huang
et al., 2014) proposed eyesight correction based on
light field displays. The light field displays can con-
trol the light field emitted from the display system,
and thus they enable us to concentrate lights on the
retina in the eyeball, even if the eyeball has weak-
sightedness. Although the light field displays can
correct weak-sightedness, they require micro lens ar-
rays in front of the display or multi-layer structure of
display planes. Thus their structures are very com-
plex, and precise calibrations of optical system are re-
quired. The light field displays also require very high
resolution 2D displaying systems in general, since
they control 4D light fields.
In this paper, we propose a method for showing
clear images to weak-sighted people using standard
displays. For this objective, we consider visual illu-
sions in human visual systems. It is known that the
human visual system observes various types of illu-
sion, such as shape distortion, color distortion and
intensity distortion. In this paper, we in particular
consider visual illusion on perceived intensity. It is
known that the intensity illusion occurs based on the
so called lateral inhibition (Ratliff, 1965) in visual
neurons. The lateral inhibition can be considered as
a natural signal filter equipped in the human visual
systems. We in this paper use the lateral inhibition
of human visual systems to visualize clear images to
weak-sighted people.
Aoki, M., Sakaue, F. and Sato, J.
Virtual Correction of Eyesight using Visual Illusions.
DOI: 10.5220/0005719801250130
In Proceedings of the 11th Joint Conference on Computer Vision, Imaging and Computer Graphics Theory and Applications (VISIGRAPP 2016) - Volume 3: VISAPP, pages 127-132
ISBN: 978-989-758-175-5
Copyright
c
2016 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All r ights reserved
127

Figure 1: Chevreul illusion caused by the lateral inhibition.
These five intensities are constant in each area. However, at
the boundary of two different intensities, the bright intensity
is observed more brightly, and the dark intensity is observed
more darkly. As a result, we perceive the change in intensity
in a constant intensity area.
2 VISUAL ILLUSION AND
LATERAL INHIBITION
We first consider visual illusion on perceived inten-
sity. There are many types of intensity illusions, but it
is known that most of the intensity illusions are based
on a simple property of human visual systems, that is
lateral inhibition. The lateral inhibition is an activity
in human visual systems, in which an excited neuron
suppresses the excitement of neighboring neurons in
visual systems. Because of the lateral inhibition, a
small difference in the input signal is emphasized in
the output signal. As a result, we perceive the over-
shoot and undershoot of intensity at the discontinuity
of original image intensity. These overshoot and un-
dershoot in perceived intensity cause various visual
illusions, such as Mach band illusion (Ratliff, 1965)
and Chevreul illusion (Chevreul, 1890). Fig. 1 shows
the example of Chevreul illusion, in which we per-
ceive the change in intensity in a constant intensity
area, which is caused by the overshootand undershoot
of perceived intensity at the boundary of two different
intensities.
The lateral inhibition can be modeled by the dif-
ference of Gaussian (DOG) or the Laplacian of Gaus-
sian (LOG) (Marr and Hildreth, 1980). In this paper
we model the lateral inhibition by using the Laplacian
of Gaussian ∇
2
G(x, y) as follows:
∇
2
G(x, y) =
d
2
dx
2
G(x, y) +
d
2
dy
2
G(x, y) (1)
Since the output signal S
o
(x, y) is the sum of the orig-
inal input signal S
i
(x, y) with the lateral inhibition, it
can be described by the following convolution:
S
o
(x, y) = L(x, y) ∗ S
i
(x, y) (2)
where, L(x, y) is a function which causes lateral in-
hibition, and can be described by using the Laplacian
of Gaussian and the Dirac delta function δ(x, y) as fol-
(a) original signal
(b) observed signal
Figure 2: Visual illusion caused by the lateral inhibition.
(a) shows the original input image signal, and (b) shows the
observed signal with the lateral inhibition.
lows:
L(x, y) = δ(x, y) − α∇
2
G(x, y) (3)
α denotes the magnitude of lateral inhibition in hu-
man visual systems, and its value must be chosen em-
pirically.
Fig. 2 shows the distortion of perceived intensity
caused by the lateral inhibition modeled by Eq. (2).
Fig. 2 (a) shows the original input signal and (b)
shows the output signal derived from Eq. (2). As
shown in this figure, the difference of intensity in the
original signal has been emphasized in the output sig-
nal. The important point is that the human visual sys-
tem can perceive higher intensity than the maximum
intensity of display system, and can also perceiveneg-
ative intensity, i.e. intensity lower than the zero level
of display system. This means the human visual sys-
tem can perceive wider dynamic range images than
those shown on the display. In the following part of
this paper, we use this property of human visual sys-
tems for correcting weak-sight in human vision effi-
ciently.
3 PRE-FILTERING FOR
WEAK-SIGHTED PEOPLE
If we have nearsightedness or farsightedness, the ob-
served images have depth blur. This depth blur can
be described by the convolution of the original input
image S
i
(x, y) with a point spread function P(x, y) as
follows:
S
o
(x, y) = P(x, y) ∗ S
i
(x, y) (4)
Thus, if we know the point spread function P(x, y) of
a weak-sighted person, the clear non-blurring image
can be observed by the weak-sighted person by show-
ing the deconvolution image generated by the follow-
ing equation:
S
′
i
(x, y) = P(x, y)
−1
∗ S
i
(x, y) (5)
By substituting S
′
i
in Eq. (5) into S
i
in Eq. (4), we
find that the observed image S
o
(x, y) will be identical
VISAPP 2016 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
128

with the original image S
i
(x, y) as follows:
S
o
(x, y) = P(x, y) ∗ S
′
i
(x, y)
= P(x, y) ∗ P(x,y)
−1
S
i
(x, y)
= S
i
(x, y) (6)
This method is proposed by Alonso and Bar-
reto (Alonso and Barreto, 2003).
However, the intensity of the new input image S
′
i
derived from the deconvolution overflows the range
of display in general, and its intensity sometimes be-
comes higher than the maximum intensity of the dis-
play, and sometimes becomes minus. Since the mi-
nus intensity and out of range intensity cannot be
shown by the display, we have to modify the dy-
namic range of the deconvolution image S
′
i
, so that
its range is within the dynamic range of the display.
However, this modification drastically degrades the
dynamic range of the observed image. For avoiding
this problem, Huand et al. (Huang et al., 2012) pro-
posed a multi-layer display system, which consists of
multiple display planes. Although is can control the
light field and correcting weak-sightedness avoiding
the dynamic range problem, the device structure of
the multi-layer display is quite complex, and it is very
difficult of construct as it is pointed out by the same
authors.
4 PRE-FILTERING BASED ON
VISUAL ILLUSION
For solving the dynamic range problem by using
the standard displaying system, we next propose a
method for generating display images based on visual
illusions in intensity.
In our method, we do not modify the dynamic
range of the input image S
i
. In stead of modifying
the dynamic range of S
i
, we simply cut out the out of
range intensity in the deconvolution image S
′
i
as fol-
lows:
S
′′
i
(x, y) = C[S
′
i
(x, y)]
= C[P(x, y)
−1
∗ S
i
(x, y)] (7)
where, C[I] is a cut out function which takes the fol-
lowing values according to the intensity I:
C[I] =
0 (I < 0)
255 (I > 255)
I (otherwise)
(8)
However, S
′′
i
is no longer identical with S
′
i
, and thus
the observed image S
o
of S
′′
i
is not identical with the
(a) sinusoidal signal (b) step signal
Figure 3: The original image signals used in our experi-
ments. (a) is a sinusoidal signal and (b) is a step signal.
original image S
i
as follows:
S
o
(x, y) = P(x, y) ∗ S
′′
i
(x, y)
= P(x, y) ∗C[P(x, y)
−1
S
i
(x, y)]
6= S
i
(x, y) (9)
Thus, what we need to do is to find a display image
S
′′
i
(x, y), which minimizes the following observation
error E:
E =
∑
x
∑
y
||S
i
(x, y) − P(x, y) ∗ S
′′
i
(x, y)||
2
(10)
As we have seen in section 2, the human visual
system can perceive higher dynamic range images
than those shown by the display system. Thus, by
using this property, we may be able to derive better
display images for human observers. For counting the
lateral inhibition L(x, y) in human vision system, we
consider the following observation error E
′
instead of
E in Eq.(10):
E
′
=
∑
x
∑
y
||L(x, y) ∗ S
i
(x, y)
−L(x, y) ∗ P(x, y) ∗ S
′′
i
(x, y)||
2
(11)
However, S
′′
i
(x, y) does not have enough freedom to
minimize E
′
effectively. Thus, we consider a high res-
olution image S
′′
i
(x
′
, y
′
) as the display image, and de-
rive the high resolution display image S
′′
i
(x
′
, y
′
) which
minimizes the following observation error E
′′
:
E
′′
=
∑
x
∑
y
||L(x, y) ∗ S
i
(x, y)
−D[L(x
′
, y
′
) ∗ P(x
′
, y
′
) ∗ S
′′
i
(x
′
, y
′
)]||
2
(12)
where, D[·] denotes the down sampling from high
resolution to the original image resolution, and
L(x
′
, y
′
) and P(x
′
, y
′
) represent lateral inhibition and
PSF in high resolution. Assuming the lateral inhibi-
tion and the PSF of the observer are known, the opti-
mum display image S
′′
i
(x
′
, y
′
) can be derived from the
objective image S
i
(x, y) by minimizing E
′′
.
5 EXPERIMENTS
We next show the efficiency of the proposed method
by using synthetic image signals and real images.
Virtual Correction of Eyesight using Visual Illusions
129
(a) normal sight
(b) normal sight
(c) weak sighted
(d) weak sighted
Figure 4: The images observed by a normal sight observer
and a weak-sighted observer. (a) and (b) show the observa-
tion of the normal sight observer, and (c) and (d) show the
observation of the weak-sighted observer respectively.
5.1 Synthetic Image Experiments
We first show results from synthetic image signals.
Fig. 3 (a) and (b) show two different original image
signals. (a) is a sinusoidal signal and (b) is a step
signal. In this experiment, we assume that the lateral
inhibition of human observer is modeled by Eq.(3),
where the standard deviation of the Gaussian function
is 1.0 pixel and α = 3.0. The PSF of the weak-sighted
observer is a Gaussian function with the standard de-
viation of 2.5 pixels. Then, Fig. 4 (a) and (b) show
the observation of a normal sight observer, and (c)
and (d) show the observation of the weak-sighted ob-
server. As shown in (c) and (d), the observations of
the weak-sighted observer are blurred. Also, the ob-
served intensity range of the weak-sighted observer is
smaller than that of the normal sight observer.
We derived display images for weak-sighted ob-
server by using four different methods, that is (1)
existing method, (2) lateral inhibition method, (3)
high resolution method, and (4) lateral inhibition with
high resolution method. The existing method derives
display images based on Eq.(7). The lateral inhibi-
tion method derives display images which minimize
Eq.(10). The high resolution method derives display
images based on Eq.(11). The lateral inhibition with
high resolution method derives display images which
minimize Eq.(12). The number of image pixels in the
high resolution display is twice of that in the normal
resolution display in this experiment. i
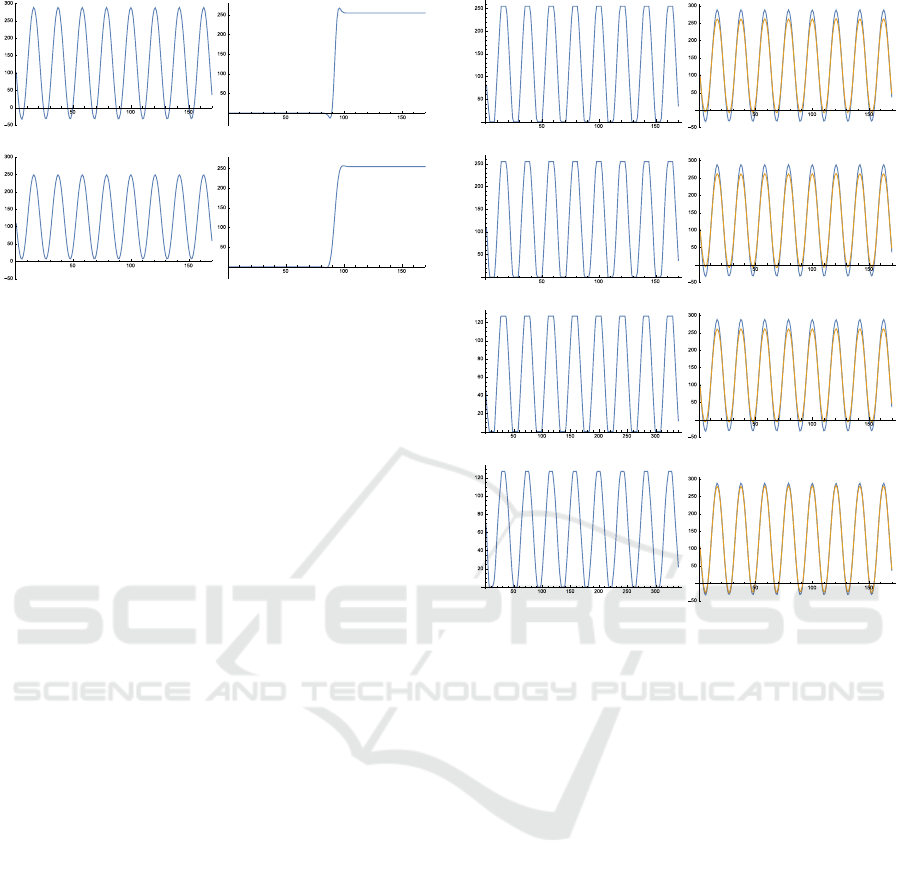
The left column of Fig. 5 shows display images
generated by using these four methods, and the right
column of Fig. 5 shows images observed by a weak-
sighted observer. The red lines show observed images
and the blue lines show their ground truth. The RMS
errors of observed images are also shown in the right
(1) existing method
RMSE = 16.13
(2) lateral inhibition
RMSE = 16.21
(3) high resolution
RMSE = 16.53
(4) lateral inhibition with high
resolution
RMSE = 4.46
Figure 5: The display images and observed images. The
left column shows display images generated from (1) exist-
ing method, (2) lateral inhibition method, (3) high resolu-
tion method, and (4) lateral inhibition with high resolution
method. The red lines in the right column show these im-
ages observed by a weak-sighted observer and the blue lines
show the ground truth of observed images.
column. Fig. 6 shows the results from the step signal.
As shown in these images, the simple lateral inhi-
bition and the simple high resolution method do not
provide us better results. However, the proposed lat-
eral inhibition with high resolution method provides
us much better results than the existing methods and
other methods. Note, the proposed method enables
us to observe negative intensities and over range in-
tensities accurately as shown in Fig. 5 (d) and Fig. 6
(d). These results show the efficiency of the combi-
nation of lateral inhibition and high resolution in the
proposed method.
5.2 Real Image Experiments
We next show results from real image experiments.
Fig. 7 (a) and (b) show original images used in our
experiments. The lateral inhibition and the PSF of a
weak-sighted observer is the same as those used in
VISAPP 2016 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
130

(1) existing method
RMSE = 4.33
(2) lateral inhibition
RMSE = 4.65
(3) high resolution
RMSE = 4.46
(4) lateral inhibition with high
resolution
RMSE = 1.73
Figure 6: The display images and observed images. The
left column shows display images generated from (1) exist-
ing method, (2) lateral inhibition method, (3) high resolu-
tion method, and (4) lateral inhibition with high resolution
method. The red lines in the right column show these im-
ages observed by a weak-sighted observer and the blue lines
show the ground truth of observed images.
(a) (b)
Figure 7: The images used in our real image experiments.
the synthetic image experiments. Fig. 4 (a) and (b)
show the observation of a normal sight observer, and
(c) and (d) show the observation of the weak-sighted
observer.
We derived display images for weak-sighted ob-
server by using the existing method and the proposed
method which combines the lateral inhibition with
(a) display image (b) observed image
(c) display image (d) observed image
Figure 8: (a) and (b) show the display image and the ob-
served image of a weak sighted observer in the existing
method. (c) and (d) show those in the proposed method.
high resolution displaying. Fig. 8(a) shows the dis-
play image derived from the existing method, and
(b) shows the image observed by a weak-sighted ob-
server. Fig. 8(c) shows the display image derived
from the proposed method, and (d) shows the image
observed by a weak-sighted observer. Fig. 9 shows
the results from another image. Note, the resolu-
tion of the observed images in the proposed method
is same as that in the existing method. As shown
in Fig. 8 (b) and (d) and Fig. 9 (b) and (d) , the
proposed method provides us better observation for
weak-sighted observer. This is because the proposed
method uses the lateral inhibition in human observers
efficiently.
Fig. 10 shows the comparison of the frequency
characteristics of observed images in the existing
method and the proposed method, i.e. lateral inhi-
bition with high resolution. Fig. 10 (a) is the fre-
quency characteristic of the ground truth observation
of Fig. 7 (a). Fig. 10 (b) is that of the existing method,
and (c) is that of the proposed method. As shown
in these images, both the existing method and the
proposed method lose high frequency components.
However, the proposed method can preserve more
high frequency components than the existing method.
Since the high frequency components correspond to
the sharpness of images, these results confirm that the
weak-sighted people can observe better images.
Virtual Correction of Eyesight using Visual Illusions
131

(a) display image (b) observed image
(c) display image (d) observed image
Figure 9: (a) and (b) show the display image and the ob-
served image of a weak sighted observer in the existing
method. (c) and (d) show those in the proposed method.
(a) ground truth
(b) existing method (c) proposed method
Figure 10: The frequency characteristics of observed im-
ages. (a) is the ground truth, (b) is the observation in the
existing method, and (c) is the observation in the proposed
method.
6 CONCLUSION
In this paper, we proposed a method for displaying vi-
sual information for weak-sighted people to see clear
images on the display. For this objective, we used the
lateral inhibition which causes visual illusions in hu-
man visual systems. The lateral inhibition enhances
input signals and thus the human visual systems can
observe wider dynamic range than that in the display
device. By using this property, we generated the op-
timum display images for weak-sighted observed to
see original clear images without wearing glasses and
contact lenses. We showed that the lateral inhibition
works efficiently by combining it with high resolution
displaying. The efficiency of the proposed method is
tested by using synthetic images and real images.
REFERENCES
Alonso, M. and Barreto, A. (2003). Pre-compensation for
high-order aberrations of the human eye using on-
screen image deconvolution. In Proc. Annual Interna-
tional Conference of the IEEE EMBS, pages 556–559.
Chevreul, M. (1890). The Principles of Harmony and Con-
trast of Colors. George Bell and Sons.
Huang, F., Lanman, D., Barsky, B., and Raskar, R. (2012).
Correcting for optical aberrations using multilayer
displays. In Proc. ACM SIGGRAPH Asia.
Huang, F., Wetzstein, G., Barsky, B., and Raskar, R.
(2014). Eyeglass-free display: Towards correcting vi-
sual aberrations with computational light field display.
In Proc. ACM SIGGRAPH.
Marr, D. and Hildreth, E. (1980). Theory of edge detection.
Proceedings of Royal Society of London, B(27):187–
217.
Ratliff, F. (1965). Mach Bands: Quantitative Studies on
Neural Networks in the Retina. Holden Day.
Wetzstein, G., Lanman, D., Hirsch, M., and Raskar, R.
(2012). Tensor displays: Compressive light field syn-
thesis using multilayer displays with directional back-
lighting. In Proc. ACM SIGGRAPH.
VISAPP 2016 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
132
