
A Development Methodology for a Stroke Rehabilitation Monitoring
Application
Pilar Mata
1
, Craig Kuziemsky
2
and Liam Peyton
1
1
Faculty of Engineering, University of Ottawa, 800 King Edward Avenue, Ottawa K1N 6N5, Canada
2
Telfer School of Management, University of Ottawa, 55 Laurier Avenue East, Ottawa K1N 6N5, Canada
Keywords: Clinical Performance Monitoring, Application Development Methodology, Stroke Rehabilitation
Monitoring, Performance Measurement, Healthcare.
Abstract: The capabilities of mobile devices (e.g. flexibility, portability, and the ability to retrieve information
quickly) have been leveraged for the development of clinical performance monitoring applications. In this
paper we assess the suitability of a methodology for development of clinical performance monitoring
applications to support stroke rehabilitation. We use a case study, with two use cases of patients recovering
from stroke events, to design a monitoring application at a conceptual level and compare it to other clinical
performance monitoring applications.
1 INTRODUCTION
Healthcare information technology (HIT) has the
potential to enhance care delivery by providing
timely access to data that can be used to deliver
patient centred care (IOM, 2012). A particular
benefit of HIT is the ability to monitor care delivery
across providers and settings (Xu et al., 2015).
Mobile devices can be particularly valuable for
monitoring care delivery. The capabilities of mobile
devices (e.g. flexibility, portability, and quick
information retrieval) have been leveraged in the
development of clinical performance monitoring
applications for practice profiling and community
care (Ferenchick et al., 2010; Ferenchick and
Solomon, 2013; Chamney et al., 2014).
Monitoring care delivery across diverse care
providers and settings requires defining
measurement goals and then consolidating data from
fragmented data sources to monitor the goals
(Vincent et al., 2014). For example, a clinical
process can involve multiple healthcare actors (e.g.
doctors, nurses, therapists, pharmacists) that
generate and store data in heterogeneous systems
(e.g. electronic health record systems, paper based
charts). Also, the same process may have different
workflows across providers, generating inconsistent
data. The overarching challenge is that data needed
to monitor a process may not be available at the
right time using existing data sources.
Developing performance monitoring applications
is a bounding problem as one needs to define the
objectives and goals to be monitored and then
identify and integrate the data needed for monitoring
to occur. There is also a need for user involvement
in the design of such applications, owing to the high
rate of failure in the implementation of HIT (Avison
and Young, 2007; Novak et al., 2012) that occurs
from a disconnect between clinicians and the HIT
development team (Avison and Young, 2007).
The predominant question is how to define the
goals and metrics to enable collecting the right data,
at the right time, for the right metrics. Much of the
existing work in this area has focused on reactive
responses to problems where issues are identified
after the fact (Kuziemsky, 2015). A better solution
would be to pro-actively identify and manage data
collection and integration issues so they can be dealt
with in real-time. However, doing that requires a
method that is robust enough to define and obtain
the necessary metrics and data but is flexible enough
to enable goals or metrics to be adapted as needed
(Vincent et al., 2014).
In this paper we assess the suitability of a
methodology for development of clinical
performance monitoring applications to support
stroke rehabilitation. We use a case study, with two
use cases of patients recovering from stroke events,
to design a monitoring application at a conceptual
400
Mata, P., Kuziemsky, C. and Peyton, L.
A Development Methodology for a Stroke Rehabilitation Monitoring Application.
DOI: 10.5220/0005785104000405
In Proceedings of the 9th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies (BIOSTEC 2016) - Volume 5: HEALTHINF, pages 400-405
ISBN: 978-989-758-170-0
Copyright
c
2016 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
level. Finally, we compare the development of the
stroke monitoring application against two other
clinical performance monitoring applications we
developed in previous research. We conclude with a
discussion of the implications for designing clinical
monitoring applications to support different types of
monitoring in healthcare delivery.
2 BACKGROUND
Stroke rehabilitation is the care processes that occur
after a patient has been stabilized from a stroke
event. Early rehabilitation interventions may
positively impact rehabilitation outcomes (i.e.
recovery of functional disabilities) and an integrated
multidisciplinary approach is key to ensure optimal
recovery (Duncan et al., 2005). Depending on the
severity of the event, the rehabilitation team may
include more than one care provider (e.g. physical
therapist, speech therapist, occupational therapist,
physician, nurse, or pharmacist). Family members
may also be involved in the rehabilitation process
(Gresham et al., 1997). Regular communication
between the care team on patient’s progress towards
common goals can positively impact patient's
rehabilitation outcomes (Cifu and Stewart, 1999).
An individualized stroke rehabilitation plan is
designed for each patient and it includes specific
rehabilitation goals and targets for each of the
exercises. The goals are defined in agreement with
the patient, family and care team (Gresham et al.,
1997). Monitoring progress of the patient’s plan
towards meeting rehabilitation goals and exercise
targets is important in order to identify gaps and
make adjustments as needed (Gresham et al., 1997).
One of the most commonly measurements used to
assess patient rehabilitation progress is the
Functional Independence Measure score (FIM)
(Duncan et al., 2005; Brown et al., 2015).
HIT is one way to increase quality of patient care
through efficient coordination and deployment of
resources in the community (Chukmaitov et al.,
2014). Recent studies have explored the use of
mobile applications in clinical settings to support the
provision of better care (Baarah et al., 2012;
Ferenchick and Solomon, 2013).
A Clinical Performance Monitoring Application
(CPMA) is a type of Business Intelligence
application (Chamney et al., 2014) that collects and
integrates data from various data sources in order to
compute metrics to instantiate goals related to the
performance of a particular clinical task or process.
In previous research, we developed a methodology
for development of CPMAs (Mata et al., 2015). Two
applications were used to show proof of concept of
the methodology: the Standards and Indicators
Dashboard (SAID) (Mata et al., 2014) and the
Resident Practice Profile (RPP) (Chamney et al.,
2014).
One core aspect of the development
methodology is to leverage user-centred design
methods to ensure user acceptance and adoption.
User centred design involves “users for a clear
understanding of user and task requirements,
iterative design and evaluation, and a multi-
disciplinary approach” (Vredenburg et al., 2002).
3 DEVELOPMENT
METHODOLOGY FOR CPMA
The development methodology for CPMA is a user-
centred design approach that engages users,
developers and project champions in an iterative
process of application modelling, implementation
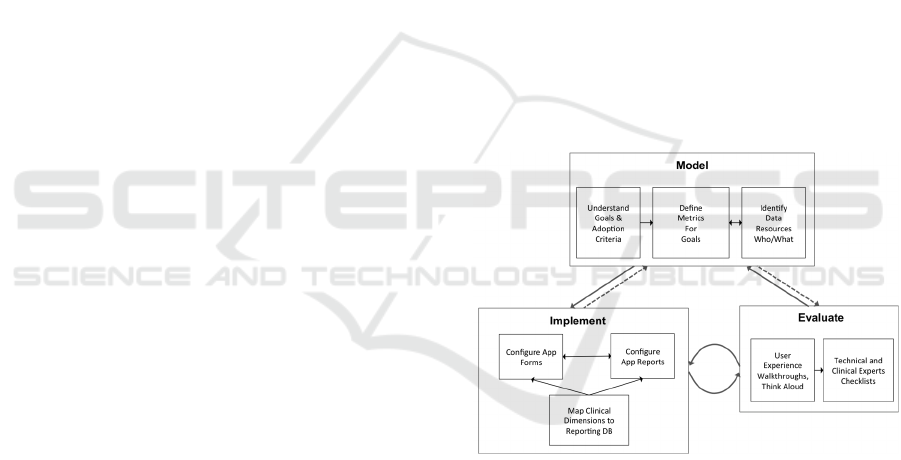
and evaluation. Figure 1 depicts the three main
phases in the development methodology.
Figure 1: CPMA Development Methodology.
The first phase in the methodology is the
modelling of goals, metrics and data sources. This
phase is led by clinical and technical experts with
the aim to understand the clinical process and define
goals for monitoring. Next, they identify and define
adoption criteria to ensure adoption and acceptance
of the technology (refined later during the evaluation
phase). Analysis of the metrics, linked to goals and
data sources used to compute the metrics, is carried
out to provide meaningful insights on the clinical
process. The point is to define who will collect what
data, how and when, in order to compute the metric.
During the implementation phase, the clinical
process or task monitored is mapped to a star-
A Development Methodology for a Stroke Rehabilitation Monitoring Application
401

schema database model (Kimball, 2013) that is
optimized for fast querying and reporting. Data
related to the clinical process or task monitored is
mapped to a fact table. Clinical dimensions are
mapped to dimensional tables that represent the
attributes used to compute metrics. Each
dimensional table is linked to a control in a form
and, values in dimensional tables supply the values
for each of the controls in the form. Same values are
used for grouping, labelling and filtering metrics in
graph and chart reports.
The evaluation phase embraces user-experience
walkthroughs and think-aloud sessions in order to
understand the context and thought processes of the
users as they use the application. Clinical and
technical experts analyse the feedback obtained from
these sessions to generate checklists for
development of the application. Checklists are often
the result of trade-offs made between user needs and
adoption criteria and limitations and constraints of
the technology. This tension drives creative
solutions and innovations in user interface design.
The cycle of Model, Implement, and Evaluate is
repeated until no significant innovations and barriers
to user acceptance and adoption are identified during
the evaluation phase. The end of a cycle is reached
when clinical users and the development team are in
sync and only minor adjustments are required.
4 CASE STUDY: STROKE REHAB
PROGRAM
In our case study, we first define two use cases that
help us conceptualize the application development
by following the development methodology for
CPMA described in section 3.
Table 1: Use Case 1. Rehabilitation Plan - Betty.
Goal Therapy Target Metrics
Increase
Mobility
(ADLs)
Physical-
walking
75% # Steps (Day
n
-
Day
n-2
) > 10
Physical-
Treadmill
75% Maximal heart
rate <= beats of
predicted
maximum +20
Improve
retrieval
of words
Retrieval of
words
90% # Words
Retrieved (Day
n
-
Day
n-1
) >5
For the first use case, we have patient Betty. She
suffered a severe stroke event and after she was
stabilized from the event, the team at the acute care
unit in the hospital assessed her condition. Her
diagnosis included disabilities in more than one area
and the care team recommended her to be admitted
to the In-Patient Rehabilitation Unit. Physical
therapy and speech therapy were included in her
rehabilitation plan. The therapists at the In-Patient
discussed rehabilitation goals with Betty and her
family members. Table 1 shows goals, metrics by
therapy and, expected rehabilitation outcome targets
for each of the therapies. Information in table 1 is
just an example as metrics can change frequently as
the patient progress in her rehabilitation program.
Table 2: Use Case 2. Rehabilitation Plan - John.
Goal Therapy Target Metric
Increase
Mobility
(ADLs)
Physical-
walking
90% # Steps (Day
n
-
Day
n-1
) > 20
Improve
retrieval of
words
Retrieval
of words
50% # Correct
pictures selected
(Day
n
-Day
n-1
)
>10
The second use case refers to patient John. He
suffered a moderate stroke and was also assessed by
the team at the acute care unit in the hospital. The
team determined he had physical and speech
deficiencies. Table 2 depicts John’s rehabilitation
plan in terms of goals, metrics by therapies, and
rehabilitation outcome targets. Although Betty and
John’s rehabilitation plans are similar in terms of the
therapies they both require, the metrics for each of
their therapies vary, and the rehabilitation outcome
expectations before discharge are also different.
Therefore, the stroke rehabilitation monitoring
application needs to have sufficient flexibility to
accommodate different goals, metrics and targets
that drive the plans.
Following the development methodology for
CPMA described in section 3, we review the
modelling, implementation and evaluation phases
for designing a Stroke Rehabilitation Monitoring
Application.
4.1 Model
Modelling goals and metrics for a stroke
rehabilitation application is complex. The first step
is to understand goals and adoption criteria.
Rehabilitation programs require the collaboration of
a multidisciplinary team of healthcare providers and
information needs from each of the providers need
to be integrated seamlessly into one single
application that reports the overall progress of the
patient and the effectiveness of the care team.
HEALTHINF 2016 - 9th International Conference on Health Informatics
402

Goals can be defined at two levels. First, goals
related to the overall rehabilitation program (all
patients) that provides insights on performance of
the healthcare team. Second, we need to define goals
that provide insights on individualized rehabilitation
plans. Definition of metrics linked to goals at the
patient level is complex as rehabilitation goals are
tailored to specific needs of each patient by therapy.
For example, in our case study, at the patient level,
both Betty and John’s rehabilitation plan include
physical walking therapy. However, the number of
steps each patient is expected to take and frequency
of the therapy varies (10 steps for Betty every two
days and 20 steps for John daily). Also, the metrics
and benchmarks can vary as the rehabilitation
progresses.
Many data sources are needed as multiple
technologies (e.g. fitness tracking bands (i.e. FitBit),
speech apps) are used to support rehabilitation plans.
In our case study, we assumed that patients
performing the same exercise use the same
technology. This way we can standardize data
formats and define a set of pre-defined values for
each exercise by therapy that allows us to track
progress of therapies at both the patient and program
level.
4.2 Implement
The development methodology leverages the use of
QuickForms (Baarah et al, 2014), which is an
application framework optimized to collect data
directly into a reporting database. The database
model is a multi-dimensional model, i.e. star-
schema, with one fact table and multiple dimensions
linked to the fact table. Table 3 depicts the database
configuration of the Stroke Rehabilitation
application.
Individualized metrics can be assigned to each
patient in table Exercise_Multi and personalized
reports can be generated from the data that show
patient progress. In Table Exercise, we assign
standardized repetition values by exercise that is
used for reporting metrics on exercises at a program
level. Finally, by setting individual therapy goals in
table Patient, we can report on the overall progress
of the patient.
4.3 Evaluate
The evaluation of the Stroke Rehabilitation
application is complex given the multidisciplinary
nature of stroke rehabilitation which involves the
collaboration of multiple actors, all of whom are
candidates for data collection. Therefore, we need to
select at least one user representing each of
disciplines (e.g. physical therapist, speech therapist,
occupation therapist, pharmacist, and physician) as
part of the evaluation process. In addition, the
application is intended to empower patients and
family members/caregivers in decision-making and
enactment of a rehabilitation plan. Patients in a
stroke rehabilitation program have multiple needs,
which will require a careful selection of user
representatives that can participate in the evaluation
sessions. To understand how the application will
impact and be received by the various actors we use
a variety of usability evaluation approaches
including think-aloud and walk-throughs (Kushniruk
et al, 2013).
Table 3: Stroke Rehabilitation Database Schema.
Clinical
Dimension
Table Type Attributes
Rehabilitation
Plan
Rehabilitation_
Progress
Fact Exercise_Multi_ID; Exercise_Summary; Date; Therapist_ID;
Patient_ID; Therapy_ID; Age_ID; Gender_ID; Severity_ID;
Facility_ID
Tracking Date Dimensional Date; Day; Month; Year; Week
Therapist Dimensional Therapist_ID; Name; Email; Type
Patient Dimensional ID; Physical therapy target; Occupational therapy target;
Recreational therapy target; Speech therapy target; Pharmacist
therapy target
Therapy Dimensional Therapy_ID; Label
Demographics Age Dimensional Age ID; Age label
Gender Dimensional Gender ID; Label
Severity Dimensional Severity ID; Label
Facility Dimensional Facility ID; Name
Care Exercise Dimensional Exercise ID; Therapy ID; Domain; Category; Repetitions
Exercise_Multi Fact Exercise_Multi_ID; Exercise_ID; Metric; Completed
A Development Methodology for a Stroke Rehabilitation Monitoring Application
403
5 DISCUSSION
In this paper we have described our work in progress
research at developing a CPMA for stroke
rehabilitation.
A key contribution from our work is an
understanding of how CPMAs design for stroke
rehabilitation differs from CPMA design in other
domains. We compare the development of the
Stroke Rehabilitation application against the two
other CPMA’s we developed in previous research,
RPP and SAID (see Table 4). In terms of modelling,
RPP and SAID are much less complex as both
applications can be defined based on one single
generic performance model with the same set of
goals and metrics for all users. The clinical process
for RPP and SAID is clearly defined. For the Stroke
Rehabilitation application, there is no one single
clinical pathway but rather goals and metrics are
defined based on each patient's specific plan. In the
case of RPP and SAID, attributes to compute metrics
come from a set of predefined values. The multiple
clinical pathways in the stroke rehabilitation
program require consideration of multiple metrics
and possible values for the attributes used to
compute the metrics.
The implementation phase for the Stroke
Rehabilitation application also introduced new
challenges. Metrics are defined according to each
patient rehabilitation plan, which dramatically
increases the number of attributes required to
include in the application. As reports and forms are
linked together via the same reporting database, the
configuration of the reports is also complex.
Multiple are the reports that can be generated, and
the values that can be used to group and labelling
data in the reports. RPP and SAID, both have one
generic performance model, and attributes to
compute metrics can be easily mapped to forms.
The evaluation phase for the Stroke
Rehabilitation application is complex as it involves
multiple users with heterogeneous information
needs, including the patient. This is the first
application we have designed that brings the patient
into the evaluation group. Users of RPP and SAID
are homogeneous in terms of information needs, and
a smaller group of users with a smaller set of user
requirements suffices for evaluation purposes.
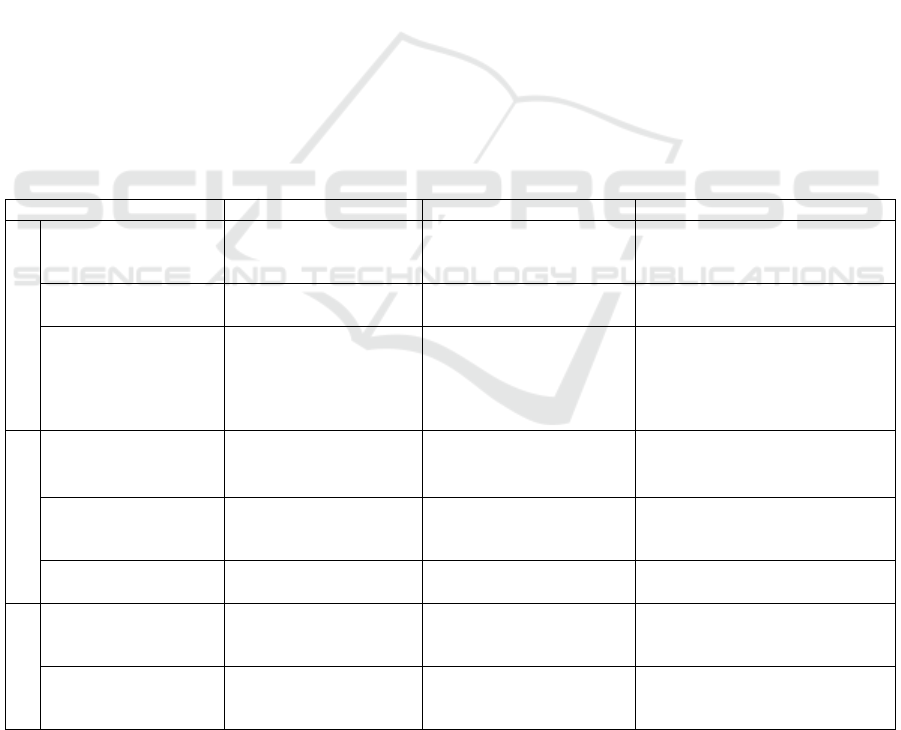
Table 4: CPMA Development Methodology - App Comparison.
Methodology RPP SAID Stroke Rehabilitation App
Model
Understand
Goals & Adoption
Criteria
Generic goals (program
curriculum).
Homogeneous users.
Generic goals (outcomes
of care). Homogeneous
users.
Individualized goals (Patient
rehabilitation goals).
Heterogeneous users.
Define Metrics For
Goals
One generic model. One generic model. Customized model for each
patient.
Identify Data
Resources Who/What
Homogeneous users.
Well-defined data
needs.
Homogeneous users.
Well- defined data needs.
Heterogeneous users. Highly
variable data needs.
Data sources are varied
Technologies as a driver
(monitoring and empowerment)
Implement
Map Clinical
Dimensions to
Reporting Database
Well-defined clinical
dimensions.
Well-defined clinical
dimensions.
Well defined clinical
dimensions.
Configure App Forms Fixed form attributes. Fixed form attributes. Variable form attributes
depending on patient’s
rehabilitation plan.
Configure App
Reports
Common metrics. Common metrics. Highly variable metrics.
Evaluate
User Experience
Walkthroughs, Think
Aloud
Homogeneous users. Homogeneous users. Heterogeneous users.
Technical and
Clinical Experts
Checklists
Residents
Programs directors
Administrative (training,
case manager)
Clinical (nurses)
Patient
Clinical (physicians, therapists,
caregivers)
HEALTHINF 2016 - 9th International Conference on Health Informatics
404

6 CONCLUSION AND
LIMITATIONS
Some adjustments to our development methodology
for CPMA are needed for development of
applications to support stroke rehabilitation
programs. The first consideration is due to the
variable clinical pathways that can be followed in a
stroke rehabilitation program, which adds
complexity to the definition of the performance
model -no one single model can be defined-.
Second, the implementation of the application is
challenging as the configuration of forms and reports
must be flexible to tailor to the specific information
needs of each patient. Third, this is the first
application that targets the patient as a user. As
multiple are the clinical pathway that can be
followed during rehabilitation, multiple are the
information needs for each patient. A careful
selection of patient representatives is key to ensure
success during the evaluation phase.
This paper presents our in-progress research on
the development of a stroke rehabilitation
application following a specific methodology for
development of CPMAs. We acknowledge our
analysis is limited in that we have not yet developed
a prototype to evaluate proof concept of our
approach.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We acknowledge funding support from the Mitacs
Accelerate program, NSERC and IBM.
REFERENCES
Avison, D., & Young, T. (2007). Time to rethink health
care and ICT? Commun.ACM, 50(6), 69-74.
Baarah, A., Mouttham, A., & Peyton, L. (2012).
Architecture of an event processing application for
monitoring cardiac patient wait times. International
Journal of Information Technology and Web
Engineering (IJITWE), 7(1), 1-16.
Brown, A. W., Therneau, T. M., Schultz, B. A., Niewczyk,
P. M., & Granger, C. V. (2015). Measure of functional
independence dominates discharge outcome prediction
after inpatient rehabilitation for stroke. Stroke; a
Journal of Cerebral Circulation, 46(4), 1038-1044.
Chamney, A., Mata, P., Viner, G., Archibald, D., &
Peyton, L. (2014). Development of a resident practice
profile in a business intelligence application
framework. ICTH-2014, Halifax, Canada.
Chukmaitov, A., Harless, D. W., Bazzoli, G. J., Carretta,
H. J., & Siangphoe, U. (2014). Delivery system
characteristics and their association with quality and
costs of care. Health Care Management Review, 40(2),
92-103.
Cifu, D. X., & Stewart, D. G. (1999). Factors affecting
functional outcome after stroke. Archives of physical
medicine and rehabilitation, 80(5), S35-S39.
Duncan, P. W., Zorowitz, R., Bates, B., Choi, J. Y.,
Glasberg, J. J., . . . Reker, D. (2005). Management of
adult stroke rehabilitation care. Stroke; a Journal of
Cerebral Circulation, 36(9), e100.
Ferenchick, G. S., Foreback, J., Towfiq, B., Kavanaugh,
K., Solomon, D., & Mohmand, A. (2010). The
implementation of a mobile problem-specific
electronic CEX for assessing directly observed
student-patient encounters. Medical Education Online,
15.
Ferenchick, G. S., & Solomon, D. (2013). Using cloud-
based mobile technology for assessment of
competencies among medical students. PeerJ, 1, e164.
Gresham, G. E., Duncan, P. W., & Stason, W. B. (1997).
Post-stroke rehabilitation DIANE Publishing.
IOM (Institute of Medicine). (2012). Health IT patient
safety: Building safer systems for better care.
Washington DC: The National Academic Press.
Kimball, R. (2013). The data warehouse toolkit,(3rd ed.).
Indianapolis, Ind. Wiley.
Kushniruk, A., Nohr, C., Jensen, S., & Borycki, E. M.
(2013). From usability testing to clinical simulations.
Yearbook of Medical Informatics, 8, 78-85.
Kuziemsky, C. E. (2015). A model of tradeoffs for
understanding health information technology
implementation. Studies in Health Technology and
Informatics, 215:116-28.
Mata, P., Chamney, A., Viner, G., Archibald, D., &
Peyton, L. (2015). A development framework for
mobile healthcare monitoring apps. Personal and
Ubiquitous Computing, 19(3-4), 623-633.
Novak, L., Brooks, J., Gadd, C., Anders, S., & Lorenzi, N.
(2012). Mediating the intersections of organizational
routines during the introduction of a health IT system.
European Journal of Information Systems, 21(5), 552-
569.
Vincent, C., Burnett, S., & Carthey, J. (2014). Safety
measurement and monitoring in healthcare: A
framework to guide clinical teams and healthcare
organisations in maintaining safety. BMJ Quality &
Safety, 23(8), 670-677.
Vredenburg, K., Mao, J., Smith, P. W., & Carey, T.
(2002). A survey of user-centered design practice.
Proceedings of the SIGCHI Conference on Human
Factors in Computing Systems, 471-478.
Xu, B., Xu, L., Cai, H., Jiang, L., Luo, Y., & Gu, Y.
(2015). The design of an m-health monitoring system
based on a cloud computing platform. Enterprise
Information Systems, 1-20.
A Development Methodology for a Stroke Rehabilitation Monitoring Application
405
