
Exploiting Ambiguities in the Analysis of Cumulative Matching Curves
for Person Re-identification
Vito Ren
`
o
1
, Angelo Cardellicchio
2
, Tiziano Politi
2
, Cataldo Guaragnella
2
and Tiziana D’Orazio
1
1
Institute of Intelligent Systems for Automation, Italian National Research Council, via Amendola 122 D/O,
70126 Bari, Italy
2
Dipartimento di Ingegneria Elettrica e dell’Informazione, Politecnico di Bari, via Orabona 4, 70126 Bari, Italy
Keywords:
Person Re-Identification, Computer Vision, Video Surveillance.
Abstract:
In this paper, a method to find, exploit and classify ambiguities in the results of a person re-identification
(PRID) algorithm is presented. We start from the assumption that ambiguity is implicit in the classical for-
mulation of the re-identification problem, as a specific individual may resemble one or more subjects by the
color of dresses or the shape of the body. Therefore, we propose the introduction of the AMbiguity rAte in RE-
identification (AMARE) approach, which relates the results of a classical PRID pipeline on a specific dataset
with their effectiveness in re-identification terms, exploiting the ambiguity rate (AR). As a consequence, the
cumulative matching curves (CMC) used to show the results of a PRID algorithm will be filtered according to
the AR. The proposed method gives a different interpretation of the output of PRID algorithms, because the
CMC curves are processed, split and studied separately. Real experiments demonstrate that the separation of
the results is really helpful in order to better understand the capabilities of a PRID algorithm.
1 INTRODUCTION
One of the most interesting topics regarding the im-
provement of video surveillance systems is person re-
identification (PRID), i.e. the re-identification of the
same individual given two (or more) different views
acquired by a set of non-overlapping cameras cover-
ing the same environment.
This task has become a crucial topic in the last few
years, when the increased need for security originated
from events like the September 11th has led to the
deployment of a great number of video surveillance
cameras over crowded areas like airports or train sta-
tions. As these cameras produce a large, and often
hardly manageable, amount of raw video data, a way
to properly analyze and classify them without the in-
tervention of an human operator is needed.
The PRID task is complicated by a certain num-
ber of related problems, which can be divided in two
categories (Saghafi et al., 2014):
• Intra-camera Issues: these issues are essentially
related to the internal configuration of each cam-
era, and may reguard the low resolution of the sen-
sor, occlusion phenomena or different acquisition
conditions;
• Inter-camera Issues: these issues are essentially
related to the configuration of the camera set, in
which each camera is subject to different lighting
conditions and may have different hardware fea-
tures.
The PRID methods proposed in literature try to
deal with these issues, extracting relevant information
from each view to properly characterize each individ-
ual. In order to do this, PRID methods use two kinds
of feature:
• Appearance: these features are related to the ap-
pearance of the individual, and include texture,
color and shape (Farenzena et al., 2010) (Gheis-
sari et al., 2006) (Roy et al., 2012) (D’Orazio and
Guaragnella, 2012);
• Non-appearance: these include features not re-
lated to the appearance of the individual, likegait
(Bauml and Stiefelhagen, 2011).
Various datasets have been acquired in order to
test the effectiveness of PRID methods (Bedagkar-
Gala and Shah, 2014), each one differing from the
others for the acquisition settings. Intuitively, not all
datasets are well suited to test every PRID algorithm,
as one dataset may present specific issues and advan-
tage the use of certain features; thus, the application
of the same algorithm to different datasets may give
484
Renò, V., Cardellicchio, A., Politi, T., Guaragnella, C. and D’Orazio, T.
Exploiting Ambiguities in the Analysis of Cumulative Matching Curves for Person Re-identification.
DOI: 10.5220/0005822104840494
In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods (ICPRAM 2016), pages 484-494
ISBN: 978-989-758-173-1
Copyright
c
2016 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

inconsistent results.
In this work, we address this problem introduc-
ing the Ambiguity Rate, an index that relies the results
given by a PRID algorithm with the specific dataset
against which this algorithm is being tested. The main
idea is to evaluate the statistical properties of the re-
sults given by the application of the PRID algorithm
of the results of the PRID method: informally speak-
ing, if an high variance is associated with these re-
sults, it may be reasonable to assume that the algo-
rithm is not well suited to operate on that specific
dataset; on the other side, if we obtain a low vari-
ance, the dataset is very ambiguous for these features,
so the algorithm works properly.
The rest of this paper is structured as follows. In
the second section, we formalize the basilar concept
of the PRID task. In the third section, we expose
our methodology, and we expose some results in the
fourth section. In the fifth section, the conclusion and
some perspectives on the future works are given.
2 MATHEMATICAL
FORMULATION OF THE PRID
TASK
2.1 PRID Task
Given a generic image dataset D which can be parti-
tioned into a gallery set G and a probe set P, asso-
ciate to each image of G the subset of the images of P
which minimize a certain distance metric d.
Given c cameras, we hypothesize that each one
of them acquire exactly one frame for each of the n
individuals who pass through the video surveillance
system, so:
|
D
|
= n ∗ c
As a consequence, in the most generic case:
D = G ∪ P
|
G
|
= n = N
G
|
P
|
= n ∗ (c − 1) = N
P
Informally speaking, G contains exactly one view
per individual, while P may contain one or more
views per individual, according to the number of cam-
eras.
The PRID task is generically ascribable to what
we define as PRID pipeline, which is usually struc-
tured in three different steps. We hypothize that D
has already been splitted in G and P.
Image Segmentation. In this phase each frame is
subject to a pre-processing step, which includes
background subtraction ((Stauffer and Grimson,
1999), (Zivkovic, 2004), (Jojic et al., 2009),
(Ren
`
o et al., 2014),(Spagnolo et al., 2004)), hu-
man detection ((Dalal and Triggs, 2005), (Corvee
et al., 2012)) and shadow suppression ((Lu and
Zhang, 2007)), in order to discard noisy informa-
tion reguarding background and shadows.
Descriptor Extraction. In this phase a robust and
discriminative descriptor is computed per each
frame combining both texture and chromatic fea-
tures.
Descriptor Matching. In this phase the descriptor
of the each image belonging to G is compared
with the descriptors of the images belonging to P,
searching for the best match (i.e. the one which
minimize the distance metric d).
Over the years, various approaches to the different
phases of the PRID pipeline have been proposed. The
proposed methods can be classified in three ways.
2.1.1 Appearance vs. Non-appearance Methods
We can discriminate the PRID algorithm basing on
the kind of features used to extract the frame descrip-
tor, as stated in the first section.
2.1.2 Single-shot vs. Multiple-shot Methods
We can discriminate the single-shot case from the
multiple-shot case evaluating both the cardinality of
G and P and the number of frames used to extract a
descriptor for the appearance of each individual.
In the single-shot case, the descriptor S
i
of the i-th
individual is computed as:
|
G
|
=
|
P
|
∀i ∈ D :
S
G
i
= g( f
G
i
)
S
P
i
= g( f
P
i
)
More informally, the cardinality of both the
gallery set and the probe set is equal to n, as there
are only two cameras which acquire exactly one view
per individual. As a consequence, for each individual
in G the signature S
G
i
is a generic function g(·) of the
unique frame f
G
related to the individual i, and this is
true also for the corresponding signature S
P
i
extracted
from the frame f
P
which depicts the individual in the
probe set.
The multiple-shot case is slightly different:
|
G
|
<
|
P
|
∀i ∈ D :
S
G
i
= g( f
G
i
)
S
P
i
= h( f
P
1,i
, ..., f
P
c,i
)
We note that the cardinality of G is strictly less
than the cardinality of P. It means that the function
Exploiting Ambiguities in the Analysis of Cumulative Matching Curves for Person Re-identification
485

g(·) used to extract S
G
i
cannot be used to compute
S
P
i
, as it has to be modified to take in account c pa-
rameters, i.e. the f
P
j
frames related to the i-th individ-
ual, with j = 1, ..., c. We denote the modified function
used to extract S
P
i
with h(·).
Obviously, multiple-shot methods may provide a
richer and more discriminative descriptor than single-
shot methods, meaning that the PRID task is easier
in the multiple-shot case. A review about single-shot
and multiple-shot methods is given in (D’Orazio and
Cicirelli, 2012).
2.1.3 Contextual vs. Non-contextual Methods
Contextual PRID methods are strictly dependent on
the context of the video surveillance system. There
are two types of contextual PRID methods:
• Camera Geometry Methods: these methods ex-
ploit the spatial and temporal relationships be-
tween cameras in the dataset (Javed et al., 2008);
• Camera Calibration: these methods exploit cam-
era calibration or homography tecniques to ex-
tract discriminative descriptor for PRID purposes
(Lantagne et al., 2003).
Non-Contextual methods do not use context infor-
mation, and may be distinguished into passive meth-
ods, which do not rely on learning techniques for de-
scriptor matching, and active methods, which employ
supervised or unsupervised learning algorithms for
descriptor extraction or matching (Bedagkar-Gala and
Shah, 2014). Active methods can be further classified
into:
• Color Calibration Methods: these methods ex-
ploit color calibration techniques to model chro-
matic relationships between cameras in a given
camera set. Usually, a brightness transfer func-
tion (BTF) (D’Orazio et al., 2009) is learned be-
tween each pair of cameras in a training stage and
used to improve PRID robustness;
• Descriptor Learning Methods: these methods
evaluate the various features used to compute
the descriptor of each frame and choose the
most meaningful ones or at least a discriminative
weighting scheme to apply to a raw feature vector
in order to extract a robust descriptor (Zheng et al.,
2009; Wang et al., 2007; Gray and Tao, 2008);
• Distance Metric Learning Methods: these meth-
ods attempt to maximize the matching accuracy
between frame descriptors, employing a training
stage where a distance metric is learned throught
the resolution of a convex programming problem
which allows to evaluate a symmetric positive-
semidefinite matrix D that will be used in a
quadratic distance framework. A comprehensive
survey on these approaches is given in (Yang and
Jin, 2006).
Finally, the results are displayed on the Cumula-
tive Matching Characteristic (CMC) curve, that rep-
resents the expectation of finding the correct match
in the top n matches of the chosen algorithm ((Faren-
zena et al., 2010)). More specifically, the x axis of
such curve represents the rank and the y one the per-
centage of recognition (or the number of images rec-
ognized). For example, a CMC value of 50% for a
rank r means that the 50% of the images taken from
the gallery set can be found in a range of ranks be-
tween 1 and r, because of the cumulative nature of
the curve. An example of CMC is shown in Figure
2(a) and 2(b).
3 METHODOLOGY
3.1 Algorithm Description
The proposed algorithm, named AMARE, is divided
in three main steps, as it is shown in figure 1:
1. Ambiguity Descriptor calculation (in blue);
2. Ambiguity evaluation (in red);
3. CMC separation (in green).
The first step takes place in a preprocessing phase,
while the other two need to be executed in a postpro-
cessing stage. This means that the PRID pipeline is
enriched by two modules that aim to quantify the ac-
curacy of a generic re-identification algorithm. At-
tention will also be focused on the computational
complexity of the whole approach, as it is pointed out
in the corresponding subsection.
3.1.1 Ambiguity Descriptor Calculation
Given a generic dataset D, an Ambiguity Descrip-
tor (ad) is calculated for each frame. The ad is an
arbitrary-rank tensor that embeds information about
the kind of scene that is being observed, allowing het-
erogeneous features to be exploited in order to define
this kind of descriptor.
Nevertheless, we start from the assumption that an
operator who is manually supervising a surveillance
system will probably try to estimate the accuracy of
the results with respect to the color of the images re-
turned by the algorithm.
We follow the framework defined in (Cardellic-
chio et al., 2015), using an ambiguity descriptor
which takes in account the tint of an image preserving
ICPRAM 2016 - International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods
486

spatial information about the location of the specific
colour. Therefore, we divide the i-th frame of D in six
horizontal stripes and then calculate the trend value of
the Hue coordinate for each stripe, assuming that the
images are in the HSV format. Hence, the ad is a six
elements vector of natural numbers:
ad
i
=
τ
1
.
.
.
τ
6
∈ N
6
(1)
∀i ∈ D
3.1.2 Ambiguity Evaluation
Given a set of q PRID algorithms to test
ALG = {α
1
, α
2
, . . ., α
q
} (2)
the best M results of each algorithm α
i
are stored in
a matrix R
α
i
while the respective ranks are stored in a
column vector K
α
i
K
α
i
=
k
1
k
2
.
.
.
k
N
G
∈ N
N
G
(3)
R
α
i
=
r
11
r
12
. . . r
1M
r
21
r
22
. . . r
2M
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
r
N
G
1
r
N
G
2
. . . r
N
G
M
∈ N
(N
G
×M)
(4)
In the matrix there is one row for each image taken
from the gallery set G and the results are ordered by
descendant score of the specific algorithm within each
row. Since an r
i j
element is an image taken by the
probe set P with an ambiguity descriptor ad
r
i j
asso-
ciated to it, also these descriptors can be stored in an
Ambiguity Descriptor Matrix ADM
α
i
∈ N
(N
G
×M)
that
has the same structure of the previous one. Conse-
quently, each element must be replaced by the de-
scriptor chosen in the preprocessing stage and ex-
ploited in order to obtain the Ambiguity Rate (AR).
In this work, the z-th row of ADM
α
i
is a matrix
ADM
z
α
i
=
ad
r
z1
, ad
r
z2
, . . . , ad
r
zM
=
=
τ
11
τ
12
. . . τ
1M
τ
21
τ
22
. . . τ
2M
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
τ
61
τ
62
. . . τ
6M
=
τS
T
1
τS
T
2
.
.
.
τS
T
6
(5)
where τS
T
i
is the row vector that contains the trend
values of the M best frames with respect to the i-th
stripe. Such rows are used to calculate the percentage
deviation (%
τ
) of the trend values while preserving
the spacial information about the Hue value using the
following formula:
%
z
τ
=
max(τS
T
1
)−min(τS
T
1
)
256
.
.
.
max(τS
T
6
)−min(τS
T
6
)
256
(6)
Finally, the AR value is calculated as the average
value of the percentage deviations
AR
z
α
i
= 1 −
1
6
6
∑
s=1
%
z
τ
(s) (7)
so that an high variation of the percentual dis-
placement returns no ambiguity. This index is ready
to be used to correct the results of the CMC curve.
This task is described in the next subsection.
3.1.3 CMC Separation
The CMC curve is calculated as described in the pre-
vious paragraph using only the information about the
ranks (equation 3). The aim of this work is to split
this curve evaluating its building blocks, and this op-
eration can be achieved with the fuzzification of the
ranks according to the AR value in the following way:
[0, 0.4] ⇒ LOW
(0.4, 0.9] ⇒ MEDIUM
(0.9, 1] ⇒ HIGH
Therefore, the CMC curves can be calculated
again considering three different contributions that re-
flect the three levels of the ambiguity rate.
3.2 Computational Complexity
The computational complexity of this approach is
strictly dependent on the parameters used to model
the ambiguities. The number of operations may sig-
nificantly vary according to the descriptor chosen,
as it can be any n-dimensional tensor. Let N
D
=
(N
G
+ N
P
) be the cardinality of the dataset that is be-
ing processed, N
px
the number of pixels and f (·) the
number of operations required by the task, the com-
putational complexities are the following:
1. Ambiguity Descriptor Calculation requires
O(k · N
px
· N
D
) operations to be processed, where
k =
K
∑
i=1
f (i)
is the sum of the number of operations needed
to calculate each element of the descriptor and K
represents the dimensionality of the descriptor.
Exploiting Ambiguities in the Analysis of Cumulative Matching Curves for Person Re-identification
487

Figure 1: Algorithm high level flowchart.
2. Ambiguity Evaluation has a complexity of O(q ·
M · N
D
)
Finally, the computational complexity of the am-
biguity rate process computation depends on N
D
,
while the one of the whole process depends on the
computational complexity of the most expensive al-
gorithm.
4 EXPERIMENTS AND RESULTS
The methodology described in this paper has been
tested on the PRID algorithms proposed in (Farenzena
et al., 2010) and (Cardellicchio et al., 2015), in order
to better understand the performances obtained on the
dataset VIPeR (Gray et al., 2007). This dataset con-
tains 632 images taken from non overlapping cameras
with arbitrary viewpoints. All the images have been
taken under varying illumination conditions and each
one is scaled to 128 × 48 pixels. In (Farenzena et al.,
2010), the authors use both color (MSCR and wHSV)
and texture (RHSP) features to recognize the subjects,
while in (Cardellicchio et al., 2015) only the color is
exploited (HSV and log RG). However, the approach
presented in this paper is focused on the interpretation
of the results with respect to the CMCs.
5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
Cumulative Matching Characteristic
Rank
Recognition percentage
(a) Overall CMC - Algorithm (Farenzena et al., 2010)
5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
Cumulative Matching Characteristic
Rank
Recognition percentage
(b) Overall CMC - Algorithm (Cardellicchio et al., 2015)
Figure 2.
Figures 2(a) and 2(b) report the overall CMC that
represent the state of art method used to measure
the performances of the algorithms on the chosen
dataset. Looking at the curves, algorithm (Farenzena
et al., 2010) works better than the other because the
ICPRAM 2016 - International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods
488

Figure 3: Results given by the traditional PRID pipeline. Visual matching for algorithm (Cardellicchio et al., 2015). The first
column GS represents the query images taken from the Gallery Set, the second one contains the Foreground Masks, while the
other columns are the responses taken from the Probe Set, ordered by the rank. The red box indicates the Ground Truth.
CMC starts from a higher value at the first rank and
the values of the other ranks are always higher than
the ones of algorithm (Cardellicchio et al., 2015).
However, this curves present some drawbacks be-
cause they effectively embed information about the
re-identification rank, but we actually don’t know if
the results for a specific rank have been obtained in
ambiguous situations or not. For example, given the
first rank, it is not possible to determine if the re-
identification percentage has been achieved in easy or
hard configurations. In fact, one would suppose that
in cases of low ambiguity, the correct result should be
returned at the first iteration. On the contrary, worst
responses should be expected when the algorithm has
to choose among ambiguous observations. Further-
more, figure 3 gives a graphical overview of a certain
number of results. In this example, the first six images
are correctly recognized by the algorithm because the
first response is the one surrounded by the red box
that represents the ground truth, i.e. the right image
taken from the probe set that depicts the same subject
of the query image. Rows from 7 to 10 show that the
algorithm is giving a rank 2 response, while the last
two represent a failure because there is no recogni-
tion in the first 20 responses. Looking at the images,
it is possible to notice that there is no regularity in the
responses with respect to the ambiguity. For exam-
ple, in the second row there is a person with a green
sweater, but the other images returned by the algo-
rithm are really different one from the other. For this
reason, the experiments presented in this section will
exploit the AR value to understand how a specific al-
gorithm is working given a specific ambiguity range.
First, the ambiguity descriptor is calculated ac-
cording to equation 1 for each image of the collection.
Then, the rest of the PRID pipeline is executed for
both algorithms and finally the results are processed
in order to calculate the ambiguity rate as described
in equation 7. In order to obtain a visual compari-
son of the least ambiguous result and the most am-
biguous one, an example of boxplot enriched by the
corresponding frames is provided in figure 5 and 6.
Each box refers to one of the stripes used to divide the
images, as noticeable in the figure, so it is represen-
tative of one row of the ADM described in equation
5. Moreover, there is a blue circle that indicates the
value of the ambiguity descriptor of the gallery set
image, i.e. the one that is being re-identified by the
algorithm. If the image taken from the gallery set is
re-identified correctly, the blue circle should lie inside
the box. Otherwise, the distance of the circle from the
box can be exploited to understand how far the im-
Exploiting Ambiguities in the Analysis of Cumulative Matching Curves for Person Re-identification
489

Table 1: Dataset separation for different values of the ambiguity rate.
Ambiguity rate (Farenzena et al., 2010) (Cardellicchio et al., 2015)
LOW 46 img 7.28 % 18 img 2.85 %
MEDIUM 559 img 88.45 % 581 img 91.93 %
HIGH 27 img 4.27 % 33 img 5.22 %
age is from the results, and so quantify how much an
algorithm is doing wrong in a specific situation. In
the first case (figures 5(a) and 5(b)) the situation is
so ambiguous that each person can easily be misin-
terpreted even by an expert human operator because
everyone wears similar clothes. In the second case
(figures 6(a) and 6(b)), the images of the probe set are
not so ambiguous, in fact the first 5 returned values
are different one from the other: different colours of
the shirt/dress (red, black, white and yellow) and dif-
ferent colours of the trousers/skirt (pink, black, red,
jeans). Hence, a boxplot with large boxes will refer
to a non ambiguous response, that should basically
imply that the algorithm is operating in an easy con-
dition, so the correct response should be given at the
first rank. On the contrary, small boxes are related to
ambiguous responses that are likely to be mistaken.
In this situation, a good PRID algorithm answers with
the correct image in one of the first ranks, but not al-
ways at rank 1.
Figure 4 shows the ambiguity rate histogram for
each response of the two algorithms. It is immediate
to notice that a small number of responses has a corre-
sponding LOW ambiguity rate (< 0.4) or a HIGH one
(> 0.9), according to the fuzzification rule presented
in section 3.1.3.
Looking at Table 1, both algorithms are isolating
about 10% of the images in the tails of the distribu-
tion, namely the 5% of the results of the algorithms
has low ambiguity and similarly another 5% has high
ambiguity. Looking at the peak of the distribution
we observe that it is located around 0.6 for algorithm
(Farenzena et al., 2010), that means that a medium
level of ambiguity is produced most of the time. For
algorithm (Cardellicchio et al., 2015), the peak is lo-
cated around 0.7, that means that the responses are
more similar one to the other. The corresponding
CMC curves for LOW, MEDIUM and HIGH ambi-
guity rate values are reported in figure 7, 8 and 9 and
are called split CMC. For each curve, the x axis re-
ports the first 100 ranks and the y axis shows the per-
centage of images that have been recognized at the
specific rank. Due to the cumulative nature of the
curve, if there is a step, it means that there are no
matches at the corresponding rank. For example, the
CMC in figure 7(b) illustrates that algorithm (Cardel-
licchio et al., 2015) does not have any match at ranks
0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
AR histogram
AR 5
Images
(a) Ambiguity rate distribution for algorithm (Farenzena et al.,
2010). The peak is located around AR = 0.6.
0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
AR histogram
AR 5
Images
(b) Ambiguity rate distribution for algorithm (Cardellicchio et al.,
2015). The peak is located around AR = 0.7.
Figure 4: Ambiguity rate histogram on VIPeR results.
2, 3, 5 − 7, 9 − 19, 21 − 70 . . . , while the one in figure
7(a) is more similar to a curve, even if in some points
it is flat (e.g. ranks 4, 5, 10 − 15. . . ). Here, algorithm
(Cardellicchio et al., 2015) shows a high percentage
than the other approach at rank 1. Such situation
should be the easiest for an algorithm, so the expected
result would be a really high percentage at rank 1.
The CMCs in figure 8(a) and 8(b) are similar to
the ones already known in literature because they are
representative of about 90% of the dataset. The last
two curves indicate the response in HIGH ambigu-
ity cases. In both cases (figure 9(a) and 9(b)) there
is an increment of the correct answers starting from
ICPRAM 2016 - International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods
490
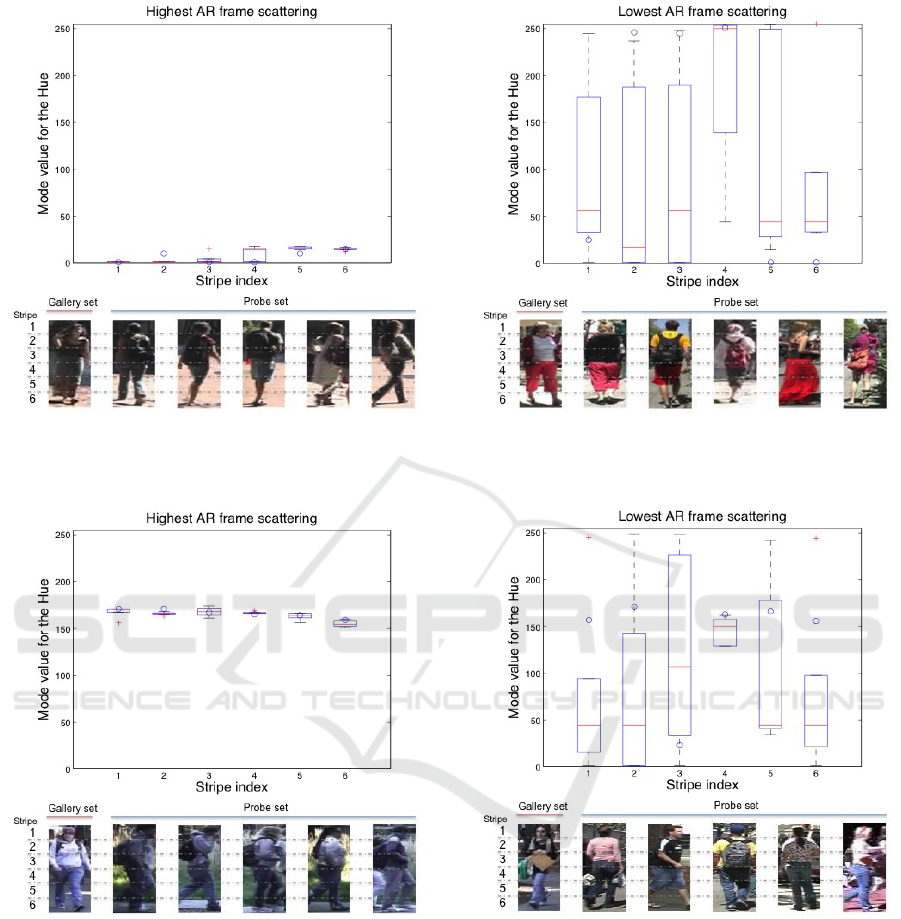
(a) Highest AR obtained with algorithm (Farenzena et al., 2010).
The visual matching represents the query image (gallery set) and
the first 5 responses. The boxes are referred to the probe set, while
the circle represents the query.
(b) Highest AR obtained with algorithm (Cardellicchio et al.,
2015). The visual matching represents the query image (gallery set)
and the first 5 responses. The boxes are referred to the probe set,
while the circle represents the query.
Figure 5: Boxplot comparison for the highest AR and visual
matching of the result.
rank 5. This is an interesting result because it means
that both approaches do not give meaningful answers
in the first iterations when operating in challenging
situations. Focusing on low ranks, we notice that
the algorithms give similar results for both LOW and
MEDIUM ambiguity values. However, we expected
that the majority of the low rank responses occurred
in the condition AR < 0.4, thus obtaining the best re-
(a) Lowest AR obtained with algorithm (Farenzena et al., 2010).
The visual matching represents the query image (gallery set) and
the first 5 responses. The boxes are referred to the probe set, while
the circle represents the query.
(b) Lowest AR obtained with algorithm (Cardellicchio et al., 2015).
The visual matching represents the query image (gallery set) and the
first 5 responses. The boxes are referred to the probe set, while the
circle represents the query.
Figure 6: Boxplot comparison for the lowest AR and visual
matching of the result.
sults in easy configurations, i.e. when the images re-
turned are really different one from the other. Finally,
an algorithm should be able to increase the number
of images that lie in LOW or HIGH ambiguity val-
ues. In the first case the recognition percentage at
rank 1 should be the highest, while in the second one
the correct response is expected within the first ranks.
These quite uniform results for each ambiguity value
Exploiting Ambiguities in the Analysis of Cumulative Matching Curves for Person Re-identification
491

10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
CMC for results with AR below 0.4
Image rank
Percentage of images
(a) CMC referred to the low ambiguity results obtained with
algorithm (Farenzena et al., 2010). The cardinality of this set
is 46 images.
10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
CMC for results with AR below 0.4
Image rank
Percentage of images
(b) CMC referred to the low ambiguity results obtained with
algorithm (Cardellicchio et al., 2015). The cardinality of this
set is 18 images.
Figure 7: CMC split comparison, LOW ambiguity values.
show how the features used by the algorithms can not
isolate easy recognizable situations for a human eye.
This is probably due to the representation of the col-
ors in different visual systems: the human one and
the digital one. For the first, peaks on different color
tones can be immediately distinguishable, while in a
digital color space the same peaks can generate values
that are likely to be classified as similar colors even if
they are different.
5 CONCLUSION
In this paper, a method to quantify the accuracy of
a re-identification algorithm exploiting the ambiguity
of its responses has been presented. This method en-
riches the PRID pipeline defining an ambiguity de-
scriptor and taking advantage of it to calculate the AR
of each response of the algorithm. This ambiguity
can be seen as a relative one, because its formulation
is dependent on the results of the chosen algorithm,
10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
CMC for results with AR between 0.4 and 0.9
Image rank
Percentage of images
(a) CMC referred to the medium ambiguity results obtained
with algorithm (Farenzena et al., 2010). The cardinality of this
set is 559 images.
10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
CMC for results with AR between 0.4 and 0.9
Image rank
Percentage of images
(b) CMC referred to the medium ambiguity results obtained
with algorithm (Cardellicchio et al., 2015). The cardinality of
this set is 581 images.
Figure 8: CMC split comparison, MEDIUM ambiguity val-
ues.
as stated in equation 7 and it can be used to under-
stand the operative conditions in which the algorithm
works. Looking at the results presented in section 4,
the performances of a generic algorithm can be stud-
ied exploiting its behaviour in ambiguous and non
ambiguous situations. Moreover, the AR histogram
(figure 4) gives an immediate graphical description of
the ambiguity distribution among the images of a spe-
cific dataset. Finally, the split CMC curves can be
studied separately using this information to measure
the performance of different algorithms that run on
the same dataset. In conclusion, the work presented in
this paper can be seen as the first step in the exploita-
tion of ambiguities in order to understand the results
of a PRID pipeline. Future research trends will re-
gard the extension of this approach in order to model
an absolute ambiguity value associated to a dataset.
Exploiting both relative and absolute ambiguities, a
generic rank of a CMC can be promoted or penal-
ized starting from the assumption that if an algorithm
gives for example a rank 3 output in an ambiguous
ICPRAM 2016 - International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods
492
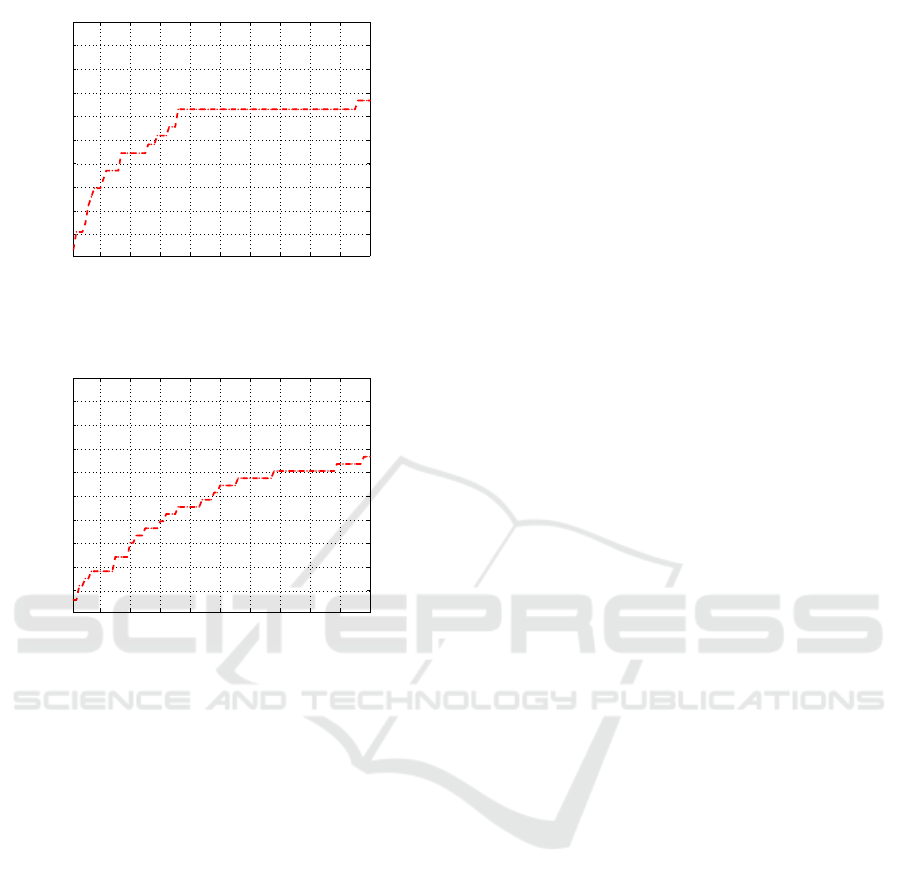
10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
CMC for results with AR above 0.9
Image rank
Percentage of images
(a) CMC referred to the high ambiguity results obtained with
algorithm (Farenzena et al., 2010). The cardinality of this set
is 27 images.
10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
CMC for results with AR above 0.9
Image rank
Percentage of images
(b) CMC referred to the high ambiguity results obtained with
algorithm (Cardellicchio et al., 2015). The cardinality of this
set is 33 images.
Figure 9: CMC split comparison, HIGH ambiguity values.
situation, then it can be promoted. Moreover, if an
algorithm does not give a rank 1 output in unambigu-
ous situations (e.g. the re-identification of the only
one person dressed with dark clothes in a controlled
environment), then it can be penalized. Finally, the
research on the absolute ambiguity value should give
to an operator the possibility to compare different al-
gorithms that run on different datasets.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors would like to thank Mr. Michele Attolico
for his technical support.
REFERENCES
Bauml, M. and Stiefelhagen, R. (2011). Evaluation of lo-
cal features for person re-identification in image se-
quences. In Adv. Video and Signal-Based Surveill.
(AVSS), 2011 8th IEEE Int. Conf. on, pages 291–296.
IEEE.
Bedagkar-Gala, A. and Shah, S. K. (2014). A survey of ap-
proaches and trends in person re-identification. Image
and Vis. Comput., 32(4):270–286.
Cardellicchio, A., D’Orazio, T., Politi, T., and Ren
`
o, V.
(2015). An human perceptive model for person re-
identification. In VISAPP-Int. Conf. on Comput. Vis.
Theory and Appl.-2015.
Corvee, E., Bak, S., Bremond, F., et al. (2012). People
detection and re-identification for multi surveillance
cameras. In VISAPP-Int. Conf. on Comput. Vis. The-
ory and Appl.-2012.
Dalal, N. and Triggs, B. (2005). Histograms of oriented
gradients for human detection. In Comput. Vis. and
Pattern Recognit., 2005. CVPR 2005. IEEE Comput.
Soc. Conf. on, volume 1, pages 886–893. IEEE.
D’Orazio, T. and Cicirelli, G. (2012). People re-
identification and tracking from multiple cameras: A
review. In Image Process. (ICIP), 2012 19th IEEE Int.
Conf. on, pages 1601–1604.
D’Orazio, T. and Guaragnella, C. (2012). A graph-based
signature generation for people re-identification in a
multi-camera surveillance system. In VISAPP, vol-
ume 1, pages 414–417.
D’Orazio, T., Mazzeo, P., and Spagnolo, P. (2009). Color
brightness transfer function evaluation for non over-
lapping multi camera tracking. In Distrib. Smart Cam-
eras, 2009. ICDSC 2009. Third ACM/IEEE Int. Conf.
on, pages 1–6. IEEE.
Farenzena, M., Bazzani, L., Perina, A., Murino, V., and
Cristani, M. (2010). Person re-identification by
symmetry-driven accumulation of local features. In
Comput. Vis. and Pattern Recognit. (CVPR), 2010
IEEE Conf. on, pages 2360–2367. IEEE.
Gheissari, N., Sebastian, T. B., and Hartley, R. (2006). Per-
son reidentification using spatiotemporal appearance.
In Comput. Vis. and Pattern Recognit., 2006 IEEE
Comput. Soc. Conf. on, volume 2, pages 1528–1535.
IEEE.
Gray, D., Brennan, S., and Tao, H. (2007). Evaluating ap-
pearance models for recognition, reacquisition, and
tracking. In Proc. IEEE Int. Workshop on Perform.
Eval. for Track. and Surveill. (PETS), volume 3. Cite-
seer.
Gray, D. and Tao, H. (2008). Viewpoint invariant pedestrian
recognition with an ensemble of localized features. In
Comput. Vis.–ECCV 2008, pages 262–275. Springer.
Javed, O., Shafique, K., Rasheed, Z., and Shah, M. (2008).
Modeling inter-camera space–time and appearance re-
lationships for tracking across non-overlapping views.
Comput. Vis. and Image Understanding, 109(2):146–
162.
Jojic, N., Perina, A., Cristani, M., Murino, V., and Frey,
B. (2009). Stel component analysis: Modeling spatial
correlations in image class structure. In Comput. Vis.
and Pattern Recognit., 2009. CVPR 2009. IEEE Conf.
on, pages 2044–2051. IEEE.
Lantagne, M., Parizeau, M., and Bergevin, R. (2003). Vip:
Exploiting Ambiguities in the Analysis of Cumulative Matching Curves for Person Re-identification
493

Vision tool for comparing images of people. In Vis.
Interface, volume 2.
Lu, J. and Zhang, E. (2007). Gait recognition for
human identification based on ica and fuzzy svm
through multiple views fusion. Pattern Recognit. Lett.,
28(16):2401–2411.
Ren
`
o, V., Marani, R., D’Orazio, T., Stella, E., and Nitti, M.
(2014). An adaptive parallel background model for
high-throughput video appl. and smart cameras em-
bedding. In Proc. of the Int. Conf. on Distrib. Smart
Cameras, ICDSC ’14, pages 30:1–30:6, New York,
NY, USA. ACM.
Roy, A., Sural, S., and Mukherjee, J. (2012). A hierarchical
method combining gait and phase of motion with spa-
tiotemporal model for person re-identification. Pat-
tern Recognit. Lett., 33(14):1891–1901.
Saghafi, M. A., Hussain, A., Zaman, H. B., and Saad, M.
H. M. (2014). Review of person re-identification tech-
niques. IET Comput. Vis., 8(6):455–474.
Spagnolo, P., Leo, M., D’Orazio, T., and Distante, A.
(2004). Robust moving objects segmentation by back-
ground subtraction. In The International Workshop
on Image Analysis for Multimedia Interactive Services
(WIAMIS).
Stauffer, C. and Grimson, W. E. L. (1999). Adaptive back-
ground mixture models for real-time tracking. In
Comput. Vis. and Pattern Recognit., 1999. IEEE Com-
put. Soc. Conf. on., volume 2. IEEE.
Wang, X., Doretto, G., Sebastian, T., Rittscher, J., and Tu,
P. (2007). Shape and appearance context modeling. In
Comput. Vis., 2007. ICCV 2007. IEEE 11th Int. Conf.
on, pages 1–8. IEEE.
Yang, L. and Jin, R. (2006). Distance metric learning: A
comprehensive survey. Michigan State Universiy, 2.
Zheng, W.-S., Gong, S., and Xiang, T. (2009). Asso-
ciating groups of people. In Proc. of the British
Machine Vis. Conf., pages 23.1–23.11. BMVA Press.
doi:10.5244/C.23.23.
Zivkovic, Z. (2004). Improved adaptive gaussian mixture
model for background subtraction. In Pattern Recog-
nit., 2004. ICPR 2004. Proc. of the 17th Int. Conf. on,
volume 2, pages 28–31 Vol.2.
ICPRAM 2016 - International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods
494
