
A Statistical Approach to the Detection of HTML Attribute Permutation
Steganography
Sedeeq Iman, Coenen Frans and Lisitsa Alexei
Department of Computer Science, University of Liverpool, Liverpool, U.K.
Keywords:
Steganography, Standard Deviation, Attribute Permutation.
Abstract:
A mechanism for monitoring WWW pages to identify the presence (or otherwise) of attribute permutation
steganography is presented. The proposed mechanism is based on a statistical approach, more specifically an
attribute position Standard Deviation (SD) measure is used to detect the modification of attribute locations
within webpages. The monitoring of web pages involves usage of a SD threshold. The determination of this
threshold involves a training process using seeded training data. Once a threshold has been learnt monitoring
can be commenced. An evaluation of the process is presented indicating that the attribute position SD concept
can be successfully used to monitor web pages for attribute permutation steganography.
1 INTRODUCTION
Steganography is the art of hiding messages within an
innocent cover carrier such as digital media (image,
audio, video, text) in such a way that casual observers
would not be aware of the existence of the hidden
message, only the sender and the intended receiver.
New networking environments, such as cloud com-
puting and wireless networks environments, and new
communication devices such as smart phones have
also created many new opportunities for steganogra-
phers(Wendzel et al., 2014; Zieli
´
nska et al., 2014).
The increasing use of social media has facilitated
a huge increase in the amount of information ex-
changed over the internet, and consequently concerns
about the threat of steganography have increased cor-
respondingly. As a result there is a significant need for
steganographic countermeasures; techniques and pro-
cesses to determine whether a file (carrier) includes a
hidden message or not, and if so techniques and pro-
cesses to extract this secret message and/or destroy it.
For steganography to operate the following char-
acteristics of the cover medium are important: (i)
be a common (popular) medium (such as web pages
or email) to avoid raising suspicion, and (ii) allow
changes to be made without this being noticeable to
casual observers. HTML encoded web pages are an
ideal cover medium. HTML is the language of the
web; HTML documents are thus the most popular
file format used to present information over the In-
ternet. Also HTML files have many enriched features
like scripts and hyperlinks that can be exploited when
wishing to embed secret messages. HTML encoded
web pages thus feature the necessary cover medium
characteristics identified above. Consequently HTML
encoded web pages have attracted the attention of
steganographers as the cover carrier of choice.
This paper presents an approach to the detection
of hidden messages that are embedded using what
is known as “attribute permutation” steganography.
The fundamental idea presented is that the monitor-
ing the Standard Deviation (SD) of attributes loca-
tions within a webpage can be used to detect the pres-
ence of hidden message. The work is based on the
conjecture that the SD increases when attribute per-
mutation steganography takes place. We provide the
empirical evidence that indeed the conjecture holds
true. In order to use it for the steganography detection
though one has to take into account that (1) SD com-
puted for different HTML encoded web pages without
any embedded messages may vary significantly; (2)
SD computed for the same web page with dynamic
content may vary from time to time. We propose a
monitoring procedure which when applied for a web
page with dynamic content, learns a normal level of
SD and its threshold value, any excess of which is in-
terpreted as the presence of a hidden message.
522
Iman, S., Frans, C. and Alexei, L.
A Statistical Approach to the Detection of HTML Attribute Permutation Steganography.
DOI: 10.5220/0005801705220527
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy (ICISSP 2016), pages 522-527
ISBN: 978-989-758-167-0
Copyright
c
2016 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

2 HTML STEGANOGRAPHY
HTML (Hyper-Text Markup Language) comprises
markup tags which tell a browser the format in which
to display tables, paragraphs, images and so on. Most
tags are paired using a start tag and an end tag, with
text content in between. According to the HTML
specification tags can also have attributes that can be
used to customize the tag, and these attributes have
values assigned to them by default or by the user.
The HTML specification does not determine the or-
der of these attributes. Moreover HTML allows for
the inclusion of hyperlinks and scripts; enriching fea-
tures that represent a fertile ground for steganography.
Steganographic techniques in HTML can be largely
classified into three groups: (i) Embedding invisible
characters (Sui and Luo, 2004), (ii) Switching tag let-
ters case (Zhao and Lu, 2007) and (iii) Attribute per-
mutation (S.Forrest, 2006; Huang et al., 2008; Shen
and Zhao, 2010). The latter is the focus of the work
presented in this paper.
2.1 Attribute Permutation
Attributes in HTML tags can come in any order, the
HTML specification does not prescribe any attribute
ordering. Therefore a tag with eight attributes has
8! = 40320 equivalent attribute configurations that are
all processed in an identical manner by a browser. The
ordering of the attributes can be used to embed a hid-
den message.
From the perspective of the steganographer at-
tribute permutation offers the same advantages as the
switching tag letter case method: (i) the presentation
of the HTML file in a browser gives no indication of
there being any hidden messages and (ii) the file size
is unaffected. However, in addition, it is difficult to
identify by inspection of the HTML source code.
Several algorithms have been proposed to achieve
attribute permutation steganography, examples can be
found in (S.Forrest, 2006; Huang et al., 2008; Shen
and Zhao, 2010). The method used with respect to the
evaluation presented in this paper is that of (Shen and
Zhao, 2010) where a relation between tag attributes
is defined using a binary string which is later trans-
formed into a set of permutations and the current tag
is randomly replaced with one of these permutations.
The attribute permutation embedding capacity of
a given web page is defined as the number of bits of
secret message that we can embed in a given web-
page H. According to the steganography algorithm
in (Shen and Zhao, 2010) we can embed (n − 1)
bits of secret message in a webpage using tags that
have more than one attribute. The Maximum Embed-
ding Capacity (MEC) in bytes can be calculated using
equation 1:
MEC(H) =
1
8
∑
T
j
∈Q
(|T
j
|−1) (1)
where Q is the set of tags featured in H of two or
more attributes, and |T
j
| is the number of attributes in
tag T
j
, the jth tag in Q. We multiply by
1
8
so that the
result is in bytes.
3 STANDARD DEVIATION OF
ATTRIBUTE LOCATIONS
The main idea presented in this paper is to identify the
presence of attribute permutation steganography by
monitoring the Standard Deviation (SD) of attributes
locations within a webpage. This is based on the as-
sumption that for the HTML pages without message
embeddings the attributes tend to be located in the
same locations for the most of the tags. By reorder-
ing attributes in tags, so as to hide a message, the
coherency of the attribute locations changes. More
specifically the dispersion of attribute locations will
increase if message hiding is taking place, in other
words the variance of attribute locations will increase.
The conjecture is that the above can be usefully em-
ployed to distinguish a stego file from a regular file.
Before presenting the proposed stego file identifi-
cation algorithm the following definitions should be
noted:
• H is a webpage.
• Q: is a set of tags in H that have two attributes or
more, Q = {T
1
, T
2
, .. . }.
• T
j
= {a
1
, a
2
, .. . , a
n
} denotes the j
th
tag in Q with
its attributes.
• |T
j
|: represents the number of attributes in the j
th
tag.
• ANS = {a
1
, a
2
, ...a
n
}: is the complete set of at-
tributes in Q.
• ALS(a
i
): A set of locations in Q for attribute a
i
.
ALS(a
i
) = {la
i1
, la
i1
, .. . la
im
}. Each attribute has
m occurrences such that : |ALS(a
i
)| = m.
• VALS(a
i
): is the variance of ALS(a
i
):
VALS(a
i
) =
∑
m
k=1
(la
ik
−av)
2
m
(2)
av =
∑
m
k=1
la
ik
m
(3)
A Statistical Approach to the Detection of HTML Attribute Permutation Steganography
523

• VQ: is the total variance of all attributes in Q. The
total variance is equal to the sum of their variances
as shown in equation 4 below:
V Q = VAR(
m
∑
i=1
VALS(a
i
)) =
m
∑
i=1
VALS(a
i
) (4)
• SD: is the standard deviation of VQ in order to
quantify the amount of variation of a set of a web-
page attribute locations. It can be calculated by:
SD =
p
V Q (5)
The process for calculating the SD of attributes
is given in Algorithm 1. The algorithm operates as
follows: The input is a webpage H. The output is the
standard deviation of the set of Q attributes locations.
Algorithm 1: Calculate standard deviation SD of attributes
locations of a webpage.
1: inputH
2: ANS = {}
3: ALS = {}
4: Find Q
5: for each tag T ∈ Q do
6: for each attribute a ∈ T do
7: ANS = ANS + a.name
8: ALS = ALS + a.location
9: end for
10: end for
11: for each attribute a ∈ ANS do
12: for i = 1 to i = m do
13: VALS(a
i
) =
∑
m
k=1
(la
ik
−av)
2
m
14: av =
∑
m
k=1
la
ik
m
15: end for
16: end for
17: V Q =
∑
m
i=1
VALS(a
i
)
18: SD =
√
V Q
4 ATTRIBUTE PERMUTATION
STEGANOGRAPHY
MONITORING PROCESS
Using the above approach we can determine the at-
tribute location SD for a given www page H. By
monitoring the attribute location SD of H over a pe-
riod of time the conjecture is that we can identify at-
tribute permutation steganography whenever unusual
SD values are detected. This requires the establish-
ment of a webpage steganography detection thresh-
old σ. The idea is that the value for σ can be learnt
by deliberately seeding a sequence of “snapshots“
C = {s
1
, s
2
, .. . ,
n
}of H with hidden messages (using
attribute permutation steganography). In other words
the monitoring commences with a “training process“
during which the value for σ is learnt. More specif-
ically snapshots of the web page of interest are col-
lected periodically at intervals of time τ over a period
of time T . For each snapshot a message of length L
is generated (L ≤ MEC(H)) and the SD before and
after message embedding calculated. The value for σ
is then calculated using equation
σ = (α ×SD
avbe f ore
) + ((1 −α) ×SD
ava fter
) (6)
Where: (i) α is a user specified sensitivity factor of
between 0.1 and 1 (ii) SD
avbe f ore
is the average SD
without message hiding and (iii) SD
ava fter
is the aver-
age SD with message hiding. Note that a high α value
will have the effect of reducing σ and making the de-
tection process more sensitive. Note that the chance
of identifying false positives increases as the value for
σ decreases.
The arguments of the monitoring process are as
follows:
• H: is (HTML encoded) web page with dynamic
content.
• α: is a sensitivity factor, 0 < α < 1.
• T : is the total training time.
• τ: is the interval to capture a webpage snapshot
periodically for example every two hours.
• L: is the length of embedded message.
The actual monitoring process then comprises three
steps:
1. Collecting snapshots of H with interval τ over
time period T to give the set C = {s
1
, s
2
, .. . , s
n
}
2. Calculating the threshold σ .
(a) For each s
i
∈C compute the SD of snapshot s
i
,
then embed a message using the algorithm in
(Shen and Zhao, 2010) and compute the new
SD.
(b) Compute the average of the SDs before embed-
ding (SD
avbe f ore
=
∑
k
i=0
SD
i
k
) and the average of
the SDs after embedding (SD
ava fter
=
∑
k
i=0
SD
i
k
);
Where k represents the number of snapshots.
(c) The σ value is then calculated using equation 6.
3. Detecting: compute SD of a suspected instance of
H and compare it with σ; If SD≥ σ then the page
is a stego page otherwise the page is an unmodi-
fied page.
ICISSP 2016 - 2nd International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy
524
5 EVALUATION
The objectives of the evaluation of the proposed ap-
proach were as follows:
1. To confirm that the conjecture that increases in the
attribute locations SD of webpages is indeed an
indicator attribute permutation steganography.
2. To compare naturally occurring changes in SD
values caused by the dynamic content with the
changes caused by message embedding.
3. To test how the type of the embedded text may
affect the changes in SD.
4. To conform that the attribute locations SD concept
could be effectively used to monitor web pages for
attribute permutation steganography.
5.1 Attribute Locations SD as an
Indicator of Attribute Permutation
Steganography
The experiments designed to establish that the at-
tribute locations SD of webpages could indeed be
used to detect attribute permutation steganography
were founded on three “snapshots“ of the landing
page of three well known websites: (i) Sony (ii) BBC
and (iii) Wikipedia. In each case attribute permu-
tation was used to embed hidden message using the
technique presented in (Shen and Zhao, 2010) (as de-
scribed previously in Section 2). Messages of differ-
ent length L were embedded from between 10% to
100% of the MEC, incrementing in steps of 10%. The
MEC for the BBC, Wikipedia, Sony pages were 70
bytes, 74 bytes and 117 bytes respectively.
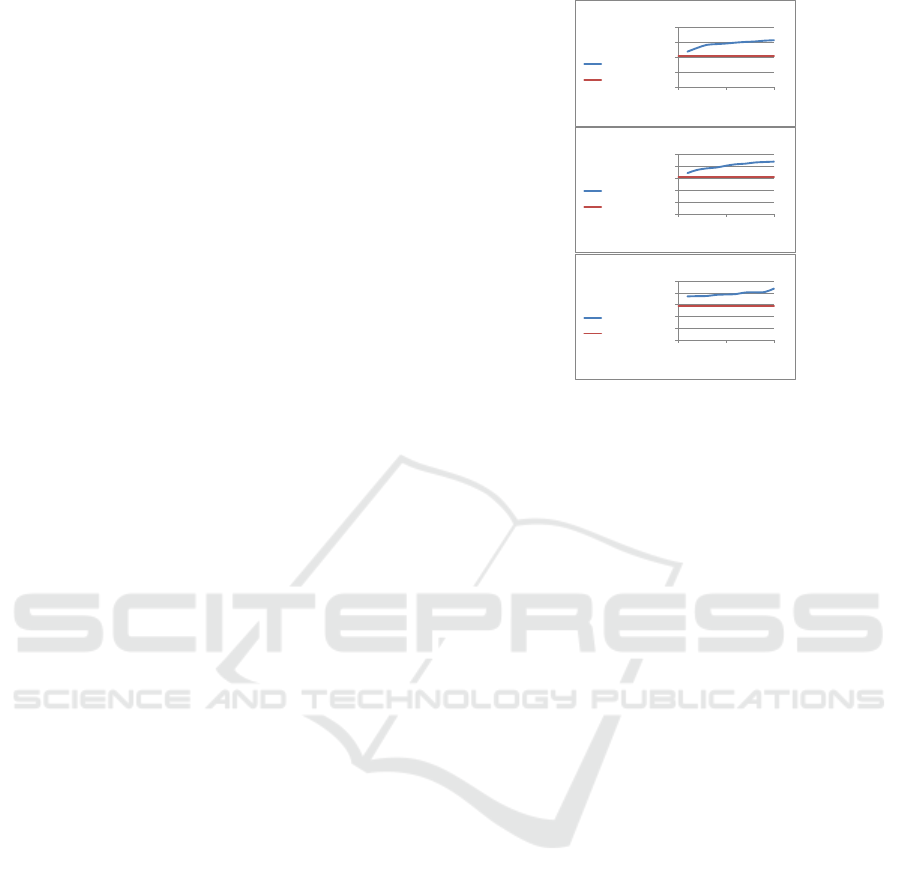
The results are as shown in Figure 1. The x-axis
lists the message size as a percentage of the MEC for
each landing page; the y-axis then gives the SD. From
the figure it can be observed that the SD starts to in-
crease, with respect to the SD for the landing page
without any hidden message embedding, as the size
of the embedded message increases. When the size
of the hidden message was equivalent to the MEC for
each given landing page the recorded increase in SD
equated to 13.1%, 14.6% and 21% respectively. Thus,
from the above, we can conclude that attributes loca-
tion SD can indeed be used for the purpose of identi-
fying attribute permutation steganography.
5.2 Natural Changes in SD vs Changes
Caused by Embedding
To compare naturally occuring changes in SD val-
ues caused by the dynamic content with the changes
0
2
4
6
8
0% 50% 100%
SD
Stego-channel Capacity
Sony.com SD before and after embedding
SDafter
SDbefore
0
1
2
3
4
5
0% 50% 100%
SD
Stego-channel Capacity
BBC.com SD before and after embedding
SDafter
SDbefore
0
1
2
3
4
5
0% 50% 100%
SD
Stego-channel Capacity
wikipedia.org SD before and after embedding
SDafter
SDbefore
Figure 1: Standard deviation SD of attributes locations de-
pendency on the message length.
caused by message embedding the following experi-
ments have been done.
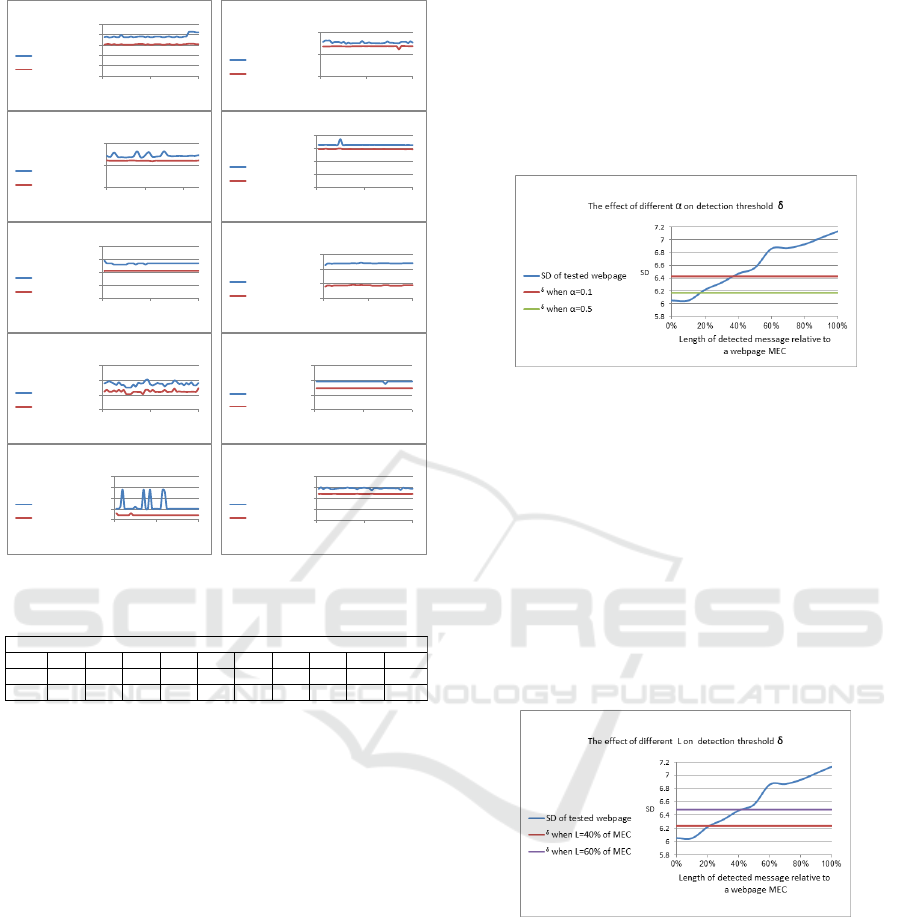
Ten sequences of snapshots (40 snapshots per se-
quence) were used based on the landing pages for
ten well known web sites covering a range of www
domains (news, education, company, shopping): (i)
BBC (ii) New York Times (iii) Wikipedia, (iv) Stack-
overflow (v) Sony (vi) The University of Liverpool
(vii) IEEE (viii) WebMD (x) Microsoft and (x) Ama-
zon. For collection purposes the following parame-
ters were used: (i) T = one week and (ii) τ = ev-
ery two hours. The length of embedded message was
L = 40% of a webpage MEC. The SD value was cal-
culated before and after message hiding. The results
are presented in Figure 2. From the figure it can be
seen that in every case changes in SD values caused
by the message embedding and the changes occurring
naturally are significantly different.
5.3 Various Types of Embedded
Messages
The goal of the next series of experiments was to test
how the type of the embedded text may affect the
changes in SD. The same ten sequences of snapshots
were used and the message embedding was conducted
with 29 different types of messages (natural language,
random letters, mixture of letters, symbols and num-
bers). The results including the mean of the standard
deviation after embedding these 29 instances of these
message samples and the standard deviation of their
SDs are presented in Table 3. As we can notice from
Table 3 the type of a hidden message has no differen-
tiable effect on SD changes.
A Statistical Approach to the Detection of HTML Attribute Permutation Steganography
525
0
5
10
0 20 40
SD
Snapshots
Amazon.com Snapshots SD before and after
embedding
SDafter
SDbefore
0
1
2
3
4
5
0 20 40
SD
Snapshots
BBC Snapshots SD before and after embedding
SDafter
SDbefore
0
2
4
6
8
0 20 40
SD
Snapshots
IEEE Snapshots SD before and after embedding
SDafter
SDbefore
0
5
10
1 11 21
SD
Snapshots
Ntimes.com Snapshots SD before and after
embedding
SDafter
SDbefore
4.5
5
5.5
6
0 20 40
SD
Snapshots
Microsoft.com Snapshots SD before and after
embedding
SDafter
SDbefore
0
2
4
6
8
0 20 40
SD
Snapshots
Sony.com Snapshots SD before and after embedding
SDafter
SDbefore
0
2
4
6
0 20 40
SD
Snapshots
wikipedia.org Snapshots SD before and after
embedding
SDafter
SDbefore
0
2
4
6
0 20 40
SD
Snapshots
Stackoverflow.com Snapshots SD before and after
embedding
SDafter
SDbefore
0
2
4
6
8
0 20 40
SD
Snapshots
WebMD.com Snapshots SD before and after
embedding
SDafter
SDbefore
4.4
4.45
4.5
4.55
4.6
0 20 40
SD
Snapshots
Liverpool University Snapshpts SD before and after
embedding
SDaftre
SDbefore
Figure 2: Standard deviation SD values before and after
message embedding.
Length of embedded message relative to a webpage MEC
100%
90%
80%
70%
60%
50%
40%
30%
20%
10%
7.16
6.99
6.91
6.83
6.81
6.65
6.52
6.34
6.14
6.05
Mean
0.17
0.15
0.16
0.12
0.12
0.11
0.12
0.10
0.06
0.04
SD
Figure 3: Mean of Standard deviation of 29 instances of
embedded messages and their SD.
5.4 Evaluation of Monitoring Process
To evaluate the proposed monitoring process the same
ten sequences of snapshots used for the foregoing ex-
periment were used within each case the first thirty al-
located to training and the last ten to testing. Message
embedding for evaluation purposes was conducted us-
ing the same attribute permutation algorithm from
(Shen and Zhao, 2010). The messages were in natu-
ral language. Once training was completed we could
go on to test the monitoring process. The testing was
conducted by embedding hidden messages in natural
language, using attribute permutation steganography
of increasing length in each of the ten web page test
sequences starting with L = 10% and increasing to
L = 100% in steps of 10%. The results are presented
in graphs 4 and 5 for IEEE webpage.
• Graph 4 demonstrated the detection threshold σ
sensitivity of α selection. We tried different α
values to get σ while L the length of embedded
message is fixed to 40% of a webpage MEC. The
x-axis represented the length of detected message
relative to a webpage MEC while the y-axis rep-
resented the SD values of a tested webpage with
σ values. As illustrated in Figure 4 σ decreased
from 6.43 to 6.17 as α went up from 0.1 to 0.5.
Decreasing σ means increasing of false positives.
Figure 4: Detection threshold σ sensitivity of different val-
ues of α when L = 40% of a webpage MEC.
• Graph 5 demonstrated the detection threshold σ
sensitivity of L selection. We tried different L val-
ues while α is fixed to 0.5 . The x-axis represented
the length of detected message relative to a web-
page MEC while the y-axis represented the SD
values of a tested webpage with σ values of dif-
ferent L. As shown in Figure 5 when L became
longer from 40% of webpage MEC to 60% and
α is fixed to 0.5, σ increased from 6.23 to 6.48
and that would miss stego webpages with hidden
messages of 40% of a webpage MEC.
Figure 5: Detection threshold σ sensitivity of different val-
ues of L while α = 0.5.
6 RELATED WORK AND
CONCLUSIONS
In this paper we propose a process for monitoring
for attribute permutation steganography in HTML en-
coded web pages. During the training phase the web
page is sampled over a period of time and on each oc-
casion is seeded with a hidden message. The SD is
calculated for the web page with and without the hid-
den message. The average SDs are then used to cal-
ICISSP 2016 - 2nd International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy
526

culate a threshold value σ which can then be used for
further monitoring. The evaluation indicated that the
conjecture that SD can be used for detecting attribute
permutation steganography was correct.
The paper (L.Polak and Z.Kotulski, 2010) in-
troduced an algorithm for attribute permutation
steganography detection using a different statistical
measure W which is based on the concept of pre-
dominant order between the pairs of attributes, it
grows linearly with the occupancy of the stego chan-
nel and similarly to our method can be used for thresh-
old based detection. The authors of (L.Polak and
Z.Kotulski, 2010) discuss the issue of stego detection
in the web pages with dynamic content and speculate
that the detection may take into account the dynamic
behavior of W : for the page containing stego mes-
sages W should either have constant high value, or
fluctuate heavily. On the other hand, natural changes
should be regular and periodical. No specific proce-
dure to distinguish these cases was proposed though.
We notice that our monitoring procedure can be easily
deployed with computing W instead of SD.
The paper (W.Jian-feng et al., 2014) proposes the
detection method for attribute permutation steganog-
raphy utilizing the statistics measures and SVM clas-
sification. English translation of (W.Jian-feng et al.,
2014) is not available to us at the moment, but based
in particular on Fig. 1 from the paper, one may con-
clude that the proposed method includes computing
two statistical measures of HTML page: mean of at-
tribute positions and variance of attribute positions,
which are both used as the inputs to a SVM classi-
fier. The paper presents the experimental results on
detection rates varying between 72.4% and 84.6% but
it is not clear for us what was exactly the setting and
whether the dependencies on the channel occupancy
have been addressed.
Future work includes the evaluation of the pro-
posed monitoring procedure for the detection the mes-
sages embedded by other steganographic algorithms
utilizing attribute permutations and its comparison
with the procedures from (L.Polak and Z.Kotulski,
2010) and (W.Jian-feng et al., 2014) on the same set
of steganographic algorithms.
REFERENCES
Huang, H., Zhong, S., and Sun, X. (2008). An algorithm of
webpage information hiding based on attributes per-
mutation. In 4th International Conference on Intelli-
gent Information Hiding and Multimedia Signal Pro-
cessing (IIH-MSP 2008), pages 257–260.
L.Polak and Z.Kotulski (2010). Sending hidden data
through www pages detection and prevention. En-
gng.Trans., 58:75–89.
S.Forrest (2006). Introduction to deogol.
http://www.wandership.ca/projects/deogol.
Shen, D. and Zhao, H. (2010). A novel scheme of webpage
information hiding based on attributes. In Information
Theory and Information Security (ICITIS), 2010 IEEE
International Conference on, pages 1147–1150.
Sui, X.-G. and Luo, H. (2004). A new steganography
method based on hypertext. In Radio Science Con-
ference, 2004. Proceedings. 2004 Asia-Pacific, pages
181–184.
Wendzel, S., Mazurczyk, W., Caviglione, L., and Meier,
M. (2014). Hidden and uncontrolled - on the emer-
gence of network steganographic threats. CoRR,
abs/1407.2029.
W.Jian-feng, H.Liu-sheng, Miao-miao, T., C.Zhi-li, and
M.Hai-bo (2014). Detection of html steganography
based on statistics and svm. Journal of Chinese Com-
puter Systems, 35(6):1221–1225.
Zhao, Q. and Lu, H. (2007). Pca-based web page water-
marking. Pattern Recogn., 40(4):1334–1341.
Zieli
´
nska, E., Mazurczyk, W., and Szczypiorski, K. (2014).
Trends in steganography. Commun. ACM, 57(3):86–
95.
A Statistical Approach to the Detection of HTML Attribute Permutation Steganography
527
