
Content-based Title Extraction from Web Page
Najlah Gali and Pasi Fränti
Speech and Image Processing Unit, School of Computing, University of Eastern Finland, Joensuu, Finland
Keywords: Title Extraction, Information Extraction, Web Data Extraction, Web Mining.
Abstract: Web pages are usually designed in a presentation oriented fashion, having therefore a large amount of non-
informative data such as navigation banners, advertisement and functional text. For a particular user, only
informative data such as title, main content, and representative images are considered useful. Existing
methods for title extraction rely on the structural and visual features of the web page. In this paper, we propose
a simpler, but more effective method by analysing the content of the title and meta tags in respect to the main
body of the page. We segment the title and meta tags using a set of predefined delimiters and score the
segments using three criteria: placement in tag, popularity within all header tags in the page, and the position
in the link of the web page. The method is fully automated, template independent, and not limited to any
certain type of web pages. Experimental results show that the method significantly improves the accuracy
(average similarity to the ground truth title) from 62 % to 84 %.
1 INTRODUCTION
Nowadays, the Internet is the main source of
information for users. Web-based applications use
search engines to collect information from websites
for their users. However, the content of the web pages
is not well-structured for easy content extraction.
Irrelevant data such as advertisements and
information related to the site that hosts the services
are often retrieved. Search engines rely on several
methods to extract data using manual, semi-
automatic, and full automatic approaches. Most of
these methods require user interaction, training data
and experimental adjustment. To improve the
performance of the search engines, and reduce the
time and efforts required by users to identify the
content of the data, fully automated techniques for
extracting the relevant content from web pages are
required.
In this paper, we aim at solving the problem of
automatic extraction of the web page title. We define
title as the most obvious description of the web page.
For example, we define Speech and Image
Processing Unit as the title for the web page
(http://www2.uef.fi/fi/sipu/). The title is important
because it gives a user a quick insight into the content
of the page and how it might be relevant to his query.
It is often the primary piece of information for users
to decide which search results to click on. It is also
useful in several applications such as social networks,
browsers and location based applications such as
MOPSI (http://cs.uef.fi/mopsi/) where title and a
thumbnail image are extracted as the minimum
information for the user’s needs.
Extracting the title from the web page is not
always trivial. Title tag would be the obvious source,
but in several cases it also includes generic keywords
such as Homepage or Contact, long descriptions that
contain slogans and advertisements such as Joensuu
Keskusta | Intersport - Sport to the people. Therefore,
a more robust solution is needed to extract an
informative title.
Several methods have been proposed to perform
the task. (Xue et al., 2007) proposed two methods that
utilize the body of the hypertext markup language
(HTML) pages. The first method is based on
formatting features that are extracted from the
document object model (DOM) tree such as font, tag,
linguistic, and format change information. The
second method is based on vision features such as
page layout, block, and unit position information. In
either method, each text node is classified as a title or
non-title using support vector machine (SVM) and
conditional random field (CRF) learning models.
Results show that combining formatting and vision
features provides best accuracy, and that CRF
outperforms SVM, and SVM with nonlinear kernels
outperforms SVM with a linear kernel for this task.
204
Gali, N. and Fränti, P.
Content-based Title Extraction from Web Page.
In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies (WEBIST 2016) - Volume 2, pages 204-210
ISBN: 978-989-758-186-1
Copyright
c
2016 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

Wang et al., (2009) proposed a method to extract
titles from news web pages. It segments the web page
into blocks using vision-based page segmentation
algorithm (Cai et al., 2003). Each block is classified
either as a candidate that contains the title or not,
using SVM and a set of features such as first screen,
largest font size, number of words, and similarity with
the content of title tag. The text with the largest font
inside the candidate block is considered the title.
Changuel et al., (2009) extracted the first twenty
text nodes from the DOM tree and for each node a
feature vector is created. Thirty-six features that are
based on the styling of the text such as font size, font
weight, color, letter capitalization, alignment, tag
information and similarity with title tag are used to
train two classifiers: decision tree (C4.5) and random
forest algorithm (Breiman, 2001). This work also
investigated the task of extracting titles using image
information such as alt attribute, but they concluded
that people rarely specify values for alt.
Mohammadzadeh et al., (2012) studied the title
extraction in case of online web news articles. All text
nodes are first extracted from the DOM tree,
tokenized into words and transformed into classical
vector representation. The words of each node are
then weighted using term frequency (TF) and term
frequency-inverse document frequency (TF-IDF).
The similarity between each text node and the text
content of title tag is computed using different
similarity metrics such as cosine similarity and
Overlap Scoring Measure (OSM) similarity
(Manning et al., 2009). The text node that has the
highest similarity with the content of title tag is
considered the title of the article.
A recent method (Jeong et al., 2014) uses the text
of the anchor element ‘<a> text </a>’ of the inlink
page (a web page that contains anchor text) to extract
the title of the landing page (a web page that does not
contain anchor text). For each landing page, the text
nodes are extracted from the DOM tree as candidate
titles. The similarity between each candidate and the
anchor texts of the inlink pages pointing to the
landing page is computed. A candidate that has higher
similarity with the anchor text is selected as the title.
Web pages are designed in a presentation oriented
fashion, having therefore much variety in their
structure, layout and content depending on their
domain, topic and purpose (Win and Thwin, 2014).
Using structural and visual features, which has been
the main focus of the previous studies, is not always
useful because the title can appear at different places
on the web page with no visual differences from other
parts of the text, especially when the logo image
contains the title (see Figure 1). Furthermore, most of
these methods require training and focus on one
specific domain such as news or education.
To avoid these limitations, we do not rely on
visual or structural features as the criteria to select the
title. Instead, we parse the DOM tree of the web page
and compare the content to that of the title and meta
tags. We segment the content of these tags using a set
of predefined delimiters. We then apply three criteria
to score the candidate segments: placement in the
tags, popularity among the header tags and the
position in the link of the web page. The segment that
achieves the highest score is selected as the title for
the web page.
Figure 1: The web page title (in red box) has no visual
differences from the surrounded text.
Our contribution is to show that the title and meta
tags can still be used for extracting the title. However,
they should not be used as such, but better approach
is to divide them into segments, which are further
analyzed using the content of the rest of the page. We
use three criteria. Web link turns out to be the most
significant, but placement in title and meta tags, and
popularity in header tags are also used. The proposed
method, Title Tag Analyzer (TTA) outperforms the
comparative methods. It is domain independent and
does not rely on certain templates or category of web
pages. It is targeted to work with all types of pages,
and not limited to certain writing style or layout of the
web page.
The proposed method is implemented in MOPSI
(Fränti et al., 2011) to show the search and
recommendation results to the mobile user.
2 TITLE EXTRACTION
The steps of the method are shown in Figure 2. We
download the HTML source of the web page and
parse it as DOM tree. DOM is an interface allowing
scripts and programs to dynamically access and
handles all the elements such as content, structure and
style of web pages. We navigate through the DOM
Logo image
Content-based Title Extraction from Web Page
205

tree to identify title and meta tags with name=title,
og:title and keywords, and extract their content. The
reason to consider title and meta tags in this method
is that they are a good source of text features. They
contain words and phrases relevant to the content of
the web page they describe, but in some cases, they
also contain bogus, repeated and long sequence of
words and phrases such as here!, layout, helpdesk,
and map and list of sports facilities on offer, which
require further processing to conclude the best
representative words or phrases. For this reason, we
use a set of criteria to identify the title in the web
page.
Figure 2: The workflow for title extraction.
After title and meta tags content have been
extracted, we use regular expression to segment the
content into words and phrases using predefined
patterns (see Table 1).
Table 1: Pre-defined delimiter patterns.
space – space space / space space . space
space : space , space space -
: space space : space |
space > space « space »
? , - , space ::
Space / -| space <
Let X={x
↓
(i) | i[1,n]} be the content extracted
from title tag where n is the number of segments in
the title tag, and Y={y
↓
(j) | j[1,m]} be the content
extracted from meta tag where m is the number of
segments in the meta tag. A set of p candidate
segments Z= {z
↓
(k) | k[1,p]} = XY is then
constructed. Special characters such as!,?, @ are
removed and duplicate segments are deleted leaving
only unique candidates.
We only consider the meta tag with name title and
og:title in Z, if the title tag is found and has a value,
otherwise, we consider meta tag with name keywords.
Next, we score the candidate segments z
k
by different
criteria:
2.1 Placement in Title and Meta Tags
According to a recent survey on search engine
ranking factors made in 2013 by MOZ
(https://moz.com/search-ranking-factors), the
position of the key segments in title tag would help
search engine optimization (SEO). It aims at showing
the most relevant web pages on the top of the results
list. The closer to the beginning of the tag the segment
is, the more useful it will be for ranking. It is also
recommended to have the brand name in the end of
the tag. Therefore, we consider a candidate z
k
that is
placed first or last in the title or meta tags is more
important than candidates that are placed in the
middle. We therefore give it higher score:
S
z
0.1 ifz
x
orx
0.1 ifz
y
or
y
0Otherwise
(1)
2.2 Popularity in Header Tags
Headlines and important segments are usually more
emphasized in the body of the web page. Therefore,
we consider candidate z
k
that appears in header tags
(H
1
, H
2
, H
3
… H
6
) is more important than other
candidates. We first navigate through the entire page
and extract the content of all header tags. We then
compare the strings to find whether the candidate z
k
appears within header tags, and apply the following
heuristics:
A candidate z
k
that appears in a bigger header like
H1 is more important than candidates in smaller
headers like H6.
A candidate z
k
that appears more than once is
more important than a candidate that appears only
once.
The following formulas represent the heuristics
above:
Fz
w
f
(2)
where f
i
is the frequency of appearance of z
k
in header
i and w
i
is the weight of header i. Similarly to [Fan et
al. 2011], the weights are fixed to values (6, 5, 4, 3, 2,
1) respectively. The score F is then normalized to the
scale of [0, 1] by the following formula:
WEBIST 2016 - 12th International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
206

S
z
Fz
F
F
F
(3)
where F
min
= min (F (z
1
), F (z
2
)… F (z
p
)) and F
max
=
max (F (z
1
), F (z
2
)… F (z
p
)) for all candidate
segments.
2.3 Position in the Web Page Link
The keywords in the link of the web page are usually
precise and relevant to the content of the page.
Therefore, a candidate z
k
that appears in the web page
link is more important than other candidates. We
score the candidate z
k
according to its position in the
link (i.e, whether it appears in the host, path or
document name) and its similarity with the content of
the link in that position. A candidate that appears at
the end of the link (document name) is more
important than candidates that appear at the beginning
of the link (host) because the segment in the latter
path of the link are more specific to the page content
than the segment appears in the host and as we go in
depth with the web page link, we get more specific
segments as was also concluded in (Kan and Thi,
2005). For example, consider the word Microsoft
appears in the host of one link and in the document
name of another link. In the first case, we understand
that the web page is located on Microsoft’s web
server, but could relate to any topic. In the second
case, the document is named Microsoft and is likely
to discuss the company itself. Another example,
suppose that we have a web page link (https:
//www.s-kanava.fi/toimipaikka/s-market-kausala/
511787202) and two candidates which are: S-market
Kausala, and S-kanava. Then, we consider that S-
market Kausala is more relevant and therefore we
give it higher weight.
Let pos(z
k
) be the position of z
k
in the link, sim be
the similarity between z
k
and the content of the link in
pos computed using Dice coefficient (Brew and
McKelvie, 1996), and w is the weight of the position,
then we can represent the relation as follows:
W
z
w
sim,
ipos
z
and w
w
(4)
The weights are empirically obtained and fixed to
values 1 for the host, 1.5 for the path and 3 for the
document name. We normalize W to the scale [0, 1]
by the following formula:
S
z
Wz
W
W
W
(5)
Where, W
min
=min (W (z
1
), W (z
2
)… W (z
r
)) and
W
max
=max (W (z
1
), W (z
2
)… W (z
r
)) for all candidate
segments.
Because the web page link is formulated using
English alphabet, we need to convert the candidates
that are written using foreign letters such as
Silmäasema before counting their appearance in the
link. For this conversion, we use Table 2.
Finally, we compute a total score for each
candidate segment as follows:
S
S
S
S
(6)
3 EXPERIMENTS
3.1 Date Set
The weight of the position in title and meta tags and
the weights of the position in the link of the web page
were empirically obtained based on collection of 100
websites.
The score for each criterion is normalized to the
Table 2: Foreign to English letter conversion (https://www.drupal.org/files/issues/i18n-ascii-full.txt).
Foreign English Foreign English Foreign English Foreign English Foreign English
À à A a È è E e Õ õ O o Ž ž Z z Ð đ D d
 â A a Ê ê E e Ø ø O o Ż ż Z z ð D
Ä ä A a É é E e Ó ó O o Ź ź Z z Ď D
Á á A a Ë ë E e Ò ò O o Û û U u ď d
à ã A a Ě ě E e Ô ô O o Ù ù U u þ Þ TH th
Ā ā A a Ē ē E e Ö ö O o Ú ú U u Ŧ ŧ T t
Å å A a Ė ė E e Ő ő O o Ü ü U u Ţ ţ T t
Ą ą A a Ę ę E e Œ œ OE oe Ű ű U u Ť ť T t
Æ æ AE ae Ì ì I i Ś ś S s ů u Ŋ ŋ NG ng
Ç ç C c Î î I i Š š S s Ł ł L l Ķ ķ K k
Č č C c Í í I i Ş ş S s Ļ ļ L l Ř ř R r
Ć ć C c Ï ï I i ß SS Ń ń N n Ñ ñ N n
Ğ ğ G g Ī ī I i Ý ý Y y Ň ň N n
Ģ ģ G g Į į I i Ý ý Y y Ņ ņ N n
Content-based Title Extraction from Web Page
207
scale [0, 1] except the position in title and meta tags
criterion, which we fix to 0.1. We experimented with
different weights (0.0, 0.1, 0.2, 0.4, 0.8, 0.9, and 1.0)
and observed that 0.1 provides better results. This
criterion has small contribution to the result, but much
smaller than the other criteria.
The same set was also used to decide the use of
the so-called Dice coefficient (Brew and McKelvie
1996) to measure the similarity of the extracted title
to the ground truth. This evaluation set is completely
different from the test data set used later.
The actual data set was collected during 18 - 31
July 2014 and 19 - 23 April 2015, by choosing
different type of websites from different regions of
the world, in order to have a reasonable geographical
diversity. This set contains 1,245 websites in eight
categories: Food & Drinks, Home & Garden, Hotels
and Accommodation, Shopping, Arts &
Entertainment, Hobbies & Leisure, Sport, and Health
& Social care, collected from Google and Google
maps (http://maps.google.co.uk) search results using
queries such as bar, restaurant, café, Pizza, Radisson
blue hotel, H&M shop, Play bar, Cavalier pub, Rosso
restaurant, Intersport shop, sauna, swimming pool
and bowling alley.
We manually extracted the titles from each web
page according to the specification defined in (Hu et
al., 2005). In the following experiments, this data is
used as a ground truth to measure the accuracy of our
web page title extraction method.
3.2 Evaluation Measure
To decide whether the detected title is correct, we
used the Dice coefficient to compare the similarity of
the extracted title to the ground truth, on average.
Dice uses 2-gram for the comparison.
It calculates the number of adjacent character
pairs contained in both strings:
Similarity
t
,t
2
|
pairs
t
∩pairs
t
|
|
pairs
t
|
|
pairst
|
(7)
Where pairs(t
1
) and pairs(t
2
) are the number of
character pairs (2-gram) in the ground truth title (t
1
)
and the extracted title (t
2
) respectively. The similarity
score between title (t
1
) and title (t
2
) are used directly
in the evaluation results, where 100% means that
perfect match is found every time.
The reason for choosing this algorithm is that it is
language independent, robust to the change of the
order of the words and treats strings with small
differences as being similar. These kinds of variations
are expected in title extraction, and therefore exact
match is not useful in this case. A measure like
levenshtein distance is also not enough because it
considers the reverse order of two strings as a
mismatch. For example, the edit distance based
similarity between the two strings nba mcgrady and
macgrady nba is 0.3 which is very low although the
strings are very similar (Wang et al., 2014).
3.3 Methods Evaluated
We compare the following methods:
Title tag (baseline)
TitleFinder (Mohammadzadeh et al. 2012)
Title tag analyzer (TTA) - Our method
3.4 Selection of the Criteria
The method is based on three criteria:
Placement in title and meta tags;
Popularity in header tags;
Position in the link of the web page.
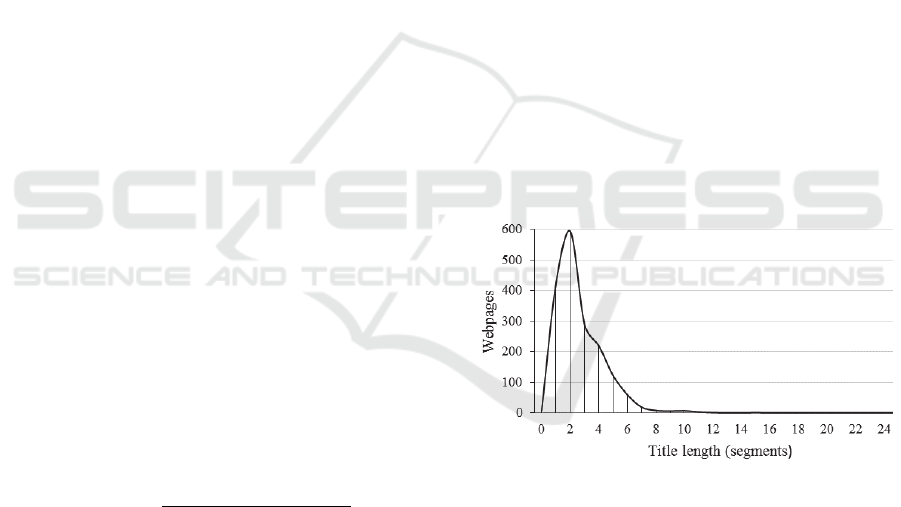
The number of segments contained in the title tag
varies from 0 to 25 as shown in Figure 3, which means
that selecting one candidate for title representation is
not trivial. From these websites, 4% have <meta
name=title> or <meta property=og:title>, and 52%
have <meta name=keywords>.
Figure 3: Number of segments in title tags, on average.
We conducted the experiments using different
combinations of criteria. From Table 3 we observe
that criterion 3 has the highest impact (0.84) because
the title or part of it usually appears in the web link.
Criteria 1 has the lowest impact (0.65). We
observed that more generic words such as home and
welcome are often placed at the beginning and then
followed by the title, and either the slogan, address or
general information about the web page is placed at
the end of the title.
Criteria 2 has slightly higher impact (0.68), but
still far less than criteria 3. This is because header tags
are not always used, and even when existing, the
WEBIST 2016 - 12th International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
208
correct title is not always there.
Combination of criteria 1 and 3 improves the
score to (0.85), but the improvement is not
statistically significant according to Mann Whitney
U-test. The results show that the score provided by
criterion 3 is statistically significant in comparison
with criteria 1 and 2 individually, and criteria 1 and 2
jointly (in the sense p value < 0.05).
Table 4 summarizes typical cases on how the
criteria work jointly, both in case of success and
failure. In total, (19 %) of the cases provide lower
similarity with the ground truth titles. This is either
because the extracted title is shorter than the ground
truth (case 2), a part of a long segment (case 3), the
correct title is not contained in the title and meta tags
(case 4), or because the applied rules select a wrong
segment especially when title and meta tags contain
general words such as order, food, or city names such
as Philadelphia, NYC and Swansea (case 5). These
kinds of words appear frequently in the content of the
page and therefore they are given a higher score by
criterion 2.
Table 3: Impact of criteria (average similarity) according to
Mann Whitney U-test, (p-value < 0.05).
Criteria Average similarity
1 0.65
2 0.68
3
0.84
1 + 2 0.70
1 + 3
0.85
2 + 3
0.82
1 + 2 + 3
0.84
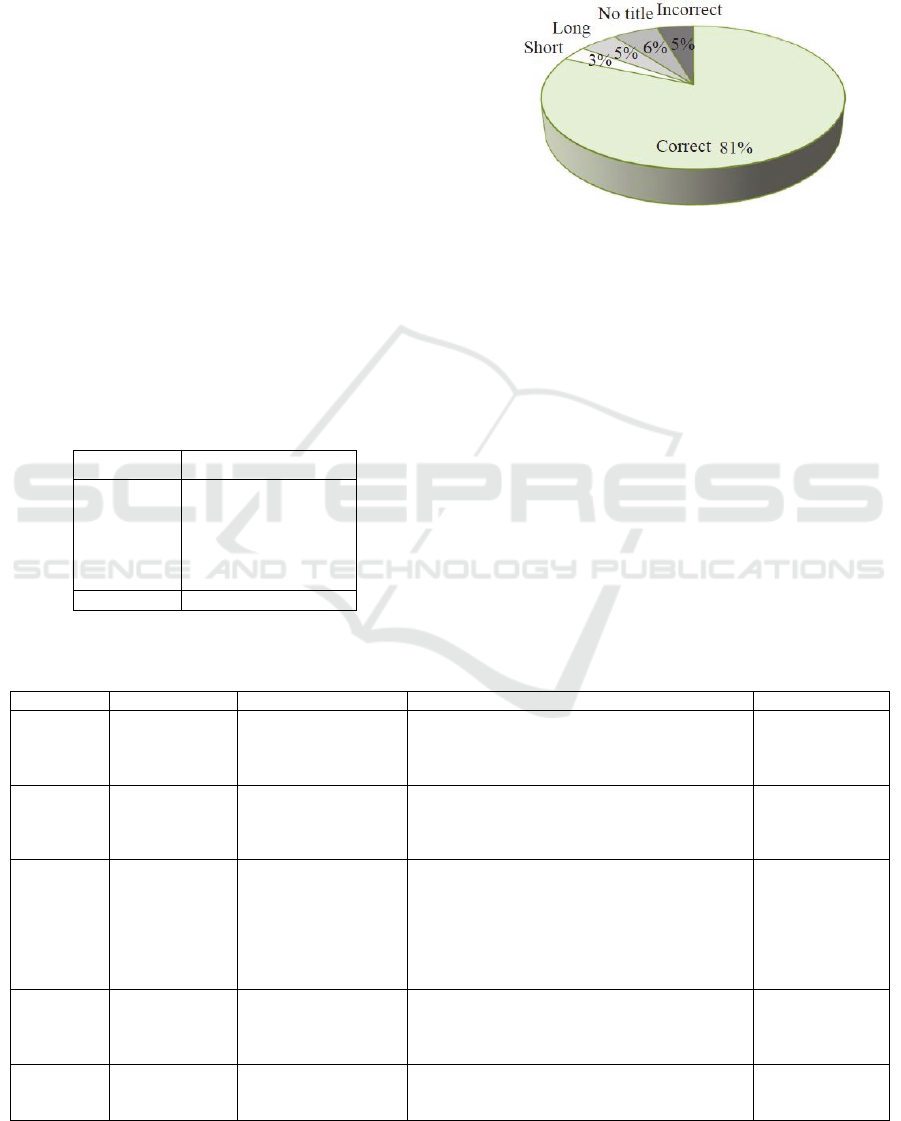
Figure 4 shows a qualitative evaluation for all
titles extracted by TTA. As we can observe, despite
of these negative cases, the overall result is still much
better than that of the baseline and TitleFinder as
shown in Table 5.
Figure 4: Qualitative analysis of the title extraction method.
3.5 Comparative Results
The results of the baseline, Titlefinder and TTA are
summarized in Table 5. TTA provides highest
similarity scores of (0.84) which outperform the
baseline (0.62) and TitleFinder (0.52). We conducted
significance test and the results indicate that the
improvements of TTA over the baseline and
TitleFinder are statistically significant (in the sense p-
value <0.05).
Figure 5 shows the distribution of the web pages
with respect to the similarity of the extracted titles
with the ground truth titles. TTA finds perfect match
with the ground truth in 1,014 of the cases, which is
significantly more than the result of baseline 276 and
TitleFinder 447.
Table 4: Examples for the Extracted Titles.
Annotated title Content of title tag Content of meta tag Selected string
Case 1
(correct title)
3 Weeds Hotel
3 Weeds Hotel | Unique
Pub | Bars | Restaurant |
Party Venue | Inner West
Sydney
Hotel , Pub, Bar, Restaurant, Dining, Party Venue,
Function, Center, Centre, Rozelle, Balmain,
Drumoyne, Glebe, Lilyfield, Annandale Sydney,
Inner West Hotel
3 Weeds Hotel
Case 2
(short title)
Irish Channel
Restaurant & Pub
Irish Channel -
Restaurant & Pub | 500 H
St NW DC (202) 216-
0046
Irish Channel
Case 3
(long title)
Secret Garden
Bed & Breakfast
Secret Garden Bed &
Breakfast (formerly
Whitegates Guest
House), near Keynsham,
Bristol: Rooms, Prices
and Guest Information
Bed and breakfast, B and B, bed, breakfast,
guesthouse, accommodation, hotel, stay, visit,
Bristol, Bath, Keynsham, Stockwood, South West,
England, garden, Whitegates Guest House,
Whitegates, Whitegate, Whitegate Nurseries, White
Gate Nursery, Christmas, open, Secret Garden
Centre, swimming pool, Cotswolds
Secret Garden Bed
& Breakfast
(formerly
Whitegates Guest
House)
Case 4
(no title)
Rio Pool
Hot Tubs, hot tub hire,
swimming pools, Bristol,
Gloucester
Hot tubs, Swimming pools, home swimming pools,
pool maintenance, wooden swimming pools, hot tub
hire, pool and spa equipment, Gloucester, Bristol,
Cheltenham, South West, UK
swimming pools
Case 5
(incorrect)
Slice and Dice
Home | Prepared Food |
Swansea | Slice and Dice
UK
Prepared food, Prepared fruit and veg, Fresh chips
supplier, Swansea
Swansea
Content-based Title Extraction from Web Page
209
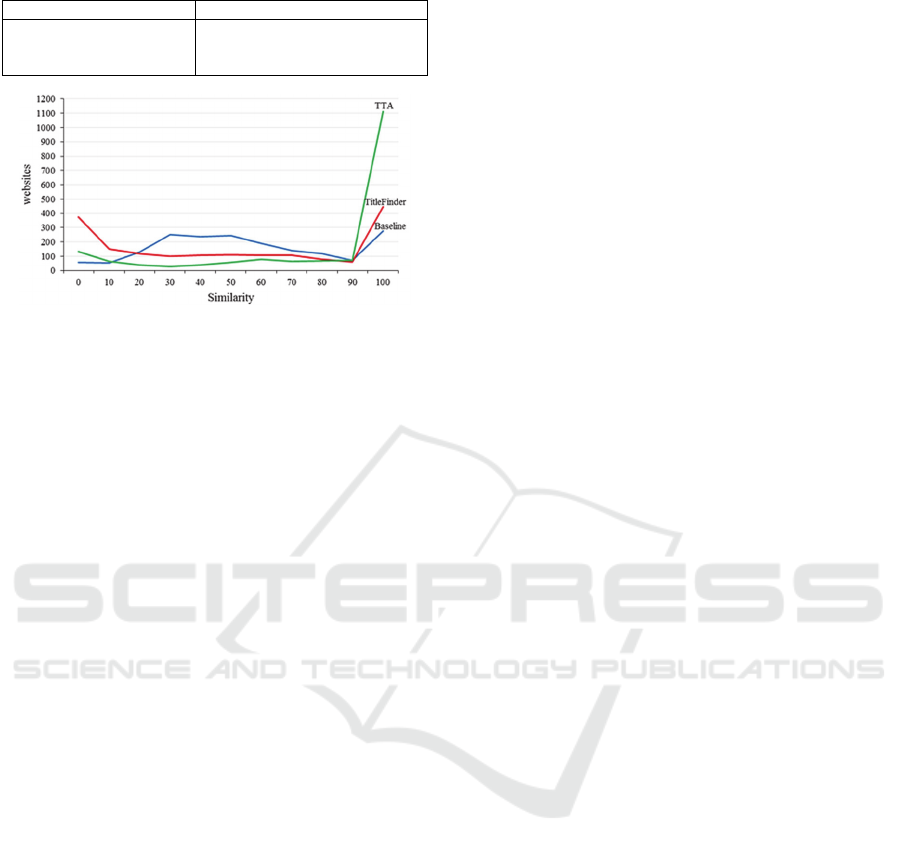
Table 5: Comparative results for title extraction methods.
Method Average similarity
Baseline 0.62
TitleFinder 0.52
TTA 0.84
Figure 5: Similarities of the detected titles with the ground
truth titles.
4 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, we propose a fully automated method to
extract titles from web pages without extensive needs
of training data or user interaction. The proposed
method analyses the content of the title and meta tags,
and it extracts suitable sub string to represent the
content of the web page. It should be short, but
informative to be used in both web and mobile
devices. The method, Title Tag Analyzer (TTA), is
integrated with Mopsi search to summarize the
retrieved web pages.
We conducted various experiments to evaluate the
performance of TTA and our findings are as follows:
The proposed method significantly outperforms
the baseline from 0.62 to 0.84 in the average
similarity.
Title and meta tags usually contain the correct
title, but they also contain irrelevant text which
needs to be processed and filtered.
The words in the web page link have the highest
impact on selecting the correct title for the page.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The work described in this paper was supported by
MOPIS project, University of Eastern Finland.
REFERENCES
Breiman, L. (2001). Random forests. Machine learning,
45(1), pp.5-32.
Brew, C. and McKelvie, D. (1996). Word-pair extraction
for lexicography. In Proceeding of the second
International Conference on New Methods in Language
Processing, pp. 45–55.
Cai, D., Yu, S., Wen, J. R., & Ma, W. Y. (2003). Vips: a
vision-based page segmentation algorithm (p. 28).
Microsoft technical report, MSR-TR-2003-79. p. 28.
Changuel, S., Labroche, N., & Bouchon-Meunier, B.
(2009). A general learning method for automatic title
extraction from html pages. In Machine Learning and
Data Mining in Pattern Recognition. pp. 704-718.
Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
Fränti, P., Chen, J., Tabarcea, A. (2011) Four Aspects of
Relevance in Sharing Location-based Media: Content,
Time, Location and Network. In WebIST, pp 413-417.
Hu, Y., Xin, G., Song, R., Hu, G., Shi, S., Cao, Y., & Li, H.
(2005). Title extraction from bodies of HTML
documents and its application to web page retrieval. In
Proceedings of the 28th annual international ACM.
SIGIR conference on Research and development in
information retrieval. pp. 250-257. ACM.
Fan, J., Luo, P., & Joshi, P. (2011). Identification of web
article pages using HTML and visual features. In
IS&T/SPIE Electronic Imaging International Society
for Optics and Photonics. pp. 78790K-78790K.
Jeong, O. R., Oh, J., Kim, D. J., Lyu, H., & Kim, W. (2014).
Determining the titles of Web pages using anchor text
and link analysis. Expert Systems with
Applications, 41(9). pp 4322-4329.
Kan, M. Y., & Thi, H. O. N. 2005. Fast webpage
classification using URL features. In Proceedings of the
14th ACM international conference on Information and
knowledge management. pp. 325-326. ACM.
Manning, C. D., & Raghavan, P. H. Sch utze. (2009). An
introduction to information retrieval.
Mohammadzadeh, H., Gottron, T., Schweiggert, F., &
Heyer, G. (2012). Finder: extracting the headline of
news web pages based on cosine similarity and overlap
scoring similarity. In Proceedings of the twelfth
international workshop on Web information and data
management .pp. 65-72. ACM.
Wang, C., Wang, J., Chen, C., Lin, L., Guan, Z., Zhu, J. &
Bu, J. (2009). Learning to extract web news title in
template independent way. In Rough Sets and
Knowledge Technology. pp. 192-199. Springer Berlin
Heidelberg.
Wang, J., Li, G., & Feng, J. (2014). Extending string
similarity join to tolerant fuzzy token matching. ACM
Transactions on Database Systems (TODS), 39(1), 7.
Win, C. S., & Thwin, M. M. S. (2014). Web Page
Segmentation and Informative Content Extraction for
Effective Information Retrieval. IJCCER, 2(2), pp 35-
45.
Xue, Y., Hu, Y., Xin, G., Song, R., Shi, S., Cao, Y., Lin C.
& Li, H. (2007). Web page title extraction and its
application. Information processing & management,
43(5). Pp 1332-1347.
WEBIST 2016 - 12th International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
210
