
Personalizing Game Selection for Mobile Learning
With a View Towards Creating an Off-line Learning Environment for Children
Mohamed Metawaa
1
and Kay Berkling
2
1
Department of Computer Science, German University of Cairo, Cairo, Egypt
2
Department of Computer Science, Cooperative State University, Kalrsruhe, Germany
Keywords:
Gamification, MOOC, Education, Children, Games, Mobile Learning.
Abstract:
Online education nowadays plays a very important role in enhancing the educational processes mostly for
adults. Given this maturing technology and the number of children that lack access to safe education, mobile
education for children is a logical next step and opens options that change their prospects. This paper is
part of a larger project on mobile learning with games for children without access to schools. Games can
motivate children to learn without the necessity of a teacher. The goal is to recommend learning games based
on children’s preferences of past choices and ratings, which can supplement other recommender systems. The
resulting implemented algorithm is designed as a plug-in to exisiting learning platforms that use games. Such
a system was implemented and evaluated in a feasibility study on adults. We show that a prediction based on
user’s choice and rating of games corresponds to a direct survey to determine the gamer types in 66% of the
cases for 61 participants.
1 INTRODUCTION
At the beginnings of the 21st century the E-learning
concept emerged uncovering many opportunities
(Bullen, 2003) of providing quality education for the
unfortunate and filling the gaps in our pre-existing ed-
ucational systems. Such gaps include and are not lim-
ited to accessibility to educational facilities and mate-
rials as well as personalization and customizability of
the educational process. While some integrated this
breakthrough in their old systems others did not and
maintained the classical way of educating students.
E-learning faces many criticisms such as the lack
of human interaction, absence of standards and the
ambiguity of the information delivery process (Tavan-
garian et al., 2004). But E-learning was introduced as
a solution to expand our educational reach and limits,
rather than a way of replacing traditional education.
With the advent of MOOCs (Massive Open On-
line Courses) the educational landscape has changed
once again to render education independent of geog-
raphy. These courses are primarily geared towards
adults; few courses on edX and Coursera are address-
ing children or adolescents. Khan academy (Thomp-
son, 2011) also offers a platform for learning, not
community based but addressing children specifically.
The platforms are generally not adaptive and addition-
ally struggle with issues of retention and motivation
(Khalil and Ebner, 2015).
Our goal is to provide a mobile platform geared
towards providing an education for children at the
elementary years regardless of their location, keep-
ing in mind minimal technological and logistic con-
straints (Berkling et al., 2016). Since it is assumed
that teachers are not available, the education must be
self-motivating. We therefore propose games, the old-
est way to learn, to be used as a vessel for learning
chunks of content leveled according to the common
core standards (National Governors Association Cen-
ter for Best Practices, 2010). To quote James Paul
Gee, ”Learning is for nearly all good games a core
mechanic” (Steinkuehler et al., 2012, p. xvii).
In this work we study the art of personalizing the
educational process and educational games by study-
ing how to provide ”The right game, for the right
student, at the right time”. While recommender sys-
tems tend to look at external factors (Felfernig et al.,
2013), we look at internal characteristics specific both
to games and users. This system can then be used
jointly with other proven recommender systems. Var-
ious psychological and gamification concepts are ana-
lyzed in order to study their application towards build-
ing an educational environment suitable for each stu-
dent. Having selected one of the models, a system
306
Metawaa, M. and Berkling, K.
Personalizing Game Selection for Mobile Learning - With a View Towards Creating an Off-line Learning Environment for Children.
In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Computer Supported Education (CSEDU 2016) - Volume 1, pages 306-313
ISBN: 978-989-758-179-3
Copyright
c
2016 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

is implemented and evaluated. In a feasibility study
the evaluation takes place on adults who share moti-
vations with children for gaming (Yee, 2006a).
Chapter 2 explores a number of learning and
personality styles and analyses their usefulness for
the application of interest. Chapter 3 describes the
methodology used in the preliminary study for a cho-
sen model. Chapter 4 will evaluate the results, fol-
lowed by a critical discussion and conclusions in
Chapter 6.
2 THEORETICAL BACKGROUND
In this section, researched learning styles, followed
by personality types and finally, gaming styles are re-
viewed. The models were examined with respect to
their suitability regarding the following requirements:
1) What type of assessment is used to identify a users
type? 2) Can this assessment be applied to children?
3) Can games be categorized based on the model? 4)
Can the category be assessed given the model?
2.1 Learning Styles
In a first approach, personalization of the online edu-
cational process might be based on how people learn.
Learning styles also constitute a mature research area
to build on.
The Grasha-Riechmann student leraning scales
(Rollins, 2015; Riechmann and Grasha, 1974), Kolb’s
learning style model (Kolb, 2005), NASSP (Keefe
et al., 1986) and Anthony Gregorgc’s learning style
models (Gregorc and Butler, 1984) have been consid-
ered for this purpose.
2.2 Personality Types
A different perspective to personalizing the website is
based on the student personality, trying to understand
their motivation in order to suggest the appropriate
game for the right student.
Myers-Briggs personality type indicator (MBTI)
is different from the previous classifications because
it defines personality types. MBTI was created based
on Jung’s typology and is one of the most widely ac-
knowledged and acceptable tests for determining per-
sonality types (Myers and Myers, 2010). MBTI uses
four bipolar scales to determine the type. These are
introversion vs. extraversion, sensing vs. intuition,
thinking vs. feeling, and structured vs. unstructured.
The four dimensions yield sixteen possible variations,
not described in detail due to space constraints.
The MBTI which is a valid and reliable test for
classifying people into 16 types and is widely used
but can detect types only 50% of the time for children
under the age of 12 (MBTI, 2015).
2.3 Gaming Styles
The third approach is based on personalizing the
users’ experience based on their game preference.
Player motivation can provide indicators regarding
their personality or learning style.
For this component we choose to look at the Bartle
test. The Bartle model was proposed as a model for
classifying gamers across so-called Multi-User Dun-
geons (MUD) (Bartle, 1996). MUDs include games,
pastimes, sports, entertainments. It has since been
shown to be more generally applicable and corre-
late with other models for games and has been ver-
ified through children questionnaires (Konert et al.,
2013). Bartle model thus represents a simple yet rep-
resentative model that is also well studied in relation
to game mechanics and validated in industry, where
slight variations of the scheme can be seen in the work
by Amy Jo Kim (Kim, 2000), who is well known for
her work on Garage Band and SIMs.
The model is convenient to categorize the games
through an analysis of game mechanics, such as
points, levels and badges, that are used to design
games and appeal to players in various ways. The
Bartle test is a survey that is valid for older children
(Andreasen and Downey, 2008).
The four player types proposed by Bartle are
”Achiever” (acting on the world), ”Killer” (acting on
the players), ”Socializer” (interacting with the play-
ers) and ”Explorer” (interacting with the world).
Table 1: Styles overview comparison (S=Survey,
U=undefined, D=defined, NA=not applicable, A=Adults,
Se=secondary, All=all ages).
GRSLSS
KOLB
NASSP
Gregorc
MBTI
Bartle
Assessm.
method
S NA S S S S
Target
group
age
A/Se All Se All >12 All
Games
cate-
gory
U D D U U D
Games
as-
sessm.
U D D U U D
Personalizing Game Selection for Mobile Learning - With a View Towards Creating an Off-line Learning Environment for Children
307

2.4 Overview
Table 1 summarizes the options with information
about the four factors we were looking for. Based on
the above analysis, GRSLSS, NASSP and MBTI were
eliminated because of the targeted group age that does
not fit children, starting in first grade. Furthermore,
it is not clear how games would be categorized given
these models. Kolbs model was eliminated because of
the absence of assessment tools. Bartle and Gregorc
remain. These models fulfilled the basic factors that
are needed for this work. Out of the remaining mod-
els, Bartle is the best option because of the system
for categorizing games. It is clearer and more infor-
mative than Gregorcs because each gamer type has a
corresponding favorite game without the need of any
further mapping of different models. Finally, creating
surveys for children is not straight forward due to lan-
guage and semantics to get reliable responses. Using
Bartle’s model through games bypasses that difficulty
as will be shown next.
3 METHODOLOGY
The goal is to build a system that collects user feed-
back in order to personalize the online educational
process. Such a system detects user gaming type and
suggests games that match in order to enrich and en-
hance the student experience. This section describes a
proposed solution for estimating students’ gamer type
based on game feedback.
The challenge is to classify both game and user
with common variables in order to recommend the
appropriate game based on a child’s play history. A
vector of four variables representing the gamer types
(Achiever, Explorer, Killer and Socializer) is chosen
to represent a students’ characteristics.
3.1 Game Classification
The classification of the game is solved through its
game mechanics. A game mechanic is a method
that is invoked by agents in order to interact with
the game and provides us with the ability to study
the systematic structure of a game and analyze how
these mechanics help developers create an emotional
experience that affects players while using a game.
Therefore, a game can be characterized as suitable
for a gamer type through the sum of its mechanics.
The 22 game mechanics given in Table 2 were used
to characterize games. Their descriptions and their
affinity with gamer types can be found on Badgeville
(Sylvester, 2013).
Table 2: Game Mechanics.
Achievements Appointments
Behavioral Momentum Blissful productivity
Combos Urgent Optimism
Bonuses Virality
Community Collaboration Countdown
Discovery Epic Meaning
Free Lunch Infinite Gameplay
Levels Lottery
Ownership Progression
Quests Reward Schedule
Status Cascaded Information
That system is then used to rank the mechanics
by their affinity to gamer type. A first approximation
is displayed in Table 3. For example, the Achieve-
ment mechanic is the goal of the Achievers so it has
the greatest effect on this gamer type. Furthermore,
Achievements are more important to the Explorers
than Killers because Explorers are all about finishing
quests aimed at exploring the world while Killers pre-
fer acting on other players. This logic towards rank-
ing them with player types is applied to every element
accordingly. (Future work will involve data driven ap-
proaches for adjusting these weights.)
Table 3: Effect of Game Mechanics.
Name
Achievers
Explorers
Killers
Socializers
Type
Achievements 4 3 2 0 Progression
Appointments 3 2 0 4 Feedback
Behavioral Momentum 2 4 3 1 Behavioral
Blissful productivity 3 2 1 4 Behavioral
Combos 3 1 4 2 Feedback
Urgent optimism 0 3 4 0 Behavioral
Bonuses 4 1 2 3 Feedback
Community collaboration 2 3 0 4 Behavioral
Virality 2 0 4 3 Behavioral
Countdown 4 2 3 0 Feedback
Discovery 3 4 0 0 Behavioral
Epic meaning 4 3 1 2 Behavioral
Free lunch 1 3 2 4 Behavioral
Infinite gameplay 3 0 4 0 Behavioral
Levels 4 2 3 0 Progression
Lottery 1 3 2 4 Behavioral
Ownership 2 3 1 4 Behavioral
Progression 4 0 3 0 Progression
Quests 3 4 2 0 Feedback
Reward schedules 4 3 2 0 Feedback
Status 2 0 4 3 Behavioral
Cascaded information 1 2 4 3 Feedback
The classification is unbalanced across game type.
Equation 1 calculates a balancing factor in order to
normalize scores.
b f a =
∑
a ∗ b f k
∑
k
, (1)
CSEDU 2016 - 8th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
308

where b f a is the balancing factor of the achiever
class, a is the values in the achiever column, b f k is the
balancing factor of the killer class and k is the values
of the killer column. All other factors are calculated
similarly, resulting in the balancing factors of 0.86 for
the Achiever, 1 for the Killer, 1.38 for the Socializer
and 0.95 for the Explorer.
When a developer plugs a game into the recom-
mender platform a list of checkboxes appears such as
shown in Figure 1, listing all game mechanics along
with their definition. The developer checks those
game mechanics that apply. The game can then use
this information to be characterized in terms of gamer
type, given a relationship between a game mechanic
and a gamer type according to Table 3.
In an example, assuming the developer has iden-
tified the following mechanics: Achievements, Ap-
pointments and Blissful Productivity, the resulting
vector will add up as shown in Table 4. After nor-
malization with the balancing factor the game profile
is obtained. Calculating the percentages results in the
game signature, indicating the profile of the gamer
type. According to this method, the example game
is preferred by Socializers.
Figure 1: Selecting Game Mechanics.
Table 4: Game Type Detection Example.
Achievers
Explorers
Killers
Socializers
achievements 4 3 2 0
appointments 3 2 0 4
Blissful productivity 3 2 1 4
Total 10 7 3 8
Game Profile 8.6 6.65 3 11.04
Game Signature 29 23 10 38
3.2 User Classification
User classification is based on the Bartle test for the
gamer psychology that classifies users into four gamer
types described above. Usually, the type is assessed
with a survey, but in the case of children this is dif-
ficult because: 1) Survey questions require too much
cognitive effort, and 2) Language effects might pre-
vent children from understanding the questions. Stud-
ies (Borgers et al., 2000) suggest that upon collecting
information from the children the following guide-
lines should be followed:
1. Avoid Yes and No questions.
2. Avoid writing questions.
3. Avoid suggestions.
4. Keep the questions simple and short.
5. Make it fun.
6. Provide assistance for poor readers.
7. Encourage free recall questions.
8. Use the Visual Analog Scale.(VAS)
Taking these points into account, rather than using a
survey, it is preferable to detect a child’s gamer type
through the history of games played in combination
with a feedback. Keeping the question short, fun,
easy to understand and using Visual Analogue scales
(VAS) as shown in Figure 2. The numbers from -2 to
2 are assigned to the emoticons, with 2, representing
”Love it!”.
Figure 2: Visual Analog Scale example.
The four variable vector for Achiever, Explorer,
Killer and Socializer carry the accumulated feedback
output of the user and are used to match the signa-
ture of the game. In an example, assume that the user
vector is initialized to be equal to 100 and the game
vector is as calculated in Table 4. The game signature
along with the feedback weighting is then used in or-
der to update the user profile. If the user loved the
game the feedback response will be equal to 2. The
change rate is therefore the feedback multiplied by
game profile and then added to the user profile. This
is examplified in a ”Love it” scenario in Table 5.
It can be observed given the positive response that
the user vector is shifted more or less towards the So-
cializer games. The next step consists of suggesting
new games that match the user signature most closely.
3.3 Training the System
Figure 3 illustrates how the whole system architecture
is connected as a simple neural network, given the fol-
lowing variables. P1 is the contribution of each im-
plemented game mechanic to the game structure F1 is
the function responsible of adding the balancing fac-
tor.
W2 is the weight or the strength of a bond towards a
certain gamer type.
F2 is the function responsible of generating the game
and user signatures out of their profiles.
Personalizing Game Selection for Mobile Learning - With a View Towards Creating an Off-line Learning Environment for Children
309

Table 5: Training the system (Scenario 1) in percentage.
Achievers
Explorers
Killers
Socializers
User profile 100 100 100 100
User signature 25 25 25 25
Game profile 8.6 6.65 3 11.04
Game signature 29.3 22.70 10.24 37.69
Feedback
response
2 (=Love it!)
change rate 17.2 13.3 6 22.08
New User pro-
file
117.2 113.3 106 122.08
New user sig-
nature
25.56 24.71 23.11 26.62
Figure 3: System overview.
P2 are the values responsible for forming a games sig-
nature.
V2 is a games signature.
W1 are the values forming the user profile and repre-
sents the bond strength to one of the gaming types.
P1 are the values responsible for forming a users sig-
nature.
V1 is a users signature.
M1 represents the matching algorithm FB represents
the Error function.
4 EVALUATION
The proposed system was evaluated by testing
whether a self-categorization using a Bartle gamer
type test agrees with the gamer type that is determined
through game history and feedback. The feasibility
study is performed with adult students as a baseline
system, removing one variability factor of submitting
elementary school children to the Bartle’s test for val-
idation purpose. Future work clearly includes valida-
tion with the target group.
4.1 Verification Experiment
The system was tested by asking 61 users to perform
the following:
• give feedback on widely popular games by stating
their like or dislike of those games
• respond to 10 behavioral questions that collect
how the respondent is more likely to do in a
certain situation (Bartles Gamer Text) to classify
gamer types.
Truth is assumed to be the outcome of the Bartle test
in this case. This truth can be compared with the re-
sult from the preferences’ survey output to study their
correspondence. In case of agreement, user feedback
would be a valid indicator of gamer type to be used in
recommending future games.
For analysis purpose, each respondents provides
three basic pieces of information that include their age
group, gender and nationality.
The respondents move on to provide their re-
sponses to 20 popular games and rate them based on
their personal preferences with ”Very bad”, ”Bad”,
”Good”, ”Very good” and ”I dont know the game”.
A neutral vote was not provided in order to enforce a
decision.
Every choice has its own value (-2. -1, 1, 2 and
0 for the choices ”Very bad”, ”Bad”, ”Good”, ”Very
good” and ”I dont know the game” respectively) that
are then multiplied with the game vector. The val-
ues assigned to the game are based on our knowl-
edge of each game’s game-mechanics and are listed
in Table 6, with 4 being the best fit and highest possi-
ble number. Their detailed calculation is omitted for
space reasons. The table shows the games in the order
of presentation in the survey.
For every question the response value is multiplied
by the game’s vector resulting in the output that is to
be used to detect the gamer type as illustrated in an
example below in Table 7.
The sum of the new values after being modified by
the response values for each gamer type is calculated
independently and then multiplied by the balancing
weights. The above mentioned 4 games are used in
an example given in Table 8. Based on these 4 games
and the 4 responses the user tends to be an Explorer
and his secondary type is Achiever.
The next step is getting the output out of the be-
havioral multiple choices questions, 10 of which are
included in the survey to be ranked by the respon-
dents.
An example score development is depicted in Ta-
ble 9, showing that this user is an Explorer and that
his secondary type is an achiever.
CSEDU 2016 - 8th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
310

Table 6: Distributed weights of games.
Game Name
Achievers
Explorers
Killers
Socializers
Farmville 3 2 1 4
Call of Duty 2 1 4 3
Chess 1 4 3 2
Angry birds 4 1 3 2
Pirate Kings 2 1 3 4
Guitar hero 3 1 4 2
Assasins’ creed 3 4 2 1
Super Mario 4 3 2 1
Trivia crack 2 1 3 4
Counter Strike 2 1 4 3
GTA 2 4 3 1
Candy crush 4 1 2 3
Zuma 2 1 3 4
2048 3 1 4 2
The Sims 2 4 1 3
Fruit Ninja 4 1 3 2
Clash of clans 1 3 2 4
Need for speed 3 2 4 1
Monopoly 1 4 2 3
Crazy taxi 4 3 2 1
Table 7: User type detection.
Game Name
Achievers
Explorers
Killers
Socializers
RATING
New Achievers
New Explorers
New Killers
New Socializers
Chess 1 4 3 2 2 2 8 6 4
Angry birds 4 1 3 2 1 4 1 3 2
Pirate Kings 2 1 3 4 -2 -4 -2 -6 -8
Guitar hero 3 1 4 2 -1 -3 -1 -4 -2
The last step is to compare the output from both
methods in order to determine whether they match.
Three methods for judging the results are employed.
1. Successful match: This means that the 2 methods
concluded that the respondent belongs to a certain
gamer type.
2. Close match: Which was included because some
analysis of responses were not entirely wrong so
some conditions to detect close results and they
are:-
(a) 5% deviation in the behavioral test.
(b) 5 points deviation in the preferences’ assess-
ment.
(c) First type came second.
(d) Second type came first.
Table 8: Adjusting User profile based on game reviews.
Achievers
Explorers
Killers
Socializers
Initial State 100 100 100 100
Responses
summation
-1 6 -1 -4
Updated state 99 106.0 99.0 96
Balancing
weights
1 1.42 0.76 1
Final State 99 150.92 75.24 96
Table 9: User type detection.
Achievers
Explorers
Killers
Socializers
First question 3 4 2 1
Second question 2 4 3 1
Third question 2 4 3 1
Fourth question 4 3 2 1
Fifth question 4 3 2 1
Sixth question 3 4 2 1
Seventh question 1 4 3 2
Eighth question 1 3 2 4
Ninth question 2 4 3 1
Tenth question 3 4 2 1
Total 25 37 24 14
3. Mismatch: All other responses that do not follow
any of the above mentioned rules.
In the examples that we used for illustration the re-
sults came out like this:
The output of game rating: Achiever:99.0; Ex-
plorer:150.92; Killer:75.24; Socializer:96.0
The output of Bartle’s test is: Achiever:25; Ex-
plorer:37; Killer:24; Socializer:14
Both methods result in Explorer, indicating a success-
ful match.
4.2 Compiled Results
The Questionnaire was released to a larger number of
people and 63 responses were collected; 2 of them
were invalid, resulting in a total of 61 responses.
Their distribution is given below.
• 11 different nationalities which are Egyptian, Ger-
man, Dutch, French, Russian, Indian, Mexican,
Indonesian, Colombian, American and Syrian.
• Gender: 34 males (55.78 %) and 27 females
(44.22 %).
• Age groups(Years old): 15 -17 (1.7 %), 18 - 21
(34.9 %), 22 - 24 (56.9 %), 25 - 28 (4.8 %) and
Older than 28 (1.7 %).
Personalizing Game Selection for Mobile Learning - With a View Towards Creating an Off-line Learning Environment for Children
311
The Questionnaire results came out to be:-
• 33 Successful matches (54.10 %).
• 16 Close matches (26.23 %).
• 12 mismatches (19.67 %).
Table 10 depicts the confusion Matrix for the results.
Table 10: Results overview.
Behavioral Questionaire
Games’ feedback
Achievers
Explorers
Killers
Socializers
Total
Achiever 4 6 1 0 11
Explorer 3 21 8 3 35
Killer 2 5 8 0 15
Socializer 0 0 0 0 0
Total 9 32 17 3 61
It is interesting to observer a non-uniform distri-
bution among player types. There are more Explor-
ers and few Socializers. One could imagine that the
questionnaire is biased. However, this result seems to
be common. As an example, middle and high school
teacher Douglas Kiang posted on Edudemic his ex-
perience when he made one of his classes take the
Bartle’s test for gamer types in order to have a bet-
ter understanding of his students and also to be able
to form collaborative groups (Kiang, 2007). His class
had 5 Achievers (21.74%), 9 Explorers (39.13%), 6
Killers (26.08%) and 3 Socializers (13.04%), a simi-
lar distribution to the one observed in our study.
4.3 Questionnaire Redesign
Trying to enhance the success rates, some of the ques-
tions that we considered insignificant were removed
because some games managed to carry almost the
same feedback for all users. One of those games is
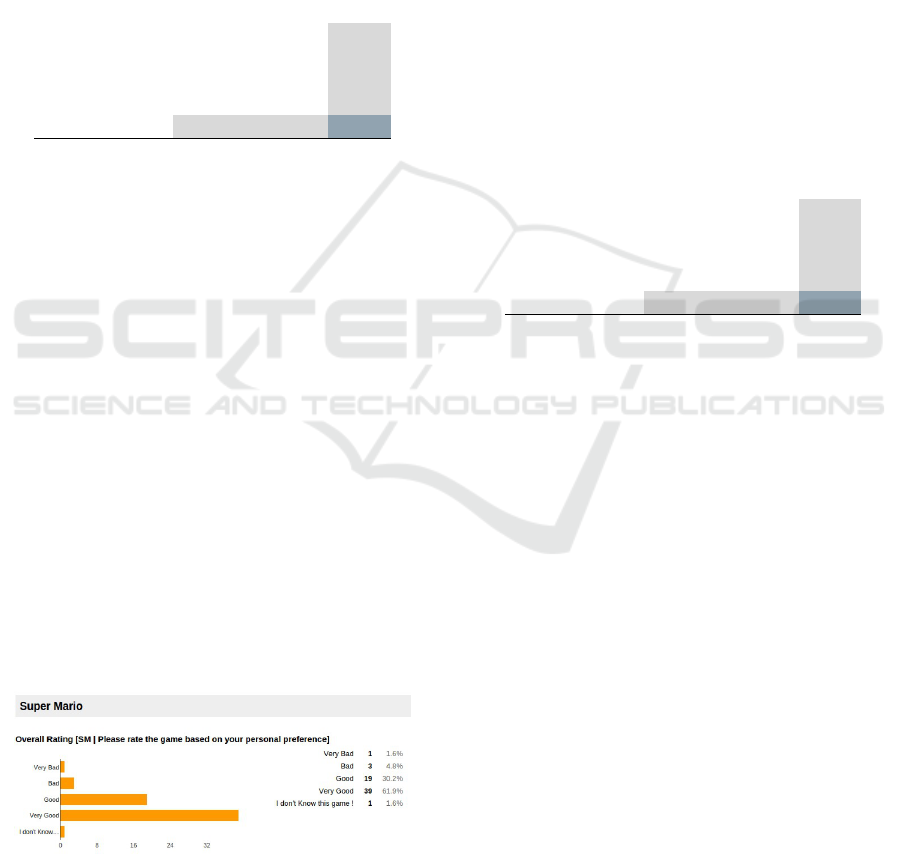
Super Mario as shown in Figure 4, which 92% of the
respondents rated as good or very good respectively.
Figure 4: Game question analysis.
Two additional games, chess and monopoli, serve
little as discriminator between gamer types. Respon-
dents thought that they are good and very good with
the rates of 92.2% and 89.1% respectively. The games
were dropped from the questionnaire.
The data was reprocessed with the remaining 17
game rating questions. After recompiling responses
using the modified questionnaire the results are given
in Table 11.
1. From 33 successful matches (54.10 %) to 40
(65.57%) with an improvement of 7 matches
(11.47%).
2. From 16 close matches(26.23 %) to 13 (21.31%)
with an improvement of 3 matches (4.92%).
3. From 12 mismatches (19.67 %) to 8 (13.11%)
with an improvement of 4 matches (6.56%).
Table 11: Results overview.
Behavioral Questionaire
Games’ feedback
Achievers
Explorers
Killers
Socializers
Total
Achiever 5 6 1 0 12
Explorer 1 21 2 1 25
Killer 3 5 14 2 24
Socializer 0 0 0 0 0
Total 9 32 17 3 61
5 CRITICAL REFLECTION AND
FUTURE WORK
This paper addresses the need for a motivating learn-
ing platform for children without access to teachers
through the use of games. We explore a recommender
system based on factors that allow us to match users
with games using Bartle’s gamer types as a first ap-
proximation.
Bartle’s test, though usable with children and
adults, has fundamental critiques as to its useful-
ness in the literature, reasoning that it is a theoretical
model. While the model may not be sufficient as the
types overlap and are not defined with enough detail
(evident in the way Table 3 had to be constructed) the
model is nonetheless a good starting point according
to Yee (Yee, 2006b). Yee breaking the types down
into motivation factors that make up various types.
His work is founded on very large data sets. Our ap-
proach is somewhat similar. We use Bartle’s types
as a guideline for understanding the game mechan-
ics. These are the factors that we use to relate players
to games. Game mechanics are consciously used by
game designers when creating their games. They are
therefore easy to use as descriptiors of the game. The
CSEDU 2016 - 8th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
312

game mechanics constitute factors in a similar way
as the motivators in Yee’s work and can be used in
turn in order to reconstruct gamer types. Bartle’s ba-
sic definition thus provides a boot-strapping method
for retraining a feature network using a knowledge-
base design. Weights can later be retrained using data
driven approaches.
Future work involves a larger collection of data
from the target audience that would allow data driven
parameter training in order to match game mechanics
to data driven user types.
The resulting recommender system can supple-
ment other such systems that have been well re-
searched in the literature.
REFERENCES
Andreasen, E. and Downey, B. (2008). Gamer Psychology -
Bartle’s Test, http://www.andreasen.org/, accessed on
Feb. 9, 2016.
Bartle, R. (1996). Hearts, clubs, diamonds, spades: Players
who suit MUDs. Journal of MUD research, 1(1):19.
Berkling, K., Elhusseni, A., Latt, D., Petrov, C., Waigand,
A., and Walther, J. (2016). Childrens mooc con-
ceptual ideas and first steps towards implementation.
In (CSEDU) International Conference on Computer
Supported Learning.
Borgers, N., Leeuw, E. d., and Hox, J. (2000). Children
as respondents in survey research: Cognitive develop-
ment and response quality 1. Bulletin de methodologie
Sociologique, 66(1):60–75.
Bullen, M. (2003). E-learning emergence. CGA Magazine.
Felfernig, A., Jeran, M., Ninaus, G., Reinfrank, F., and Re-
iterer, S. (2013). Toward the next generation of rec-
ommender systems: applications and research chal-
lenges. In Multimedia Services in Intelligent Environ-
ments, pages 81–98. Springer.
Gregorc, A. F. and Butler, K. A. (1984). Learning is a matter
of style. VocEd, 59(3):27–29.
Keefe, J. W., Monk, J. S., Languis, M., Letteri, C., and
Dunn, R. (1986). NASSP Learning style profile. Re-
ston, VA: National Association of Secondary School
Principals.
Khalil, M. and Ebner, M. (2015). A stem mooc for school
childrenwhat does learning analytics tell us? In In-
teractive Collaborative Learning (ICL), 2015 Interna-
tional Conference on, pages 1217–1221. IEEE.
Kiang, D. (2007). Use the Four Gamer Types to Help Your
Students Collaborate, http://edtechteacher.org/use-
the-four-gamer-types-to-help-your-students-
collaborate-from-douglas-kiang-on-edudemic/,
last checked Nov. 6, 2015.
Kim, A. J. (2000). Community building on the web:
Secret strategies for successful online communities.
Addison-Wesley Longman Publishing Co., Inc.
Kolb, A. Y. (2005). The Kolb learning style inventory—
version 3.1 2005 technical specifications. Boston, MA:
Hay Resource Direct, 200.
Konert, J., G
¨
obel, S., and Steinmetz, R. (2013). Modeling
the player, learner and personality: Independency of
the models of Bartle, Kolb and NEO-FFI (Big5) and
the implications for game based learning. In European
Conference on Games Based Learning, page 329.
MBTI (2015). MBTI Basics,
http://www.myersbriggs.org/my-mbti-personality-
type/mbti-basics/, last checked Nov. 6, 2015.
Myers, I. and Myers, P. (2010). Gifts differing: Understand-
ing personality type. Nicholas Brealey Publishing.
National Governors Association Center for Best Practices,
C. o. C. S. S. O. (2010).
Riechmann, S. W. and Grasha, A. F. (1974). A rational ap-
proach to developing and assessing the construct va-
lidity of a student learning style scales instrument. The
Journal of Psychology, 87(2):213–223.
Rollins, M. (Jan. 7, 2015). The Grasha-
Riechmann Student Learning Styles Scale
http://elearningindustry.com/learning-style-
diagnostics-grasha-riechmann-student-learning-
styles-scale, last checked Nov. 6, 2015.
Steinkuehler, C., Squire, K., and Barab, S. A. (2012).
Games, learning, and society: Learning and mean-
ing in the digital age. Learning in doing. Cambridge
University Press, Cambridge.
Sylvester, T. (2013). Designing games: A guide to engi-
neering experiences. O’Reilly, first edition.
Tavangarian, D., Leypold, M. E., N
¨
olting, K., R
¨
oser, M.,
and Voigt, D. (2004). Is e-learning the Solution for In-
dividual Learning. Electronic Journal of E-learning,
2(2):273–280.
Thompson, C. (2011). How khan academy is changing the
rules of education. Wired Magazine, 126:1–5.
Yee, N. (2006a). The demographics, motivations, and de-
rived experiences of users of massively multi-user on-
line graphical environments. Presence, 15(3):309–
329.
Yee, N. (2006b). Motivations for play in online games. Cy-
berpsychology & behavior : the impact of the Internet,
multimedia and virtual reality on behavior and soci-
ety, 9(6):772–775.
Personalizing Game Selection for Mobile Learning - With a View Towards Creating an Off-line Learning Environment for Children
313
