
Investigation of Gait Representations in Lower Knee
Gait Recognition
Chirawat Wattanapanich and Hong Wei
Computational Vision Group, School of Systems Engineering, University of Reading, Reading, United Kingdom
Keywords: Gait, Gaussian, Entropy, SVM, PCA.
Abstract: This paper investigates the effect of lower knee gait representations on gait recognition. After reviewing three
emerging gait representations, i.e. Gait Energy Image (GEI), Gait Entropy Image (GEnI), and Gait Gaussian
Image (GGI), a new gait representation, Gait Gaussian Entropy Image (GGEnI), is proposed to combine
advantages of entropy and Gaussian in improving the robustness to noises and appearance changes.
Experimental results have shown that lower knee gait representations can successfully detect camera view
angles in CASIA Gait Dataset B, and they are better than full body representations in gait recognition under
the condition of wearing coat. The gait representations involving the Gaussian technique have shown
robustness to noises, whilst the representations involving entropy provide a better robustness to appearance
changes.
1 INTRODUCTION
Gait recognition is a biometric technique which has
become a challenge research area in the last few
decades. This technique classifies people by the way
their walk that does not directly contact with human
body. Input images can be captured in a long distance
with low resolution and it does not disturb the target
activity. Therefore gait recognition can cooperate
with CCTV which has become a common facility in
surveillance systems.
Gait representating are divided into two categaries
based on previous gait research (Shirke et al., 2014).
The first categary is model-based that creates the
target model which is used in gait feature extractionv.
Another is model-free which directly extracts gait
features from sequence of human silhouette (Rong et
al., 2004, Hu, 2011). This study focuses on the second
approach.
There are various gait features which have been
used in the model free approach such as the center of
mass, width, height, step-size, height of knee,
unwrapping boundary, and area or number of pixels
(Zeng et al., 2014, Nandy et al., 2014). The whole
silhouette could be also used as a gait feature. A
sequence of silhouettes has been combined to
represent gait, called Gait Energy Image (GEI) (Han
and Bhanu, 2006). This technique is commonly used
because it is very simple, fast, and representative to
some extent. However it is sensitive to some
conditions, such as object carrying and clothing.
Hence there are emerging research that aim to
improve the performance of the whole silhouette gait
representation, such as Gait Entropy Image (GEnI)
(Bashir et al., 2010), Active Energy Image (AEI)
(Zhang et al., 2010), Flow Histogram Energy Image
(FHDI) (Yang et al., 2014) and Gait Gaussian Image
(GGI) (Arora and Srivastava, 2015).
We proposed a new gait representation which
combines Gaussian and Entropy concepts together,
namely Gait Gaussian Entropy Image (GGEnI). It
takes advantage in correlation between image frames
from Gaussian membership function and motion
information capturing from Entropy technique.
Different walking conditions affect gait
classification results, such as cloth, object carrying,
speed transition (Mansur et al., 2014), view angle
(Haifeng, 2014, Zheng et al., 2011), curve projection
(Iwashita et al., 2014) and incomplete gait cycle
(Chattopadhyay et al., 2014). This study begins with
view angle detection. We assume that all training
sample have already been labelled with camera view
angles. When an unknown person is tested, the
recognition system first identifies the view angle, and
then compares the input images with the sample
images only in the same view angle.
Most walking motion parts in a body are clearly
678
Wattanapanich, C. and Wei, H.
Investigation of Gait Representations in Lower Knee Gait Recognition.
DOI: 10.5220/0005817006780683
In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods (ICPRAM 2016), pages 678-683
ISBN: 978-989-758-173-1
Copyright
c
2016 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

Figure 1: Overview of Gait Recognition System.
arms and legs. Nevertheless, people usually intend to
change cloth and object carrying in different seasons
and weather conditions, for example sweater, coat,
jacket, shorts, skirt, shoe, scarves, gloves, hat and
bag. These changes most likely affect above knee
appearance except of heel shoe, boots and long skirt.
This study also discusses and compares gait
recognition based on both full body and lower knee.
The rest of this paper is organized as follows.
Section 2 presents a gait recognition system which
shows the system overview and techniques used in
gait recognition. Section 3 demonstrates experiments
and results, and Section 4 summaries this study.
2 METHODOLOGY
The overview of gait recognition
system is shown in
Figure 1. Both training and recognition phases start
with background subtraction which separates human
silhouette in each frame of a video sequence. All
sequential silhouette images are used to generate gait
representation which is described in next section. In
the training phase, principal components analysis
(PCA) is applied to calculate an optimal feature map
for each view angle and condition. Next, gait features
are extracted from the optimal feature map as the gait
(a) Full body
(b) Lower Knee
Figure 2: Gait Representation example: GEI, GEnI, GGI
and GGEnI (from lef to right).
representation. SVMs (Supporting Vector Machines)
are used for training and classification.
2.1 Gait Representation
We investigate four gait representations in this
research, as shown in Figure 2.
2.1.1 Gait Energy Image (GEI)
This is a common technique in gait recognition. The
average silhouette image, calculated from averaging
all binarized silhouette images at a same view angle,
is used as the representation of personal gait. The
final representation is a gray level image. This
technique has increased noise tolerance and reduced
the memory space.
GEI has been defined as:
(
,
)
=
1
(
,
)
(1)
where N is the number of silhouette frames in walking
sequence, t is the frame number in the walking
sequence,
(
,
)
is the binary image at time t and
(x, y) is the pixel coordinate in a frame.
2.1.2 Gait Entropy Image (GEnI)
This technique aims to limit unnecessary appearance
information in motion images. Thus it is robust to
appearance changes. Same as GEI, sequential
silhouette images of a personal gait cycle are used as
an input which calculates Shannon entropy by
equation (2).
=
(
,
)
=
(,)
(,)
(2)
Investigation of Gait Representations in Lower Knee Gait Recognition
679

where , is pixel coordinate and
(,) is the
probability which have =2 because input
images are binary image. This paper follows the basic
concept in (Bashir et al., 2009) so that
(
,
)
=
(,) in equation (1) and
(
,
)
=1−
(
,
)
.
2.1.3 Gait Gaussian Image (GGI)
GGI is similar to GEI however it uses a Gaussian
function instead of the average function. It reduces
the noise effect from an individual frame in the
interested gait cycle. The Gaussian function is
defined as follows:
(
)
=
(
)
(3)
where
is Gaussian membership,
is the
corresponding pixel value of
frame, is the mean
of respective pixel in all frames and is the variance
of the pixel vector.
Then the output pixel
is calculated from the
average of the multiplied result between
corresponding pixel and Gaussian membership, as
shown in equation (4).
=
1
(4)
where is the pixel position, is the frame number,
is the pixel value of
frame and is the number
of frames.
2.1.4 Gait Gaussian Entropy Image
(GGEnI)
The aim of this newly proposed gait representation is
for improving robustness against appearance changes
in GGI, thus the GEnI concept is applied with GGI in
this representation. GGEnI is calculated by equation
(2), with the probability function changes to Gaussian
membership function.
GGEnI is defined as:
=
(
,
)
(
,
)
(
,
)
=
(
(,)(,))
(
,
)
=
1
(
,
)
(,)
(
,
)
=1−
(
,
)
(5)
where , is pixel coordinate, and
(,) is the
probability,
(,) is Gaussian membership of
frame,
(,) is pixel value of
frame, (,)
is the mean of all frames at (,) coordinate, is the
variance of pixel vector and
(,) is the
probability.
2.2 Principal Component Analysis
(PCA)
PCA or Karhunen-Loeve (KL) transformation is a
basic statistical technique which has been widely used
to reduce data dimensions in pattern recognition and
computer vision. The 2D gait representation is
reduced into a 1D feature vector through an optimal
feature map which is calculated from eigenvectors of
input data. The fundamental of PCA is defined in
(Jackson, 2003, Jolliffe, 2002). This paper
implements PCA with “cov()” and “eig()” in the
MATLAB toolbox.
2.3 Support Vector Machines (SVMs)
SVM is a popular classification method which is
basically used as a binary classification. However, it
can be extended for multi-class classification by two
approaches: one-against-one and one-against-all.
This study implements one-against-all SVM by
libSVM package (Chang and Lin, 2011). Two
important functions are “svmtrain()”, and
“svmpredict()”. The first function receives the
training label vector, training data matrix, and a
training string as input arguments and returns a model
of each subject as the output. Another function
receives the probe vector, probe data, model of each
subject, and predicts a probability string as the input
arguments and returns a probability as the output.
3 EXPERIMENTS
There currently are many gait databases available for
research, for example CASIA (Yu et al., 2006),
SOTUN (Shutler et al., 2002), and CMU (Ralph,
2001). In the experiments, CASIA gait dataset B was
chosen because it includes gait data in three kinds of
appearance (normal walking, clothing, and bag
carrying) and eleven camera view angles. It provides
video sequence, human silhouette and GEIs.
Three main experiments were conducted. The first
is view angle detection test.. The second tests the
effect of appearance change in case of full body and
lower knee gait representation. The third investigates
ICPRAM 2016 - International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods
680
the effect of different number of training dataset in
recognition phase.
All experiments set up by the same process that
has been shown in Figure 1, nonetheless, training
gallery and testing probe are always different. All
silhouette images which were used in experiments
were cropped, centralized and resized. Image size is
120x120 pixels for full body and 120x36 pixels for
lower knee. All experiments used 40 principal
components and the polynomial kernel function was
applied for SVMs.
3.1 Experiment 1
The first experiment is about view angle detection to
understand the view angle of unknown walking
direction
. Fifty five normal walk gait representation
images, five from each view angle, have been used on
training. Then all data with unknown view angles,
different subjects and different conditions (normal
walking, clothing, and bag carrying) were classified
by SVM predicting. Results are shown that all four
gait representations produce 100% correct rate in
view angle detection. And the result of low knee is as
good as the full body in view angle detection and
provides 100% accuracy.
3.2 Experiment 2
The second experiment tested the correct
classification rate (CCR) with different training and
testing datasets. All sub experiments used one dataset
for training except of the mixed dataset training
which has included all three datasets from three kinds
of appearance i.e. normal walk, wearing coat and
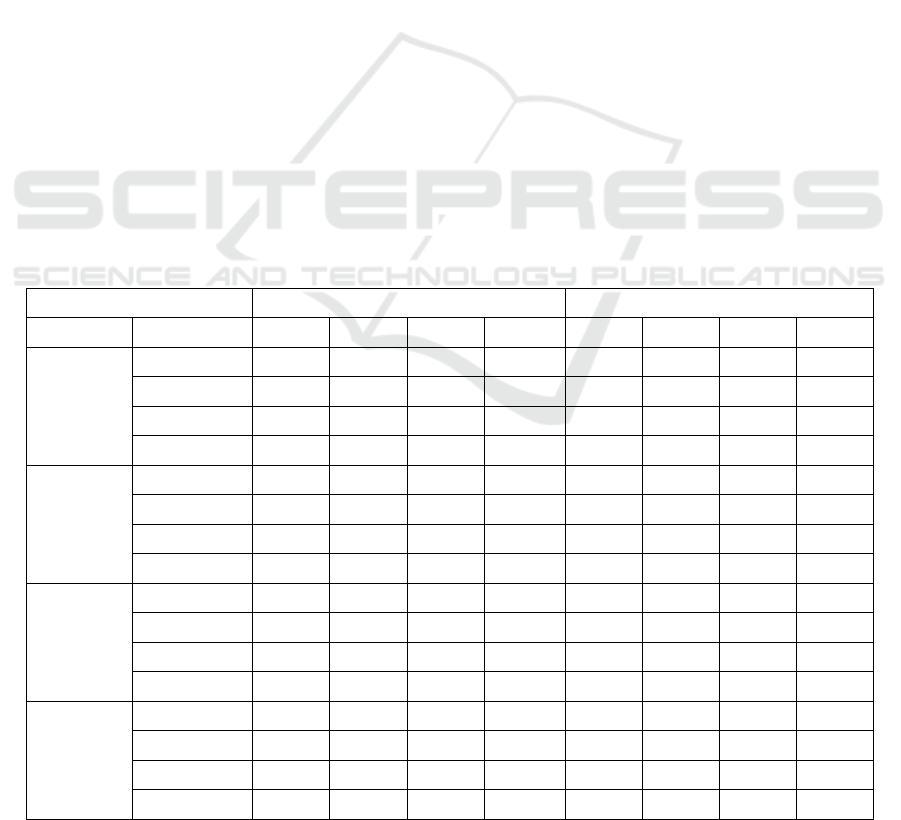
carrying bag.. Results have been shown in Table 1.
When all types of appearance datasets have been used
in the training phase, the CCR of full body is clearly
higher than that of lower knee region. Although full
body has higher CCR when gallery and probe are with
the same appearance, the CCR of full body gait
recognition is significantly affected by appearance
change. Especially in the case of individual wearing
coat, lower knee classification has shown the higher
CCR than that of full body. With regards to the
average CCR in Table 1, lower knee and full body
give very similar accuracy in the three cases.
In the case of mixed appearance training, the
average technique is more robust than the Gaussian
technique. GEI and GEnI have higher average CCR
than GGI and GGEnI. At the same time, the entropy
technique can enhance performance of the average
and Gaussian techniques. GEnI has higher CCR than
GEI, in the same way, GGEnI has higher CCR
than GGI.
Table 1: Average CCR summary.
Case study full body lower knee
Gallery Probe GEI GGI GEnI GGEnI GEI GGI GEnI GGEnI
Normal
Normal 96.27% 94.61% 94.61% 93.59% 84.47% 71.57% 82.19% 72.54%
Bag 51.27% 35.34% 57.49% 40.69% 41.36% 29.72% 48.64% 32.35%
Coat 35.55% 17.96% 41.36% 18.79% 58.76% 43.15% 59.87% 42.73%
Average 61.03% 49.31% 64.49% 51.02% 61.53% 48.15% 63.57% 49.21%
Bag
Normal 52.88% 35.02% 57.68% 34.28% 47.05% 30.58% 53.31% 33.37%
Bag 89.98% 85.49% 90.85% 83.95% 80.61% 69.50% 80.56% 71.94%
Coat 32.37% 12.40% 40.17% 14.89% 50.36% 26.57% 56.08% 29.56%
Average 58.41% 44.30% 62.90% 44.37% 59.34% 42.22% 63.32% 44.96%
Coat
Normal 38.07% 17.71% 37.92% 17.98% 61.63% 39.20% 61.16% 40.78%
Bag 26.25% 11.66% 31.91% 14.66% 39.91% 24.09% 43.53% 26.54%
Coat 96.97% 94.33% 96.35% 93.39% 87.43% 73.04% 86.29% 75.28%
Average 53.77% 41.23% 55.39% 42.01% 62.99% 45.44% 63.66% 47.53%
Mix
Normal 94.29% 81.82% 93.87% 83.09% 87.04% 67.93% 86.68% 71.25%
Bag 89.53% 77.95% 90.06% 78.82% 81.19% 68.42% 81.90% 68.35%
Coat 94.34% 80.97% 94.83% 81.05% 88.39% 70.56% 88.87% 73.45%
Average 92.72% 80.25% 92.92% 80.99% 85.54% 68.97% 85.82% 71.02%
Investigation of Gait Representations in Lower Knee Gait Recognition
681

3.3 Experiment 3
The third experiment focused on investigation of
effects of different number of training datasets on the
gait recognition. Normal walk has been chosen for
this experiment because there are six normal walk
datasets while there are only two wearing coat and
carrying bag datasets. Firstly a normal walk dataset
has been selected as a probe in the recognition phase
and other five datasets have been increasingly used as
the gallery in the training phase. Results are shown in
Table 2.
Table 2: The effect of number of dataset in training phase.
number of
datasets
1 2 3 4 5
Full Body
GEI
96.3% 96.6% 97.2% 97.5% 98.5%
GGI
94.6% 97.9% 98.6% 98.7% 98.9%
GEnI
94.6% 96.0% 97.3% 97.5% 98.3%
GGEnI
93.6% 97.2% 98.3% 98.7% 98.8%
Lower Knee
GEI
84.5% 90.8% 92.6% 93.8% 94.9%
GGI
71.6% 82.8% 88.9% 91.5% 92.0%
GEnI
82.2% 89.5% 93.0% 94.4% 94.8%
GGEnI
72.5% 82.5% 89.0% 92.1% 93.6%
In the full body case, the Gaussian technique (GGI
and GGEnI) has higher CCR when the number of
training dataset has been greater or equal to two. In
the case of lower knee, CCR is greatly increasing
when the number of train dataset increases, especially
in case of the Gaussian technique. In this experiment,
the average technique shows a better result than the
Gaussian technique. Nonetheless, in the general trend
the Gaussian technique is better than the average
technique.
4 CONCLUSIONS
This paper presents the combination gait
representative technique between Gaussian and
Entropy, called Gait Gaussian Entropy Image or
GGEnI. It has been compared with GEI, GEnI and
GGI in full body and lower knee gait classification.
The contribution can be summaries as follows
(1) The investigation proves that lower knee gait
representation is equally good as relevant full
body gait representation in camera view angle
detection based on the CASIA gait dataset B. It
dramatically reduce the computational cost by
using lower knee for this purpose.
(2) The lower knee gait representation have a similar
classification rate compared to full body when
using a single appearance in training and mixed
appearance in testing.
(3) The average technique shows a robust way in
dealing with appearance change in gait
recognition, whilst the Gaussian technique gives
better CCR when appearance keeps similar in
both gallery and probe samples. The Entropy
technique has slightly increased the appearance
change robustness, GGEnI has higher CCR than
GGI. This proves the hypothesis that the Gaussian
technique takes the advantage of statistics to
represent gait information.
(4) The Gaussian technique has higher classification
rate in case of a fixed appearance when the
number of datasets used in training is sufficient.
Lower knee classification rate has greatly
increased when the number of training datasets
increases. All lower knee gait representations give
a relatively high CCR over 90% when the number
of the training datasets is greater than four.
REFERENCES
Arora, P. & Srivastava, S. Gait Recognition Using Gait
Gaussian Image. Signal Processing And Integrated
Networks (Spin), 2015 2nd International Conference
On, 19-20 Feb. 2015 2015. 791-794.
Bashir, K., Tao, X. & Shaogang, G. Gait Recognition Using
Gait Entropy Image. Crime Detection And Prevention
(Icdp 2009), 3rd International Conference On, 3-3 Dec.
2009 2009. 1-6.
Bashir, K., Xiang, T. & Gong, S. 2010. Gait Recognition
Without Subject Cooperation. Pattern Recognition
Letters, 31, 2052-2060.
Chang, C.-C. & Lin, C.-J. 2011. Libsvm: A Library For
Support Vector Machines. Acm Trans. Intell. Syst.
Technol., 2, 1-27.
Chattopadhyay, P., Sural, S. & Mukherjee, J. 2014. Frontal
Gait Recognition From Incomplete Sequences Using
Rgb-D Camera. Information Forensics And Security,
Ieee Transactions On, 9, 1843-1856.
Haifeng, H. 2014. Multiview Gait Recognition Based On
Patch Distribution Features And Uncorrelated
Multilinear Sparse Local Discriminant Canonical
Correlation Analysis. Circuits And Systems For Video
Technology, Ieee Transactions On, 24, 617-630.
Han, J. & Bhanu, B. 2006. Individual Recognition Using
Gait Energy Image. Pattern Analysis And Machine
Intelligence, Ieee Transactions On, 28, 316-322.
Hu, N. H.-L., Tong; Wooi-Haw, Tan ; Timothy Tzen-Vun,
Yap; Pei-Fen, Chong; Junaidi, Abdullah 2011. Human
Identification Based On Extracted Gait Features.
International Journal On New Computer Architectures
And Their Applications (Ijncaa), 1(2).
ICPRAM 2016 - International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods
682

Iwashita, Y., Ogawara, K. & Kurazume, R. 2014.
Identification Of People Walking Along Curved
Trajectories. Pattern Recognition Letters, 48, 60-69.
Jackson, J. E. 2003. A User's Guide To Principal
Components, Canada, John Wiley & Sons.
Jolliffe, I. T. 2002. Principal Component Analysis, 2nd
Edition, New York, Springer-Verlag New York, Inc.
Mansur, A., Makihara, Y., Aqmar, R. & Yagi, Y. Gait
Recognition Under Speed Transition. Computer Vision
And Pattern Recognition (Cvpr), 2014 Ieee Conference
On, 23-28 June 2014 2014. 2521-2528.
Nandy, A., Pathak, A., Chakraborty, P. & Nandi, G. C. Gait
Identification Using Component Based Gait Energy
Image Analysis. Signal Propagation And Computer
Technology (Icspct), 2014 International Conference
On, 12-13 July 2014 2014. 380-385.
Ralph, G. J., Shi 2001. The Cmu Motion Of Body (Mobo)
Database Technical Report. Robotic Institute, Carnegie
Mellon University.
Rong, Z., Vogler, C. & Metaxas, D. Human Gait
Recognition. Computer Vision And Pattern
Recognition Workshop, 2004. Cvprw '04. Conference
On, 27-02 June 2004 2004. 18-18.
Shirke, S., Pawar, S. S. & Shah, K. Literature Review:
Model Free Human Gait Recognition. Communication
Systems And Network Technologies (Csnt), 2014
Fourth International Conference On, 7-9 April 2014
2014. 891-895.
Shutler, J., Grant, M., Nixon, M. S. & Carter, J. N. 2002.
On A Large Sequence-Based Human Gait Database.
Fourth International Conference On Recent Advances
In Soft Computing.
Yang, Y., Tu, D. & Li, G. Gait Recognition Using Flow
Histogram Energy Image. Pattern Recognition (Icpr),
2014 22nd International Conference On, 24-28 Aug.
2014 2014. 444-449.
Yu, S., Tan, D. & Tan, T. A Framework For Evaluating The
Effect Of View Angle, Clothing And Carrying
Condition On Gait Recognition. Pattern Recognition,
2006. Icpr 2006. 18th International Conference On, 0-0
0 2006. 441-444.
Zeng, W., Wang, C. & Yang, F. 2014. Silhouette-Based
Gait Recognition Via Deterministic Learning. Pattern
Recognition, 47, 3568-3584.
Zhang, E., Zhao, Y. & Xiong, W. 2010. Active Energy
Image Plus 2dlpp For Gait Recognition. Signal
Processing, 90, 2295-2302.
Zheng, S., Zhang, J. G., Huang, K. Q., He, R. & Tan, T. N.
2011. Robust View Transformation Model For Gait
Recognition. 2011 18th Ieee International Conference
On Image Processing (Icip).
Investigation of Gait Representations in Lower Knee Gait Recognition
683
