
3D Interaction Techniques for Virtual Shopping: Design and Preliminary
Study
Eulalie Verhulst
1,2
, Paul Richard
1
, Emmanuelle Richard
1
, Philippe Allain
2
and Pierre Nolin
3
1
Laboratoire Angevin de Recherche en Ing
´
enierie des Syst
`
emes (LARIS - EA 7315), Universit
´
e d’Angers, Angers, France
2
Laboratoire de Psychologie des Pays de la Loire (LPPL EA 4838), Universit
´
e d’Angers, Angers, France
3
Laboratoire de Recherche Interdisciplinaire en R
´
ealit
´
e Virtuelle (LARI-RV),
Keywords:
Virtual Reality, Interaction Techniques, Virtual Supermarket, User Study.
Abstract:
Virtual Reality is now recognized as a powerful tool for the assessment and rehabilitation of both motor and
cognitive impairments. In this context, effective Virtual Environments (VEs) that simulate everyday tasks
must be proposed. We have developed a virtual supermarket (VS) in which the user can explore and collect
various items using a shopping cart. Four interaction techniques have been designed and compared in terms
of usability, performance and workload with healthy volunteer participants. These techniques go beyond
the desktop paradigm by offering a more immersive and intuitive way of interaction. Results showed that
participants were more efficient in terms of performance (completion time and travelled distance) using the
game-pad rather than using full body gestures. However, they had more fun performing the task under these
conditions.
1 INTRODUCTION
Virtual Reality (VR) is now recognized as a powerful
tool for the assessment and rehabilitation of both mo-
tor and cognitive impairments (Merians et al., 2002;
Broeren et al., 2002; Flynn et al., 2003; Katz et al.,
2005). Indeed, VR provides a unique medium for
the achievement of several requirements of effective
rehabilitation intervention: repetitive practice, feed-
back about performance, and motivation to endure
practice (Riva, 2003; Gaggioli et al., 2009; Raspelli
et al., 2012; Cipresso et al., 2012; Villani et al., 2013;
Pallavicini et al., 2013). In addition, VR techniques
lead to constantly monitor patient’s performance and
to quantify his improvements. Another important ad-
vantage of VR is related to the benefits of the immer-
sive experience or presence in the virtual environment
(VE) (Cipresso et al., 2013; Repetto et al., 2013; Riva
et al., 2011).
The most common navigation techniques used for
the virtual supermarket (VS) is based on desktop
hardware such as a computer mouse, keyboard, or a
joystick. However, even if most people usually work
or play with a computer mouse or a keyboard, they
usually don’t use them in an optimal way for navi-
gation tasks (McClymont et al., 2011) and the use of
a joystick appears to be more convenient than a key-
board (Vera et al., 2007). Some systems use more
complex interaction techniques or expensive devices,
and are therefore somehow difficult to set-up outside
the lab or in clinical environments (von Kapri et al.,
2011; Cruz-Neira et al., 1992; Williams et al., 2007).
To be effective in the context of virtual rehabil-
itation, VEs and 3D interaction techniques have to
be easy-to-use or easy-to-learn. However, although
many research has been carried out to make it easier,
interacting with VEs is still not straightforward, es-
pecially for people with special needs, disabilities or
deficiencies. Therefore, more research is needed in
this context.
The goal of this research is to provide differ-
ent navigation and selection techniques ranging from
desktop interaction techniques based on the use of
joystick or game-pad to interaction techniques based
on body gestures. In this context, we have designed
and compared different 3D interaction technique in
terms of usability performance and workload. The re-
sults provide information about different interaction
techniques and which aspects of the techniques could
bring benefits to users with special needs, disabilities
or deficiencies in a context of rehabilitation and train-
ing in a VS.
Verhulst, E., Richard, P., Richard, E., Allain, P. and Nolin, P.
3D Interaction Techniques for Virtual Shopping: Design and Preliminary Study.
DOI: 10.5220/0005725402690277
In Proceedings of the 11th Joint Conference on Computer Vision, Imaging and Computer Graphics Theory and Applications (VISIGRAPP 2016) - Volume 1: GRAPP, pages 271-279
ISBN: 978-989-758-175-5
Copyright
c
2016 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
271

The paper is organized as following: the next sec-
tion provides a survey of the related work concern-
ing the use of virtual supermarkets in the context
of virtual rehabilitation and the techniques proposed
for navigation and selection. Section 3 presents an
overview of the developed system, including the de-
scription of the virtual supermarket and the proposed
interaction techniques. In Section 4, we describe our
user study aimed at comparing the proposed inter-
action techniques. Section 5 provides a discussion
concerning the participants’ performance (completion
time, distance travelled, and errors) and the subjective
data collected using questionnaires. Section 6 con-
cludes the paper and discusses directions for future
work.
2 RELATED WORKS
2.1 Virtual Supermarkets
During the last decade, researchers have investigated
the potentials of virtual supermarkets (VS) to evalu-
ate executive functions in several populations (Elbaz
et al., 2009; Josman et al., 2014). In this context,
different VS have been developed such as the Vir-
tual Interactive Shopper (VIS) (Hadad, 2012) or the
V-Mall (Rand et al., 2009).
Although they have similar configurations, the
proposed VS differ in terms of interaction techniques
and experimental set-up. For example, Rand et
al. (Rand et al., 2005) developed a virtual mall to treat
post-stroke patients. They used a relatively expensive
system which requires video studio conditions (i.e. a
green backdrop, lighting and large space).
Castelnuovo et al. (Castelnuovo et al., 2003) de-
scribed the V-Store as a rehabilitation tool where pa-
tients with neurological damaged could be involved
in several tasks with higher degree of complexity de-
signed to stimulate the executive function, program-
ming, categorical abstraction, short-term memory and
attention. The authors provide no results of evaluation
with patients. Lee et al. (Lee et al., 2003) designed a
VS for the assessment and rehabilitation of daily-life
activities. They mainly focused on the usability of
the VE and tested it on patients with traumatic brain
injury and stroke. A Eye tred
T M
FMD-250Z head-
mounted display, a Intertrax2
T M
position sensor and
a Airstik
T M
2000 joystick were used for observation,
navigation and interaction.
Other studies were carried out using VS. For ex-
ample, Carelli et al. (Carelli et al., 2008; Carelli et al.,
2009) conducted a feasibility study of a shopping task
developed using VR techniques. The task was to
choose and buy products from a shopping list. The
objective of the study was to investigate the usability
of the system. Twenty healthy adults had to navigate
in the VS using a handle (pushing right/left buttons)
and select the items by pressing a button. Cardoso et
al. have developed a VS to assess cognitive disabil-
ity of patients with a left hemisphere stroke (Cardoso
et al., 2006). The patients had to navigate within the
VS and collect items using a mouse. Task was to com-
plete a shopping list. Each time the patient selected
a given item, a window appeared, asking him/her to
choose the price which corresponded to the product.
Klinger (Klinger et al., 2003; Klinger et al., 2006)
and Mari
´
e et al. (Mari
´
e et al., 2003) designed the vir-
tual action planning supermarket (VAP-S). The par-
ticipants, seated in front of a 2D monitor, were in-
structed to explore the supermarket using a keyboard
for navigation and a mouse for items collection (Jos-
man et al., 2006; Josman et al., 2008).
2.2 3D Interaction Techniques
3D interaction techniques are the main components
of VR systems. They have been classified as fol-
lows (Mine, 1995; Bowman, 1998; Bowman and
Hodges, 1999): selection, manipulation, navigation
and application control. During the two last decades
several navigation techniques have been proposed and
evaluated (Ruddle et al., 1997; Bowman et al., 1999;
Usoh et al., 1999; Sutcliffe and Kaur, 1999; Vila et al.,
2003; Suma et al., 2007; von Kapri et al., 2011; Bolte
et al., 2011; Cirio et al., 2012).
Bowman et al. (Bowman et al., 1997) pro-
posed a framework for the design and evaluation
of navigation techniques for specific tasks in VEs.
Later, Arns proposed extended Bowman’s taxonomy
and distinguished real translation/rotation and virtual
ones (Arns, 2002). Results from experiments indi-
cated that pointing techniques are advantageous rela-
tive to gaze-directed steering techniques. It was how-
ever observed that navigation techniques which in-
stantly teleport users to new locations are correlated
with increased user disorientation. Some generic
hand directed motion techniques have also been pro-
posed for navigation. The position and orientation of
the hand determine the direction of motion through
the VEs. These techniques appear efficient but tiring
since the user has to constantly move his/her arms in
space.
To be efficient, navigation techniques must allow
the user to move easily within VEs while looking
around. Therefore, researchers tried to develop in-
tuitive interaction techniques for navigation and item
selection. For exemple Renner et al. (Renner et al.,
GRAPP 2016 - International Conference on Computer Graphics Theory and Applications
272

2010) proposed a VS in which the user is able to nav-
igate and look around at the same time using well-
known interaction techniques based of body gestures.
The authors used several methods like path draw-
ing where subject use the Wii Remote
T M
to navigate
through the VE by drawing a path, the walking in
place where they make step-in-place on a Wii Bal-
ance Board
T M
to navigate in the VE. The authors also
use non immersive interaction technique like world
in miniature where users could see the VE like a
map, and move from one point to another. More
recent gaming input devices like the Nintendo Wii
Remote
T M
and the Nintendo Wii Balance Board
T M
have been used for navigation and interaction with
VEs (Fischer et al., 2011).
The most effective navigation techniques are
based on real or real-like walking. Real-like walking
techniques such as step-in-place have been developed
and evaluated in a general context (Templeman et al.,
1999; Bouguila et al., 2004; Richard et al., 2007).
Beckhaus, Blom and Haringer (Beckhaus et al., 2005)
present a navigation method based on the dance-pad,
a physical device that has directional arrows acti-
vated by stepping. Real walking techniques have also
been developed (Slater et al., 1995; Choi and Ricci,
1997) and proved to be very efficient (Suma et al.,
2009). However, this approach either limits the users
navigation space (Williams et al., 2007), or require
some complex set-up such as cyberspheres (Fernan-
des et al., 2003), omnidirectional treadmills (Darken
et al., 1997; Iwata, 1999; Suryajaya et al., 2010) or
complex robotics system (Iwata et al., 2005).
3 EXPERIMENT
Our motivation to conduct this experiment relies on
the need to get both objective and subjective data al-
lowing to analyse user performance and preference
for different interaction techniques in the context of
shopping activities. The main objective is to identify
the advantages, drawbacks and limits of the proposed
interaction techniques.
3.1 Apparatus
The experiment was carried out using the VR plat-
form illustrated in Figure 1. The platform is made
of a back-projected screen (2m large x 2m high).
The projector used for the experiment is an Optoma
HD141X Full HD 3D 1080p Projector. The platform
provides low-cost interaction devices such as the Mi-
crosoft Xbox
T M
360 ones : the game-pad controller
and the Kinect
T M
sensor. For real-time head tracking,
we used a TrackIR
T M
device.
Figure 1: Set-up used for the experiment.
3.2 Virtual Environment
The supermarket is of relatively limited size so that it
can be explored in a relatively limited time. It consists
of two shelves, a frozen food area, a bakery area, a
magazine space, a cool space and two areas dedicated
to fruits and vegetables (Figure 2). The 3D models
were developed using 3DS Max. Then, they were ex-
ported in .fbx format and imported into the Unity3D
game engine. The user can freely navigate inside the
store and collect items. Once selected, the items are
automatically put in the shopping cart that is placed
in front of the user (Figure 3). Different disruptors
(audible or visual) may be embedded in the simula-
tion. Similarly, avatars can wander around the store
and behave differently vis-
`
a-vis the environment or
the participants. The system records all movements
and actions performed by the participants within the
VE.
Figure 2: First-person view of the virtual shop.
3D Interaction Techniques for Virtual Shopping: Design and Preliminary Study
273

3.3 Design and Procedure
Eighty volunteer students from our school of Engi-
neers were recruited to participate in the study. They
were split in four groups of twenty students each.
Each group performed the task in a different condition
(C
1
, C
2
, C
3
, and C
4
). Each subject was installed in
front the visual display which was set in monoscopic
viewing mode.
In condition C
1
(mean age : 19.0 ; SD : 1.41),
illustrated in Figure 4 (a), the participants used the
Xbox
T M
360 controller for travelling in the VE (left
joystick), looking around (right joystick) and select
items (green button).
In condition C
2
(mean age : 19.04 ; SD : 1.78),
illustrated in Figure 4 (b), the subjects used the left
joystick of the Xbox
T M
360 controller for travelling,
and a low-cost head tracking device (TrackIR
T M
) for
looking around.
In the condition C
3
(mean age : 22.05 ; SD : 2.25),
illustrated in Figure 4 (c), the participants navigated
in the VS using dynamic body gestures, similar to the
ones used for operating a real shopping cart. Thus,
to move the cart forwards, the users have to put both
hands forwards. To move the cart backwards, they
have to put both hands backwards. The navigation in
the VS is based on hand movements, so to turn right
or left, participants have to move up their hand in the
chosen way. So to turn right, subjects have to place
their right arm perpendicularly to their body.
Figure 3: Shopping cart containing some collected items.
As in the previous condition, the TrackIR
T M
sys-
tem was used for looking around. To collect the items,
participants have to point on them and clap their
hands. The Kinect
T M
was used to capture participants
arm movements. Motion data were processed using
FAAST
T M
(Flexible Action and Articulated Skeleton
Toolkit).
In condition C
4
(mean age : 19.94 ; SD : 1.77), il-
lustrated in Figure 4 (d), the users navigated in the VS
using a step-in-place technique. To move forwards
the subjects have to step-in-place in front of the vi-
sual display. Turning right or left was made using
upper body’s (shoulders) orientation.To collect items,
participants had to point on them and clap their hands.
As in the previous condition, the Kinect
T M
sensor and
FAAST
T M
were used. The four conditions were cho-
sen to be easy to use and based on low-cost devices.
(a) (b)
(c) (d)
Figure 4: Interaction techniques : (a) using the game-pad
only, (b) using the game-pad and the TrackIR
T M
, (c) and
(d) using the Kinect
T M
and the TrackIR
T M
.
3.3.1 Task
The task asked to the participants was to navigate in-
side the supermarket and collect the seven items from
a list using one of the interaction techniques previ-
ously described. The list is positioned on the shop-
ping card and is available to the subject during the
completed task (Figure 3). User scan see the list in
its integrity by changing his point of view. The pur-
chased items are not delete when they are selected .
Once the subject considered that all the items from
the list were collected, they had to reach the cash reg-
ister as quickly as possible. As the subject reached
this area, the task was considered to be completed and
the simulation ended. Each participant completed the
task twice. At the end of the experiment, participants
were asked to fill in the NASA TLX and the subjec-
tive questionnaires.
3.3.2 Collected Data
In order to compare the different interaction tech-
niques, we collected performance data such as the
task completion time and the travelled distance. We
didn’t observe any error. Users would made errors if
they didn’t respect the items of the list.
In addition, we used the NASA Task Load Index
(NASA TLX) to assess the task’s mental, physical and
GRAPP 2016 - International Conference on Computer Graphics Theory and Applications
274
temporal demand, the user’s perceived performance,
effort and frustration. A non standardized usability
questionnaire was used to assess participants’ habits
in playing video games and to evaluate on a seven
Likert scale their enjoyment during the task and over-
all system usability. We also observed the subjects
while performing the task and noted their comments,
strategies and behaviour.
3.4 Results
The R statistical software was used to analyse the
data, at a significance level of 0.05. Kruskall-Wallis
test was used to compare the four conditions C
1
, C
2
,
C
3
and C
4
using performance data (time, errors and
distance travelled) and using the data collected via
the questionnaires. Post-hoc analyses, conducted with
a Mann-Withney test for independent samples, were
used to compare the different conditions and a Cliff
Delta was conducted to measure size effect. A mod-
ified T-test (Crawford and Howell, 1998) was con-
ducted to compare an individual score against the
norm. It was used in the context of comparing in-
dividuals with no experiences in video games to the
the rest of participants of her/his group with habits in
video games.
The results are presented in the following order.
First, we look at the task completion time associated
with each condition. Then, we report about the dis-
tance travelled by the subjects while performing the
task. Finally, the data collected using the question-
naires (NASA TLX and usability) are presented.
The results revealed that no subject has made mis-
takes during the task and have collected all the items
of the list. Comparisons between trials 1 and 2 was
made with a U Mann-Whitney test. For all conditions,
trial 2 was better than trial 1 in terms of completion
time, numbers of errors and distance travelled. In this
section, we present the data for the second trial only.
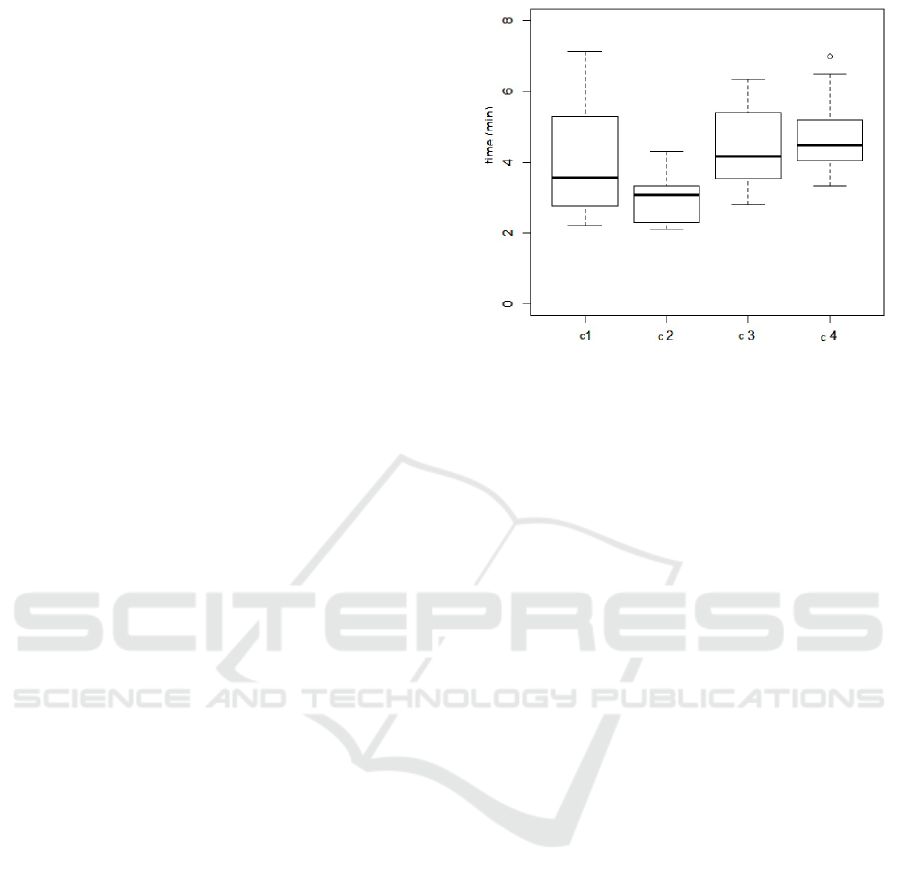
3.4.1 Completion Time
Results are illustrated in Figure 5. To complete the
task, users needed significantly less time in C
2
condi-
tion (game-pad + head tracking) than in C
1
condition
(game-pad only) (U = 124 ; p = 0.04*)(∆ = -0.38),
C
3
(arms movement + head tracking) (U = 46.5 ; p =
0.00005***) (∆ = -0.75) and C
4
(step in place + head
tracking) (U = 16.5 ; p = 0.000001***)(∆= -0.91).
There is no significant different between C
3
and C
4
,
conditions (U = 137 ; p = 0.21).
.
Figure 5: Time to complete the task (second trial) in the
four conditions.
3.4.2 Distance Travelled
Results are illustrated in Figure 6. They showed that
in C
2
condition (game-pad + head tracking) partici-
pants travelled significant shorter distances than those
in C
1
(U = 128.5 ; p = 0.05*)(∆ = -0.35), C
3
(U = 622
; p = 0.0003***) (∆ = -0.67) and C
4
conditions (U =
58 ; p = 0.0002***)(∆ = -0.69).
3.4.3 Effect of Skill
A modified T-test was realized to analyse the per-
formance of players with bad skills in video games.
Some of them needed significantly more time to com-
plete the task. Indeed, the analysis shows that sev-
eral subjects with bad skills in video games had
poor time’s performance. In C
2
(game-pad + head
tracking), one participant presents bad skills in video
games and took significantly more time to complete
the task (t = 2.14). In C
3
(arms movement + head
tracking), seven participants were unfamiliar with
video games and only one took significantly more
time to complete the task (t = 1.9). In the first con-
dition with game-pad, over seven participants, one
took significantly more time to complete the task (t
= 2.1), and another made a significantly longer path (t
= 2.09).
In the two conditions C
1
and C
3
, there were seven
users with bad skills in video games, so these condi-
tions were divided in two groups: one with users who
have good skills in video games and the other with
participants who have a strong experience of video
games.
In the game-pad conditions, the group with bad
skills in video games made significantly longer paths
(U = 17 ; p= 0.02*)(∆ = -0.62) and needed signifi-
3D Interaction Techniques for Virtual Shopping: Design and Preliminary Study
275

Figure 6: Distance travelled (second trial) in the four con-
ditions.
cantly more time to complete the task (U = 5.5 ; p =
0.01*) (∆ = -0.88). However, in the Kinect
T M
condi-
tions, there was no significant difference between the
group with good skills and the group with bad skills,
in term of travelled distance (U =53; p =0.53) and
completion time (U = 34 ; p= 0.39).
3.4.4 Subjective Data
We observed that two scales of the NASA TLX were
significantly different : effort and frustration. Partici-
pants from the C
2
condition (game-pad + head track-
ing) produced less effort than those from the C
3
con-
dition (arms movement + head tracking) (U= 101 ;
p= 0.01*)(∆ = -0.46) , and less effort than those from
the C
4
condition (step-in-place + head tracking)(U=
89 ; p= 0.004**)(∆ = -0.53). Results of the frustra-
tion scale indicated that the participants from the C
2
condition felt less frustration than those from the C
3
condition (U= 11.6 ; p= 0.04*) (∆ = -0.38) and those
from the C
4
condition (U= 66.5 ; p= 0.0005***) (∆
= -0.65). Participants from the C
4
condition also felt
more frustration than those from the C
1
condition (U
= 261 ; p = 0.02) (∆ = 0.44).
Participants were asked to complete a question-
naire about easiness of the interaction technique and
the task’s enjoyment. The Kruskal-Wallis test indi-
cated no difference between the four navigation tech-
niques (p=0.08). Participants from the C
1
condition
found the task less funny than those from the C
3
con-
dition (U = 286.5, p=0.02*) (∆ = 0.36) and those from
the C
4
condition (U=250 ; p = 0.04* )(∆= 0.31). Sim-
ilarly, participants from the C
2
condition found the
task less funny than those from the C
3
condition (U =
128.5 ; p = 0.02*) (∆ = -0.38) and from the C
4
condi-
tion (U= 121.5 ; p = 0.03*) (∆ = -0.36).
4 DISCUSSION
We developed a virtual supermarket for the assess-
ment and rehabilitation of patients with cognitive im-
pairments. In order to get both performance and sub-
jective control data, we carried out a user study with
volunteer students. The goal was to compare navi-
gation and selection techniques ranging from desk-
top interaction techniques using a game-pad to full
body gestures. Navigating and collecting items us-
ing full body gestures seem a-priori more intuitive
and natural, especially for the step-in-place technique
(C
4
condition). However, desk-top devices such as
the game-pad are easy-to-use (Vera et al., 2007) and
most people who play video games know how to use
it very well. We observed, that no matter the inter-
action techniques, in all conditions, participants were
significantly more efficient in performing the task af-
ter one trial. They all travelled shorter distances in
the supermarket and spent less time to complete the
task. Thus, the proposed interaction techniques and
the task are easy-to-learn.
Interaction techniques based on the Kinect
T M
was
proposed for people unfamiliar with video games be-
cause of their easiness (Roup
´
e et al., 2014). Indeed,
full body gestures are more suited for people with
no skills in video games. According to a previous
study (Roup
´
e et al., 2014), results show that the par-
ticipants with no skills in video games could perform
the shopping task as well as participants with good
skills in video games. However for the game-pad con-
ditions, participants with no skills in video games got
lower performance, and needed more time to perform
the task.
Previous studies present various results. Consis-
tent with our results, Teixeira et al. (Teixeira et al.,
2012) showed that the game-pad was more effective
than a step-in-place navigation technique (Teixeira
et al., 2012; Figueiredo et al., 2014). However in Ren-
ner et al. (Renner et al., 2010), the step-in-place con-
dition was the most effective for navigating in a vir-
tual shop. In another VE, the walking-in-place condi-
tion was better than a joystick condition (Riecke et al.,
2010). In this study, users worn an HMD and had
to find some hidden items in a VS. The poor perfor-
mance with the joystick may be due to the lack of
visual exploration of the VE (Riecke et al., 2010).
Results of the NASA TLX indicated that partic-
ipants produced more effort in the Kinect
T M
condi-
tions than in the game-pad conditions. This is not sur-
prising since the participants have to move their arms
(condition C
3
) or their whole body (condition C
4
) to
control the shopping cart and collect items. Results
also revealed that in these conditions, the participants
GRAPP 2016 - International Conference on Computer Graphics Theory and Applications
276

felt some frustration because of the difficulty to con-
trol the cart (DSouza, 2011). Thus, such interac-
tion techniques do not appear to be the most effec-
tive ones, especially for the elderly people or people
with motor impairments, however participants found
them more enjoyable than those with game-pad. In
addition, producing efforts to navigate and interact
with VEs may increase user’s sensation of immer-
sion (Herrewijn et al., 2013).
Time and distance travelled in a VE appear to be
the good data to assess users performance and the us-
ability of interaction techniques. Indeed, interaction
techniques are considered effective when the user can
build up a cognitive map with the acquisition of spa-
tial knowledge (Bowman and Wingrave, 2001). In
this context game-pad devices are the most effective
but need several trials to be used with optimum abili-
ties, whereas full body gestures interaction techniques
based on motion capture devices such as the Kinect
T M
are more easy to use for people unfamiliar in video
games. In addition, navigating using body gestures
made the task more enjoyable for the users.
Change the interaction techniques may be inter-
esting according the task or the difficulties encoun-
tered by the patient. For example, according the
mood of the patient, we may simplify the interac-
tion technique. Indeed, rehabilitation training could
be long and repetitive, so the interaction technique
with Kinect
T M
may permit to raise the patients moti-
vation when he/she is fed up with doing the same task
again. On another side, if the patient wants to see his
progress, an interaction technique based on game-pad
may be effective.
5 CONCLUSION AND
PERSPECTIVE
In the paper, we have presented a VE that simulates
an everyday task to assess cognitive impairments: go-
ing shopping at the supermarket. A user study has
been carried out to collect baseline control data us-
ing volunteer students from our school of engineers.
The task was to collect various items within the super-
market using a shopping cart. Four different interac-
tion techniques have been compared ranging from the
desktop paradigm to natural interaction techniques
based on full-body gestures. We observed that sub-
jects were more efficient in terms of completion time
using a game-pad but enjoyed more the interaction
techniques based on full-body gestures. However, the
NASA TLX questionnaire revealed that these inter-
action techniques led to more fatigue and frustration.
As future work, we plan to evaluate users sensation
of presence associated with the different proposed in-
teraction techniques using questionnaires and physio-
logical responses.
REFERENCES
Arns, L. (2002). A new taxonomy for locomotion in virtual
environments. PhD thesis, Iowa State University.
Beckhaus, S., Blom, K., and Haringer, M. (2005). Intu-
itive, hands-free travel interfaces for virtual environ-
ments. In IEEE Virtual Reality International Confer-
ence (VR’2005) - New Directions in 3D User Inter-
faces Workshop, Bohn, Germany. IEEE Computer So-
ciety.
Bolte, B., Steinicke, F., and Bruder, G. (2011). The jumper
metaphor: An effective navigation technique for im-
mersive display setups. In Proceedings of theVirtual
Reality International Conference (VRIC’11), pages 6–
8, Laval, France.
Bouguila, L., Evequoz, F., Courant, M., Hirsbrunner, B.,
and Richard, P. (2004). Active locomotion interface
for virtual environments.
Bowman, D. (1998). Interaction techniques for common
tasks in immersive virtual environments.
Bowman, D., Davis, E., Badre, A., and Hodges, L. (1999).
Maintaining spatial orientation during travel in an im-
mersive virtual environment. Presence : Teleopera-
tors & Virtual Environments, 18:619–631.
Bowman, D. and Hodges, L. (1999). Formalizing the de-
sign, evaluation, and application of interaction tech-
niques for immersive virtual environments. J. Visual
Languages and Computing, 10:37–53.
Bowman, D. A., Koller, D., and Hodges, L. F. (1997). In
Travel in Immersive Virtual Environments: An Eval-
uation of Viewpoint Motion Control Techniques, vol-
ume 215, pages 45–52, Los Alamitos, CA, USA.
Bowman, D. A. and Wingrave, C. (2001). Design and eval-
uation of menu systems for immersive virtual environ-
ments. In Proceedings of IEEE Virtual Reality, pages
149–156.
Broeren, J., Bjorkdahl, A., Pascher, R., and Rydmark, M.
(2002). Virtual reality and haptics as an assessment
device in the postacute phase after stroke. Cyberpsy-
chol Behav, 5:207–211,
Cardoso, L., da Costa, R., Piovesana, A., Costa, M., Penna,
L., Crispin, A., Carvalho, J., Ferreira, H., Lopes, M.,
Brandao, G., and Mouta, R. (2006). Using virtual
environments for stroke rehabilitation. In 5th Inter-
national Workshop on Virtual Reality Rehabilitation
(IWVR), pages 1–5, New York City, USA.
Carelli, L., Morganti, F., Patrice, L., Weiss, T., Kizony, R.,
and Riva, G. (2008). A virtual reality paradigm for
the assessment and rehabilitation of executive func-
tion deficits post stroke: Feasibility study. IEEE,
6:99–104,
Carelli, L., Morganti, F., Poletti, B., Corra, B., Weiss, P.,
Kizony, R., Silani, V., and Riva, G. (2009). A neurovr
based tool for cognitive assessment and rehabilitation
of post-stroke patients: two case studies. Stud Health
Technol Inform, 144:243–247,
3D Interaction Techniques for Virtual Shopping: Design and Preliminary Study
277

Castelnuovo, G., Priore, C. L., Liccione, D., and Cioffi, G.
(2003). Virtual reality based tools for the rehabilita-
tion of cognitive and executive functions: the v-store.
Psychology, pages 311–326,
Choi, I. and Ricci, C. (1997). Foot-mounted gesture de-
tection and its application in virtual environments. In
Proc. IEEE Int. conf. on Systems, Man and Cybernet-
ics, volume 5, pages 4248–53. IEEE Computer Soci-
ety.
Cipresso, P., Gaggioli, A., Serino, S., Pallavicini, F.,
Raspelli, S., Grassi, A., and Riva, G. (2012). Eeg
alpha asymmetry in virtual environments for the as-
sessment of stress-related disorders. Studies In Health
Technology And Informatics, 173:102–104.
Cipresso, P., Paglia, F. L., Cascia, C. L., Riva, G., Al-
bani, G., and Barbera, D. L. (2013). Break in voli-
tion: A virtual reality study in patients with obsessive-
compulsive disorder. Experimental Brain Research.
Cirio, G., Vangorp, P., Chapoulie, E., Marchal, M., L
´
ecuyer,
A., and Drettakis, G. (2012). Walking in a cube:
Novel metaphors for safely navigating large virtual
environments in restricted real workspaces. IEEE
Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graph-
ics, 18(4):546–554.
Crawford, J. R. and Howell, D. C. (1998). Comparing an in-
dividuals test score against norms derived from small
samples. The Clinical Neuropsychologist, 12(4):482–
486.
Cruz-Neira, C., Sandin, D., DeFanti, T., Kenyon, R., and
Hart, J. (1992). The cave: audio visual experience au-
tomatic virtual environment. Communications of the
ACM, 35(6):65–72.
Darken, R., Cockayne, W., and Carmein, D. (1997). The
omni-directional treadmill: A locomotion device for
virtual worlds. In Proceedings of of UIST 97.
DSouza, Pathirana, M. . A. (2011). Kinect to architec-
ture. In IVCNZ 201, pages 155–160, Auckland, New
Zealand.
Elbaz, J. N., Schenirderman, A., Klinger, E., and Shevil,
E. (2009). Using virtual reality to evaluate executive
functioning among persons with schizophrenia: A va-
lidity study. Schizophrenia Research, 115:270–277,
Fernandes, K. J., Raja, V., and Eyre, J. (2003). Cybersphere:
the fully immersive spherical projection system. Com-
munications of the ACM, 46(9):141–146.
Figueiredo, L. S., Pinheiro, M., Vilar Neto, E., Menezes, T.,
Teixeira, J. a. M., Teichrieb, V., Alessio, P., and Fre-
itas, D. (2014). In-place natural and effortless naviga-
tion for large industrial scenarios. In Proceedings of
the Third International Conference on Design, User
Experience, and Usability. User Experience Design
for Diverse Interaction Platforms and Environments
- Volume 8518, pages 550–561, New York, NY, USA.
Springer-Verlag New York, Inc.
Fischer, L., Oliveira, G., Osmari, D., and Nedel, L. (2011).
Finding hidden objects in large 3d environments: The
supermarket problem. In XIII Symposium on Virtual
Reality, pages 106–109.
Flynn, D., van Schaik, P., Blackman, T., Femcott, C.,
Hobbs, B., and Calderon, C. (2003). Developing a
virtual reality-based methodology for people with de-
mentia: a feasibility study. Cyberpsychology and Be-
haviour, 6:591–611,
Gaggioli, A., Keshner, E., Weiss, P., and Riva, G. (2009).
Advanced technologies in rehabilitation - empowering
cognitive, physical, social and communicative skills
through virtual reality, robots, wearable systems and
brain-computer interfaces. .
Hadad (2012). Rehabilitation tools along the reality contin-
uum: from mock-up to virtual interactive shopping to
a living lab. In 9th Intl Conf. Disability, Virtual Reality
& Associated Technologies (ICDVRAT), pages 47–52,
Laval, France.
Herrewijn, L., Poels, K., and Calleja, G. (2013). The
relationship between player involvement and immer-
sion: an experimental investigation. In 8
th
Inter-
national Conference on the Foundations of Digital
Games, page 4, Chania, Crete, Greece.
Iwata, H. (1999). The torus treadmill: Realizing locomotion
in ves. IEEE Computer Graphics and Applications,
19(6):30–35.
Iwata, H., Yano, H., Fukushima, H., and Noma, H. (2005).
Circulafloor: A locomotion interface using circulation
of movable tiles. In IEEE Virtual Reality Interna-
tional Conference (VR’2005), pages 223–230, Bohn,
Germany. IEEE Computer Society.
Josman, N., Hof, E., Klinger, E., Marie, R., Goldenberg, K.,
Weiss, P., and Kizony, R. (2006). Performance within
a virtual supermarket and its relationship to execu-
tive functions in post-stroke patients. In International
Workshop on Virtual Rehabilitation, pages 106–109.
Josman, N., Kizony, R., Hof, E., Goldenberg, K., Weiss,
P., and Klinger, E. (2014). Using the virtual action
planning-supermarket for evaluating executive func-
tions in people with stroke. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis,
23(5):879–887,
Josman, N., Klinger, E., and Kizony, R. (2008). Perfor-
mance within the virtual action planning supermarket
(vap-s): an executive function profile of three differ-
ent populations suffering from deficits in the central
nervous system. In ICDVRAT, pages 33–38, Maia,
Portugal.
Katz, N., Ring, H., Naveh, Y., Kizony, R., Feintuch, U., and
Weiss, P. (2005). Interactive virtual environment train-
ing for safe street crossing of right hemisphere stroke
patients with unilateral spatial neglect. Disability Re-
habilation, 27:1235–1243,
Klinger, E., Chemin, I., Lebreton, S., and Mari
´
e, R. (2003).
A virtual supermarket to assess cognitive planning.
Cyberpsychololgy and Behaviour, 7(3):292–293,
Klinger, E., Chemin, I., S, S. L., and Mari
´
e, R. M. (2006).
Virtual action planning in parkinson disease : Acon-
trol study. Cyberpsychology and Behaviour, 9:342–
347,
Lee, J., Ku, J., Cho, W., Hahn, W., Kim, I., and et al, S. L.
(2003). A virtual reality system for the assessment
and rehabilitation of the activities of daily living. Cy-
berpsychology and Behaviour, 6:383–388,
Mari
´
e, R. M., Klinger, E., Chemin, I., and Josset, M. (2003).
Cognitive planning assessed by virtual reality. In
Laval Virtual Conference (VRIC 2003), pages 119–
125, Laval, France.
McClymont, J., Shuralyov, D., and Stuerzlinger, W. (2011).
Comparison of 3d navigation interfaces. In VECIMS,
pages 7–12, l.
GRAPP 2016 - International Conference on Computer Graphics Theory and Applications
278

Merians, A., Jack, D., Boian, R., Tremaine, M., Burdea, G.,
and Adamovich, S. (2002). Virtual reality-augmented
rehabilitation for patients following stroke. Physical
Therapy, 82:898–915,
Mine, M. (1995). Virtual environment interaction tech-
niques.
Pallavicini, F., Cipresso, P., Raspelli, S., Grassi, A., Serino,
S., Vigna, C., Triberti, S., Villamira, M., Gaggioli, A.,
and Riva, G. (2013). Is virtual reality always an effec-
tive stressors for exposure treatments? some insights
from a controlled trial. BMC Psychiatry, 13(52):265–
272.
Rand, D., Katz, N., Shahar, M., Kizony, R., and Weiss, P.
(2005). The virtual mall: a functional virtual environ-
ment for stroke rehabilitation. Annu Rev Cyberther
Telemed, 3:193–198,
Rand, D., Weiss, P. T., and Katz, N. (2009). Training multi-
tasking in a virtual supermarket: A novel intervention
after stroke. American Journal of Occupational Ther-
apy, 63:535–542.
Raspelli, S., Pallavicini, F., Carelli, L., Morganti, F., E,
E. P., Cipresso, P., Poletti, B., Corra, B., Sangalli, D.,
Silani, V., and Riva, G. (2012). Validating the neuro
vr-based virtual version of the multiple errands test:
preliminary results. Presence-Teleoperators And Vir-
tual Environments, 21:31–42.
Renner, P., Dankert, T., Schneider, D., Mattar, N., and Pfeif-
fer, T. (2010). Navigating and selecting in the virtual
supermarket: review and update of classic interaction
techniques. In Virtuelle und Erweiterte Realitae : 7th
Workshop der GI-Fachgruppe VR/AR, pages 71–82.
Repetto, C., Gaggioli, A., Pallavicini, F., Cipresso, P.,
Raspelli, S., and Riva, G. (2013). Virtual reality and
mobile phones in the treatment of generalized anxi-
ety disorders: a phase-2 clinical trial. Personal And
Ubiquitous Computing, 17(2):253–260.
Richard, P., Bouguila, L., Courant, M., and Hirsbrunner, B.
(2007). Enactive navigation in virtual environments:
evaluation of the walking-pad. In Proc. 4
th
Int. Conf.
on Enactive Interfaces (ENACTIVE’07), pages 225–
228, Grenoble, France.
Riecke, B. E., Bodenheimer, B., McNamara, T. P.,
Williams, B., Peng, P., and Feuereissen, D. (2010).
Do we need to walk for effective virtual reality navi-
gation? physical rotations alone may suffice. Spatial
Cognition, VII:234–247.
Riva, G. (2003). Applications of virtual environments in
medicine. Methods Inf Med., 45(5):524–534.
Riva, G., Gaggioli, A., Grassi, A., Raspelli, S., and Ci-
presso, P. (2011). Neurovr 2–a free virtual reality plat-
form for the assessment and treatment in behavioral
health care. Stud Health Technol Inform, 163:493–
495.
Roup
´
e, M., Bosch-Sijtsema, P., and Johansson, M. (2014).
Interactive navigation interface for virtual reality us-
ing the human body. Computers, Environment and
Urban Systems, 43:4250.
Ruddle, R. P., Payne, S. J., and Jones, D. M. (1997). Navi-
gating buildings in desk-top virtual environments: ex-
perimental investigations using extended navigational
experience. Journal of Experimental Psychology Ap-
plied, 3(2):143–159.
Slater, M., Usoh, M., and Steed, A. (1995). Taking steps:
The influence of a walking metaphor on presence in
virtual reality. ACM Transactions on Computer Hu-
man Interaction, 2(3):201–219.
Suma, E., Babu, S., and Hodges, L. (2007). Comparison
of travel techniques in a complex, multi-level 3d envi-
ronment. In IEEE Symposium on 3D User Interfaces
(3DUI’07), pages 10–11.
Suma, E., Finkelstein, S., Reid, M., Ulinski, A., and
Hodges., L. (2009). Real walking increases simula-
tor sickness in navigationally complex virtual environ-
ments. In IEEE Virtual Reality International Confer-
ence (VR’2009), pages 245–246, ?? ??
Suryajaya, M., Lambert, T., Fowler, C., Stothard, P., Lau-
rence, D., and Daly, C. (2010). Omniwalker: omni-
directional stroller-based walking platform. In Pro-
ceedings of theVirtual Reality International Confer-
ence (VRIC’10), pages 181–182, Laval, France.
Sutcliffe, A. and Kaur, K. (1999). Evaluating the usability
of virtual reality user interfaces. Behaviour & infor-
mation technology, 19(6):415–426.
Teixeira, L., Vilar, E., Duarte, E., Rebelo, F., and da Silva,
F. M. (2012). Comparing two types of navigational
interfaces for virtual reality. Journal of Prevention,
Assessment and Rehabilitation, 41:2195–2200.
Templeman, J. N., Denbrook, P. S., and Sibert, L. E. (1999).
Virtual locomotion: Walking in place through virtual
environments. Presence - Teleoperators and Virtual
Environments, 8(6):598–617.
Usoh, M., Arthur, K., C.Whitton, M., Bastos, R., Steed,
A., Slater, M., and Brooks, F. J. (1999). Walk-
ing, walking-in-place, flying in virtual environments.
In Proc. 26
th
Ann Conf. on Computer Graphics and
Interactive Techniques (ACM SIGGRAPH’99), pages
359–64. ACM.
Vera, L., Campos, R., Herrera, G., and Romero, C. (2007).
Computer graphics applications in the education pro-
cess of people with learning difficulties. Computers &
Graphics, 31(4):649–658,
Vila, J., Beccue, B., and Anandikar, S. (2003). The gen-
der factor in virtual reality navigation and wayfinding.
Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences,
4:101b.
Villani, D., Repetto, C., Cipresso, P., and Riva, G. (2013).
May i experience more presence in doing the same
thing in virtual reality than in reality? an answer from
a simulated job interview. Interacting With Comput-
ers, 24(4):265–272.
von Kapri, A., Rick, T., and Feiner, S. (2011). Comparing
steering-based travel techniques for search tasks in a
cave. In IEEE Virtual Reality International Confer-
ence (VR 2011), page ??, Singapore. IEEE Computer
Society.
Williams, B., Narasimham, G., Rump, B., McNamara, T. P.,
Carr, T. H., Rieser, J., and Bodenheimer, B. (2007).
Exploring large virtual environments with an hmd
when physical space is limited. In ACM symposium
on Applied Perception in Graphics and Visualization,
pages 41–48.
3D Interaction Techniques for Virtual Shopping: Design and Preliminary Study
279
