
Power Management of Personal Computers based on User Behaviour
Brian Setz, Faris Nizamic, Alexander Lazovik and Marco Aiello
Distributed Systems Group, Johann Bernoulli Institute, University of Groningen,
Nijenborgh 9 (Bernoulliborg), 9747 AG, Groningen, The Netherlands
Keywords:
Context Aware Power Management, Timeout Optimization, Green Computing, Energy Efficiency.
Abstract:
It has been shown that up to 64 percent of personal computers in office buildings are left running during after-
hours. Enabling power management options such as sleep mode is a straightforward method to reduce the
energy consumption of computers. However, choosing the right timeout can be challenging. A sleep timeout
which is too low leads to discomfort, whereas a timeout which is too high results in poor energy saving
efficiency. Having the users choose their own sleep timeout is not viable as research shows that most users
disable the sleep timeout completely, or choose a suboptimal timeout. Unlike existing context based power
management systems which use predefined rules, we propose a solution which can determine a personalized
sleep timeout for any point in time solely based on the users behaviour. We propose multiple models which
have the goal of maximizing the energy savings while minimizing discomfort. The models are tested on the
computers of employees of the University of Groningen over several weeks. We analyse the results of the
experiments and determine which model performs best. We can potentially save between 4.02 and 17.17 kWh
per computer per year, depending on the model that used.
1 INTRODUCTION
A report from the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate
Change indicates that the increase in CO
2
levels in the
atmosphere is caused by human intervention with a
probability of over 90 percent (Solomon et al., 2007).
Their report shows that countries shall have to reduce
CO
2
emission levels by 60 to 90 percent by 2050. If
not, temperatures will rise globally with more than 2
degrees Celsius by the end of 2050.
The IT sector is a large consumer of electricity
around the world according to a report by the climate
group on behalf of the Global eSustainability Initia-
tive. They state that between 2 percent and 10 percent
of the world wide energy consumption is attributed
to the IT sector (GeSI, 2008). Personal computers in
particular account for a large amount of the energy
consumption within modern buildings such as offices,
universities and libraries (Roth et al., 2002). In most
cases there is very little incentive to save energy for
the occupants of these types of buildings, since they
are not paying the electricity bills. Therefore, energy
savings without interfering with the user’s workflow
would be preferable.
It is common to encounter personal computers
which are powered on while they are not in use (idle).
While each individual computer does not consume
much energy, all idle computers combined do waste
a significant amount of energy. Saving that energy by
putting idle computers to sleep appears to be an ob-
vious solution for decreasing energy consumption, as
sleep mode reduces the consumption by more than 95
percent. However, in practice it appears that putting
computers to sleep is not as common as one might
think, as in some cases up to 64 percent of personal
computers are still turned on after work-hours (Web-
ber et al., 2006).
In our research we aim to decrease the energy con-
sumption of personal computers by using the sleep
mode of these computers in an intelligent manner. We
believe this can be done more intelligently than ex-
isting solutions, as we can exploit the fact that users
leave their computers at certain times, for example
during lunch, or for meetings that take place regu-
larly. By learning these patterns we can predict that
their computer will be idle at certain time. Thus we
can adjust their personalized sleep timeout such that
their computers will go to sleep when they are away,
ultimately saving energy without causing discomfort.
The process to determine a personalized sleep
timeout is supported by the data which Sleepy col-
lects from computers. Sleepy is the context aware
power management software application which was
developed as a part of this research. The collected
Setz, B., Nizamic, F., Lazovik, A. and Aiello, M.
Power Management of Personal Computers based on User Behaviour.
In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Smart Cities and Green ICT Systems (SMARTGREENS 2016), pages 409-416
ISBN: 978-989-758-184-7
Copyright
c
2016 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
409

data is used as part of a learning process to find the
optimal sleep timeout for individual users. The prob-
lem of finding the personalized sleep timeout can be
generalized as an optimization problem for sensors
which have some type of timeout that is influenced
by user behaviour. An optimal timeout is a time-
out that balances the benefits and the costs that come
with a certain timeout setting. In this case, the time-
out is the sleep timeout of personal computers. The
costs and benefits are user comfort versus energy sav-
ings. Three different models have been defined in or-
der to find the balance between the benefits and costs
constraints. We use machine learning to learn linear
regression models using the linear least squares ap-
proach.
The approach we propose differs from existing so-
lutions as we dynamically build a profile based on the
user’s behaviour and uses this to determine the opti-
mal sleep timeout at any given point in time. The ex-
isting context aware power management systems are
most commonly based on predefined rules entered by
the user, or depend on specific hardware devices to
function optimally. We propose a solution which; 1)
does not require any manual actions from the user in
order to achieve energy savings, 2) can function on a
wide range of computers as it does not depend on spe-
cific hardware devices, and 3) aims to keep user com-
fort high and maintain the user’s productivity levels.
We perform experiments in order to verify the en-
ergy savings which could be achieved when using a
certain model. The experiments are performed on a
number of computers of the University of Groningen.
These computers are personal computers located in
the Bernoulliborg, which is home to the Faculty of
Mathematics and Natural Sciences.
The paper is organized as follows: Section 2
presents the background of this work and related
works. Section 3 describes the architecture of our so-
lution. Section 4 shows the results of using the solu-
tion in practice. Section 5 discusses the results and
future works.
2 BACKGROUND
In a study by (Webber et al., 2006) it is discovered
that up to 64 percent of all computers in offices are
still powered on during after-hours. Only 6 percent of
all computers made use of the available power man-
agement options, such as sleep mode. Of the moni-
tors attached to the computers around 75 percent were
powered on during after-hours. However, 66 percent
of all monitors used some form of power manage-
ment. We can conclude that there are significant sav-
ings still to be made by putting computers to sleep. A
report from the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate
Change (Karayi, 2007) suggests that computers are
powered on and left unattended about 28 percent of
the time. The authors also show that 49 percent of
users never or rarely turn off their computer. Fur-
thermore, findings in (Chiaraviglio and Mellia, 2010)
also confirm that computers are usually left powered
on. Their findings show that laptops are often turned
off, but the more power hungry desktop computers are
not. Up to 50 percent of these desktop computers are
still running during off peak hours. Of these comput-
ers, over 75 percent could be turned off in order to
achieve energy savings. According to (Nordman and
Christensen, 2009) the energy consumption of desk-
top computers is around 80 watts when idling. When
also including a 17-inch display monitor the energy
consumption increases to around 115 watts. Many
users already assume their computer has sleep mode
enabled, although in reality it is likely that the sleep
mode has in fact been disabled, as is indeed the case
at the University of Groningen.
These numbers show that there is a lot of potential
for energy savings in this area. Especially if these
savings could be achieved in an unobtrusive manner.
An issue that arises when putting computers to
sleep is that they are no longer available over the net-
work. This is an issue when users want to be able
to access their files remotely, and when IT adminis-
trators want to be able to manage computers at any
given time. In (Christensen and Gulledge, 1998) a
solution to this problem is proposed by introducing
Sleep Proxies. These proxies allow computers to have
a network presence while they are asleep. An actual
implementation of this concept is described in (Reich
et al., 2010). More research and information on the
topic of sleep proxies can be found in (Nordman and
Christensen, 2007), (Khan et al., 2012) and (Cheshire,
2008).
Windows Power Management Events are used by
the sleep proxy to detect changes in the power state of
the computer. We adopt this basic technique and use
this in our learning process. Sleep proxies themselves
do not adapt to the user’s behaviour. This is an aspect
which the solution presented in this paper attempts to
improve on.
Dynamic sleep timeout optimization is needed in
order to minimize the user impact of computers en-
tering sleep mode. In (Durand et al., 2013b) the
sleep time-outs of printers are dynamically changed
based on the time between print requests. The ap-
proach chosen in this research is to apply Hidden
Markov Models to create a statistical framework for
timeout optimization. More details regarding how
SMARTGREENS 2016 - 5th International Conference on Smart Cities and Green ICT Systems
410

to model power management using Markov Models
can be found in (Durand et al., 2013a) and in (Benini
et al., 1999).
There are software based solutions which also fo-
cus on Context Aware Power Management. One of
these software solution is PoliSave (Chiaraviglio and
Mellia, 2010). PoliSave works by allowing the user to
enter a schedule for their computer: the user can spec-
ify at which time and day the computer should per-
form some power management action such as sleep,
turn on or turn off. This allows for a great deal of
personalization of the power management on user-
basis. The authors indicate that usually 56 percent
of the computers they monitored were turned on at all
time. After applying their techniques this percentage
was reduced to 6 percent. The average daily uptime
of computers was reduced by more than 6 hours per
working day, from 15.9 hours to 9.7 hours. As a re-
sult savings of over 219 kWh per year were achieved
in their specific environment. The downside of the
approach taken by PoliSave is that the users need to
manually manage their schedule for the computers.
A different approach is taken by E-Net-Manager
(Brienza et al., 2014). The similarity between E-
Net-Manager and PoliSave is the fact that they both
use a schedule based approach to power management
in which the end user manually needs to enter the
schedule. The difference is that E-Net-Manager em-
ploys other sensors which determine whether a user
is present or not. These sensors include BlueTooth
sensors which take advantage of how the BlueTooth
handshake mechanism works. They also take advan-
tage of other wireless techniques such as using the
radio connectivity of smart-phones to determine the
presence of specific users. The computer is turned on
and off based on this presence. The manual calender
based schedule is there for back-up in this case. An-
other software based solution for power management
is Gicomp (Jarus and Oleksiak, 2013). Gicomp real-
izes a centralized power management platform. The
software is able to change the power management pol-
icy of large numbers of personal computers simulta-
neously. The software, however, does not allow per-
sonalization of power management policies.
Our solution does not attempt to take over control
of the operating system, instead it lets the operating
system decide whether the computer is in use or if it is
not. We also reuse the built in sleep timeout system of
the operating system and optimize it by personalized
timeout adjustments. The advantage of this approach
is that computers are only put into sleep mode when
they are not actually used. Furthermore, our approach
does not require predefined rules and schedules, in-
stead it adapts to the user in an automatic, unobtrusive
manner. And finally, the system we propose does not
have any specific hardware requirements; it works on
every personal computer.
3 ARCHITECTURE
As part of this research a software application is de-
veloped, named Sleepy. This application manages the
sleep timeout of personal computers and monitors the
computer usage. The sleep timeout determines when
the computer enters sleep mode after being idle for
a set amount of time. Sleepy also monitors and col-
lects data from the computers on which it is installed.
Before we take a closer look at the models, we have
to understand the data sets on which the models are
based.
3.1 Data Set
The data set used in our research is obtained by mon-
itoring computers for an extended period of time us-
ing the Sleepy-software. For each computer three dif-
ferent types of data are collected: state data, activity
data, feedback data. The way Sleepy collects this in-
formation about the state of a computer is by listening
to System Power Management events.
State Data - State data gives insight into the state
of the computer. The state refers to the power man-
agement state of the computer and can assume three
values: On, Sleeping and Off.
Activity Data - Activity data is collected in order
to detect if a computer is actually being used while it
is turned on. The activity value can be either Active,
Idle or Inactive. Active means the computers is ac-
tively being used, whereas idle means the computer is
turned on but not in use. A computer is inactive when
it is turned off. Sleepy monitors the activity of the
computer by reading the LASTINPUTINFO structure.
Feedback Data - Feedback is collected in order to
determine whether Sleepy is working with a minimal
user impact. We only collect negative feedback, and
we react immediately as soon as negative feedback is
received. As a result the user does not have to provide
any feedback when everything is working as expected
but only when things are not working as they should.
Users can explicitly report their feedback using a tray
icon presented by Sleepy in the system tray. Right
clicking on this tray icon provides the user with the
menu option to disable Sleepy until reboot. When this
menu option is selected the user will be shown a dia-
log in which they can specify the reason for disabling
Sleepy. When a computer enters sleep mode and is
woken up before a certain time has passed it is also
Power Management of Personal Computers based on User Behaviour
411

considered negative feedback as this could mean that
the sleep timeout was too low. The information about
the length of a sleep period can be extracted from the
state data set.
Activity Probability - The activity probability is
based on the activity data set. It represents the proba-
bility that a certain computer is actively being used at
a given moment in time. This probability is calculated
by looking at the historical activity data of the same
day of the week, over the past few weeks.
Idle Time - Idle time can also be extracted from
the activity data set. It is trivial to determine the idle
time of a computer: the current state of the computer
can be determined by looking at the most recent value
in the activity data set. If this activity state is idle then
the idle time is simply the amount of time since the
activity state changed to idle. Using the idle time one
can determine how long it has been since the com-
puter has been actively used.
3.2 Models
Three models have been defined to optimize the sleep
timeout. These models share a common goal: to min-
imize the amount of time in which a computer is in
the idle state. Reducing this idle period is done by
putting the computer to sleep. In turn, putting com-
puters to sleep leads to energy savings. However, it is
important that the negative feedback remains minimal
to maintain a high level of user comfort and produc-
tivity.
In order to determine the performance of each
model they are graded according to some cost func-
tion. The cost for choosing a certain sleep timeout
can only be determined after a certain amount of time
has passed, as negative feedback is not always instan-
taneous. The cost function for determining the per-
formance of the model for a given timespan is defined
as:
A
idle
= {z ∈ A
t
|z = idle} (1)
E(t) =
∑
z∈A
idle
z + (1 +
N(t)
h(t)
)N(t) (2)
=
∑
z∈A
idle
z + N(t) +
N(t)
2
h(t)
(3)
Where A
t
is the set of activity data containing
time intervals for every activity change for timespan t.
A
idle
is the set of activity data only containing the time
intervals during which the activity was idle. N(t) rep-
resents the negative feedback collected for timespan
’t’. h(t) is the hours of sleep measured for the given
timespan. It can be argued that an increase in negative
feedback (decrease in user comfort) is more costly
than an increase in idle time (decrease in energy sav-
ings), therefore
N(t)
h(t)
, the ratio of negative feedback
per hours of sleep, is used to adjust this cost. This
ratio an indication of how expensive in terms of dis-
comfort each hour of sleep is. E(t) is the resulting
cost for the given model over timespan ’t’.
Three concrete models have been developed based
on three different types of data: activity probability,
negative feedback and idle time. The models return
a personalized sleep timeout for a given time, s(t),
returning the sleep timeout in minutes, where t is an
instant in time. The first model is a rule based model
whereas the remaining two models are linear regres-
sion models. The weights for these linear regressions
models (denoted as w
x
) are obtained using linear re-
gression.
The goal of Model 1 is to have a high sleep time-
out whenever there is a chance of user activity at that
given moment in time. The sleep timeout becomes
low when there is a low probability of user activity.
s(t) =
(
s
max
, if P
a
(t) > ε.
s
min
, otherwise.
(4)
• P
a
(t) – Activity probability at time t
• ε – Activity threshold
• s
min
– Minimum sleep timeout value
• s
max
– Maximum sleep timeout value
The goal of Model 2 is to find the most optimal
sleep timeout based on two different input parame-
ters: activity probability and negative feedback.
s(t) = w
2
P
a
(t) + w
1
N(t) + w
0
(5)
• P
a
(t) – Activity probability at time t
• N(t) – Negative feedback count at time t
A higher activity probability should lead to an in-
crease of the sleep timeout, if the probability of a
computer being in use is high it should not enter sleep
mode. Furthermore, an increase in negative feedback
should also lead to an increase of the sleep timeout.
The difference is that an increase in negative feed-
back should increase the sleep timeout more than an
increase in activity probability. The negative feedback
at time t also includes negative feedback received be-
fore time t.
The goal of Model 3 is to find the most optimal
sleep timeout based on three different input parame-
ters: activity probability, negative feedback and idle
time.
s(t) = w
3
P
a
(t) + w
2
N(t) + w
1
I(t) + w
0
(6)
SMARTGREENS 2016 - 5th International Conference on Smart Cities and Green ICT Systems
412
• P
a
(t) – Activity probability at time t
• N(t) – Negative feedback count at time t
• I(t) – Idle time in minutes at time t
The first two parameters of this model work ac-
cording to the same principles as described for Model
2. The third parameter, idle time, also increases the
sleep timeout as its own value increases. The rate of
increase should be somewhere in between those of the
first two parameters.
4 EXPERIMENTS
Experiments have been performed to determine the
effectiveness of the three different models previously
defined. The experiments were performed over the
course of three weeks, starting on the 1st of June 2015
and ending on the 22nd of June 2015. These dates
were chosen such that no holidays occurred during
the experiments, to prevent skewed results. Our so-
lution was deployed two months prior, in April 2015,
in order to begin the collection of data and test the
stability in the operating environment.
A total of fourteen computers were part of the ex-
periments. These are computers used by staff mem-
bers in the Bernoulliborg, a building of the University
of Groningen. These staff members include; profes-
sors, lecturers and researchers but also faculty staff.
By including staff members with different roles we
try to simulate a realistic environment and test if our
solution is still effective when the user’s activity is
less predictable. The participants were split into three
groups. For each week, each group tested a different
model. Each model has been tested and evaluated for
exactly six days, starting on Monday and ending on
Saturday. The seventh day of the week, Sunday, was
used for transitioning between models.
4.1 Computer Usage Profiling
Predicting when a computer will be in use is a very
important aspect when determining the personalized
sleep timeout. Each of the three models take this into
account by calculating the activity probability. The
activity probability represents the probability of see-
ing activity on a computer at a certain moment in
time. A usage profile can be generated by calculat-
ing the activity probability at multiple points during a
given time interval.
The data appears to have a weekly seasonality as
users often work on the same days every week. There-
fore, historical data from the same day of the week
is used to predict the future activity. Data from up to
four weeks ago is used in the prediction of the activity
probability. When predicting the activity probability
for a certain moment in time a window of ten min-
utes is used. Equation 7 shows how the profiles are
calculated.
P
activity
(t) =
∑
n
i=1
f (t − weeks(n))
n
f (t) =
(
0, if no activity
1, if some activity
(7)
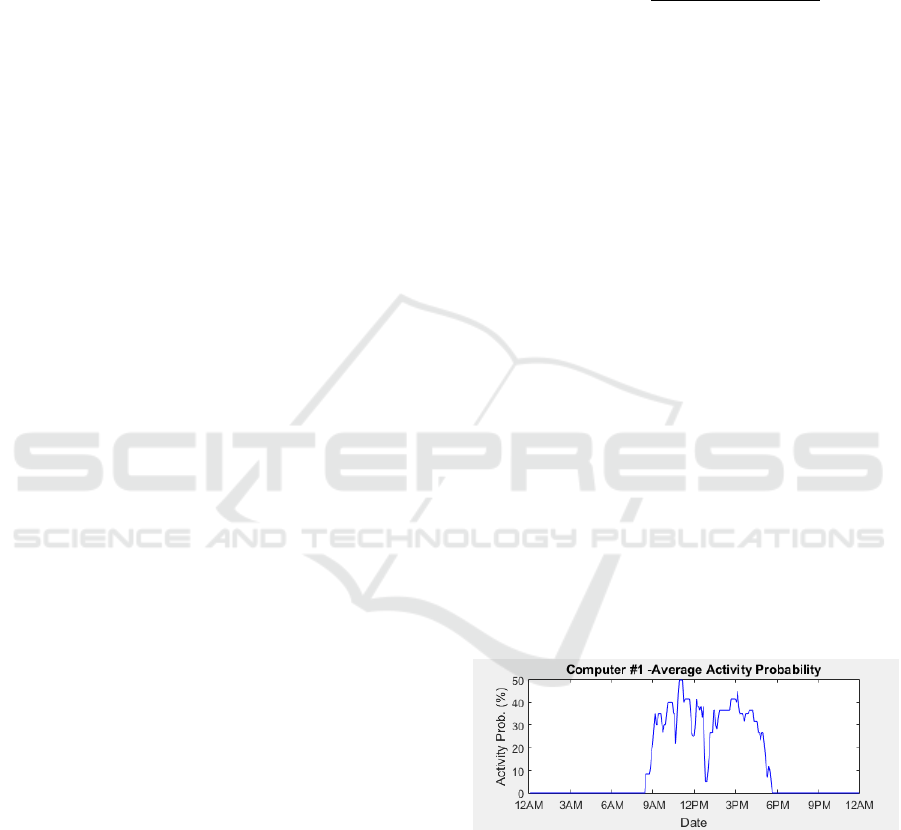
The profiles shown in the following figures are the
average profile of all three weeks. The probability
ranges anywhere from zero to one hundred percent.
Where zero percent indicates there is no predicted ac-
tivity, and one hundred percent indicating that there is
a probability of a hundred percent of seeing activity.
These average profiles were generated by combining
the daily profiles. A number of patterns can be seen
in most of the profiles, where the activity probability
drops at certain times. The most common drop oc-
curs at around 1 PM. This can be explained by users
leaving their computer for their lunch break. Another
common pattern is a drop in the activity probability
around 10 PM or 11 PM. Another pattern that can also
be seen in the activity profiles is that most users use
their computer almost exclusively between 8AM and
7PM. Both these patterns can be seen in Figure 1, Fig-
ure 2 and Figure 3. The patterns verify that there are
indeed opportunities to save energy, even if users shut
down their computer at the end of every day. Assum-
ing an average working day of eight hours and a lunch
break of thirty minutes means that the computer could
potentially sleep for at least 6.25% of the time during
a full working day.
Figure 1: Computer 1 - average activity probability.
4.2 Results
For the experiments the following parameters have
been set for Model 1: the minimum sleep timeout s
min
is five minutes. The maximum sleep timeout s
max
is
sixty minutes. The activity threshold ε is set to a value
of 0.05, or 5 percent.
For determining the initial timeout we use train-
ing data that is based on expert knowledge of which
Power Management of Personal Computers based on User Behaviour
413
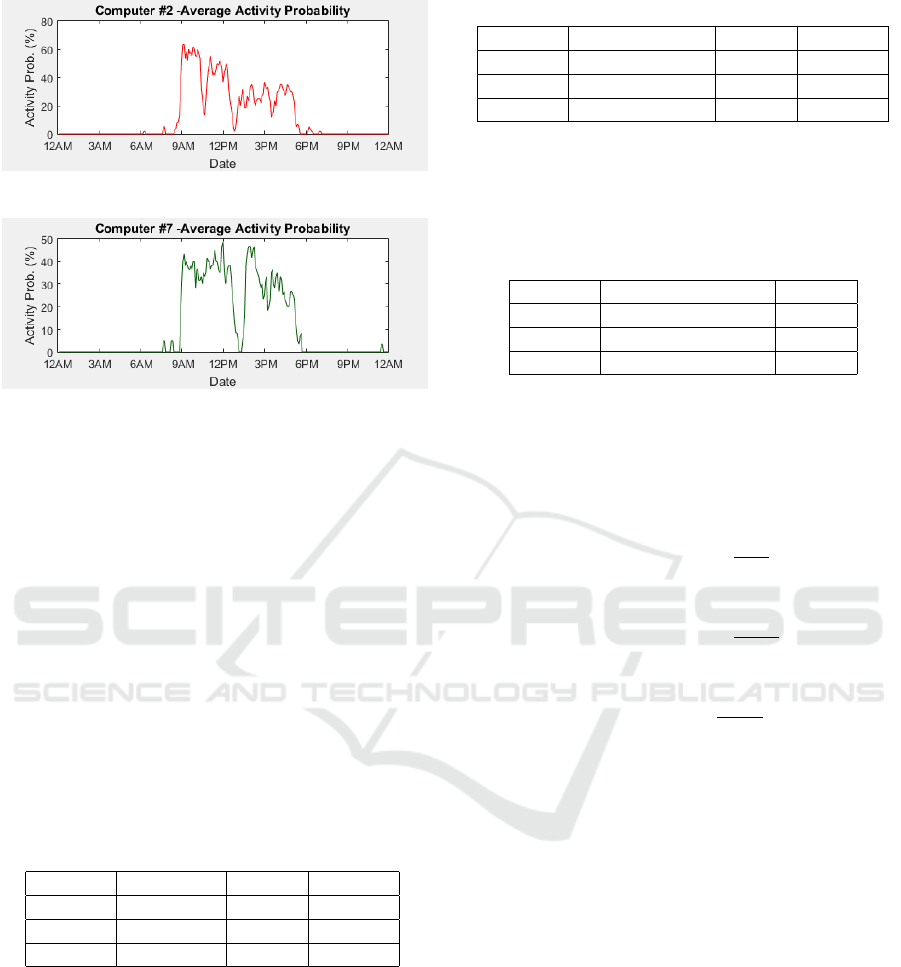
Figure 2: Computer 2 - average activity probability.
Figure 3: Computer 7 - average activity probability.
timeout should be associated to the given input pa-
rameters. It allows us to have a reasonable sleep time-
out to start with, and prevent negative feedback that
would be associated with a complete cold start. The
data is split into training data and test data. Sixty per-
cent of the data is used for training and the remain-
ing fourty percent is used to test the trained model.
Once this model has been trained it is automatically
adjusted based on the parameters. Spark MLlib pro-
vided the implementation for solving these regression
problems.
Table 1 shows the idle time per model in hours,
and also the average idle time per computer. Model
3 becomes more aggressive, with regards to decreas-
ing the sleep timeout, the longer a computer is idle.
Therefore it is as expected that this model has the least
amount of idle time.
Table 1: Total idle time in hours per model.
Model Hours Idle Per PC Std. dev.
Model 1 31.19h 2.60h 1.73
Model 2 27.05h 2.25h 1.76
Model 3 19.57h 1.63h 1.56
The exact number of hours of sleep for each model
are shown in Table 2. Using Model 2 or Model 3 re-
sults in over four times as many hours of sleep com-
pared to Model 1. The difference in hours of sleep is
due to the fact that the first model puts the computer to
sleep when there is almost zero probability of seeing
activity. Which means that there are fewer moments
when it puts the computer to sleep, when compared
to the other two models. The second and third models
are more aggressive when with regards to determining
the sleep timeout, and therefore result in more hours
of sleep.
Table 2: Total sleep in hours per model.
Model Hours Sleeping Per PC Std. dev.
Model 1 5.54h 0.46h 0.42
Model 2 22.26h 1.85h 2.29
Model 3 23.68h 1.97h 3.17
An overview of the negative feedback occurrences
can be seen in Table 3. Model 1 did not generate any
negative feedback. This can be explained by the fact
that this model is the least aggressive model.
Table 3: Negative feedback occurances.
Model Negative Feedback Per PC
Model 1 0 0.0
Model 2 11 0.917
Model 3 14 1.167
We can apply the previously defined cost func-
tion (eq. 3) to determine the ranking of each model.
A lower score means that the model performs better.
We can input the values for the idle time, the negative
feedback and hours of sleep. The equations for each
model become:
E
model1
(t) = 31.19 + 0 +
0
2
5.54
= 31.19 (8)
E
model2
(t) = 27.05 + 11 +
11
2
22.26
= 43.48 (9)
E
model3
(t) = 19.57 + 14 +
14
2
23.68
= 41.84 (10)
These results show that model 1 is the optimal
model in terms of minimizing user discomfort.
The energy consumption of a computer is around
115 watts according to Nordman et al (Nordman and
Christensen, 2009). According to Roberson et al
(Roberson et al., 2002) the power consumption of
desktop computers is around 105 watts. In (Bluejay,
2012) the authors conclude that the energy consump-
tion of computers ranges anywhere from 77 watts to
322 watts. All sources agree that the power consump-
tion when sleeping is around 5 watts. In the follow-
ing calculations we shall use 150 watts as the average
power consumption. This is based on measurements
taken from computers in the Bernoulliborg. Further-
more, we shall use the energy tariffs in the Nether-
lands, which is 22 eurocents per kilowatt-hour (Mileu
Centraal, 2015a) at the time of writing.
The number of computers in the Bernoulliborg is
estimated to be around 500. This estimation is based
on the fact that there is room for 350 employees,
where we assume at least one computer per employee.
We also have to include the number of computers for
SMARTGREENS 2016 - 5th International Conference on Smart Cities and Green ICT Systems
414
students, this number is estimated to be around 150.
This is based on the fact that there are six large com-
puter rooms on the second floor with around 25 com-
puters each.
The amount of sleep per computer per month is
shown in Table 4. The difference between Model 1
and the other models is significant: Model 1 results in
only 2.31 hours of sleep whereas both other models
result in 9 to 10 hours of sleep. The monthly hours
of sleep were calculated by multiplying the sleep per
computer times 5. This is because the hours of sleep
per computer was taken over a 6 day period. It is im-
portant to know the number of hours a computer is
asleep in order to determine the monthly kWh savings
per model.
Table 4: Sleep per month in hours.
Model Total Sleep Per PC PC per Month
Model 1 5.55h 0.46h 2.31h
Model 2 22.26h 1.85h 9.27h
Model 3 23.68h 1.97h 9.87h
To determine the monthly energy savings we have
to determine two things: the kWh consumed per com-
puter while it was sleeping and the kWh the computer
would have consumed if it would have been turned on
instead of asleep. These numbers can be seen in Table
5.
Table 5: kWh consumption per month per computer.
Model Sleeping Turned On Savings
Model 1 0.012 kWh 0.35 kWh 0.33 kWh
Model 2 0.046 kWh 1.39 kWh 1.35 kWh
Model 3 0.049 kWh 1.48 kWh 1.43 kWh
Over the course of a year the savings per computer
add up to a significant number as can be seen in Ta-
ble 6. Even using Model 1 saves around 4 kWh per
computer per year. This equals to around 90 euro-
cents worth of energy savings per computer per year.
Using Model 2 or Model 3 results in 16 to 17 kWh of
energy savings, or 3.55 euro to 3.77 euro of economic
savings.
Table 6: Estimated annual savings per computer.
Model Savings per PC Savings per PC
Model 1 4.02 kWh e0.89
Model 2 16.13 kWh e3.55
Model 3 17.17 kWh e3.77
Finally, let us take a look at the annual savings that
could be achieved in an actual office building. The
results for the Bernoulliborg can be seen in Table 7.
If all computers in Bernoulliborg used Model 1 then
the annual savings would be 2010.68 kWh, which
amounts to 442.35 euro. The biggest savings can be
achieved using Model 3: the savings are 8583.49 kWh
or 1888.37 euro.
Table 7: Estimated annual savings in Bernoulliborg.
Model Savings (kWh) Savings (euro)
Model 1 2010.68 kWh e442.35
Model 2 8067.44 kWh e1774.84
Model 3 8583.49 kWh e1888.37
5 CONCLUSION AND FUTURE
WORK
We have looked at how context aware power man-
agement based on user behaviour can be implemented
and used in practice. We have also looked at several
different models and the savings which were achieved
by each of these models by performing experiments
over the course of a month. Considering the number
of typical office buildings around the world, the num-
ber of computers used, and the potential savings per
computer, if this solution were widely applied its en-
vironmental impact would be significant.
Besides measured savings, our solution provides
valuable additional information about computer usage
in a workspace. Using this information we can in-
troduce additional savings for other control solutions
by increasing the sensor data accuracy. For instance,
computer usage information provides higher accuracy
of algorithms for presence and activity recognition
that are used for lighting, appliances and heating con-
trol.
Furthermore the research opens an interesting area
to which other machine learning techniques can be
applied. Instead of using linear regressions models
one can also look at other methods of modelling a per-
sonalized sleep timeout. A good candidate would be
to explore the possibilities that reinforcement learn-
ing offers. We plan to improve on a number of points
in our future work. The experiments were performed
on fourteen computers of staff members in a building
of the University of Groningen.
For more statistically significant results, we will
repeat the experiments on a larger sample of computer
which contain more different types of users. More-
over, it will be interesting to compare the results from
staff member computers with those from the publicly
available student computers. Besides energy and eco-
nomic savings, we will investigate the proposed solu-
tion from the perspective of user acceptability.
By deploying our solution on a number of com-
puters within the Bernoulliborg we were able to save
energy quite effectively, allowing us to save up to
17.17 kWh per year per computer. These savings
Power Management of Personal Computers based on User Behaviour
415

were achieved despite the fact that the environment
in which we performed the experiments was already
reasonably energy efficient, as all participants turned
their computer off during off-peak hours. The amount
of energy saved within building Bernoulliborg, when
using Model 3 for a year on all computers, would be
8583.49 kWh. Which is enough energy to power an
average sized Dutch household for almost two and a
half years (Mileu Centraal, 2015b).
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We thank Marco Wiering for his feedback, support,
and the valuable discussions regarding the models.
We also thank Tuan Anh Nguyen for numerous dis-
cussions and active involvement. Furthermore we
thank Ronald Zwaagstra for providing equipment for
our development process, as well as to the CIT per-
sonnel for their support with deploying our solution
in the Bernoulliborg building of the University of
Groningen. The work is supported by The Nether-
lands Organisation for Scientific Research NextGenS-
mart DC project, contract no. 629.002.102.
REFERENCES
Benini, L., Bogliolo, A., Paleologo, G., and Micheli, G. D.
(1999). Policy optimization for dynamic power man-
agement. 18:813–833.
Bluejay, M. (March 2012). How much electricity do com-
puters use? http://michaelbluejay.com/electricity/
computers.html.
Brienza, S., Bindi, F., and Anastasi, G. (2014). E-net-
manager: A power management system for networked
pcs based on soft sensors. In Smart Computing
(SMARTCOMP), 2014 International Conference on,
pages 104–111. IEEE.
Cheshire, S. (February 2008). Method and apparatus for
implementing a sleep proxy for services on a network.
United States Patent N. 7,330,986.
Chiaraviglio, L. and Mellia, M. (2010). Polisave: Effi-
cient power management of campus pcs. In Software,
Telecommunications and Computer Networks (Soft-
COM), 2010 Int. Conference on, pages 82–87.
Christensen, K. J. and Gulledge, F. B. (1998). En-
abling power management for network-attached com-
puters. International Journal of Network Manage-
ment, 8(2):120–130.
Durand, J.-B., Girard, S., Ciriza, V., and Donini, L. (2013a).
Optimization of power consumption and device avail-
ability based on point process modelling of the request
sequence. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Se-
ries C (Applied Statistics), 62(2):151–165.
Durand, J.-B., Girard, S., Ciriza, V., and Donini, L. (2013b).
Optimization of power consumption and user impact
based on point process modeling of the request se-
quence. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society Series
C, 62(2):151–165.
GeSI (2008). Smart2020: Enabling the low carbon econ-
omy in the information age. The Climate Group -
Global eSustainability Initiative.
Jarus, M. and Oleksiak, A. (2013). Gicomp and greenof-
fice monitoring and management platforms for it and
home appliances. In Pierson, J.-M., Da Costa, G.,
and Dittmann, L., editors, Energy Efficiency in Large
Scale Distributed Systems, volume 8046 of Lecture
Notes in Computer Science, pages 58–62. Springer
Berlin Heidelberg.
Karayi, S. (2007). Pc energy report 2007. http://
www.1e.com/energycampaign/downloads/1E%20
Energy%20Report%20US.pdf.
Khan, R., Bolla, R., Repetto, M., Bruschi, R., and
Giribaldi, M. (2012). Smart proxying for reducing
network energy consumption. In Performance Eval-
uation of Computer and Telecommunication Systems
(SPECTS), 2012 Int. Symposium on, pages 1–8.
Mileu Centraal (2015b). Gemiddeld energieverbruik. http://
www.milieucentraal.nl/energie-besparen/snel-besparen/
grip-op-je-energierekening/gemiddeld-energieverbruik/.
Mileu Centraal (July 2015a). Energieprijzen. http://
www.milieucentraal.nl/energie-besparen/snel-besparen/
grip-op-je-energierekening/energieprijzen/.
Nordman, B. and Christensen, K. (July 2009). Greener pcs
for the enterprise. IEEE IT Professional.
Nordman, B. and Christensen, K. (October 2007). Improv-
ing the energy efficiency of ethernet-connected de-
vices: A proposal for proxying. Ethernet Alliance.
Reich, J., Goraczko, M., Kansal, A., and Padhye, J. (2010).
Sleepless in seattle no longer. In USENIX Annual
Technical Conference. USENIX.
Roberson, J. A., Homan, G. K., Mahajan, A., Nordman, B.,
Webber, C. A., Brown, R. E., McWhinney, M., and
Koomey, J. G. (July 2002). Energy use and power
levels in new monitors and personal computers. Envi-
ronmental Energy Technologies Division.
Roth, K., Goldstein, F., and Kleinman, J. (January 2002).
Energy consumption by office and telecommunica-
tions equipment in commercial buildings volume i:
energy consumption baseline. National Technical In-
formation Service (NTIS), US Department of Com-
merce, Springfield, VA, 22161.
Solomon, S., Qin, D., Manning, M., Chen, Z., Marquis,
M., Averyt, K., Tignor, M., and Miller, H. (October
2007). Climate change 2007: The physical science ba-
sis. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United
Kingdom and New York, NY, USA.
Webber, C. A., Roberson, J. A., McWhinney, M. C., Brown,
R. E., Pinckard, M. J., and Busch, J. F. (2006). After-
hours power status of office equipment in the usa. En-
ergy, 31(14):2823 – 2838.
SMARTGREENS 2016 - 5th International Conference on Smart Cities and Green ICT Systems
416
