
Automatic Concepts Classification based on Bloom’s Taxonomy using
Text Analysis and the Naïve Bayes Classifier Method
Fatema Nafa, Salem Othman and Javed Khan
Department of Computer Sciences Kent State University, Media Communications and Networking Research Laboratory,
Kent, Ohio, U.S.A.
Keywords: Relationships Extraction, Higher Order Thinking Skills, Domain Knowledge, Feature.
Abstract: This paper aims to add Bloom’s Taxonomy levels as tags to the contents (e.g. concepts) of any given text-
book which is written in formal English and given as a course material. Bloom’s Taxonomy levels defines
concepts and knowledge of learning as six levels. Preparing the material of any course based on these six
could help the students to better understand the course’s concepts and their interrelationships. However, the
relations between concepts are highly sophisticated and require a human judgment. A set of methods have
been proposed to extract the relations among concepts. We use the naïve Bayes classifier which is the best
known and most successful classification technique in Machine Learning (Mahesh Kini M et al., 2015). This
work presents a naive classifier method which identifies the Bloom’s Taxonomy levels in text paragraphs
based on some rules in the training set. We evaluate and validate the proposed method on a text-book. By
utilizing the concepts of computer science for determining its knowledge domain. As a result of the proposed
method achieves an accuracy of average 70-85%, which is significantly high. Furthermore, we show that
taking Bloom’s Taxonomy levels into account in course design is valuable and our method can be used to
achieve.
1 INTRODUCTION
Text analysis is one of the most important and
complicated research topics. One of its goals is trying
to extract the hidden relations between concepts in a
text which might be useful for realistic use. There
exist several types of relations between concepts. In
this work we extract Bloom's taxonomy relations
between concepts. One of the application is
reordering of the content of a given text based on its
concepts relatedness. Bloom's taxonomy is a model
of classifying thinking according to six cognitive
levels of complexity. Bloom’s Taxonomy has been
functional in many educational fields, such as
computer science. Educational taxonomies can be
deployed in education research, to classify concepts
and investigate the range of learning. Bloom’s
taxonomy (Bloom and Krathwohl, 1956) attempts to
provide a set of levels of the cognitive skills
engagement with the material being learned. It is
usually presented as a generic framework. However,
taxonomies are not simple to use and researchers find
it challenging to reach agreement on the classification
of concepts (Johnson and Fuller, 2006).
Bloom’s Taxonomy provides a shared language
for describing what we learn and how we perform
learning. Bloom’s Taxonomy is generally used to
describe the learning steps at which a learner is. It is
important to develop a common understanding of
how the revised Bloom’s taxonomy (Anderson et al.,
2001) is interpreted in the domain of computer
science. In this paper we present a supervised learning
naive classifier method to classify Bloom’s
Taxonomy relations among noun concepts in text-
paragraphs for the book which is used as a reference
for courses. Overview of the process method
illustrated in Figure 1.
This paper presents the naïve Bayes classifier
which is a method that uses sample probabilities to
make the prediction and it is one of the most tested
methods for the classification task (Mahesh Kini M et
al., 2015).Actually, it is a supervised learning method
we used to classify relations between concepts based
on Bloom’s Taxonomy levels, using some features
that are extracted from text-paragraphs.
The rest of the paper is structured as follows.
Section 2 provides an overview of the related work.
Section 3, presents the pre-processing step to our text.
Sections 4 and 5 present how features are extracted
Nafa F., Othman S. and Khan J.
Automatic Concepts Classification based on Bloomâ
˘
A
´
Zs Taxonomy using Text Analysis and the NaÃ
´
rve Bayes Classifier Method.
DOI: 10.5220/0005813303910396
In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Computer Supported Education (CSEDU 2016), pages 391-396
ISBN: 978-989-758-179-3
Copyright
c
2016 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
391
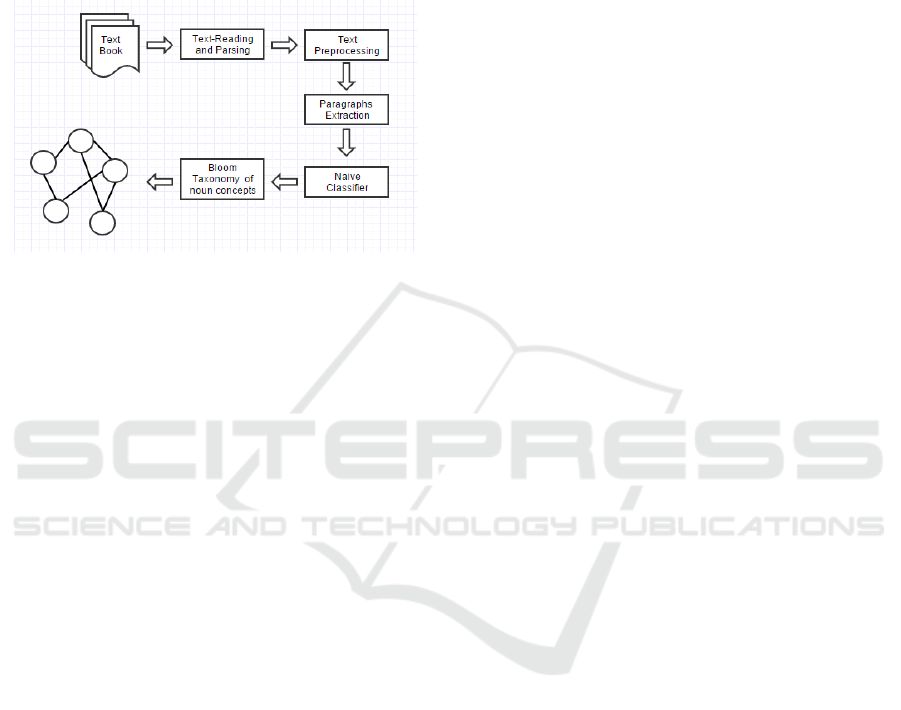
and naïve classifier respectively. Section 6 illustrates
Bloom’s Taxonomy relations. Section 7 cross
validation and then Section 8 presents results which
demonstrate the dramatic improvement in the
extracted Bloom’s Taxonomy relations between the
noun concepts. Section 9 presents the conclusion and
the future work.
Figure 1: A text-paragraphs classification model.
2 RELATED WORK
In this section we briefly introduce the related work
from two different perspective, Relation Extractions
and Bloom’s taxonomy.
From the relation extraction view, we investigated
a number of techniques for extracting the relations
between concepts link-based, WordNet based and
machine learning based methods, including un-
supervised, supervised learning and semi-supervised
techniques. There is also a mixed approach which
achieves good performance for the extraction. Some
studies have been performed on a specific domain
(Ben Abacha and Zweigenbaum, 2011). We present a
verb based relations extraction. Algorithm (Nafa F.,
and Khan J, 2015) to extract relations between
concepts in the text.
From the Bloom’s Taxonomy perspective,
theorists developed three different taxonomies to
represent the three domains of learning: a cognitive
taxonomy focused on intellectual learning, an
affective taxonomy concerned with the learning of
values and attitudes, and a psychomotor taxonomy
that addressed the motor skills related to learning.
One cognitive taxonomy (Bloom et al., 1956) is
known widely as the Bloom's taxonomy. This
taxonomy recognized six levels of cognitive skills
ranging from the lowest level of knowledge to the
highest level of evaluation. Bloom's taxonomy is
developed to Bloom's Revised Taxonomy (Anderson
et al., 2001). Bloom's Revised Taxonomy not only
improved the usability of Bloom's taxonomy by using
action words, but added a cognitive and knowledge
matrix which has widely used in the domain of
computer science.
Bloom’s taxonomy has been applied to the
computer science for course design (Scott, 2003),
comparing the cognitive difficulty levels of computer
science courses (Oliver et al., 2004), and structuring
assessments (Lister et al., 2003).They recommended
grading using Bloom’s Taxonomy rather than grading
on a curve. (Johnson et al., 2006) asked whether the
Bloom taxonomy is appropriate for computer science.
More recent research was done by others.
We think that it is significantly important to
develop a common understanding of how the revised
Bloom’s taxonomy is interpreted in the domain of
computer science. In this paper we provide an
interpretation of the taxonomy as it applies to a text
book. We will limit the discussion to the cognitive
domain. The analysis of Bloom’s Taxonomy will be
discussed in a future paper.
3 TEXT PRE-PROCESSING
Text pre-processing is an important step to give us
more control over our data (text book). Pre-
processing steps are as follows:
i) Tokenization: in this step the text book is
divided into paragraphs using a TextTiling technique
(Baeza-Yates, 1999) and then we divide each
paragraph into a group of sentences then we divide
sentences into noun concepts and verb concepts by
removing punctuations encoded letters and numbers.
ii) Removing stop words, the words that are not
related to the domain to reduce noise from the data.
iii) Verb extraction: converting a paragraph into two
groups based on the verb in each sentence in the
paragraphs into Bloom’s Taxonomy sentences based
on the Bloom’s Taxonomy verb list (Anderson et al.,
2001) which can be used for further tasks effectively.
4 FEATURES SELECTIONS
Feature selection is one of the most important steps
for the classification task (Loga Soumiya, and et al.,
2014). To classify the knowledge domain as one of
Bloom's Taxonomy tags. We need to choose a good
set of features which provide the differences between
Bloom’s Taxonomy tags. The following three
features are used:
First, the suffixes (ing and ed) for noun concepts
are useful for identifying Bloom Taxonomy tags in
CSEDU 2016 - 8th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
392

the paragraphs for the concepts. Second, the verbs
that relate the noun concepts connected with Bloom’s
Taxonomy verbs (Bloom, and Krathwohl, 1956) are
the best feature to classify concepts as Bloom’s
Taxonomy. Third, the position of the noun concepts
according to the paragraph they exist in is the best
sign to extract the Bloom’s Taxonomy tags. This is
because we notice that the noun concepts in the
beginning and the end of a paragraph are the most
important ones.
In extracting the values for each of the three
attributes we followed some rules. To extract all the
features from text-paragraphs we pre-processed the
text as explained in Section 3.As for the second
attribute, we implemented and refined our verb
extraction algorithm (Nafa F., and Khan J, 2015). We
split the text into (paragraphs), and estimated the
probability of a verb occurring in two given noun
concepts. The verb relation is considered valid if the
probability of the specific verb occurring in the two
given noun concepts is equal to or greater than the
alpha threshold 0.5.
For the third attribute Hearst’s TextTiling
algorithm (Baeza-Yates, 1999) is used to divide text
data into paragraphs. It is a moving window approach
that uses lexical overlap as a means of detecting the
topic in the text. We use the features number as an
index to refer to the used attributes.
5 NAIVE BAYES CLASSIFIER
In this section we present a Machine Learning
techniques as a method to classify Bloom’s
Taxonomy relations within concepts in the
paragraphs. There are concept domains in a paragraph
and our purpose is to identify whether concepts in
text-paragraphs belong to a tags (class) of Bloom's
Taxonomy because each text-paragraph represents a
topic or sub-topic and we need to map each topic to
different Bloom Taxonomy tags in order to
reorganize the text-paragraphs according to the
required cognitive skills and this will guide us to
reorganize the whole book according to the required
cognitive skills.
As with other machine learning methods (Mahesh
Kini M et al., 2015) , we assume that there is a
training set that can be used to learn how to identify
Bloom's Taxonomy tags at the paragraph level and
use the knowledge gained from the training set to
learn the model. Bayesian Theory (C. Tseng, N. Patel,
and H. Paranjape, 2012) is a fundamental statistical
approach. It assumes that the problem is given in
probabilistic form and the necessary values are
already given. Then it decides on the best class that
gives the minimum error with the given text’s
paragraphs. In cases where there is no distinction
made in terms of cost between classes for the
classification of errors, Bayesian Theory chooses the
class that is most likely with the highest probability.
We use the naïve Bayesian classifier to classify
concepts as Bloom’s relations by using the features
value that map the training set. We focus on the
classification task to classify the concepts into one of
the Classes (Bloom Taxonomy Tag) as shown in
Table 1.
Table 1: Bloom Taxonomy Tags for Concepts.
Bloom Taxonomy Tag Concepts
Remember and
Understanding
Program,search,table,
sorting,algorithm,tree
Analyzing Running time,
Polynomial time,
Worst-case
Apply and Evaluate Linear program, Spanning
tree
Creation Hash table,
Merge sort
The input is labelled paragraphs as in Bloom’s
Taxonomy using verbs that are included in
paragraphs. Each paragraph contains a group of
concepts (nouns and verbs) that are connected by a
Bloom’s thinking tag which is labelled in the
following form:
|
=
,
+∝
+∝
(1)
Where:
Count (A
i
, B
j
) is the number of occurrences of the
attribute value Ai present in the text with Bloom class
Bj,Count (B
j
) is the number of texts classified as
Bloom Bj,and ∝ : A smoothing parameter to control
the behave of our text.
6 EXTRACTED BLOOM
TAXONOMY RELATIONS
A concept graph G (N, L) is a Bloom Taxonomy
graph with nodes N and links L where each node
represents a concept and each link represent a verb.
Figure 2 and Figure 3 explained Bloom's
Taxonomy relations extracted by the naïve Bayes
classifier for two topics just with most five
frequencies concepts in two paragraphs from the book
and those concepts are in Bloom’s Taxonomy Level
Automatic Concepts Classification based on Bloomâ
˘
A
´
Zs Taxonomy using Text Analysis and the NaÃ
´
rve Bayes Classifier Method
393

1 which is the Understanding level, which means that
those concepts are in the basic level .If we need to
introduce those concepts to the learner it must be in
the beginning of the course.
Relations extraction analysis for the paragraphs is
using the proposed methodology for paragraph 1, and
paragraph 2 in Table 3 and Table 4 respectively.
Using this way the ordering of book paragraphs will
be changed according to Bloom’s Taxonomy tags. It
means that connecting text-paragraphs concepts
using Bloom’s Taxonomy relations will help connect
the sequence of learning from the text book. For
example, the book introduction to Algorithm
introduces some concepts in different text-paragraphs
without explaining them clearly. Consequently, it
wasn’t needed for anything later.
Table 2: Bloom Taxonomy Relations Topic 1.
Noun verb Noun
Graphs are adjacency-matrices
Edges connect vertices
Edges give vertices
Graph is Edges
Graph is adjacency-lists
vertices are Edges
Graph represent adjacency-lists
adjacency-
lists
use Adjacency matrices
Table 3: Bloom Taxonomy Relations Topic 2.
Concept1 Verb Concept2
Graphs discover vertices
adjacency-lists discover vertices
vertices explores Edges
breadth-first-
search
is discovered-
vertices
Graphs is path
vertices represented adjacency-lists
Figure 2: Graphical representation of the Topic 1 for most
five frequency concepts.
Figure 3: Graphical representation of the Topic 2 for most
five frequency concepts.
7 CROSS VALIDATION
Using the same set of texts for the training and
validation of an algorithm yields an overoptimistic
result (S. C. Larson, 1931). Cross Validation is based
on the principle that testing the algorithm on a new
set of data yields a better estimate of its performance.
The dataset is split into half creating the training set
and the test set. The training sample is used to train
the algorithm and the validation sample is used to
evaluate the performance of the algorithm (S. Arlot,
2010). We used a holdout method for cross
validation. The holdout method of the dataset is split
into halves creating the training set and the test set.
In our preliminary experiments we used the
training set of the text-book (Introduction to
Algorithm) during the training phases. We divided the
text-book into paragraphs 18444 and we used some of
the paragraphs as a training set to label the test set as
Bloom’s Taxonomy tags .A feature extractor is used to
convert each paragraph to a feature set . Here we used
three features which are discussed in Section 4. These
feature sets, capture the basic information that should
be used to classify each paragraph. The feature sets
and labels are fed into the naïve classifier to generate a
model. These feature sets are then fed into the model,
which generates the predicted Bloom Taxonomy tags.
The training set contains 6, 400 paragraphs, which
were tagged with the following values: Tag1 :(
Remembering and Understanding), Tag2 :( Analyzing)
Tag3 :( Appling and Evaluating) and Tag4: (Creation).
8 EVALUATION AND RESULTS
One of the most important support to obtain and
improve the result is the dissuasion in (Mahesh Kini
CSEDU 2016 - 8th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
394

M et al., 2015) and (Loga Soumiya et al., 2014).
To test and evaluate the model, 90% of the Book
is used and 10% was removed as noise while we pre-
processing the text book. Pre-processing and feature
selection are extracted and then served as input data
for machine learning algorithm. The system can be
measured using recall, and precision. The
mathematical form is:
Precision = ( Bloom
ℎ correct)/ ( all
)
Some good sample relations extracted are shown
in Table 3, and Table 4. We extended the Extraction
algorithm to improve the precision of predicting verbs
given nouns. With this extension, the precision
improved from 75% to 85% and we noticed that the
system can improved each time by improving the
input.
9 CONCLUSIONS
Adding Bloom’s Taxonomy tags for concepts provide
various interesting aspects. The goal is to present any
given book materials according to Bloom’s Taxonomy
of the cognitive domain. Our results show that by using
the best features, a Naive Bayes classifier can be used
to do the classification the task perfectly.
The ideas used in this paper are to present a text
book in a modified way using Bloom’s Taxonomy
tags. We can gather all tags that represent the lower
tags of Bloom’s Taxonomy as a definitions and basic
concepts then the intermediate concepts are the
theoretical part of the book, and the high tags are the
designing techniques that we can apply to algorithms.
It means that sequencing of the concepts by their tags
in this orders consistent with the Bloom’s Taxonomy
strategy. Results were interesting, because the ordering
of the book changed. Several topics which were
described as advanced levels in the book now became
intermediate level. As a result, it is possible to conclude
that by using Bloom’s Taxonomy we can decide which
parts of the prescribed book to use and at which level
of Bloom to match the skills. This generates a way that
can be used to identify a range of different learning
trajectories. We obtain strong results on strength
relations. Experimental results show an accuracy of
85.5%, which is significantly high.
REFERENCES
Anderson, L. W., Krathwohl, 2001. A taxonomy for
learning, teaching, and assessing: A revision of
Bloom's taxonomy of educational objectives, abridged
edition. White Plains, NY: Longman.
Baeza-Yates, R. and Ribeiro-Neto, B. 1999. Modern
Information Retrieval. Addison Wesley.
Ben Abacha, A., Zweigenbaum, P., 2011. A hybrid
approach for the extraction of semantic relations from
MEDLINE abstracts. In: 12th International Conference
on Intelligent Text Processing and Computational
Linguistics CICLING2011, Tokyo, Japan, pp. 139–
150.
Bloom, B. S., & Krathwohl, D. R. 1956. Taxonomy of
educational objectives: The classification of
educational goals. Handbook I: Cognitive domain.
Hearst, M.A, 1993. TextTiling: A quantitative approach to
discourse segmentation. Technical report, University of
California, Berkeley, Sequoia.
Johnson, C.G. and Fuller, U., 2006, February. Is Bloom's
taxonomy appropriate for computer science?. In
Proceedings of the 6th Baltic Sea conference on
Computing education research: Koli Calling 2006 (pp.
120-123). ACM.
Lister, R., & Leaney, J. 2003. Introductory programming,
criterion-referencing, and bloom. In ACM SIGCSE
Bulletin (Vol. 35, No. 1, pp. 143-147). ACM.
Loga Soumiya,Miraclin Joyce Pamila 2014 Performance
Evaluation and Experiment with Data-Driven
Techniques to Sentiment Classification of Movie
Review using Naïve Bayes classification International
Journal of Advances in Computer Science and
Communication Engineering.
Machanick, P. 2000. Experience of applying Bloom’s
Taxonomy in three courses. In Proc. Southern African
Computer Lecturers’ Association Conference (pp. 135-
144).
Mahesh Kini M, Saroja Devi H , Prashant G Desai, Niranjan
Chiplunkar 2015 Text Mining Approach to Classify
Technical Research Documents using Naïve Bayes
International Journal of Advanced Research in
Computer and Communication Engineering .
Manaris, B. and McCauley, R. 2004.Incorporating HCI into
the undergraduate curriculum: Bloom's taxonomy
meets the CC'01 curricular guidelines. Frontiers in
Education. FIE 34th Annual Meeting, 2004, T2H/10-
T2H/15.
Marie-Catherine de Marneffe, Bill MacCartney and
Christopher D. Manning. 2006. Generating Typed
Dependency Parses from Phrase Structure Parses. In
LREC 2006.
McCallum, Andrew, and Kamal Nigam. 1998 A
comparison of event models for naive bayes text
classification. AAAI-98 workshop on learning for text
categorization.
Nafa F. and Khan J. 2015. Conceptualize the Domain
Knowledge Space in the Light of Cognitive Skills. In
Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on
Computer Supported Education.
Oliver, D, Dobele, T., Greber, M. and Roberts, T., 2004,
January. This course has a Bloom Rating of 3.9. In
Proceedings of the Sixth Australasian Conference on
Automatic Concepts Classification based on Bloomâ
˘
A
´
Zs Taxonomy using Text Analysis and the NaÃ
´
rve Bayes Classifier Method
395

Computing Education-Volume 30 pp. 227-231
Australian Computer Society, Inc.
Pang, Bo, and Lillian Lee. 2004. A sentimental education:
Sentiment analysis using subjectivity summarization
based on minimum cuts. Proceedings of the 42nd
annual meeting on Association for Computational
Linguistics. Association for Computational Linguistics,
S. Arlot and A. Celisse, 2010 A survey of cross-validation
procedures for model selection, in Statistics Surveys.
Scott, T., 2003. Bloom's taxonomy applied to testing in
computer science classes. Journal of Computing
Sciences in Colleges, 19(1), pp.267-274.
CSEDU 2016 - 8th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
396
