
Ontology-based Access Control Management: Two Use Cases
Malik Imran-Daud, David Sánchez and Alexandre Viejo
UNESCO Chair in Data Privacy, Computer Science and Mathematics, Universitat Rovira i Virgili,
Avinguda Països Catalans, 26, 43007, Tarragona, Spain
Keywords: Ontologies, Access Control, Social Networks, Cloud, Privacy.
Abstract: Access control management is an important area of research within the security field. Several models have
been proposed to manage the access rights of users over restricted resources, which are mainly based on
defining rules between specific entities and concrete resources. Though these approaches are enough to
manage organizations involving a limited number of entities and resources, the specification of rules or
constraints for large and heterogeneous scenarios may imply a considerable burden to the administrators. To
palliate this problem, we propose a generic ontology-based solution to manage the access control that can
greatly simplify and speed up the definition of rules in complex scenarios and that can also improve the
interoperability between heterogeneous settings. Moreover, we show its potential by applying it in two highly
dynamic and large scenarios, i.e., Online Social Networks (OSNs) and the Cloud.
1 INTRODUCTION
Thanks to the advent of the Internet, computer
resources (which include hardware, computer
services, data, etc.) can be easily shared in distributed
environments in order to increase the productivity of
users and companies. In recent years, worldwide
environments such as Online Social Networks
(OSNs) or the Cloud have attracted billions of users
willing to share online resources and outsource data
and computation. Nevertheless, because of the
potential confidentiality of the data to be shared,
access control management is required to avoid
privacy threats.
The management of access rights implies granting
or denying access to specific resources according to
the credentials of the users, the content of the resource
and the privacy requirements of the owner. To
achieve this goal, system designers have offered
several solutions that are based on either RBAC or
ABAC as generic models to manage access control.
These include: classifying resources into categories
(Cheng et al., 2012), itemizing profile data into
different elements (Aimeur et al., 2010) or classifying
users into lists (e.g., blacklist users) (Cramer et al.,
2015). However, these methods do not scale well in
large and complex environments because of: i) the
growing privacy configuration requirements and the
incapability of existing solutions to handle them in an
efficient manner (Beato et al., 2009), and ii) the
burden of the definition and management of rules by
users and administrators (Daud et al., 2015).
To overcome these shortcomings, the scientific
community has proposed solutions to manage access
control that model entity types as graphs (Pang and
Zhang, 2014; Cramer et al., 2015); within ontologies
(Masoumzadeh and Joshi, 2010; Carminati et al.,
2011; Choi et al., 2014); for role-based access control
(Ben-Fadhel et al., 2015); or for attribute-based
access control (Smari et al., 2014). Ontologies are
particularly helpful to formally specify the
conceptualization and interrelations of a domain
(Mika, 2007), so that specific entities (e.g., users and
resources) can be defined as instances of this
conceptualization. Then, access control can be easily
managed according to the (privacy-oriented)
interrelations defined in the ontology for the involved
entities. Usually, ontology-based approaches define
ad-hoc ontologies for concrete scenarios, which limit
their generality and hamper the interoperability
between heterogeneous settings (i.e., each one is
based on a different ontological backbone) (e.g., see
(Pang and Zhang, 2014)).
To tackle these limitations, we present a generic
ontology-based solution inspired in the Attribute-
based Access Control (ABAC) paradigm that models
entities and their access policies. This system
provides the following benefits: i) a generic ontology
244
Imran-Daud, M., Sanchez, D. and Viejo, A.
Ontology-based Access Control Management: Two Use Cases.
DOI: 10.5220/0005777902440249
In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART 2016) - Volume 1, pages 244-249
ISBN: 978-989-758-172-4
Copyright
c
2016 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

that can be easily extended for specific environments,
so that access control can be defined at different
levels of granularity; and ii) it simplifies the
definition and enforcement of rules, thanks to the
automatic ontology-based inference of rules. In order
to demonstrate its applicability and benefits, we have
applied it to two large and open scenarios: OSNs and
the Cloud.
2 A GENERAL ONTOLOGY FOR
ACCESS CONTROL
MANAGEMENT
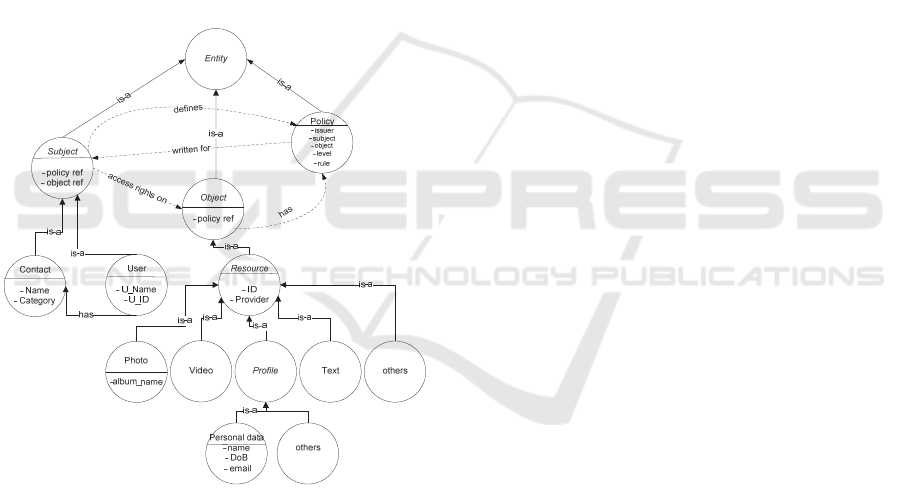
The backbone of our ontology (which is shown in
Figure 1) is inspired in the ABAC model. It models
the three basic (ABAC) entities required to manage
access control: subject, object and policy. Subjects
can be the owners of the resources that define access
rights for other users or they can be the target users
over whom the access control should be enforced.
Objects are the resources (e.g., services, files,
messages, etc.) that require protection from
unauthorized access; they are protected by defining
policies that contain access rules. The access rule is
represented by the following tuple.
rule ≡ < s
i
, o
j
, a >
where s
i
is the subject target user, o
j
represents the
object resource and the element a is the action that
holds access decision (e.g., allow, deny).
The ontological property (i.e., access rights on)
between the subject and the object determines the role
of the user w.r.t. the resource (i.e., owner of the
resource or the one who requests access to the
resource). Likewise, the defines property between the
subject and the policy indicates the relationship of
policy maker with the policy, whereas, the written for
property shows the relationship between the target
user and the policy itself. Finally, each resource is
associated with the policy through the has property.
The generic design of the ontology allows us to
define general rules that refer to the abstract classes
(i.e., subject, object and policy) rather than to specific
entities. Then, entities involved in the specific
scenario (i.e., concrete users and resources) can be
represented as instances of ontological classes and,
thus, access control over these entities can be
enforced on the basis of general rules by relying on
the ontological structure (i.e., specific rules at an
entity level can be automatically derived from the
general rules defined at a class level). Moreover, the
generic ontology can be specialized with more
specific classes that are appropriate for a concrete
scenario and, accordingly, more specific rules can be
tailored (in any case, without require to define them
on entity-basis).
is-a
Figure 1: Access control ontology.
In order to take authorization decisions, the access
control mechanism evaluates the interrelationship
and the attributes of subject, object and policy, as
stated in the ABAC model. Specifically, the system
determines the following information from the
ontology: i) the resource requestor, ii) the owner of
the resource, iii) the resource itself, and iv) the policy
defined by the owner of resource.
In the following subsections, we show how our
generic ontology can be extended to model the
entities involved in two widespread scenarios: OSNs
and the Cloud.
3 OSNs USE CASE
Nowadays, billions of users are active members of
OSNs and share digital information (e.g. photos,
videos, text, profile data, etc.) with their social circle
of friends. In many occasions, this information may
carry sensitive data such as political and religious
orientations, medical data or other sensitive
information that can be misused by third parties for
discriminatory purposes (Viejo et al., 2013). To
prevent the misuse of such data, an access control
mechanism should be implemented. For that purpose,
in the following we extend our general ontology for
OSNs.
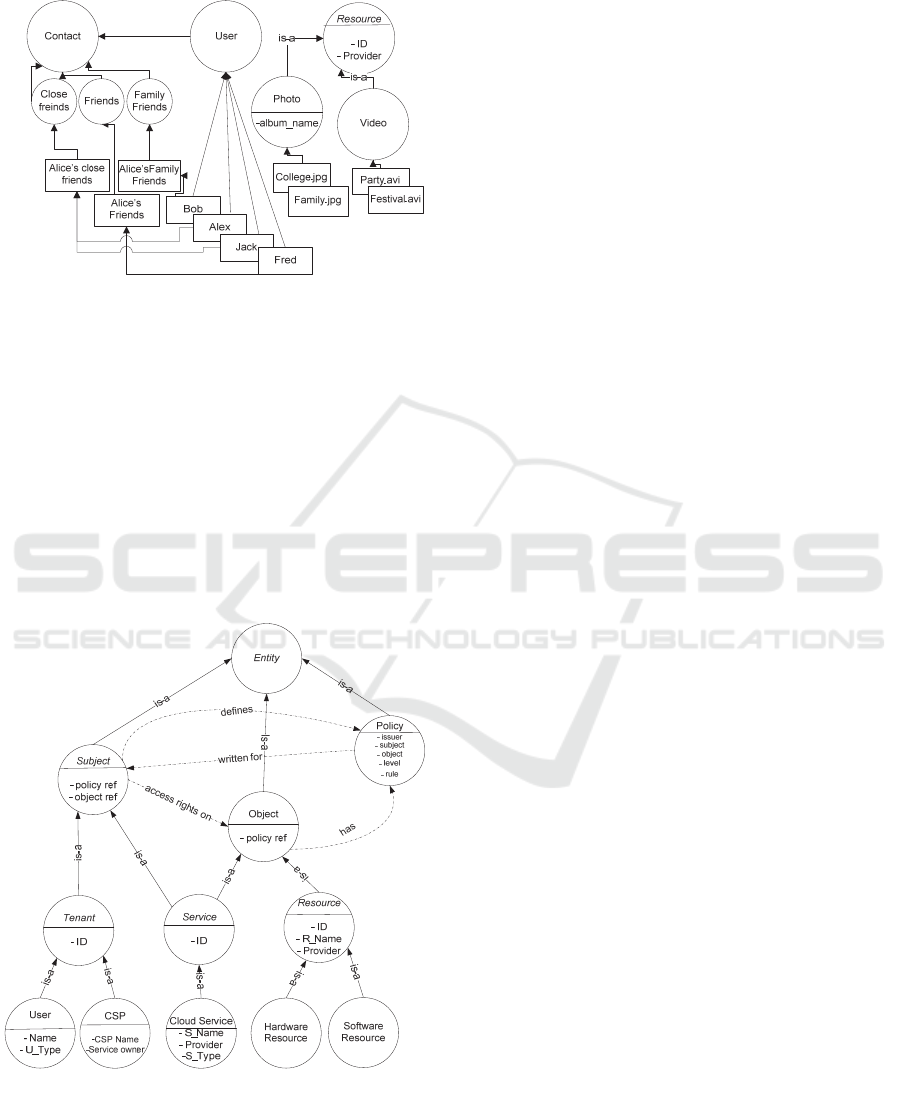
Figure 2 depicts the extended ontology that
models OSN entities and their interrelationships. In
Ontology-based Access Control Management: Two Use Cases
245
this scenario, the subject entities of the OSN (i.e.,
owners of the resources) manage their access rights
on objects (e.g., photos, text messages, videos, etc.)
by defining access control policies over other subjects
(i.e., other users with whom the owners are in
contact). The rules are the attributes of these policies
that hold access right decisions (i.e., allow or deny
access to a resource uploaded by the owner). Since
OSNs allow users to classify their contacts into
different categories (e.g., close friends, family
friends, strangers, etc.), the subject class has been
specialized with a contact subclass that encompasses
the contact types of the users. This specialization is
also helpful for the users to define different access
rules according to the contact category of the users.
Finally, user is modeled in a subclass of the subject
class; their membership to a certain contact type of
the owner of a resource is represented with the has
property.
Figure 2: Extended access control ontology for OSNs.
The object class constitutes the resources that
require protection from unauthorized access. In the
context of OSNs, objects are specialized in specific
resource types (i.e., photo, video, profile, text, etc.) so
that a more fine-grained access control can be
enforced; that is, managing access control on each
resource type rather than applying the same rule for
all the resources. The profile class is further classified
into two subclasses: i) profile data, which details the
identity of the users, and whose access could be
protected in order to avoid identity disclosure and ii)
other related information (e.g., interests of the users),
which may refer to confidential information.
Even though this ontology represents the entity
types involved in an OSN, it can be further extended
to accommodate the specificities of a particular
vendor (e.g., Facebook), such as predefined contact
types or more specific resource types.
3.1 Access Control Management
and Enforcement
As discussed in section 2, a user may limit the access
to her resources by defining an access rule for a set of
target users. With our ontology-based approach, the
rule can be defined for ontological classes at any level
of abstraction so that it would be automatically
enforced for the corresponding subclasses and,
finally, instances (entities) of such classes. Within the
OSNs scenario, the default rule for all the resources
is deny access, so that the user only needs to define
allow permissions. The following example illustrates
the extension and instantiation of the OSN ontology
for a specific scenario and the automatic inference of
rules and their enforcement.
Example 1: Figure 3 illustrates the ontological
specialization and instantiation of social network
entities associated to the Alice’s social account (e.g.
Facebook). As privacy preferences, she defines a rule
to allow her family friends to access her resources
(i.e., rule
Alice
≡ < family friends, resource, ‘allow’>).
This rule is encompassed in the policy instance that is
linked with the instance of the resource being
referenced and the instance of the target subject (i.e.,
contact type family friends). Since, this rule is defined
at a class level (i.e., family friends in contact and
resource as a whole), by ontological inference, it will
be automatically enforced on all the subsequent
entities. Since Bob is a family friend of Alice and by
the inference of generic rule, the system grants full
access to Bob on photo and video instances.
Specifically, the following rules are generated for the
instances of the user that are family friends of Alice
(only Bob in the given case).
rule
Alice
≡ < Bob, “college.jpg”, ‘allow’ >
rule
Alice
≡ < Bob, “family.jpg”, ‘allow’ >
rule
Alice
≡ < Bob, “party.avi”, ‘allow’ >
rule
Alice
≡ < Bob, “festival.avi”, ‘allow’ >
In any case, Alice can also define rules for specific
instances of the user class. For example: Alice may
only allow Alex, from close friends contacts, to access
all of her photos (i.e., rule
Alice
≡ < Alex, photos,
‘allow’>). Thus, the following rules are inferred from
this generic rule.
ICAART 2016 - 8th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
246
rule
Alice
≡ < Alex, “college.jpg”, ‘allow’ >
rule
Alice
≡ < Alex, “family.jpg”, ‘allow’ >
Figure 3: Instantiation of the OSN ontology for user Alice.
4 CLOUD USE CASE
Cloud computing provides a ubiquitous platform to
share resources and to provide cloud services to
tenants. Because of its open nature, it requires a
scalable mechanism that manages access control on
the shared resources. For this purpose, we extend our
general ontology to incorporate the cloud entities and
the attributes that are relevant to manage access rights
in the cloud environment.
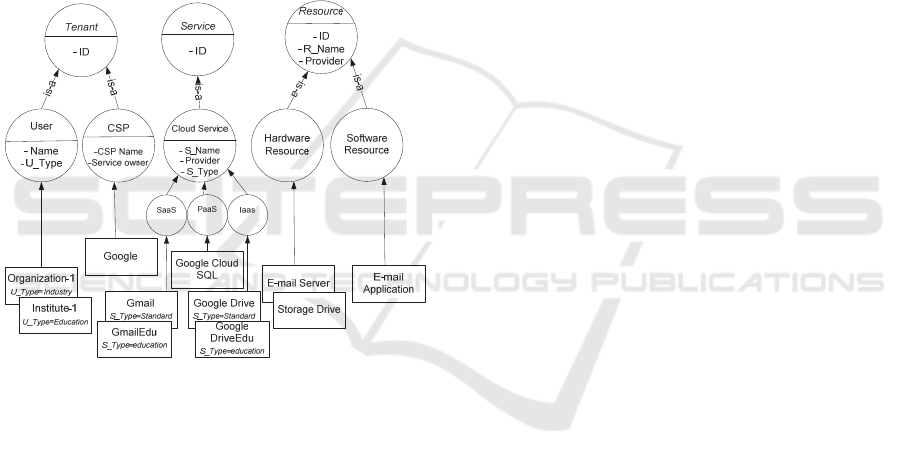
Figure 4: Extended access control ontology for the cloud.
Figure 4 illustrates the extended ontology that lists
cloud entities (tenant, cloud service and cloud
resource) and their interrelationships. In this
illustration, tenant is a subclass of subject that holds
cloud actors, which are: i) user (which use cloud
services) and ii) cloud service provider (CSP) (which
provides and shares cloud services). Likewise,
service is a subclass of subject that represents the
services provided by the CSPs, these services may
require access to shared resources to accomplish their
tasks. On the other hand, service is also a subclass of
object because the tenants may access them as cloud
service. Finally, cloud resources can be hardware
resource (e.g., servers, storage space, etc) or software
resource (e.g., web application, web services, etc.).
Cloud service providers can manage the access to
their shared resources and services by defining a rule
that is encompassed within a policy, as explained for
OSNs in the previous section. The following example
illustrates the enforcement of rules in the cloud
scenario.
4.1 Access Control Management
and Enforcement
Example 2: Figure 5 illustrates the extension and
instantiation of the cloud ontology for CSP (Google)
that offers its services and resources to the users. In
this example, Google offers different cloud services
at different service levels (i.e., SaaS, PaaS and IaaS)
for standard users and educational institutions (e.g.,
educational institutions are offered more space on
Google drive and a professional domain for email).
Google configures the access to its resources and
services with the following two rules: i) it allows
SaaS services to access all the resources (hardware
and software); and ii) it grants users belonging to any
educational institution with special access to its Cloud
services that are meant for an educational purpose. In
this last case, and in coherency with the ABAC
model, we can rely on the attributes defined for the
ontological classes and instances. Thus, the following
generic rules are defined:
rule
Google-R1
≡ < SaaS, resource, ‘allow’ >
rule
Google-R2
≡ < Users <U_Type=“Education”>, Cloud
Services
<S_Type=“Education”>, ‘allow’ >
The rule
Google-R1
is defined at the conceptual level
(i.e., at resource and SaaS classes) of the ontology
and, thus, it covers all the entities below the hardware
resource and software resource classes. By inferring
specific rules at the instance level, we obtain the
following ones:
rule
Google-R1
≡ < Gmail, e-mail server, ‘allow’ >
rule
Google-R1
≡ < Gmail, storage drive, ‘allow’ >
rule
Google-R1
≡ < Gmail, e-mail applications, ‘allow’>
Ontology-based Access Control Management: Two Use Cases
247
rule
Google-R1
≡ < GmailEdu, e-mail server, ‘allow’ >
rule
Google-R1
≡ < GmailEdu, storage drive, ‘allow’ >
rule
Google-R1
≡ <GmailEdu, e-mail applications,
‘allow’ >
On the other hand, rule
Google-R2
grants access to
cloud services that are specifically allocated to
educational institutions. To manage this, the type of
users is determined through the value of the U_Type
attribute of the entities, whereas the educational
services are determined by the value of the S_Type
attribute. As a result, the educational instances of the
user class are distinguished and granted access to all
cloud services that are allocated for educational
institutions. The following rules are, thus, generated
due to the inference of this generic rule.
rule
Google-R2
≡< Institute-1,GmailEdu, ‘allow’ >
rule
Google-R2
≡<Institute-1,Google DriveEdu, ‘allow’ >
Figure 5: Instantiation of the Cloud ontology for Google.
5 RELATED WORK
To manage access control in OSNs, Masoumzadeh
and Joshi (2010) proposed ontologies that model
OSN resources (e.g., photos, messages, etc.) and the
access rights of the users. The proposed solution is
ad-hoc in nature and only models entities (e.g. digital
object, person and event) and their relationships for a
specific OSN (i.e., Facebook). Furthermore, it offers
coarse-grained access management that allows or
denies access to the whole resource and it does not
support access management on a specific instance of
the resource (e.g., restriction on photos will prohibit
access to all photos and there is no mechanism for
access management on the single instance of photos).
Choi et al., (2014) proposed ontology-based
content-aware approach for the cloud that determines
the type of users (i.e., service provider or normal
user), their context information from the ontology
(i.e., relationship type of the user with the resource)
and their access rules from the policies that are
managed locally in a repository. The ontology they
propose only provides context information of the
users and resources (i.e., type of users and their
relationship with the resources) and it does not model
policies defined for these entities. Thus, the system
needs to map context information with the policy
database in order to get appropriate policy, which is
an extra burden and makes it more complex to process
any access request.
In another approach, Liu (2014) modeled, by
means of an ontology, a set of operations of cloud
business services: i) payment status (to keep record of
users’ payment to access cloud resources), ii) service
level agreement (the level of access on the resource)
to manage access control of the users on cloud
resources and iii) role of users (to distinguish valued
users from standard ones). In addition, several rules
are specified to tackle policy conflicts and to manage
unauthorized access of users. Again, the ontology is
not generic and it is limited to model specific cloud
services, thus, it provides ad-hoc inference system for
rules.
In an ABAC-based approach, Jin et al., (2012)
proposed a unified model that adopts the advantages
and tackles the limitations of the discretionary access
control (DAC), mandatory access control (MAC) and
RBAC models. In this model, the unified features of
existing models are represented in the form of
attributes that are associated with the subjects and
objects of the system. The backbone of this system is
the ABAC model that manages access control. This
model, however, only details high-level concepts and
does describe how it can be implemented in the real
scenarios.
In comparison, our solution does not rely on the
ad-hoc graphs/ontologies but on a general purpose
ontology inspired in the standard ABAC model that
can be easily extended for heterogeneous
environments by specializing classes. Moreover, due
to the fact that the backbone of the ontology (Figure
1) is common for all specific scenarios, it is also
possible to achieve interoperability between the rules
and the instances defined between different scenarios
(e.g., between users and resources shared between
clouds and OSN).
ICAART 2016 - 8th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
248

6 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, we proposed a generic ontology that
models entities, their interrelationships and access
control policies, and it can be easily extended for
specific environments. To show its applicability, we
extended it for two large and open scenarios: OSNs
and the cloud. We also illustrated through examples
how the definition of rules and the management of
access control are greatly simplified for system
administrators, because they can be intuitively made
at a conceptual –class- level. Then, specific (and
dynamic) rules can be automatically inferred
according to the specific entities, which would also be
likely dynamic in open scenarios such as those
tackled in the paper.
As future work, we plan to extend the generic
ontology to other specific scenarios (e.g., business
organizations) and propose automatic and scalable
inference mechanisms to manage other aspects of
access control (e.g., delegation). At this respect we
will study and formalize more complex inference
rules that exploit the ontological structure, and
develop algorithms to deal with cases in which policy
conflicts may appear. Moreover, we also plan to study
the interoperability issues that arise in access control
between heterogeneous systems and evaluate whether
our ontology-based mechanism (with its common
ontological backbone) may provide a suitable
solution to interoperate between rules and entities of
different scenarios.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was partly supported by the European
Commission under H2020 project CLARUS, by the
Spanish Ministry of Science and Innovation (through
projects CO-PRIVACY TIN2011-27076-C03-01 and
ICWT TIN2012-32757) and by the Government of
Catalonia (under grant 2014 SGR 537).
REFERENCES
Aimeur, E., S. Gambs, et al. (2010). Towards a Privacy-
Enhanced Social Networking Site. In ARES '10,
International Conference on Availability, Reliability,
and Security.
Beato, F., M. Kohlweiss, et al. (2009). Enforcing access
control in social networks. HotPETs: 1-10.
Ben-Fadhel, A., D. Bianculli, et al. (2015). "A
comprehensive modeling framework for role-based
access control policies." Journal of Systems and
Software 107: 110-126.
Carminati, B., E. Ferrari, et al. (2011). "Semantic web-
based social network access control." Computers &
Security 30 (2-3): 108-115.
Cheng, Y., J. Park, et al. (2012). A User-to-User
Relationship-Based Access Control Model for Online
Social Networks. Data and Applications Security and
Privacy XXVI, Springer Berlin Heidelberg. 7371: 8-24.
Choi, C., J. Choi, et al. (2014). "Ontology-based access
control model for security policy reasoning in cloud
computing." The Journal of Supercomputing 67(3):
711-722.
Cramer, M., J. Pang, et al. (2015). A Logical Approach to
Restricting Access in Online Social Networks.
Proceedings of the 20th ACM Symposium on Access
Control Models and Technologies. Vienna, Austria,
ACM: 75-86.
Daud, M. I., D. Sánchez, et al. (2015). Ontology-Based
Delegation of Access Control: An Enhancement to the
XACML Delegation Profile. Trust, Privacy and
Security in Digital Business. S. Fischer-Hübner, C.
Lambrinoudakis and J. López, Springer International
Publishing. 9264: 18-29.
Jin, X., R. Krishnan, et al. (2012). A Unified Attribute-
Based Access Control Model Covering DAC, MAC
and RBAC. Data and Applications Security and Privacy
XXVI. N. Cuppens-Boulahia, F. Cuppens and J.
Garcia-Alfaro, Springer Berlin Heidelberg. 7371: 41-
55.
Liu, C.-L. (2014). "Cloud service access control system
based on ontologies." Advances in Engineering
Software 69: 26-36.
Masoumzadeh, A. and J. Joshi (2010). "An ontology-based
access control model for social networking systems."
IEEE Social Computing (SocialCom): 751 – 759.
Mika, P. (2007). "Ontologies are us: A unified model of
social networks and semantics." Web Semantics:
Science, Services and Agents on the World Wide Web
5(1): 5-15.
Pang, J. and Y. Zhang (2014). A new access control scheme
for Facebook-style social networks. Ninth International
Conference on Availability, Reliability and Security
(ARES), 2014, IEEE: 1-10.
Smari, W. W., P. Clemente, et al. (2014). "An extended
attribute based access control model with trust and
privacy: Application to a collaborative crisis
management system." Future Generation Computer
Systems 31: 147-168.
Viejo, A., J. Castellà-Roca, et al. (2013). Preserving the
User’s Privacy in Social Networking Sites. Trust,
Privacy, and Security in Digital Business. S. Furnell, C.
Lambrinoudakis and J. Lopez, Springer Berlin
Heidelberg. 8058: 62-73.
Ontology-based Access Control Management: Two Use Cases
249
