
Crowd Behavior in Alternative@
Conflicts in the Decision-making between an Individual and the Group
Noriyuki Hatakenaka
1
, Shigemasa Matsuo
1
, Kiriko Sakata
1
and Munehiro Nishida
2
1
Graduate School of Integrated Arts and Sciences, Hiroshima University, Higashi-Hiroshima, 739-8521, Japan
2
Graduate School of Advanced Sciences of Matter, Hiroshima University, Higashi-Hiroshima, 739-8530, Japan
Keywords:
Group Decision Making, Agent-based Simulations, Social Force Model.
Abstract:
Crowd behavior depends on social interaction among group members. In particular, there has been consid-
erable interest in the decision-making of such a group on their movement during travel. Here we discuss the
decision-making processes in choice selection between two things, i. .e., alternative, by means of numerical
simulations based on social force model developed by Helbing et al. This allows us to introduce an individ-
ual decision-making process into the decision-making of the whole group through psychological parameter,
the so-called dependence p, equivalent to panic parameter in an emergency evacuation. We demonstrate the
conflict that arises in the decision-making between an individual and the group in alternative. In addition, we
reconfirmed a similar stochastic collective behavior in the decision-making processes observed by Couzin et
al. in traveling animals at the large p regimes even if there are no leaders in the group. On the other hand,
individualistic behavior is pronounced in smaller p regimes. This feature prevents the formation of group,
leading to no collective decision-making anymore. Therefore, the parameter p is a key to consider in the
decision-making of both the individual and the group.
1 INTRODUCTION
Human behaviors in social activities are, in general,
incredibly complicated so that no direct approach has
ever established to understand them. However, recent
advances in information technology enable us to in-
vestigate tremendously huge data behind human be-
haviors, the so-called “big data”. Among these is the
crowd behavior which has become the primary issue
in the study of fundamental attributes and character-
istics of humans in social interaction among group
members. As a matter of fact, collective motion and
self-organized behaviors have become a major objec-
tive in many fields such as theoretical biology (War-
burton and Lazarus, 1991), biological physics (Vic-
sek et al., 1995) and control engineering (Leonard and
Fiorelli, 2001).
In particular, there has been considerable interest
in the decision-making of such a group, for example,
on their movement during travel (Couzin et al., 2005).
Here we discuss the decision-making processes in the
simplest situation such as in making a choice between
two things, i. e., alternative, on the movement by
means of numerical simulations based on social force
model developed by Helbing et al. (Helbing et al.,
2000) from the viewpoint of conflicts in the decision-
making between an individual and the group.
Couzin et al. have succeeded to elucidate the
decision-making of an animal group with effective
leaders. However, an essential element in the idea
behind the decision making is conclusively missing
in their approach for our purpose, .i.e., there are no
individual free will in each agent which plays a role
as follower. In addition, flocking was also assumed
in their study since a cohesive force has been intro-
duced in the beginning. Thereby, it was difficult to
discuss the conflicts in the decision-making between
an individual and the group. However, the social force
model has allowed us to study the decision-making
processes ranging from microscopic ( individual) to
macroscopic ( group) scales as a whole since it is, in
principle, able to introduce an individual free will in
each agent.
2 AGENT-BASED SIMULATIONS
Suppose that a group consisting of N individuals
(agents here) travels in two possible pathways simi-
lar to the situation originally set by Couzin et al. as
258
Hatakenaka, N., Matsuo, S., Sakata, K. and Nishida, M.
Crowd Behavior in Alternative@ - Conflicts in the Decision-making between an Individual and the Group.
DOI: 10.5220/0005819202580261
In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART 2016) - Volume 1, pages 258-261
ISBN: 978-989-758-172-4
Copyright
c
2016 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

shown in Fig. 1. In contrast to them, this study is
made different in such a way that there are no in-
formed leaders and that each agent has his preferred
direction. By reason of social interaction, the individ-
ual must decide whether he follows or not the pref-
erence of the others from time to time. In turn, this
can affect the group movement which may influence
the movement of individuals as well. Thus, the col-
lective decision primarily depends on the individual
dependence to others as better understood in psychol-
ogy. In our numerical simulation, the panic parameter
introduced by Helbing et al. in their study of escape
panic plays a role as the i-th individual dependence p
i
defined through the desired direction e
e
e
0
i
(t) in the next
section.
2.1 Social Force Model
There are several approaches to simulate social be-
haviors of animals including human such as an
agent-based simulation (Reynolds, 1987) and particle
swarm optimization (Kennedy and Eberhart, 1995).
Here we employ a social force model (Helbing et al.,
2000) based on an agent-based simulation to intro-
duce individual will or preference into each agent as
shown in the equations below. Social behavior of the
i-th individual agent is modeled by a particle with
mass m
i
and velocity v
v
v
i
influenced by both psycho-
logical and social forces, and is then governed by the
equation of motion with appropriate forces given as
m
i
dv
v
v
i
dt
= f
f
f
will
i
+
∑
j
f
f
f
ij
. (1)
The first term of the right hand side (rhs) in Eq.(1)
stands for the force of agent’s “will” expressed as
f
f
f
will
i
= m
i
v
0
i
(t)e
e
e
0
i
(t) − v
v
v
i
(t)
τ
i
. (2)
Each agent, say i, likes to move with a certain desired
speed v
0
i
in a certain direction e
e
e
0
i
expressed as
e
e
e
0
i
(t) = Norm[(1− p
i
)e
e
e
i
+ p
i
he
e
e
0
j
(t)i
i
] (3)
where Norm(z
z
z) = z
z
z/|z
z
z| denotes normalization of a
vector z
z
z. The unit vector e
e
e
i
stands for the preferred
direction of i-th agent and he
e
e
0
j
(t)i
i
for the average di-
rection of his neighbours j in a certain radius. The
parameter p
i
is the i-th individual dependence which
plays a role as the individual decision-making. It is
noteworthythat this parameter also determines the be-
haviors of either the individual or the group such that
the individual behavior appears if p
i
is low otherwise
the herding behavioris exhibited if p
i
is high as shown
in Fig. 1. The time τ
i
is a characteristic time required
in changing the motion which will be described later.
On the other hand, the second term of the rhs in
Eq. (1) describes the psychological force between two
agents, i and j. These two agents are separated from
each other brought by a repulsive force that is often
employed by a typical example expressed as,
f
f
f
ij
= A
i
e
(r
ij
−d
ij
)/B
j
n
n
n
ij
(4)
where A
i
and B
i
denote the interaction strength and
the range of the repulsive interaction, respectively. r
ij
is the sum of the their radii r
i
and r
j
, i.e. r
ij
= r
i
+ r
j
.
d
ij
is the distance between agent i and agent j, and
n
n
n
ij
= (r
r
r
i
− r
r
r
j
)/d
ij
with r
r
r
i( j)
being a position vector
for agent i( j) denotes a normalized vector pointing
from agent i to agentj.
2.2 Equation of Motion for a Group
Now let us consider the collective behaviors of agents
in alternative. This is done using the concept for the
motion of the center of mass in a system of particles.
Summing all over the equations of motion of an indi-
vidual agent in Eq. (1) results to:
∑
i
m
i
dv
v
v
i
dt
=
∑
i
f
f
f
will
i
+
∑
ij
f
f
f
ij
. (5)
By using the definition of center of mass Mr
r
r
G
=
∑
i
m
i
r
r
r
i
with M =
∑
m
i
and v
v
v
G
≡ dr
r
r
G
/dt, as well as
the relation in the law of action-reaction
∑
ij
f
f
f
ij
= 0,
which yields,
M
dv
v
v
G
dt
+ M
1
τ
v
v
v
G
(t) =
1
τ
∑
i
m
i
v
0
i
(t)e
e
e
0
i
(t) (6)
under the assumption that the characteristic time τ
i
and the dependence p
i
are equal in all agents (τ = τ
i
and p = p
i
for i = 1,2,··· ,N). The second term of
the left hand side (lhs) in Eq. (6) is nothing but the
friction term as represented by the friction coefficient
1/τ. While the terms in the rhs of Eq. (6) characterize
the driving forces due to individual agents with free
will. Expanding further the rhs of Eq. (6) gives,
∑
i
m
i
v
0
i
(t)e
e
e
0
i
(t)
=
∑
i
m
i
v
0
i
(t)[(1− p)e
e
e
i
+ phe
e
e
0
j
(t)i
i
]
= (1− p)
∑
i
m
i
(v
0
i
(t)e
e
e
i
) + p
∑
i
m
i
v
0
i
(t)he
e
e
0
j
(t)i
i
= (1− p)M(v
0
G
(t)e
e
e
G
) + pMv
0
G
(t)he
e
e
0
j
(t)i, (7)
where we use again the definition of center of mass
and large view radius approximation, i.e. he
e
e
0
j
(t)i =
he
e
e
0
j
(t)i
i
,(i = 1, · · · N). Note that there are no individ-
ual indices anymore in this expression. Incorporating
Crowd Behavior in Alternative@ - Conflicts in the Decision-making between an Individual and the Group
259

Eq. (7) into Eq. (6), we now have
M
dv
v
v
G
dt
+ M
1
τ
v
v
v
G
(t)
=
1
τ
(1− p)M(v
0
G
(t)e
e
e
G
) + pMv
0
G
(t)he
e
e
0
j
(t)i
. (8)
This expression is the first remarkable result of this
paper. It describes the social behavior of a group
regarded as a single virtual agent with its own will
v
0
G
(t). The element v
0
G
(t)e
e
e
G
in the first term of the rhs
of Eq. (8) denotes the free will of the virtual represen-
tative agent that determines the action in consultation
with inherent members through the element he
e
e
0
j
(t)i in
the second term. Finally, it is regarded that this ex-
pression is formally true for whole ranges of p values
and is highly effective when p values are large enough
to form a group as mentioned above.
3 SIMULATION
Suppose that initially the agents (N = 100) are dis-
tributed randomly near the coordinate origin without
touching each other. Their initial velocities are also
random at an approximate rate of 1 m/s. The mass of
each agent is 80 kg. The diameter r is 0.75m while
the desired speed v
0
is 1 m/s. The acceleration time τ
is 2.0 s. The parameters A and B are A = 2000N and
B = 0.08m, respectively. The numerical calculations
were carried out by Leap-Frog method (Birdsall and
Langdon, 2004) with second-order accuracy in coor-
dinates.
3.1 Group Formation: The Role of p
First of all let us consider the dependence p effect on
social behaviors of agents. Figure 1 shows the tra-
jectories for each agent with various p values at fixed
agent number (60 agents among N = 100 agents) to-
ward the destination A. At lower p values, an agent
behavesindependentlywith other agents which shows
a trajectory of smooth curve (see Fig.1 (a):p = 0.2).
On the other hand, the intermediate p values exhibit a
trajectory of wavy curves(see Fig. 1(b):p= 0.5) since
the agent is no longer independent of the other agents,
and mutual interactions have caused unexpected be-
haviors. At higher p values, a number of agents coop-
eratively form a group, moving toward the destination
A (see Fig. 1 (c): p = 0.8). Therefore, it is necessary
to use higher values of psychological dependence p in
numerical calculation based on social force model, in
order to investigate the decision making of the group.
−100 0 100
0
50
100
−100 0 100
0
50
100
x
x
Y
Y
A
A
B
B
−100 0 100
0
50
100
x
Y
A B
(a)
−100 0 100
0
50
100
x
Y
A
A
B
(b)
(c)
(d)
Figure 1: Trajectories for each agent from the origin to each
destinations A or B. 60 agents intend to move the destina-
tion A. (a) p = 0.2, (b) p = 0.5, (c) p = 0.8 and (d) a su-
perposition of all for easier comparison. X and Y denote
coordinates.
3.2 Collective Decision Making in
Alternative
Now let us discuss collective decision making in al-
ternative. Figure 2 shows the number of agents who
finally reached at the destination A (N
A
(t
final
)) as a
function of the number of agent initially intended to
move toward the destination B (N
B0
(t
initial
)). The de-
pendence p is set to 0.9 to form a group. At N
B0
= 0,
all the agents naturally move to their common desti-
nation A. Upon increasing N
B0
in the group, one can
observe that the total number of agents N
A
remains
unchanged even if the N
B0
increases until N
B0
≃ 40.
Strictly speaking, the number of agents corresponding
to the difference N
A
− N
B0
follows the group behav-
ior or group decision than their personal will. There-
fore, this clearly shows an evidence of conflicts in the
decision-making between an individual and the group
which now highlights the second remarkable result
of this paper. This is nothing but a majority rule in
decision-making of human society. Over N
B0
> 40,
N
A
rapidly decreases with an increasing N
B0
. This
means the group is split or a member leaves the group.
Finally, we present an interesting result of our
agent-based simulation in decision making. Figure 3
shows again the trajectories of each agent at p = 0.9
when agents move as if a single object as mentioned
previously. An important thing to say here is that
group member is a fifty-fifty chance in following their
ICAART 2016 - 8th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
260
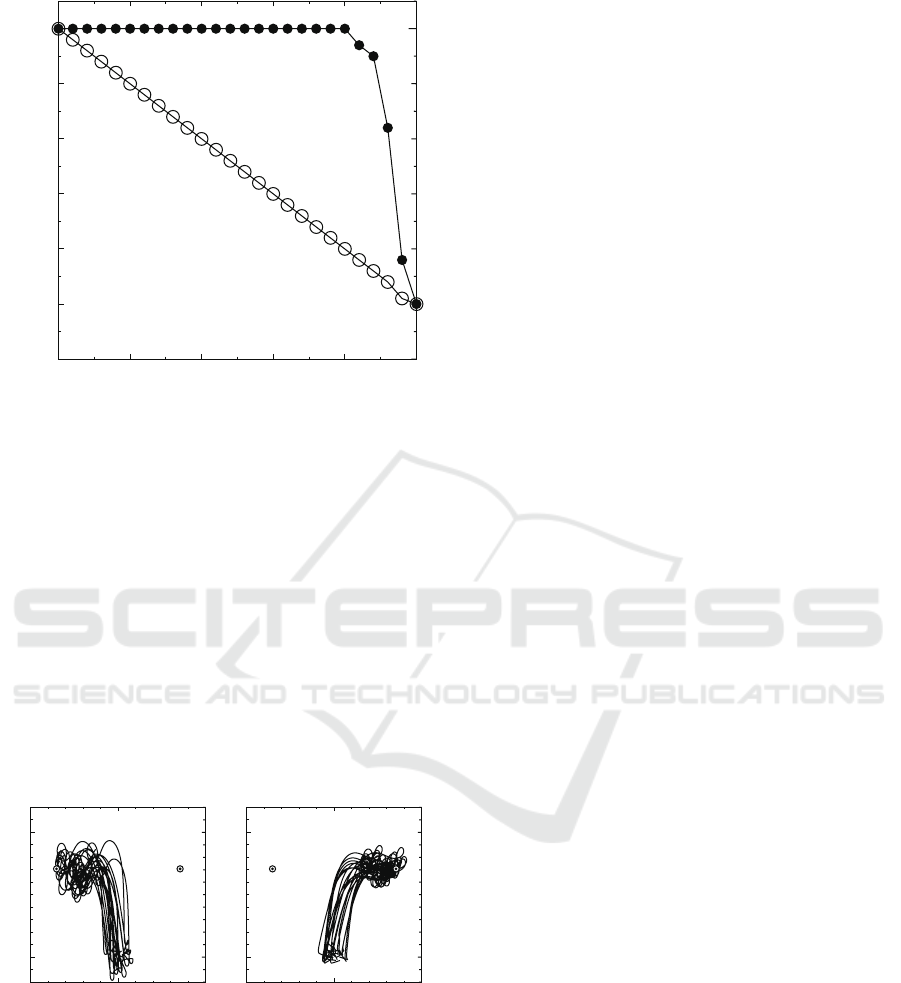
0 10 20 30 40 50
40
60
80
100
N
A
(t
final
)
N
B0
(t
initial
)
Figure 2: The total number of agents reached at the destina-
tion A versus the number of agents intended to go to the des-
tination B. The solid circle represents the number of agents
that have reached the destination A regardless of their own
intended orientation direction. On the other hand, the circle
stand for the number of agents reached at the destination A
originally intended to go.
intended destinations. These two distinct results oc-
casionally occur in our simulations. They resemble
the stochastic phenomenathat occur at unstable points
like a saddle point in the double-minimum potential
of classical mechanics. These results reveal an analo-
gous study made by Couzin et al. such that the group
changes from moving in the average preferred direc-
tion of all agents to selecting randomly one of the two
preferred directions.
−100 0 100
0
50
100
−100 0 100
0
50
100
A AB
B
YY
x x
Figure 3: Trajectories for each agent from the origin to each
destinations A or B. A half of all the agents (50 agents) in-
tend to move the destination A at p = 0.9. X and Y denote
coordinates. The group changes from moving in the aver-
age preferred direction of all agents to selecting randomly
one of the two preferred directions on the way to final des-
tination.
4 CONCLUSIONS
We have numerically investigated the crowd behav-
iors consisting of N agents with free will under the
social forces in the case of choice selection between
two things. We pointed out that social force model
can naturally incorporate the individual free will of an
agent into the decision making of the group to which
he is part of. We have also derived an equation of
motion for a group regarded as a single virtual agent
which provides a strong tool for investigating collec-
tive dynamics of a system of agents. In addition, we
have affirmed the study made by Couzin et al. that
similar stochastic collective behaviour in decision-
making of the group appears in the large p regimes by
using social force model. On the other hand, individu-
alistic behaviour is pronounced in smaller p
i
regimes.
This means that the formation of group is inhibited
leading to no more collective decision-making any-
more. Therefore, the dependence p
i
is the key deter-
minant to consider in the decision-making of both the
individual and the entire group.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was supported in part by KAKENHI (Grant
No. 25560164) from MEXT of Japan and special re-
search projects on Integrated Arts and Sciences of Hi-
roshima University.
REFERENCES
Birdsall, C. K. and Langdon, A. B. (2004). Plasma Physics
via Computer Simulations. CRC Press, London,
ebook edition.
Couzin, I. D., Krause, J., Franks, N. R., and Levin, S. A.
(2005). Effective leadership and decision-making in
animal groups on the move. Nature, 433:513.
Helbing, D., Farkas, I., and Vicsek, T. (2000). Simulating
dynamical features of escape panic. Nature, 407:487.
Kennedy, J. and Eberhart, R. (1995). Particle swam opti-
mization. page 1942.
Leonard, N. E. and Fiorelli, E. (2001). Virtual leaders, ar-
tificial potentials and coordinated control of groups.
page 2968.
Reynolds, C. W. (1987). Flocks, herds and schools: A dis-
tributed behavioral model. page 25.
Vicsek, T., Czir´ok, A., Ben-Jacob, E., Cohen, I., and
Shochet, O. (1995). Novel type of phase transition
in a system of self-driven particles. Phys. Rev. Lett.,
75:1226.
Warburton, K. and Lazarus, J. (1991). Tendency-distance
models of social cohesion in animal groups. J. Theor.
Biol., 150:473.
Crowd Behavior in Alternative@ - Conflicts in the Decision-making between an Individual and the Group
261
