
On using Longer RNA-seq Reads to Improve Transcript Prediction
Accuracy
Anna Kuosmanen
1
, Ahmed Sobih
1
, Romeo Rizzi
2
, Veli M
¨
akinen
1
and Alexandru I. Tomescu
1
1
Helsinki Institute for Information Technology HIIT, Department of Computer Science,
University of Helsinki, Helsinki, Finland
2
Department of Computer Science, University of Verona, Verona, Italy
Keywords:
RNA-seq, Long Reads, Transcript Prediction, Network Flow, Splicing Graph, Minimum Path Cover.
Abstract:
Over the past decade, sequencing read length has increased from tens to hundreds and then to thousands of
bases. Current cDNA synthesis methods prevent RNA-seq reads from being long enough to entirely capture all
the RNA transcripts, but long reads can still provide connectivity information on chains of multiple exons that
are included in transcripts. We demonstrate that exploiting full connectivity information leads to significantly
higher prediction accuracy, as measured by the F-score. For this purpose we implemented the solution to
the Minimum Path Cover with Subpath Constraints problem introduced in (Rizzi et al., 2014), which is an
extension of the classical Minimum Path Cover problem and was shown solvable by min-cost flows. We
show that, under hypothetical conditions of perfect sequencing, our approach is able to use long reads more
effectively than two state-of-the-art tools, StringTie and FlipFlop. Even in this setting the problem is not
trivial, and errors in the underlying flow graph introduced by sequencing and alignment errors complicate the
problem further. As such our work also demonstrates the need for a development of a good spliced read aligner
for long reads. Our proof-of-concept implementation is available at http://www.cs.helsinki.fi/en/gsa/traphlor.
1 INTRODUCTION
With the advent of third-generation PacBio and Ox-
ford nanopore sequencers, the sequencing read length
has increased from a few hundred to many thou-
sand bases. These long reads have caused a break-
through with genome assembly, but they have not yet
been widely adopted in use for transcriptome analy-
sis. However, it is very likely that there will be a shift
from short RNA-seq reads to long RNA-seq reads in
the near future as well.
The optimal case for long read RNA-seq would
naturally be the sequencing of full-length transcripts.
However, while the sequencing technologies might
allow for this, current cDNA synthesis methods un-
fortunately do not. In experiments it has been shown
that full-length reads are less likely to be observed
with transcripts longer than 2.5 kb (Sharon et al.,
2013). But even with non-full-length reads we can
gain valuable information about the connectivity of
non-neighboring exons from long reads.
The idea of using long reads in transcript predic-
tion pre-dates the development of RNA-seq. (Florea
et al., 2005) proposed a method where expressed se-
quence tag (EST) sequences were used to score can-
didate transcripts, which were gained by enumerat-
ing over all the paths in the splicing graph, to mea-
sure their suitability for gene annotation. In the era
of RNA-seq, several papers have similarly formulated
the assembly problem as that of finding the minimum
number of RNA transcripts such that every read is
contained in at least one of them (Rizzi et al., 2014;
Bao et al., 2013). Such a parsimony criterion is
also found in methods dealing with shorts reads alone
(Trapnell et al., 2010; Song and Florea, 2013).
While the polynomial time algorithm given in
(Bao et al., 2013) for this problem was not complete,
(Rizzi et al., 2014) proved that this problem is indeed
polynomially solvable by network flows. In this pa-
per we implemented this network flow approach as a
proof-of-concept software. While it is instinctively
obvious that increasing read length should increase
the transcript prediction accuracy, this topic has not
yet been explored in an experimental setting. Our ex-
periments show that in general this statement about
higher prediction accuracy holds when long reads are
properly modeled, but if the model does not take long
reads into account, the sensitivity of the prediction
272
Kuosmanen, A., Sobih, A., Rizzi, R., Mäkinen, V. and Tomescu, A.
On using Longer RNA-seq Reads to Improve Transcr ipt Prediction Accuracy.
DOI: 10.5220/0005819702720277
In Proceedings of the 9th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies (BIOSTEC 2016) - Volume 3: BIOINFORMATICS, pages 272-277
ISBN: 978-989-758-170-0
Copyright
c
2016 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

(a)
(b)
Figure 1: Fig. 1(a): an example of a splicing graph, in which
three subpath constraints are drawn in red. The square
nodes are the ones where the solutions paths are allowed
to start or to end. Fig. 1(b): the minimum number of paths
covering all nodes and subpath constraints.
can decrease as read length increases.
Even under hypothetical conditions of perfect se-
quencing, the transcript prediction problem is not triv-
ial, and errors introduced to the underlying graph by
sequencing and alignment errors complicate the prob-
lem further. Our work demonstrates that correctly
aligned long reads combined with a model taking into
account the long reads can raise transcript prediction
accuracy to a new level, and highlights the need for
the development of a good spliced long read aligner.
2 METHODS
Our algorithm consists of two main parts: creating a
splicing graph and solving the assembly problem on
top of this graph.
From the read alignments, we construct a splicing
graph (Heber et al., 2002), where nodes are exons, and
arcs are exons consecutive in some read alignment.
Since a splicing graph is constructed from read align-
ments, it is also acyclic. The long read alignments
give some paths of the graph (referred to as subpath
constraints) which need to be covered entirely by a
collection of paths (the assembled transcripts).
Our assembly objective is to have a minimum
number of paths covering all nodes and all subpath
constraints, and among such collections of paths, to
have one that minimizes a certain cost, as we will
explain below. This problem was formulated as the
“Minimum Weight Minimum Path Cover with Sub-
path Constraints (MW-MPC-SC)” problem by (Rizzi
et al., 2014), and proved solvable by minimum-cost
network flows. See Fig. 1 for a simple example. We
implemented a slightly modified version of the solu-
tion from (Rizzi et al., 2014), which we briefly de-
scribe next.
Recall from (Rizzi et al., 2014; M
¨
akinen et al.,
2015) that a minimum collection of paths covering
every node (a minimum path cover) which also min-
imizes the sum of the weights of the arcs used by
its paths can be solved by network flows as follows.
Subdivide every node v into two nodes v
in
and v
out
connected by an arc (v
in
, v
out
), with demand 1. All
in-neighbors of v become in-neighbors of v
in
, and all
out-neighbors of v become out-neighbors of v
out
. Add
a global source s connected to every node from where
a path is allowed to start. Also add a high weight on
these arcs, which will force the solution to have the
minimum number of paths. Likewise, add a global
sink and arcs from every node in which a path is al-
lowed to end. Then compute a minimum-cost flow on
this acyclic flow network, and arbitrarily decompose
it into paths, which will form an optimal solution.
(Rizzi et al., 2014) observed that this reduction
can be modified to solve the MW-MPC-SC problem
as well. The idea is to model every subpath constraint
with first node u and last node w by adding an arc
(u
out
, w
in
) with cost equalling the sum of the costs
of its arcs and demand 1. Also, the demands on its
nodes have to be set back to 0. The main difficulty is
to deal with overlapping subpath constraints, as these
new arcs may increase the optimum number of paths
needed to satisfy all the constraints. See Fig. 2 for
more details. (Rizzi et al., 2014) proved that the op-
timal solutions are preserved if constraints sharing a
longest suffix-prefix overlap are merged iteratively.
Even though this strategy preserved the minimum
number of solution paths, we observed experimen-
tally that this iterative greedy and local merging does
not produce the best results. Therefore, we merge
subpath constraints in a more globally informed man-
ner, similarly to (Ntafos and Hakimi, 1979). We cre-
ate another flow network with the subpath constraints
as nodes. An arc is added between two nodes if the
constraints they represent share a suffix-prefix over-
lap, and the weights on the arcs are set based on the
difference of coverage between their endpoints (see
Fig. 3 for a simple example). A high weight is set,
as above, on each arc exiting from the global source
of the network, to prefer solutions with the minimum
On using Longer RNA-seq Reads to Improve Transcript Prediction Accuracy
273

≥ 0≥ 0≥ 0
≥ 1
(a)
≥ 0≥ 0≥ 0
≥ 1
≥ 1
(b)
≥ 0≥ 0≥ 0
≥ 1 ≥ 1
≥ 0
(c)
Figure 2: Fig. 2(a): each node v in a subpath constraint was subdivided into the arc (v
in
, v
out
) with demand 1. A subpath
constraint (red) is modeled as an arc from the out copy of its first node to the in copy of its last node. The demands of its
nodes are set back to 0, and the demand of the new arc is set to 1. Fig. 2(b): a subpath constraint (green) is fully included
in another subpath constraint (red). Fig. 2(c): a subpath constraint (red) has a suffix-prefix overlap with another subpath
constraint (green). In both of these cases, modelling the subpath constraints as described in Fig. 2(a) increases the minimum
number of solution paths.
(a)
(b)
Figure 3: Fig. 3(a): an example of a splicing graph with four
subpath constraints with suffix-prefix overlaps. Fig. 1(b):
the flow network created from the overlapping constraints
and the minimum number of paths covering all the nodes.
The square nodes are the global source and the global sink
of the flow network.
number of paths. The resulting minimum-cost flow
(solved with the LEMON library (Lemon, 2014)) is
then split into paths. Finally, the constraints repre-
sented by the nodes belonging to a same path are
merged. At the end of this process the resulting con-
straints have no suffix-prefix overlap.
3 RESULTS
We compared our method’s performance against
two state-of-the-art transcript assemblers,
StringTie (Pertea et al., 2015) and FlipFlop (Bernard
et al., 2014). All three of the tools use a network
flow-based approach.
Since StringTie was shown to have superior per-
formance (Pertea et al., 2015) over short read assem-
blers Cufflinks (Trapnell et al., 2010), Isolasso (Li
et al., 2011), Scripture (Guttman et al., 2010) and
Traph (Tomescu et al., 2013), we did not include any
of them in this comparison.
For real data there is no ground truth to com-
pare against, thus we used simulated data. Flux Sim-
ulator (Griebel et al., 2012), which simulates both
the library preparation and sequencing, does not to
our knowledge support simulating long reads, and we
used the RNASeqReadSimulator (Li, 2012), which
only simulates sequencing, instead. For the simula-
tion we used all human transcripts (GRCh37/hg19)
that were at least one kilobase long, as provided by
the UCSC Genome Browser (Karolchik et al., 2014).
First we sampled weights for the transcripts from
log-normal distribution (µ = −4, σ = 1) to simulate
expression levels. With these parameters, the simu-
lated expression levels of the transcripts vary by three
orders of magnitude. While this is significantly lower
than the six orders of magnitude that have been ob-
served in expression levels in cells (Holland, 2002), it
is more informative for our purposes, as our experi-
ments showed that with high variance, very high read
coverage is required to find evidence for more than
one transcript per gene locus.
Reads were then sampled from the transcripts
based on the simulated weights, with the starting po-
sitions of the reads on the transcript following uni-
form distribution. To exclude the effect the increas-
ing coverage has on transcript predictions, we opted
to keep the coverage constant by decreasing the num-
ber of simulated reads as read length was increased.
We used a total of eight data sets: 60 million 400 bp
reads, 30 million 800 bp reads, 20 million 1200 bp
reads, 15 million 1600 bp reads, 12 million 2000 bp
reads, 10 million 2400 bp reads, 8.6 million 2800 bp
reads and 7.5 million 3200 bp reads. In the case that
the transcript was shorter than the chosen read length,
the whole transcript was added to the data set.
We considered two cases: the ideal conditions
of perfect read alignments (created by converting
the simulated reads into alignments with BED-
Tools (Quinlan and Hall, 2010)) and reads aligned
with an alignment software (in this case, GMAP (Wu
BIOINFORMATICS 2016 - 7th International Conference on Bioinformatics Models, Methods and Algorithms
274

and Watanabe, 2005)). For the latter case, we did not
introduce any sequencing errors into the simulation of
the reads.
For the experiments we used Dell PowerEdge
M610 with 32 GB of RAM and 2 Intel Xeon E5540
2.53GHz CPU:s. Default parameters were used for all
the assemblers. When processing the GMAP align-
ments, FlipFlop attempted to allocate over 50 GB of
RAM and as such failed to run on the machines avail-
able to us.
For validation, we followed the example of (Li
et al., 2011). All predicted transcripts are matched
against all annotated transcripts used in creating the
data sets, and two transcripts consisting of more than
one exon are considered to match if (1) they include
the same set of exons and (2) all internal boundary
candidates are identical (beginning of first exon and
end of last exon do not need to match). Single exon
transcripts are considered to match if the overlapping
area occupies at least 50% of the length of each tran-
script. Contrary to Li’s et al. approach where multiple
predicted transcripts could match a single annotated
transcript, we chose a criteria that only one predicted
transcript can match a single annotated transcript.
We define sensitivity as the number of matched
transcripts divided by the number of annotated tran-
scripts and precision as the number of matched tran-
scripts divided by the number of predicted transcripts.
F-score, the standard measure of performance, is the
harmonic mean of sensitivity and precision.
In the development of our method we favored high
sensitivity over high precision, and as can be seen in
Figure 4(a) and Figure 5(a), our method has signifi-
cantly higher sensitivity than StringTie and FlipFlop
as read length increases. However, high sensitivity
comes at the cost of lowered precision, especially
when alignment errors are introduced into the data
(as can be seen in Figure 5(b)). With perfect map-
pings, it can be seen in Figure 4(c) that using the stan-
dard measure of performance, f-score, our method
performs more accurately than the competitors when
read length increases above 400 bp.
4 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
WORK
In this article we demonstrated the utility of long
RNA-seq reads in transcript prediction. We imple-
mented the solution to the “Minimum Weight Min-
imum Path Cover with Subpath Constraints” prob-
lem by (Rizzi et al., 2014), which models long reads
as subpath constraints, that is, sequences of exons
that have to be fully contained in one of the solu-
400 800 1,200
1,600
2,000 2,400 2,800 3,200
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
0.9
Read length
Sensitivity
FlipFlop
Our method
StringTie
(a) Sensitivity
400 800 1,200
1,600
2,000 2,400 2,800 3,200
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
0.9
Read length
Precision
FlipFlop
Our method
StringTie
(b) Precision
400 800 1,200
1,600
2,000 2,400 2,800 3,200
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
Read length
F-score
FlipFlop
Our method
StringTie
(c) F-score
Figure 4: Sensitivity, precision and F-score with perfect
alignments.
tion paths. We showed with simulated data that, with
proper models, increasing read length can improve
transcript prediction accuracy significantly (as mea-
sured by the F-score). We also showed that our proof-
of-concept software is able to use long reads more ef-
fectively than the competitors StringTie and FlipFlop,
while also remaining on par with modest read lengths.
It should be noted though that while StringTie and
FlipFlop can use long reads, they were designed for
short reads.
As our problem formulation requires all the sub-
On using Longer RNA-seq Reads to Improve Transcript Prediction Accuracy
275
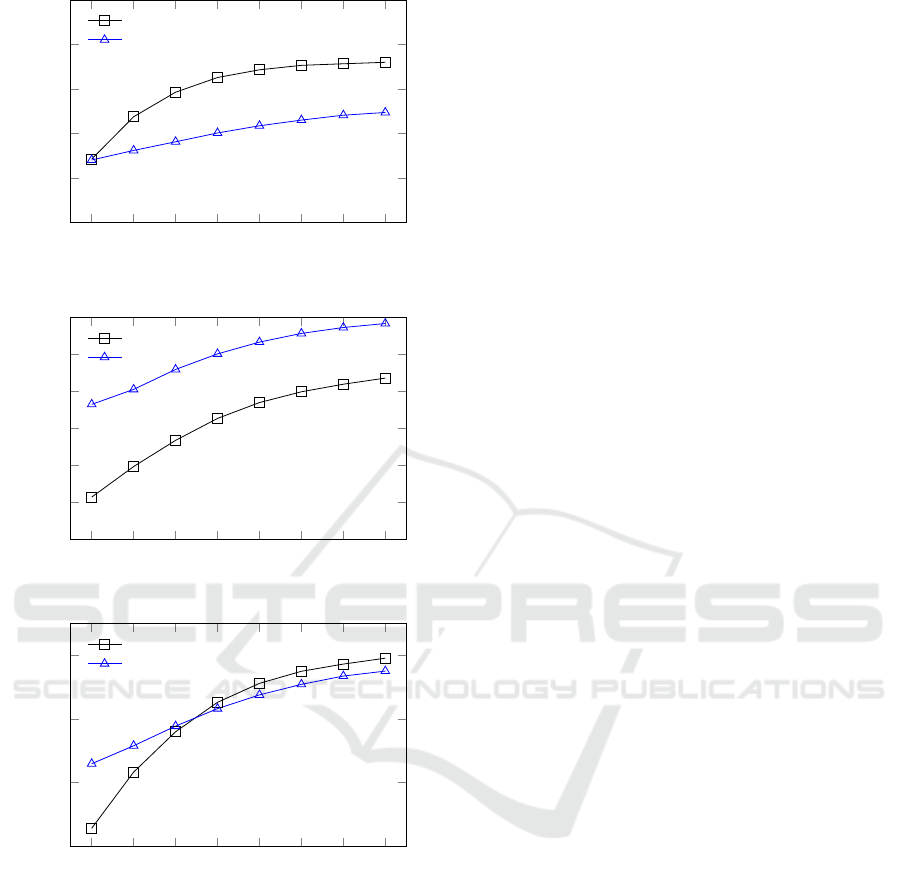
400 800 1,200
1,600
2,000 2,400 2,800 3,200
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
Read length
Sensitivity
Our method
StringTie
(a) Sensitivity
400 800 1,200
1,600
2,000 2,400 2,800 3,200
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
0.9
Read length
Precision
Our method
StringTie
(b) Precision
400 800 1,200
1,600
2,000 2,400 2,800 3,200
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
Read length
F-score
Our method
StringTie
(c) F-score
Figure 5: Sensitivity, precision and F-score using align-
ments from GMAP.
path constraints to be contained in one of the solution
paths, the model is sensitive to high levels of noise,
e.g. alignment errors near splice sites. Our initial ex-
periments showed that even with modest indel rates
(1%) finding the splice sites reliably was too challeng-
ing for any publicly available high-throughput tool we
are aware of. This problem could be tackled with an
exon chaining approach (Gelfand et al., 1996); how-
ever this is solvable only in quadratic time, and scal-
ing it to high-throughput sequencing read alignment
would require massive parallelism. Finding effec-
tive methods for spliced long read alignment has been
the subject of several PhD theses (Kopylova, 2013;
Vyverman, 2014), and our work further demonstrates
the need for finding such a method.
We are, however, confident that long RNA-seq
reads can in the end be utilized even without a per-
fect spliced read aligner: Our method only requires
the connectivity information, that is, a chain of exons
forming each long read. The exons can be predicted
reliably with short RNA-seq reads, and therefore a
hybrid approach appears amenable. This suggests to
study a relaxed version of the spliced alignment prob-
lem, where the correctness of the chain of exons is op-
timized rather than the global alignment score. This
is a subject of another manuscript.
Last, note that currently our approach produces
only transcript sequences, but there exist a multitude
of tools for quantifying transcript abundances (Li and
Dewey, 2011) and differential expression analysis be-
tween samples (Robinson et al., 2010; Anders and
Huber, 2010; Glaus et al., 2012) that can be applied
to our tool’s output. Adding the quantification step to
the tool is also one possible direction for future work.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We would like to thank all the anonymous reviewers
for their constructive feedback.
Funding: This work was partially supported by
the Academy of Finland [284598 to A.K., A.S. and
V.M., 274977 to A.I.T.].
REFERENCES
Anders, S. and Huber, W. (2010). Differential expres-
sion analysis for sequence count data. Genome Biol,
11(10):R106.
Bao, E., Jiang, T., and Girke, T. (2013). BRANCH: boost-
ing RNA-Seq assemblies with partial or related ge-
nomic sequences. Bioinformatics, 29(10):1250–1259.
Bernard, E., Jacob, L., Mairal, J., and Vert, J.-P. (2014). Ef-
ficient RNA isoform identification and quantification
from RNA-Seq data with network flows. Bioinformat-
ics, 30(17):2447–2455.
Florea, L., Di Francesco, V., Miller, J., Turner, R., Yao, A.,
Harris, M., Walenz, B., Mobarry, C., Merkulov, G. V.,
Charlab, R., Dew, I., Deng, Z., Istrail, S., Li, P., and
Sutton, G. (2005). Gene and alternative splicing an-
notation with AIR. Genome Res, 15(1):54–66.
Gelfand, M. S., Mironov, A. A., and Pevzner, P. A. (1996).
Gene recognition via spliced sequence alignment.
Proc. Natl Acad Sci U S A, 93(17):9061–6.
BIOINFORMATICS 2016 - 7th International Conference on Bioinformatics Models, Methods and Algorithms
276

Glaus, P., Honkela, A., and Rattray, M. (2012). Identi-
fying differentially expressed transcripts from RNA-
seq data with biological variation. Bioinformatics,
28(13):1721–1728.
Griebel, T., Zacher, B., Ribeca, P., Raineri, E., Lacroix,
V., Guig
´
o, R., and Sammeth, M. (2012). Modelling
and simulating generic RNA-Seq experiments with
the flux simulator. Nucleic Acids Res, 40(20):10073–
10083.
Guttman, M., Garber, M., Levin, J. Z., Donaghey, J.,
Robinson, J., Adiconis, X., Fan, L., Koziol, M. J.,
Gnirke, A., Nusbaum, C., Rinn, J. L., Lander, E. S.,
and Regev, A. (2010). Ab initio reconstruction of
cell type-specific transcriptomes in mouse reveals the
conserved multi-exonic structure of lincRNAs. Nat
Biotechnol, 28(5):503–510.
Heber, S., Alekseyev, M., Sze, S.-H., Tang, H., and Pevzner,
P. A. (2002). Splicing graphs and EST assembly prob-
lem. Bioinformatics, 18 Suppl 1:S181–S188.
Holland, M. J. (2002). Transcript abundance in yeast
varies over six orders of magnitude. J Biol Chem,
277(17):14363–14366.
Karolchik, D., Barber, G. P., Casper, J., Clawson, H., Cline,
M. S., Diekhans, M., Dreszer, T. R., Fujita, P. A., Gu-
ruvadoo, L., Haeussler, M., Harte, R. A., Heitner, S.,
Hinrichs, A. S., Learned, K., Lee, B. T., Li, C. H.,
Raney, B. J., Rhead, B., Rosenbloom, K. R., Sloan,
C. A., Speir, M. L., Zweig, A. S., Haussler, D., Kuhn,
R. M., and Kent, W. J. (2014). The UCSC Genome
Browser database: 2014 update. Nucleic Acids Res,
42(Database issue):D764–D770.
Kopylova, E. (2013). New algorithmic and bioinformatic
approaches for the analysis of data from high through-
put sequencing. PhD thesis, Universit
´
e des Sciences
et Technologie de Lille-Lille I.
Lemon (2014). Library for Efficient Modeling and
Optimization in Networks. http://lemon.cs.elte.hu/.
Li, B. and Dewey, C. N. (2011). RSEM: accurate transcript
quantification from RNA-Seq data with or without a
reference genome. BMC Bioinformatics, 12:323.
Li, W. (2012). http://alumni.cs.ucr.edu/∼liw/
rnaseqreadsimulator.html.
Li, W., Feng, J., and Jiang, T. (2011). IsoLasso: a LASSO
regression approach to RNA-Seq based transcriptome
assembly. J Comput Biol, 18(11):1693–1707.
M
¨
akinen, V., Belazzougui, D., Cunial, F., and Tomescu,
A. I. (May 2015). Genome-Scale Algorithm Design—
Biological Sequence Analysis in the Era of High-
Throughput Sequencing. Cambridge University Press.
URL www.genome-scale.info.
Ntafos, S. C. and Hakimi, S. L. (1979). On path cover
problems in digraphs and applications to program test-
ing. IEEE Transactions on Software Engineering, SE-
5(5):520–529.
Pertea, M., Pertea, G. M., Antonescu, C. M., Chang, T.-C.,
Mendell, J. T., and Salzberg, S. L. (2015). StringTie
enables improved reconstruction of a transcriptome
from RNA-seq reads. Nat Biotechnol, 33(3):290–295.
Quinlan, A. R. and Hall, I. M. (2010). BEDTools: a flex-
ible suite of utilities for comparing genomic features.
Bioinformatics, 26(6):841–842.
Rizzi, R., Tomescu, A. I., and M
¨
akinen, V. (2014). On
the complexity of Minimum Path Cover with Subpath
Constraints for multi-assembly. BMC Bioinformatics,
15(S-9):S5.
Robinson, M. D., McCarthy, D. J., and Smyth, G. K.
(2010). edgeR: a Bioconductor package for differ-
ential expression analysis of digital gene expression
data. Bioinformatics, 26(1):139–140.
Sharon, D., Tilgner, H., Grubert, F., and Snyder, M. (2013).
A single-molecule long-read survey of the human
transcriptome. Nat Biotechnol, 31(11):1009–1014.
Song, L. and Florea, L. (2013). CLASS: constrained tran-
script assembly of RNA-seq reads. BMC Bioinformat-
ics, 14 Suppl 5:S14.
Tomescu, A. I., Kuosmanen, A., Rizzi, R., and M
¨
akinen, V.
(2013). A novel min-cost flow method for estimating
transcript expression with RNA-Seq. BMC Bioinfor-
matics, 14 Suppl 5:S15.
Trapnell, C., Williams, B. A., Pertea, G., Mortazavi, A.,
Kwan, G., van Baren, M. J., Salzberg, S. L., Wold,
B. J., and Pachter, L. (2010). Transcript assembly and
quantification by RNA-Seq reveals unannotated tran-
scripts and isoform switching during cell differentia-
tion. Nat Biotechnol, 28(5):511–515.
Vyverman, M. (2014). ALFALFA: Fast and Accurate Map-
ping of Long Next Generation Sequencing Reads. PhD
thesis, Ghent University.
Wu, T. D. and Watanabe, C. K. (2005). GMAP: a genomic
mapping and alignment program for mRNA and EST
sequences. Bioinformatics, 21(9):1859–1875.
On using Longer RNA-seq Reads to Improve Transcript Prediction Accuracy
277
