
A Hypercube Queuing Model Approach
to the Police Units Allocation Problem
Nilson Felipe Matos Mendes and Andr
´
e Gustavo dos Santos
Departamento de Inform
´
atica, Universidade Federal de Vic¸osa, Av. P. H. Rolfs s/n - 36570-900 Vic¸osa, MG, Brazil
Keywords:
Optimization, Stochastic Model, Police Allocation, Hypercube Queuing Model, Metaheuristics.
Abstract:
Providing security requires efficient police services. Considering this, we deal in this paper with the police
units allocation problem. To describe the problem a probabilistic model based on Hypercube Queuing Model
is proposed. Considering an action radius and constraints for minimal coverage and mandatory closeness,
the model aims to allocate police units on several points of an urban area to minimize the expected distance
traveled by these units when they are answering calls for service. A VND heuristic is used to solve the
model, and we analyse the improvement of using a Tabu Serach method instead of a random initialization. We
experiment the methods in scenarios with different parameters values to verify the robustness and suitability
of the proposed model. The results presented a high influence of service time on solutions quality, some
difficulties in getting feasible solutions.
1 INTRODUCTION
Public safety is one of the main concerns in the mod-
ern society and has direct impact on the quality of life.
Brazil is a notable case where the violence actions af-
fect the wellfare of all social classes.
As presented in (Waiselfisz, 2013), the homi-
cide rate per 100 thousand people was 11,7 in 1980,
reaches 28,9 in 2003, and has barely lowered to 27,1
in 2011. In 2013, over 50 thousand people were killed
in the country, besides around 1,2 million robberies
and 50 thousand rapes (F
´
orum Nacional de Seguranc¸a
P
´
ublica, 2013). These numbers put Brazil as one of
the most violent countries in the world, even when
considering those involved on wars (Cerqueira, 2005).
Some of important causes of this situation are
strategic and technical failures on the area of pub-
lic safety management. We can highlight the lack of
training of police force in many aspects, as those re-
lated with use of external resources, statistics, histor-
ical informations or softwares and digital devices for
helping their work.
Considering the context described, in this paper
we propose a mathematical model to describe and op-
timize the problem of police unit allocation. This
model aims to work on two factors which directly af-
fects the perception of violence and satisfaction with
police services (Cihan et al., 2012): police units visi-
bility and speedy response to calls for service.
The model aims to reduce the expected distance
traveled within an action radius for responding calls
for service and to provide a minimal expected cover-
age beside ensuring a mandatory expected proximity
among all points within an urban area to at least one
patrol unit.
The model presented is based on the Minimum
Expected Response Location Problem (MERLP), a
stochastic model proposed originally for emergency
medical services by Rajagopalan and Saydam (Ra-
jagopalan and Saydam, 2009) that has good results
on this field. This model, in turn, was built over fun-
damentals of the Hypercube Queuing Model (Larson,
1974), which describes queuing systems where the
servers go towards the clients in a determined loca-
tion, such as in emergence services.
The contribution brought by our paper is a model
that corrects and turns the MERLP more general, by
adding constraints of mandatory expected response
coverage and also support for servers of different
kinds (cars, motorcycles, police agents on foot, etc...).
The last feature does not change directly the model,
but impacts the solutions evaluation. Furthermore, the
number of vertex and edges on the graph used in this
paper is much bigger than in previous works.
In order to solve the presented model, we use a
heuristic based on the VND (Variable Neighborhood
Descent) metaheuristic. The main goal, however, is
not to test the efficiency of the heuristic proposed in
70
Mendes, N. and Santos, A.
A Hypercube Queuing Model Approach to the Police Units Allocation Problem.
In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS 2016) - Volume 2, pages 70-81
ISBN: 978-989-758-187-8
Copyright
c
2016 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

solving the model, but to show the suitability of using
this model to describe the problem. In other words,
we argue in this work that once the model proposed
is quickly solvable by using the VND heuristic and
presents solutions that satisfy the scenarios tested, it
may be useful for real contexts.
In the next sections, we present the details of the
proposed model and the solving approaches experi-
mented. On section 2, we present a review of previous
works about problems related with this one. Next, in
section 3, the Hypercube Queuing Model and the ap-
proximative method for estimating the parameters of
this model, the Jarvis Approximation, are presented.
On section 4, we present the models used as base for
the model proposed and the VND heuristic for solving
it. After that, section 5 explains how the experiments
were performed ending up on section 6 with a discus-
sion of results.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
According to Larson (Larson, 1974), one of the first
researches that focus the police work was published in
a book by Smith (Smith, 1961) in 1961. The work was
about the design of sectors for patrol beats, aiming to
minimize the mean intersector travel time.
In the late 60’s, the New York City Rand Insti-
tute (NYCRI) was founded, conducting a profund im-
pact research on the area of emergence services mod-
els (Green and Kolesar, 2004), as such the Hyper-
cube Queuing Model (Larson, 1974), explained on
next section; and the Patrol Car Allocation Model
(PCAM) (Chaiken and Dormont, 1976): a software
that uses results from Queue Theory to assist police’s
departments in determining the number of patrols cars
and their locations while on duty (Larson and Rich,
1987), that is still used in more recent researches, as
in (D’Amico et al., 2002a).
On late 80’s and early 90’s, criminology experi-
ments showed the high concentration of call or inci-
dents at few places in a city (denominated hot spots)
and the efficacy of a geographically focused police
service (Telep and Weisburd, 2012) (Weisburd and
Eck, 2004), generating several studies around this
fact, as those described on (Keskin et al., 2012),
(Chawathe, 2007) and (Li et al., 2011). The first aims
to determine, for several police cars, patrol routes on
highways to visit hot spots, while they are “hot”, in
other words, during a specific period of the day (on
one or more days) when more car crashes happens.
The second builds a model where a city is a graph,
each street considered an edge and each corner a ver-
tex. With each street having a weigh, corresponding
to its “hotness”, and a length, the author defines a
strategy to get the route with higher density. The last
uses an algorithm based on cross-entropy for building
a randomized route, point by point, through a Markov
Chain Model.
Some papers swap the concept of hot spot by the
concept of target, that are specific points on a area.
We cite in this direction (Basilico et al., 2012) and
(Perrucci, 2011), which uses a game theory to guide a
robot in a graph. The first looks for a leader-follower
equilibrium and the second aims to find the shortest
path to visit all targets.
The above mentioned papers which deal with hot
spots or target concepts are routing problems. Pa-
trolling routes are also object of study of other papers,
not using those concepts. We cite some that build
non-deterministic routes based on Markov Chains
Model (Chen, 2013) (Ruan et al., 2005) (Lin et al.,
2013), and (Vasconcelos, 2008) that uses a genetic al-
gorithm for calibrating routing simulation parameters.
Papers dealing with the issue of dividing a area in
several disjoint police districts are also relevant. We
can cite (D’Amico et al., 2002b) that uses a simulat-
ing annealing approach; a comparative work devel-
oped by Zhang et. al. (Zhang et al., 2013), where
three methods for district design had their result put
side by side. It is also notable the series of stud-
ies conducted by Zhang and Brown. The first de-
scribed at (Zhang and Brown, 2013) a simulation and
a geographic information system were used to reg-
ister the call of service data as a base to create dis-
tricts with workload balance; the second (Zhang and
Brown, 2014a) describes an adjusted simulated an-
nealing and finally (Zhang and Brown, 2014b) uses a
sophisticated method of response surface for the same
objectives.
More related with this paper subject, on police
duty context, coverage problems are studied by Sal-
adin (Saladin, 1982), who created a goal program-
ming model to police patrol allocation, using PCAM
to evaluate the solutions found; Curtin et. al. (Curtin
et al., 2010), that deal with a coverage and a backup
coverage model, where in the last, the objective is to
get the maximum coverage by at least two police units
on each point; And Mendes et. al (Mendes et al.,
2014) and Mendes and Santos (Mendes and dos San-
tos, 2015), that proposed a model for maximizing a
profit related with a coverage, with mandatory close-
ness constraints using patrol units with different ac-
tion radius.
More inovative models were proposed by
Dell’Olmo et. al. (Dell’Olmo et al., 2014) and Araz
et. al. (Araz et al., 2007). The first models safety
camera allocation, for traffic surveillance, where a
A Hypercube Queuing Model Approach to the Police Units Allocation Problem
71

set of cameras changes their positions through time
to avoid to be memorized by drivers who try to
hide their infractions. The second model is a fuzzy
multi-objetive model, for dealing with the uncertainty
of emergency services.
For those who want a more deep view of re-
searches developed in this subject, we suggest the sur-
veys written by Simpson and Hancook (Simpson and
Hancock, 2009), Maltz (Maltz, 1996) and Green and
Kolesar (Green and Kolesar, 2004).
3 THEORICAL BACKGROUND
In this section we present a brief description of the
theorical background of our model. A detailed expla-
nation of the themes presented here can be found at
the original papers (Larson, 1974), (Jarvis, 1985) and
in the tutorial written by Chiyoshi et. al. (Chiyoshi
et al., 2011).
The Hypercube Queuing Model (henceforth refer-
enced as HQM) is a queuing model proposed by Lar-
son at 1974 to address problems of facility location
and design of action areas (Larson, 1974). HQM has
showed itself a powerful tool to describe any queuing
system where the servers need to go where clients are.
In the queuing system described by HQM, a fi-
nite set V of points j ∈ V represents the location of
clients and and a subset of V represents the position
of servers. With this configuration, is calculated the
time required to any server arrive at any client from
its positions. Then, for each client a server dispatch
order is fixed, with the closer servers being first.
Once a call for service arrives on the system from
a point j, the first idle server following the dispatch
order is selected to answer the call.
In our implementation, when all servers are busy,
the call is ignored and not answered (loss systems).
To represent a state s, HQM uses a n-uple of 0’s
and 1’s, where each digit represents the current state
of a single server (0 if a server is idle and 1 other-
wise). For instance, a system with 4 servers can as-
sume states such as: s
1
= (1,0,0, 1) or s
2
= (0,0,1, 1),
where this last represents a state with servers 1 and 2
busy. Designing state trasition graph we get a hyper-
cube. This result gives to HQM its name.
To estimate the performance measures of this
queuing system, it is necessary to calculate the steady
state probabilities of being in each state. For each
state one equation is built. This generates a linear sys-
tem that has 2
n
equations and unknowns to be solved
for getting all steady state probabilities. For any rea-
sonable number of servers, this resolution becomes
costly in terms of computer time.
To deal with this problem we use the Jarvi’s Ap-
proximation, a generalization of the approximation
proposed by Larson (Larson, 1975), where the service
time distribution can be a general distribution depen-
dent on both client and server (Rajagopalan and Say-
dam, 2009).
The Jarvi’s Approximation consists basically on
a iterative method for calculating the busy probabil-
ity of servers. To do this, it relaxes the servers inter-
dependence, treating servers busy probabilities as be-
ing independent. Then, for trying to correct errors
caused by this assumption, a Q(m, ρ,k) factor is de-
fined as bellow:
Q(m,ρ, j) = C
m−1
∑
k= j
(m − k)(m
k
)(ρ
k− j
)
(k − j)!
∀ j ∈ V (1)
C =
(m − j − 1)!
m!(1 − P
m
)
j
∗
P
0
1 − ρ(1 − P
m
)
(2)
The Q(m,ρ, j) factor value (Equations (1) and (2)), is
a function of the number of servers m, probability of
the all nodes being idle P
0
, the probability of all nodes
being busy P
m
, and the average system busy probabil-
ity ρ = λτ/m, where τ is the system wide mean ser-
vice time and λ the system wide arrival rate.
The values involved in the evaluation of Q(m,ρ, j)
factor, together with the number of servers m, as well
as ρ and τ have their value fixed through an iterative
method, that converges in few iterations. This method
begins with the initialization of ρ
i
and τ, made by
Equation (3) and (4) respectively.
ρ
i
=
∑
j:α
j1
=i
λ
j
τ
i j
∀i (3)
τ =
n
∑
j=1
λ
j
λ
τ
α
j1
, j
(4)
These equations basically make this estimation
through the values of the total demand λ and individ-
ual node demand λ
j
, as well as the expected service
time of server i on point j, represented by τ
i j
. Note
that this evaluation uses yet a variable α
jl
that defines
the index of this l
th
preferred server for responding a
demand at node j.
After this first step, we can estimate ρ (as afore-
mentioned), P
0
and P
m
, following the Erlang’s Loss
Formula for M/M/m/K queues, with K = m.
Then, we use the Q factor value to update ρ
i
val-
ues, making it equal to
V
i
V
i
+1
, where V
i
is defined as
bellow:
V
i
=
m
∑
k=1
∑
j:a
jk
=1
λ
j
τ
i j
Q(m,ρ, k − 1)
k−1
∏
l=1
ρ
a
jl
∀i (5)
If the maximum variation between the previous and
the current values of ρ
i
is lower than a specified small
ICEIS 2016 - 18th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
72

ε > 0 (in this implementation 0.10), the method stops.
Otherwise, f
i j
, the probability of a server i to be as-
signed to respond a demand at node j, is evaluated,
through Equation (6) and normalized with Equation
(7). For calculating this probability, it is necessary to
know that the server i is the k
th
preferred server to re-
spond a demand at node j and the value of its busy
probability ρ
i
.
f
i j
= Q(m,ρ, k − 1)(1 − ρ
i
)
k−1
∏
l=1
ρ
α
jl
∀i, j (6)
f
0
i j
= f
i j
1 − P
m
∑
m
i=1
f
i j
(7)
Finally, τ in Equation (8) value is updated, and the
method goes to a new iteration, beginning from the
update of Q(m,ρ, k) factors.
τ =
n
∑
j=1
λ
j
λ
"
m
∑
i=1
τ
i j
f
i j
1 − P
m
#
(8)
Once the method converges, the Q(m,ρ,k) factor and
ρ
i
values are used as a good approximation to the
HQM.
4 MATERIAL AND METHODS
4.1 Police Units Allocation Model
The Police Units Allocation Model used here was pre-
viously proposed by Mendes e Santos (Mendes and
dos Santos, 2015) for defining an allocation of diverse
kinds of police units in an urban area for maximizing
the profit related with the allocation. It is a version
of the Maximal Coverage Problem with mandatory
closeness constraints, defined by Church e ReVelle
(Church and ReVelle, 1974) that supports a set Q of
unit types with different coverage radius.
In this model, the city is defined as a graph with
a set of segment streets E and corners V . Each seg-
ment r ∈ E has a length and a covering profit. The
time spent to travel from a corner to other depends
of factors like distance, speed of the type unit, traf-
fic sense, period of the day, passage forbidden for the
units, among others, provided in advance, or obtained
in a real time flow through of softwares that could
colect all this data.
The decision variable x
i j
defines how many units
of type i are located at corner j. The auxiliary binary
variables a
r
and a
0
r
define if the street segment r is
reached by any assigned police unit in a time lower
than T
MAX
and 2T
MAX
respectively, where T
MAX
is a
travel time limit from the position of any unit position
to a point to be considered covered, and 2T
MAX
is the
maximal distance allowed from a point to the closest
unit.
The model is presented bellow:
maxZ =
∑
r∈E
l
r
a
r
(9)
∑
j∈V
x
i j
≤ U
i
, ∀i ∈ Q (10)
a
r
≤
∑
i∈Q
∑
j∈V
p
r ji
x
i j
∀r ∈ E (11)
a
0
r
≤
∑
i∈Q
∑
j∈V
p
0
r ji
x
i j
∀r ∈ E (12)
∑
r∈E
a
0
r
= |E| (13)
x
i j
∈ Z
+
, ∀i ∈ U, j ∈ V (14)
a
r
∈ {0,1}, ∀r ∈ E (15)
a
0
r
∈ {0,1}, ∀r ∈ E (16)
The objective function (9) maximizes the sum of the
profits l
j
of covered street segments a
j
. Constraint
(10) states that the number of units of each type allo-
cated cannot exceed U
i
, the number of units of type
i available. In constraints (11) and (12), the param-
eters p
r ji
and p
0
r ji
defines if the time spent to reach
a street segment r with an unit of type i located at j
is lower than T
MAX
and 2T
MAX
respectively, determin-
ing which streets segments are covered. In constraint
(13), the mandatory closeness is defined, stating that
all nodes should be reachable from an unit location in
a time lower or equal than 2T
MAX
. Finally, the others
constraints (14), (15) and (16) define the valid values
of the variables.
4.2 Minimum Expected Response
Location Problem
The term Minimum Expected Response Location
Problem (MERLP) is a denomination created by Ra-
jagopalan and Saydam to the models presented by
them for addressing the problem ambulance allo-
cation in an urban area (Rajagopalan and Saydam,
2009). In this section we show a version of the model
called by them MERLP
2
in their paper, chosen due
to the fact of being the queuing model with greater
resemblance with the police units allocation model
described on the previous section among the models
known by the authors. Some corrections are also pre-
sented.
In MERLP, m non distinguishable ambulances
must be allocated in n points of an area. This allo-
cation is used to define, for each point, a preference
A Hypercube Queuing Model Approach to the Police Units Allocation Problem
73

order to dispatch an ambulance from its position when
a service is required at that point.
Once are available: the number of ambulances, the
position of those ambulances, the dispatching prefer-
ences for each client and the expected response ser-
vice times for each pair of server/client; the Jarvis
Approximation can estimate the values of the Q fac-
tor and the busy probability p
k
of ambulance k. The
model can be thus defined as following:
minZ =
n
∑
j=1
m
∑
k=1
d
jk
h
j
y
j
Q(m,ρ, k −1)(1 − ρ
α
jk
)
k−1
∏
l=1
ρ
α
jl
(17)
"
1 −
∏
k∈N
j
ρ
α
jk
Q(m, ρ, Γ
j
− 1)
#
≥ αy
j
∀ j (18)
n
∑
l=1
∑
k∈N
j
x
lk
= Γ
j
∀ j (19)
n
∑
j=1
h
j
y
j
≥ c (20)
n
∑
j=1
m
∑
i=1
x
i j
= m (21)
x
i j
∈ {0,1} ∀i, j (22)
y
j
∈ {0,1} ∀ j (23)
Γ
j
∈ Z
+
∀ j (24)
Two decision variable sets are used in MERLP. The
first one, y
j
, defines, for each point j if it is covered
(set as 1) or not (set as 0). The second one, x
jk
, defines
if a server k is located at point j.
In the objective function (17), the distance from
an ambulance to a point is multiplied by the prob-
ability that the ambulance will respond a call from
that point and the fraction of calls comming from that
point, represented by the parameter h
j
. This prod-
uct is accounted in the objective value function if the
point is considered covered, which is defined by the
value of variable y
j
.
By its turn, in (18), for each point, the product of
busy probability of all ambulances that can cover that
point is calculated, multiplied by the Q factor. The
result corresponds to the probability of not covering
that point. Then, if, and only if, the probability of
covering is greater than an α reliability level prede-
termined, the point is said covered.
The constraint (19) defines the number of servers
that can cover each node from their position Γ
j
. In the
constraint (20) the minimum fraction of calls c that
must be answered with reliability rate α is set. Finally,
the constraint (21) defines that exactly m servers will
be used.
4.3 MERLP With Mandatory Expected
Closeness Constraints
The model proposed here is called Minimum Ex-
pected Response Location Problem with Mandatory
Expected Closeness Constraint (MERLP-MECC).
This model basically is the MERLP with the set of
constraints (26) to (31) shown bellow and replace-
ment of third parameter of Q factor on constraint (18)
by Γ
j
− κ
j
, generating the equation (25). In other
words, is a merge of the models presented at sec-
tions 4.1 and 4.2, being more similar to this last. This
model improves MERLP by providing a better gen-
eral area coverage, instead of a coverage with lower
distance between the points and lower demand, just
the enough to satisfy the constraint of minimal cover-
age (20).
1 −
∏
k∈N
0
j
ρ
α
jk
Q(m, ρ, Γ
j
− κ
j
)
≥ αy
j
∀ j (25)
1 −
∏
k∈N
0
j
ρ
α
jk
Q(m, ρ, Γ
j
− κ
j
)
≥ βy
j
∀ j (26)
κ
j
≤ Γ
j
∀ j (27)
Γ
j
≤ Mκ
j
∀ j (28)
n
∑
j=1
y
0
j
= n (29)
Γ
j
∈ Z
+
, ∀ j (30)
κ
j
,y
0
j
∈ {0,1}, ∀ j (31)
Now, besides of constraint (18) of MERLP there is a
second constraint (26) for defining which vertex are
covered. The covering verified at (26) is equivalent
to that verified in (12) and is used for stating which
node have an expected coverage greater than a β value
(such as β ≤ α) in a time lower than 2T
MAX
. With the
constraint (26), it is defined that for all j, y
0
j
must be
equal to one, creating a mandatory expected closeness
constraint (29).
Finally, constraints (27) and (28) define the value
of the variable κ
j
, created for avoiding the third ar-
gument of Q factor assume a negative value when the
sum of constraint (19) is equal zero. On equation (28)
a parameter M is set as being any big number greater
than m.
4.4 VND Heuristic
This section presents the algorithm used for solving
the MERLP-MECC. As mentioned in (Rajagopalan
ICEIS 2016 - 18th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
74

and Saydam, 2009), commercial solvers such as
CPLEX are unable to solve MERLP or models de-
rived from it. To deal with this, we use a Variable
Neighboorhood Descent - (VND) heuristic (Mladen-
ovi
´
c and Hansen, 1997) (Talbi, 2009, p .150).
In our approach, three local searches are avail-
able and are selected according to the number of it-
erations without improvement of the best global ob-
jective value. These local searches were inspired on
those tested by (Mendes and dos Santos, 2015), which
have reached good results in exploring the solutions
space. In the best of our knowledge and belief, there
are no studies using this metaheuristic to stochastic
coverage problems similar to this one, although it was
successful used on some location problems as cited in
(Glover and Kochenberger, 2003).
The Algorithm 1 describes the overall scheme of
the VND algorithm here implemented. As can be seen
at line 1, the execution starts with a function for ini-
tializing the solution. This function may build a solu-
tion in a randomized way, choosing where each unit
will be located, unit by unit. A variant proposed uses
the tabu search heuristic proposed by (Mendes and
dos Santos, 2015) for solving the coverage model of
section 4.1, in a strategy similar to that employed by
(Rajagopalan and Saydam, 2009) for finding an initial
feasible solution.
Algorithm 1: VND Heuristic Pseudocode.
1: s∗ ← initializeSolution()
2: s ←s*
3: NoImprove ← 0
4: bestOb j ← Evaluate(s∗)
5: while NoImprove < Max No Improvements do
6: NoImprove + +
7: if NoImprove < 0.8 ∗ m then
8: LSearchOne(s, s∗, NoImprove, bestOb j)
9: else if NoImprove ≤ 1.4 ∗ m then
10: LSearchTwo(s, s∗, NoImprove, bestOb j)
11: else
12: LSearchThree(s, s∗, NoImprove,
bestOb j)
13: return s∗
At line 5, there is a loop controlled by the number
of iterations without improvement of the global best
objective value. The Max No Improvements value
used on final tests is equal to 2m.
For selecting which local search to execute on
each iteration, the number of iterations without im-
provements is used again, as can be seen at lines 7, 9
and 11. The values chosen as limit for changing the
local search used, as the stop criteria described on pre-
vious paragraph, were defined after some preliminary
runs. The objective was to get low run times, without
getting significantly worse solutions.
The local search execution order was also defined
with the objective of reducing the run time, verified
on preliminary runs. It does not follow the common
rule of the VND, that uses broader and more intensive
local searches in advanced steps. The Local Search
Two, for instance, explores a more tight neighborhood
than Local Search One. It is useful for bringing im-
provements on the good solutions already found by
Local Search One, that has no mechanisms to cor-
rect small imperfections. In another hand, the Local
Search Three is a more intensive and broader local
search than the previous, following the VND tradi-
tional behavior.
Local Search One does the following: selects a
unit u by random and then selects 10 nodes from the
set of those that can be reached in a time lower than
T
MAX
from the position of u. After to put the unit u
in each of these then nodes, the node where the best
objective function value was found is choosen as the
new location of unit u. If the lowest value found in
this local search is lower than the best global objec-
tive function value, this value is set as the new best
global objective function, as well as the solution is set
as the best one, and the variable counting the number
of iterations without improvements is reset to zero.
The Local Search Two uses a similar strategy, but
selecting just the adjacent nodes of current position
of the server selected. It evaluates all adjacent nodes,
instead of a subset of them, which differs from Local
Search One.
The Local Search Three is similar to Local Search
One. The differences are the number of nodes se-
lected to the local search (15 now, instead of 10)
and definition of node set from where these 15 nodes
will be selected, which now is the node set reachable
within 2T
MAX
.
Unfeasible solutions are penalized in two ways,
depending of which constraint is not satisfied. When
constraint of minimal coverage (20) is not satisfied,
the objective value is multiplied by the ratio of de-
sired coverage c and the reached coverage of the solu-
tion. When the mandatory closeness constraint (29) is
not satisfied, the objective value is multiplied by the
product m ∗ n and divided by number of nodes cov-
ered following the conditions of (26). This penaliza-
tion is stronger because our intention is to give pri-
ority to satisfy more quickly the mandatory closeness
constraint.
A Hypercube Queuing Model Approach to the Police Units Allocation Problem
75

5 EXPERIMENT DESCRIPTION
For testing the efficiency and efficacy of the VND
heuristic to solve the MERLP-MECC, we build an in-
stance set based on real street track data of Brazilian
city of Vic¸osa, Minas Gerais state, with a population
around 90 thousand people.
The city has its street track data modeled as a
graph, where each street segment is an edge and each
corner a vertex, summing up 5100 edges and 2125
edges. Each edge received a random weight, meaning
the demand on that edge. However, once the model
proposed considers vertex demands instead of ver-
texes demands, they were defined as the sum of inci-
dent edges weight, divided by two, to avoid a doubled
counting.
Regarding to the servers, some configurations of
numbers of units available were defined. Aside this,
their coverage radius was defined as being approxi-
mately the distance which they could reach in a time
interval lower than four minutes, following statistical
data obtained in (Coupe and Blake, 2005) about ef-
fects of quick responses in arrests after burglaries.
Considering the service time as non negligible at
demand point, situations with service time fixed in 15
and 30 were tested. The default total demand was
fixed from medium to low levels, and as a Poisson
random variable, with λ = 7 and λ = 15.
For each instance and method tested, 40 repeti-
tions of execution were performed. The tests were
executed in a computer with processor Intel Core i5-
3300 with 3.00GHz, 8GB of RAM and Windows 8.
6 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Three main measures were chosen for evaluation of
the heuristic quality: objective function value, feasi-
bility and run-time. It is important to say that there
is a strong relation between objective function value
and feasibility. This relation is discussed in along the
text.
In the first subsection, the results with standard
conditions are described, comparing the efficiency of
each method for initializing the VND heuristic. Af-
ter that, once that is confirmed a better performance
of tabu search, we describe the solutions obtained
in more realistic scenarios, with higher demands and
services times.
6.1 Standard Conditions
In the tests described in this section the action ra-
dius of motorcycles is 2,6km; of cars is 2,0km and
of pedestrians units is 0,8km.
Regarding the method of initialize solutions, a de-
tailed comparison between the results found by using
each one of them are presented on Table 1. The two
first columns describe the instance, being the first the
number of units available (pedestrians(P), motorcy-
cles(M) and cars(C) respectively), the second defines
the constants of MERLP-MECC, and the following
the results associated with those instances.
The first point of comparison is the number of fea-
sible solutions (columns V ) found by each method.
What can be seen in this sense is a proximity of per-
formance. In ten of eighteen instances, the tabu search
got a higher value on column V . The random initial-
ization got the better value seven times and in only
one had a tie. This equality can be explained by look-
ing to the columns V
α
and V
β
, that represents the num-
ber of runs where solutions satisfying the constraint
of minimum coverage and mandatory closeness were
obtained, respectivelly. While the tabu search initial-
ization has better results in almost all instances, con-
sidering the V
β
column, it does not maintain this qual-
ity when the column V
α
is observed.
The result described above was partially expected.
Firstly, because the tabu search aims, in some way, to
satisfy the mandatory closeness constraint (29) of the
MERLP-MECC, once it needs to respect the manda-
tory closeness constraint of Police Units Allocation
Model. When the algorithm do this, it can deliver
a solution far from satisfying the constraint of min-
imum coverage (20).
We can see also in Table 1 an equilibrium among
the best feasible solutions found by each method
(columns min
OF
f easible). Beside this, we observe
that in the majority of the instances, in special on
those with motorcycles available, the average run-
time (µ
t
) of VND with tabu search initialization was
close to the version with random initialization. This
indicates that the additional time spent on execution
of tabu search heuristic is not significant and pre-
serves the low average run-time.
This scenario of equality seems to disappear when
the average objective value found by each initializa-
tion method is observed. The values obtained using
the tabu search initialization were significantly better
in all instances with no motorcycles. In the remain-
ing instances, the results were almost equal in four of
them, with a slightly advantage to random initializa-
tion.
Both results presented on the last two paragraphs
can be attributed to the better performance of tabu
search in satisfying the mandatory closeness con-
straints (29), that is more penalized when not satis-
fied. It is notable yet that once the motorcycles are
ICEIS 2016 - 18th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
76
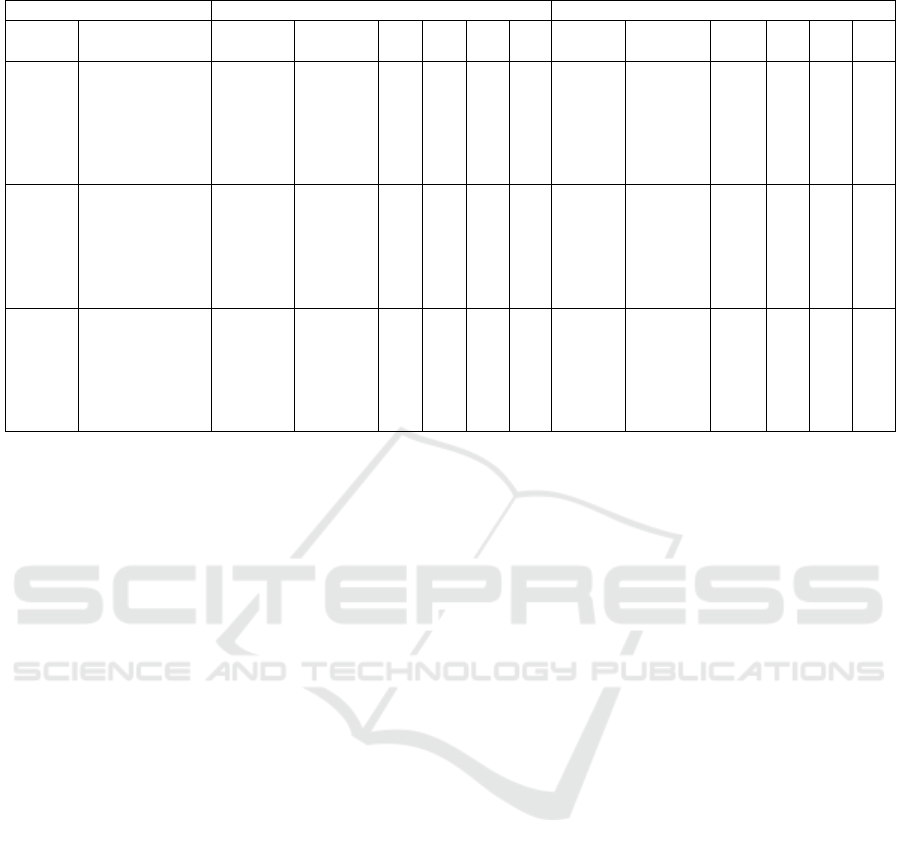
Table 1: Comparison of results found by the VND heuristic with different initializations.
Instances Random initialization Tabu search initialization
P/M/C α;β;c µ
OF
min
OF
f easible
µ
T
V
α
V
β
V µ
OF
min
OF
f easible
µ
T
V
α
V
β
V
7/0/7
0,90 ; 0,50 ; 60 9407,5
1265,8
6 16 22 13 3771,6
1422,8
13 20 32 18
0,90 ; 0,50 ; 80 9065,8
1882,0
8 4 23 3 4185,5
1758,4
14 3 34 3
0,95 ; 0,60 ; 60 9619,6
1427,1
6 9 21 8 4935,7
1058,7
11 11 30 11
0,95 ; 0,60 ; 80 9039,7
1943,1
7 2 26 2 4143,4
-
13,7 0 32 0
0,99 ; 0,75 ; 60 7121,0
1243,9
5 13 27 12 2848,5
1164,7
13 18 32 18
0,99 ; 0,75 ; 80 11764,0
1819,2
7 2 22 2 3527,0
1741,5
13 3 36 3
8/0/8
0,90 ; 0,50 ; 60 6952,1
1356,8
8 20 19 17 1584,8
1207,4
13 19 40 19
0,90 ; 0,50 ; 80 10797,2
2073,2
9 3 25 3 1796,2
1665,4
16 4 40 4
0,95 ; 0,60 ; 60 6430,5
1258,2
7 24 30 19 2117,7
1252,0
14 16 39 16
0,95 ; 0,60 ; 80 10742,3
1610,6
9 7 26 6 2717,1
1829,3
18 3 39 3
0,99 ; 0,75 ; 60 7020,7
1128,4
7 15 29 15 1470,3
1154,7
14 17 40 17
0,99 ; 0,75 ; 80 11839,7
1694,8
9 8 24 8 3041,3
1830,2
17 5 37 5
5/5/5
0,90 ; 0,50 ; 60 1877,0
1243,6
8 36 40 36 348,8
1263,6
14 37 40 37
0,90 ; 0,50 ; 80 1967,0
1746,6
13 19 40 19 1998,0
1811,2
15 20 40 20
0,95 ; 0,60 ; 60 1785,2
1511,6
9 35 40 35 1941,0
1284,6
13 33 40 33
0,95 ; 0,60 ; 80 1954,5
1894,0
9 14 40 14 2045,8
1830,5
13 21 40 21
0,99 ; 0,75 ; 60 1791,7
1351,6
6 30 40 30 2464,3
1511,7
10 28 39 28
0,99 ; 0,75 ; 80 1931,6
1702,7
11 15 40 15 1997,6
1877,5
14 13 40 13
included there is a high improvement on quality of
solutions obtained through the random initialization,
while this does not happen with solutions provided by
the VND when initialized with tabu search.
For assuring definitely the difference of perfor-
mances among the two methods of initialization,
a two-way ANOVA test with repetitions was per-
formed. With these data, when compared the over-
all average objective function value of solution, better
values were found when tabu search initialization was
used. Beside this, a p-value around 5, 0 ∗ 10
−29
was
found, with a critical value of F equals to 3,85 and F
equals to 130,8, conditions that are sufficient to dis-
card the hypothesis of results equality.
6.2 Results with Demand and Service
Time Variations
After we have certified the efficiency of tabu search
initialization, in this section we describe the results of
the sensitivity tests performed. These tests were done
to observe the changes on solutions quality caused by
variations on demand and service time values.
A first overview of results is presented on Table
2. In this table the solutions obtained with the de-
fault demand (λ = 7) and doubled demand (λ = 15)
are compared.
One surprisingly result was referent to the number
of feasible solutions obtained. In ten of eighteen in-
stances more feasible solution on runs with demand
doubled were found and, in another two there was
a tie. Looking to the components of these numbers
(columns V
α
and V
β
), we can note that the values of
V
β
have dropped, and mainly, the values of V
α
have
increased. It maybe did the likelihood of a solution to
be feasible improves.
However, this result is not reflected on the aver-
age values of objective function. Observing this mea-
sure, the values obtained on runs with doubled de-
mand were always worse. It is an effect of the higher
distance traveled for responding the calls for service.
When we look to the minimum objective value
among the feasible solutions we see that the increase
of demand makes the objective values worse. This
does not mean, necessarily, that the solutions are
worse. The same allocation can have different ob-
jective values with different total demands due to the
impact on the value of Q factor, that depends indi-
rectly of value of λ. In the other hand, it is important
to note that the parameter h
j
continues with the same
values if the edges have their demands multiplied by
the same factor, as we done, because it represents a
fraction of total demand instead of an absolute value.
In the following tests, we abandoned the simpli-
fication of considering the service time equals to the
travel time from the unit location to the demand node.
The doubled demand was kept for providing a de-
scription of a more realistic scenario.
Two values of average service time were used, 15
minutes (1/4 hour) and 30 minutes (1/2 hour). Those
times were added to the travel time from the unit po-
sition to the demand node and was not accounted the
time spent to return.
On the Fig. 1 a comparative of the number on fea-
sible solutions, as such the number of solutions sat-
isfying the constraints of minimal coverage (20) and
A Hypercube Queuing Model Approach to the Police Units Allocation Problem
77
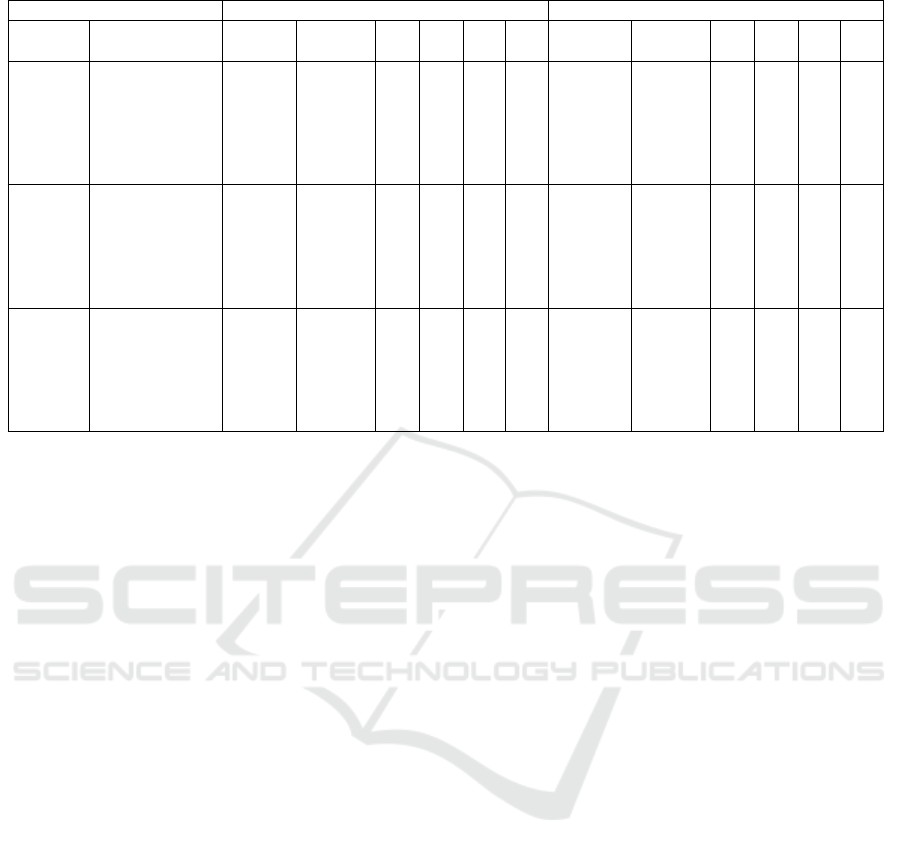
Table 2: Comparison of results found by the VND heuristic with different levels of demand.
Instances Default demand Doubled demand
P/M/C α;β; c µ
OF
min
OF
f easible
µ
T
V
α
V
β
V µ
OF
min
OF
f easible
µ
T
V
α
V
β
V
7/0/7
0,90 ; 0,50 ; 60 3771,6
1422,8
13 20 32 18 9525,4
1573,5
11 18 21 18
0,90 ; 0,50 ; 80 4185,5
1758,4
14 3 34 3 7885,5
-
12 0 29 0
0,95 ; 0,60 ; 60 4935,7
1058,7
11 11 30 11 6873,5
1973,5
12 24 30 24
0,95 ; 0,60 ; 80 4143,4
-
14 0 32 0 9772,3
3636,1
11 3 28 3
0,99 ; 0,75 ; 60 2848,5
1164,7
13 18 32 18 11189,3
2831,8
12 21 25 19
0,99 ; 0,75 ; 80 3527,0
1741,5
13 3 36 3 11395,4
2961,0
11 3 24 3
8/0/8
0,90 ; 0,50 ; 60 1584,8
1207,4
13 19 40 19 4485,5
1587,4
15 25 33 25
0,90 ; 0,50 ; 80 1796,2
1665,4
16 4 40 4 6178,7
2966,7
14 5 29 5
0,95 ; 0,60 ; 60 2117,7
1252,0
15 16 39 16 8347,1
1012,1
14 23 26 22
0,95 ; 0,60 ; 80 2717,1
1829,3
18 3 39 3 7425,0
2764,3
15 7 30 7
0,99 ; 0,75 ; 60 1470,3
1154,7
14 17 40 17 4111,0
1551,1
14 23 30 23
0,99 ; 0,75 ; 80 3041,3
1830,2
17 5 37 5 8251,8
2572,0
13 8 27 8
5/5/5
0,90 ; 0,50 ; 60 1948,1
1263,6
14 37 40 37 3099,8
1174,4
15 36 39 36
0,90 ; 0,50 ; 80 1998,0
1811,2
15 20 40 20 2978,3
2878,2
16 12 39 12
0,95 ; 0,60 ; 60 1941,0
1284,6
13 33 40 33 2909,6
1862,0
16 31 38 31
0,95 ; 0,60 ; 80 2045,8
1830,5
13 21 40 21 3099,5
2675,4
15 16 39 16
0,99 ; 0,75 ; 60 2464,3
1511,7
10 28 39 28 3620,7
1094,3
14 36 37 35
0,99 ; 0,75 ; 80 1997,6
1877,5
14 13 40 13 2785,4
2837,5
13 8 37 8
mandatory closeness (29) is presented. Each bar color
represents a different average service time.
The instances without motorcycles (with IDs from
0 to 11) presented low levels of satisfactibility of min-
imum coverage constraint (20). These levels do not
decreased much with the rise of service time, being
the higher variation a decrease of 37,5% when com-
pared the first and third column, at instance 11. How-
ever, in the instances with motorcycles, the variations
were bigger, with decreases of at least 25%, except to
the instances 14 and 17, on the second column.
The three central columns of Fig. 1 present the
number of solutions satisfying the mandatory close-
ness constraint (29). As we can see, these numbers
are more regular than those related to the first three
columns. They are no just higher, but neither have
big oscillations between the instances. Although the
scores were higher in instances with motorcycles (IDs
12 to 17) with the default service time, this difference
become irrelevant in tests with 30 minutes of service
time.
This result lead us to an intuitive conclusion: as
longer the average service time, less relevant the type
of vehicle used by the unit, because the travel time
starts to be just a minor variable. It does not mean,
however, that the location of units also becomes less
relevant. It is desirable to put more units for cover-
ing places with higher demand, even when the speed
of these units does not impact significantly the total
service time.
The number of feasible solutions (showed on the
last three columns) follows approximately the num-
bers of the three first columns and it is not much in-
fluenced by the three central columns. This result
suggests that the number of solutions respecting the
constraint of minimal coverage is the bottleneck of
solutions feasibility.
7 CONCLUSION
In this paper we addressed the police unit allocation
model, presenting a hypercube queuing model to de-
scribe it and a VND heuristic approach to solve this
model. Our objective was mainly show the suitability
and viability of using the proposed model (MERLP-
MECC) and the hypercube queuing approach to de-
scribe a realistic scenario of police unit allocation
where mandatory closeness constraint are presented.
Considering this objective, we can state that this
model is able to deal with a realistic scenario of locat-
ing police units. The presence of feasible solutions on
many of situations tested and the low run time spent to
find them are evidences sufficiently strong to confirm
this statement.
Regarding to the tests of VND efficiency to solv-
ing the model, basically three measurements were
considered: run-time, feasibility and objective func-
tion value. At the majority of the analysis, we focused
the solutions feasibility and its influence on average
objective function values.
Although we have found satisfactory values in
both measures to some instances, few feasible solu-
tions were found.
The problem with feasibility of solution, however,
was already expected, once it was reported by (Ra-
ICEIS 2016 - 18th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
78

Figure 1: Number of feasible solutions got by VND with Tabu Search initialization using different services times.
jagopalan and Saydam, 2009) which introduced the
MERLP, that was used as base to the MERLP-MECC.
On our paper, whose model contains more constraints
and the instances have tights action radius, this diffi-
cult would naturally appear. Beside this, as we have
mentioned on previous section, the number of solu-
tions satisfying the minimum coverage constraint can
be a bottleneck for getting feasible solutions. Our in-
tuition says that maybe through a strongest penalty
when the minimum coverage constraint was not re-
spected this problem could be solved. This hypothesis
is a point to be tested on future works.
We highlight however that the feasibility, although
desirable, is not always mandatory for our proposes.
Almost feasible solutions could be satisfactory and
some relaxations can be adopted on real situations,
without a degradation of coverage quality, as for ex-
ample, the lowering the α or β values, to adapt to
some less probable scenarios. Some authors have
used goal programming (Saladin, 1982) and fuzzy
programming approaches (Araz et al., 2007) for deal-
ing specifically with those situations.
We have seen also that the results obtained here
were not so dependent of demand rates but, in another
hand, the service time has a big impact on solutions
quality. With the absence of these information, esti-
mates may be done based on the literature, as we did,
but if they were not near from real numbers, the effi-
ciency of model to suggest a good allocation can be
strongly affected.
Another question, that was not dealt on the text,
but can be problematic is the imbalance of work-
load. The MERLP, as the MERLP-MECC, does not
make any consideration about balancing the work-
load. This could be done with additional constraints
on the model or a multi-objective approach, which
can be a good source for future researches.
Another possibility is to built new models that not
just states where police units should stay, but how
they could patrol areas close to where they were put
for optimizing some objective. Integrated models like
this, that joins a coverage and a routing problem are
still rare on the literature and can be explored starting
from good deterministic or stochastic models.
Finally, a possibly more useful and hard to accom-
plish continuation to this research would be a study of
case of implementation of this model in a city. This
last suggestion is more challenging due to the ethical
issues and bureaucracy involved.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors acknowledge CAPES, FAPEMIG and
GAPSO for the partial funding of the project. The first
author worked in the project with funding of CAPES.
REFERENCES
Araz, C., Selim, H., and Ozkarahan, I. (2007). A
fuzzy multi-objective covering-based vehicle location
model for emergency services. Computers & Opera-
tions Research, 34(3):705 – 726. Logistics of Health
Care Management Part Special Issue: Logistics of
Health Care Management.
Basilico, N., Gatti, N., and Amigoni, F. (2012). Patrolling
security games: Definition and algorithms for solv-
A Hypercube Queuing Model Approach to the Police Units Allocation Problem
79

ing large instances with single patroller and single in-
truder. Artificial Intelligence, 184:78–123.
Cerqueira, D. (2005). O jogo dos sete mitos e a mis
´
eria da
seguranc¸a p
´
ublica no Brasil. IPEA, Rio de Janeiro.
Chaiken, J. M. and Dormont, P. (1976). A patrol car alloca-
tion model. Technical report, DTIC Document.
Chawathe, S. S. (2007). Organizing hot-spot police patrol
routes. In Intelligence and Security Informatics, 2007
IEEE, pages 79–86. IEEE.
Chen, X. (2013). Police patrol optimization with security
level functions. Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Sys-
tems, IEEE Transactions on, 43(5):1042–1051.
Chiyoshi, F., Iannoni, A. P., and Morabito, R. (2011).
A tutorial on hypercube queueing models and some
practical applications in emergency service systems.
Pesquisa Operacional, 31(2):271–299.
Church, R. and ReVelle, C. (1974). The maximal cover-
ing location problem. Papers of the Regional Science
Association, 32(1):101–118.
Cihan, A., Zhang, Y., and Hoover, L. (2012). Police re-
sponse time to in-progress burglary a multilevel anal-
ysis. Police Quarterly, 15(3):308–327.
Coupe, R. T. and Blake, L. (2005). The effects of patrol
workloads and response strength on arrests at burglary
emergencies. Journal of Criminal Justice, 33(3):239–
255.
Curtin, K. M., Hayslett-McCall, K., and Qiu, F. (2010). De-
termining optimal police patrol areas with maximal
covering and backup covering location models. Net-
works and Spatial Economics, 10(1):125–145.
D’Amico, S. J., Wang, S.-J., Batta, R., and Rump, C. M.
(2002a). A simulated annealing approach to police
district design. Computers & Operations Research,
29(6):667–684.
D’Amico, S. J., Wang, S.-J., Batta, R., and Rump, C. M.
(2002b). A simulated annealing approach to police
district design. Computers & Operations Research,
29(6):667 – 684. Location Analysis.
Dell’Olmo, P., Ricciardi, N., and Sgalambro, A. (2014).
A multiperiod maximal covering location model for
the optimal location of intersection safety cameras on
an urban traffic network. Procedia - Social and Be-
havioral Sciences, 108(0):106 – 117. Operational
Research for Development, Sustainability and Local
Economies.
F
´
orum Nacional de Seguranc¸a P
´
ublica (2013). 8
o
anu
´
ario
de seguranc¸a p
´
ublica. Technical report.
Glover, F. and Kochenberger, G. A. (2003). Handbook of
metaheuristics. Springer Science & Business Media.
Green, L. V. and Kolesar, P. J. (2004). Anniversary arti-
cle: Improving emergency responsiveness with man-
agement science. Management Science, 50(8):1001–
1014.
Jarvis, J. P. (1985). Approximating the equilibrium behavior
of multi-server loss systems. Management Science,
31(2):235–239.
Keskin, B. B., Li, S. R., Steil, D., and Spiller, S. (2012).
Analysis of an integrated maximum covering and pa-
trol routing problem. Transportation Research Part
E: Logistics and Transportation Review, 48(1):215 –
232. Select Papers from the 19th International Sym-
posium on Transportation and Traffic Theory.
Larson, R. C. (1974). A hypercube queuing model for facil-
ity location and redistricting in urban emergency ser-
vices. Computers & Operations Research, 1(1):67–
95.
Larson, R. C. (1975). Approximating the performance of
urban emergency service systems. Operations Re-
search, 23(5):845–868.
Larson, R. C. and Rich, T. F. (1987). Travel-time analysis of
new york city police patrol cars. Interfaces, 17(2):15–
20.
Li, L., Jiang, Z., Duan, N., Dong, W., Hu, K., and Sun, W.
(2011). Police patrol service optimization based on
the spatial pattern of hotspots. In Service Operations,
Logistics, and Informatics (SOLI), 2011 IEEE Inter-
national Conference on, pages 45–50.
Lin, K. Y., Atkinson, M. P., Chung, T. H., and Glazebrook,
K. D. (2013). A graph patrol problem with random
attack times. Operations Research, 61(3):694–710.
Maltz, M. D. (1996). From poisson to the present: Applying
operations research to problems of crime and justice.
Journal of Quantitative Criminology, 12(1):3–61.
Mendes, N. F. M. and dos Santos, A. G. (2015). A tabu
search based heuristic for police units positioning. In
2015 Latin American Computing Conference, CLEI
2015, Arequipa, Peru, October 19-23, 2015, pages 1–
11.
Mendes, N. F. M., Santos, A. G., and Gonc¸alves, L. B.
(2014). M
´
etodos para o problema de posicionamento
de unidades policiais. In Anais do XVLI Simp
´
osio
Brasileiro de Pesquisa Operacional, XLVI SBPO,
pages 639–650.
Mladenovi
´
c, N. and Hansen, P. (1997). Variable neigh-
borhood search. Computers & Operations Research,
24(11):1097–1100.
Perrucci, A. (2011). Algoritmi esatti per la ricerca di strate-
gie ottime nel problema di pattugliamento con singolo
pattugliatore.
Rajagopalan, H. K. and Saydam, C. (2009). A minimum ex-
pected response model: Formulation, heuristic solu-
tion, and application. Socio-Economic Planning Sci-
ences, 43(4):253–262.
Ruan, S., Meirina, C., Yu, F., Pattipati, K. R., and Popp,
R. L. (2005). Patrolling in a stochastic environment.
Technical report, DTIC Document.
Saladin, B. A. (1982). Goal programming applied to police
patrol allocation. Journal of Operations Management,
2(4):239 – 249.
Simpson, N. and Hancock, P. (2009). Fifty years of oper-
ational research and emergency response. Journal of
the Operational Research Society, pages S126–S139.
Smith, R. D. (1961). Computer applications in police man-
power distribution. Field Service Division, Interna-
tional Association of Chiefs of Police.
Talbi, E.-G. (2009). Metaheuristics: from design to imple-
mentation, volume 74. John Wiley & Sons.
ICEIS 2016 - 18th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
80

Telep, C. W. and Weisburd, D. (2012). What is known
about the effectiveness of police practices in reduc-
ing crime and disorder? Police Quarterly, page
1098611112447611.
Vasconcelos, D. d. (2008). Gapatrol - uma abordagem evo-
lutiva para otimizac¸
˜
ao de rotas de patrulha policial via
calibrac¸
˜
ao de simulac¸
˜
ao multiagens.
Waiselfisz, J. J. (2013). Mapa da viol
ˆ
encia 2013. homic
´
ıdio
e juventude no brasil. Technical report, Centro
Brasileiro de Estudos Latino Americanos.
Weisburd, D. and Eck, J. E. (2004). What can police do to
reduce crime, disorder, and fear? The Annals of the
American Academy of Political and Social Science,
593(1):42–65.
Zhang, Y. and Brown, D. (2013). Police patrol districting
method and simulation evaluation using agent-based
model & gis. Security Informatics, 2:1–13.
Zhang, Y. and Brown, D. (2014a). Simulation optimization
of police patrol district design using an adjusted simu-
lated annealing approach. In Proceedings of the Sym-
posium on Theory of Modeling & Simulation - DEVS
Integrative, DEVS ’14, pages 18:1–18:8, San Diego,
CA, USA. Society for Computer Simulation Interna-
tional.
Zhang, Y. and Brown, D. (2014b). Simulation optimiza-
tion of police patrol districting plans using response
surfaces. Simulation, 90(6):687–705.
Zhang, Y., Huddleston, S. H., Brown, D. E., and Learmonth,
G. P. (2013). A comparison of evaluation methods
for police patrol district designs. In Proceedings of
the 2013 Winter Simulation Conference: Simulation:
Making Decisions in a Complex World, pages 2532–
2543. IEEE Press.
A Hypercube Queuing Model Approach to the Police Units Allocation Problem
81
