
Learning Path Specification for Workplace Learning based on Business
Process Management
Venkatapathy Subramanian
1,2
and Antonia Bertolino
2
1
GSSI, L’Aquila, Italy
2
CNR-ISTI, Pisa, Italy
Keywords:
Business Process Management, Learning Path, Monitor, Workplace Learning.
Abstract:
In modern society, workers are continuously challenged to acquire new skills and competencies while at
work. Novel approaches and tools to support effective and efficient workplace learning in collaborative and
engaging ways are needed. On the other hand, Business Process Management (BPM) is more and more
employed to support and manage the complex processes carried out within organizations. We propose to use
BPM also to drive workplace learning, with the advantage of aligning real tasks to training tasks. We introduce
a specification of learning path that maps BPM tasks and activities into sequences of learning tasks that can
be customized to learners competence. The learning path specification can be used to both drive learning
sessions, and to inform a monitor that can assess learner’s progress. We describe a platform that is under
development, and provide a simple motivational example to illustrate the approach. The goal is to combine
work and learning in natural and effective way.
1 INTRODUCTION
In the modern knowledge society education plays a
key role. At all ages and in varying contexts we are
called to assimilate a great amount of information and
capacities that are continuously communicated thanks
to pervasive Information and Communication Tech-
nologies (ICT). As a matter of fact, learning is no
longer confined to formal courses in school or Uni-
versity, but happens more and more as a continuous
and lifelong process.
Indeed, advanced countries see investing in people
education and qualification as a necessary condition
to overcome the economic crisis and support innova-
tion and future recovery. One significant part of adult
education needs to take place at work, where peo-
ple must continuously develop new skills and compe-
tences to overcome evolution of processes and tech-
nology. A culture of collaborative workplace learn-
ing must be shared between employers and workers
within a win-win strategy.
Hence, the need arises for putting in place means
to support workplace learning, while successful indi-
vidual learning becomes an important parameter for
the successful functioning of an organization. In re-
cent years, many training and e-learning methods and
frameworks are developed to help the employees of an
organization to learn about the business activities they
are involved. However the training and e-learning ses-
sions were not as successful as aimed because:
• often the training session is out of working time,
implying that workers need to devote extra-work
time that is demanding and exhausting
• the learning curve for the training session itself
was steep and apart from their business activities
and hence workers were hesitant to take up the
task
• setting up a learning environment similar to the
working environment is very difficult for the com-
pany and usually costly and so workplace training
becomes difficult for the company to setup
Companies look for alternative approaches to train
the employees that can address the above issues.
What companies are looking for is workplace learn-
ing in which employees can take lessons while they
are at work. In our view the requirements for success-
ful workplace learning should include:
• capability to simulate the actual working environ-
ment for the employees
• efficient and cost-effective set up of the training
environment
172
Subramanian, V. and Bertolino, A.
Learning Path Specification forWorkplace Learning based on Business Process Management.
In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Computer Supported Education (CSEDU 2016) - Volume 1, pages 172-180
ISBN: 978-989-758-179-3
Copyright
c
2016 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

• capability to track and customize learning tasks to
the profile of the employees
On the other hand, nowadays ICT penetration
within the functioning of business organizations is
deep and it can be very confidently stated that they
help in every step of the functioning of the organi-
zation. As the adoption of ICT increases, the in-
teraction between actual physical business transac-
tions and software technology become heavily inter-
twined and inter-dependent. Several methodologies
have been proposed to make the integration of ICT
and work procedures easier and more efficient. One
such methodology is Business Process Management
discipline, which helped the organizations to view
their function as processes.
BPM have matured for the last couple of decades
and has penetrated many large scale organization in
their design of business process as well as the re-
lated software applications needed to execute the pro-
cesses. BPM can also be easily integrated into legacy
systems and other applications that reside outside
of normal scope the organization’s software appli-
cational needs. Systems that are developed using
BPM techniques are called as Business Process Man-
agement Systems. BPM success stories are many.
Austin Energy, one of the leading energy utility com-
pany used BPM techniques to create an integrated
IT infrastructure that spans the entire enterprise, to
employ a powerful software framework for develop-
ment, management and operations, enabling better
service and to provide end-to-end monitoring, control
and management of generation and distribution to im-
prove responsiveness and utilization of resources lev-
els. (IBM-BPM, 2009) With robust IT infrastructure
available, there is a need now to use them for enabling
learning at workplace.
We believe that the current methodologies of BPM
techniques can help organizations build such work-
place learning environment. This idea is at the core
of the ongoing Learn PAd European Project, where
we are developing a new approach and a platform to
learning at work that exploits BPM models as both
learning content and guide for personalized and col-
laborative learning sessions.
In the context of such wide goal, in this paper, we
propose BPMS as a tool that can be used to develop
workplace learning and training within an organiza-
tion. Many facilities needed for using a BPMS to de-
sign a learning systems are already in place such as
collaborative execution between different users, web-
service integration, etc However BPM is not origi-
nally conceived for learning. In this work, we focus
on defining a learning path specification that can be
used to extend a BPMS for workplace learning. We
call it as Business Process Management-based Learn-
ing System (BPMLS).
As defined in (Janssen et al., 2008a), a sequence
of activities and learning objectives customized to the
needs and competencies of a learner is called a learn-
ing path. Therefore, after some background notions
(Section 2), in Section 6 we introduce a definition of
a learning path mapped on BPM models. Then in Sec-
tion 4 we describe a BPMLS framework under devel-
opment that can be for declaring and assessing learn-
ing activities of workplace learners. In Section 5 we
walk through an example to show how the approach
is used. Related work and Conclusions sections com-
plete the paper.
2 BACKGROUND
This section will provide an overview of background
concepts and technologies that are at basis of our
work. In particular, our learning path specification
uses and combines concepts and definitions related to:
• Business Process Management discipline;
• Business Activity Monitoring systems;
• Workplace Learning approaches;
• Learning Path specification.
We already introduced informally Business Pro-
cess Management (BPM) in Section 1. More for-
mally, we adopt here van der Aalst and coauthors
operational definition of BPM (van der Aalst et al.,
2003) as a discipline supporting business processes
using methods, techniques, and software to design,
enact, control, and analyze operational processes in-
volving humans, organizations, applications, docu-
ments and other sources of information.
BPM spans over a complex life-cycle including
stages of design, configuration, enactment, and diag-
nosis (van der Aalst et al., 2003) . A Business Process
Management System (BPMS) is a suite of software
tools that leverage BPM concepts and covers some of
the important components of the BPM life-cycle. Us-
ing a BPMS, process models are automated as work-
flow models that are then executed by a process en-
gine. (Van Der Aalst and Van Hee, 2004)
Business Process Management Notation 2.0
(bpmn.org, 2011) (in the following referred to sim-
ply as BPMN) provides a standardized graphical no-
tation for modeling executable business processes in
a workflow. A workflow contains a sequence of busi-
ness activities, the work of a person, group, or any
business applications. BPMN is one of the most suit-
able standards for developing process-oriented enter-
prise systems.
Learning Path Specification forWorkplace Learning based on Business Process Management
173

BPMS frameworks provide tools for: i. Process
modeling, ii. Process Execution, and iii. Business
Activity Monitoring (Van Der Aalst et al., 2003),
among other things. In particular, Business Activity
Monitoring (BAM) software can provide real-time
access to critical business performance indicators
for business activities executed by BPMS. BAM
uses Complex Event Processing (CEP) techniques
(Buchmann and Koldehofe, 2009), to process simple
software-level events and derive higher level business
events. BAM collects data of interest during the
run-time business process execution. Collected data
are later analyzed by Complex Events Processor
(CEP) and correlated to Key Performance Indicators
(KPIs) and Goals defined for the process models.
(Calabro et al., 2015; Koetter and Kochanowski,
2012)
By adopting a model-driven approach, BPMS can
easily be adapted for the design of platforms that
can both inform and mimic business scenarios. This
idea is at the basis of the ongoing Learn PAd project,
which is developing a technology-enhanced platform
for adult learning. In fact, when the modeled BP re-
produces operational process in the offices, such plat-
forms can provide opportunities for the employees to
acquire knowledge by actually doing the activity. This
kind of learning is called as workplace learning (Bil-
lett, 2001). Workplace learning emphasizes on partic-
ipatory business practices for individual knowledge-
gain. (Billett, 2004)
Within the learning context, Learning path is
described as the chosen route, taken by a learner
through a range of learning activities, which allows
them to build knowledge progressively. (Clement,
2000) It can be used to formally describe learning
scenarios. (Janssen et al., 2008a) A learning path in-
cludes a learnflow which contains orchestration de-
tails for learning activities, roles and other learning
resources. (Mari
˜
no et al., 2007) Learning path speci-
fication should also define learning objectives or out-
comes.
Many platform-independent Educational Model-
ing Languages have been proposed to describe learn-
ing path. IMS Global Consortium released the IMS-
Learning Design specification that allows for defining
the learning path as a Unit of Learning (UOL). (IMS-
Global, 2003) Janssen and coauthors have provided a
generic learning-path model that are mapped to IMS-
LD designs. (Janssen et al., 2008a)
The aim of this paper is to introduce a learning
path specification that can be integrated to BPMS
for workplace learning. Our specification draws to-
gether the key concepts and definitions from Business
Process Management discipline as well as Workplace
Learning approaches explained above.
3 LEARNING PATH
SPECIFICATION
IMS-LD and Janssen et al (IMS-Global, 2003;
Janssen et al., 2008a) learning path specifications em-
phasize on learnflow that consists of a sequence of
activities and learning objectives based on the com-
petencies of the learner. However, when it comes to
defining learning path for business process models,
specification of learnflow and learning objectives dif-
fer due to the following reasons:
• Learning flow for workplace learning should align
to the business activities of an organization. What
an employee learns should conform to the busi-
ness process sequence rules established by the or-
ganization.
• Learning objectives of workplace learning should
be correlated to Key Performance Indicators
(KPIs) of business activities that are executed dur-
ing the learning process.
• Learning path should be able to capture differ-
ent business scenarios of the same business pro-
cess. An employee’s business activity may change
based on the inputs he receives during the busi-
ness process execution
The above key aspects are captured in our learn-
ing path specification. Our specification maps KPIs of
business processes to objectives of the learning path.
Figure 1, represents the model of our learning path
specification. We extend the BPMN model to intro-
duce attributes related to LearningPath. This specifi-
cation allows defining Learning path on top of BPMN
specification. In the figure, classes of BPMN model
are represented in gray background. Classes with the
yellow background are related to the learning path
specification. An overview of the model is explained
in detail below.
A Business Process Model defined using
BPMN.2.0 specification can have one or more
Learning Paths. Learning Paths are defined only for
BPMN models with parameter isExecutable set to
true. This is to ensure that learning paths are defined
only for deployable BPMN process models (refer
BPMN Specification). Each instance of Learning
Path model represents one learning session, and
executes a process instance in BPMLS, with KPIs
and monitoring parameters defined by the Learning
Path model. Learning Paths fulfill learning objectives
which are represented as KPIs. KPIs are used to
CSEDU 2016 - 8th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
174

Figure 1: Learning path specification for business process model.
evaluate key business metrics that are crucial during
the execution of the process instance. Mapping KPIs
to Learning objectives ensures that learning sessions
caters to the business goals of the organization.
A Learning Path can have one or more Learning
tasks. LearningTask class is extended from the Task
of BPMN. Learning Tasks define one or more Param-
eter objects which are used to calculate KPIs during
the learning session.
LearningTask can contain a set of DataInput ob-
jects that defines a set of input data thatis expected for
the corresponding learning task. Similarly DataOut-
put objects defines output data expected from the
learning task. DataInput and DataOutput are ex-
tended from their counterparts from BPMN specifica-
tion.
In this section we have provided a learning path
specification for business process models. In the next
section we will provide an architectural framework
that uses this specification for building BPMLS. In
Section 5, we provide an example to explain how the
business process and learning are related, and how
learning path specification help in business process
learning.
4 FRAMEWORK FOR
BPMS-BASED LEARNING
SYSTEM
BPMS which can be used for modeling and execution
of BPMN-based process models can be extended into
BPMLS, if we can define:
• A Model to specify Learning Path on top of
Business Process Models: This is what we pro-
vide in Section 6.
• A Platform to Design Learning Models: It can
be a tool developed on top of BPMS modeling
tools. This work is currently in progress, and we
are not covering this in this paper.
• Methods to Monitor and Assess the Learning
Progress of a User: Preliminary result of this
can be found in our work. (Subramanian and
Bertolino, 2016)
In this section, we will provide the architecture
of BPMLS. The framework is conceived such that an
employee who needs to learn about a business process
can log into the system and will find an environment
Learning Path Specification forWorkplace Learning based on Business Process Management
175
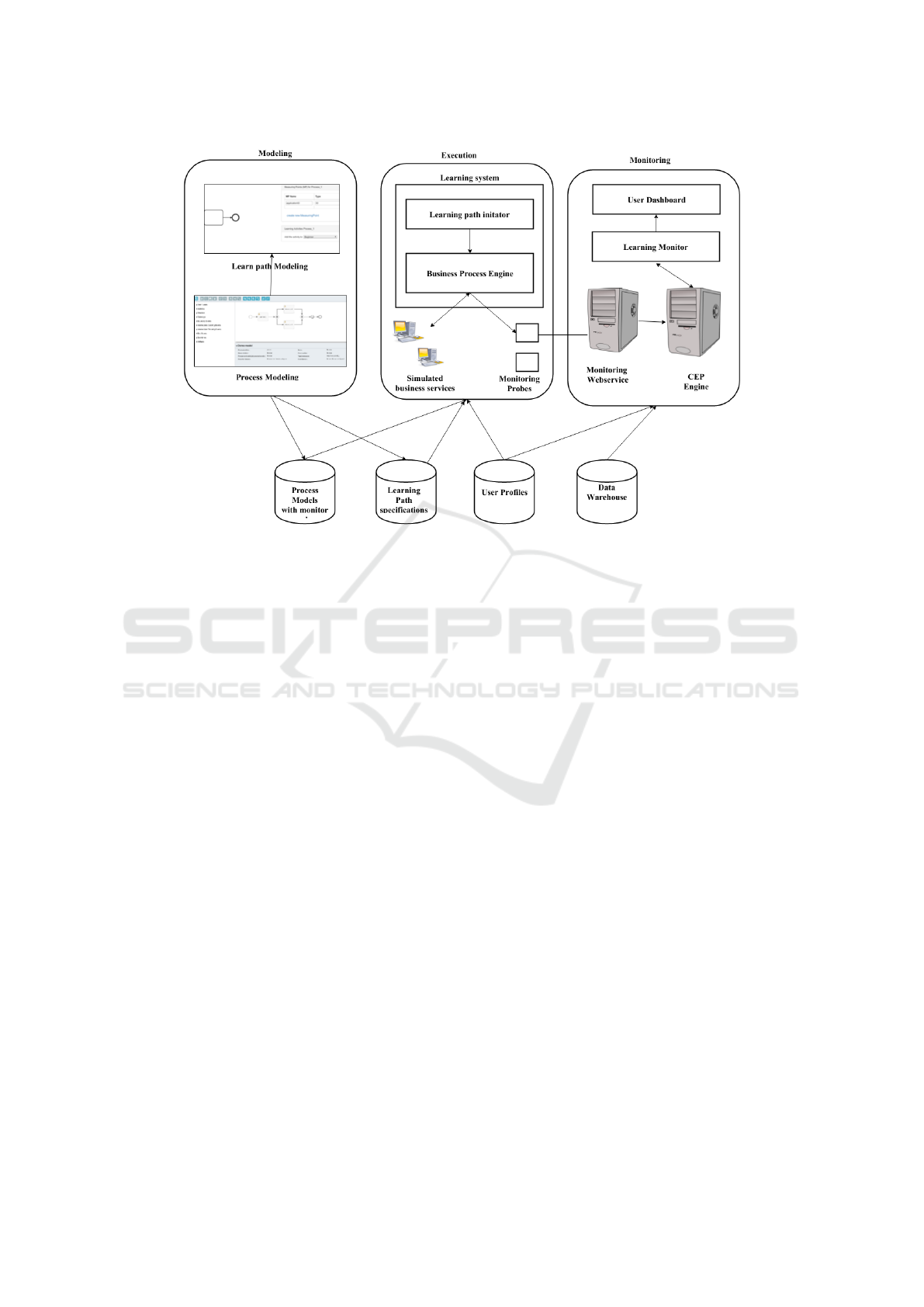
Figure 2: Framework of BPMS based Learning and Monitoring System.
mimicking the real business process for learning pur-
poses. Project Learn PAd, of which this work is a
part, aims at developing a learning environment that
supports, among other things, a procedural learning
approach based on simulation and monitoring (learn-
ing by doing). This research work will provide meth-
ods to define learning path as well as to execute and
monitor the learning progress during a learning ses-
sion. Since providing actual components for creating
a learning scenario is beyond the scope of this work,
we will use existing business process engine for pro-
cess execution. Later we will integrate our framework
with the simulation environment of Learn PAd.
The framework provides components: i. to define
learning path for business process models, ii. to cre-
ate a learning session and deploy the corresponding
process instance in a process engine (simulation en-
gine in the later period of time, when it is been devel-
oped). iii. to monitor the learning session to verify if
the learning path satisfies the learning outcomes. The
overall framework of our BPMS-based learning sys-
tem and monitoring system is given in Figure 2.
The architecture covers three phases of a BPM
life-cycle, namely Modeling, Execution and Monitor-
ing. During the modeling phase, learning paths are
defined for a given process model based on our spec-
ification. A document will be created for each learn-
ing path. When writing this paper, we are in the pro-
cess of developing a tool for XML serialization of the
LearningPath specification. The document will con-
tain the business process model as well as of the learn-
ing path model.
During the execution phase when one of the
learning path is selected for execution, model-
transformation technique is applied to transform the
learning path model into business process model.
Model-transformation from Learning path model to
Business Process model is an ongoing work and is be-
yond the scope of this paper. Some of the initial work
can be found at (will be reference to submitted paper
not included due to double-blind review procedure).
After the transformation is complete, a learning
scenario will be created by executing the correspond-
ing process instance in BPMLS business process en-
gine. Monitoring uses BAM techniques to monitor
the learning path execution and provides real-time re-
sults of the learning progress.
In the next sections, we will see an example and
the prototype that we developed for the execution of
learning path model.
5 MOTIVATIONAL EXAMPLE
In this section we will see a motivational example,
to understand the learning path specification that was
defined earlier.
European Union Framework Program (FP7) pro-
vide funding opportunities for many organizations
within Europe to support Research and Development.
Organizations working within FP7 programs should
understand the complexity involved during the suc-
CSEDU 2016 - 8th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
176
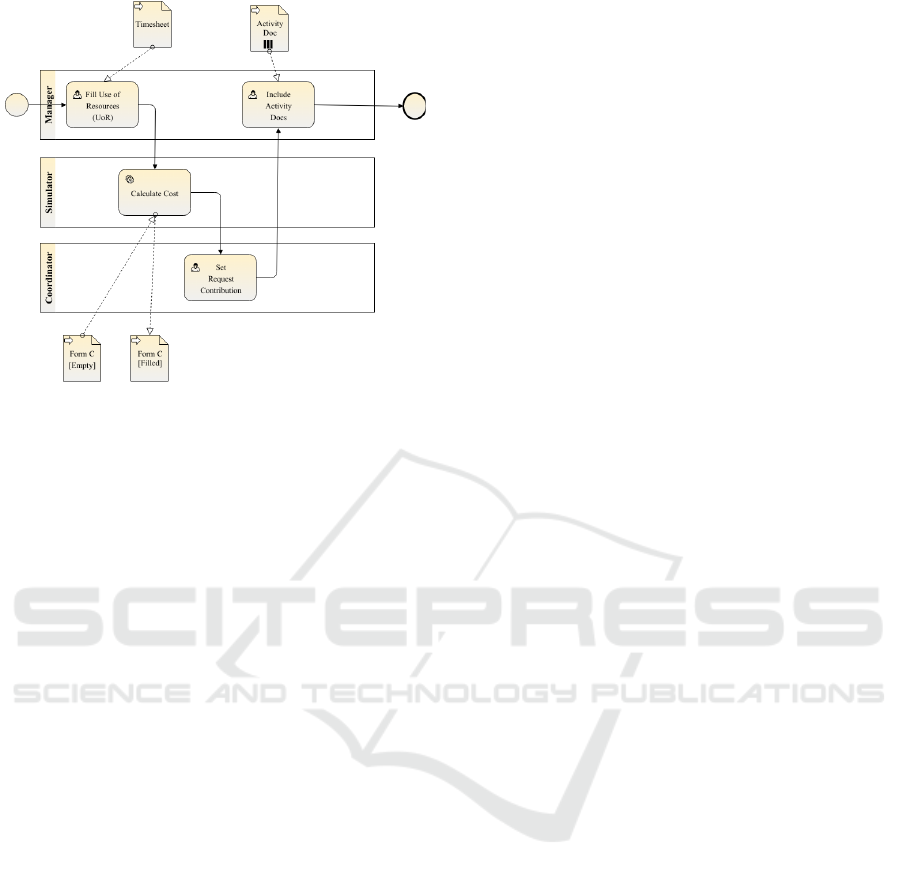
Figure 3: Example Process- Periodic Budgeting Report.
cessful execution of their projects. Understanding the
different processes involved is crucial for the success
of the project. For example, participants in an EU
financed project are obliged to report periodic bud-
geting activities for the tasks performed within the
project. This process is quite complex but yet ex-
tremely important for the employees of the organi-
zation to understand. Workplace learning for such
scenarios is the need of the hour for such organiza-
tions. We will consider below a motivational example
that will highlight the usefulness of our learning path
specification workplace learning for the above sce-
nario. Figure 3 represents a simplified BPMN model
for the periodic budgeting report of an organization
that is involved in the FP7 project. It is a collabora-
tive process between a project manager and a project
coordinator. In the first task ‘Fill Use of Resources
(UoR)’, the project manager has to fill a predefined
timesheet form to reflect the different resources used
for the project during a particular period. Next task
is an automated service task (typically a web-service
call), that mimic the process to calculate project costs
based on the timesheet filled earlier. At the end of the
‘Calculate Cost’ task, a filled ‘Form C’ document will
be provided to Project Coordinator. The coordinator
will set a contribution in the next task called ‘Set Re-
quest Contribution’ based on the details available in
Form C. In the final step, the manager has to attach a
list project activity documents relevant to the project.
The task is called ‘Include Activity Docs’ in the busi-
ness process model. With the submission, the process
will be completed.
Though it is a simplified version of EU budget re-
porting, the above example is still complex enough
to be reproduced in a standard Learning Management
System (LMS). We will see how our BPMLS frame-
work makes it easier for creating a learning environ-
ment for such scenarios.
5.1 Learning Path for Periodic Budget
Reporting
Our First goal is to provide a learning path specifica-
tion for the above example. Figure 4 provides the in-
stance model of the Learning Path specification. The
instance captures one learning scenario for the ex-
ample. The learning path is created for the budget-
ing scenario of ‘Project X’. The details of the sam-
ple project scenario is provided as DataInput to the
learning task ‘Fill Use of Resource’. Note that in the
representational figure just the name of the project is
provided. However additional details can be provided
as an array of DataInput object (not provided in the
figure for the sake of brevity). The learning task also
contains a Parameter object called ‘Total Time’ that
will be used within KPI. ‘Set Request Contribution’
is another learning task of the learning path specifi-
cation. It also contains a Parameter object called
‘Request Cost’ to capture the cost set by the project
coordinator.
Both the Parameter objects are used within the
calculate function of KPI class which is defined as:
TotalTime < 100 && RequestCost < 10000
The KPI function verifies if the collaborators of
the ‘ Project X’ is able to fill the forms accurately.
In our specification, KPIs are used to monitor if the
‘Total Time’ entered by the project manager is less
than 100 (hours) and the ‘Request Cost’ entered by
the project cost is less than 10000 (Euros). And this
KPI is set as learning objective of our learning path
specification. This way our learning path specifica-
tion can ensure that the learning scenario caters to the
business goals of the organization.
5.2 Prototype Evaluation
A prototype was developed to evaluate the learning
path model transformation and assessment tech-
niques. Learning path specification are created as
mentioned above. Model transformation is performed
in a semi-automated way, where the BPMN models
are generated automatically and later manually up-
dated with the additional learning tasks parameters.
We already have developed a semi-automated model
transformation technique in our work. (reference
to submitted work, omitted here for double-blind
process) We are in the process of automating the
transformation technique.
Learning Path Specification forWorkplace Learning based on Business Process Management
177

Figure 4: Learning Path Specification- Periodic Budgeting
Report.
Figure 5: Learning Path Specification- Periodic Budgeting
Report.
Figure 6: Monitoring- Periodic Budgeting Report.
For the Process Execution Engine, we used
Apache Activiti, an open-source Java-Based BPM
Platform. (Rademakers, 2012) For learning path mon-
itoring we used Drools Fusion (Drools Fusion 6.0.3,
2015) based CEP engine. Apache Activiti Explorer
was used to design, and execute the process mod-
els. Learning path model and its corresponding busi-
ness process models, CEP rules were created sepa-
rately. The explorer interface was modified to detect
and display the learning progress to the users. Figure
5 provides a screenshot in which the ‘Fill Use of Re-
sources’ task is executed. Figure 6 provides a screen-
shot of a simplified web page where the progress of
the learner is registered.
6 RELATED WORK
Using BPM concepts for the management of col-
laborative learning processes have long been consid-
ered by the research community. Marino and coau-
thors (Mari
˜
no et al., 2007) proposed a method to
transform learning design models defined using the
IMS-LD specification to business process execution
model called XML Process Definition Language. The
goal was to use IMS-LD for defining a learning de-
sign and use business process engine as a delivery
platform for the learning designs. In (Karampiperis
and Sampson, 2007), Karampiperis and coauthors ex-
amine using of BPMN as a common representation
notation for learning flows modeled using Business
Process Execution Language (BPEL) and present an
algorithm for transforming BPEL Workflows to IMS-
LD learning flows.
Vantroys and Peter (Vantroys and Peter, 2003) pre-
sented Cooperative Open Workflow (COW), a flex-
ible workflow engine that can be used to transform
IMS-LD into XPDL designs to enact the learning
models in the platform. Another e-learning plat-
form called Flex-el (Lin et al., 2002), is also been
built on top of workflow technology. It provides a
unique environment for teachers to design and de-
velop process-centric courses and to monitor student
progress. Project TRAILER, BPMN is used as a
model to define a methodology and developing tools
to learning as well as the management of competences
and skills acquired through informal learning experi-
ences, both from the perspective of the user and the
institution or company. (Penalvo et al., 2012; ?)
Above discussed methodologies and platforms fo-
cus on using BPM techniques and technologies for
designing learning specifications for academic sce-
narios and do not focus on workplace learning.
Regarding learning path specification, Janssen and
coauthors proposed learning path information model
that can represent a formal learning path model.
(Janssen et al., 2008b) However, the specification
is generic and does not address the requirements of
workplace learning based on BPM. We already raised
the issues in Section 6.
CSEDU 2016 - 8th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
178

As far as we know none of the existing work focus
on using BAM for workplace learning monitoring. In
their work, Adesina et al focus on visually tracking
the learning progresses of a cohort of students in a
Virtual Learning Process Environment (VLPE) based
on the Business Process Management (BPM) concep-
tual framework. (Adesina and Molloy, 2012) Their
work focus on learning specifications for academic
scenarios and do not focus on workplace learning.
Tracking the learning progress also do not leverage
upon BAM systems.
Our work defines a precise specification that can
be used for defining learning path for business process
models, as well as transformation techniques for us-
ing standard business activity monitoring techniques
to monitor learning progress of an employee.
7 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
WORK
Our work aims at exploiting the potential of BPM to
support effective and realistic workplace learning ac-
tivities. BPMS solutions used at work are very pow-
erful and widely used, but they are not conceived for
training. To the best of our knowledge there is no ex-
isting proposal for adapting BPMS to learning needs.
Our work stays within the context of the European
Learn PAd project, that aims at exploiting enriched
BPMN models for deriving both recommender sys-
tems and simulation sessions used expressly for learn-
ing the modeled sequence of tasks.
This work, in particular, aims at filling the gap be-
tween BPM used for work, and workplace learning
needs. We introduced a specification of learning path
that extends the standard BPMN specification by in-
cluding learning relevant concepts. The development
of a platform using such definition both for driving the
learning session and for assessing learners progress is
still ongoing. We are currently refining platform im-
plementation, and testing it on several scenarios de-
fined within the Learn PAd project.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This research has been partially supported from the
European Union’s Seventh Framework Programme
[FP7/2007-2013] under Grant Agreement N. 619583
(Project Learn PAd - Model Based Social Learning
for Public Administrations).
REFERENCES
Adesina, A. and Molloy, D. (2012). Virtual learning pro-
cess environment: Cohort analytics for learning and
learning processes. World Academy of Science, Engi-
neering and Technology, 65.
Billett, S. (2001). Learning in the Workplace: Strategies for
Effective Practice. ERIC.
Billett, S. (2004). Workplace participatory practices: Con-
ceptualising workplaces as learning environments.
Journal of workplace learning, 16(6):312–324.
bpmn.org (2011). Business process modeling notations.
[Online; accessed 7-November-2015].
Buchmann, A. and Koldehofe, B. (2009). Complex event
processing. it-Information Technology Methoden und
innovative Anwendungen der Informatik und Informa-
tionstechnik, 51(5):241–242.
Calabro, A., Lonetti, F., and Marchetti, E. (2015). Mon-
itoring of business process execution based on per-
formance indicators. In Software Engineering and
Advanced Applications (SEAA), 2015 41st Euromicro
Conference on, pages 255–258. IEEE.
Clement, J. (2000). Model based learning as a key research
area for science education. International Journal of
Science Education, 22(9):1041–1053.
Drools Fusion 6.0.3 (2015). Drools Fusion: Complex
Event Processor. http://www.jboss.org/drools/drools-
fusion.html. Last Accessed: 27th November 2015.
IBM-BPM (2009). Ibm-bpm success stories whitepaper.
[Online; accessed 11-February-2016].
IMS-Global (2003). Ims- learnind design. [Online; ac-
cessed 7-November-2015].
Janssen, J., Berlanga, A., Vogten, H., and Koper, R.
(2008a). Towards a learning path specification. Inter-
national journal of continuing engineering education
and life long learning, 18(1):77–97.
Janssen, J., Hermans, H., Berlanga, A. J., and Koper, R.
(2008b). Learning path information model. Retrieved
November, 9:2008.
Karampiperis, P. and Sampson, D. (2007). Towards a com-
mon graphical language for learning flows: Trans-
forming bpel to ims learning design level a represen-
tations. In Advanced Learning Technologies, 2007.
ICALT 2007. Seventh IEEE International Conference
on, pages 798–800. IEEE.
Koetter, F. and Kochanowski, M. (2012). Goal-oriented
model-driven business process monitoring using pro-
goalml. In Business Information Systems, pages 72–
83. Springer.
Lin, J., Ho, C., Sadiq, W., and Orlowska, M. E. (2002).
Using workflow technology to manage flexible e-
learning services. Journal of Educational Technology
& Society, 5(4):116–123.
Mari
˜
no, O., Casallas, R., Villalobos, J., Correal, D., and
Contamines, J. (2007). Bridging the gap between e-
learning modeling and delivery through the transfor-
mation of learnflows into workflows. In E-Learning
Networked Environments and Architectures, pages
27–59. Springer.
Learning Path Specification forWorkplace Learning based on Business Process Management
179

Penalvo, F. J. G., Zangrando, V., Holgado, A. G., Gonza-
lez, M. A. C., Pardo, A. S., Griffiths, D., Forment,
M. A., Mykowska, A., Janssen, J., Alves, G. R., et al.
(2012). Trailer project overview: Tagging, recogni-
tion and acknowledgment of informal learning expe-
riences. In Computers in Education (SIIE), 2012 In-
ternational Symposium on, pages 1–6. IEEE.
Rademakers, T. (2012). Activiti in Action: Executable busi-
ness processes in BPMN 2.0. Manning Publications
Co.
Subramanian, V. and Bertolino, A. (2016). Monitoring
of learning path for business process models. In
AMARETTO - International Workshop on domAin
specific Model-based AppRoaches to vErificaTion and
validaTiOn. SciTePress.
van der Aalst, W., ter Hofstede, A., and Weske, M. (2003).
Business process management: A survey. In van der
Aalst, W. and Weske, M., editors, Business Process
Management, volume 2678 of Lecture Notes in Com-
puter Science, pages 1–12. Springer Berlin Heidel-
berg.
Van Der Aalst, W. and Van Hee, K. M. (2004). Workflow
management: models, methods, and systems. MIT
press.
Van Der Aalst, W. M., Ter Hofstede, A. H., and Weske, M.
(2003). Business process management: A survey. In
Business process management, pages 1–12. Springer.
Vantroys, T. and Peter, Y. (2003). Cow, a flexible platform
for the enactment of learning scenarios. In Group-
ware: Design, Implementation, and Use, pages 168–
182. Springer.
CSEDU 2016 - 8th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
180
