
Memory Efficient de novo Assembly Algorithm using Disk Streaming of
K-mers
Yuki Endo
1
, Fubito Toyama
2
, Chikafumi Chiba
3
, Hiroshi Mori
2
and Kenji Shoji
2
1
Collaboration Center for Research and Development, Utsunomiya University, Yoto 7-1-2,
Utsunomiya, Tochigi, 321-8585, Japan
2
Graduate School of Engineering, Utsunomiya University, Yoto 7-1-2, Utsunomiya, Tochigi, 321-8585, Japan
3
Faculty of Life and Environmental Sciences, University of Tsukuba, Tennoudai 1-1-1, Tsukuba, Ibaraki 305-8572, Japan
Keywords:
Bioinfomatics, Next Generation Sequencing, de novo Assembly.
Abstract:
Sequencing the whole genome of various species has many applications, not only in understanding biological
systems, but also in medicine, pharmacy, and agriculture. In recent years, the emergence of high-throughput
next generation sequencing technologies has dramatically reduced the time and costs for whole genome se-
quencing. These new technologies provide ultrahigh throughput with a lower per-unit data cost. However, the
data are generated from very short fragments of DNA. Thus, it is very important to develop algorithms for
merging these fragments. One method of merging these fragments without using a reference dataset is called
de novo assembly. Many algorithms for de novo assembly have been proposed in recent years. Velvet and
SOAPdenovo2 are well-known assembly algorithms, which have good performance in terms of memory and
time consumption. However, memory consumption increases dramatically when the size of input fragments is
larger. Therefore, it is necessary to develop an alternative algorithm with low memory usage. In this paper, we
propose an algorithm for de novo assembly with lower memory. In the proposed method, memory-efficient
DSK (disk streaming of k-mers) to count k-mers is adopted. Moreover, the amount of memory usage for
constructing de bruijn graph is reduced by not keeping edge information in the graph. In our experiment using
human chromosome 14, the average maximum memory consumption of the proposed method was approxi-
mately 7.5–8.8% of that of the popular assemblers.
1 INTRODUCTION
Determining whole genome sequences of various
species has many applications not only in understand-
ing biological systems, but also in medicine, phar-
macy, and agriculture. In recent years, the emer-
gence of high-throughput next-generation sequenc-
ing (NGS) technologies has dramatically reduced the
time and cost for whole genome sequencing. These
new technologies provide ultrahigh throughput with a
lower per-unit data cost. However, these technologies
generate sequence data from many very small frag-
ments (sometimes fewer than 100 base pairs) of DNA.
These fragments are typically called reads. The pre-
cision of NGS is not perfect, and reads might include
sequencing errors. Thus, developing algorithms for
merging these reads is very important. Merging reads
without reference data is called de novo assembly.
The de novo assembly algorithms can be classi-
fied into two approaches based on their features :
overlap-layout-consensus(OLC) and de Bruijn graph.
OLC relies on an overlap graph. Edena (Hernandez
et al., 2008), MIRA (Chevreux et al., 2004), Celera
(Miller et al., 2008), SSAKE (Warren et al., 2007),
and VCAKE (Jeck et al., 2007) assemblers are based
on the OLC approach. In the OLC strategy, over-
laps are found by all-against-all pair-wise compari-
son. Overlap graphs are constructed from pair-wise
overlaps. In the overlap graphs, a vertex represents
a read and an edge denotes an overlap between two
connected vertices (reads). Consensus sequences are
determined by tracing paths in the graph. On the other
hand, Velvet (Zerbino and Birney, 2008), ABySS
(Simpson et al., 2009), ALLPATHS (Butler et al.,
2008), and SOAPdenovo (Li et al., 2010) assemblers
are based on de Bruijn graph approach. In the de
Bruijn graph, a vertexrepresentsa sequence of k bases
(k-mer), where k is any positive integer. An edge rep-
resents an overlap of k-1 bases. Thus, two connected
vertices are denoted by a k-1 overlap between their
vertices (k-mers). After the de Bruijn graph is con-
structed from reads obtained by NGS, contigs are de-
266
Endo, Y., Toyama, F., Chiba, C., Mori, H. and Shoji, K.
Memory Efficient de novo Assembly Algorithm using Disk Streaming of K -mers.
DOI: 10.5220/0005798302660271
In Proceedings of the 9th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies (BIOSTEC 2016) - Volume 3: BIOINFORMATICS, pages 266-271
ISBN: 978-989-758-170-0
Copyright
c
2016 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
termined by tracing paths in the graph. The de Bruijn
graph approach is most widely applied to the short
reads from Solexa and SOLiD platforms. In this ap-
proach, fixed-length (k-1) overlaps are found and re-
dundant k-mers (subsequences) are compressed, mak-
ing it suitable for assembling vast quantities of short
reads. However, memory consumption increases dra-
matically when the size of input reads is extremely
large (more than several gigabytes) and it is hard to
use them for large-scale assemblies.
To overcome this problem, several algorithms
(Conway and Bromage, 2011; Bowe et al., 2012;
Chikhi and Rizk, 2012; Chikhi et al., 2014) have
been proposed in recent years. These algorithms are
also based on de Bruijn graph approach. In these
algorithms, the data structures for representing the
de Bruijn graphs are designed with small size. To
realize the compact de Bruijn graph, succinct data
structures (Conway and Bromage, 2011; Bowe et al.,
2012), Bloom filter(Chikhi and Rizk, 2012) and FM-
index(Chikhi et al., 2014) are used. However, the
overall costs, including the costs for constructing the
compact graph, are not discussed in detail because
these papers focused on how to represent the com-
pact de Bruijn graph. In general, the processes of
constructing de Bruijn graph (such as k-mer count-
ing) consume much memory and time. Therefore,
developing an algorithm in consideration of overall
costs is very important. On the other hand, an al-
gorithm called DSK (disk streaming of k-mers) for
k-mer counting with low memory usage (Rizk et al.,
2013) has been proposed. In this algorithm, the disk
storage (such as HDD and SSD) is used during pro-
cessing of k-mer counting. Thus, the amount of main
memory usage for k-mer counting can be greatly re-
duced in DSK.
In this paper, we propose an algorithm for large
scale de novo assembly with low memory usage. In
our method, k-mers are extracted using DSK. Al-
though our algorithm is based on de Bruijn graph ap-
proach in the same way as Velvet, edge information
is not kept in the main memory. Thus, the amount of
memory usage can be greatly reduced by our method.
The maximum memory usage in overall assembly
processes is evaluated and compared in our experi-
ments. Therefore, in the proposed method, the overall
costs for de novo assembly are taken into account. In
addition, the data structure for representing de Bruijn
graph is simple. In our experiments using the human
chromosome 14, the average maximum memory con-
sumption of the proposed method was approximately
7.5–8.8% of that of the popular assemblers.
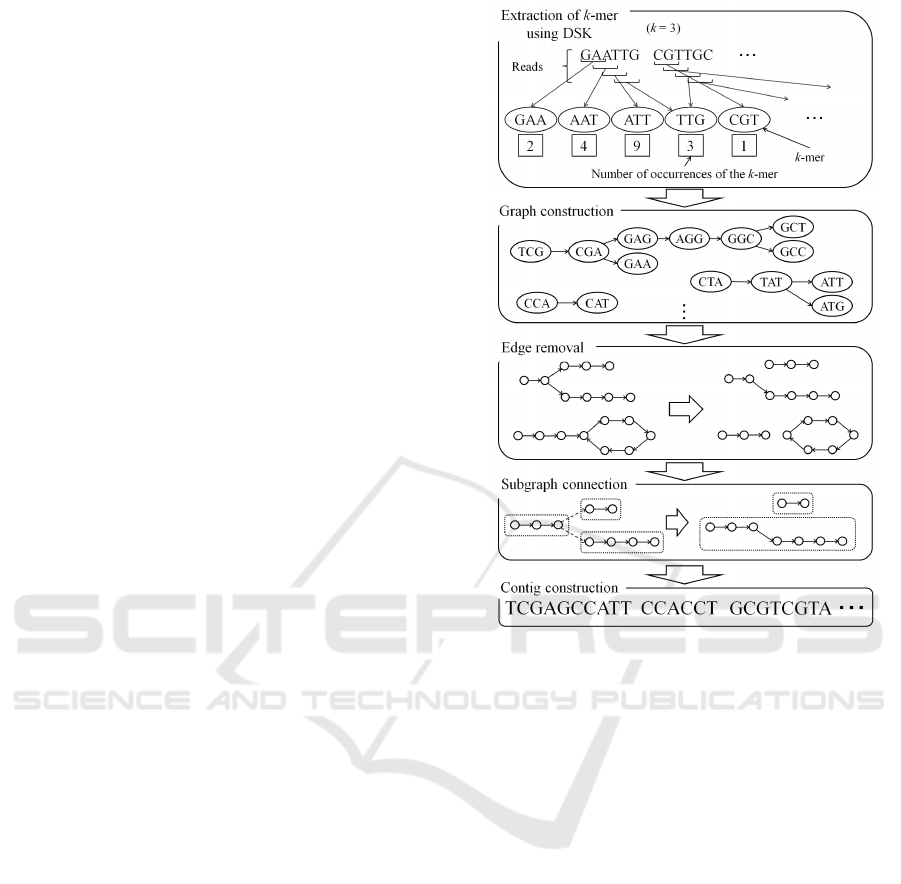
Figure 1: Outline of the proposed method.
2 ASSEMBLY ALGORITHMS
WITH LOW MEMORY
CONSUMPTION
In this paper, we propose an algorithm for large scale
de novo assembly with low memory usage. The pro-
posed method uses a memory-efficient de novo as-
sembly algorithm (Endo et al., 2014), and k-mers are
extracted using DSK (Rizk et al., 2013). For more
detail on these algorithms refer to the each papers.
Figure 1 shows the outline of our algorithm. First,
from all reads, k-mers are extracted using DSK. At
the same time, the number of occurrences of each k-
mer is also counted. Second, all k-mers and number of
occurrences obtained by DSK are loaded. Third, the
de Bruijn graph is constructed using k-mers. Then,
the graph is partitioned into subgraphs such that the
subgraph has a simple path or a simple cycle. The
simple path does not have repeating vertices or edges
in the graph. Then subgraphs are connected to make a
larger simple path. The data about the number of oc-
currences of a k-mer are used to make an informed
selection of path connections. Finally, contigs are
Memory Efficient de novo Assembly Algorithm using Disk Streaming of K-mers
267
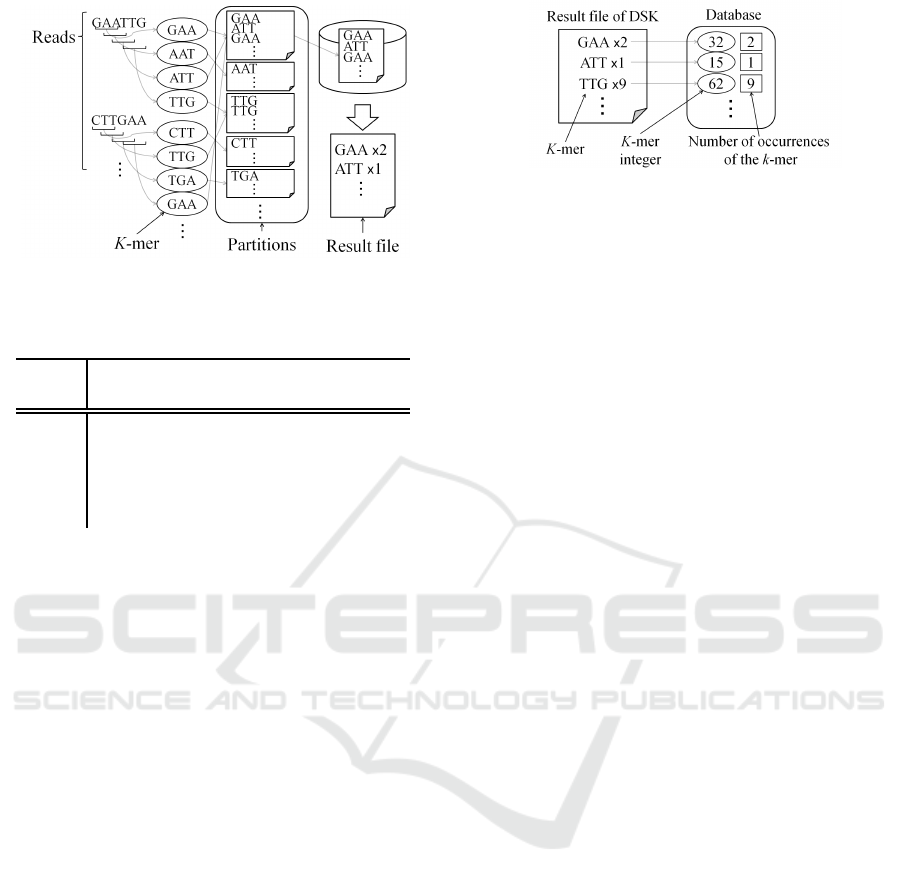
Figure 2: Outline of the DSK.
Table 1: k-mer sequence corresponding to k-mer integer
(in case of 3-mer).
k-mer Quaternary Binary
k-mer integer
(decimal)
AAA 0 0 0
AAC
1 1 1
AAG 2 10 2
AAT
3 11 3
ACA 10 100 4
ACC
11 101 5
generated by tracing vertices in each of the connected
graphs.
2.1 Counting K-mers using DSK
From all reads, k-mers and the number of occurrences
of each k-mers are extracted using DSK in the pro-
posed method. DSK is an algorithm for k-mer count-
ing, and can output k-mers and the number of occur-
rences of each k-mers. In this algorithm, the disk stor-
age (such as HDD and SSD) is used during processing
of k-mer counting. Although this approach requires
relatively large capacity disk, the amount of memory
usage can be greatly reduced.
Figure 2 shows the outline of DSK. First, the
multi-set of all k-mers present in the reads is parti-
tioned, and partitions are saved to disk. Next, the each
partition is separately loaded in main memory. The
size of each partition is comparatively small. Thus,
the required memory consumption can be reduced.
All k-mers are counted by traversing each partition.
As a result, all k-mers and the number of occurrences
of each k-mer are counted, these results are written to
a file.
2.2 Loading K-mers
All k-mers and the number of occurrences obtained
by DSK are loaded. They are kept in a database in
the memory as “k-mer integers”. As shown in Table
Figure 3: Collection of k-mer and the contents of database
in the proposed method (in case of 3-mer).
1, a k-mer integer is a one-to-one numeric represen-
tation of each k-mer. Using the k-mer integer repre-
sentation, the amount of memory for k-mer sequences
can be reduced. In this work, k-mer integers and the
number of occurrences of the k-mers corresponding
to the k-mer integer are kept in the main memory. In
order to lower memory usage, other data are not kept
in the main memory. The k-mer sequences in which
the number of occurrences is small (less than a thresh-
old) are not used in the graph construction because it
is likely that such k-mer sequences contain sequenc-
ing errors. In our experiments, the threshold was set
to 2. Figure 3 shows the collection of k-mers and the
contents of the database in the proposed method.
2.3 Graph Construction
The de Bruijn graph is constructed using loaded k-
mers. In the de Bruijn graph, each vertex represents
a k-mer. An edge represents an overlap of k-1 bases.
Thus, two connected vertices denote a k-1 overlap be-
tween their vertices (k-mers).
In conventional algorithms using de Bruijn
graphs, when the graph is constructed, edge informa-
tion about which vertices are connected to each other
is also kept in main memory. Since there are many
edges in the graph, keeping all the edge information
consumes a huge amount of memory. In our method,
the edge information is not kept in main memory. The
existence of the edge is calculated only when it is re-
quired. Specifically, the vertices that are connected
by a directed edge from a vertex have only 4 types of
k-mers because the k-mers, which are represented by
the connected vertices, overlap by k-1 bases. Thus,
the connected vertices (k-mer sequences) can be ob-
tained by checking for four values of k-mer integers in
the database. Only the data representing the vertices
are kept in the database. Construction of the graph is
finished by registering the k-mer integers from all k-
mer sequences and the number of occurrences of each
in our database.
BIOINFORMATICS 2016 - 7th International Conference on Bioinformatics Models, Methods and Algorithms
268
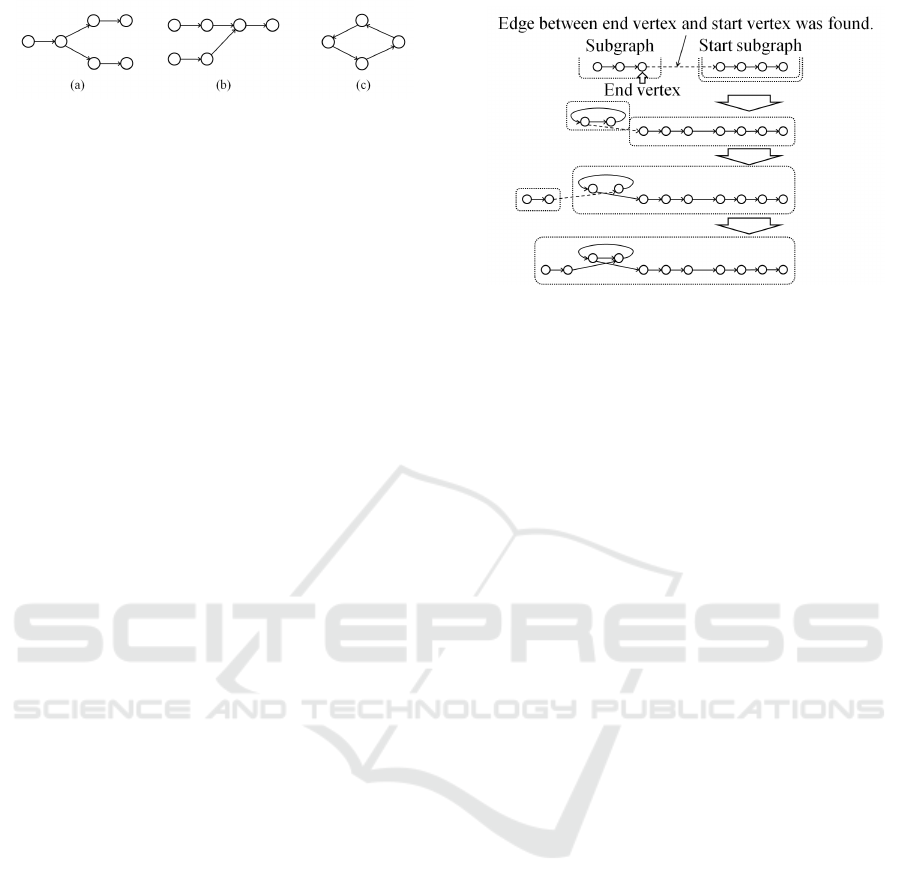
Figure 4: Examples of branches and cycle.
2.4 Edge Removal
The constructed graph has numerous branches and
cycles. Consequently, it is important to select the
connections in the path from which a contig is con-
structed. Figure 4 shows examples of branches and
cycle. A vertex with multiple edges connecting to
other vertices is illustrated in Fig. 4 (a) and 4 (b).
Figure 4 (c) shows an example of a cycle. In order to
solve these probrems, The edge removal process we
have used is as follows.
1. A start vertex (k-mer) that has the largest number
of occurrences is selected.
2. The start vertex is set to the current vertex.
3. Check for vertices that are connected to the cur-
rent vertex.
(a) If one connected vertex is found, the vertex is
set to the current vertex. Go to 3.
(b) If multiple connected vertices are found, one of
them is set to the current vertex. (The details
are described in later in this section.) Go to 3.
(c) If the connected vertex is not found, the current
vertex is regarded as the end vertex. Go to 4.
4. Check for additional vertices that have not been
selected yet.
(a) If there are additional vertices that have not
been selected, a newstart vertex with the largest
number of occurrences is selected from the ver-
tices that have not been checked yet. Go to 2.
(b) If all vertices have been checked, the process is
finished.
In this process, the vertices that are put together in
a path are assigned the same label. A path from the
start vertex to the end vertex represents a subgraph.
Multiple subgraphs are created in this process.
The inclusion of branches and cycles in vertex se-
lection is as follow: when there are multiple outgoing
(incoming) edges from the current vertex as shown
Fig. 4 (a) and 4 (b), the edge connected to the vertex
in which the number of occurrences is the largest is
selected, and the other outgoing (incoming) edges are
removed. The current vertex is also regarded as the
end vertex when the label of the selected vertex is the
same as that of the current vertex as shown in Fig. 4
(c) (in the case of a cycle).
Figure 5: Example of subgraphs connection.
2.5 Subgraph Connection and Contig
Construction
To construct a longer path, subgraphs obtained by the
process described in previous section are connected.
The outline of the subgraph connection process is as
follows. First, a subgraph with simple path is se-
lected. The subgraph with the longest path is selected
from those subgraphs that have not previously been
selected. This subgraph is set as the start subgraph.
Next, the subgraphs in which the start vertex or the
end vertex are connected to the start or end vertex of
the selected subgraph are searched. If a connecting
subgraph is found, the start (end) vertex is connected
to the end (start) vertex, and the two subgraphs are
merged into a single subgraph. This graph expanding
process is repeated until no more merges can be made.
If there are multiple subgraphs that can be connected,
the subgraph with longer simple path is selected. Fig-
ure 5 shows an example of connecting subgraphs. The
connection in this example is on the left side. The
same process is also performed on the right side.
After the subgraphs are connected, a list of the
vertices is obtained by tracing all the paths that are
included in the subgraphs. A contig is generated
by merging the various k-mers that are referenced
from the vertices to eliminate the overlapping bases
as shown in Fig. 6. The final contigs are obtained by
repeating this process for all subgraphs. Any contigs
that are longer than a given threshold are output. The
threshold was set to 200bp.
3 EXPERIMENTS AND RESULTS
To evaluate the performance of the proposed method,
we compare the performance of our method with that
of Velvet(Ver. 1.2.08) and SOAPdenovo2 (Ver. 2.04).
Velvet (Zerbino and Birney, 2008) is one of the most
popular de novo assembly algorithms based on the de
Memory Efficient de novo Assembly Algorithm using Disk Streaming of K-mers
269
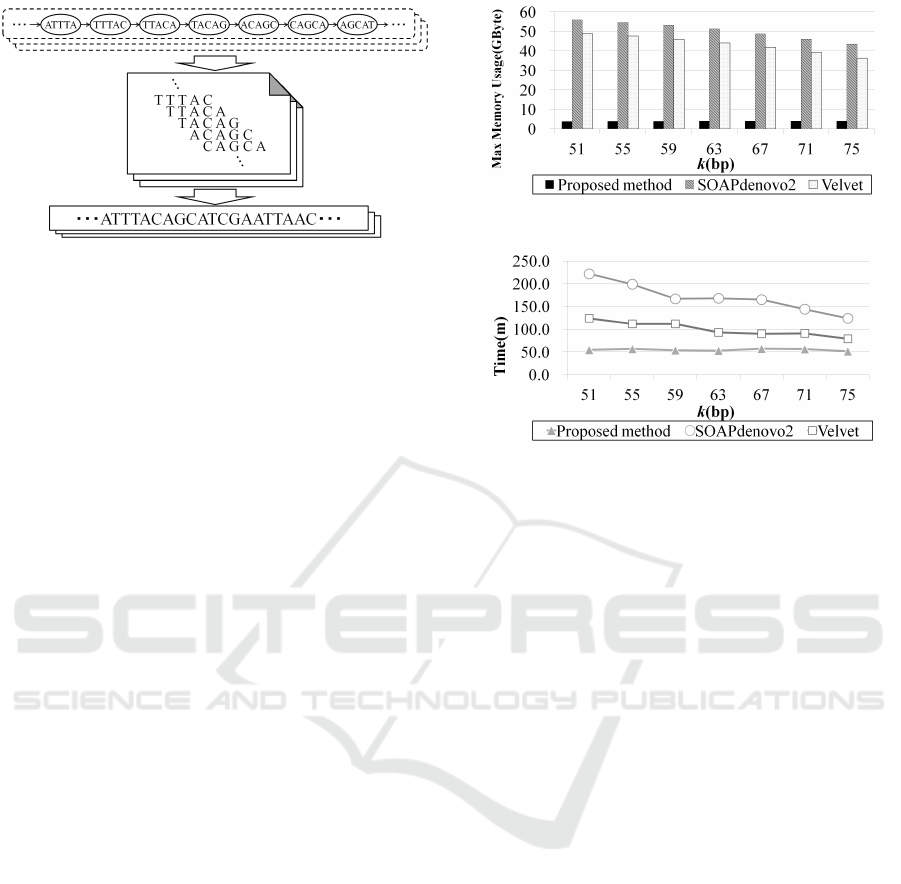
Figure 6: Generation of contigs.
Bruijn graph. In many papers on de novo genome as-
sembly, Velvet is used as a comparison to assess the
assembly performance. SOAPdenovo (Li et al., 2010)
is also a popular de novo assembler based on the de
Bruijn graph, which is designed to assemble large
genomes. SOAPdenovo has been successfully used
to assemble many published genomes. SOAPdenovo2
is the successor of SOAPdenovo. In SOAPdenovo2,
assembly performance in memory consumption, ac-
curacy, and coverage is improved. In the proposed
method, we used Ver. 2.0.7 of DSK. In our exper-
iment, the complete DNA sequence for human chro-
mosome 14 was used. The sequence length is approx-
imately 107Mbp, the ungapped sequence is approx-
imately 88Mbp. Assemblies were performed using
the reads form GAGE (Salzberg et al., 2012) datasets.
The GAGE (Genome Assembly Gold-standardEvalu-
ations) is one of the performance comparison datasets
used for de novo assembly algorithms. GAGE has
focused on the quality of the assembly, but not on
memory requirements. We used the dataset as a single
end and FASTA format, converted from the reads in
GAGE datasets, which are paired end and FASTQ for-
mat. The dataset is approximately 61 million reads,
and the size of read is 101bp. The assemblers were
run with k-mer sizes of 51, 55, 59, 63, 67, 71, and
75. We assessed the maximum memory consump-
tion, the running time, the contig length, and the accu-
racy of contigs from these programs in comparison to
ours. The experimental assemblies using these three
programs were all carried out on the same machine.
(CPU: Intel Xeon E5-2660 2.2GHz 8-core, Memory:
189GByte)
Figures 7 and 8 show the maximum memory us-
age and the running time of each assembly algorithm
for each tested k-mer. As shown in Fig. 7, The aver-
age maximum memory consumption of the proposed
method was approximately 7.5% of SOAPdenovo2,
and approximately 8.8% of Velvet. Therefore, we met
our goal of reducing memory usage. The amount of
memory usage was reduced for increased k-mer size
in both SOAPdenovo2 and Velvet. In the proposed
Figure 7: Comparison of maximum memory consumption.
Figure 8: Comparison of running time.
method, a relationship between k-mer size and maxi-
mum memory usage was not consistent for the human
assembly. Moreover, as shown in Fig. 8, the average
running time of the proposed method was faster than
both of the other methods. Table 2 shows the results
of the assemblies. The N50 length is defined as the
length of the shortest contig where the sum of contigs
of an equal length or longer is at least 50% of the total
length of all contigs. The best k-mer size was the size
providing the largest N50. As shown in Table 2, the
N50 length of the proposed method was shorter than
that of the others, and the error rate was higher than
that of the others. In addition, the number of contigs
is more than that of the others. This is likely due to
the simplicity of the path-tracingalgorithm of the pro-
posed method. Thus, these results could be improved
with a more complicated path-tracing algorithm. On
the other hand, there were not large differences in the
genome coverage.
4 CONCLUSION
In this paper, we propose an algorithm for large-
scale de novo assembly with low memory usage. In
our experiments using the human chromosome 14,
the average amount of memory used in the proposed
method was approximately 7.5–8.8% of SOAPden-
ovo2 and Velvet. These results showed that the pro-
posed method outperformed SOAPdenovo2 and Vel-
vet for memory consumption. On the other hand, the
N50 and error rate of contigs obtained by the pro-
posed method were worse than that of the other as-
BIOINFORMATICS 2016 - 7th International Conference on Bioinformatics Models, Methods and Algorithms
270

Table 2: Comparison of assemblies.
Assembler
Best k-mer
size (bp)
N50
(bp)
# of
contigs
Total
(kbp)
Genome
covered (%)
Genome covered
without gaps (%)
Error rate
(%)
Proposed method 55 2,801 127,326 91,796 76.733 93.298 7.764
SOAPdenovo2 63 4,005 43,032 85,648 78.695 95.684 0.128
Velvet
63 5,166 29,179 84,335 77.075 93.714 1.350
semblers. Further investigation is needed to improve
the N50 and error rate of contigs in our method by
modifying the path-tracing algorithm.
REFERENCES
Bowe, A., Onodera, T., Sadakane, K., and Shibuya, T.
(2012). Succinct de bruijn graphs. In WABI, volume
7534 of Lecture Notes in Computer Science, pages
225–235. Springer.
Butler, J., MacCallum, I., Kleber, M., Shlyakhter, I. A.,
Belmonte, M. K., Lander, E. S., Nusbaum, C., and
Jaffe, D. B. (2008). ALLPATHS: de novo assembly
of whole-genome shotgun microreads. Genome Res.,
18(5):810–820.
Chevreux, B., Pfisterer, T., Drescher, B., Driesel, A. J.,
Muller, W. E., Wetter, T., and Suhai, S. (2004). Using
the miraEST Assembler for Reliable and Automated
mRNA Transcript Assembly and SNP Detection in
Sequenced ESTs. Genome Res., 14(6):1147–1159.
Chikhi, R., Limasset, A., Jackman, S., Simpson, J., and
Medvedev, P. (2014). On the representation of de
bruijn graphs. In RECOMB, volume 8394 of Lecture
Notes in Computer Science, pages 35–55. Springer.
Chikhi, R. and Rizk, G. (2012). Space-efficient and exact
de bruijn graph representation based on a bloom filter.
In WABI, volume 7534 of Lecture Notes in Computer
Science, pages 236–248. Springer.
Conway, T. C. and Bromage, A. J. (2011). Succinct data
structures for assembling large genomes. Bioinfor-
matics, 27(4):479–486.
Endo, Y., Toyama, F., Chiba, C., Mori, H., and Shoji, K.
(2014). De Novo Short Read Assembly Algorithm
with Low Memory Usage. In Proceedings of Inter-
national Conference on Bioinformatics Models, Meth-
ods and Algorithms (BIOINFORMATICS2014), pages
215–200.
Hernandez, D., Francois, P., Farinelli, L., Osteras, M., and
Schrenzel, J. (2008). De novo bacterial genome se-
quencing: millions of very short reads assembled on a
desktop computer. Genome Res., 18(5):802–809.
Jeck, W. R., Reinhardt, J. A., Baltrus, D. A., Hicken-
botham, M. T., Magrini, V., Mardis, E. R., Dangl,
J. L., and Jones, C. D. (2007). Extending assembly
of short DNA sequences to handle error. Bioinformat-
ics, 23(21):2942–2944.
Li, R., Zhu, H., Ruan, J., Qian, W., Fang, X., Shi, Z., Li,
Y., Li, S., Shan, G., Kristiansen, K., Li, S., Yang, H.,
Wang, J., and Wang, J. (2010). De novo assembly
of human genomes with massively parallel short read
sequencing. Genome Res., 20(2):265–272.
Miller, J. R., Delcher, A. L., Koren, S., Venter, E., Walenz,
B. P., Brownley, A., Johnson, J., Li, K., Mobarry,
C., and Sutton, G. (2008). Aggressive assembly of
pyrosequencing reads with mates. Bioinformatics,
24(24):2818–2824.
Rizk, G., Lavenier, D., and Chikhi, R. (2013). Dsk: k-mer
counting with very low memory usage. Bioinformat-
ics, 29(5):652–653.
Salzberg, S. L., Phillippy, A. M., Zimin, A., Puiu, D.,
Magoc, T., Koren, S., Treangen, T. J., Schatz, M. C.,
Delcher, A. L., Roberts, M., et al. (2012). GAGE: A
critical evaluation of genome assemblies and assem-
bly algorithms. Genome Res., 22(3):557–567.
Simpson, J. T., Wong, K., Jackman, S. D., Schein, J. E.,
Jones, S. J., and Birol, I. (2009). ABySS: a parallel
assembler for short read sequence data. Genome Res.,
19(6):1117–1123.
Warren, R. L., Sutton, G. G., Jones, S. J., and Holt, R. A.
(2007). Assembling millions of short DNA sequences
using SSAKE. Bioinformatics, 23(4):500–501.
Zerbino, D. R. and Birney, E. (2008). Velvet: algorithms for
de novo short read assembly using de Bruijn graphs.
Genome Res., 18(5):821–829.
Memory Efficient de novo Assembly Algorithm using Disk Streaming of K-mers
271
