
Factors Affecting University Instructors’ Continuance Intention to
Use Learning Management Systems: The Blackboard System Case
Samar Mouakket¹ and Anissa M. Bettayeb²
¹Department of Management Information Systems, College of Business Administration, University of Sharjah,
Sharjah, U.A.E.
²Information Technology Center, University of Sharjah, Sharjah, U.A.E.
Keywords: The Expectation-Confirmation Model, Learning, Management Systems, University Instructors, Training,
User-Interface Design, Technical Support, Computer Self-efficacy.
Abstract: Although academic institutions have invested heavily in Learning Management Systems (LMS) to support
e-learning platform, few studies have examined the factors affecting their usage, particularly by university
instructors. To fill this research gap, this study proposes a framework based on the expectation-confirmation
model (ECM) to examine the influence of several critical independent factors related to organizational,
technological and individual characteristics on university instructors’ perceived usefulness of Blackboard
system as one well-known LMS, which in turn will affect their continuance intention to use this technology.
Data was gathered from 158 university instructors at a university in the United Arab Emirates (UAE).
Structural equation modeling technique was used to validate the causal relationships between the different
variables.
1 INTRODUCTION
Academic institutions around the world are investing
heavily in various Learning Management Systems
(LMS) to deliver and manage e-learning services
(Cheng, 2014; Caputi and Garrido, 2015). LMS,
such as Web Course Tools (WebCT) and
Blackboard system, are among the most commonly
used types of e-learning systems for both students
and instructors in academic institutions (Sun, 2008;
Liaw, 2008; Cheng, 2014). The focus of previous
research has been on the student’s perception of
LMS (Yi and Hwang, 2003; Ngai et al., 2007;
Limayem and Cheung, 2008; Paechter et al., 2010;
Tarhini et al., 2013; Chang, 2013; Liaw and Huang,
2013; Chen, 2014) with less emphasis on the
instructor’s attitude (Sørebø et al., 2009; Al-Busaidi
and Al-Shihi, 2012). This study contributes to the
literature by developing a model for the post-
adoption context, based on the expectation-
confirmation model (ECM, Bhattacherjee, 2001), to
investigate the factors affecting instructors’
continuance usage intention of Blackboard system as
one well-known LMS in academic institutions in the
United Arab Emirates (UAE). In this study, the
constructs of the ECM have been selected based on
their widespread use and relevance to the LMS
context. Hence, we have adopted the following
constructs from ECM: perceived usefulness and
continuance intention.
In this study, we propose a framework which
provides a comprehensive view of the critical factors
that influence university instructors’ perceived
usefulness of LMS and consequently continuance
intention to use this technology. According to our
framework, these critical factors are related to the
following characteristics: individual, organizational
and technological. We suggest that the individual
characteristics include computer self-efficacy (Ball
and Levy, 2008; Sawang et al., 2013; Chen, 2014),
the organizational characteristics include technical
support and training (Sumner and Hostetler, 1999;
Bradford and Florin, 2003; Al-Busaidi and Al-Shihi,
2012), and the technological characteristics include
user-interface design (Jeong, 2011; Chen, 2014). We
believe that taking into consideration these different
characteristics will provide us with a more complete
picture of LMS adoption and usage by university
instructors.
This study is organized as the following. After
the introduction in section 1, the research model and
hypotheses are proposed in section 2. The research
Mouakket, S. and Bettayeb, A.
Factors Affecting University Instructors’ Continuance Intention to Use Learning Management Systems: The Blackboard System Case.
In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS 2016) - Volume 2, pages 215-222
ISBN: 978-989-758-187-8
Copyright
c
2016 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
215

method used in this study is described in section 3.
The results of the collected data analyzed using
structural equation modeling (SEM) are reported in
section 4. Section 5, discusses the findings of the
study, and finally section 6 presents the implications
and venues for further research.
2 RESEARCH MODEL
This research investigates the influence of the
following characteristics: organizational
characteristics (training and technical support),
technological characteristics (user-interface design),
and individual characteristics (computer self-
efficacy) on perceived usefulness, which in turn will
affect university instructors’ continuance intention to
use LMS. Figure 1 presents the research model.
Figure 1: Research model.
Continuance intention is the degree to which an
individual is willing to continue using an
information system (IS) in the future and to
recommend it to others (Chang, 2013). Perceived
usefulness refers to an individual’s perception that
the usage of IS will improve work performance
(Davis, 1989). Previous studies have found that the
extent to which users perceive an information
system to be useful positively affect their
continuance intention (Bhattacherjee, 2001; Lin et
al., 2005; Limayem et al., 2007, Hoehle et al., 2011).
Within LMS context, prior studies have found
that perceived usefulness significantly influences
continuance intention to use LMS among university
students (Limayem and Cheung, 2008; Lee, 2010).
Drawing on the findings of previous studies, we
hypothesize that as instructors feel the usefulness of
the Blackboard system, their intention to continue
using it will increase. Thus, we postulate the
following:
H1: Perceived Usefulness has a Positive Effect on
the Continuance Intention to use Blackboard
System. Training is considered one of the
organizational factors which can influence the
success of IS implementation (Bradford and Florin,
2003). It is a process needed to obtain IS skills
required to perform specific tasks (Nelson and
Cheney, 1987). Because of the increased use of
information systems in the educational field,
academic institutions need to provide adequate
training programs for their instructors on the use of
new IS (Lareki et al., 2010). Training programs can
be effective for improving the level of utilization of
LMS and for enabling users to obtain the benefits of
this technology (Randeree and Narwani, 2009). Prior
research has reported that training influences
technology acceptance indirectly through its
influence on perceived usefulness (Amoroso and
Cheney, 1991; Igbaria et al., 1997). Similarly, within
LMS context, we postulate that training offered to
university instructors will influence their perceived
usefulness:
H2: Training has a Positive Effect on the
Perceived Usefulness of Blackboard System.
Technical support is another organizational
characteristic which refers to answering questions
regarding information systems usage and offering
support to users when requested by expert
individuals in help desk and information technology
center (Ngai et al., 2007; Bhattacherjee and Hikmet,
2008). Prior studies have shown that technical
support is a key factor influencing attitude of
instructors and students (Williams, 2002). Thus, lack
of technical support will make teachers frustrated
with the technology which may discourage them
from using it, whereas providing appropriate
technical support to teachers will help them to
integrate new technologies easily into their teaching
(Tong and Triniada, 2005). Previous studies have
found that technical support positively influences
perceived usefulness of LMS (Ngai et al., 2007).
Drawing on prior studies, we suggest that having
technical support will enhance the usefulness of
Blackboard system, thus the following hypothesis is
proposed:
H3: Technical Support has a Positive Effect on
the Perceived Usefulness of Blackboard System.
A good menu design with control tool bars will
enable the functions of a system to be easily
accessible to the user, thus enhancing its perceived
ICEIS 2016 - 18th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
216

usefulness (Cho et al., 2009). Several studies have
examined the impact of user-interface design on user
attitude towards IS (Jeong, 2011; Cyr et al., 2006).
Within LMS context, a good user-interface design is
an important factor for supporting user acceptance
and usage of e-learning services (Cho et al., 2009).
In this study, we hypothesize that user-interface
design of Blackboard system enable university
instructors to achieve their goals effectively which
would help them to enhance the usefulness of the
system. Thus, the following hypothesis is suggested:
H4: User-interface Design has a Positive Effect on
the Perceived Usefulness of Blackboard System.
Computer self-efficacy refers to the individual’s
ability to use a computer to perform a specific task
(Compeau and Higgins, 1995). Prior studies suggest
that computer self-efficacy is a significant
determinant of an individual’s decision to use
computers through perceived usefulness (Agarwal et
al., 2000). Similarity, in this study, we argue that
instructors who have higher computer self-efficacy
will recognize the usefulness and value of
Blackboard system. Accordingly, the following
hypothesis will be tested:
H5: Computer Self-efficacy has a Positive Effect
on the Perceived Usefulness of Blackboard
System.
3 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3.1 Data Collection Procedures and
Sample
In order to empirically assess the proposed model
and hypotheses, we have conducted a paper-based
survey method as well as an online survey method to
university instructors who use Blackboard system on
a voluntary basis in one well-known university in
the United Arab Emirates. Since our study focuses
on users during the post-adoption stage of LMS, we
have targeted university instructors who used
Blackboard system before, and they were assured
that anonymity would be maintained. The study is
conducted in three steps. First, the questionnaire is
developed in English language and translated to
Arabic language since the teaching method in the
university is both in English and Arabic. Two
English university instructors who are experts in
translation have examined the questionnaire and
made suggestions about the clarity of the translated
items. Second, the questionnaire is pilot-tested with
5 randomly selected university instructors in the
university. Based on the feedback from the pilot test,
the questionnaire is refined and a revised final
questionnaire has been developed. Third, a paper-
based questionnaire is self-administered by the
researchers to university instructors in different
colleges who volunteered to participate in this
survey. Some university instructors have helped the
researchers by distributing the questionnaires among
their colleagues and later collecting them before
giving them back to the researchers. The
questionnaire is also distributed online and faculty
members are encouraged to complete it and send it
via email to the researchers.
The researchers distributed 200 questionnaires,
and they received 115 questionnaires back. 7
questionnaires were eliminated due to missing
values and wrong data provided, making the number
of completed questionnaires 108. To increase the
response rate, a second round of follow-up was
carried out by the researchers themselves making the
number of returned questionnaire 167. After
checking the questionnaires for completeness and
any missing values, 9 questionnaires were
eliminated. The final number of valid responses was
158. Approximately 74% of the respondents are
male while 25.9% are female. 20.9% of the
respondents are between 30 and 39, while 79.1% are
40 and above. 79.1% of the respondents are Arabs
while 20.9% are non-Arab. The highest number of
respondents is from the engineering College, 20.3%,
while the lowest numbers is from the Fine Art
College, 3.8%. 48.7% of the respondents are
assistant professors, while 10.1% of the respondents
are full professors. The number of respondents who
teach in English is 70.9%, while the number of
respondents who teach in Arabic is 29.1%. Finally,
27.2% of the respondents have between 1 and years
of teaching experience, while 33.5% of the
respondents have more than 15 years of teaching
experience. 34.8% of the respondents spend more
than 120 minutes on the Internet daily. 58.9% of the
respondents spend 30 minutes or less daily using
Blackboard system.
3.2 Measurement Items
The questionnaire is divided into two main parts.
The first part consists of 9 items. It contains
demographic data about the university instructors
(gender, age, nationality, college, job rank, teaching
experience, frequency of Internet usage, and
frequency of Blackboard system usage). The second
part, which consisted of 27 items to assess the
proposed seven constructs, is measured using a five-
Factors Affecting University Instructors’ Continuance Intention to Use Learning Management Systems: The Blackboard System Case
217

point Likert scale ranging from 1-strongly agree to
5-strongly disagree, with the mid-point (3)
representing the state of unsure or neutral.
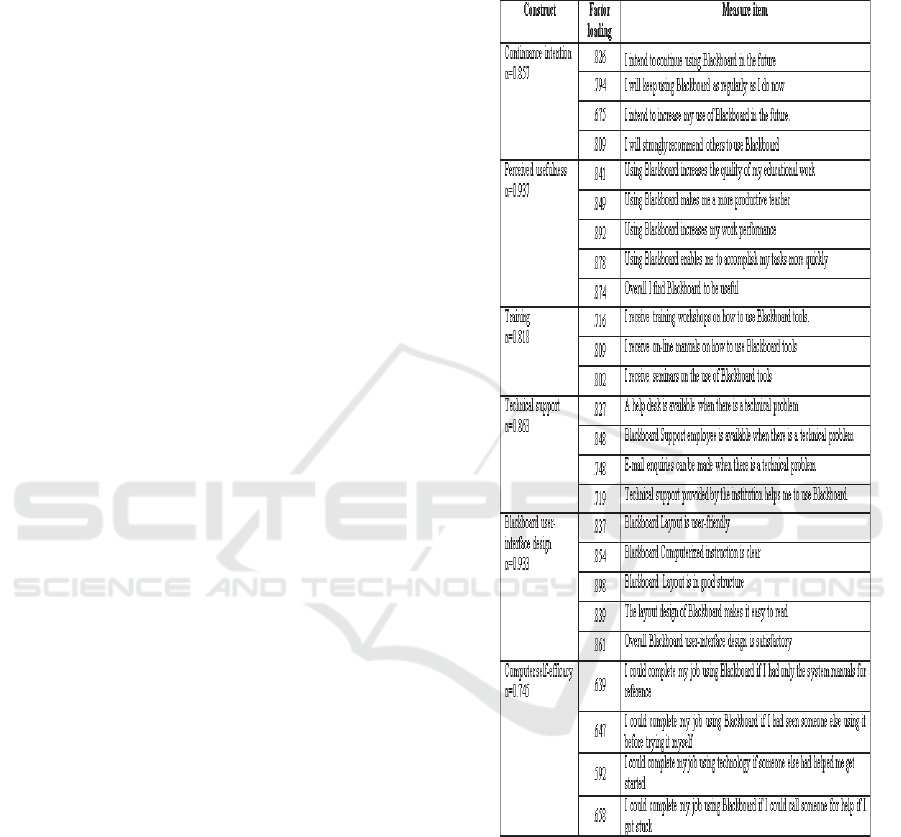
Measurement items in the survey are adapted
from prior studies to fit the context of learning
management systems. Items of organizational
characteristics which include training (3 items) and
technical support (4 items) are adapted from Al-
Busaidi and Al-Shihi (2012) and Ngai et al., (2007).
Items of technological characteristics which include
user-interface design (5 items) are adapted from Cho
et al., (2009) and Liu et al., (2010). Items of
individual characteristics which include computer
self-efficacy (6 items) is adapted from Chatzoglou et
al. (2009), Lee et al., (2009) and Chiu and Wang
(2008). Perceived usefulness (5 items) is adapted
from Yoon and Kim (2007) and Sørebø and Sørebø
(2009). Continuance intention (4 items) is adapted
from Chiu et al., (2005), Kim (2010) and Lee
(2010). The items of each variable are listed in the
appendix.
4 DATA ANALYSIS AND
RESULTS
The data has been analyzed as the following. The
first step involves analyzing the measurement model
to establish the reliability and validity of the
measures while the second step tests the structural
relationships of the model. SPSS has been used to
analyze the demographic data and to evaluate the
Cronbach’s alpha. AMOS has been used to conduct
structural equation modeling (SEM) to examine our
measurement model and then to test the structural
model.
To test the measurement models of our model,
we have examined the following: (1) factor loading
for each item, (2) reliability of measures and (3)
composite reliability and average variance extracted.
First, this study has conducted a confirmatory factor
analysis (CFA) to examine if the measurement items
of each construct are loaded as predicted on their
respective constructs. Based on the recommended
values provided in the literature, a factor should
have at least two items and each item factor loading
should be greater than 0.40 (Hair et al., 1998). As a
result of the CFA, two items from computer self-
efficacy were dropped due to low factor loading,
while the factor loading of the remaining items in
this study ranged between 0.592 and 0.898. The
items and their factor loading are listed in the
Appendix.
Second, the reliability of each measurement scale
is computed by applying the Cronbach’s alpha. The
reliability coefficients range from 0.745 to 0.937
(See Appendix), which is higher than the
recommended level of 0.70 suggested in the
literature (Nunnally and Bernstein, 1994; Hair et al.,
2006). Third, the values of composite reliability
(CR) have exceeded 0.70 and the average variance
extracted (AVE) is higher than the recommended
value of 0.50 (Fornell and Larcker, 1981). Thus, we
can conclude that the scales used in this study are
both reliable and valid.
This study has used five goodness-of-fit indices
to investigate the goodness-of-fit of the
measurement model and then the structural model.
According to researchers, the value of Chi²/ Degree
of freedom (df) should be less than 5.0 (Bentler and
Bonett, 1980). Comparative fit index (CFI), normed
fit index (NFI), and incremental fit index (IFI)
should be 0.90 and above (Hair et al. 2006). Root
mean square error of approximation (RMSEA)
should not exceed 0.10 (Anderson and Gerbing,
1988). All the values of the measurement model
used in this research have been above the
recommended values by researchers, with the
exception of the value of NFI which is slightly low.
The results are as the following:
Chi²/df=638.524/238=2.683, CFI=0.903,
NFI=0.891, IFI=0.902 and RMSEA=0.090.
Figure 2: Results of hypotheses tests (***p<0.001, dotted
line=Not significant).
The results of the structural model have been
very close to the measurement model which
provides evidence that the structural model fits the
observed data well. Thus, we proceed to examine the
hypothesized relationships within the model. As can
ICEIS 2016 - 18th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
218

be shown in figure 2, all the path coefficients are
significant in our structural model, supporting all
hypotheses with the exception of H5. The results
show that the characteristics related to the
organizational and technological factors positively
influence perceived usefulness, while the
characteristics related to the individual factors have
no impact on perceived usefulness.
5 DISCUSSION
This study investigates university instructors’
continuance intention to use Blackboard system as a
learning management system to support e-learning
platform in the UAE. Our study is motivated by the
need to examine a “university instructor”
perspective, which has not been highly investigated
in the literature. We believe that the results of the
study will further offer scholars and researchers
some insights of the influence of the proposed
factors on motivating university instructors’
continuance intention to use leaning management
systems.
Our findings indicate that all the hypotheses
related to the direct relation between perceived
usefulness are supported with the exception of the
influence of computer self-efficacy. First, we have
found that the technological characteristics,
represented by user-interface design, influence
perceived usefulness of Blackboard system. Second,
we have found that having good technical support
and proper training, as factors of organizational
characteristics, can increase the feeling of the
benefits of Blackboard system, suggesting that
regular training and offering technical support to
users will allow them to become familiar with LMS
and consequently realize the benefits of these
technologies. Our results are consistent with
previous research, which has reported that technical
support and user-interface significantly determine
perceived usefulness within e-learning context (Cho
et al., 2009). Our findings also draw attention to the
importance of the technological factors in
influencing the perceived usefulness of Blackboard
system and, eventually increase continuance
intention to use this technology by university
instructors. Thus, we suggest that a good Blackboard
system user-interface design which is user friendly
and simple will allow university instructors to feel
the benefits of this technology, and motivate them to
have continuance intention to use it. Our result
contradicts with the finding of Hong et al., (2011)
who have found that interface design has no
influence on perceived usefulness of digital archives
system among users in Taiwan.
On the other hand, our findings have indicated
that users with individual characteristics represented
by high computer self-efficacy does not positive
influence of perceived usefulness of Blackboard
system. This suggests that high computer-self
efficacy does not necessarily enable university
instructors to perceive Blackboard system as useful.
Hence, further research is needed to validate the
influence of this characteristic and its link to
technology continuance adoption of LMS.
As for the relation between perceived usefulness
and continuance intention, our finding shows that
users who feel the benefits of the Blackboard will
have positive intention to continue use it. Our results
are consistent with the study of Sørebø and Sørebø
(2009) which has found that university teachers’
continuance intention toward e-learning technology
in connection with on-site courses is influenced by
perceived usefulness of these technologies.
Similarly, Cho et al., (2009) have found that
perceived usefulness determine university students’
continuance intention to use e-learning tools in Hong
Kong.
6 IMPLICATIONS AND
SUGGESTIONS FOR FUTURE
RESEARCH
Although prior studies have investigated the post-
adoption of management learning systems from a
student perspective, there has been little research
examining post-adoptive continuance intention from
a university instructor perspective. This study
attempts to fill this gap and thus its results have
several theoretical and practical implications.
From a theoretical perspective, the results of this
study suggest that our proposed model provides a
better understanding of the factors influencing
instructors’ decision to continue using Blackboard
system. In fact, to our knowledge this is one of the
few empirical studies which have investigated the
factors influencing post-adoptive intention towards
Blackboard system for university instructors. We
believe that our results will encourage further
research to apply our model to other management
learning systems, such as WebCT.
From a practical perspective, our research reports
that perceived usefulness positively influence
continuance intention towards Blackboard system.
Hence, universities should organize seminars and
Factors Affecting University Instructors’ Continuance Intention to Use Learning Management Systems: The Blackboard System Case
219

workshops to explain the benefits of Blackboard
system and familiarize the instructors with any
updates of the system which can be useful in order
to motivate them to have continuance intention to
use it. As for the exogenous factors influencing
perceived usefulness, this study recommends
considering the organizational and the technological
characteristics to emphasize the usefulness and the
benefits of Blackboard system.
In terms of user-interface Design, our findings
have revealed that when Blackboard system design
is developed in a more user-friendly manner, users
will be able to perceive its benefits and be satisfied
with it, which will eventually encourage them to
continue using it. Thus, web developers of LMS
should consider developing user-friendly systems so
that their customers will feel comfortable with the
features of the website, which will influence their
decision to continue using it. Also, having a good
user-interface will allow the users to obtain the
benefits of the system, which will also encourage
them to consider using it again.
In terms of training, universities using LMS are
encouraged to provide additional flexible and
voluntary training sessions for the instructors’
personal development, so that they can be familiar
with the capabilities and the benefits of these
technologies. Furthermore, universities can offer
instructors personalized online training sessions
which will be customized according to their
individual needs. Finally, in terms of technical
support, universities can offer instructors various
methods which will allow them to ask questions
about any technical problem they encounter while
using the LMS, such as online chatting as well as
direct phone number or email. Effective technical
support will help instructors to become comfortable
with the LMS which will lead to their understanding
of the system’s benefits.
Although this study has provided valuable
findings, it has several limitations. First, this study
examines the influence of several factors on
continuance intentions to use Blackboard system.
We propose investigating the influence of those
factors on other LMS to enhance the generalizability
of our findings. Second, this research has been
conducted in a university in the UAE, where using
Blackboard system is voluntary. Thus, further
research is needed to test our model in other
academic institutions where using Blackboard
system is mandatory. Third, this study has
investigated the influence of certain variables on
user continuance intention to use Blackboard
system. Future research can incorporate other
factors, such as computer anxiety and subjective
norms, to investigate their effects. Furthermore,
future research could take into consideration
investigating the role of individual differences, such
as gender and personality traits. Finally, this study
has investigated the influence of critical factors
which are related to the individual, organizational
and technological characteristics on perceived
usefulness. Further research can examine the
influence of other characteristics such as
environmental characteristics.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The framework in this study is a modified model
adopted from the second author’s thesis in the
fulfillment of Master of Science degree in
Information Technology Management. The modified
framework has been applied to a larger sample size
and utilized different statistical tools to analyze the
data. Consequently the results are different.
REFERENCES
Agarwal, R., Sambamurthy, V., Stair, R. M., 2000.
Research report: The evolving relationship between
general and specific computer self-efficacy—An
empirical assessment, Information Systems Research,
Vol. 11, No. 4, pp. 418–430.
Al-Busaidi, K. L., Al-Shihi, H., 2012. Key factors to
instructors’ satisfaction of learning management
systems in blended learning, Journal of Computing in
Higher Education, Vol. 24, No. 1, pp. 18–39.
Amoroso, D. L., Cheney, P. H., 1991. Testing a causal
model of end-user application effectiveness, Journal
of Management Information Systems, Vol. 8, No. 1,
pp. 63–90.
Anderson, J. C., Gerbing, D. W., 1988. Structural equation
modeling in practice: A review and recommended
two-step approach, Psychological Bulletin, Vol. 103,
No. 3, pp. 411-423.
Ball, D. M., Levy, Y., 2008. Emerging Educational
Technology: Assessing the Factors that Influence
Instructors’ Acceptance in Information Systems and
Other Classroom, Journal of Information Systems
Education, Vol. 9, No. 4, pp. 431-444.
Bentler, P. M., Bonett, D. G., 1980. Significance tests and
goodness of fit in the analysis of covariance structure,
Psychological Bulletin, Vol. 88, No. 3, pp. 588–606.
Bhattacherjee, A., 2001. Understanding information
systems continuance: An expectation-confirmation
model, MIS Quarterly, Vol. 25, No. 3, pp. 351-370.
Bhattacherjee, A., Hikmet, N., 2008. Reconceptualizing
organizational support and its effect on information
ICEIS 2016 - 18th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
220

technology usage: evidence from the health care
sector, Journal of Computer Information Systems, Vol.
48, 4, pp. 69-76.
Bradford, M., Florin, J., 2003. Examining the role of
innovation diffusion factors on the implementation
success of enterprise resource planning systems,
International Journal of Accounting Information
Systems, Vol. 4, No. 3, pp. 205-225.
Caputi, V., Garrido, A., 2015. Student-oriented planning
of e-learning contents for Moodle, Journal of Network
and Computer Applications, Vol. 53, pp. 115–127.
Chang, C-C., 2013. Exploring the determinants of e-
learning systems continuance intention in academic
libraries, Library Management, Vol. 34, No. 1/2, pp.
40-55.
Chatzoglou, P. D., Sarigiannidis, L., Vraimaki, E.,
Diamantidis, A., 2009. Investigating Greek
employees’ intention to use web-based training,
Computers & Education, Vol. 53, No. 3, pp. 877–889.
Chen, Y-C, 2014. An empirical examination of factors
affecting college students’ proactive stickiness with a
web-based English learning environment, Computers
in Human Behavior, Vol. 31, pp. 159–171.
Cheng, Y-M, 2014. Roles of interactivity and usage
experience in e-learning acceptance: a longitudinal
study, International Journal of Web Information
Systems, Vol. 10, No. 1 pp. 2 – 23.
Chiu, C. M., Hsu, M. H., Sun, S. Y., Lin, T. C., Sun, P. C.,
2005. Usability, quality, value and e-learning
continuance decisions, Computers & Education, Vol.
45, No. 4, pp. 399–416.
Chiu, C-M., Wang, E. T. G., 2008. Understanding Web-
based learning continuance intention: The role of
subjective task value, Information & Management,
Vol. 45, No. 3, pp. 194–201.
Cho, V., Cheng, T.C. E., Lai, M.W. J., 2009. The role of
perceived user-interface design in continued usage
intention of self-paced e-learning tool, Computers &
Education, Vol. 53, No. 2, pp. 216–227.
Compeau, D. R., Higgins, C. A., 1995. Computer Self-
Efficacy: Development of a Measure and Initial Test,
MIS Quarterly, Vol. 19, No. 2, pp. 189-211.
Cyr, D., Head, M., Ivanov, A., 2006. Design aesthetics
leading to m-loyalty in mobile commerce, Information
& Management, Vol. 43, No. 8, pp. 950-963.
Davis, F. D., 1989. Perceived usefulness, perceived ease
of use and user acceptance of information technology,
MIS Quarterly, Vol. 13, No. 3, pp. 319–340.
Fornell, C., Larcker, D. 1981. Structural equation models
with unobservable variables and measurement error,
Journal of Marketing Research, Vol. 18, No. 1, pp.
39–50.
Hair, J. F., Anderson, R. E., Tatham, R. L. and Black, W.
C. (1998), Multivariate data analysis with readings
(5th ed.), New York, NY: Macmillan.
Hair, J., Black, W., Babin, B., Anderson, R., Tatham, R.
L., 2006. Multivariate Data Analysis, Pearson
Education: Harlow, 6
th
edition.
Hoehle, H., Sid Huff, S., Goode, S., 2011. The role of
continuous trust in information systems continuance,
Journal of Computer Information Systems, Vol. 52,
No. 4, pp. 1-9.
Hong, J-Ch, Hwang, M-Y, Hsu, H-F, Wong, W-T, Chen,
W-Y, 2011. Applying the technology acceptance
model in a study of the factors affecting usage of the
Taiwan digital archives system, Computers &
Education, Vol. 57, No. 3, pp. 2086–2094.
Igbaria, M., Guimaraes, T., Davis, G., Zinatelli, N., Cragg,
P., Cavaye, L. M., 1997. Computing acceptance
factors in small firms: A structural equation model,
MIS Quarterly, Vol. 21, No. 3, pp. 279–305.
Jeong, H., 2011. An investigation of user perceptions and
behavioral intention towards the e-library, Library
Collections, Acquisitions, & Technical Services, Vol.
35, No. 2, pp. 45–60.
Kim, B., 2010. An empirical investigation of mobile data
service continuance: Incorporating the theory of
planned behavior into the expectation–confirmation
model, Expert Systems with Applications, Vol. 37, No.
10, pp. 7033–7039.
Lareki, A., Martínez de Morentin, J. I., Amenabar, N.,
2010. Towards an efficient training of university
faculty on ICTs”, Computers & Education, Vol. 54,
No. 2, pp. 491–497.
Lee, H., Choi, S. Y., Kang, Y. S., 2009. Formation of e-
satisfaction and repurchase intention: Moderating roles
of computer self-efficacy and computer anxiety,
Expert Systems with Applications, Vol. 36, No. 4, pp.
7848–7859.
Lee, M-C, 2010. Explaining and predicting users’
continuance intention toward e-learning: An extension
of the expectation–confirmation model, Computers &
Education, Vol. 54, No. 2, pp. 506-516.
Liaw, S-S, 2008. Investigating students’ perceived
satisfaction, behavioral intention, and effectiveness of
e-learning: A case study of the Blackboard system,
Computers & Education, Vol. 51, pp. 864–873.
Liaw, S-S, Huang, H-M., 2013. Perceived satisfaction,
perceived usefulness and interactive learning
environments as predictors to self-regulation in e-
learning environments, Computers & Education, Vol.
60, pp. 14–24.
Limayem, M., Hirt, S.G., Cheung, C.M.K., 2007. How
habit limits the predictive power of intention: The case
of information systems continuance, MIS Quarterly,
Vol. 31, No. 4, pp. 705-737.
Limayem, M., Cheung, C.M.K., 2008. Understanding
information systems continuance: The case of Internet-
based learning technologies”, Information &
Management, Vol. 45, pp. 227–232.
Lin, C.S., Wu, S., Tsai, R.J., 2005. Integrating perceived
playfulness into expectation-confirmation model for
web portal context, Information & Management, Vol.
42, No. 5, pp. 683-693.
Liu, I-F, Chen, M. C., Sun, Y. S., Wible, D., Kuo, C-H,
2010. Extending the TAM model to explore the factors
that affect Intention to use an online learning
community, Computers & Education, Vol. 54, pp.
600–610.
Ngai, E.W.T., Poon, J.K.L., Chan, Y.H.C., 2007.
Factors Affecting University Instructors’ Continuance Intention to Use Learning Management Systems: The Blackboard System Case
221
Empirical examination of the adoption of WebCT
using TAM, Computers & Education, Vol. 48, No. 2,
pp. 250-267.
Nelson, R. R., Cheney, P., 1987. Training End Users: An
Exploratory Study, MIS Quarterly, Vol. 11, No. 4, pp.
547-559.
Nunnally, J. C., Bernstein, I. H., 1994. Psychometric
theory, McGraw-Hill, New York, 3rd edition.
Paechter, M., Maier, B., Macher, D., 2010. Students’
expectations of, and experiences in e-learning: Their
relation to learning achievements and course
satisfaction, Computers & Education, Vol. 54, No. 1,
pp. 222–229.
Randeree, K., Narwani, A., 2009. Managing Change in
Higher Education: An Exploration of the Role of
Training in ICT Enabled Institutions in the United
Arab Emirates, The International Journal of Learning,
Vol. 16, No. 4, pp. 447-456.
Sørebø, A. M., Sørebø, Ø., 2009. Understanding e-
learning satisfaction in the context of university
teachers”, International Journal of Humanities and
Social Sciences, Vol. 3, No. 4, pp. 309-312.
Sumner, M., Hostetler, D., 1999. Factors influence the
adoption of technology in teaching, Journal of
Computer Information Systems, Vol. 40, No. 1, pp.
81–87.
Sun, P-C, Tsai, R. J., Finger, G., Chen, Y-Y, Yeh, D.,
2008. What drives a successful e-Learning? An
empirical investigation of the critical factors
influencing learner satisfaction, Computers &
Education, Vol. 50, No. 4, pp. 1183–1202.
Sawang, S., Newton, C., Jamieson, K. 2013. Increasing
learners’ satisfaction/intention to adopt more e-
learning, Education + Training, Vol. 55, No. 1, pp. 83
– 105.
Tarhini, A., Honea, K., Liua, X., 2013. User acceptance
towards web-based learning systems: investigating the
role of social, organizational and individual factors in
European higher education, Procedia Computer
Science, Vol. 17, pp. 189 – 197.
Tong, K.P., Triniada, S.G., 2005. Conditions and
constraints of sustainable innovative pedagogical
practices using technology, Journal of International
Electronic for leadership in learning, Vol. 9, No. 3,
pp. 1-27.
Williams, P., 2002. The learning Web: the development,
implementation and evaluation of Internet-based
undergraduate materials for the teaching of key skills,
Active Learning in Higher Education, Vol. 3, No. 1,
pp. 40–53.
Yi, M. Y., Hwang, Y, 2003. Predicting the use of web-
based information systems: self-efficacy, enjoyment,
learning goal orientation, and the technology
acceptance model, International Journal of Human-
Computer Studies, Vol. 59, No. 4, pp. 431–449.
Yoon, C., Kim, S., 2007. Convenience and TAM in a
ubiquitous computing environment: The case of
wireless LAN, Electronic Commerce Research and
Applications, Vol. 6, No. 1, pp. 102–112.
APPENDIX
Note: Two items were dropped from computer self-
efficacy due to low factor loading.
ICEIS 2016 - 18th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
222
