
Emotion Recognition through Body Language using RGB-D Sensor
Lilita Kiforenko and Dirk Kraft
Maersk Mc-Kinney Moller Institute, University of Southern Denmark, Campusvej 55, 5000 Odense C, Denmark
Keywords:
Emotion Recognition, Body Language Recognition.
Abstract:
This paper presents results on automatic non-acted human emotion recognition using full standing body move-
ments and postures. The focus of this paper is to show that it is possible to classify emotions using a consumer
depth sensor in an everyday scenario. The features for classification are body joint rotation angles and meta-
features that are fed into a Support Vector Machines classifier. The work of Gaber-Barron and Si (2012) is
used as inspiration and many of their proposed meta-features are reimplemented or modified. In this work we
try to identify ”basic” human emotions, that are triggered by various visual stimuli. We present the emotion
dataset that is recorded using Microsoft Kinect for Windows sensor and body joints rotation angles that are
extracted using Microsoft Kinect Software Development Kit 1.6. The classified emotions are curiosity, confu-
sion, joy, boredom and disgust. We show that human real emotions can be classified using body movements
and postures with a classification accuracy of 55.62%.
1 INTRODUCTION
Emotion recognition is an important feature when de-
veloping communication between artificial systems
and humans. No matter if it is an avatar or a robotic
platform, everywhere where there is a need to inter-
act in some way with humans, systems will benefit
greatly if they can perceive human emotions.
Automatic emotion recognition is not a new topic.
Many attempts have been made to create emotion
recognition systems, for example, recording of hu-
man facial expressions, body movements, postures or
speech. A lot of research is done also using electroen-
cephalography and results are promising (Schaaff and
Schultz, 2009) (Singh et al., 2012). The problem is
that even in the best scenario you need to use a spe-
cially made ”sensor cap”, and this is not realistic in
everyday life.
Most solutions therefore focus on facial expres-
sion and speech. Facial emotion recognition has
proven to be very successful, achieving e.g. an av-
erage 93.2% classification rate of neutral, happy, sur-
prised, angry, disgusted, afraid, sad (Azcarate et al.,
2005). Such work typically relies on an consumer
camera like the one used in our work. Speech analysis
also achieves good performance in recognising emo-
tion, achieving a 80.60% for such emotions as bore-
dom, neutral, anger, fear, happiness, sadness, disgust
(classification from the Berlin Emotion Database).
While studies of which human facial features are most
useful in discriminating between emotions exist, there
is no corresponding investigation of distinguishing
features of speech or of body postures and move-
ments.
Many attempts have been made to automatically
classify emotions from body movements and posture,
but most of this research is unfortunately based on
acted emotions. With acted emotions, researchers
have achieved a high recognition rate of up to 96%
(Kapur et al., 2005) (Glowinski et al., 2011). Few at-
tempts have been made to classify real human emo-
tions and all of them either detect a limited range
of emotions (for example, only engagement level
(Sanghvi et al., 2011) or require a special recording
system (for example, a Gypsy 5 motion capture sys-
tem (Gaber-Barron and Si, 2012) or body pressure
measurement system (DMello and Graesser, 2009)).
To the best of our knowledge, at the time of the re-
search recorded in this paper, there was no research
on multiple body language emotion recognition using
an off-the-shelf sensor.
This paper presents an approach for automatic
emotion recognition using body movements and pos-
tures. Using a Kinect we extract skeleton joint rota-
tions and meta-features. Using Dynamic Time Warp-
ing, to align sequence length, and Support Vector Ma-
chines we learn to classify natural emotions into the
following types: curiosity, confusion, joy, boredom
and disgust.
The main contributions of the paper are: a dataset
400
Kiforenko, L. and Kraft, D.
Emotion Recognition through Body Language using RGB-D Sensor.
DOI: 10.5220/0005783403980405
In Proceedings of the 11th Joint Conference on Computer Vision, Imaging and Computer Graphics Theory and Applications (VISIGRAPP 2016) - Volume 3: VISAPP, pages 400-407
ISBN: 978-989-758-175-5
Copyright
c
2016 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

of non-acted bodily expressed emotions (Sec. 3), an
approach for emotion recognition using body posture
and movements (Sec. 4) and quantitative results of
the method used (Sec. 5).
2 RELATED WORK
Human emotion is a well studied topic. Many dif-
ferent emotion models have been proposed, but there
is no clear feature definition for all possible emotion
expressions. Even the amount of different emotions
is still a debated topic. Therefore scientists try to
search for basic (primary, true, fundamental)
1
emo-
tions. The idea behind basic emotions is that if people
around the world are expressing the same emotion in
the same way (which means that we can find the same
features) then these are instinctive emotions. Emo-
tions, that we want to categorise, are defined here as
movements where humans do not consciously control
their muscles — humans presumably have emotions
in order to deal with fundamental life-tasks (Ekman,
1992). Ortony and Turner (1990) summarised the ba-
sic emotions proposed in different works. There is
a lot of disagreement between theorists, and some of
the emotions have different names that mean the same
thing, for example, joy and happiness or fear and anx-
iety. Most of them include such emotions as anger
(rage), joy (happiness), sadness, fear (anxiety), dis-
gust, surprise. These emotions were the ones we tried
to trigger in this work by the use of visual stimuli.
Research on emotions in psychology is mostly
based on facial expressions in still images. Never-
theless there are multiple attempts to evaluate a se-
quence of actions, for example, research in Keltner
and Haidt (1999) shows that there exists a sequence
of movements for an embarrassment emotion which
has a duration of 5 sec.
According to Wallbott (1998), Ekman and
Friesens’ (1974) opinion, body movement expresses
the intensity of the emotion, not its quality. Re-
searchers have also shown that there exists a distinc-
tive body movement or posture that helps people to
recognise specific emotions (Scherer and Wallbott,
1990), (Ekman and Friesen, 1974), (Camras et al.,
1993). Wallbott’s (1998) research focussed on the
analysis of body movements and postures with refer-
ence to specific emotions. He provided evidence that
there are specific movements and postures that are as-
sociated with different emotions.
As stated earlier there have been attempts to auto-
matically recognise human emotions from body pos-
1
Different literature uses different terms.
tures and movements. Kapur et al. (2005) presented
an approach for recognising emotions in acted scenar-
ios from standing, full-body joint recordings. The ve-
locity and position of body joints were extracted from
VICON motion capture system recordings and used
to classify sadness, joy, anger and fear. The classi-
fication accuracy achieved was up to 92%. Glowin-
sky et al. (2011) also used acted emotions, recorded
using consumer video cameras. From a standing po-
sition for classification they used body posture repre-
senting through changes in joint extension, arm and
upper body position. The non-acted human emotions
from body language are recognised in the research
of Sanghvi (2011), Gaber-Barron and Si (2012), and
DMello and Graesser (2009). Sanghvi et al. (2011)
from the upper body of children playing chess with
a iCat robot, extracted meta-features related to the
movement and posture cues. They achieved a classifi-
cation rate of 82.2%. Gaber-Barron and Si (2012) ex-
tracted meta-features from joint rotation angles. They
achieved up to 66.5% classification accuracy for pre-
dicting such emotions as triumphant, concentrated,
defeated and frustrated. Recently Lee at al. (2014)
measured the engagement level of children while per-
forming different tasks on the computer, similar to the
research of Sanghvi (2011). They used a Kinect with
the upper body skeleton tracking. The engagement
level was classified into two classes: high and low.
The highest achieved recognition rate was 77.35%.
In contrast to others, in this work we are focus-
ing on non-acted human emotions that are triggered
by different visual stimuli and that are recorder us-
ing a Kinect. The recognised emotions are: curiosity,
confusion, joy, boredom, and disgust.
3 DATA ACQUISITION
There is no existing emotion database available that
contains the body posture and movements of a person
experiencing ”basic” non-acted emotions, recorded
using an easily accessible standard sensor. Klein-
smith et al. (2011) presented a dataset of body joints
emotion expression while playing video games. The
recordings were made using a Gypsy 5 motion capture
system. The disadvantage is that the emotions (defeat,
frustration, triumph and concentration) recorded are
usually related to interaction with games, but in this
research we were interested in getting more everyday
emotions.
To be able to acquire such data we developed
through a series of experiments and different set-ups a
recording system using a Kinect RGB-D sensor. The
recordings were made with 15 frames per second. The
Emotion Recognition through Body Language using RGB-D Sensor
401

participants were 13 students from age 20 till 29 — 4
females and 9 males.
Figure 1: Recording set-up.
Each participant, alone in the room, was shown a
set of videos and one game on a 32-inch flat-screen
TV with an Kinect device on top. The participants’
starting position was around 2 m away from the TV.
They were allowed to move in different directions.
The TV was placed 1.7m above the floor, the height
was chosen based on participants average height and
Kinect positioning recommendations. The recording
set-up is shown in Figure 1.
For triggering emotional responses, we used dif-
ferent visual stimuli. In order to acquire the six ”ba-
sic” emotions, preliminary tests were conducted using
different people. The videos most successful at elic-
iting emotional responses were chosen empirically.
First, the videos were tested on two or three sub-
jects. Their response was recorded and afterwards
they were asked how they felt. Based on their an-
swers and reactions, that specific video was removed
from the set or kept. After several rounds of such tests
a set of 13 different videos was collected, ranging in
length from 0:58 to 3:36 minutes.
One does not always get the same response to
the same video from different people. Experiments
showed that an emotion such as anger or surprise is
very hard to trigger by displaying a short video with-
out knowing the person. In order to record anger
a special voice controlled game was developed that
would irritate the participant on purpose. This was
achieved by randomly ignoring the users’ input.
For extracting body joint rotation angles The
Kinect for Windows Software Development Kit 1.6
was used. It has a skeleton tracking method imple-
mented, that out-of-the-box provides the position and
orientation of 20 joints (see Figure 2).
We used the recording system Kinect Toolbox 1.2,
developed by David Catuhe (Catuhe, 2013), modified
and improved to remove stream synchronization is-
sues and recording failures.
Different numbers of randomly chosen videos
for each participant were shown, depending on their
length. At the end people played the game. In order
Knee Left(KL)
Hip Left (HipL)
Foot Left
Foot Right
Knee Right (KR)
Hip Right (HipR)
Hip Center (HC)
Spine (S)
Wrist Right
Hand Right (HR)
Hand Left (HL)
Elbow Left (EL)
Shoulder Left (SL)
Wrist Left
Ankle Left (AL)
Ankle Right (AR)
Shoulder Center (SC)
Head
Shoulder Right (SR)
Elbow Right (ER)
Figure 2: Joint positions and abbreviations. Wrist and ankle
joints were not used in processing. Joints in blue represent
Right Arm, magenta – Left Arm , red – Head, green - Torso,
orange - Right Leg and purple - Left Leg joint combinations.
for a participant to feel more comfortable and make
it easier to start the system, the participant started
it by himself, using his hand to control the mouse.
This also functioned as a calibration test ensuring that
the skeleton was fully detected. Videos were shown
one after another, the recording turned on when each
video started and turned off and saved when the video
ended. The same is true for the game.
The recorded dataset is available at
https://gitlab.com/caro-sdu/covis-data/visapp 2016.
It contains each participants skeleton joint recordings
in xml format and labelling information.
3.1 Recording Segmentation
The observation of recorded participants’ responses
showed that during one video a participant could ex-
press multiple emotions. For example, at the begin-
ning the participant might show boredom and later
joy. Therefore the recorded videos were segmented in
order to get one (or multiple) emotions per sequence.
From the recorded sequences we extracted a skele-
ton’s 16 joint Hierarchical Rotation (HR) angles, Pro-
jective Coordinates
2
and World Coordinates
3
. The 2
wrist and 2 ankle joints were omitted (see Figure 2)
because their detection was unstable.
From observation of our recorded data we have
defined the following hypotheses: if a human is ob-
serving some video input and suddenly starts to move,
then it is very likely that it is the visual input he sees
that makes him move. Taking this into consideration
2
consist of 3D vector x,y,z, where x and y are point pixel
values and z is real world distance, expressed in millimetres.
3
is the projection of point x and y values into Euclidean
space, x and y are expressed in meters, z in millimetres.
VISAPP 2016 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
402

Figure 3: Emotion segmentation example. Different colours represents different joints rotations. Not all used joints are shown
in the image. PE stands for possible emotion sequence.
the idea is that the participant’s sudden movements
are possibly an emotion being expressed.
To find these sudden movements, changes in joint
hierarchical rotation from frame to frame were calcu-
lated using Euclidean distance from skeleton rotation
angles from frame n + 3 to n, for example, from frame
3 to frame 0. Rotation angle changes were calculated
for each joint and “significant” changes in the joint
rotation angles were defined to be over the thresh-
old value of 0.02 degrees, chosen empirically. The
sequence was cut using the threshold ±10 frames,
which also was found empirically. After finding the
ranges for each joint, which were manually combined,
finding the smallest and the highest frame number.
An example of one sequence segmentation in show
in Figure 3.
3.2 Sequence Labelling
From the recordings we extracted a set of 304 po-
tential emotion sequences. In this experiment it was
not possible to get the ground truth of what the ob-
served person was feeling in specific moment, so the
labelling was performed manually, using a group of
four people. This group of labellers was not told the
total number of emotions nor were they told which
emotions to look for. 250 sequences were classified
as containing emotions. The knowledge about what
the participant was watching in each video was given
to the labellers after they classified the sequences.
Once labellers knew what the participant was watch-
ing, some of the emotions that had been labelled as
bored, became disgust. Only the videos where all
four people agreed on the emotional label were pre-
served. Five clusters or classes contained most of the
sequence fragments. These five classes differed from
that initially expected, being curiosity, confusion, joy,
boredom, disgust, where we expected the classes to
be anger, joy, sadness, fear, disgust, surprise.
The class bored contained much more data than
the other emotions, so some of the bored fragments
were removed randomly. The total number of remain-
ing emotion sequences is 187 and length statistics are
shown in the Table 1.
Table 1: Recorded data. seq stands for sequences.
Min/Max/Mean is the number of frames.
Emotion
Number of
Min Max Mean
seq people
Curiosity 31 10 10 145 37.80
Joy 41 8 13 129 58.39
Confusion 36 10 18 142 46.65
Boredom 41 12 46 133 78.12
Disgust 38 7 10 151 52.15
4 METHODOLOGY
For emotion classification we are using raw data (joint
Hierarchical Rotation angles) and meta-features ex-
tracted from joint data. The emotion classification di-
agram is shown Figure 4.
Figure 4: Emotion classification diagram.
The following section presents a detailed explana-
Emotion Recognition through Body Language using RGB-D Sensor
403

tion of the meta-features and classifier used.
4.1 Meta-feature Extraction
Many publications, e.g. (Glowinski et al., 2011)
(Gaber-Barron and Si, 2012) (Gunes and Piccardi,
2005) (DMello and Graesser, 2009) (Sanghvi et al.,
2011), show that the use of meta-features is better
than raw joint data in emotion classification. Cur-
rently the work with the highest success rate on real
human emotion is by Garber-Barron and Si (2012).
Their work is used as inspiration for our research and
most of the meta-features that they propose are imple-
mented here, plus some additions. Please note that in
contrast to the work of Garber-Barron and Si, we are
using our own dataset, in order to get normal and not
game-related emotions.
Garber-Barron and Si divide their meta-features
into three different groups to test their performance,
in this work we are using the same groups. The group
names are: Posture Group, Limb Rotation Movement
Group and Posture Movement Group.
The Posture Group contains ten different features
of theirs plus two additional features proposed in this
work:
1. Pose Difference (HR
4
) (Left Arm, Right Arm)
2. Pose Difference (HR) (Left Leg, Right Leg, Head)
3. Pose Symmetry (HR) (Left Arm, Right Arm,
Head)
4. Directed Symmetry (HR) (Left Arm, Right Arm,
Head)
5. Pose Symmetry (WC
5
) (Left Leg, Right Leg, Hip)
6. Directed Symmetry (WC) (Left Leg, Right Leg,
Head)
7. Head Offset
8. Head Alignment
9. Head Chest Ratio
10. Leg Hip Openness
11. Body Lean
12. Body Openness
The meta-features are listed and explained in Ta-
ble 2. Pseudo code for the new meta-features intro-
duced – Body Lean and Body Openness – is given be-
low:
procedure BodyLean (SL, SR, HipL, HipR)
avgShoulders = average(SL, SR)
avgHips = average (HipL, HipR)
return avgShoulders - avgHips
end procedure
4
Joint Hierarchical Rotation.
5
Joint World Coordinate.
procedure BodyOpenness (SL, EL, HL, SR, ER, HR)
result = 0
if (SL/SR_x >= EL/ER_x & SL/SR_x >= HL/HR_x)
result += 0.5
else
if (SL/SR_x >= EL/ER_x & SL/SR_x <= HL/HR_x)
result += 0.25
return result
end procedure
Body Lean is the feature that is often used in hu-
man interest recognition e.g. (DMello and Graesser,
2009), (Kapoor et al., 2004). Observations in this
work showed that such a meta-feature could be use-
ful when describing the emotion curiosity. Following
Garber-Barron and Si (2012) and their use of “lower
body openness” (see Leg Hip Openness in Table 2),
we compute upper body openness – the alignment of
the shoulder, elbow and hand in order to see if this
feature is important in emotion recognition too.
Each element from the Posture Group is computed
for each frame in a sequence.
The Limb Rotation Movement Group contains 3x6
features that are computed per each frame. For each
feature, inputs are combined joint data, the possible
combinations (6) and their names are shown in Figure
2. Each combination is an average value of joints, for
example, torso is a 3D vector, where each value is
average(SC
n
, S
n
, HipC
n
). Limb Rotation Movement
Group features are:
1. Average Rate of Change (Joint combinations)
2. Relative Movement (Joint combinations)
3. Smooth-Jerk (Joint combinations)
The third group –Posture Movement Group – com-
bines movement features. It contains 3x12 features:
1. Average Change of Rate (Posture Group)
2. Relative Movement (Posture Group)
3. Smooth-Jerk (Posture Group)
4.2 Classification
To classify emotion sequences we used a Support
Vector Machine (SVM) classifier. SVM was cho-
sen, because it performs well on data sets that have
many attributes, it requires only few training sam-
ples, and it is often used in sequence classification.
We used the SVM classifier implementation from data
mining software Weka (Witten et al., 2011), that is
trained using a sequential minimal optimization al-
gorithm (SMO). SVM implementations cannot deal
with different length sequences, therefore emotion se-
quence length was normalized to extend all sequence
lengths to match the longest one. We used Dynamic
Time Warping (DTW) (Ratanamahatana and Keogh,
VISAPP 2016 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
404
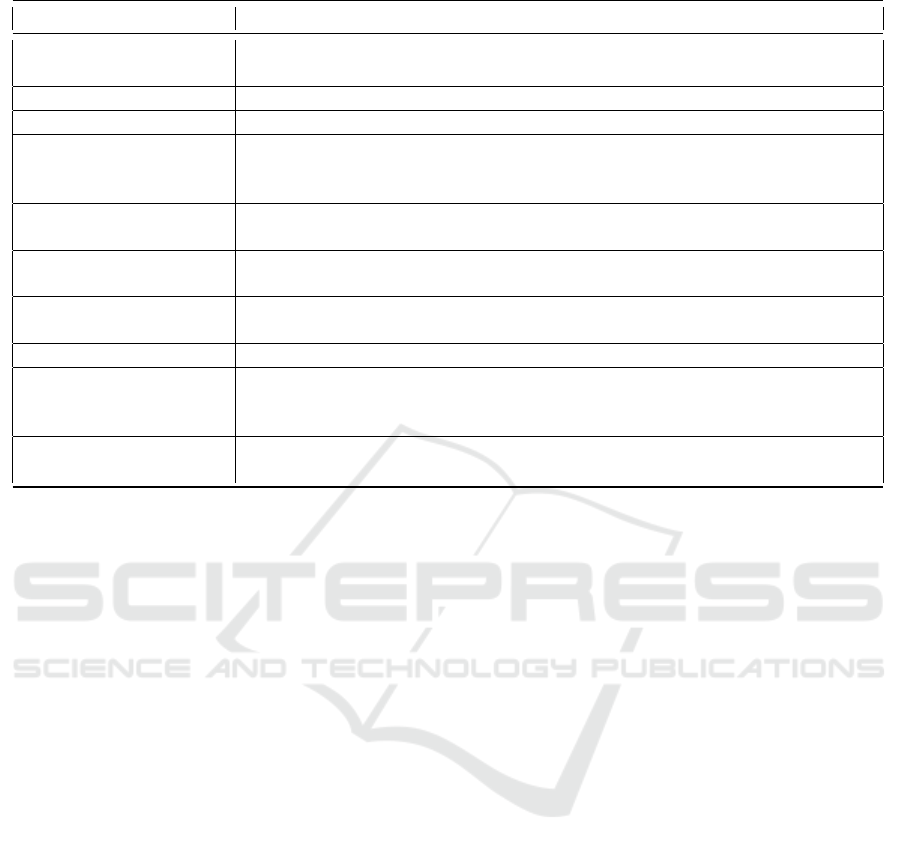
Table 2: Meta-features. For a more detailed description, please refer to Garber-Barron and Si (2012).
Meta-feature name Explanation
Pose Difference Represents the Euclidean distance between left and right parts of the body and
returns the mean.
Pose Symmetry Represents joints misalignments/asymmetry.
Directed Symmetry Calculates the direction of the asymmetry in Pose Symmetry.
Head Offset Alignment Estimates the relationships between head and chest, head and hips. It returns
three values – the Euclidean distance between head location and hip centre,
head rotation, and average hip rotation.
Leg Hip Openness Represents the openness of the lower part of the body by computing the ratio
between the hip-ankle distance and knee distance.
Average Rate Of Change Estimates the speed of changes of the feature over a specified time interval
(window). The feature changing can be joint angle, Pose Difference, etc.
Relative Movement Represents the amount of movement of a feature over a period of time (window)
compared to the entire sequence.
Smooth-Jerk Represents feature relative variance over specific time period.
Body Lean Body Lean is the difference between average hips and shoulder position, which
shows the direction and amount of movement in the z axis. As an input feature,
it uses joints 2D coordinates.
Body Openness Calculates the alignment of the shoulder, elbow and hand. As an input feature,
it uses joints 2D coordinates.
2005) using the NDTW library (Oblak, 2013) and
fine-tuned the parameters for both DTW and SVM.
The DTW parameters for raw data are: no constraints
and Manhattan distance, for meta-features – Sakoe-
Chiba band (50) and Euclidean distance.
For meta-features we set the window size to 20%.
Initial results showed that it is better to perform DTW
first, then extract meta-features. A problem may
arise due to short sequences being stretched, since
the movements are flattened out which produces a
lot of zeros in meta-features that calculate changes
and especially rates of change in body movements
and postures. This could potentially lead to a prob-
lem whereby the classifier could only classify short
or long sequences. To show that this is not the case,
we looked at the emotion sequence length variance
within each emotion class. The variance is high for all
classes, indicating that both short and long sequences
are present.
The parameters used for raw data for SVM are:
C = 23 and Polynomial kernel (exponent = 4); for
meta-features: RBF kernel C = 18 and γ = 10
−4
.
5 RESULTS
This section gives the results for emotion classifica-
tion using joint hierarchical rotation data (raw data)
and meta-features individually and combined. For
comparison we use the overall classification percent-
age, performing 10-fold cross-validation on the entire
emotion dataset.
5.1 Raw Data Result
Results (see Figure 5) show that by using all 16 joints,
the classification accuracy is 43.32%. For five emo-
tions random choice would lead to an average classi-
fication rate of 20%.
We also evaluated the performance of each joint
separately: the mean value for all joints is 27.07%, the
worst classification accuracy (15.51%). This worst
accuracy is obtained when using only the HipLeft
joint, suggesting that this joint either performed very
small movements or that the same movements were
done with this joint across all the emotion classes.
The highest (32.62%) classification accuracy occurs
when using the KneeRight joint.
5.2 Meta-features Result
Each group of features that was predefined in Sec. 4
is evaluated and the result summary can be seen in
Figure 5. We also evaluated the performance of each
individual feature in a group.
The Posture Group has the lowest classification
accuracy across meta-feature groups – 31.55%. The
strongest feature from the Posture Group is Body
Lean, with a classification rate of 27.81%.
When using all features from the Limb Rotation
Emotion Recognition through Body Language using RGB-D Sensor
405

Classification (%)
0 20 40 60 80
Raw data (16 Joints Hierarchical Rotations)
Posture Group (PG)
Limb Rotation Movement Group (LRMG)
Posture Movement Group (PMG)
Meta−features (PG + LRMG + PMG)
Raw data + Meta−features
43.32
31.55
40.11
42.78
48.66
55.62
Figure 5: Emotion classification results for different fea-
tures.
Movement Group (Joint combinations) the classifi-
cation accuracy is 40.11%. The best performance
achieved for the Smooth Jerk (Joint combinations)
group – 33.16%.
The last group Posture Movement Group has the
highest classification accuracy – 42.78%. Smooth
Jerk (Posture Group) performed best at 34.76%,
while Average Rate of Change (Posture Group) per-
formed worst at 24.06%.
Gaber-Barron and Si (2012) also found that the
performance of Posture Movement Group was a lit-
tle better than that of the other groups. This result
shows that it is better to look at how a specific fea-
ture changes over time rather than just consider static
postures (e.g. pose symmetry, head relationship with
hips).
5.3 Raw Data and Meta-feature
Combined Result
The overall results show that combining all meta-
features performs better than just using the raw data.
The highest performance (55.62%) is achieved by
combining both all raw data and all meta-features.
The confusion matrix of the combined result is shown
in Figure 6. From these results we can conclude that
disgust and boredom are the most correctly recog-
nised emotions. Figure 6 shows that the expression
of joy and confusion cause similar body postures and
movements. There are also similarities between joy
and boredom.
6 CONCLUSIONS
In this work we show that real human emotions can be
classified through recorded body movements and pos-
Figure 6: Combined result confusion matrix.
tures collected using a standard RGB-D sensor. First,
an emotional dataset was collected: snippets of emo-
tional reaction to visual cues. The human skeleton
data was extracted, preprocessed, and the labelled se-
quences used for classification. The results were eval-
uated through experimentation.
Our results show that using a combination of joint
rotation data and meta-features the classification of
emotions is higher then using them individually.
The highest classification accuracy achieved is
55.62% for our five emotions. To our knowledge
there is no other research that classified the same real
humans emotions using recordings made by Kinect.
Therefore we can not directly compare our results
with others. The closest work is by Garber-Barron
and Si (2012), they classified four emotions (tri-
umphant, concentrated, defeated, frustrated) using
non-acted human responses and achieved overall ac-
curacy of 66.5%. They also showed that by using
meta-features it is possible to get higher classifica-
tion accuracy. Other works in emotion recognition
from body posture and movements are mostly based
on acted emotions. These achieve impressive classifi-
cation rates, but acted emotions are more intense and
actors normally use the same initial position and can
reliably repeat very similar actions and action dura-
tion to express the same emotion, which makes the
classification easier.
Our conclusion as to why the classification rate
is only 55.62% is that there is not enough data —
people express emotions in too many ways: Ekman
and Friesen (1993) found 60 different ways to ex-
press anger. The intensity of the emotion is also an
important factor — by observing the recorded data,
the ”short” emotions (1–2 seconds) seem to be simi-
lar in body movements across five emotions. In this
work the reflex and habit actions, that according to
Darwin (1872) has a significant influence on emo-
tion expressed, have not been examined and excluded
from the emotional data. And it has been observed
VISAPP 2016 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
406

that some participants perform the same short action
sequence while expressing any emotion and keeping
these actions in our dataset could lead to faulty re-
sults. Such action examples are coughing or covering
mouth with the hand when yawning.
In a future work there are multiple aspects that can
be improved, for example, the emotion segmentation
method, make recordings in a real environment, try
different classifiers.
REFERENCES
Azcarate, A., Hageloh, F., S, K. V. D., and Valenti, R.
(2005). Automatic facial emotion recognition.
Camras, L., Sullivan, J., and Michel, G. (1993). Do infants
express discrete emotions? Adult judgements of fa-
cial, vocal, and body actions. Journal of Nonverbal
Behavior, 17:171–186.
Catuhe, D. (2013). Kinect toolbox. [Online; accessed 04-
April-2013].
Darwin, C. (1872). Expression of the emotions in man and
animals. John Murray.
DMello, S. and Graesser, A. (2009). Automatic detection
of learners affect from gross body language. Applied
Artificial Intelligence, 23:123–150.
Ekman, P. (1992). An argument for basic emotions. Cogni-
tion & Emotion, 6(3–4):169–200.
Ekman, P. (1993). Facial expression and emotion. American
Psychologist, 48:384–392.
Ekman, P. and Friesen, W. (1974). Detecting deception
from the body or face. Journal of Personality and So-
cial Psychology, 29:288–298.
Gaber-Barron, M. and Si, M. (2012). Using body move-
ment and posture for emotion detection in non-acted
scenarios. Fuzzy Systems (FUZZ-IEEE), 2012 IEEE
International Conference on 10-15 June 2012, pages
1–8.
Glowinski, D., Dael, N., Camurri, A., Volpe, G., Mortillaro,
M., and Scherer, K. (2011). Toward a minimal repre-
sentation of affective gestures. IEEE Transactions on
affective computing, 2(2):106–116.
Gunes, H. and Piccardi, M. (2005). Affect recognition from
face and body: Early fusion versus late fusion. IEEE
International Conference of Systems, Man, and Cy-
bernetics, pages 3437–3443.
Kapoor, A., Picard, R., and Ivanov, Y. (2004). Probabilis-
tic combination of multiple modalities to detect inter-
est. International Conference of Pattern Recognition,
3:969–972.
Kapur, A., Kapur, A., Virji-Babul, N., Tzanetakis, G., and
Driessen, P. F. (2005). Gesture-based affective com-
puting on motion capture data. In Affective Computing
and Intelligent Interaction, pages 1–7. Springer.
Keltner, D. and Haidt, J. (1999). Social functions of emo-
tions at four levels of analysis. Cognition & Emotion,
13(5):505–521.
Kleinsmith, A., Bianchi-Berthouze, N., and Steed, A.
(2011). Automatic recognition of non-acted affective
postures. Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part B: Cy-
bernetics, IEEE Transactions on, 41(4):1027–1038.
Lee, D., Yun, W. h., Park, C. k., Yoon, H., Kim, J., and
Park, C. H. (2015). Measuring the engagement level
of children for multiple intelligence test using kinect.
volume 9445, pages 944529–944529–5.
Oblak, D. (2013). Ndtw. [Online; accessed 30-May-2013].
Ortony, A. and Turner, T. (1990). What’s basic about basic
emotions? Psychological Review, 97(3):315–331.
Ratanamahatana, C. and Keogh, E. (April 21-23, 2005).
Three myths about dynamic time warping data min-
ing. SIAM International Conference on Data Mining,
Newport Beach, CA.
Sanghvi, J., Castellano, G., Leite, I., Pereira, A., McOwan,
P., and Paiva, A. (2011). Automatic analysis of affec-
tive postures and body motion to detect engagement
with a game companion. In Billard, A., Jr., P. H. K.,
Adams, J. A., and Trafton, J. G., editors, Proceedings
of the 6th International Conference on Human Robot
Interaction, HRI 2011, Lausanne, Switzerland, March
6-9, 2011, pages 305–312. ACM.
Schaaff, K. and Schultz, T. (ACII 2009. 3rd International
Conference on 10-12 Sept. 2009). Towards emo-
tion recognition from electroencephalographic sig-
nals. Affective Computing and Intelligent Interaction
and Workshops.
Scherer, K. and Wallbott, H. (1990). Mimik im Kontext—
Die Bedeutung verschiedener Informationskomponen-
ten fr das Erkennen von Emotionen. Hogrefe.
Singh, G., Jati, A., Khasnobish, A., Bhattacharyya, S.,
Konar, A., Tibarewala, D., and Janarthanan, R. (Third
International Conference on 26-28 July 2012). Nega-
tive emotion recognition from stimulated eeg signals.
Computing Communication & Networking Technolo-
gies (ICCCNT).
Wallbott, H. (1998). Bodily expression of emotion. Euro-
pean Journal of Social Psychology, 28:879–896.
Witten, I. H., Frank, E., and Hall, M. A. (2011). Data
Mining: Practical Machine Learning Tools and Tech-
niques. Elsevier, 3rd edition.
Emotion Recognition through Body Language using RGB-D Sensor
407
