
Numerical Experiments with a Primal-Dual Algorithm for Solving
Quadratic Problems
Derkaoui Orkia and Lehireche Ahmed
University Djillali Liabes of Sidi Bel Abbes, Computer Science Department, BP 89 City Sidi Bel Abbes 22000, Algeria
Keywords: Interior-point Methods, SemiDefinite Programming, Linear Research, Primal-Dual Interior-Point Method,
Predictor-corrector Procedure, HRVM/KSH/M Search Direction.
Abstract: This paper provides a new variant of primal-dual interior-point method for solving a SemiDefinite Program
(SDP). We use the PDIPA (primal-dual interior-point algorithm) solver entitled SDPA (SemiDefinite
Programming Algorithm). This last uses a classical Newton descent method to compute the predictor-
corrector search direction. The difficulty is in the computation of this line-search, it induces high
computational costs. Here, instead we adopt a new procedure to implement another way to determine the
step-size along the direction which is more efficient than classical line searches. This procedure consists in
the computation of the step size in order to give a significant decrease along the descent line direction with a
minimum cost. With this procedure we obtain à new variant of SDPA. The comparison of the results
obtained with the classic SDPA and our new variant is promising.
1 INTRODUCTION
We consider the standard primal form of
semidefinite program (1), and its dual (2) in block
diagonal form:
∗
:
..
, ≻0
(1)
∗
:
•
..
•
1,2,…,
,≻0,
(2)
Where
, belong to the space
of
real symmetric matrices, c
,…,
∈
is
the cost vector and x
,…,
∈
is the
variables vector. The operator • denotes the standard
inner product in
, i.e.,
•
∑
, and ≻0 means that is positive
semidefinite (∈
, see for example Figure 1.1.
The values
∗
and
∗
are the optimal value of the
primal objective function and the optimal value of
the dual objective function respectively.
Semidefinite Program is an extension of LP
(Linear Program) in the Euclidean space to the space
of symmetric matrices. These problems are linear.
Their feasible sets involving the cone of positive
semidefinite matrices, a non polyhedral convex cone
and they are called linear semidefinite programs.
Such problems are the object of a particular attention
since the papers by Alizadeh (Alizadeh, 1995) and
(Alizadeh at al., 1994), as well on a theoretical or an
algorithmical aspect, see for instance the following
references (Alizadeh and Haberly, 1998; Benterki et
al., 2003; Jarre, 1993; and Nesterov and
Nemirovskii, 1990.
Figure 1.1: Boundary of the set of semidefinite matrices
in
.
SDP is not only an extension of LP but also
includes convex quadratic optimization problems
and some other convex optimization problems. It has
a lot of applications in various fields such as
combinatorial optimization (Goemans and
Williamson, 1995), control theory (Boyd et al.,
1994), robust optimization (Ben-Tal and
Nemirovskii, 2001) and (Wolkowicz et al., 2000)
and quantum chemistry (Nakata at al., 2001) and
204
Orkia, D. and Ahmed, L.
Numerical Experiments with a Primal-Dual Algorithm for Solving Quadratic Problems.
DOI: 10.5220/0005813802040209
In Proceedings of 5th the International Conference on Operations Research and Enterprise Systems (ICORES 2016), pages 204-209
ISBN: 978-989-758-171-7
Copyright
c
2016 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
(Nakata et al., 2002). See (Todd, 2001),
(Vandenberghe and Boyd, 1994), (Vandenberghe
and Boyd, 1995) and (Wolkowicz et al., 2000) for a
survey on SDPs and the papers in their references.
The duality theory for semidefinite programming
is similar to its linear programming counterpart, but
more subtle (see for example (Alizadeh, 1995),
(Alizadeh et al., 1994), (Alizadeh and Haberly,
1998)). The programs
1
and
2
satisfy the weak
duality condition:
∗
∗
, at the optimum, the
primal objective
is equal to the dual
objective
•.
Our objective is to solve the SDP in optimal time
following our work (Derkaoui and Lehireche, 2014).
The SDP problem is solved with interior point
methods. These last use a classical Newton descent
method to compute the search direction. The
difficulty is in the line-search, it induces high
computational costs in classical exact or
approximate line-searches. Here, instead we use the
procedure of (Crouzeix and Merikhi, 2008). This last
proposes another ways to determine the step-size
along the direction which are more efficient than
classical line searches.
This paper is organized as follows. In Section 2,
we present some useful notions and results about
semidefinite programming. In Section 3, an
overview of the interior point methods used for the
resolution of SDP is considered. In Section 4, the
primal-dual and the step size procedure algorithms,
bases of the new variant, are described. In Section 5,
the computational experience is described. A brief
description of the used tools is given and the
obtained results with the new versions and the
classical method are compared.
2 BACKGROUND FOR
SEMIDEFINITE
PROGRAMMING
Semidefinite Programming is currently the most
sophisticated area of Conic Programming that is
polynomially solvable. More precisely, SDP is the
optimization over the cone of positive semidefinite
matrices of a linear objective function subject to
linear equality constraints. It can also be viewed as a
generalization of Linear Programming where the
nonnegativity constraints on vector variables are
replaced by positive semidefinite constraints on
symmetric matrix variables.
The past few decades have witnessed an
enormous interest for SDP due to the identification
of many theoretical and practical applications, e.g.,
combinatorial optimization (graph theory), spectral
optimization, polynomial optimization, engineering
(systems and control), probability and statistics,
financial mathematics, etc... In parallel, the
development of efficient SDP solvers, based on
interior point algorithms, also contributed to the
success of this method.
Although many solvers have been developed in
the last twenty years to handle semidefinite
programming, this area, unlike LP, is still in its
infancy, and most codes are offered by researcher to
the community for free use and can handle moderate
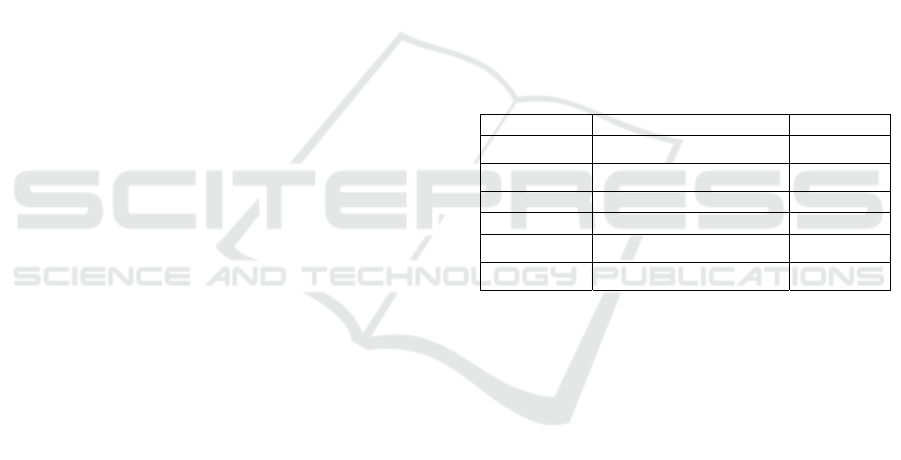
sized problems. The Table 2.1 identifies the different
software and their associated programming
language. Another simple possibility for comparing
several solvers is to use the standard file format
SDPA (Fujisawa and Kojima, 1995), where several
LMI (Linear Matrix Inequality) constraints are
possible. This format is accepted by most of the SDP
solvers.
Table 2.1: The different SDP solvers.
Software Algorithm Interface
CSDP
IPM (Primal-Dual path)
C
DSDP
Potential reduction
C, Matlab
SeDuMi Self-dual method Matlab
SB Bundle method C/C++
SDPA
IPM (Primal-Dual path)
C++
SDPLR
Augmented Lagrangian
C, Matlab
For more details about these solvers see
respectively (Borchers. 1999), (Benson et al., 2000),
(Sturm, 1998), (Helmberg and Rendl, 2000),
(Yamashita et al., 2010) and (Burer and Monteiro,
2003).
The PDIPA (primal-dual interior-point
algorithm) (Jarre, 1993), (Nesterov and Todd, 1995),
(Helmberg et al., 1996) and (Monteiro, 1997) is
known as the most powerful and practical numerical
method for solving general SDPs. The method is an
extension of the PDIPA (Wolkowicz et al., 2000)
and (Tanabe, 1988) developed for LPs. The SDPA
presented in this paper is a PDIPA software package
for general SDPs based on the paper (Fujisawa et al.,
1997) and (Jarre, 1993).
3 RESOLUTION OF SDP
Interior-points methods (IPM) for SDP have
sprouted from the seminal work of Nesteror &
Nemirovksi (Nesterov and Nemirovskii, 1994) and
Numerical Experiments with a Primal-Dual Algorithm for Solving Quadratic Problems
205

(Nesterov and Nemirovskii, 1993). Indeed, in 1988,
a major breakthrough was achieved by them
(Alizadeh, 1995), (Alizadeh et al., 1994) and
(Alizadeh and Haberly, 1998).
They stated the theoretical basis for an extension
of interior-methods to conic programming and
proposed three extensions of IPM to SDP : the
Karmarkar’s algorithm, a projective method and
Ye’s potential reduction method. In parallel, in
1991, Alizadeh (Alizadeh, 1995) also proposed a
potential reduction projective method for SDP. Then
in 1994, Boyd and Vandenberghe presented an
extension of Gonzaga & Todd algorithm for LP that
uses approximated search direction and able to
exploit the structure of the matrix. These methods
conserve the polynomiality under relevant
conditions. For this reason, these methods are crucial
for convex optimization. To explain the basic idea of
interior point method we need two ingredients:
Newton’s method for equality constrained
minimization and barrier functions.
Interior-point methods can be classified into
three major categories depending on the type of
algorithm:
Affine-scaling algorithms ;
Projective methods with a potential function ;
Path-following algorithms.
However, in extending primal-dual interior-point
methods from LP to SDP, certain choices have to be
made and the resulting search direction depends on
these
choices. As a result, there can be
several search directions for SDP corresponding to
a single search direction for LP. We can cite the
following four search directions:
HRVW/KSH/M direction (proposed by
Helmberg, Rendl, Vanderbei and Wolkowicz
(Helmberg et al., 1996)),
MT direction (proposed by Monteiro and
Tsuchiya (Monteiro and Tsuchiya, 1996)),
AHO direction (proposed by Alizadeh,
Haeberly, and Overton (Alizadeh et al.,
1994)),
NT direction (proposed by Nesterov and
Todd (Nesterov and Todd, 1995)).
The convergence property of the interior-point
methods algorithm varies depending on the choice of
direction.
To compute the search direction, the SDPA
employs Mehrotra type predictor-corrector
procedure (Mehrotra, 1992) with use of the
HRVW/KSH/M search direction (Helmberg et al.,
1996), (Vandenberghe and Boyd, 1994) and (Kojima
et al., 1989).
With this work, we intend to obtain a predictor-
corrector primal-dual interior point algorithm with
better performance and more precise than the other
algorithms of the same type already known.
We present a new variant of the algorithm used
in the SDPA solver with the procedure proposed in
(Crouzeix and Merikhi, 2008) in order to determine
the step-size along the direction which is more
efficient than classical line searches.
4 PRIMAL-DUAL PATH
FOLLOWING ALGORITHM
FOR SDPA WITH
PREDICTOR -CORRECTOR
TECHNIQUE
In this paragraph, we report the algorithm proposed
in (Helmberg et al., 1996) and implemented in the
solver SDPA (Fujisawa and Kojima, 1995). This
primal-dual path following method uses the
predictor-corrector technique of Mehrotra and has
the advantage of not requiring any specific structure
of the problem matrices.
Roughly speaking, the SDPA starts from a given
initial point ,, satisfying ≻0, ≻0and
numerically traces the central path
,
,
:0 that forms a smooth
curve converging to an optimal solution ,,
which corresponds to an optimal solution of (1) and
(2), as →0. Letting , it chooses a target point
,
,
on the central path to move from
the current point . Then the SDPA compute a search
direction to approximate the point, and updates the
current point ,,.Then the SDPA computes a
search direction,, to approximate the
point
,,
←
dx,
dX,
dY, where
and
are primal and dual step
lengths to keep
dX and
dY positive
definite. The SDPA repeats this procedure until it
Figure 4.1: The graphical representation of the interior
points algorithm.
ICORES 2016 - 5th International Conference on Operations Research and Enterprise Systems
206

attains an approximate solution
∗
,
∗
,
∗
of
problems (1) and (2), see Figure 4.1.
In our work, we propose a new variant of SDPA
with another computation of the step sizes. We use
the procedure in (Crouzeix and Merikhi, 2008) that
gives an alternative ways to determine the step-size
along the direction which are more efficient than
classical line searches.
4.1 The Step-Size Procedure
In (Crouzeix and Merikhi, 2008), the problem (1) is
approximated by a barrier problem. This problem is
solved via a classical Newton descent method. The
difficulty is in the line-search: the presence of a
determinant in the definition of the barrier problem
induces high computational costs in classical exact
or approximate line-searches. Here, instead of
minimizing the barrier problem along the descent
direction at the current point , we minimize a
function with its upper-approximaty
functions. This last reduce the computational cost of
the algorithm compared with classical methods. This
function needs to be appropriately chosen so that the
optimal step length is easily obtained and to be close
enough to in order to give a significant decrease of
the barrier problem in the iteration step. In
(Crouzeix and Merikhi, 2008), they propose
functions θ for which the step-size optimal solution
is explicitly obtained. For more details about this
procedure see (Chouzenoux et al., 2009), (Crouzeix
and Merikhi, 2008), (Benterki and Merikhi, 2001)
and (Benterki at al., 2003). In this paper we apply
this procedure to compute the step length in the
Primal-Dual Interior-Point Algorithm of SDPA.
4.2 Description of the Algorithm
SDPA has the highest version number 6.0 among all
generic SDP codes, due to its longest history which
goes back to December of 1995. We use the version
6.0 of SDPA.
The Primal-Dual Interior-Point Algorithm
(PDIPM) of SDPA
Step 0 (Initialization): Choose an initial point
,
,
satisfying
≻0
and
≻0
.
Let k = 0.
Step 1 (Checking Feasibility): If
,
,
is an
-approximate optimal solution of the (1) and (2),
stop the iteration.
Step 2 (Computing a search direction): As
described in (Mehrotra, 1992), apply Mehrotra type
predictor-corrector procedure to generate a search
direction,,.
Step 3 (Generating a new iterate): We use the
procedure (Crouzeix and Merikhi, 2008) to compute
and
as primal and dual step lengths so that
and
remain positive semidefinite.
We set the next iterate
,
,
,
,
.
Let ←1. Go to Step 1.
5 COMPUTATIONAL
EXPERIENCE
Now, we will describe the computational experience
that we have done to compare the new version of
our predictor-corrector variant and the classical
predictor-corrector method, described in the
previous sections.
5.1 Brief Description of the Used Tools
The computational tests were performed in Intel(R)
Core™ i5 2.50 GHz with 4Go memory under Linux
11. To implement the new predictor-corrector
variant we used the 6.0 version of the source code of
the package SDPA by Makoto Yamashita, Katsuki
Fujisawa and Masakazu Kojima (Fujisawa and
Kojima, 1995). The code was modified to achieve
two main purposes: it was adapted to be possible to
implement the different version of the predictor-
corrector variant and it was optimized to become
faster and more robust.
To compare the performance of the algorithms,
we generated automatically particular quadratic
programs. These results are preliminaries.
5.2 Results
We present the results corresponding to the new
predictor-corrector variant described earlier and
compare those results with the ones obtained with
the classical predictor-corrector algorithm. To test
our procedure, we generated particular quadratic
programs automatically for which we know the
primal objective value. We thus allow to validate our
procedure in experiments with comparison. We
solved the semidefinite relaxation of the problem
considered with the two variants of SDPA and then
we compare the results.
The motivation to consider this example is to
show the effectiveness and the realizability of our
procedure and to generate big instances.
We use the graphic with information about some
instances of the problem and the CPU time (in
Numerical Experiments with a Primal-Dual Algorithm for Solving Quadratic Problems
207
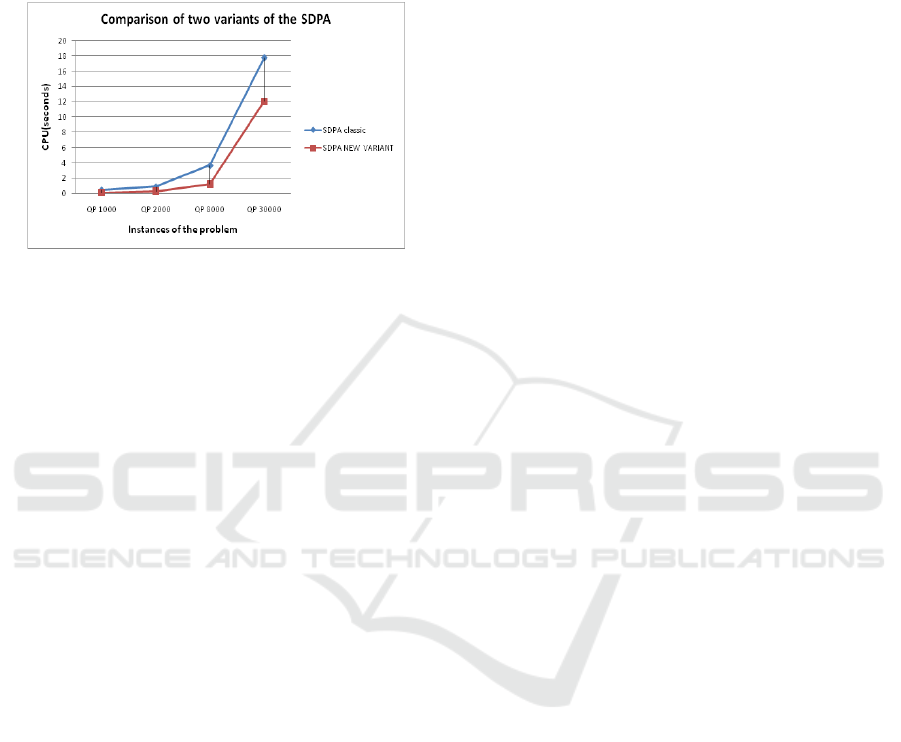
seconds), see Figure 5.1.
We consider the quadratic program:
..
2,
1..
.
(3)
Figure 5.1: Comparison of the CPU with SDPA classic
and SDPA new variant.
6 CONCLUSION AND FUTURE
WORKS
In this paper, we have applied a new procedure to
solve the SDP in optimal time. The logarithmic
barrier approach with the technique of upper-
approximaty functions reduce the computational cost
of the algorithm compared with classical methods.
The preliminaries numerical results show the
performance of this procedure. This work opens
perspectives for exploring the potentiality of
semidefinite programming to provide tight
relaxations of NP-hard, combinatorial and quadratic
problems. Our future work is to program another
line-searches and another barrier functions. We will
test the performance of the algorithms with the
SDPLIB collection of SDP test problems (Borchers,
1999) .
REFERENCES
Alizadeh, F., 1995. Interior point methods in semidefinite
programming with application to combinatorial
optimization, SIAM journal on Optimization, 5:13–51.
Alizadeh, F., Haberly, J.-P., and Overton, M.-L.. 1998.
Primal-dual interior-point methods for semidefinite
programming, convergence rates, stability and
numerical. SIAM J. Optim.8 746–768.
Benterki, D., Crouzeix, J.-P., and Merikhi., B., 2003. A
numerical implementation of an interior point method
for semi-definite programming. Pesquisa Operacional
23–1, 49–59.
Fujisawa, K. and Kojima, M., 1995. SDPA(Semidefinite
Programming Algorithm) Users Manual. Technical
Report b-308, Tokyo Institute of Technology.
Jarre. F., 1993. An interior-point method for Programming
minimizing the maximum eigenvalue of a linear
combination of matrices. SIAM Journal on Control
and Optimization, 31:1360–1377.
Nesterov Y. E., and Nemirovskii. A. S., 1990.
Optimization over positive semidefinite matrices:
Mathematical background and user’s manual.
Technical report, Central Economic & Mathematical
Institute, USSR Acad. Sci. Moscow, USSR.
Nesterov Y. E., and Nemirovskii. A. S., 1993. Interior
Point Polynomial Methods in Convex Programming :
Theory and Algorithms. SIAM Publications,
Philadelphia.
Vandenberghe, L. and Boyd. S., 1995. Primal-dual
potential reduction method for problems involving
matrix inequalities. Mathematical Programming,
69:205-236.
Nesterov, Y.E., and Nemirovskii, A.S., 1994. Interior-
Point Polynomial Algorithms in Convex
Programming. SIAM Studies in Applied Mathematics
13. SIAM, Philadelphia, PA, USA. 185, 461, 564, 584,
602.
Nesterov, Y. E., and Todd, M. J., 1995. Primal-dual
interior-point methods for self-scaled cones. Technical
Report 1125, School of Operations Research and
Industrial Engineering, Cornell University, Ithaca,
New York, 14853-3801.
Crouzeix, J.P. Merikhi, B., 2008, A logarithm barrier
method for semidefinite programming, R.A.I.R.O-
Oper. Res. 42, pp. 123-139.
Benterki, D., Merikhi, B., 2001. A modified algorithm for
the strict feasibility problem, RAIRO Oper. Res. 35,
pp. 395-399.
Monteiro, R.D.C., 1997. Primal-dual path- following
algorithms for semidefinite programming. SIAM
Journal on Optimization, 7, pp. 663-678.
Derkaoui, O., Lehireche, A, 2014. Safe bounds in
Semidefinite programming by using interval
arithmetic. American Journal of Operations Research,
Vol. 4 No. 5, septembre, PP. 293-300. DOI:
10.4236/ajor.2014.45029.
Helmberg, C., Rendl, F., Vanderbei, R.J., and
Wolkowicz, H., 1996. An interior point method for
semidefinite programming. SIAM Journal on
Optimization, 6:342–361.
Monteiro, R. D. C., and Tsuchiya, T., 1996. Polynomial
convergence of a new family of primal-dual
algorithms for semidefinite programming.Technical
report, Georgia Institute of Technology,Atlanta,
Georgia, USA.
Mehrotra, S., 1992. On the implementation of a primal-
dual interior point method, SIAM Journal on
Optimization 2 575-601.
Monteiro, R. D. C., 1997. Primal-dual path following
algorithms for semidefinite programming, SIAM
Journal on Optimization 7 663-678.
Nakata, M., Nakatsuji, H., Ehara, M., Fukuda, M.,
ICORES 2016 - 5th International Conference on Operations Research and Enterprise Systems
208

Nakata, K. and Fujisawa, K., 2001. Variational
calculations of fermion second-order deduced density
matrices by semidefinite programming algorithm,
Journal of Chemical Physics 114 8282-8292.
Nakata, M., Ehara, M., and Nakatsuji, H., 2002. Density
matrix variational theory: Application to the potential
energy surfaces and strongly correlated systems,
Journal of Chemical Physics 116 5432-5439.
Ben-Tal, A., and Nemirovskii, A., 2001. Lectures on
Moden Convex Optimizatin Analysis, Algorithms, and
Engineering Applications, (SIAM, Philadelphia).
Boyd, S., Ghaoui, L. E., Feron, E., and Balakrishnan, V.,
1994. Linear matrix inequalities in system and control
theory, Society for Industrial and Applied
Mathematics Philadelphia, PA, ISBN 0-89871-334-X.
Goemans, M. X., and Williamson, D. P., 1995. Improved
approximation alogrithoms for maxmum cut and
satisfiability problems using semidefinite
programming, Journal of Association for Computing
Machinery 42(6) 1115-1145.
Todd, M. J., 2001. Semidefinite optimization, Acta
Numerica 10 515-560.
Vandenberghe, L., Boyd, S., 1994. Positive-Definite
Programming, Mathematical Programming: State of
the Art J. R. Birge and K. G. Murty ed.s, U. of
Michigan.
Wolkowicz, H., Saigal, R., and Vandenberghe, L., 2000.
Handbook of Semidefinite Programming, Theory,
Algorithms, and Applications, (Kluwer Academic
Publishers, Massachusetts.
Kojima, M., Mizuno, S. and Yoshise, A., 1989. A Primal-
Dual Interior Point Algorithm for Linear
Programming, in: N. Megiddo, ed., Progress in
Mathematical Programming: Interior Point and
Related Methods (Springer-Verlag, New York) 29-47.
Tanabe, K., 1988. Centered Newton Method for
Mathematical Programming, in: M. Iri and K. Yajima,
eds., System Modeling and Optimization (Springer,
New York) 197-206.
Borchers. B., 1999. CSDP, a C library for semidefinite
programming. Optimization Methods and Software,
11.
Benson, S. J., Ye, Y., and Zhang, X., 2000. Solving
large-scale sparse semidefinite programs for
combinatorial optimization. SIAM Journal on
Optimization, 10(2):443–461.
Sturm, J. F., 1998. Using SeDuMi 1.02, a MATLAB
toolbox for optimization over symmetric cones.
Yamashita, M., Fujisawa, K., Nakata, K., Nakata, M.,
Fukuda, M., Kobayashi, K., and Goto, K.., 2010. A
high-performance software package for semidefinite
programs: SDPA 7. Technical report, Dept. of
Mathematical and Computing Science, Tokyo Institute
of Technology.
Burer, S., and Monteiro, R. D. C., 2003. A nonlinear
programming algorithm for solving semidefinite
programs via low-rank factorization. Math. Program.,
95(2):329–357.
Helmberg, C., and Rendl. F., 2000. A spectral bundle
method for semidefinite programming. SIAM Journal
on Optimization, 10:673–696.
Borchers, B., 1999. SDPLIB 1.2, a library of semidefinte
programming test problems, Optimization Methods
and Software 11 & 12 683-690.
Chouzenoux, E., Moussaoui, S., Idier, J., 2009. A
Majorize-Minimize line search algorithm for barrier
function optimization. EURASIP European Signal and
Image Processing Conference, Aug, Glasgow, United
Kingdom. pp.1379-1383, 2009. <hal-00456013>.
Numerical Experiments with a Primal-Dual Algorithm for Solving Quadratic Problems
209
