
Lightweight Trust Model with High Longevity for Wireless Sensor
Networks
Hela Maddar
1
, Wafa Kammoun
1
, Omar Cheikhrouhou
2,3
and Habib Youssef
1
1
PRINCE Research Unit ISITcom, Sousse University, Hammam Sousse, Sousse, Tunisia
2
CES Research Unit ENIS, Sfax University, Sfax, Tunisia
3
College of Computers and Information Technology, Taif University, Alhawi, Saudi Arabia
Keywords: The Wireless Sensor Network (WSN), Trust Management.
Abstract: Due to their inherent features Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) are vulnerable to many security threats.
Moreover, traditional security mechanisms cannot be directly used in WSNs as they present constrained
resources in terms of communication, computation and energy. Trust management models have recently
been suggested as an eective security mechanism for WSNs. The already found solutions are very
expensive in terms of energy and memory, which seriously affects the lifetime of such networks. In this
paper, we will present a lightweight trust management model, which guarantees the reliability and
robustness of the network, seeking to increase its lifetime compared to existing models.
1 INTRODUCTION
The use of sensor networks is increasing more and
more in many areas, such as scientific, medical,
domestic, military, etc. However, this type of
networks still suffers from an energy autonomy
limitation that restricts the network lifetime. Energy
is a vital component for WSNs. Namely, trust and
energy are the two most critical axes vitally
affecting the efficiency and lifetime of the network.
Trust has been the focus of researchers for a long
time. The general idea of trust in WSNs is to observe
the behaviour of the sensors. Our trust model must
take into account the hardware and software
requirements of these networks and their
specificities. It is simple, not expensive in terms of
energy. This model is designated for domestic,
environmental and medical applications that do not
require a massive security rates. To ensure a high
confidence, we seek to analyze the different actions
of a sensor node and order these actions depending
on the detected behaviour. If the behaviour is
normal, node is confident. However, if the behaviour
of the node is not normal, node will be penalized. A
detected bad behaviour is not always caused by a
malicious node, it may be caused by the hardest
environment in which
the network operates or by a
transmission error. All the aforementioned is
considered by our model. This paper is organized as
follows: section 2 presents the related work, section
3 describes our proposed scheme, section 4 presents
simulation results, and finally section 5 concludes
the paper.
2 RELATED WORK
Trust has been the focus of researchers for a long
time. It started in social sciences where trust
between humans was studied. Trust was used in the
context of e-commerce (
Yoon and Occena, 2015),
peer-to-peer networks system
(Boutaba and Marshall?
2006)
and ad-hoc networks (Cheikhrouhou, 2015).
From 2004, trust and reputation systems have been
adapted for WSNs
(Chen et al., 2007). These systems
must be light enough to ensure proper operation
without harming the functionality of the systems
(Ozdemir, 2008). The general idea of trust in WSNs
is to observe the behaviour of the sensors, their
compliance with respect to what is expected, and to
calculate and assign confidence values to different
participating nodes (Ganeriwal et al., 2004). The
first trust management system used in the field of
WSNs is the Beta reputation system that has been
proposed by Josang & Ismail in 2002 (Josang and
Ismail, 2002). This system was created to integrate
548
Maddar, H., Kammoun, W., Cheikhrouhou, O. and Youssef, H.
Lightweight Trust Model with High Longevity for Wireless Sensor Networks.
DOI: 10.5220/0005811005480553
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy (ICISSP 2016), pages 548-553
ISBN: 978-989-758-167-0
Copyright
c
2016 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

the notion of reputation in the e-commerce context.
Some researches like Ganeriwal and Srivatava in
RFSN (Reputation-based Framework for high
integrity Sensor Networks) (Yao, et al., 2008) used
the work of Josang & Ismail presented in 2002
(Ganeriwal et al., 2004) based on the probability
beta function in the creation of their trust models for
wireless sensor networks. This work is the first
model of trust and reputation exclusively developed
for wireless sensor networks. Authors in ATSAN
(Agent-based Trust Model in Wireless Sensor
Networks) (Chen et al., 2007) propose an agent
model based on trust to detect malicious nodes.
ATSAN runs in the middleware of each agent node
that uses the watchdog scheme to monitor the
behaviour of nodes in the radio range. Unlike RFSN
(Ganeriwal et al., 2004), using a single watchdog for
all nodes. Some researches use a security
mechanism to ensure confidence like PLUS
(Parameterized and Localized Trust Management
Scheme) (Yao, et al., 2008). PLUS may not be
suitable for WSNs with high traffic rates. NBBTE
(Node Behavioural strategies Belief theory of the
Trust Evaluation algorithm) (Feng et al., 2011) is
another trust model based on direct observation. It
use the fuzzy theory to measure how the confidence
value of a node belongs to his confidence. Another
model specially developed for WSN is the GTMS
(Group-Based Trust Management Scheme) (Deng et
al., 2009). In this model, only one trust value is
calculated for each group. Because the
vulnerabilities of wireless transmission channels, an
intruder can easily attack the information transmitted
via the transmission channel. For that, many
researches focus on data transmission evaluation like
DFDI (Distinguish Forged Data Illegal) (Hur et al.,
2005). Recently, some hybrid models like (Na et al.,
2014), (Kumar et al., 2014) integrate both
confidence of data and communication. In (Na et al.,
2014), the authors propose a trust model that
provides both, communication security and data
security with the integration of encryption. The real
problem experienced by trust management models is
the large amount of energy dissipated in order to
maintain trust. Similarly most of the existing models
in the literature are probabilistic models such RFSN
(Ganeriwal et al., 2004), ATSAN (Chen et al.,
2007), GRSSN (Momani and Challa, 2010). The
mathematical methods usually used to obtain more
precise values of trust as PLUS (Yao et al., 2008)
which includes hashing. Despite the performance
that the existing models have, they suffer from a
great amount of dissipated energy and some of them
need a specific type of nodes that have more
performers like ATSAN (Chen et al., 2007). The
sensor network is a rapidly developing area that
requires more confidence models, more reliable,
more secure and less expensive. For this purpose, we
design a new model named LTMHL: Lightweight
Trust Model with High Longevity. We demonstrated
that LTMHL is a powerful model that guaranties
reliability, robustness and high longevity.
3 DESCRIPTION OF OUR
MODEL
3.1 Metrics of Trust
Confidence factors that will be used in our work are:
Direct observation, indirect observation, reputation,
aging, and finally the updates. In our work, direct
observation is based on the experience of the node
itself, its observations and direct interaction with its
neighbours. Indirect observation is based on
recommendations received from other trusted node
on the network. The reputation in our context is the
behaviour of a node towards its neighbours. Ageing
means that a node with an exhausted energy will be
excluded from the network. The nodes in
interactions with an exhausted energy node will be
informed to limit identity usurpation attack. In fact,
a node can spy the identity of an excluded node and
communicate in the network without being detected.
Finally, the updates are essential in order to remain
able to any changes on the network.
3.2 Establishment of the Trust
The establishment of trust between nodes in a
wireless sensor network is the most important
dynamic aspect that ensures network efficiency.
Establishing of trust is generally based on the two
most important sources for calculating, the direct
trust and indirect trust. In our model, the
establishment of trust is based on direct observation,
indirect observation, updating and ageing. The
calculation of confidence is based on the direct and
indirect observation. These observations affect the
decision of allowing a node to enter or refusing to
communicate with another node. Aging and update
are factors that ensure efficiency and robustness of
our model. The figure below describes the
establishment of trust in our model.
Lightweight Trust Model with High Longevity for Wireless Sensor Networks
549
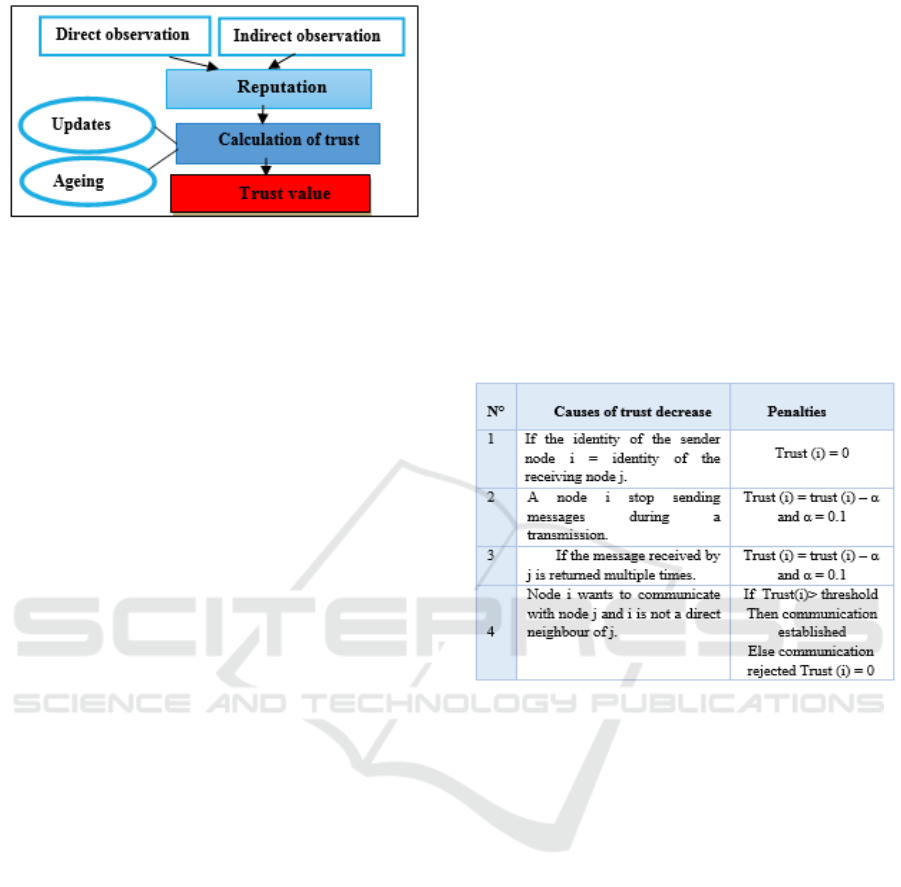
Figure 1: General model for trust calculating.
3.3 General Model of Trust
In our model, we consider a hierarchical network,
where the collection station is considered trusted.
Initially, upon deployment, all nodes are considered
trusted view that an adversary can be integrated in
the network and compromise a node after 10
seconds of deployment according to (Anderson and
Kuhn, 1996). This time is enough sufficient for the
network to take place where each node can
communicate in its surrounding trustfully. We
assume that the data transfer is done periodically.
Nodes must send their data every time slot. Before
deployment, a node is preloaded by the identity of
its neighbouring nodes which will communicate
with them based on the value of direct observation.
Initially, each node is confident and has a confidence
value equal to 1. In our model, a confidence
threshold is set at 0.5. A node is considered
confident if its confidence is greater or equal to 0.5.
When node A sends a message to node B for the first
time, B creates a trusting table for node A. The
confidence value is the same for each success
transmission. Each time the node observes an
untrusted node, it performs directly a trusted
decrease of the confidence value of the node and
sends a message to inform the cluster head to update
its trusted table. When a node is considered
untrusted in a transmission, its value will be reduced
by 0.1 from its neighbour node which detects this
malignancy. After minimizing the trust value of this
malicious node, the neighbour node sends a message
to its cluster head to update its confidence table
regarding this malicious node. If the confidence
value record in the cluster head will be less or equal
to 0.4, this malicious node will be excluded from the
network. Each time a cluster head detect an
untrusted node, it removes it from the table and
sends a broadcast message to all nodes to exclude it.
Then the cluster head sends a message to inform the
sink about the change. It updates its confidence
table. Similarly, the cluster head is in the trusted
table of all neighbouring nodes. If a cluster head will
be detected as untrusted in a transaction, the node
detecting this malicious sends a message to the
nearest cluster head that informs the sink.
Subsequently the sink updates its confidence table.
In case of detection of a malicious cluster head with
a trust lower than 0.5, the node which detect this
malice send a message to a nearest node of a
neighbour group in its communication range that
transmit this information to the sink. The base
station sends a broadcast to all group nodes to
inform them of the exclusion of their leader. In our
network communication, trust value of node j
decreases by referring to the table below:
Table 1: Nodes behavioural evaluation metrics.
In the first rule cited in Table 3, the reduction
must be drastic. This assessment is based on direct
observation and it concerns only neighboring nodes.
In order to know the identity of a malicious node,
the node must make listen to different messages
exchanged between its neighbor nodes and detect
which one has usurped its identity. Similarly a node
which uses a false identity will stop sending its own
messages with its real identity, so it will be detected
as malicious and penalized (according to rule 2). In
the second rule, as the transmission of data is
performed periodically, each node must send its data
in its corresponding transmission slot. A stop of
transmission can be directly detected. This can be
done by transmission error caused by the hardest
environment or by a malicious behavior (selfish
behavior). The minimization of trust does not cause
the elimination of the network node, but if the fault
occurs several times it is considered that it is made
by an intruder. The choice of the minimization of
trust every malicious event seeks to differentiate
between a real attack and a simple transmission
error, and for that we avoid increasing the value of
trust when the node behaves well. In the third case,
ICISSP 2016 - 2nd International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy
550

fake nodes can use old message. This message can
be resend by false nodes that aims to exhaust the
energy of honest nodes. For that, a nonce value is
used to verify the message freshness. A node always
saves the value of the last received nonce. At each
new forwarding this value must be incremented by
1. If this is not the case, a malice is detected. In rule
4, when node j receives a message from node i, and
node i is not a direct neighbour. In this case, node j
decision to accept communication will be based on
the indirect observation trust value. For this purpose
node j send a request message to its cluster head.
The cluster head searches if it has a trust value for
node i, if yes and this value exceeds the threshold,
communication can be done securely else the cluster
head contact the collection station to see the
confidence value of the nodes involved. If the value
exceeds the threshold, the node will be considered
trusted, otherwise it is untrusted and communication
will be rejected.
3.4 Trust Calculation Process
The general idea of the process of trust calculation is
to verify if a node is confident or not. For that, a
confidence value is fixed by our model ‘S’ that
represents the minimum level of confidence. For
further explanation of this process, we take the
example of two nodes i and j that want to
communicate. If a node i wants to communicate with
a node j, then j will appear in its confidence table if
it has an old experience with i., so it is based on the
value of direct observation ‘A’. If the value ‘A’ is
superior than the value of the required threshold,
which is the minimum value for node to be able to
communicate with another node, the communication
cannot be achieved, otherwise, the two nodes can
communicate safely. If there are no direct
observation, node i must contact the cluster head and
see if there was a recommendation on node j, it’s the
indirect trust 'B'. The direct trust value ‘A’ is defined
by the following mathematical expression at a given
moment t:
(,) (, 1)
ii
Tjt Tjt x=−−
(1)
Where x = 0 if there is no malice, x = 0.1 in cases of
malice detection and x =
i
T (j,t-1) in cases of identity
usurpation (see Table 1). The expression
i
T (j,t-1)
represents the direct trust value of node j in base of
node i at t-1. This value can be changed after a
transaction at time t. If a transaction is performed
without any failure the confidence value remains the
same and x is set to 0. The value of indirect trust 'B'
is defined by the following mathematical expression
at a given moment t:
'1
(,) (, 1)
n
CHi CHi
i
TjtTjt X
=
=−−
∑
(2)
Where
(,)
CHi
Tjt is the node j trust value recorded
in the cluster head database. It represents the value
of indirect observation 'B', which will be
subsequently transferred to the nodes that want to
interact with j at time t and is not in direct
communication with it. The value n represents all
the nodes in direct interaction with j and sent a
negative recommendation to cluster head in a
specific time t. More precisely, the confidence value
(,)
CHi
Tjt is the result of aggregation of different
observations of communicating nodes with j in the
same area.
3.5 Energy Trust
A node with depleted energy can be exploited by the
wrong nodes. A malicious node can spy the identity
of a node with exhausted energy and place itself as
an authorized node enjoying the good reputation
record in trusted tables of nodes. Eventually, it
begins to cause damage in the network by modifying
and sharing false data in the network. To limit this
kind of attack, a check in the amount of power
remaining is performed. A node with energy below
than 10% sends a request to its cluster head to
inform it of its critical energy state. Eventually the
cluster head informs the neighbouring nodes and the
base station.
4 EXPERIMENT
To evaluate the features of our model, we used the
MATLAB simulator. We have created a topology
composed of 25 nodes to test the performance of our
model, where each node communicates directly with
three neighbours. Our trust model can be applied for
most sensor networks management protocols. In our
work, we have applied our model to the LEACH
protocol (Heinzelman et al., 2000). The choice of
LEACH is based on its popularity and largest usage
rates. In our work, our test dimension: 100*100 m²,
the nodes are static, and initial normal node energy
is equal to 0,5 Joule. A percentage equal to 0,1 of
advanced nodes, with an initial energy of 1 joule.
4.1 Performance of Our Life Time
Model
To test and validate the performance of our proposed
Lightweight Trust Model with High Longevity for Wireless Sensor Networks
551

solution LTMHL, we applied it to the LEACH
protocol. We named it trust-LEACH.
Figure 2: The amount of residual energy.
Figure 2 shows the performance of our energy
consumption perspective model. It is clear from the
curve that the energy consumed by the LEACH and
Trust-LEACH protocol is nearly equal and the
difference has appeared near 1000 rounds. To know,
a round is composed by two phases, cluster
formation and cluster transmission. This clearly
shows the performance of our model standpoint
energy consumption. This ensures that our trust
model provides very good longevity to the network.
Unlike existing models in the literature that are very
expensive on energy consumption causing serious
affects by limiting their lifetime. To better
demonstrate this performance, we calculated the
number of dead nodes during 1200 rounds.
Figure 3: Number of dead nodes.
From Figure 3, we can determine very clearly the
nearest quantity of dead nodes in the network at
different time. We interpret that at 1200 rounds we
have 11 dead nodes for both protocols. This ensures
excellent durability offered by our trust model and
validates its performance.
4.2 Resilience against Attacks
Ordinary Wireless Sensor Networks protocols such
as LEACH, do not show any resilience against
attacks. To show the contribution of our proposed
model in terms of trust we compared LEACH and
TUST-LEACH robustness against classical attacks.
We created three attacks, usurpation attack of a
receiver node, replication attack and collusion attack
then we confronted LEACH and trust-LEACH to the
three previous attacks.
Figure 4: LEACH and Trust-LEACH facing three attacks.
From the figure above, we clearly notice that the
LEACH protocol has no resilience against attack and
the three attacks are well detected by trust-LEACH.
That’s show the performance of our model.
4.3 Attacks Analysis
To better show the performance of our model, we
will describe the different attacks that our model has
resilience against them.
Denial of Service Attack: A denial of service
attack seeks to minimize network robustness. DoS
attacks can be managed successfully in our trust
model.
Bad-mouthing Attack: It is the risk of receiving
dishonest recommendations from false nodes to
report honest nodes as dishonest. Minimizing the
confidence value in our model is carried out after the
detecting of malicious event. A recommendation that
is not justified from one node of the network cannot
be considered.
Selective Behaviour Attack: A selective
behaviour attack means that a node performs well
and badly at once. In our model, each malicious
action leads to a minimization of the value of trust.
The bad behaviour of a node brings to eliminate it
from network even if it behaves well with some
others.
Usurpation Attack: A node tries to impersonate a
legitimate node. In our model, we tried to look for a
way to limit usurpation attacks. For that, we have
treated two scenarios: The first scenario is the
usurpation of the identity of a receiver node. In this
case, the identity of attacker will be detected
immediately by our model. The second scenario
resides on the usurpation of neighbour identity. In
ICISSP 2016 - 2nd International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy
552
this case, neighbour cannot detect any changes
because they do not have the ability to distinguish
the real message sender.
Replication Attack: An adversary tries to replay
old messages. A replicated message will be well
detected by our model through nonce that will be
checked at every message transfer to ensure the
freshness of the data.
Collusion Attack: On detecting of untransfered
message the trust decreases.
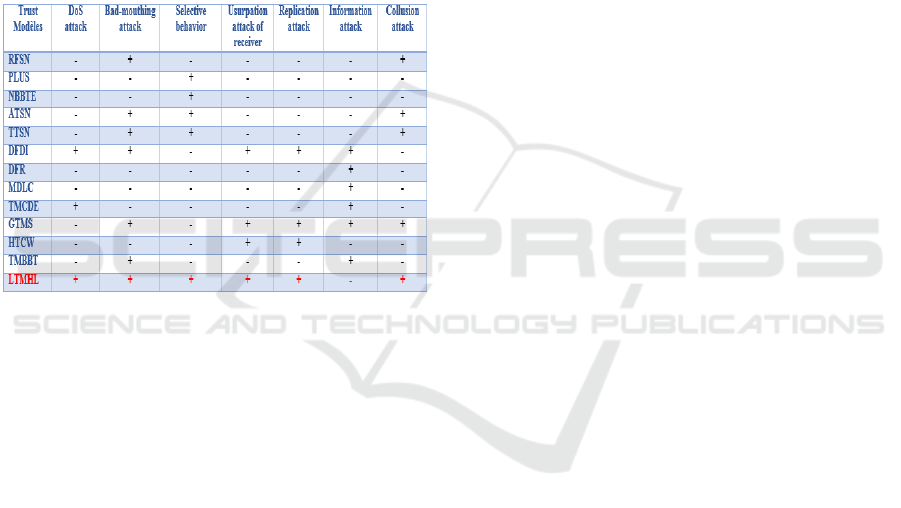
A comparison is presented in the table below
based on a study made by (Han et al., 2014) to
compare our model with some existing models in the
literature
.
Table 2: Comparison between models.
5 CONCLUSIONS
From experiment described above, we can clearly
conclude that our proposed model LTMHL
(Lightweight Trust Model with High Longevity) is
lightweight in terms of energy, and is reliable, robust
and resist against most of the attacks threatening
wireless sensor networks. In our model, every
malicious event leads to a minimization of the
confidence value nodes whatever that is caused by
transmission error or by a malicious behaviour.
However, LTMHL cannot detect an information
attack. In future work, we will seek to integrate the
trust information in the trust model. To minimize the
amount of energy consumed by the trust data, we
will seek to integrate the cloud.
REFERENCES
Anderson, R., and Kuhn, M., 1996. Tamper resistance
cautionary note. In Proceedings of the 2nd USENIX
Workshop on Electronic Commerce, USENIX.
Boutaba, R., Marshall, A., ,2006. Management in peer-to-
peer systems: Trust, reputation and security. Computer
Networks, Elsevier.
Cheikhrouhou, O., 2015. Secure Group Communicati-on
in Wireless Sensor Networks:A survey. In Journal of
Network and Computer Applications, Elsevier.
Chen, H., Wu, H., Zhou, X., and Gao, C., 2007. Agent-
based Trust Model in Wireless Sensor Networks. In
Eighth ACIS International Conference on Software
Engineering, Artificial Intelligence, Networking, and
Parallel/Distributed Computing, IEEE.
Deng, H., Sun, X., Wang, B., and Cao, Y., 2009. Selective
Forwarding Attack Detection using Water markin
WSNs”. In International Colloquium on Computing,
Communication, Control, and Management, IEEE.
Feng, R., Xu, X., Zhou, X., and Wan, J., 2011. ATrust
Evaluation Algorithm for Wireless Sensor Networks
Based on Node Behaviorsand D-S Evidence Theory.
In sensores, MDPI.
Ganeriwal, S., Balzanoand, L., Srivastava, M., 2004.
Reputation-based Frame work for High Integrity
Sensor Networks. In Proceedings of the2nd ACM
workshop on Security of adhoc and wsn, ACM.
Han, G., Jiang, J., Shu, L., Niu, J., Chao, H., 2014.
Management and applications of trust in Wireless
Sensor Networks: A survey. In Journal of Computer
and System Sciences, Elsevier.
Heinzelman, W., Chandrakasan, A., Balakrishnan, H.,
2000. In Energy-efficient communication protocol for
wireless microsensor networks. Proceedings of the
33rd annual Hawaii international conference, IEEE .
Hur, J., Lee, Y., Yoon, H., Choiand, D., and Jin, S., 2005.
Trust Evaluation Model for Wireless Sensor
Networks. In The 7
th
International Conference on
Advanced Communication Technology, IEEE.
Josang, A., and Ismail, R., 2002. The Beta Reputation
System. In The 15th Bled Electronic Commerce
Conference.
Momani, M., and Challa, S., 2010. Trust models in
wireless sensor networks: a survey. In Recent Trends
in Network Security and Applications, Springer.
Na, W., and Liping, G., and Chunxue, W., 2014. A Light-
Weighted Data Trust Model in WSN. In International
Journal of Grid & Distributed Computing.
Ozdemir, S. 2008. Functional reputation based reliable
data aggregation and transmission for wireless sensor
networks. In Computer Engineering Department, Gazi
University, Turkey, Elsevier.
Kumar, M., Alex, L., et al., 2014. A Hybrid Trust Based
Secure Model for Wirless Sensor. In International
Journal of Technology in Computer Science.
Yao, Z., Kimand, D., Doh, Y., 2008. PLUS: Paramet-
erized and Localized trust management Scheme for
sensor network ssecurity. In International Conference
on Mobile Adhoc and Sensor Systems, IEEE.
Yoon, H., Occena, L., 2015. Influencing factors of trust in
consumer-to-consumer electronic commerce with
gender and age. In International Journal of
Information Management, Elsevier.
Lightweight Trust Model with High Longevity for Wireless Sensor Networks
553
