
Can a Wii Bowling Tournament Improve Older Adults’ Attitudes
towards Digital Games?
Fan Zhang, Simone Hausknecht, Robyn Schell and David Kaufman
Faculty of Education, Simon Fraser University, 8888 University Drive, Burnaby, Canada
Keywords: Wii Bowling, Digital Games, Game Attitudes, Older Adults, Social Fun and Competition.
Abstract: This study examined the effectiveness of a Wii Bowling tournament for improving older adults’ attitudes
towards digital games. A total of 142 older adults were recruited from 14 senior centers; 81 were placed in
the experimental group and 61 in the control group. Participants in the experimental group played in teams
of four members formed within each participating site. The 81 participants in the experimental group
formed a total of 21 teams, which played against one another in an 8-week tournament. The findings
indicate that the Wii Bowling tournament was an effective way to improve older adults’ attitudes towards
digital games (t = 2.53, p = .01). Consistent with the findings in previous studies, this research found that
co-located social gaming creates a natural context for fun, immersion, and competition.
1 INTRODUCTION
1.1 Age-related Health Problems
The percentage of older adults in our population has
increased in the past decades and continues to do so.
By 2050, one in five people in the world will be
aged 60 or older (Akitunde, 2012). People are living
longer as a result of better health and living
conditions. However, with advanced age, older
adults experience declines in social contacts,
physical abilities, and cognitive function. Impaired
balance and falls can lead to injury, increased
morbidity, fear of falling, loss of independence,
death, and direct medical costs (Lai et al., 2012).
Cognitive decline is associated with decreased
ability to perform everyday tasks required for
functional independence, such as car driving and
financial management (Boot et al., 2013). What’s
more, many older adults face key social and
psychological challenges such as loneliness,
depression, and lack of social support due to
decreased social contact. Since these changes
negatively affect older adults’ quality of life (Aison
et al., 2002), there are growing needs to understand
and find ways to prevent or reshape age-related
physical and cognitive decline and to increase older
adults’ social interaction. One of the possible ways
that has been gaining researchers’ attention is digital
gameplay.
1.2 Older Adults and Digital Games
Digital games (e.g., action, strategy, role-play,
sports, and casual games) can be complex, offering
flexible activities that use multiple cognitive
abilities. Games that require progressively more
accurate and more challenging judgments at higher
speed, and the suppression of irrelevant information,
can drive positive neurological changes in the brain
systems that support these behaviors. Today, playing
digital games has become a social activity (Ekman et
al., 2011). Online games such as Massively
Multiplayer Online Role-Playing Games
(MMORPGs, e.g., World of Warcraft) allow
thousands of players from around the world to
interact with each other in the same virtual
environment. With advances in virtual-reality
interaction technology, somatosensory digital games
that combine traditional digital games and physical
activities provide older adults with alternative
leisure opportunities (Chiang et al., 2012); for
example, the Nintendo Wii Fit includes more than
40 activities such as yoga postures, strength training,
and balance designed to engage the player in
physical exercise.
These games can be played with family and
friends in real-world situations. Face-to-face
contacts and frequent, meaningful social interactions
Zhang, F., Hausknecht, S., Schell, R. and Kaufman, D.
Can a Wii Bowling Tournament Improve Older Adults’ Attitudes towards Digital Games?.
In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Computer Supported Education (CSEDU 2016) - Volume 2, pages 211-218
ISBN: 978-989-758-179-3
Copyright
c
2016 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
211

can happen through “interacting with other people,
spending time with friends, watching others play,
chatting and talking about the game, seeing other
people’s reactions and expressions, gloating when
beating a friend, or feeling pride when they win”
(Sweetser andWyeth, p.11). Engagement in social
activities not only meets older adults’ psychological
needs for social interaction, but also keeps them
physically and mentally active – the “use it or lose
it” metaphor.
In addition, games are designed to be fun to play.
They appeal to older adults’ desires and needs for
entertainment
, mental fitness enhancement,
competition and success, a satisfying use of time,
and, in social games, a sense of belonging (Hoppes
et al., 2001, cited in Whitlock et al., 2012). Digital
gameplay is inherently enjoyable and motivating, a
state which can be described in terms of
Csikszentmihalyi’s (2000) flow experience. Flow
describes a mental state of complete absorption,
accompanied by positive feelings. Gamberini et al.
(2008) pointed out that digital games can provide
older adults with new opportunities for leisure and
entertainment, combined with training that avoids
both intimidating task complexity and boredom.
There is now substantial evidence showing that
playing digital games can improve older adults’
physical, cognitive, and psychological health.
Jorgensen et al. (2012) examined postural balance
and muscle strength in healthy community-dwelling
older adults using biofeedback-based Nintendo Wii
training for a period of 10 weeks. Results showed
that the Wii training resulted in significant
improvements in maximal leg muscle strength and
overall functional performance in participants.
Pompeu et al. (2012), investigating the effect of
Nintendo Wii-based motor cognitive training on
activities of daily living in patients with Parkinson’s
disease, found that participants showed improved
performance in activities of daily living after 14
sessions of balance training. Basak, Boot, Voss, and
Kramer (2008) reported on the use of a real-time
strategy video game for the enhancement of
executive control processes of older adults. They
found that after a period of 23.5 hours gameplay, the
experimental group improved significantly more
than the control group in executive control functions
such as task switching, working memory, and visual
short-term memory. Jung, Li, Janissa, Gladys, and
Lee (2009) examined the impact of playing
Nintendo Wii on the psychological and physical
well-being of seniors in a long-term care facility.
Results showed that playing Wii yielded a positive
impact on loneliness, self-esteem, and well-being
among older adults, compared to a control group that
played traditional board games. Previous studies
have also suggested that regular and occasional
gamers exhibit significantly higher levels of well-
being and lower levels of loneliness compared to
non-gamers (Allaire et al., 2013; Jung et al., 2009).
These findings demonstrate the potential of digital
games to improve older adults’ quality of life.
1.3 Older Adults and New Technology
Older adults are stereotypically viewed as having
negative views towards technology. However,
although physical and cognitive declines may
hamper their ability to use technology as effectively
or proficiently as younger people, older adults have
been found to be willing to use technology when
they are aware of the benefits such technology can
offer them (Eisma et al., 2004; Heinz et al., 2013).
Reviewing studies that compare older and younger
adults’ attitudes towards and abilities with
computers, Broady, Chan and Caputi (2010) found
that lack of knowledge of the capabilities of modern
technologies and how to use them is a major
influence on older adults’ avoidance of technology.
Other barriers include confusion regarding usage
procedures, fear of the unknown, lack of confidence,
and lack of understanding of the value of products
and services. Understanding technology as being
personally relevant and useful, as well as
overcoming the initial fears and external factors (e.g.
how one is viewed and treated by others) are crucial
to overcoming those barriers. Overall, Broady et al.
(2010) concluded that older people appear eager to
accept technological advancements and exhibit
attitudes that are as positive as young peoples’
towards the use of computers. In addition, first-hand
experience can trigger older adults' interest and
provide opportunities for improving attitudes
towards a new technology (Bandura, 2001;
Melenhorst, 2002; cited in Gajadhar, Nap, de Kort,
and IJsselsteijn, 2010).
1.4 Research Purpose
Despite potential physical, cognitive, and social
benefits, older adults are far less likely than younger
people to play digital games (McKay and Maki,
2010). Older gamers are playing more and more
games, but only 29% of gamers are over the age of
50 (Galarneau, 2014). In the U.S., some 61% of
gamers are younger than 36-years old
(Entertainment Software Association, 2014). It is
understandable that older adults play fewer digital
CSEDU 2016 - 8th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
212

games, as many did not grow up with computer and
information technologies. However, encouraging
their engagement with these new technologies could
help to realize the potential of digital games to
address a variety of health, social-psychological, and
functional needs for older adults.
Social interaction has an important effect on
older adults’ successful aging (Lewi, 2014) and is a
strong motivator among older people for playing
digital games (Rice et al., 2012). Competition is
another important factor that affects their in-game
enjoyment (De Schutter, 2011). Previous research
has shown that playing together in the same place, as
opposed to remotely, significantly contributes to fun,
challenge, and perceived competence in the game as
older adults prefer co-located co-play to playing
with other people online (Gajadhar, de Kort, &
IJsselsteijn, 2008; Gajadhar et al., 2010). Therefore,
the purpose of this study was to examine whether a
co-located Wii Bowling digital game tournament
could improve older adults’ attitudes towards digital
games.
2 METHODOLOGY
2.1 Intervention Tool
In a qualitative focus group study, Diaz-Orueta,
Facal, Nap, and Ranga (2012) identified digital
game features of most interest to older adults: the
social aspect of the experience, the challenge it
presents, the combination of cognitive and physical
activity, and the ability to gain specific skills. Wii
Bowling is a game that offers these features.
Wii Bowling offers a convenient platform for
multiple players. The Wii console allows users to
interact with the game via remote, using natural
body movements that are recognized by motion
sensors. The game action is displayed on a large
screen. Wii Bowling was selected for this study
because: 1) most older adults are familiar with
bowling; 2) bowling and the WII are fun to play; 3)
the game is relatively simple to learn and to play;
and 4) bowling is a social activity that allows a
group to play together.
2.2 Outcome Measure
Participants’ attitudes toward the game were
assessed by 8-items selected from the Computer
Game Attitude Scale (Chappell and Taylor, 1997),
which measures the level of positive attitude toward
digital games. Items were rated on a 5-point Likert-
scale ranging from 1 (Strongly disagree) to 5
(Strongly agree). Higher scores indicated higher
level of positive attitude towards the social aspects
of digital game. Its reliability is .79.
2.3 Participants and Procedure
Participants were older adults aged 60 and over. A
total of 142 older adults were recruited from 14
centers, 81 were placed in the experimental group
and 61 were in the control group. The participants in
the experimental group played in teams of four
members formed within each participating site.
Since older adults might have appointments,
commitments, or illnesses that prevented them from
attending a session, only the top three scores of each
game were recorded each week, even if four players
attended that session. This approach allowed some
flexibility when one team member was absent.
A total of 21 teams played against one another in
the tournament. To avoid potential issues (e.g.,
social anxiety, time conflicts) that might have
affected outcomes, team members, team names,
availability and avatar names in the Wii Bowling
game were all decided by participants. Follow-up
interviews found that the teams were formed based
on availability. Before the tournament, participants
had one practice session, where observations and
interviews showed that most participants felt tired
after playing two games in succession. To sustain
participants’ interest to the game but not make them
feel overwhelmed, the experimental group played
two games in one week.
A research assistant (RA) was assigned to each
team. During the eight-week tournament, the RA
visited the site every week, set up the game for the
team, and recorded each member’s score and the
team’s weekly score. A weekly observation protocol
was designed that informed how RAs were to take
field notes, collect feedback, and identify any
problems. The RA also posted each team’s weekly
score on a tournament website and provided the
scores in hard copy to the team
The control group didn’t play digital games
during the tournament, but they were welcome to
watch the gameplay of the experimental group. After
the tournament, both the experimental and control
groups completed the post-test.
Can a Wii Bowling Tournament Improve Older Adults’ Attitudes towards Digital Games?
213
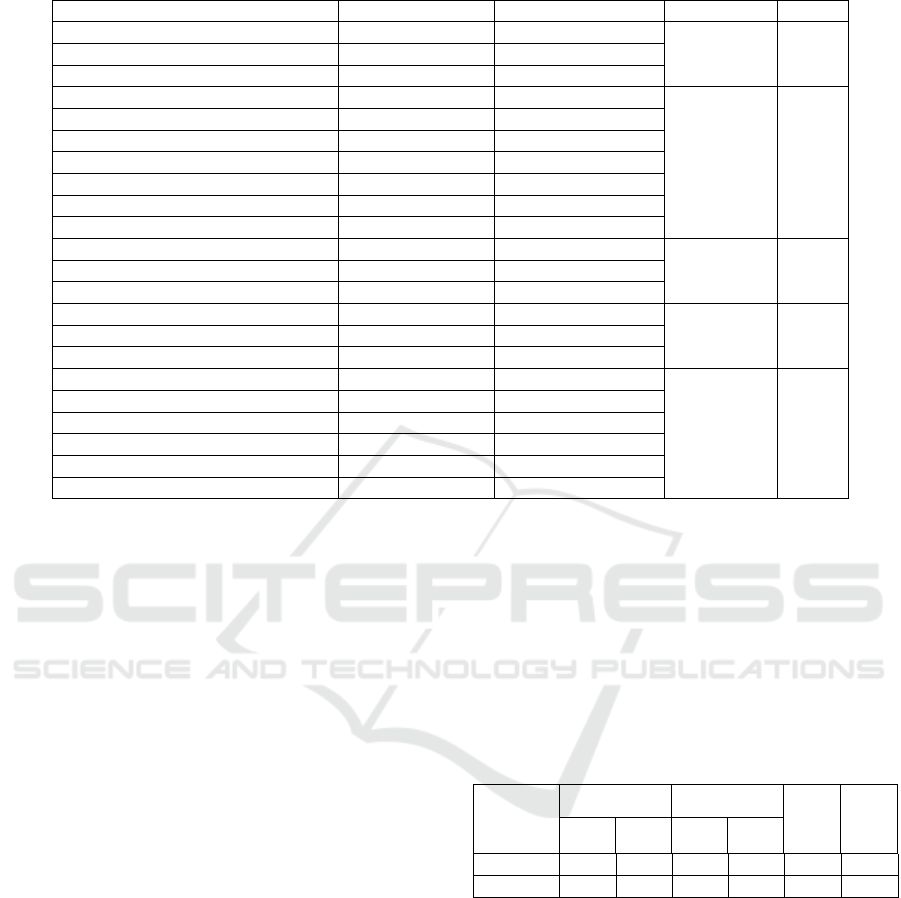
Table 1: Baseline Characteristics of Participants and Outcome Measure in Each Group.
Variables Contro Group Experiment Group Chi-square p
Gender(frequency, percent)
1.35 .25 Male 13(21.3%) 24(30.0%)
Female 48(78.7%) 56(70.0%)
Age (frequency, percent)
8.33 .14
60-69 5(8.2%) 16(20.0%)
70-74 4(6.6%) 8(10.0%)
75-79 8(13.1%) 16(20.0%)
80-84 19(31.1%) 14(17.5%)
85-89 15(24.6%) 14(17.5%)
>=90 10(16.4%) 12(15.0%)
Current relationship status
3.61 .06
Married/Common law 6(10.9%) 18(24.0%)
Single/Windowed 49(89.1%) 57(76.0%)
Living arrangement
2.58 .11
Alone 44(83.0%) 53(70.7%)
With someone 9(17.0%) 22(29.3%)
Education level(frequency, percent)
.86 .93
Less than high school 4(6.6%) 4(5.1%)
High school or equivalent 24(39.3%) 34(43.0%)
Some college/CEGEP 14(23.0%) 18(22.8%)
Two-year degree 7(11.5%) 6(7.6%)
University degree 12(19.7%) 17(21.5%)
2.4 Data Analysis
Data analysis was carried out using IBM SPSS
Statistics V22. Demographic characteristics of the
participants in each group were compared using chi-
squared analysis to examine whether the two groups
were equivalent at baseline. Then, independent t-test
analyses were conducted to compare the difference
between the two groups both before and after the
intervention. For qualitative analysis the field notes
were imported into MaxQDA for coding. Codes
were collected under major themes
3 RESULTS
Demographic information for both groups is
provided in Table 1. Participants in the two groups
did not differ in terms of gender, age, current
relationship status, living arrangements, or education
level. However, the majority of participants in each
group were single or widowed and lived alone.
Because of this, it is possible that they had smaller
social networks than those in other circumstances.
3.1 Quantitative Results
For game attitudes, there was no statistically
significant difference between the two groups in the
pre-test (t = 1.51, p = .13). As shown in Table 2, the
levels of game attitudes increased from 3.72 (SD =
.58) to 3.89 (SD = .70) in the experimental group ,
but only from 3.54 (SD = .66) to 3.55 (SD = .73) in
the control group. The experimental group generally
had higher levels of positive attitudes towards digital
games than control group. More importantly, the
post-test showed a significant difference between the
two groups (t = 2.53, p = .01).
Table 2: Results of Independent T-Test on Game
Attitudes.
Control Experiment
t p
M SD M SD
Pre-test 3.54 .66 3.72 .58 1.51 .13
Post-test 3.55 .73 3.89 .70 2.53 .01
3.2 Qualitative Results
Data from weekly interviews indicated that the
majority of participants enjoyed playing Wii
Bowling. By analyzing the weekly field notes, five
elements were identified that contributed to
maintaining participants’ interest in Wii Bowling
and to changing their attitudes towards digital
games:
(1) In-Situation Teaching
Team members worked together to accomplish each
team’s objectives. Direct teaching from team
CSEDU 2016 - 8th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
214

members was quite frequent, happening whenever a
player wanted to get a strike or had a high possibility
of losing. For example, on one occasion, D wanted
to get a strike (all pins hit down in one throw)
because all of the other three team members had
already gotten one, leading to the following
conversation:
A: Move the line over.
B: Make sure your hand is straight.
A: Get your hand straight.
C: You can do it, D.
(2) Encouragement from Team Members
Encouragement was a key aspect of team members’
social interactions. One player was left-handed, and
her ball always ran slowly. When she didn’t do very
well in one throw, her teammates said, “At least,
that’s a fast bowl” and “It’s good. At least, it’s
straight.” On another occasion, she got many curves
and couldn’t make the ball run straight. When her
bowl ran slowly and gradually changed direction,
her teammates murmured, “Come on, come
on”;”Yes, yes…” Finally, the ball hit the last pin.
Everyone in the room applauded and cheered for her
with “Good for you”; “You have some suspenders.”
At another site, a participant’s vision was so poor
that she needed help to locate the button in the
controller and the pins in the screen, but she did very
well every week. Her teammates said: “You are
remarkable. You always inspire us.” On one
occasion, she had technical problems and needed
several tries to let the bowl go. She was
disappointed, saying “I’m sorry. At least, I let it go,”
but her team members were kind and supportive,
saying “It’s fine”; “That’s OK. You can’t hit them
all the time”; “You participated. It’s fine.”
(3) Audience Support
Audiences played important roles in supporting
players and sustaining their interest and passion
during the tournament. Support from the audiences
made the players believe what they were doing was
interesting. They felt proud of themselves because
they were doing something that they never thought
they could do. As shown in Table 1, approximately
half of the players were aged 80 and over. People at
this age are likely to suffer from some age-related
functional limitations (Bouma, 2000). For example,
at one session an audience member who sat next to a
player and coached that player every week was late
arriving for the game The players were quite
reserved, and didn’t interact with each other as much
as they had in previous weeks. However, once the
audience member walked in, the four players
became alive and said: “We need you, coach.”
(4) Humor
Humor was another key aspect of social interactions
among team members, contributing significantly to
players’ enjoyment of the game. Team members
liked to joke and laugh together during gameplay, as
in the following conversation about a pin that didn’t
fall down:
A: Stupid pins.
B: Silly pins.
C: Not smart pins.
D: The nice pin is going to fall down.
(5) The Game
Wii Bowling enables enactive interactions, or motor
acts used in real life such as swinging arms to play
bowling (Vanden Abeele & De Schutter, 2010).
One advantage of enactive interaction was that
players could focus on hitting the pins rather than
having to learn complex mappings between in-game
actions and specific button presses (Vanden Abeele
& De Schutter, 2010). So, the game was easy to
learn and understand, although difficult to master.
For example, skill was needed to achieve a split
(knocking all pins down in two throws of the ball).
Some participants mentioned minor medical effects
from playing the game; one said that she was
surprised that she didn’t feel arm pain when
swinging her arm.
4 DISCUSSION
The findings of this study support the conclusion
that the Wii Bowling tournament was effective for
improving older adults’ attitudes towards digital
games. In addition, the qualitative data demonstrate
that participants enjoyed the experience of engaging
in the Wii Bowling tournament. Although many
participants had no prior experience with digital
games before the intervention, the majority of them
indicated that they would be interested in playing
digital games in the future.
The possibility of using Wii Bowling to improve
older adults’ attitudes towards digital games is
appealing for many reasons. First, participants were
fully immersed in the game. They were excited and
even danced whenever they got a strike or several
strikes in a row, especially when there was an
audience cheering for them. Second, many
participants mentioned that they enjoyed the
competition and cared about their team’s position
among all the teams. One participant said: “It’s great
to beat another team because we have two teams
here (in an assisted living center).” Third, emotional
Can a Wii Bowling Tournament Improve Older Adults’ Attitudes towards Digital Games?
215

support from team members was a key factor that
contributed a significant part to participants’
enjoyment. Encouragement from team members,
jokes, and applause created a natural social context
in which participants felt free to express themselves.
Fourth, the positive experience of gameplay
improved participants’ confidence with the new
technology. Many participants indicated that they
were proud of themselves; they hadn’t played the
game before the intervention, but they were able to
master the game by the end of the eight-week
tournament. During each session, participants were
provided with directions for each game and
individual assistance from a research assistant. This
on-demand support helped them to acclimate to the
game controls, alleviating potential confusion and
frustration. Last but not least, Wii Bowling was easy
for older adults to interact with since it allowed
participants to interact naturally with the game. The
game also provided clear and positive feedback to
promote players’ self-confidence. Marston (2013)
pointed out that older adults will only invest their
time in such entertainment if they can understand
and see the purpose of their actions.
Nap, de Kort and IJsselsteijin (2009) found that
the majority of older adults have negative
perceptions about multiplayer gaming. Gajadhar et
al. (2010) pointed that older adults’ negative
perceptions about playing against other human
players could be caused by the fear of failure. In this
study, many participants highlighted their positive
experiences of competing with other teams.
Therefore, we suggest that in the context of co-
located gameplay, older adults enjoy team
competition or social competition. The findings of
this study support Gajadhar et al.’s (2010) conclusion
that co-located social gaming is a “mix of social fun
and involvement and social competition” (p.80).
There are two limitations to this study. One
limitation is that the participants were recruited
based on their availability and interest in this study.
Therefore, the results cannot be generalized to other
populations, such as older adults who are not
interested in Wii Bowling. Another limitation is that
health condition was not one of the sample inclusion
criteria. Some participants had to sit to play due to
Parkinson’s disease or physical impairments. We are
unsure whether participants’ physical health affected
attitudes towards playing Wii Bowling.
5 CONCLUSIONS
We are confident that the Wii Bowling
tournament provided positive gaming experiences to
the older adults in this study and was an effective
way to improve their attitudes towards digital
games. Older adults are willing to use digital games
if they are motivated and understand the purpose of
their actions. These findings could encourage other
researchers to investigate in more depth how to help
older adults benefit from digital games. In addition,
the social use of Wii Bowling may enable older
adults to take-up this activity within many senior
centers, thus enriching their daily activities and
enhancing their physical and cognitive function and
social interactions.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We wish to thank the Social Sciences and
Humanities Research Council of Canada (SSHRC)
for supporting this project financially through a four-
year Insight grant.
REFERENCES
Akitunde, A. (2012). Aging Population: 10 Things You
May Not Know About Older People. Retrieved from
http://www.huffingtonpost.com/2012/10/02/aging-
population_n_1929464.html.
Aison, C., Davis, G., Milner, J., & Targum, E. (2002).
Appeal and Interest of Video Game Use Among the
Elderly. Retrieved from http://www.booizzy.com/jrmil
ner/portfolio/harvard/gameselderly.pdf.
Allaire, J. C., McLaughlin, A. C., Trujillo, A., Whitlock,
L. a., LaPorte, L., & Gandy, M. (2013). Successful
aging through digital games: Socioemotional
differences between older adult gamers and Non-
gamers. Computers in Human Behavior, 29(4), 1302–
1306. doi:10.1016/j.chb.2013.01.014.
Bandura, A. (2001). Social cognitive theory of mass
communications. In J.Bryant & D.Zillman (Eds),
Media effects: Advances in theory and research (2nd
ed.) (pp.121-153). Hillsdale, New Jersey: Lawrence
Erlbaum.
Basak, C., Boot, W.R., Voss, M.W, & Kramer,
A.F.(2008). Can Training in a Real-Time Strategy
Digital Game Attenuate Cognitive Decline in Older
Adults? Psychology and Aging, 23(4), 765-777.
Boot, W.R., Champion, M., Blakely, D.P., Wright, T.,
Souders, D.J., & Chamess, N. (2013). Video games as
a means to reduce age-related cognitive decline:
attitudes, compliances, and effectiveness. Frontiers in
Psychology, 4, 1-9.
Bouma, H. (2000). Document and interface design for
older citizens. In P. Westendorp, C. Jansen, & R.
Punselie (Eds.), Interface design & document design
(pp.67-80). Amsterdam: Rodopi.
CSEDU 2016 - 8th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
216

Broady, T., Chan, A., & Caputi, P. (2010). Comparison of
older and younger adults’ attitudes towards and
abilities with computers: Implications for training and
learning. British Journal of Educational Technology,
41(3), 473-485.
Chappell, K.K., & Taylor, C.S. (1997). Evidence for the
reliability and factorial validity of the computer game
attitude scale. Journal of Educational Computing
Research, 17(1), 67-77.
Chiang, I.T., Tsai, J.C., & Chen, S.T. (2012). Using Xbox
360 Kinect games on enhancing visual performance
skills on institutionalized older adults with
wheelchairs. In Proceedings of Fourth IEEE
International Conference on Digital Game and
Intelligent Toy Enhanced Learning - DIGITEL
2012(pp. 263-267). Los Alamitos, CA: IEEE
Computer Society. doi:10.1109/DIGITEL.2012.69.
Csıkszentmihalyi, M. (2000). Beyond Boredom and
Anxiety. Experiencing Flow in Work and Play. 25th
Anniversary Edition. San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
Deary, I.J., Corley, J., Gow, A.J., Harris, S.E., Houlihan,
L.M., Marioni, R.E…Starr, J.M. (2009). Age-
associated cognitive decline. British Medical Bulletin,
92, 135-152.
De Schutter, B. (2011). Never Too Old to Play: The
Appeal of Digital Games to an Older Audience.
Games and Culture, 6(2), 155-170.
Diaz-Orueta, U., Facal, D., Nap, H.H., & Ranga, M.M.
(2012). What Is the Key for Older People to Show
Interest in Playing Digital Learning Games? Initial
Qualitative Findings from the LEAGE Project on a
Multicultural European Sample. Games for Health
Journal. 1(2), 115-123. doi:10.1089/g4h.2011.0024.
Eisma, R., Dickinson, A., Goodman, J., Syme, A., Tiwari,
L. & Newell, A.F. (2004). Early user involvement in
the development of information technology-related
products for older people. Universal Access in the
Information Society, 3, 131-140.
Ekman I, Chanel G, Järvelä S, Kivikangas JM, Salminen
M, Niklas Ravaja N (2012) Social interaction in games
measuring physiological linkage and social presence.
Simulation & Gaming 43(3): 321-338.
doi:10.1177/1046878111422121.
Entertainment Software Association (2014) Essential facts
about the computer and video game industry.
Washington, DC: Entertainment Software Association.
Retrieved from http://www.theesa.com/wp-
content/uploads/2014/10/ESA_EF_2014.pdf.
Gajadhar, B.J., de Kort, Y., & IJsselsteijn, W. (2008).
Shared fun is doubled fun: player enjoyment as a
function of social setting. In P.Markopoulos, B. de
Ruyter, W.IJsselsteijn & D.Rowland (Eds.) Fun and
Games (pp.106-117). New York: Springer.
Gajadhar, B.J., Nap, H.H., de Kort, Y.A.W., &
IJsselsteijn, W.A. (2010). Out of Sight, out of Mind:
Co-Player Effects on Seniors’ Player Experience.
Proceedings of Fun and Games, Leuven, Belgium.
Galarneau, Lisa. (2014). 2014 Global Gaming Stats:
Who’s Playing What, and Why? Retrieved from
http://www.bigfishgames.com/blog/2014-global-
gaming-stats-whos-playing-what-and-why/
Gamberini, L., Alcaniz, M., Fabregat, M., Gonzales, A.L.,
Grant, J., Jensen, R.B…Zemmerman, A. (2008).
Eldergames: Videogames for empowering, training
and monitoring elderly cognitive capabilities.
Gerontechnology, 7(2), 111.doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.40
17/gt.2008.07.02.048.00.
Ghosh, R., Ratan, S., Lindeman, D., & Steinmetz, V.
(2013). The new era of connected aging: A framework
for understanding technologies that support older
adults in aging in place. Oakland, CA: Center for
Technology and Aging.
Heinz, M., Martin, P., Margrett, J.A., Yearns, M., Franke,
W., Yang H.I….Chang, C.K. (2013).Perceptions of
Technology among Older Adults. Journal of
Gerontological Nursing, 39(1), 42-51.
Hoppes, S., Wilcox, T., & Graham, G. (2001). Meanings
of play for older adults. Physical Occupational
Therapy in Geriatrics, 18(3), 57-68.
Jorgensen, M.G., Laessoe, U., Hendriksen, C., Nielsen,
O.B.F., & Aagaard, P. (2012). Efficacy of Nintendo
Wii Training on Mechnical Leg Muscle Function and
Postural Balance in Community-Dwelling Older
Adults: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Journals of
Gerontology: MEDICAL SCIENCES, 1-8.
Jung, y., Li, K.J., Janissa, N.S., Gladys, W.L.C., & Lee,
K.M. (2009). Games for a Better Life: Effects of
Playing Wii Games on the Well-Being of Seniors in a
Long-Term Care Facility, Proceedings of the Sixth
Australasian Conference on Interactive Entertainment.
NY: USA.
Lewis, J. (2014). The Role of the Social Engagement in
the Definition of Successful Ageing among Alaska
Native Elders in Bristol Bay, Alaska. Psychology &
Developing Societies, 26(2), 263–290.
Lai, C.H., Peng, C.W., Chen, Y.L., Huang, C.P., Hsiao,
Y.L., & Chen, S.C. (2012). Effects of interactive
digital-game based system exercise on the balance of
the elderly. Gait Posture, 1-5.
Marston, H.R. (2013). Digital Gaming Perspectives of
Older Adults: Content vs. Interaction. Educational
Gerontology, 39(3), 194-208.
McKay, S.M., & Maki, B.E. (2010). Attitudes of older
adults toward shooter video games: An initial study to
select an acceptable game for training visual
processing. Gerontechnology, 9(1), 5-17.
Melenhorst, A.S. (2002). Adopting communication
technology in later life: The decisive role of benefits.
Doctoral dissertation. The Netherlands: Eindhoven
University of Technology.
Nap, H.H., de Kort, Y.A.W., & IJsselsteijn, W.A. (2009).
Senior Gamers: Preferences, Motivations and Needs.
Gerontechnology, 8, 247-262.
Pompeu, J.E., Mendes, F.A., Silva, K.G., Lobo, A.M.,
Oliveira, T.P., Zomigani, A.P., & Piemonte, M.E.
(2012). Effect of Nintendo Wii-based motor and
cognitive training on activities of daily living in
patients with Parkinson’s disease: A randomized
clinical trial. Physiotherapy, 98, 196-204.
Can a Wii Bowling Tournament Improve Older Adults’ Attitudes towards Digital Games?
217

Rice, M., Cheong, Y. L., Ng, J., Chua, P. H., & Theng,
Y.L. (2012). Co-creating games through
intergenerational design workshops. In Proceedings of
the Designing Interactive Systems Conference on -
DIS ’12 (pp. 368–377). Newcastle, UK.
http://doi.org/10.1145/2317956.2318012.
Sweetser, P., & Wyeth, P. (2005). GameFlow: A Model
for Evaluating Player Enjoyment in Games. ACM
Computers in Entertainment, 3(3), 1-24.
Vanden Abeele, V., & De Schutter, B. (2010). Designing
intergenerational play via enactive interaction,
competition and acceleration. Personal and
Ubiquitous Computing, 14(5), 425–433.
Whitlock, L. A., McLaughlin, A. C., &Allaire, J. C.
(2012). Individual differences in response to cognitive
training: Using a multi-modal, attentionally
demanding game-based intervention for older adults.
Computers in Human Behavior, 28(4), 1091-1096.
doi:10.1016/j.chb.2012.01.012.
CSEDU 2016 - 8th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
218
