A Novel Key Frame Extraction Approach for Video Summarization
Hana Gharbi, Sahbi Bahroun and Ezzeddine Zagrouba
Research Team on Intelligent Systems in Imaging and Artificial Vision (SIIVA), Laboratory RIADI,
Institut Supérieur d'Informatique (ISI), Université Tunis Elmanar, 2 Rue Abou Rayhane Bayrouni, 2080 Ariana, Tunisia
Keywords: Video Summarization, Key Frame Extraction, Interest Point, PCA, HAC.
Abstract: Video summarization is a principal task in video analysis and indexing algorithms. In this paper we will
present a new algorithm for video key frame extraction. This process is one of the basic procedures for video
retrieval and summary. Our new approach is based on interest points description and repeatability
measurement. Before key frame extraction, the video should be segmented into shots. Then, for each shot, we
detect interest points in all images. After that, we calculate repeatability matrix for each shot. Finally, we
apply PCA and HAC to extract key frames.
1 INTRODUCTION
Video summarization wants to reduce the amount of
data that must be examined in order to retrieve
particular information in a video. It is an essential step
in video archiving, retrieval and indexing. With the
last developments in video applications, a great work
of researches has been done on content-based video
summary and retrieval. In this paper, we will try to
present a novel approach to extract visual summary
of a video database. This visual summary will be
composed by the key frames extracted from the video
database. The user can start his query by selecting one
image from the presented visual summary. Each
video from the database will be presented by some
key frames. It reduces significantly the amount of
data that must be examined by providing a concise
and accurate representation of the video. The goal of
key frame extraction is to convert the entire video into
a small number of representative images which
maintain the salient content of the video while
eliminating all redundancy.
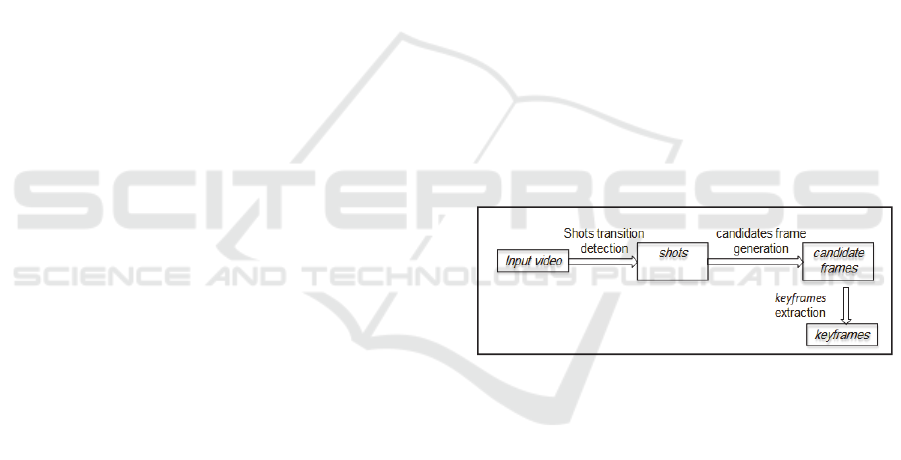
As shown in figure 1, the input video is segmented
into shots using the shot change detection techniques
and then once the shot is identified, the key frames
can be extracted from the candidate frames to
represent each shot. All the key frames can be
combined together to create a video summary which
will represent the video as a whole.
In Section 2, we will present some recent
approaches of key frame extraction for video
summary and retrieval. We will describe the key
frame proposed approach steps in section 3. The
results and observations of the new key frame
extraction method and comparison with other recent
works are discussed in section 4. We will conclude
and give some perspectives in section 5.
Figure 1: Key frames extraction steps.
2 RELATED WORK
In the literature, many works have been proposed to
extract key frames. In general, these methods
supposed that the video is already segmented into
shots by a shot detection algorithm. After that, key
frames are extracted from each shot.
Some early works proposed too naïve key frame
extraction methods. One of these possible approaches
is to take as the key frame the first frame in the shot,
the middle one or the first and last ones of each shot
as the key frame (Ueda et al., 1991).
In other works the authors time sample the shots
at predefined intervals (Pentland et al., 1994) and they
take the key frames from a set location within the
shot, or, in an alternative approach where the video is
148
Gharbi, H., Bahroun, S. and Zagrouba, E.
A Novel Key Frame Extraction Approach for Video Summarization.
DOI: 10.5220/0005725701460153
In Proceedings of the 11th Joint Conference on Computer Vision, Imaging and Computer Graphics Theory and Applications (VISIGRAPP 2016) - Volume 3: VISAPP, pages 148-155
ISBN: 978-989-758-175-5
Copyright
c
2016 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

time sampled regardless of shot boundaries. These
approaches do not consider the dynamics in the visual
content of the shot but rely on the information
regarding the sequence’s boundaries. They often
extract a fixed number of key frames per shot. Other
approaches try to group the key frames into visually
similar clusters. Zhuang et al., (1998) group the
frames in clusters then the key frames are selected
from the largest ones. In Girgensohn and Boreczky,
(2000) constraints on the position of the key frames
in time are also used in the clustering process; a
hierarchical clustering reduction is performed,
obtaining summaries at different levels of abstraction.
In Gong and Liu (2000) the video are summarized
with a clustering algorithm based on Single Value
Decomposition (SVD). The video frames are time
sampled then visual features are computed from
them. The refined feature space obtained by the SVD
is clustered, and one key frame is extracted from each
cluster. The main advantage of clustering based
methods is that they generate less redundant
summaries as compared to the consecutive frame
difference based techniques. The problem with most
of the clustering methods (less time constrained
clustering) is that temporal information of the frames
is not considered. In order to take into account the
visual dynamics of the frames within a sequence,
some approaches compute the differences between
pairs of frames in terms of color histograms, motion,
or other visual descriptions. Key frames are selected
by analyzing the obtained values. Mundur et al.,
(2006) developed a method based on Delaunay
Triangulation DT. It starts by pre-sampling the
original video frames. Each one is represented by a
color histogram which is represented by a row vector
then the vectors of each frame are concatenated into
a matrix. Principal Components Analysis (PCA) is
applied in order to reduce the dimensions of the
matrix. After that, the Delaunay diagram is built. The
clusters are obtained by separating edges in the
Delaunay diagram. In the last step, for each cluster,
the frame that is nearest to its centre is selected as the
key frame.
Luo et al., (2009) introduced STIMO (Still and
Moving Video Storyboard), a summarization
technique designed to produce onthefly video
storyboards. STIMO is composed of three steps. First,
the video is analyzed in order to extract the HSV color
description. Then for each input frame, a 256-
dimensional vector is extracted. After that these
vectors are stored in a matrix and then, in the second
phase, the clustering algorithm is applied to extracted
data. The authors exploited the triangular inequality
in order to filter out useless distance computations.
The pairwise distance of consecutive frames is
computed to obtain the number of clusters. If this
distance is greater than a threshold C, the number of
clusters is incremented. The last phase aims at
removing meaningless video frames from the
produced summary.
In the works of Guironnet et al., (2007), the key
frames were selected according to the rules defined
on sequence and the magnitude of camera motions.
The multiple features like automatic scene analysis,
camera viewpoint selection, and adaptive streaming
for summarizing videos was used by Chen et al.,
(2011). The camera and motion based techniques may
work well for certain experimental settings and
specified domain. However, such techniques are
dependent on heuristic rules extracted from a rather
limited data set. Therefore, such schemes may fail in
situations where videos have complex and irregular
motion patterns which were not tested initially
(Truong and Venkatesh, 2007). After this study of the
related work of key frame extraction, we can remark
that different methods are either too naïve or too
complex. The most simple of these techniques sorely
compromise the key frames extracted quality and the
most sophisticated ones are computationally very
expensive. Also, some of these methods give us key
frames with approximately the same content. Our
proposed work gives a good agreement between
quality and complexity of results and this will be
proved in experimental results.
3 PROPOSED APPROACH
In key frame extraction, most of the state of the art
methods used global image description. In this paper,
we proved that the use of local image description is a
very fruitful alternative and will give us an
improvement in the quality of the extracted key
frames in terms of redundancy.
The first step of our key frame extraction
proposed approach is applying a shot detection based
on the χ2 histogram matching (Cai et al., 2005). Then
for each shot we apply the proposed approach
describe in figure 2 to extract key frames which is
composed by these three steps:
1) First Step: apply the SIFT (Lowe, 2004) detector
to extract interest points for all images in the Shot.
2) Second Step: build the repeatability table
(repeatability matrix RM). This table describes
the repeatability inter-frame (between all images
in the same shot). So, for each shot we will build
a repeatability matrix. The repeatability between
A Novel Key Frame Extraction Approach for Video Summarization
149
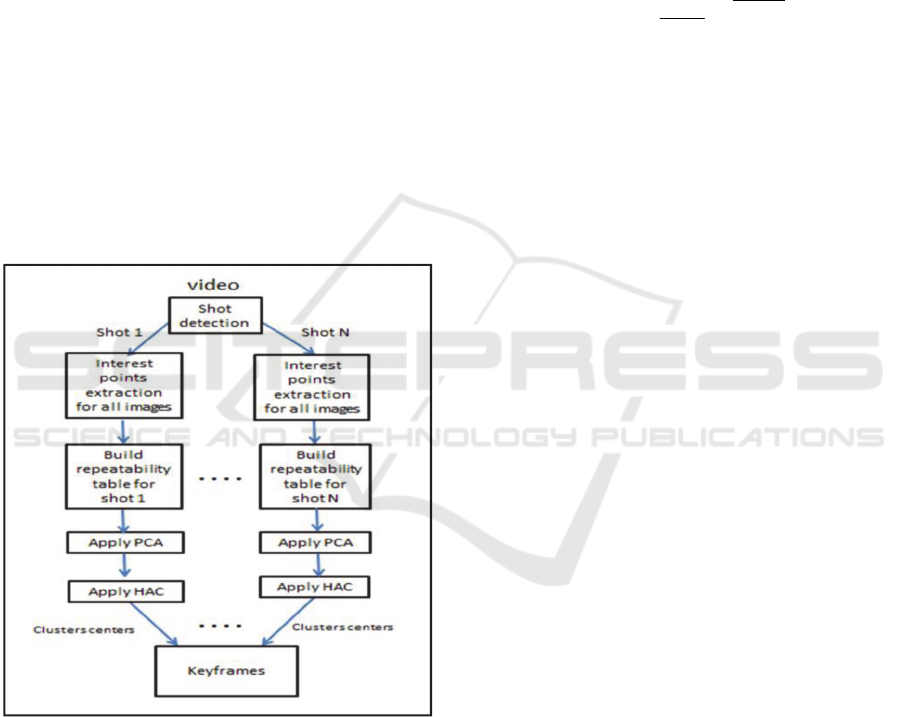
two images belonging the same shot is computed
using the matching algorithm presented by Gharbi
et al., (2014).
3) Third Step: apply the Principal Component
Anallysis PCA and the Hierarchical Ascendant
Clustering algorithm HAC (Berkhin, 2002) on the
repeatability matrix to extract groups of similar
images and the corresponding key frames. Since
the repeatability matrix RM is square and has a
big dimension N*N where N is the number of
images in the shot). RM(i,j) is the repeatability
between images i and j which are belonging to the
same shot. If a group of images has the same
repeatability so they can have the same content.
The PCA is applied to reduce the dimension of the
clustering problem and it is coupled with the HAC
to extract groups of images which have similar
repeatability value. The HAC is a non-supervised
clustering method that extracts automatically the
final number of groups. Each group will be
presented by its cluster center. The center of each
cluster is the keyframe.
Figure 2: Proposed approach steps.
3.1 SIFT Detector
Our approach is based on key frame extraction with
interest points, The first question that we asked,
which interest point detector we will use. In (Bahroun
et al., 2014), we did a performance comparison
between SIFT, SURF and Harris detectors and we
found that SIFT gives the best in rotation, translation
and scale invariance which are the most important
transformations in video. That's why we will use
SIFT detector in our approach. In order to achieve
scale invariance, SIFT uses a DoG (Difference of
Gaussian) function, shown in formula (1), to do
convolution on an image. It obtains different scale
images by changing σ. Then, it subtracts the images
which are adjacent in the same resolution to get a
DoG pyramid. The DoG function (3) is a kind of an
improvement of a Gauss-Laplace algorithm, shown as
formula (2).
2
22
2
)(
.
2
1
),,(
yx
eyxG
(1)
),(),,(),,( yxIyxGyxL
(2)
),,(),,(),,(
yxLkyxLyxD
(3)
where I (x, y) denotes an input image, and k denotes
a scale coefficient of an adjacent scale-space factor.
SIFT compares each point with its adjacent 26 pixels,
which is the sum of eight adjacent pixels in the same
layer and nine pixels in the upper and lower adjacent
layers. If the point is minimum or maximum, the
location and scale of this point are recorded.
Therefore, SIFT gets all extreme points of DoG scale-
space, and locates extreme points exactly. After that,
it removes low contrast and unstable edge points. It
further removes interference points, using 2×2
Hessian matrix obtained from adjacent difference
images.
3.2 Build of the Repeatability Table
After detecting interest points in each image from the
video shots, we will compute the repeatability matrix.
Repeatability is a criterion which proves the stability
of the interest points detector: It is the average
number of corresponding interest points detected in
images under noise or changes undergone by the
image (Schmid et al., 2000). This matrix is built from
all images belonging to each shot. We must compute
repeatability between each two images in a shot. The
repeatability computation is based on a robust interest
point matching algorithm presented in Gharbi et al.,
(2014).
- Matching based on local feature: it consists on
forming groups of matching candidates based on
comparisons across the LBP descriptor (Gharbi et
al., 2014). This first step gives for each interest
point in image 1 some potential matching
candidates from image 2. These candidates are
interest points with similar visual features.
VISAPP 2016 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
150

- Matching based on spatial constraints and
geometric invariants: in order to reduce the
number of false candidates and minimize
complexity, for each interest point and his
potentially matched point we make a spatial test
based on angle and distance relations then another
test base on geometric invariants.
If a shot contains N images, this will give us a
repeatability matrix with size N*N which is carried
out using the algorithm below.
Inputs:
RM: matrix with N x N
dimension
N: number of frames in the shot
Outputs:
RM: matrix filled with the
repeatability values
Begin
for (int i = 0; i < N ; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < N ; j++)
//
apply matching algorithm for
this two images
// compute the repeatability between I
and J frames
RM[i][j]=Repeatability i,j
End
End
End
3.3 Classifying Repeatability Table
The PCA converts a set of observations of possibly
correlated variables into a set of values of linearly
uncorrelated variables. The number of final variables
is less than the original one and allows us having a
graphical representation of point clouds. Clustering in
low dimension is always more efficient than
clustering in high dimension, that’s why we use PCA
before HAC. The resulting matrix is with dimension
N x N where N is the number of images in a shot.
Since, this repeatability matrix is with high
dimension, if we want to draw points in 2D space to
extract significant correlation between groups of
images, we have to apply the principal component
analysis (PCA) to reduce the dimension of the
representative space. But we will lose some
information from the original matrix witch will not
affect the classification results.
Indeed PCA algorithm facilitates the visualization
and understanding of data and reduces the storage
space required. The PCA algorithm allows us to
present the repeatability table into point clouds shown
in 2 dimensions. Then we need to divide the point
clouds into clusters. That’s why we choose for this
step the classification algorithm HAC (Hierarchical
Ascendant Classification). But the problem that
persists is which image choosing from each class to
be the key-frame? The advantage of HAC algorithm
is that it is simple, extracts automatically the final
number of clusters and gives us the center of each
cluster. The group of these centers represents our key
frames.
4 EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS
To evaluate the efficiency of our proposed key frame
extraction method, we did experimental tests on some
videos (news, cartoons, games,…). These video
illustrate different challenges (camera motion,
background-foreground similar appearance, dynamic
background,…). Results proved that the method can
extract efficiently key frames resuming the salient
semantic content of a video with no redundancy.
To verify the effectiveness of the proposed
method, we first use qualitative evaluation since the
subjective evaluation of the extracted key frame is
efficient and it was used in many state of the art
methods. In a second step, we will complete the
evaluation with a qualitative study by calculating
fidelity and compression rate. The use of quantitative
and qualitative evaluation enhances the provement of
the effectiveness of our proposed approach.
In experimental setup, the experiments were done
on movies from YUV Video Sequences
(http://trace.eas.asu.edu/yuv/) and some other
standard test videos with different sizes and contents.
In this paper we will show experiments done only on
7 movies as example. These movies were already
segmented into shots by the χ2 histogram matching
method (Cai et al., 2005). The figures below (3 and 4)
show two examples of shots from the same movie
“filinstone.mpg”. Table 1 shows the number of frames
and shots for the 7 movies:
Figure 3: Example of frames from shot 1 from Filinstone
movie.
A Novel Key Frame Extraction Approach for Video Summarization
151

Figure 4: Example of frames from another shot from
Filinstone movie.
Table 1: The video characteristics.
Movie Nb frames Nb shots
Filinstone.mpg 510 10
Housetour.mpg 664 10
Foreman.avi 297 5
Mov1.mpg 377 6
HallMonitor.mpg 299 4
MrBean.avi 2377 8
Coast-guard.mpg 299 2
4.1 Validity Measures
4.1.1 Fidelity
The fidelity measure is based on semiHausdorff
distance to compare each key frame in the summary
with the other frames in the video sequence. Let V
seq
= {F
1
,F
2
,... F
N
} the frames of the input video sequence
and let KF all key frames extracted KF = {F
K1
,
F
K2
,…., F
KM
...}. The distance between the set of key
frames and F
belonging toV
seq
is defined as follows:
toMjFFDiffMinKFFDIST
Kj
1,),((),(
(4)
Diff() is a suitable frame difference. This difference
is calculated from their histograms: a combination of
color histogram intersection and edge histogram-
based dissimilarity measure (Ciocca and Schettini,
2006) .The distance between the set of key frames KF
and the video sequence V
seq
is defined as follows:
NiKFFDISTMaxKFVDIST
iseq
,..,1,),(),(
(5)
So we can define the fidelity as follows:
),(),( KFVDISTMaxDiffKFVFIDELITY
seqseq
(6)
MaxDiff is the largest value that can take the
difference between two frames Diff (). High Fidelity
values indicate that the result of extracted key frames
from the video sequence provides good global
description of the visual content of the sequence.
4.1.2 Compression Rate
Keyframe extraction result should not contain many
key frames in order to avoid redundancy. That's why
we should evaluate the compactness of the summary.
The compression ratio is computed by dividing the
number of key frames in the summary by the length
of video sequence. For a given video sequence, the
compression rate is computed as follows:
framescard
keyframescard
CR 1
(7)
Where card(keyframes) is the number of extracted
key frames from the video. Card(frames) is the
number of frames is the video.
4.1.3 Signal to Noise Ratio
We calculate also the signal to noise ratio (PSNR) for
each couple (F
u
,F
v
) of selected key frames with size
(N*M), we compute the PSNR between them and the
mean value is considered for each video.
N
x
M
y
vu
vu
yxFyxF
MN
FFPSNR
11
2
2
),(,
255..
log10),(
(8)
4.2 Qualitative Evaluation
Now, we will present some results for 2 examples of
videos. The first one is "filinstone.mpg" which has
510 frames segmented into 10 shots. The figure 6
shows the 14 resulting key frames. As we can see the
first image in figure 6 is the keyframe relative to the
first shot of “filinstone” video presented in figure 3
which is very logic.
Figure 5: Segments of the video “filinstone.mpg”.
Figure 6: Key frames extracted.
VISAPP 2016 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
152
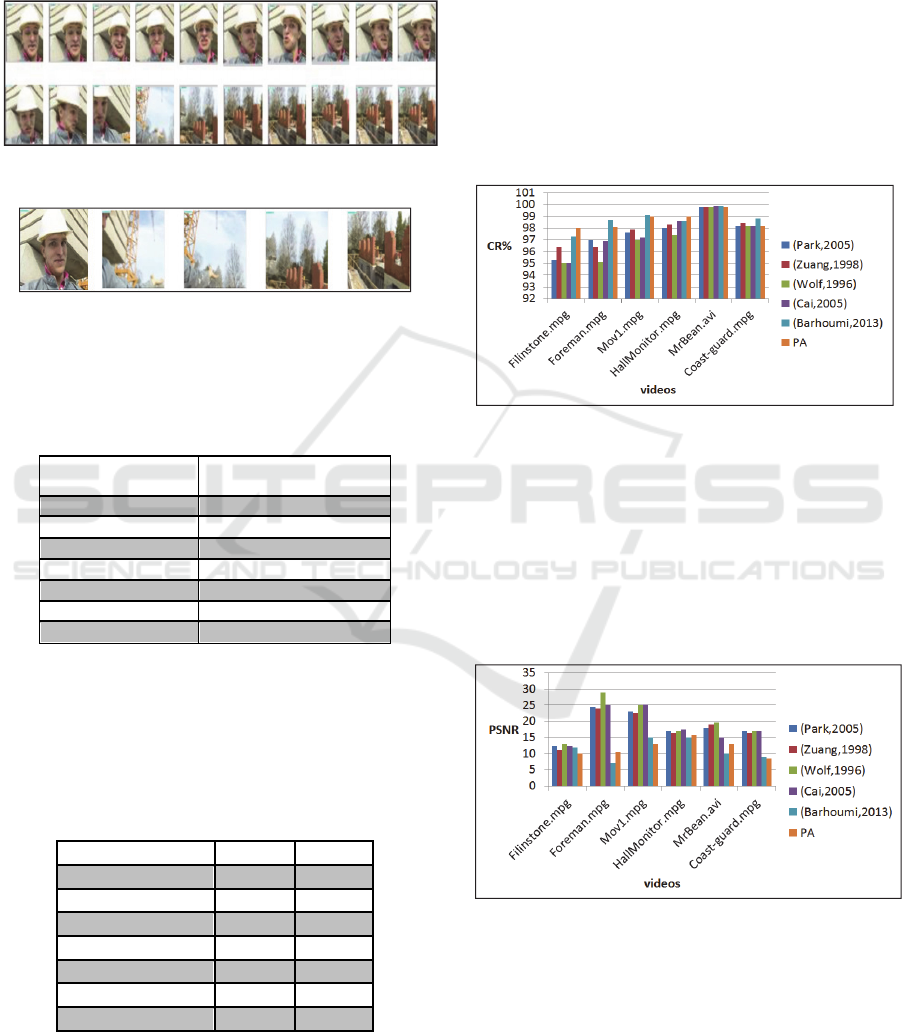
The second video is "foreman.avi" it is composed
of 297 frames and segmented into 5 shots. The figure
8 shows the resulting key frames for all the video. In
the same way the first image of figure 8 is the
keyframe relative to the first shot of “foreman” video.
Figure 7: Segments of the video “foreman.avi”.
Figure 8: Key frames extracted.
This table summarizes the number of key frames
extracted for each video.
Table 2: Number of keyframes for different video tests.
Movie Number of key frames
Filinstone.mpg 14
Housetour.mpg 10
Foreman.avi 5
Mov1.mpg 7
HallMonitor.mpg 4
MrBean.avi 9
Coast-guard.mpg 3
4.3 Quantitative Evaluation
We measured now for each movie, the fidelity and the
compression rate (CR %). The table 3 illustrates these
results.
Table 3: Results in terms of fidelity and Compression rate.
Movie Fidelity CR(%)
Filinstone.mpg
0.78 99, 44
Housetour.mpg
0.81 97,99
Foreman.avi
0.74 98.11
Mov1.mpg
0.78 99.20
HallMonitor.mpg
0.71 98.66
MrBean.avi
0.80 99.78
Coast-guard.mpg
0.77 98.99
While looking to the results in Table 3 by the
compression ratio (CR) values, it is clear that the
proposed method minimizes considerably the
redundancy of the extracted key frames which
guarantees encouraging compression ratios while
maintaining minimum requirements of memory
space. The Fidelity values confirm the same
interpretation that we get by looking to the
compression rate.
In order to give an objective evaluation, we
compared the resulting quality measures of
compression rate of our proposed method with some
state of the art methods (Park et al., 2005), (Zhuang
et al., 1998), (Wolf, 1996), (Cai et al., 2005) and
(Barhoumi and Zagrouba, 2013) and this for the six
tested videos in Table 3.
Figure 9: Comparison of the quality of the extracted key
frames in term of compression rate (CR).
In Figure 9, we show a comparison between our
proposed approach (PA) and six state of the art
methods in terms of compression rate. As the CR
value is high as we have different key frames. We can
see in Figure 9 that our proposed approach (PA)
reduced considerably the redundancy of extracted key
frames.
Figure 10: Comparison of the quality of the produced
results in term of PSNR values.
In Figure 10, we show a comparison between our
proposed approach (PA) and six state of the art
methods in terms of PSNR. As the PSNR is low as we
have different key frames. Therefore, from Figure 10,
we can see that our proposed approach gives the
lowest values for PSNR. So, we can conclude, that it
A Novel Key Frame Extraction Approach for Video Summarization
153

gives lowest redundancy in key frames according to
CR and PSNR values. All these results demonstrate
the feasibility and efficiency of the proposed method.
Our method can offer us a video summary with a little
number of key frames and also with a low
computational cost since it is based on PCA algorithm
coupled with HAC. We can see also that in some
cases our approach doesn’t always give the best result
compared with the other state of the art method. This
is due to the quantity of information lost after
applying PCA whitch is ranging from 7% to 20%.
This is a compromise. We win in complexity
computation and time cost but we lose some
information.
5 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, we presented an innovative algorithm
for key frame extraction. In this paper, we have
proposed a simple and effective technique for key
frame extraction based on local description "interest
points" and using a new interest points matching
method. This interest points matching method is
based on local description around each interest point
and also spatial constraints coupled with geometric
invariants. After that we computed a repeatability
matrix for each shot. We applied PCA and HAC to
extract key frames. We used an unsupervised
classification method to generate clusters regrouping
forms with the same content. While choosing the
center of each cluster as a key frame, we eliminate the
redundancy. The experiments showed that the
proposed algorithm gives a set of image that covers
all significant events in the video while minimizing
information redundancy in these key frames. We
studied some state of the local description. Most of
them are based on global image description.
As a perspective, we will try to apply other non-
supervised clustering methods. We want to see what
is the effectiveness of using PCA before clustering.
As a second perspective and after extracting
keyframes from all the videos in the database, we will
try to give the visual summary which is composed by
the most representative objects in the videos database.
The user can initiate his visual query by selecting one
or some of these objects.
REFERENCES
Ueda, H., Miyatake, T., and Yoshizawa, S., 1991. An
interactive natural-motion-picture dedicated multime-
dia authoring system. Proc. ACM CHI Conference, 343
-350.
Pentland, A., Picard, R.,Davenport G., and Haase , K.,
1994. Video and image semantics, advanced tools for
telecommunications. IEEE Multimedia. 73-75.
Zhuang, Y., Rui, Y., Huang, T. S, Mehrotra, S., 1998. Key
Frame Extraction Using Unsupervised Clustering.
ICIP’98, Chicago, USA, 866-870.
Girgensohn, A., Boreczky, J., 2000. Time-Constrained
Keyframe Selection Technique. Multimedia Tools and
Application, 347-358.
Gong Y., and Liu, X., 2000. Generating optimal video
summaries. Proc. IEEE Int. Conference on Multimedia
and Expo, 3:1559-1562.
Mundur, P., Rao, Y. and Yesha Y., 2006 .Keyframe-based
video summarization using Delaunay clustering.
International Journal on Digital Libraries, vol. 6, no.
2, pp. 219–232.
Luo, J., Papin, C., Costello, K., 2009. Towards extracting
semantically meaningful key frames from personal
video clips: from humans to computers. IEEE
Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video
Technology 19 (2) 289–301.
Guironnet, M., Pellerin, D., Guyader, N., 2007. Ladret,
P.,Video summarization based on camera motion and a
subjective evaluation method. EURASIP Journal on
Image and Video Processing, 12.
Chen, F., Delannay, D., Vleeschouwer, C., 2011. “An
autonomous framework to produce and distribute
personalized team-sport video summaries: a basketball
case study. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia 13 (6)
1381–1394.
Truong, B.T., Venkatesh, S., 2007. Video abstraction: a
systematic review and classification, ACM
Transactions Multimedia Computing. Communications
and Applications. 3 (1).
Cai et al., 2005. A Study of Video Scenes Clustering Based
on Shot Key Frames. Series Core Journal of Wuhan
University (English) Wuhan University Journal of
Natural Sciences Pages 966-970.
Lowe D. G., 2004. Distinctive image features from scale
Invariant keypoints. Int. J. Computer Vision, vol. 60,
no. 2, pp. 91–110.
Bahroun, S., Gharbi, H., and Zagrouba, E., 2014. Local
query on satellite images based on interest points.
International Geoscience and Remote Sensing
Symposium, Quebec.
Gharbi, H., Bahroun, S., and Zagrouba, E., 2014. Robust
interest points matching based on local description and
spatial constraints. International Conference on Image,
Vision and Computing, Paris.
Park, K. T., Lee, J. Y., Rim, K. W., Moon, Y. S., 2005. Key
frame extraction based on shot coverage and distortion.
LNCS, 3768:291-300.
Wolf, W., 1996. Key frame selection by motion analysis.
Int Conf on Acoustic. Speech and Signal Processing.
Barhoumi, W., and Zagrouba, E., 2013. “On-the-fly
extraction of key frames for efficient video
summarization. AASRI Procedia 4, 78 – 84.
Ciocca, G., and Schettini, R. 2006. An innovative algorithm
for key frame extraction in video summarization. J. of
VISAPP 2016 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
154

Real-Time Image Processing 1(1): 69-88.
Schmid, C., Mohr, R., Bauckhage, C., 2000. Evaluation of
Interest Point Detectors. International Journal of
Computer Vision.
Berkhin, P., 2002. Clustering DataMining Techniques.
Accrue Software, San Jose.
A Novel Key Frame Extraction Approach for Video Summarization
155
