
Study of a Low-cost Sensitive Point-of-Care Testing System using
Screen Printed Biosensors for Early Biomarkers Detection Related to
Alzheimer Disease
Sarah Tonello
1
, Mauro Serpelloni
1
, Nicola Francesco Lopomo
1
, Giulia Abate
2
,
Daniela Letizia Uberti
2
and Emilio Sardini
1
1
Department of Information Engineering, University of Brescia, Via Branze, 38 - 25123 Brescia, Italy
2
Department of Molecular and Translational Medicine, University of Brescia, Via Branze, 38 - 25123 Brescia, Italy
Keywords: Screen Printing, Electrochemical Biosensors, Biomarkers, Alzheimer Disease, Point of Care Testing.
Abstract: Among neurodegenerative diseases, Alzheimer Disease (AD) represents one of the most serious pathology,
for which an early diagnosis is still missing. A peculiar expression of an altered conformational isoform of
p53 protein was reported to be a biomarker able to distinguish AD subjects from healthy population,
quantifiable using a blood-based enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). In order to overcome ELISA
limitations related to reliability and to improve sensitivity, this study aimed to realize a low cost highly
sensitive portable point-of-care (PoC) testing system based on screen printed electrochemical sensors (SPES).
The development of the platform specifically included both the design of the sensing probe and of the
electronic circuit devoted to the conditioning and acquisition of the transduced electric signal. In particular,
silver, carbon and silver-silver chloride were selected respectively to realize conductive tracks, working and
counter electrodes, reference electrode in a three-electrodes configuration focusing on Anodic Stripping
Voltammetry (ASV). The conditioning circuit was designed following the scheme for a common potentiostat,
and produced as a Printed Circuit Board (PCB). Initial testing of the circuit were performed recording changes
in the conductivity of NaCl solution and quantifying electrodes coating with antibodies using Electrochemical
Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS) principle. Preliminary results obtained with saline solution, showed the ability
of the circuit to give the best response corresponding to low changes in NaCl concentration (sensitivity 13
mA/(mg/ml)), suggesting a good sensitivity of the platform. Results from EIS showed the ability of the circuit
to discriminate between different concentrations of antibodies coatings (sensitivity 70 mA/µg). The study is
on-going and after a proper calibration, the circuit is intended to be optimized to quantify unknown
concentration of unfolded p53 in samples of real patients, compared results with the one from ELISA analysis,
aiming to realize a low cost, easy usable and highly precise platform.
1 RESEARCH PROBLEM
The number of people over 65 years is rapidly
increasing; nowadays, in Europe, it represents the
16% of the whole population and this percentage will
reach the 25% within the end of 2030. Ageing usually
conveys several issues, which may include
degenerative or chronic disorders. The impact of
these diseases on the single person and on the whole
society could become huge and difficult to support in
the early future. In this perspective, the actual
researches and innovations are pushing to improve
the understanding of the causes and mechanisms
underlying ageing and the associated diseases, thus to
ensure elderlies with a healthy and active condition.
Among neurodegenerative diseases, Alzheimer
Disease (AD) represents indeed one of the most
investigated and serious pathologies, for which an
early reliable diagnosis is still missing. Therapies
currently available help in fact to alleviate the
symptoms of this disease, but they are not able to
specifically slow down the neurodegenerative
process. AD presents a long pre-symptomatic period,
that could last for 20 years, and which is characterized
by biochemical and molecular events that are able to
foresee the beginning of the disease. The ability to
identify early reliable biomarkers (e.g. proteins) to
effectively diagnose the pathology at an early stage is
one of the actual priority of biomedical research in
term of neurology and geriatrics.
Tonello, S., Serpelloni, M., Lopomo, N., Abate, G., Uberti, D. and Sardini, E.
Study of a Low-cost Sensitive Point-of-Care Testing System using Screen Printed Biosensors for Early Biomarkers Detection Related to Alzheimer Disease.
In Doctoral Consortium (DCBIOSTEC 2016), pages 15-23
15

Recently, among several studies addressing this
issue, different approaches to identify the specific AD
biomarkers have been established and novel one
discussed. To date, the most advanced and accepted
methods to diagnose AD with high specificity and
sensitivity are represented by enzyme-linked
immunosorbent assay (ELISA) measurements in
cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and imaging biomarkers,
like volumetric magnetic resonance imaging and
positron emission tomography, evaluating glucose
utilization or ligands binding to amyloid plaque. In
addition to these methods, a great challenge is
represented by the search for novel biomarkers in
CSF and in blood by using modern potent methods,
such as microarrays, mass spectrometry,
bioinformatics, since only a combined analysis of
several biomarkers seems the promising path to help
in defining a patient-specific diagnose in the future
(Thal et al., 2006; Humpel, 2011)
In this perspective, scientific literature recently
reported how a peculiar expression of an altered
conformational isoform of p53 protein in AD patients
was able to distinguish them from healthy subjects
with a sensitivity of 90% and a specificity of 77%
(Buizza et al., 2012; Lanni et al., 2008; Uberti et al.,
2006). On this basis, the levels of p53 unfolded could
be an interesting starting point to a reliable blood-
based ELISA performed with a specific
conformational anti-p53 antibody. Even if ELISA
assay actually represents the gold standard technique
used for the detection and quantification of this p53
biomarker, some limitations are related to its
diffusion. These issues specifically include high costs
of the assay implementation, high operator
dependence, lack of standardization and impossibility
to lower the limit of detection, thus to detect the
biomarker in the early stage of the disease when it
would be more useful for the clinicians.
Biosensors represent the emerging technology
that promises to address this challenge, bringing
promising solutions in term of cost and sample use
reduction, ease of use, high portability and sensitivity
(Yager et al., 2008; Polese et al., 2014; Feng et al.,
2015).
In light of this, the development of a portable
point-of-care (PoC) testing system based on a screen
printed electrochemical sensor (SPES), could
represent an innovative and low cost solution to solve
these problems, improving and bringing to a higher
level of sensitivity the specific biomarkers detection
and quantification, with a strong impact on the
possibility to early diagnose AD (Dhawan et al.,
2015).
2 OUTLINE OF OBJECTIVES
The main objective of this project addresses the
design and development of a low-cost portable point-
of-care testing platform for the detection and sensitive
quantification of the unfolder p53, as biomarker for
early detection of AD.
The development of the platform specifically
includes both the design of the sensing probe, with
particular attention to the choice of the materials and
geometry, and of the electronic circuit devoted to the
conditioning and acquisition of the electric signal.
The electrodes were specifically designed to be easily
implemented by means of screen printing
methodology. In details, the outline of the project
could be organized in the following phases:
1. preliminary characterization of the electrodes, and
evaluation of compatibility of screen printing
materials and substrate with wet lab practices;
2. design and production of the screen printed
electrochemical sensor;
3. design and development of the conditioning
electronical circuit to perform the electronical
measurements, which are directly related to the
concentration of the specific protein on the
biological sample;
4. calibration of the sensors and evaluation of the
circuit;
5. functionalization of the sensors and protein
quantification using Electrochemical Impedance
Spectroscopy (EIS) and Anodic Stripping
Voltammetry (ASV).
6. optimization of the acquisition workflow.
7. validation of the sensor by using primary
antibodies specific for p53 unfolded proteins and
real samples from AD patients, compared to the
ELISA assay.
Each reported phase addresses specific objectives.
3 STATE OF THE ART
One of the most pervasive challenges of the research
in medical diagnosis is related to the ability to detect
a specific pathology in its earliest development
(Jacobs et al., 2014). To achieve this goal, in the last
decades, new rapid, low cost and easily accessible
methodologies have been increasingly investigated,
supported by the interest toward customized medicine
and toward rapid and home accessible diagnostic
results (Chan et al., 2013).
DCBIOSTEC 2016 - Doctoral Consortium on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies
16

For these reasons, the idea to identify and quantify
specific biomarkers in the early stages of a disease
appears to be really promising (Jr et al., 2010;
Svobodova et al., 2012). Biomarkers represent an
indicator of the biological status, which can give
useful information concerning biological processes
happening in physiological or pathological conditions
and during different medical treatments.
As previously stated, in the specific case of AD,
recent studies related to its diagnosis reported how the
presence of a particular conformation of a specific
protein (p53) could be able to discriminate patients
affected by AD from healthy patients (Uberti et al.,
2006; Lanni et al., 2008; Buizza et al., 2012).
In this perspective, clinicians require technologies
able to identify quickly and with a high sensitivity
specific biological biomarkers related to the disease.
Biosensors integrated in lab on a chip (LoC)
devices could represent promising methods to reduce
time, cost and sample needed to perform the analysis.
(Song et al., 2014).
Thanks to their ability to be functionalized and
customized for the detection of different analytes (e.g.
DNA, proteins), electrochemical biosensors represent
the ideal starting point to realize complete platforms,
by integrating the sensor with the conditioning circuit
needed for the electronical measurements, realizing
portable and self-standing devices, useful for PoC
applications (Yager et al., 2008).
Printed electronics represents a successful tool to
realize low cost and sensitive biosensors for these
specific applications. In particular, screen printing
(also defined thick film printing) is the most used
method to realize this kind of electrochemical
sensors, as it arises in several works in the literature
for the sensitive and specific quantification of
different proteins (Silva et al., 2014; Elshafey et al.,
2013; Yun et al., 2011). Protein detection and
quantification is usually obtained by performing the
same functionalization as used in the multiwells
ELISA. More in details, the working electrode of the
sensor is functionalized with the primary antibodies
specific for the proteins that need to be quantified,
thus allowing the formation of an immunocomplex.
After that, the electrode is washed with the sample
containing the proteins and with a solution containing
a specific secondary antibody. After the
immunocomplex is realized, different methods can be
used to quantify the specific proteins.
A label free method is represented from EIS,
which measures the changes of impedance deriving
from a different electrons exchange between the
functionalized surface of the electrode and a
conductive solution (usually potassium ferricyanide),
depending on the concentration of the recognized
proteins (Silva et al., 2014; Elshafey et al., 2013). For
this specific technique, 2–electrode conformation -
including a working (WE) and a reference electrode
(RE) - or 3- electrode conformation – including WE,
RE and a counter electrode (CE) as reference for the
current – have been used to ensure the correct
acquisition of the proteins concentration, depending
on the level of precision and sensitivity required.
A different technique often used is represented by
voltammetry. In this case, the 3-electrodes
conformation is usually adopted. The potential
between RE and WE is varied arbitrarily - either step
by step or continuously - and the actual current value
between WE and CE is measured as the dependent
variable. As reported in different works, this method
can be performed both with the sensor completely
immersed in a buffer solution (Elshafey et al. 2013)
or by placing a drop of solution which cover the three
electrodes (Escamilla-Gómez et al. 2009). Anodic
stripping voltammetry (ASV) represents a very
sensitive kind of voltammetry technique. Several
groups optimized this measurement technique to
detect both proteins (Escamilla-Gómez et al., 2009)
or DNA sequences (Martínez-Paredes et al., 2010),
with limit of detection in the order on ng/ml.
Using the catalyzing action of Alkaline
Phosphatase (AP), ionic silver is selectively reduced
in its metallic form only where the proteins are
recognized, thus allowing the quantification of
proteins converting the amount of deposited silver
into a proportional peak of current during a stripping
step, varying the potential between WE and RE.
To further improve the specificity and the
sensitivity of this technology, limit of detection lower
than 100 pg/ml have been achieved thanks to the
integration of the SPES with nanostructured
materials. Gold nanoparticles for example or carbon
nanotubes or a combination of the two has been used
to modify the surface of the working electrode
allowed to better recognize antigens and DNA
sequences (Escamilla-Gómez et al., 2009; Kara et al.,
2010; Martínez-Paredes et al., 2010; Jeong et al.,
2013).
4 METHODOLOGY
The experimental activities of the project are divided
into 3 main parts:
- a first part dedicated to the evaluation of the
compatibility of the screen printing materials and the
circuit components with the wet lab practices.
Study of a Low-cost Sensitive Point-of-Care Testing System using Screen Printed Biosensors for Early Biomarkers Detection Related to
Alzheimer Disease
17

- a second part dedicated to the design and
realization of the sensor and the conditioning circuit.
- a final part dedicated to the calibration of the
platform (sensor and circuit) and to p53 protein
quantification.
4.1 Initial Sensors Characterization
Preliminary characterizations are required to assess
the compatibility of the sensor with wet lab practices
and to evaluate how antibodies can be coated on to
electrode surface in order to select the best materials
for the sensor production.
Alumina is identified as the optimal material used
as substrate for the printing of the working electrodes.
The adhesion of different concentration of antibodies
solutions has to be evaluated, in order to optimize the
best concentration for an efficient functionalization of
the sensor. Two different techniques have been
specifically chosen for the analysis: an electronic
method, EIS, and an optical one, evaluating the light
intensity thanks to fluorescent labels on the secondary
antibody.
EIS measurements are performed in presence of
Potassium Ferricyanide (K
3
[Fe(CN)
6
]) in a solution
of KCl. This technique is based on the measurement
of the impedance on a wide range of frequencies (200
Hz – 200 KHz), between a carbon WE and a silver-
silver chloride RE, both immersed in an electrolytic
solution of 5 mM K
3
[Fe(CN)
6
] in 1 M KCl.
Different designs (single electrodes and multiwell
electrodes) and materials (alumina, glass and
polystyrene) are evaluated in this first optimization
phase in order to better understand the technology to
be implemented in the final layout of the sensor. For
each of this different design, different protocols are
adapted to obtain reliable and repeatable results.
Impedance measurements are specifically
performed using an impedance analyzer (HP4194A),
compared with the fluorescence measurements
registered using a light intensity quantifier
(Odyssey® Fc Dual-Mode Imaging System from LI-
COR Biosciences).
4.2 Sensors Design and Production
The layout is designed using QCAD software. Each
layer, corresponding to a different conducting
material, is separately designed, in order to produce
the masks required to screen print layer by layer the
final structure of the sensor. A specific care should be
put to realize conductive tracks with a resolution
compatible with the printing performance of the
screen printer employed (A2 Model, Baccini srl,
Italy).
Figure 1: Final SPES layout.
Once the geometry is optimized - with a WE of
8.0 mm of diameter - it is printed on a lucid sheet by
means of inkjet printing, thus to allow the realization
by UV photolithography of the mask required for the
screen printing process.
On a 0.4 mm thick alumina substrate, the 3 layers
are consequently printed: firstly the silver for the
conductive tracks, then carbon for the working
electrode and finally silver-silver chloride for the
reference electrode. In order to allow a better
conduction of the signal, the conductive tracks are
isolated using a conductive spray specific for printed
circuit, leaving the terminal part of the tracks free for
the connection with the conditioning circuit (Fig. 1)
The reproducibility of sensor geometry in the
different printing processes is ensured thanks to a
specific care in performing a standardized protocol
while realizing each sensor. Each sensor is accurately
observed under an optical microscope to evaluate the
homogeneity of the printed layer and the resistance
evaluated with a tester.
4.3 Circuit Design and Production
Parallelly to the realization of the electrochemical
sensor, the conditioning circuit is designed in order to
allow the production of a complete PoC testing
platform.
The design of the circuit is performed following
the scheme of a common potentiostat. Its aim is to
control the potential between the functionalized WE
and the RE, and then to measure the current flowing
between WE and CE.
DCBIOSTEC 2016 - Doctoral Consortium on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies
18

The electronic schematic is realized with OrCAD
software (OrCAD©- Cadence Design Systems -San
Jose, CA) whereas the design for the Printed Circuit
Board is prepared using OrCAD Layout Plus tool
(OrCAD©- Cadence Design Systems -San Jose, CA).
The final PCB realized using OSH Park - community
printed circuit board (PCB) order (Fig. 2).
Figure 2: Schematic of the conditioning circuit.
Figure 3: Final PCB of the conditioning circuit.
All the SMD electronic components are soldered
and the board inserted in a metallic box to avoid
noises on the signal recording and to improve the
sensor sensitivity and precision.
4.4 Calibration and Measurements
After optimizing the design, the platform is tested
following three different protocols, using before a
saline solution, with different concentrations of NaCl,
then performing EIS with Potassium Ferricyanide and
after that performing ASV functionalizing the WE
with proteins.
4.4.1 NaCL Solution Measurements
The first test of the circuit is performed using a saline
solution, varying the concentration of NaCl in order
to change the conductivity of the solution, and
evaluating the ability of the circuit to quantify these
changes as changes in the current peak flowing
between WE and CE.
In the first test the concentrations of the solution
evaluated are 0.0, 15.0, 22.5, 30.0, 37.5 and 45.0
mg/ml. After that, a second round of concentrations
is tested, to evaluate the linearity of the circuit
response in a range between 0.0 and 10.0 mg/ml, in
particular: 0.0, 1.0, 2.2, 4.0, 5.5, 6.0, 10.4 mg/ml.
Finally, the circuit is evaluated with concentrations
lower than 1.0 mg/ml, in particular: 0.00, 0.44, 0.66,
0.88, 1.00 mg/ml.
In each experiment, drop of 2 ml of saline solution
are dropped on WE, CE and RE, assuring that the
drop stays in place with the help of a mask applied on
top of the sensor.
For this analysis, the input signal is considered as
a triangular wave, with amplitude 300 mV and
frequency 40 mHz, obtained using a pulse generator
(HP8116A pulse/function generator 50 MHz
Hewlett-Packard )
The signal is then acquired using an oscilloscope
(Tektronik TDS 1001B – two channel digital storage
oscilloscope 40 MHz, 500 MS/s)).
Experiments are always performed in triplicate.
All graphical and tabulated data are usually displayed
as mean ± mean standard error.
4.4.2 Antibodies Quantification using EIS
EIS is also applied in order to measure changes of the
current detected between WE and CE to quantify
different concentrations of the primary antibodies
released and adhered on WE surface. In particular,
three antibodies concentrations were considered: 0, 4
and 8 µg/ml.
After an overnight incubation at 4 °C the
measurements were performed in presence of a
conductive electrolytic an solution of 5 mM
K3[Fe(CN)6] in 1 M KCl. Once the functionalization
was performed, a drop of 2 ml was placed in order to
cover WE, RE and CE and allow current flow, and the
electronic measurement were performed, giving a
ramp as signal input, and recording the current
between WE and CE using an oscilloscope. In
particular, a first analysis was performed using
triangular waves four different frequencies (40 mHz,
100 mHz, 200 mHz and 1 Hz) with an amplitude of
300 mV, and then a second one fixing the frequency
to 50 mHz.
Study of a Low-cost Sensitive Point-of-Care Testing System using Screen Printed Biosensors for Early Biomarkers Detection Related to
Alzheimer Disease
19
4.4.3 Protein Measurements
The protocol followed to quantify protein
concentration, both for the preliminary test using a kit
with human interleukin and for the real samples
containing p53 proteins, is represented by the
following steps:
- sensor wash with Phosphate Buffer Saline (PBS)
- WE coating with optimized primary antibody
concentration (8 µg/ml).
- Overnight incubation at 4°C
- Block with a Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA)
solution.
- 2 hours incubation with desired solution
containing a defined concentration of proteins (in
the calibration phase) or with the sample.
Temperature mantained stable at 25°C
- Block with BSA solution.
- 1 hour incubation with biotin labelled secondary
antibodies.
- Block with BSA solution.
- 30 min incubation with streptavidin labelled
Alkaline Phosphatase.
- Block with BSA solution.
- 20 min incubation with a solution of 3 mM AA-p
e 4 mM AgNO3, protected from light.
Once the functionalization is performed, a drop of 2
ml is placed in order to cover WE, RE and CE and
allow current flow, and the electronic measurement
are performed, giving a ramp as signal input, and
recording the current between WE and CE using an
oscilloscope, in the same way indicated in the
previous paragraph.
5 EXPECTED OUTCOME
The complexities and the heterogeneity associated
with AD, requires high precision and sensitivity in the
reliable detection and quantification of specific
biomarkers, able to allow an early diagnosis of the
disease in the pre-symptomatic phase and to acquire
additional information both from the biological and
from the pathoclinical point of view.
The main expected outcome of this project is the
realization of a self-standing portable point-of-care
testing system, able to support clinicians to diagnose
AD from its earliest stages.
The proposed methodology can be used in a
routine automatized diagnosis technique, specifically
quantifying the unfolded p53 biomarker. Following
the development of the platform, this project
inherently addresses different outcomes, specifically
related to:
1. Optimized calibration of the sensor and
conditioning/acquisition electronics (Fig. 3), thus
to discriminate defined protein concentrations
2. Protein sensitive quantification modifying the
sensor materials (e.g. using gold nanoparticles).
3. Final optimization of the platform to realize a self-
standing point of care
Each step described addressed from one side an
increasing in the sensitivity of the sensor itself and
from the other the optimization of the portable point
of care design, aiming to a low cost, easy usable and
highly precise platform.
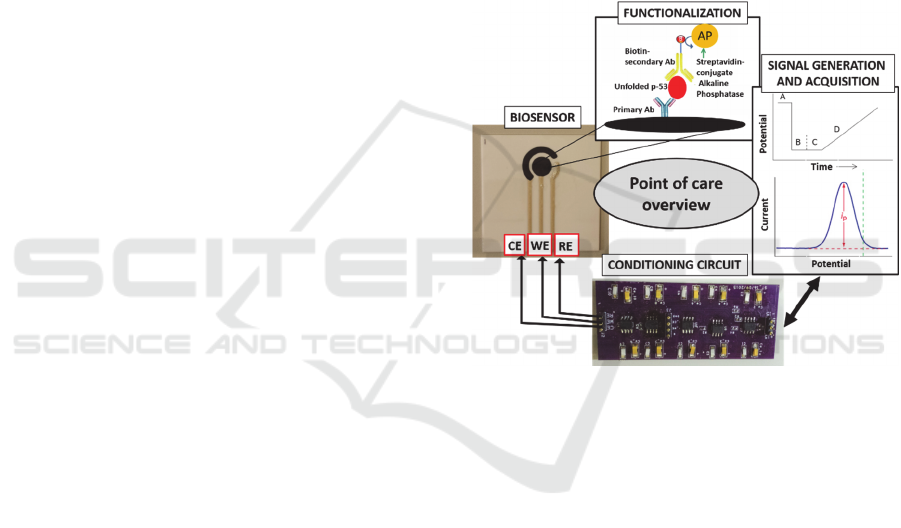
Figure 4: Point of care overview.
6 STAGE OF THE RESEARCH
6.1 Initial Sensors Characterization
Regarding the compatibility of the materials and of
the printing process with wet lab practices, alumina
substrate represented the optimal solution. Thanks to
the intrinsic porosity of the material, electrodes
printed in this substrate did not show any variation
when washed with water-based solutions during
functionalization steps. On the contrary, electrodes
printed in glass and polystyrene, because of their low
porosity, did not show an efficient adhesion, with
critical modifications during the functionalization
step, compromising the uniformity of the primary
antibodies coating on the WE and the effective
complex formation with the secondary antibody.
Among the different primary antibody
concentrations evaluated (2.0, 2.6, 3.0, 4.0, 4.8, 6.0,
DCBIOSTEC 2016 - Doctoral Consortium on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies
20

8.0, 10.0 µg/ml), 8.0 µg/ml was identified as the
optimal one to achieve a homogeneous coating of the
WE.
Figure 5: Image obtained from the optical analysis of WE
coated with different primary antibody concentrations.
Figure 6: Electronical measurements (EIS) of different
antibody concentration coatings.
The fluorescence signal recorded from the
Odyssey showed a fluorescence intensity
proportional to the concentration of primary antibody
coated in the range between 2 and 6 µg/ml. (Fig. 4).
Impedance measurements performed on the same
electrodes, showed results in agreement with what
previously evaluated with optical analysis. More
specifically, the linearity observed for concentration
of 0.0, 6.0, 8.0 µg/ml, could be observed with EIS as
well.
Using electrodes printed on ceramic substrates,
thanks to the good compatibility of the materials with
wet lab practices, results obtained appeared to be
repeatable and reliable for all the electrodes tested.
The impedance module measured for electrodes
coated with 8.0 µg/ml primary antibody solution
resulted to be superior in all the frequencies range
evaluated, compared with the one of blank electrodes,
treated with a buffer solution (mean 15.5 ± 4.6 Ohm
between 2 and 20 kHz; max 30 Ohm at 2 kHz and
minimum of 9 Ohm at 200 kHz). The impedance
module measured with electrodes treated with 6.0
µg/ml showed a trend comprised between the
previous two (Fig. 5). Using electrodes printed on
glass substrates, the average difference between the
impedance module of reference electrodes and
electrodes treated with 8.0 µg/ml of primary antibody
was 7.6 ± 1.1 Ohm, constant in the range between 200
and 2 MHz. Because of the poor adhesion and
compatibility of the glass printing process with wet
lab practices, measurements performed on electrodes
coated with intermediate concentrations showed
results compatible with the non-uniform coating
highlighted from the fluorescence analysis.
6.2 Calibration and Measurements
The present stage of the research, after that the design
and development of the sensor and
conditioning/acquisition circuit has been optimized,
is addressing the calibration of the sensor, firstly with
NaCl solution, and then with human interleukin, in
order to optimize the detection protocol and to
prepare the platform for the following step of p53
proteins detection and quantification.
6.2.1 NaCl Solution Measurements
Results from the evaluation of circuit response to
changes in saline solution conductivity showed a
linear response for the specific ranges of
concentrations evaluated. After evaluating the
linearity using high concentration of NaCl, a
narrower range of concentrations was evaluated in
order to understand if the circuit was able to recognize
small changes in solution conductivity and small
current between WE and CE.
Figure 7: Calibration of SPES with NaCl solution.
Study of a Low-cost Sensitive Point-of-Care Testing System using Screen Printed Biosensors for Early Biomarkers Detection Related to
Alzheimer Disease
21

Performing the same measures with lower
concentration a particular behaviour could be noticed.
Two different slopes could be observed respectively
for concentration lower and higher than 1.0 mg/ml. In
particular, a higher sensitivity was shown for the
concentration lower than 1.0 mg/mg (13 mA/
(mg/ml)), indicating a higher sensitivity of the sensor
for small changes of conductivity and small currents
(Fig. 6). This behaviour suggested that the range of
concentration in which the circuit was able to give the
best response corresponds to low changes in
concentration, resulting in small ionic currents. On
the contrary, high changes in concentration, causing
high changes in conductivity, were discriminated
with an inferior sensitivity (170 mA/(mg/ml))
because they brings to current which cause the circuit
to saturate, and not to be able to discriminate the
difference.
6.2.2 Antibodies Quantification using EIS
Results from EIS measurements showed a
proportional decreasing of the peak of current flowing
between CE and WE, indicating an increased
impedance of the system due to an increasing
concentration of antibodies coated on WE surfaces
resulting in a reduced electrons exchange between
WE surface and electrolytic solution (Fig 8 and 9).
Figure 8: Difference in CE current measured at different
frequencies, evaluating with EIS different concentration
primary antibodies coatings.
Figure 9: Difference in CE current measured at 50mHz,
evaluating with EIS different concentration primary
antibodies coatings.
The same behaviour was observed at all the
frequencies evaluated. Increasing the concentration
of antibodies coated on the WE resulted in reducing
the differences of currents exchanged at different
frequencies (Fig. 9). As showed in Fig. 9, the
sensitivity of the sensor in detecting the change in
antibodies coating concentration was of 70 mA/µg.
6.2.3 Protein Measurements
The activity actually going on refers to the
implementation of the same protocol using
interleukin protein, of dedicated kit DuoSet®
development system for ELISA, Human CXCL8/IL-
8. The different concentrations of proteins are going
to be recognized with two different techniques:
- using EIS in presence of Potassium Ferricyanide
in KCl solution.
- using ASV as described in the methodologies
section.
This phase is essential for an effective calibration of
the platform, in order to proceed with the
quantification of unknown concentration of p53
proteins.
7 FUTURE OUTLOOKS AND
CONCLUSION
In light of the positive results described, the activity
actually going on refers to the implementation of the
same protocol described in the materials and methods
section using interleukin protein, of dedicated kit
(DuoSet® development system for ELISA, Human
CXCL8/IL-8). Different concentrations of proteins
(order of ng/ml) will be recognized using both the
techniques described (EIS and ASV). This phase is
essential for an effective calibration of the platform,
in order to proceed with the quantification of
unknown concentration of p53 proteins. Specifically
regarding ASV, the same protocol will be adopted to
quantify protein concentrations, both for interleukin
and for p53 proteins. It will be characterized by the
use of immucomplexes of primary antibody-protein-
secondary antibody labelled with Alkaline
Phosphatase, as functionalization of the WE. In this
way, through a selective chemical deposition of
silver, the current flowing between WE and CE will
be proportional to the amount of deposited silver,
which in its turns will be proportional to the
recognized protein. Before proceeding with unknown
proteins concentrations, an accurate calibration of the
biosensor will be performed. After the validation, the
DCBIOSTEC 2016 - Doctoral Consortium on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies
22

proposed methodology and the platform design will
be optimized in order to be easily accessible for a
routine automatized diagnosis technique in the
clinical environment. From these bases, particular
attention will be then addressed to increase the
sensitivity of the method itself, including both the
introduction of nanostructured materials for the
working electrodes and proper ASV measurements.
All this, with the aim to realize an innovative self-
standing portable point-of-care, a low cost, easy
usable and highly precise platform able to support
clinicians to diagnose AD from its earliest stages.
REFERENCES
Buizza, L. et al., 2012. Conformational Altered p53 as an
Early Marker of Oxidative Stress in Alzheimer ’ s
Disease. , 7(1), pp.1–11.
Chan, K.C.A. et al., 2013. Cancer Genome Scanning in
Plasma : Detection of Tumor-Associated Copy Number
Aberrations , Single-Nucleotide Variants , and Tumoral
Heterogeneity by Massively Parallel Sequencing. , 224,
pp.211–224.
Dhawan, A.P. et al., 2015. Current and Future Challenges
in Point-of-Care Technologies: A Paradigm-Shift in
Affordable Global Healthcare With Personalized and
Preventive Medicine. Translational Engineering in
Health and Medicine, IEEE Journal of, 3, pp.1–10.
Elshafey, R. et al., 2013. Electrochemical impedance
immunosensor based on gold nanoparticles-protein G
for the detection of cancer marker epidermal growth
factor receptor in human plasma and brain tissue.
Biosensors & bioelectronics, 50, pp.143–9. Available
at: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23850780.
Escamilla-Gómez, V. et al., 2009. Simultaneous detection
of free and total prostate specific antigen on a screen-
printed electrochemical dual sensor. Biosensors and
Bioelectronics, 24, pp.2678–2683.
Feng, S., Roseng, L.E. & Dong, T., 2015. Quantitative
detection of Escherichia coli and measurement of
urinary tract infection diagnosis possibility by use of a
portable, handheld sensor. Medical Measurements and
Applications (MeMeA), 2015 IEEE International
Symposium on, pp.586–589.
Humpel, C., 2011. Identifying and validating biomarkers
for Alzheimer’s disease. Trends in Biotechnology,
29(1), pp.26–32. Available at: http://
www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3016495/.
Jacobs, J. et al., 2014. Harmonization of malaria rapid
diagnostic tests : best practices in labelling including
instructions for use. , pp.1–10.
Jeong, B. et al., 2013. Increased Electrocatalyzed
Performance through Dendrimer- Encapsulated Gold
Nanoparticles and Carbon Nanotube-Assisted Multiple
Bienzymatic Labels: Highly Sensitive Electrochemical
Immunosensor for Protein Detection.
Jr, C. R. J. et al., 2010. Hypothetical model of dynamic
biomarkers of the Alzheimer’s pathological cascade.
9(1), pp.1–20.
Kara, P. et al., 2010. Aptamers based electrochemical
biosensor for protein detection using carbon nanotubes
platforms. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 26, pp.1715–
1718.
Lanni, C. et al., 2008. Conformationally altered p53 : a
novel Alzheimer ’ s disease marker ? , pp.641–647.
Martínez-Paredes, G., González-García, M.B. & Costa-
García, A., 2010. Genosensor for detection of four
pneumoniae bacteria using gold nanostructured screen-
printed carbon electrodes as transducers. Sensors and
Actuators, B: Chemical, 149, pp.329–335.
Polese, D. et al., 2014. Investigation on nanostructured
biosensor for Biotin detection. SENSORS, 2014 IEEE,
pp.1627–1630.
Silva, M.M.S. et al., 2014. A thiophene-modified screen
printed electrode for detection of dengue virus NS1
protein. Talanta, 128, pp.505–510. Available at:
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2014.06.009.
Song, M.J. et al., 2014. Electrochemical serotonin
monitoring of poly(ethylenedioxythiophene):
Poly(sodium 4-styrenesulfonate)-modified fluorine-
doped tin oxide by predeposition of self-assembled 4-
pyridylporphyrin. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 52,
pp.411–416. Available at:
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2013.08.040.
Svobodova, Z. et al., 2012. Development of a magnetic
immunosorbent for on-chip preconcentration of
amyloid b isoforms : Representatives of Alzheimer ’ s
disease biomarkers. , 024126, pp.1–12.
Thal, L.J. et al., 2006. The Role of Biomarkers in Clinical
Trials for Alzheimer Disease. Alzheimer disease and
associated disorders, 20(1), pp.6–15. Available at:
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC18208
55/.
Uberti, D. et al., 2006. Identification of a mutant-like
conformation of p53 in fibroblasts from sporadic
Alzheimer ’ s disease patients. , 27, pp.1193–1201.
Yager, P., Domingo, G.J. & Gerdes, J., 2008. Point-of-care
diagnostics for global health. Annual review of
biomedical engineering, 10, pp.107–144.
Yun, Y.H. et al., 2011. A glucose sensor fabricated by
piezoelectric inkjet printing of conducting polymers
and bienzymes. Analytical sciences : the international
journal of the Japan Society for Analytical Chemistry,
27(4), p.375.
Study of a Low-cost Sensitive Point-of-Care Testing System using Screen Printed Biosensors for Early Biomarkers Detection Related to
Alzheimer Disease
23
