
Inter-brain Synchronization between Nurse and Patient During
Drawing Blood
Tsuneo Kawano
1
, Yukie Majima
2
, Yasuko Maekawa
3
, Mako Katagiri
4
and Atsushi Ishigame
2
1
Faculty of Science and Engineering, Setsunan University, Ikeda-Nakamachi, Neyagawa, Osaka, Japan
2
Graduate School of Engineering, Osaka Prefecture University, Naka-ku Gakuencho, Sakai, Osaka, Japan
3
Faculty of Nursing, Kansai University of Social Welfare, Shinden, Ako, Hyogo, Japan
4
Technology Research Institute of Osaka Prefecture, Ayumino, Izumi, Osaka, Japan
Keywords: Nursing Skills, Tacit Knowledge, Blood Drawing, Nurse and Patient, EEG, Alpha Wave Band,
Synchronization.
Abstract: Tacit knowledge such as "proficient skills" and "knacks" in nursing skills seems not to be applied by nurse
alone but by the interaction between nurse and patient. The purpose of this study is to analyze their
interaction from the point of interbrain synchrony. In this study blood drawing technique was adopted as
nursing skills and experiments of drawing blood were carried out in nurse-patient pairs. Experimental
participants were 4 nurses and 6 patients. The brain waves in the occipital portion of nurse and patient were
simultaneously measured using portable EEG devices during drawing blood. The ratios of alpha-band
power were calculated for each of the nurse and patient, and the cross-correlations were obtained between
every pairs of them. The results indicated that the brain waves of patient were synchronized with those of
nurse by several seconds behind. Furthermore the synchronization was not recognized in abnormal
circumstances that nurses failed in the drawing blood.
1 INTRODUCTION
Tacit knowledge such as "proficient skills" and
"knacks" in nursing skills seems not to be applied by
nurse alone but by the interaction between nurse and
patient. Evaluation of nursing skills is assumed to
depend on the interaction. Therefore, it is important
to reveal the interaction between nurse and patient in
order to build a learning support system for the
nursing skills. The purpose of this study is to
analyze their interaction from the point of interbrain
synchrony.
The perfect nursing skills could ease patient’s
pain or fears by the proficient technique and good
communications with the patient. If the relations
between the perfect nursing skills and interbrain
synchrony of nurse and patient are successfully
quantified, proficiency level of beginning nurse can
be evaluated by the interbrain synchrony. It means
that quantification of the interbrain synchrony
between nurse and patient could contribute to
establish entirely-new learning support system for
beginning nurses. Thereby decrease of medical
errors and increase of patient’s safety are also
expected.
Recently the research regarding "inter-brain
synchronization" came to be conducted. Dumas et al.
discovered that states of interactional synchrony
correlate with the emergence of an interbrain
synchronizing network between two persons who
are engaged in spontaneous imitation of hand
movements (Dumas et al., 2010). Regarding the
persons who are watching a movie, Kauppi et al.,
suggested that several regions within the frontal and
temporal lobes showed inter-subject correlation
predominant-ly at low frequency bands, whereas
visual cortical areas exhibited inter-subject
correlation also at higher frequencies (Kauppi et al.,
2010). Hari et al. introduced the synchrony of brains
and bodies during implicit interpersonal face-to-face
interaction (Hari et al., 2013).
Neurobehavioral studies of interaction of nurse
and patient are few because of difficulties to
measure brain waves during working. Our previous
study has successfully attempted to measure the
brain waves of nurse and patient simultaneously
Kawano, T., Majima, Y., Maekawa, Y., Katagiri, M. and Ishigame, A.
Inter-brain Synchronization between Nurse and Patient During Drawing Blood.
DOI: 10.5220/0005825605070511
In Proceedings of the 9th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies (BIOSTEC 2016) - Volume 5: HEALTHINF, pages 507-511
ISBN: 978-989-758-170-0
Copyright
c
2016 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
507
during blood drawing task (Maekawa et al., 2013).
The differences in the changing state of tension or
concentration between nurses and beginners from
the EEG data were discussed. One of the remarks
was that nurses were in a state of concentration with
calm during the injection performance. In another
study it concluded that the increase of alpha-band
power had to do with the successful injection
operation (Kishida et al., 2015).
In this study blood drawing technique was
adopted as nursing skills and experiments of
drawing blood were carried out in nurse-patient pairs.
The brain waves in the occipital portion of nurse and
patient were simultaneously measured using portable
EEG devices during drawing blood. The ratios of
alpha-band power were calculated for each of the
nurse and patient, and the cross-correlations were
obtained between every pairs of them.
2 EXPERIMENTAL METHODS
Participants for nurses were 4 women in their thirties
and forties. They have over 8 years of nursing
experience. Participants for patients (5 men and 1
woman) were in their twenties.
After the ethical committee of the institute
reviewed the study protocol, the authors explained
ethical considerations to participants and obtained
written consent before the study.
Blood drawing was actually conducted using
three kind of intravenous injection trainers
(Adam,Rouilly Limited) instead of actual arm of the
patients. One of them was a type of arm shape. It
was an easy trainer model A to draw the blood
because a blood vessel had come to the surface of
the skin. Another one was a same type but it was a
difficulty trainer model B because of invisible vein.
The other one C was a fit-on type of wrapping
human arm, which had a realistic feeling. These
types of arm model were employed to investigate the
effect of the nurse’s performance to the synchro-
nization between nurse and patient.
There were 14 pairs in combinations of nurse and
patient. The trials of drawing blood were repeated 5
times with each pair. Muse Brain System (Digital
Medic, Inc.) was used to measure the brain waves.
This was a portable EEG device with a single
electrode for occipital cortex. The electrode was set
at the midoccipital point (Oz in the International 10-
20 System) (Teplan, 2002).
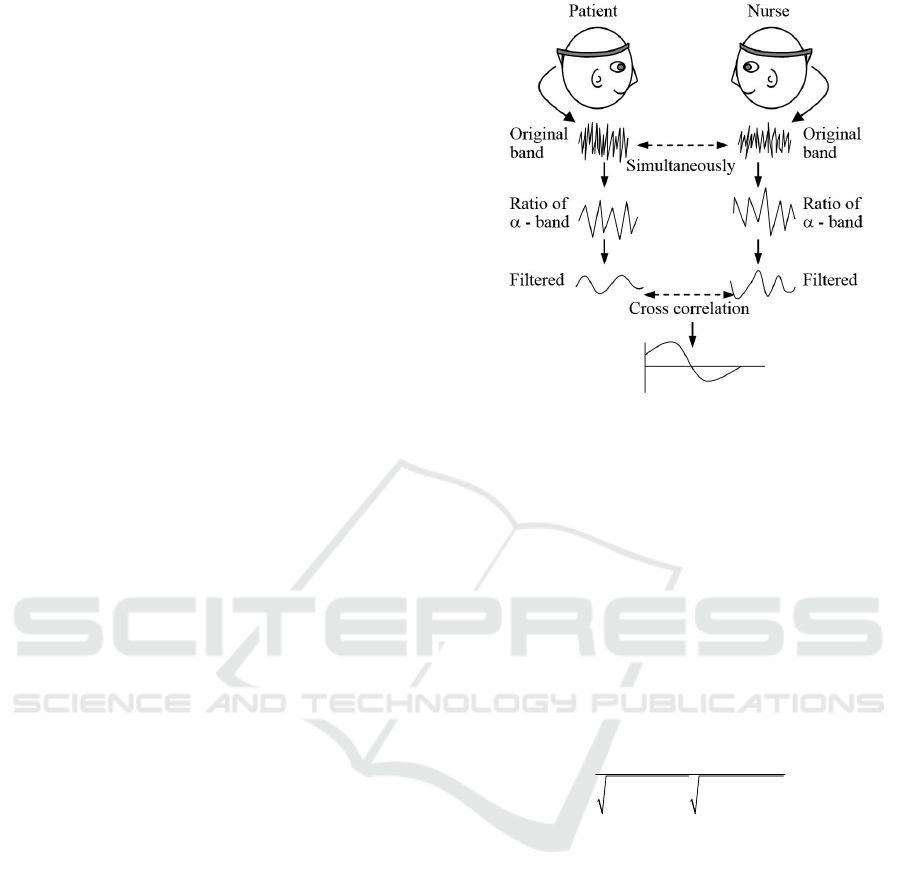
Figure 1 shows general concept of inter-brain
synchronization between nurse and patient. Firstly,
original brain waves were measured simultaneously
Figure 1: General concept of inter-brain synchronization
between nurse and patient.
for the nurse and patient during drawing blood. The
original data were transformed into a frequency
domain signal by Fourier transform every second.
Secondly, the ratios of alpha, beta, delta band power
were calculated every second. Thirdly, the ratio data
were smoothed by a second-order Butterworth filter
to distinguish the trend. The cut off frequency was
set to 0.1Hz. Finally, the relation of the alpha-band
between nurse and patient was evaluated by using
the following cross-correlation function C(τ) in
every pair (Watanabe et al., 2004).
1
22
11
{() }{( ) }
()
{() } {() }
n
xy
i
nn
xy
ii
xi yi
C
xi yi
τ
μτμ
τ
μμ
−
=
==
−+−
=
−−
∑
∑∑
(1)
Where μ
x
and μ
y
are the mean values of x and y,
respectively, x and y is for nurse and patient,
respectively, n is the number of data, and τ is time
delay.
In general the changes of ratios of alpha and beta
band power are in opposite phases like a seesaw.
Therefore human state of tension or relax can be
investigated with either of the alpha or beta band
power. In this study alpha band power is taken into
consideration. Actual measured data of alpha band
power are discussed in the next chapter.
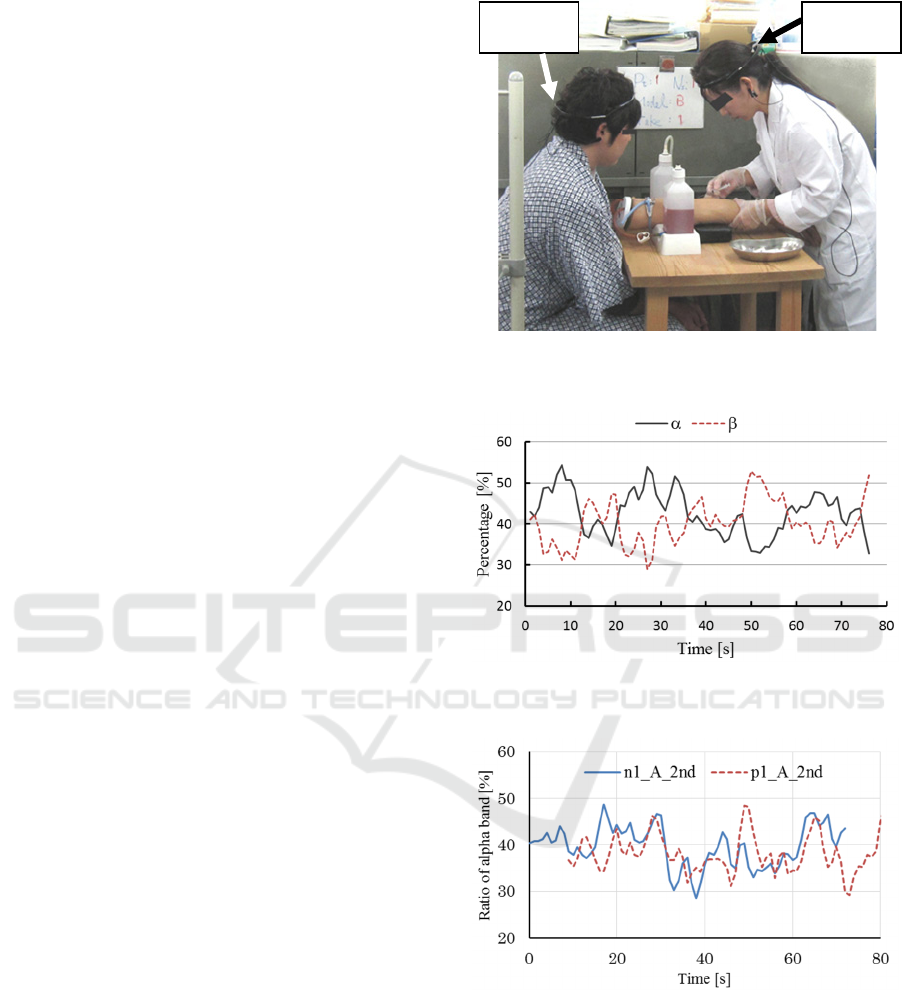
Figure 2 shows experimental appearance. The
nurse is going to prick with a needle to the arm
model. The patient gazes at the arm model.
HEALTHINF 2016 - 9th International Conference on Health Informatics
508
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Figure 3 shows the changes of ratio of the alpha and
beta band power measured from a nurse n1 during
drawing blood. As mentioned before, it is found that
their changes have mutually reverse-phase relations.
Figure 4 shows an example of time variation of
ratio of alpha band power in pairs of nurse n2 and
patient p2. In this case time delay τ is 9 seconds, and
cross correlation coefficient becomes maximum
0.326. The graph indicates that the ratio of alpha
band power (component of relaxation) of patient is
almost synchronized with that of nurse by 9 seconds
behind.
Figure 5 shows examples of cross correlation
function. Figure (a) is the successful case in drawing
blood. The functions become largest at τ =2, 3, 7,
respectively. It means that alpha band of the brain
waves is synchronized between nurse and patient at
that delay. Figure (b) is the case of the first trial in a
pair of nurse and patient and the failure case in
drawing blood. In these cases large plus cross-
correlation values do not exist. Due to the nerves of
nurse and patient at first trial and the failure of
drawing blood with repeated insertion of the needle,
it is assumed that the brain rhythms are disturbed.
Table 1 shows the results of all trials in pairs of
nurse and patient. In the table success or failure of
the drawing blood, synchronization or non-
synchronization, and time delay are listed.
Synchronization or non-synchronization is decided
by 5% significance level. In table 1 on the trials of
synchronization due to the success, the marks of the
double circle are displayed. On the trials of non-
synchronization due to the failure, the marks of the
single circle are displayed. The marks of dotted
circle are displayed in case of the first trial and non-
synchronization in spite of the success. In the 9 trials
synchronizations do not occur due to the failure of
drawing blood. In the first trials in pairs of nurse and
patient, synchronizations do not often occur even if
the trials are successful. It is considered that it is
caused by the tension of nurse and patient because of
the first combination. The percentage of non-
synchronization in case of the first trials or failure
drawing blood is 76.5%.
In the case of the 32 trials, synchronizations
occur due to the success of drawing blood. When the
patient felt anxious or fearful, synchronization did
not occur even if the drawing blood was successful.
The marks of “anxious” or “fearful” are displayed
on the table. The patients tend to feel fearful when
using a fit-on type arm model C because of the
realistic feeling. The percentage of synchronization
Figure 2: Simultaneous measurement of brain waves for
nurse and patient during drawing blood.
Figure 3: Changes of ratio of the alpha and beta band
power measured from a nurse n1 during drawing blood.
Figure 4: Example of time variation of ratio of alpha band
power in pairs of nurse n1 and patient p1 (τ = 9).
in case of the successful drawing blood without the
first trials and the case of anxious or fearful feeling
is 69.0%.
The time delay of cross correlation was 6.18
seconds in average. Therefore, the brain waves of
patient are synchronized with those of nurse by
about 6 seconds behind.
EEG
electrode
EEG
electrode
Inter-brain Synchronization between Nurse and Patient During Drawing Blood
509
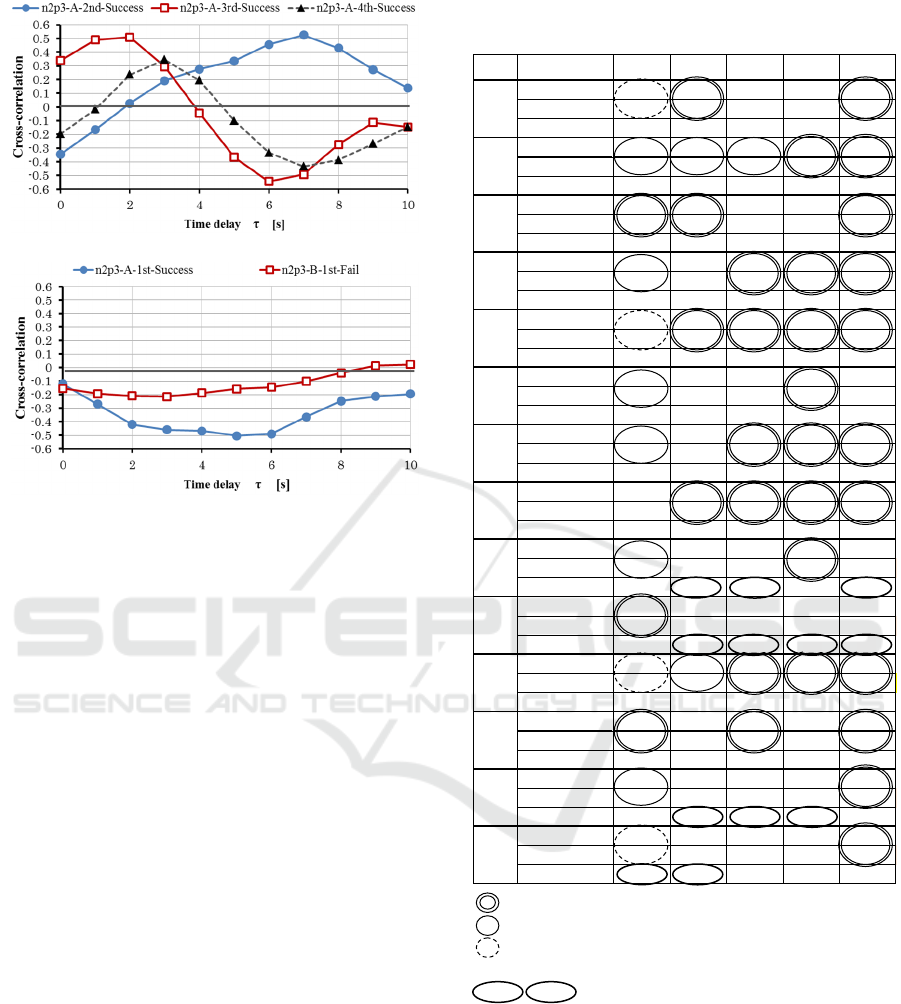
(a) Example of successful case in drawing blood
(b) Example of failure in drawing blood
Figure 5: Cross-correlation of alpha band power between
nurse and patient.
4 CONCLUSIONS
In order to analyze nurse-patient interaction from the
point of interbrain synchrony, in this study blood
drawing technique was adopted as nursing skills and
experiments of drawing blood were carried out in
nurse-patient pairs. The brain waves in the occipital
portion of nurse and patient were simultaneously
measured using portable EEG devices during
drawing blood. The ratios of alpha-band power were
calculated for each of the nurse and patient, and the
cross-correlations were obtained between every pairs
of them. The results indicated that the brain waves
of patient were synchronized with those of nurse by
several seconds behind. Furthermore the synchro-
nization was not recognized in abnormal
circumstances that nurses failed in the drawing
blood. It is suggested that the proficiency level of
beginning nurse can be evaluated by the interbrain
synchrony. In the future data accumulation for more
experimental participants will be an issue to validate
the findings.
Table 1: Relation between success of drawing blood and
inter-brain synchronization.
Synchronization due to the success of drawing blood
Non-synchronization due to the failure of drawing blood
Non-synchronization due to the first trials in pairs of nurse
and patient
Patient felt anxious or fearful
REFERENCES
Dumas, G., Nadel, J., Soussignan, R., Martinerie, J.,
Garnero, L., 2010. Inter-Brain Synchronization during
Social Interaction, PLoS ONE, Vol.5, Issue 8, e12166,
pp.1-10.
Hari, S., Himberg, T., Nummenmaa, L., et al., 2013.
Synchrony of brains and bodies during implicit
First trial 2nd 3rd 4th 5th
Success / Failure Success Success Success Success Success
Syncronization Non Sync Non Non Sync
Time delay [s]
-
10
--
8
Success / Failure Failure Failure Failure Success Success
Syncronization Non Non Non Sync Sync
Time delay [s]
---
10 9
Success / Failure Success Success Success Success Success
Syncronization Sync Sync Non Non Sync
Time delay [s] 10 8
--
8
Success / Failure Failure Success Success Success Success
Syncronization Non Non Sync Sync Sync
Time delay [s]
--
10 4 4
Success / Failure Success Success Success Success Success
Syncronization Non Sync Sync Sync Sync
Time delay [s]
-
83310
Success / Failure Failure Success Success Success Success
Sync Non Non Non Sync Non
Time delay [s]
---
5
-
Success / Failure Failure Success Success Success Success
Syncronization Non Non Sync Sync Sync
Time delay [s]
--
665
Success / Failure Failure Success Success Success Success
Syncronization Sync Sync Sync Sync Sync
Time delay [s]29944
Success / Failure Failure Success Success Success Success
Syncronization Non Non Non Sync Non
Time delay [s]
---
2
-
Success / Failure Success Success Success Success Success
Syncronization Sync Non Non Non Non
Time delay [s] 0
----
Success / Failure Success Failure Success Success Success
Syncronization Non Non Sync Sync Sync
Time delay [s]
--
31010
Success / Failure Success Success Success Success Success
Syncronization Sync Non Sync Non Sync
Time delay [s] 5
-
1
-
6
Success / Failure Failure Success Success Success Success
Syncronization Non Non Non Non Sync
Time delay [s]
----
9
Success / Failure Success Success Success Success Success
Syncronization Non Non Non Non Sync
Time delay [s]
----
3
n3p5-A
n3p5-C
n3p6-B
n4p5-A
n4p6-B
n4p6-C
n1p1-A
n1p1-B
n1p2-A
n1p2-B
n2p3-A
n2p3-B
n2p4-A
n2p4-B
anxious
anxious
fearful
fearful
fearful fearful
anxious anxious anxious
fearful
fearful
anxious fearful
anxious
HEALTHINF 2016 - 9th International Conference on Health Informatics
510

interpersonal interaction, Trends in Cognitive
Sciences, Vol.17, No.3, pp.105-106.
Kauppi, J.P., Jääskeläinen, I.P., Sams, M., Tohka, J., 2010.
Inter-subject correlation of brain hemodynamic
responses during watching a movie: localization in
space and frequency, Frontiers in Neuroinformatics,
Volume 4, Article 5, pp.1-10.
Kishida, N., Ishigame, A. Majima, Y., 2015. Study on
Synchronization of Brain Waves and Injection
Technology, HEALTHINF 2015 - International
Conference on Health Informatics, pp.592-597.
Maekawa, Y., Majima, Y., Kawano, T., Katagiri, M.,
2013. Characteristics of Practical Nursing Knowledge
from Biological Data Analyses of EEG in Performing
Blood Collection, Proceedings of 6th International
Conference on Intelligent Interactive Multimedia
Systems and Services on Knowledge-Based and
Intelligent Information & Engineering Systems,
pp.251-260.
Teplan, M., 2002. Fundamentals of EEG measurement,
Measurement Science Review, Volume 2, Section 2,
pp.1-11.
Watanabe, T., Ogikubo, M., Ishii, Y., 2004. Visualization
of respiration in the embodied virtual communication
system and its evaluation, International Journal of
Human-Computer Interaction Vol.17, No.1, pp.89-
102.
Inter-brain Synchronization between Nurse and Patient During Drawing Blood
511
