
On the Development of Strategic Games based on a Semiotic
Analysis: A Case Study of an Optimized Tic-Tac-Toe
César Villacís, Walter Fuertes, Mónica Santillán, Hernán Aules, Ana Tacuri,
Margarita Zambrano and Edgar Salguero
Computer Siences Department, Universidad de las Fuerzas Armadas - ESPE, Sangolquí, Ecuador
Keywords: Semiotics, Tic-Tac-Toe, Videogames, Artificial Intelligence, Semiotic Models for Videogames.
Abstract: A picture can express something instead of having a thousand words that cannot do it. This phrase, which
symbolically connotes a whole scheme of a signs system, is known as Semiotics. This paper presents the
process of an educational video game development based on semiotic analysis. We used Extreme Programing
Agile Methodology combined with a proposal of the modified Elemental Tetrad Game Design Model to
develop a video game known as “Tic-Tac-Toe”. The mathematical model was implemented with Artificial
Intelligence algorithms and a graphical user interface including Semiotics; this was optimized for producing
an enjoyable and interactive environment. With the purpose of stimulating cognitive development of children,
this research combines theories about stimulating cognitive development of children; game design model,
Semiotic Analysis harnesses the Model of Aleferenko, and uses algorithms based on heuristics and numerical
methods in client-server architecture. The concept was tested with a representative sample of seven to eleven
years old children. The results demonstrated that educational video games with Semiotics stimulate the
cognitive development of children.
1 INTRODUCTION
Aware of the importance of psychomotor activity and
its impact on stimulating thought; teachers and early
childhood specialists value motor activities and
games. One of the most fundamental resources
available for educators is educational video games.
Therefore, researchers are permanently exploring
new learning strategies to encourage children through
educational video games. Nowadays, semiotic
domains are emerging more notably and potentially,
could make the videogame more attractive for
children. One example of this is the customisation of
the avatar in the first-person-shooter video games
(Gee, 2008).
Visualization is better than verbal description; this
phrase symbolically connotes a whole system of
signs. Its analysis or decoding is called Semiotics.
According to the Oxford Advanced Learner's
Dictionary, Semiotic is “a general philosophical
theory of signs and symbols that deals especially with
their function in both artificially constructed and
natural languages and comprises syntactic, semantics,
and pragmatics”. It studies the phenomena and
objects of significance, sign systems, and the process
of senses production (Halliday, 1978).
The connection between educational video games
and semiotics has been studied for three decades. The
study of Myers (1991) discusses symbols within
computer games and how those symbols are
transformed during play. Thorne et al. (2012)
describe an exploratory study of the massively
multiplayer online games with a complex form of
semiotic ecologies. Huber (2013) addresses the
problem by proposing a model for the interpretation
of videogames based on the semiotic theory of
Charles S. Peirce. Ruiz et al. (2014) used videogames
to help High School students to improve their
understanding of numerical evaluation of algebraic
expressions. Baceviciute et al. (2014) explain the
convergence and hybridization process between
cognitive sciences, computer science and Artificial
Intelligence (AI). Kendall, 2015 analyses serious
games and Semiotics separately. Those studies claim
for an integration of semiotic and artificial
intelligence in video games.
The present study developed a process of an
educational video game based on semiotic analysis;
and tested the hypothesis of an application of
Villacís, C., Fuertes, W., Santillán, M., Aules, H., Tacuri, A., Zambrano, M. and Salguero, E.
On the Development of Strategic Games based on a Semiotic Analysis: A Case Study of an Optimized Tic-Tac-Toe.
In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS 2016) - Volume 1, pages 425-432
ISBN: 978-989-758-187-8
Copyright
c
2016 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
425

Semiotics in the Tic-Tac-Toe videogame improves
the motivation of the childhood senses and stimulates
their cognitive development.
We have used the Extreme Programing Agile
Methodology (XP) combined with the Elemental
Tetrad Game Design Model, in order to ensure the
quality of the software using Artificial Intelligence
techniques in client-server architecture. The video
game that has been developed and optimized is called
Tic-Tac-Toe. The concept has been tested with a
representative sample of seven to eleven years old
children at an elementary school.
The key contributions of this study are: (1) two
prototypes software developed for the Tic-Tac-Toe
game, one with Semiotics; (2) a class library
implemented that represents the environment and the
rules of a third party using Artificial Intelligence
based on heuristics and numerical methods; and (3) a
game developed combining a novel mathematical
model and semiotic analysis that requires algorithms
of Software Engineering to optimize the Tic-Tac-
Toe’s ability to apply learning theories.
2 THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK
2.1 The Elemental Tetrad Game
Design Model
This model is currently used for game design.
According to Gibson (2014), this model uses the
events of the story and states purpose of the game. It
evaluates the human-computer interaction by using
the game technologies. Furthermore, it separates the
basic elements of a game into four sections: (1)
Mechanics: the rules for interaction between the
player and the game; (2) Aesthetics: describe how the
game is perceived by the five senses; (3) Technology:
this element covers all the underlying technology that
makes the game work; (4) Story: this describes the
sequence of events in the game.
2.2 Extreme Programming (XP)
XP is an agile software development methodology. It
is a lightweight methodology using a set of existing
software development practices in conjunction
(Schneider, 2003). According to Beck (2000), the
project lifecycle of XP includes the following phases:
Exploration, Planning, Iterations to Release, the
Product ionizing, and Maintenance. The practices
taken from XP focused on software coding needed for
the game.
2.3 Semiotic Analysis of Aleferenko
This model integrates several areas of the knowledge,
and allows making a connotative and denotative
analysis of the symbols. For Aleferenko (Tokarev,
2014) a pyramid constitutes the coalition of the
Pierce’s triad. It includes two new elements:
Meaning/ Connotation; and Significant/ Denotation.
This allows to create a pyramid organized with the
following elements: (1) Sign; (2) Object/Referent; (3)
Significant/ Denotation; (4) Meaning/Connotation;
and Concept. The pyramid of Aleferenko integrates
the bases of Semiotics. In contrast to Pierce and Frege
(Wisse, 2002), Aleferenko considers outlined models
and creates a new complete model, where the
connotation is the agent of analysis that engenders a
deep knowledge that leaves an appropriation of the
receiver.
2.4 Theories to Stimulate Cognitive
Development of Children
Tic-Tac-Toe stimulates cognition of children, and the
game is part of the culture as it is included in common
educational practices. Lev Vygotsky (1967) assigned
the game into the category of instrument and socio-
cultural promoter of children’s mental development,
and the results showed that facilitates the
development of higher functions. These are acquired
through interaction with the surrounding world. The
approach of mediation according to Vygotsky is
perceived as the presence of people, objects, and
situations that interact in various socio-cultural
contexts, which can be verbal, visual and physical,
and can generate experiences that affect cognitive
development. Vygotsky elaborated the concept
known as Zone of Proximal Development Theory
(Brown, 1999), explained as: (1) the distance between
the actual developmental level is determined by the
ability to independently solve a problem; and, (2) the
level of potential development is determined by
problem solving under the mediation of an adult.
Feuerstein (1991) considers that the subject’s
interactions with the environment can have two
modalities: (1) direct exposure to stimuli; and, (2)
learning experiences through mediators. As
suggested by Feuerstein, it is crucial to consider that
all human beings are modifiable. To be able to fulfil
this condition, we should understand mediation as an
intervention strategy that tries to affect the body of
mediator, seeking greater efficiency in the process of
information and therefore the cognitive structure.
Finally, Lipman (2002), developed his educational
philosophical proposal known as “critical thinking”,
ICEIS 2016 - 18th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
426
that is interested in forming a thought careful, orderly,
prudent and reasonable. In this sense the children are
be able to make judgments as part of the practice of
their own learning process in which case an
educational game is considered like a learning
activity.
All these theoretical assumptions analysed
converge in cognitive modifiability through the visual
mediation using games. We conclude therefore, that
children exposed to the complexity experience of the
games, shows increased cognitive skills such as
spatial navigation, reasoning, memory and three
dimensional perceptions.
3 EXPERIMENTAL SETUP
3.1 Development Process
The process of development of the video game with
Semiotics was based on the life cycle of XP that
performs iterative and incremental tasks (Beck,
2000), (Schneider, 2003). The research team carried
out an incremental delivery of the product in each
iteration.
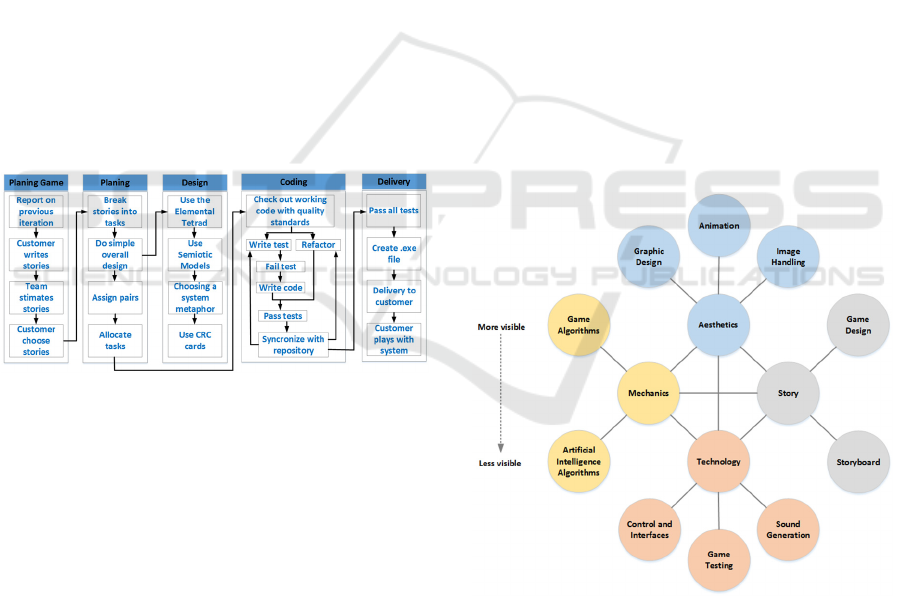
Figure 1: The Extreme Programming iterations game.
The experiment considered three iterations: (1)
The design and development of the graphic user
interfaces of the video game, for which we applied
elementary Tetrad Game Design modified Model; (2)
The construction of the inference engine, based in
technical heuristics of Artificial Intelligence
implemented with numerical methods that generate
different levels of difficulty in the game; (3) The
processing and storage of information, that keeps the
users scores in files, considering the three levels of
difficulty. In these iterations, liberated parts of the
product were inspected and evaluated to increase the
functionality and also to improve the quality
compared to the previous versions of the game
(Villacís, 2015), which has been implemented
without using Semiotics. Fig. 1 shown the XP
iterations game model modified based in the proposed
model by Drake et al. (2006).
3.2 Design and Development of the
GUI
The design and the development of the graphic user
interface of the Tic-Tac-Toe video game were based
on the Elementary Tetrad Game Design Model
(Schell, 2014). For each one of the four sections of
this model, we considered a series of elements related
to programming computer games proposed by
Walnum (2001), among them are: (1) Game design;
(2) Graphic design; (3) Controls and interfaces; (4)
Generation of sound; (5) Image handling; (6)
Animation; (7) Algorithms; (8) Artificial
Intelligence; (9) Game Testing. Additionally, it was
necessary to include the Storyboard proposed by Páez
(2013). Based on all of these elements, we propose
the modified model illustrated in Fig. 2. The
Mechanics section includes game algorithms and
Artificial Intelligence algorithms. The Technology
section includes graphic design, animation and image
handling. The Aesthetics section includes control and
interfaces, sound generation and game testing. The
story section includes game design and storyboard.
Figure 2: A proposal of the modified Elemental Tetrad
Game Design Model for this study.
3.2.1 Game Design
The concept was based on real-world events related
to the design and creation of boards for the game of
Tic-Tac-Toe. This is a fun game that appeals to both
children and adults because it is a game of strategy.
On the Development of Strategic Games based on a Semiotic Analysis: A Case Study of an Optimized Tic-Tac-Toe
427

3.2.2 Graphic Design
The game screen of Tic-Tac-Toe has a form
programmed in C# .NET, which is very similar to the
dialogue frames of the Windows System. In this form
is placed a series of objects that allowed to structure
the game, such as: (1) Nine buttons for checkers,
mathematically located in specific locations; (2) Four
buttons to manage the game options (i.e. New,
Choose players, Choose language and Exit); (3) Four
group boxes or containers (Group Box); (4) One label
for static text; (5) Four radio buttons to control the
different levels of the game; (6) One picture box,
which shows an animated icon; (7) A menu bar with
File, Help and View options, and their respective
submenus.
3.2.3 Control and Interfaces
Implementation
The GUI was constructed based on components
(COM+), and basic controls (ActiveX) that provided
the Visual C# .NET programming language. The
scores in the game were stored in XML flat files, and
the data are displayed within the Data Grid View
control. Fig. 3 illustrates the GUI of the game:
Figure 3: Graphical User Interface of the Tic-Tac-toe game
using Semiotics.
3.2.4 Image Handling
We organized all the visual interfaces to handle
images via ActiveX controls. For example, the
Picture Box control allows loading animated gif files
and the Button control is designed and constructed
with geometric shapes which can load images in
various formats. We have defined four categories in
the game related to the nine buttons of the board,
which are available for the user being: (1) Super hero:
Selection between twelve super heroes and twelve
villains; (2) Princesses: Selection between twelve
princesses of fairy tales and twelve villains of those
same fairy tales; (3) Animals: Selection between
twenty four animals among which are both wild and
domestic animals; (4) Miscellany characters:
Selection between several well-known children’s
characters with their respective antagonistic
characters. Finally no special background (i.e.
Background Image property) was included, only
colours, which is more attractive to children and
generates much less distraction.
3.2.5 Sound Generation
Because the real world is a place with sound, the
game needs to include sound so that it seems realistic.
The Tic-Tac-Toe game is not the exception.
Therefore, MIDI sounds type was implemented using
Windows Media Player control.
3.2.6 Animation
A virtual assistant and speech recognition libraries for
both: Spanish and English language were
implemented using MS Agents by Microsoft.
3.2.7 Game Algorithms
One of the most important algorithms in the game is
the algorithm that allows two users to play each other
on the same computer or a user to play against the
computer with AI. Depending on the level that the
user chooses for which the function Play() has been
implemented inside the form frmTicTacToe whose
algorithm is presented at the end of this subsection.
The parameters of the managed objects explained
above are: (1) board: whose value depends on the
category chosen by the user; (2) btnTicTacToe: whose
value depends on which the button has been clicked
by the user; (3) type: whose value depends on the
fictitious good or bad character chosen by the user;
(4) player1: whose value depends on the character,
animal or object chosen by the user based of the type
and the board; (5) player2: this parameter represents
the non-player character (NPC) selected by the user
for the confrontation; (6) grbTicTacToe: this control
represents the container that hold the nine buttons and
when the game is over this control disables these
buttons; (7) dgvData: this control shows the final
results of the players saved on XML files; (8)
listButtons: this parameter is used exclusively by the
non-player character (NPC) in which case the button
is selected depends on the heuristics techniques of
Artificial Intelligence.
ICEIS 2016 - 18th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
428

3.2.8 Artificial Intelligence Algorithms
Within the context of this study, the Artificial
Intelligence algorithms focuses on providing capacity
to computers to perform tasks that require human
intelligence. This means, the ability of the computer
to act or participate as an opponent in the game
(Walnum, 2001). In the Tic-Tac-Toe game, the
computer has the ability to play with the user,
according to three different levels of difficulty: basic
level, intermediate level, and advanced level. For the
Artificial Intelligence model of the application we
have used both weak and strong heuristics techniques.
Here we use numeric method based on numeric series
that is represented by linked lists and arrays. These
kind of structures store different movements made by
the same application that is the non-player character
(NPC) controlled by the computer that plays with the
user. The numeric method based on finite series is
indicated in Table 1, where each finite series has been
obtained based on a sum that represents a value
accumulated in a certain row, column or diagonal of
the Tic-Tac-Toe game. In Table 2, the initial state of
the whole array is depicted (i.e., that is zero) and it
corresponds to an empty space or a free cell. Some
cases are described below:
Table 1: Numeric method based on finite series.
Case 1: The non-player character (NPC)
obstructs the user. In this case the following
instruction should be considered: if ((a = 2) ˅ (b
= 2) ˅ (c = 2) ˅ (d = 2) ˅ (e = 2) ˅ (f = 2) ˅ (g =
2) ˅ (h = 2)) then: if (v[k] = 0) then v[k]:= 3 →
NPC obstructs the user;
Case 2: The non-player character (NPC) wins.
In this case the following instruction should be
considered: if ((a = 6) ˅ (b = 6) ˅ (c = 6) ˅ (d =
6) ˅ (e = 6) ˅ (f = 6) ˅ (g = 6) ˅ (h = 6)) then: if
(v[k] = 0) then v[k]:= 3 → NPC beats the user;
Case 3: Obstruct in the diagonals. In this case
the following instruction should be considered:
if ((x = 5) ˅ (y = 5)) then: if (v[k] = 0) then
v[k]:= 3 → NPC obstructs the user;
Case 4: Obstruct in the corner squares. In this
case the following instruction should be
considered: if (((p = 2) ˅ (q = 2) ˅ (r = 2) ˅ (s =
2)) ˄ (v[k] = 0)), where k = 0, 2, 6, 8; then: if
(v[k] = 0) then v[k]:= 3 → NPC obstructs the
user in the corners close to the edges occupied
by the user.
Table 2: Finite State Machine of the Game.
Object Weight
User 1 1
Non-player character (NPC) 3
Blank space 0
3.2.9 Semiotic Model of the Game
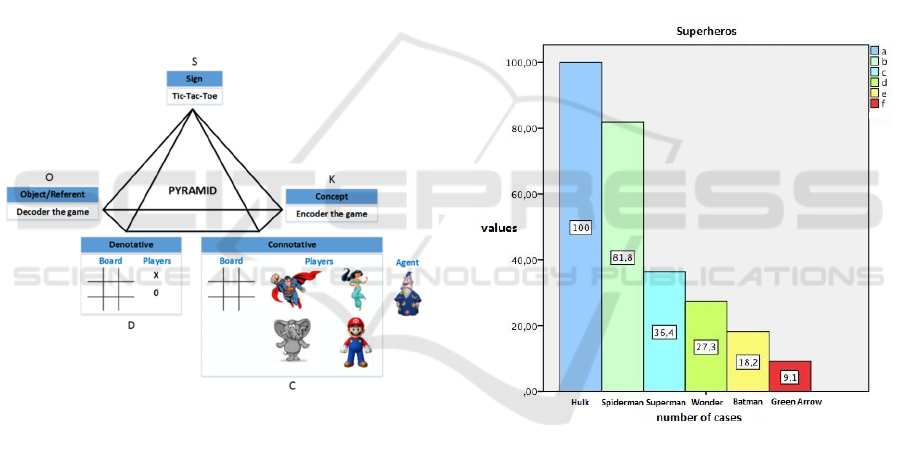
Figure 4 shows the model of Aleferenko (Tokarev,
2014) which completes: K=S+O+D+C; where K is
the Concept, S is the Sign, O it is the object, D it is
the denotation and C it is the connotation. This model
demonstrates the real state of the construction of the
knowledge on the receiver’s part since it is unable to
jump the denotation and connotation process to arrive
at the concept.
In the first instance, the sign is the word that
corresponds to the game. In our case the sign begins
the code process to obtain knowledge. In the second
instance, the object referent corresponds to the code
of the game. In the third instance, the receiver passes
to the connotative process where it identifies the signs
as symbols. Therefore it is not an arbitrary process of
significance. The connotation process is in the fourth
instance, where the receivers are the children that play
the game, in an appropriate atmosphere. Also,
according to their preferences, the sign that doesn’t
has the character of arbitrary in this case because they
become symbols. For instance, in the case of the
Superman – sign (the symbol of a super hero), which
would correspond to K that is the concept of the sign
S, and in similar form is Lex Luthor – sign (the
antagonistic or villainous symbol with respect to
superman). Finally, the result is the concept or
knowledge decoded due to the process of connotation
of the sign.
On the Development of Strategic Games based on a Semiotic Analysis: A Case Study of an Optimized Tic-Tac-Toe
429
3.2.10 Principle of Arbitrariness of the Sign
According to Holdcroft (1991), the principle of
arbitrariness of the sign consists in the bond among
the meaning with the significance of arbitrary. This,
since the sign is equivalent to the association of a
significant with a meaning. For this reason the game
of the Tic-Tac-Toe is decoded like it was mentioned
previously, being a matrix with two elements: a ‘cero’
and an ‘x’ letter, generally constructed in paper or
with wood. The concept or significance of Tic-tac-
Toe is not bound for any relationship with the
sequence of sounds “t-i-c-t-a-c-t-o-e” that serves by
itself significance to the word. It could be represented
by any other sequence of sounds, for example the
“Tic-Tac-Toe” game in English corresponds to “Tres
en Raya” in Spanish and in Russian, it corresponds to
“крестики-нолики”, where it doesn't only change the
sound but even the system of signs that doesn't
correspond to the Latin alphabet, and the system
corresponds to the Cyrillic one instead.
Figure 4: The semiotic model Aleferenko for the game.
3.2.11 Testing the Game
We applied the game to a public school, forty seven
to eleven years old children were randomly chosen to
play the game during 30 minutes. A group of children
were exposed to the traditional Tic-Tac-Toe game
(i.e. without Semiotics) versus the optimized Tic-
Tac-Toe game (with Semiotics). After, the children
tested the game, we proceeded to perform statistical
processing of the scores provided by the game. As
noted in this study, it has been optimized as the Tic-
Tac-Toe game, incorporating the semiotic model of
Aleferenko. This research has involved superheroes,
princesses, other animals and world comics.
4 EVALUATION RESULTS AND
DISCUSSION
4.1 Results of the Evaluation
There were differences of comic figures preferences.
Fig. 5 illustrates that there is a superhero that has the
popularity of 100% (i.e. Hulk), followed by another
one with 81.8% (i.e. Spiderman). The other two with
36.4% (i.e. Superman), and Wonder Woman with
27.3%. Batman and Green Arrow with 18.2% and
9.1%, respectively. This means that two superheroes
were known to more than half of the children with
more than 50% of the total popularity, while 14 other
superheroes yielded amounts between 18.2% and
36.4% on average, and just six below 9.1%. This
leads to the conclusion that 16 boys were interested
in recreational games with superheroes.
Figure 5: Bar chart of the most popularly superheroes
selected in the game.
In the case of girls the results were: Two
princesses reached total popularity of 100% (i.e.
Anna and Elsa), while five reached popularity
amounts between 16.7% and 41.7% (i.e. Rapunzel,
Ariel, Goethel, Jasmine, and, Cinderella). These
amounts are all above average. However 17 are
almost unknown to the children as they reached
popularity values below 8.3% (Snow White,
Pocahontas, Queen Grim Hilde, Shan Yu, Hans,
Bella, Mulan, Tiana, Merida, Aurora, Lady Tremaine,
Ursula, Jafar, John Ratcliffe, Dr Facilier, Queen
Elinor, and Maleficent).
The results accomplished by children in the fifth
grade of elementary school at the intermediate level
ICEIS 2016 - 18th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
430

shows that the modified Tic-Tac-Toe game (with
semiotics) conducted the successful challenge by the
children., but gender difference were detected. Fig. 6
illustrates that in the normal game did not crystallize
any winners, but there were three losses and three ties
(i.e. equal finish). The girls in turn drew all. On the
other hand, Fig. 7 demonstrates two boys won, having
just three losses and one draw. Girls continue getting
the same draws. However, in the case of girls no
improvement could be reached. This analysis was
performed in each grade and with different levels (i.e.
basic, intermediate and advanced) demonstrating
better results with the game optimized with
Semiotics, contrasting the research hypothesis
convincingly.
Figure 6: Results obtained using Tic-Tac-Toe game without
semiotics.
Finally, the illustration in Fig. 8 has been obtained by
the means of the method of Natural and Hyman. In
this figure it is demonstrated, that the frequency curve
of the normal variable change fairly its tendency
compared to the curve generated by the semiotic
variable. This leads to the conclusion, of the existence
of a greater homogeneity of the data of the semiotics
variable compared with normal variable. Thus, we are
able to suggest, that it is more difficult to resolve
recreational games with normal conditions when a
semiotic modelling applies. Therefore, we deduce
that semiotics grows proportionally affecting more
positively the learning in an objective and scientific
way. Similarly, based on the study conducted at
different grades (second to sixth grade) in an
elementary school we obtained a similar behaviour
.
Figure 7: Results obtained using Tic-Tac-Toe game with
semiotics.
Figure 8: Results obtained adjusting an algebraic
polynomial from the absolute cumulative frequencies.
4.2 Discussion
It is considered that the Aleferenko model integrates
the foundations of Semiotics. Another important fact
that carried this model to the desktop platform game
is its friendly appearance. Therefore, it has been
empowering for the comprehensive knowledge of
children between 7 and 11 years old and can be used
as part of the teaching-learning process of
schoolchildren, because this game is a strategy
educational game that is using to stimulate logical and
spatial reasoning. In this study, that was achieved due
to the implication of connotative analysis in deep
through Artificial Intelligence and Software
Engineering, which causes the receiver (user) uses
tactics and strategies to beat the computer. Thus, a
dynamic environment was created in the game for the
On the Development of Strategic Games based on a Semiotic Analysis: A Case Study of an Optimized Tic-Tac-Toe
431

receivers who can have their own signs according to
the age. They lose their arbitrariness and the symbols
become the identifiers with which the children are
related and can create relevance and internalization of
the knowledge, and above all to create interactivity.
Another important aspect when evaluating the game
includes the use of signs and symbols and their
diagnostic meaning for the children. Therefore, this
creates a natural, interesting, efficient and motivating
learning.
5 CONCLUSIONS
This research focused on how to optimize an
educational video game named Tic-Tac-Toe by
means of semiotics analysis, in order to stimulate
logical and spatial reasoning of children. The main
issue in our study has been to design a mathematical
model, which is implemented with AI algorithms and
a graphical user interface including Semiotics,
applied to an incremental methodology with the aim
of producing an enjoyable and interactive
environment. To carry out this study, we have used
the Extreme Programing (XP) agile methodology for
the codification and testing of the incremental
products in each iteration (sprint), combined with the
modified Elemental Tetrad Game Design Model for
defining the performance of the game’s models, in
order to ensure the quality of the software used. To
validate our results, the proof of concept and testing
has been performed with a representative sample at
an elementary school, focused on children with ages
ranging from seven to eleven years old. The results
imply that educational video games with Semiotics
stimulate cognitive development of children.
REFERENCES
Gee, J. P., 2008. Learning in semiotic domains. Literacies,
global and local, 137-149.
Halliday, M. A. K., 1978. Language as social semiotic: The
social interpretation of language and meaning.
Maryland. University Park Press.
Myers, D., 1991. Computer game semiotics. Play &
Culture, 4(4), 334-345.
Thorne, S. L., Fischer, I., & Lu, X., 2012. The semiotic
ecology and linguistic complexity of an online game
world. ReCALL, 24(03), 279-301.
Kendall, N., 2015. What is a 21st Century Brand? New
Thinking from the Next Generation of Agency Leaders.
Kogan Page Publishers.
Huber, W. H., 2013. The Foundations of Videogame
Authorship.
Ruiz, J. G., et al., 2014. Evaluating the Communicability of
a Video Game Prototype: A Simple and Low-Cost
Method. In Proc. of the 5th Mexican Conference on
Human-Computer Interaction (p. 30). ACM.
Baceviciute, S., Bruni, L., 2014. Experience Cognitive
Experiences, ICoN2014 - 1st International Congress of
Numanities. The role of Humanities in Contemporary
Society: Semiotics, Culture, and Tech.
Villacís, C., Fuertes, W., Bustamante, A., Almachi, D.,
Procel, C., Fuertes, S., & Toulkeridis, T. 2014. Multi-
player Educational Video Game over Cloud to
Stimulate Logical Reasoning of Children. In
Proceedings of the IEEE/ACM 18th International
Symposium on Distributed Simulation and Real Time
Applications (pp. 129-137). IEEE Computer Society.
Gibson, J., 2014. Introduction to Game Design,
Prototyping, and Development: From Concept to
Playable Game-with Unity and C#. Pearson Educ.
Beck, K., 2000. Extreme programming explained: embrace
change. Addison-Wesley Professional.
Schneider, J. G., & Johnston, L., 2003. Extreme
Programming at universities: an educational
perspective. 25th International conference on software
engineering (pp. 594-599). IEEE Computer Society.
Tokarev, G.B., 2014. Introducción a la Semiótica, Flinta
Nauka, Moscú, pág. 62.
Villacís, C. J., Fuertes, W. M., Bustamante, C. A.,
Zambrano, M. E., Torres, E. P., Aules, H. M., &
Basurto, M. O. (2014). Optimización del juego tres en
raya con niveles de dificultad utilizando heurísticas de
inteligencia artificial. AtoZ: Novas Práticas em
Informação e Conhecimento, 3(2), 95-106.
Wisse, P., 2002. Semiosis & Sign Exchange: design for a
subjective situationism, including conceptual grounds
of business information modeling.
Vygotsky, L. S., 1967. Play and its role in the mental
development of the child. Soviet psychol, 5(3), 6-18.
Brown, A. L., & Ferrara, R. A., 1999. Diagnosing zones of
proximal development. Vygotsky: Critical
assessments: The zone of proximal dev., 3, 225-256.
Feuerstein, R., Klein, P. S., & Tannenbaum, A. J. (Eds.),
1991. Mediated learning experience (MLE):
Theoretical, psychosocial and learning implications.
Lipman, M., & Sharp, A. M., 2002. La filosofía en el aula
(Vol. 4). Ediciones de la Torre.
Drake, P., & Kerr, N., 2006. Developing a computer
strategy game in an undergraduate course in software
development using extreme programming. Journal of
Computing Sciences in Colleges, 22(2), 39-45.
Schell, J., 2014. The Art of Game Design: A book of lenses.
CRC Press.
Walnum, C., 2001. Sams Teach Yourself Game
Programming With Visual Basic in 21 Days. Sams.
Holdcroft, D., 1991. Saussure: signs, system and
arbitrariness. Cambridge University Press.
ICEIS 2016 - 18th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
432
