
An Educational Game for Teaching Search Algorithms
Foteini Grivokostopoulou, Isidoros Perikos and Ioannis Hatzilygeroudis
Department of Computer Engineering and Informatics, University of Patras, Patras, Greece
Keywords: Educational Game, Gabe-based Learning, Search Algorithms, Algorithm Visualization, Pacman,
Game Learning Efficiency.
Abstract: Search algorithms constitute an important topic in the Artificial Intelligence curriculum and are
acknowledged by most tutors to be a hard and complex domain for teachers to teach and students to deeply
understand. In this paper, we present an educational computer game, designed to teach search algorithms,
based on the popular Pacman game. The purpose of the educational Pacman game is to assist students to
understand the artificial intelligence topic of search algorithms in an entertaining, interactive and motivating
way. During their experience with the game, students can examine the behaviour of various search
algorithms and a graphical annotated depiction of them through suitable visualizations. Visualizations can
demonstrate the operational functionality of algorithms and are designed in line with the principles of
student’s active learning. Various learning activities were designed and request students to apply specific
search algorithms in various example cases with or without the assistance and feedback of the game. An
evaluation study was conducted in real classroom conditions and revealed quite satisfactory results. The
results indicate that the educational Pacman game is an effective way to enhance students’ engagement and
help them to deeper understand the AI search algorithms.
1 INTRODUCTION
Over the past few years, special attention has been
focused on the integration of digital technologies
and games in education and there is an increased
interest in the utilization of games as educational
instruments to assist students’ learning and teachers’
teaching procedures (Wu et al., 2012). More and
more educational systems and serious games are
developed and utilized by teachers in the context of
their courses. The rapid advancement of web and the
technological spread of devices like tablets,
smartphones and laptops have greatly facilitated the
integration of digital games in educational
procedures.
Recently, the development and integration of
computer games and game based learning
approaches in educational procedures has become a
significant focus of attention and has attracted the
interest of tutors, educational institutes and
researchers. In an effort to attract and engage
students and enhance the overall efficiency of
learning procedures, digital technologies and
computer educational games are examined to add
fun factors and make teaching more attractive and
appealing (Mihail et al., 2013). In our days, a great
part of the students, like most individuals, spend a
large part of their free time playing computer games
and in this line, the integration of games into courses
curriculum could increase students’ interest and
stimulation and provide opportunities for learning in
an entertaining way.
Computer games can be used to teach almost
every area of computer science and researchers point
out that they could constitute an effective way to
provide more interesting learning environments for
knowledge acquisition and construction (Sung and
Hwang, 2013). Computer games have been used
successfully in both introductory computer science
courses (Parberry et al. 2005, Bayliss 2007) and
general artificial intelligence classes (Wong et al.,
2010; Taylor, 2011; Sosnowski et al., 2013; DeNero
and Klein, 2010) to scaffold learning and bring
excitement and enthusiasm among students. Indeed,
through games students are given motives to
increase their interest and teachers to implement the
learning by doing or by participating principle
(Papastergiou, 2009). So, the students have a
framework for better grasping or understanding
computer science and artificial intelligence concepts.
In an Artificial Intelligence (AI) curriculum, a
fundamental topic is the domain of search
Grivokostopoulou, F., Perikos, I. and Hatzilygeroudis, I.
An Educational Game for Teaching Search Algorithms.
In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Computer Supported Education (CSEDU 2016) - Volume 2, pages 129-136
ISBN: 978-989-758-179-3
Copyright
c
2016 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
129

algorithms and it is a part of almost any introductory
artificial intelligence and computer science course
and textbook (Russell and Norvig, 2003). It is vital
for students to get a strong understanding of the way
search algorithms work and also of their application
to various problems. However search algorithms,
including blind and heuristic search algorithms, are
considered to be challenging for the tutors to
effectively teach and students to deeply understand.
Specifically, from a tutors’ perspective, teaching and
explaining how search algorithms operate is
challenging and in general requires a lot of
explanations, illustrations and teaching aids other
than blackboard to assist students in understanding
algorithms better (Baecker, 1998). In addition, from
a learners’ perspective, the algorithms constitute a
very challenging task for students to deeply
comprehend as they usually model complicated
concepts and also refer to abstract mathematical
notions (Shabanah et al., 2010). When students learn
new abstract concepts such as algorithm heuristics, it
can be hard for them without appropriate connection
to concrete examples (Ma et al., 2014). Visualization
of their functionality and the interactive application
in various exercises and learning activities can help
students connect abstract concepts and procedures to
concrete experiences and examples. Furthermore,
learners can recognize and comprehend virtual
graphical representations faster and deeper than
textual instructions and static representations
(Shabanah et al., 2010).
In this paper, we present an educational
computer game that is based on the famous Pacman
game. The purpose of the educational Pacman game
is to assist students to understand the artificial
intelligence search algorithms in an entertaining,
interactive and motivating way. During their
interaction with the game, students can see the
behavior of search algorithms and graphical
annotated depictions of them through algorithm
visualizations. Visualizations can demonstrate the
operational functionality of algorithms and are
designed in line with the principles of student’s
active learning. Various learning activities were
designed that instruct students to apply specific
search algorithms in various example cases with or
without the assistance and feedback of the game. An
extended evaluation study was conducted in real
classroom conditions and revealed quite satisfactory
results. The results indicate that the educational
Pacman game is an effective way to enhance
students’ motivation and help them to deeper
understand the AI search algorithms. In addition, the
game can benefit students' learning motivation and
also assist them get a deeper understanding of search
algorithm functionality.
The structure of the rest of this paper is as
follows: In Section 2, related work on the utilization
of games in teaching concepts of Artificial
Intelligence and Computer Science are presented. In
Section 3, we present a game to assist students in
learning search algorithms. In Section 4, the
evaluation study conducted and the results collected
are presented. Finally, Section 5 concludes the paper
and provides directions for future work.
2 GAMES FOR TEACHING AI
In recent years, the design and integration of games
in education and courses curriculum have attracted
the attention of researchers. A detailed and complete
overview of approaches can be found in (Michael
and Chen, 2005; Connolly et al., 2012; De Gloria et
al., 2014; Gibson and Bell, 2013).
In literature, there is great research interest and
many works study the design of educational
procedures and the development of games for
teaching the domain of computer science. In (Levitin
and Papalaskari, 2002), the authors present the using
of the puzzles in teaching design and analysis of
algorithms. In (Markov et al., 2006), authors
presents a work that uses machine learning as a
theme to unify core AI topics typically covered in
the AI course using the N-puzzle game and
provides several pedagogical possibilities for the
game. In (Sosnowski et al., 2013), authors present
SEPIA which stand for Strategy Engine for
Programming Intelligent Agents and is a game
environment for AI teaching. SEPIA is based on a
real-time strategy game, modified extensively to
preferentially support the development of artificial
agents. Another effort is presented in (Chang et al.,
2008) where a game-based learning approach is used
to help students learn graph theory topics and more
specifically Kruskal’s, Prim’s and Dijkstra’s
algorithms. The game is called Ticket to Ride and
the students through the missions that they choose
about connecting one city to another, come across
the implementation of the above algorithms.
In (Hatzilygeroudis et al., 2012), authors present
an educational game to assist students in
understanding the Constraint Satisfaction
algorithms. The game aims to offer an entertaining,
interactive and most of all motivating way to
students to experience with and learn about aspects
of constraint satisfaction problems, constraint
propagation and algorithms for constant consistency.
CSEDU 2016 - 8th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
130

Robocode (Hartness, 2004) is a programming Java
game where the goal is to develop a robot battle tank
to battle against other tanks programmed by other
players. It is designed to help students to learn Java
programming and used into an artificial intelligence
class to provide students tools for developing
practical versions of algorithms. Moreover, the robot
battles are running in real-time and are suitable to all
kind of programmers from beginners to experts. In
the work presented in (Eagle and Barnes, 2008),
authors introduce the Wu’s Castle game that is a two
dimensional role playing game teaching loops and
arrays in an interactive, visual way. The game
provides to the students immediate feedback and
helps them visualize the execution of their code in a
safe environment.
3 TEACHING AI ALGORITHMS
VIA A GAME
3.1 Learning Objectives
The learning objective of the game has an
educational goal and it aims to assist and to motivate
students to learn and deeper understand AI search
Algorithm. In our game, several learning activities
were designed to offer students various opportunities
to study and examine the way that search algorithms
operate and the learning activities are based on the
revision of bloom taxonomy.
The Bloom Taxonomy (Bloom, 1956) is a
classification of different levels of cognitive learning
objectives that tutors can set for students. It is an
important instrument in designing teaching
procedures that can provide a detailed understanding
of the learning objectives and can also help to design
activities based on the learning goals. For the
learning objectives of the game, the Bloom's
Revised Taxonomy (Anderson et al., 2001) was
utilized. It describes six progressive levels of
learning, which are starting from the foundation
towards the pinnacle and are the following:
Remembering, Understanding, Applying, Analyzing,
Evaluating, Creating.
Initially, regarding the theoretical aspects of the
search algorithms domain, the game can present
basic background topics and the description of the
algorithms. Specifically, it presents the basic textual
description of algorithms and their corresponding
graphical flowchart along with their pseudocode.
The aim is to assist students in studying and
constructing their knowledge. The playing process
mainly requires of students to apply their knowledge
of the algorithms in specific scenarios in our
educational Pacman game. During the game playing,
students need to analyze a specific algorithm
selected to study into its main sub-steps and specify
correctly the next moves. Also, the students can
select a specific algorithm to study and the
theoretical topics are presented to illustrate the way
the algorithm operates. Finally, evaluating the
students engage in checking and critiquing the
incorrect selection and it helps the student think
about why they have made an incorrect choice.
3.2 Design of the Game
The design of the game was based on the popular
Pacman game and was developed by our university
team using Java programming language. The game
is a one player game that the students can study,
examine and implement the blind and heuristic
search algorithms in various maze scenarios. The
game consists of two main modes that are the
"Educational mode" and the “Playing mode” and the
starting menu of the game is illustrated in Figure 1.
Figure 1: The main game modes of the game.
In the educational mode, the student can select
the type of the algorithm to study and the game can
present textual description of the algorithm and the
graphical flowchart along with its pseudocode. The
game offers the student the opportunity to study the
algorithm via visualizations and in this approach the
game illustrates the functionality of the algorithm in
example mazes of Pacman. Thus, students can study
the theoretical aspects of an algorithm in line with
appropriate explanations and algorithm
visualizations on various Pacman mazes.
Algorithm visualizations and animations are well
pointed to assist students in learning algorithms
(Hundhausen et al., 2002). Indeed, the
visualizations, when used properly in a learning
process, can help a student deeper understand the
way that an algorithm operates, by demonstrating
how it works and how it makes proper decisions
An Educational Game for Teaching Search Algorithms
131
based on parameters, such as heuristic and cost
functions (Hansen et al., 2002; Naps et al., 2002). In
the game, during the visualization of an algorithm,
every decision that the algorithm makes, such as for
example which node(s) to expand/visit, is properly
presented and explained to the student. The Pacman
game explains how a decision was made by the
algorithm and how the values of the parameters,
such as the heuristic and the cost functions (if any),
were calculated for each algorithm’s step. Although
visualizations are utilized in various systems and
games, they are in most cases integrated without
aspects and opportunities to engage and interact with
students during the animation process (Shabanah et
al., 2010). In the game, a noticeable aspect of
algorithm visualizations is that they have been
developed according to the essence of student active
learning. More specifically, the visualizations have
been designed based on the principle of engaging the
student as much as possible in the demonstration
process and making student to think hard at every
step of the algorithm’s animation. The principles of
active learning maintain that the more the users
directly manipulate and act upon the learning
material, the higher the mental efforts and
psychological involvement and therefore the better
the learning outcome ( Lee and Rößling, 2010).
In this spirit, during an animation demonstrating
the implementation of an algorithm in a maze, the
game and the Pacman can stop at a random step of
the algorithm and ask the student to specify some
aspects regarding the operation of the algorithm. The
animation may engage the student and request from
him/her to specify the next grid position on the maze
to be visited or ask him/her to justify why a
movement was made. In general, such justifications
mainly concern either the last action (or actions)
conducted by the Pacman simulating the algorithm
or the specification and proper justification of the
next action to be conducted. The interaction with the
student and the questions asked are either interactive
questions or multiple choice questions. The
interactive exercises may require of the student to
interact with Pacman in the maze and specify the
next movement based on the algorithm’s step. For
example, during visualization the Pacman can pause
and ask the student to specify the next algorithm’s
step by selecting the proper next grid position. In
case of a correct student’s answer, it can also request
from student to justify the reason, by offering
additional multiple choice question(s). In case of an
erroneous answer, knowledge of correct response
and proper explanations are immediately offered to
the student. After an interaction with the learner, the
animation process continues. In this line, during an
algorithm’s visualization in an example exercise
scenario, multiple interactions with the learner can
be made.
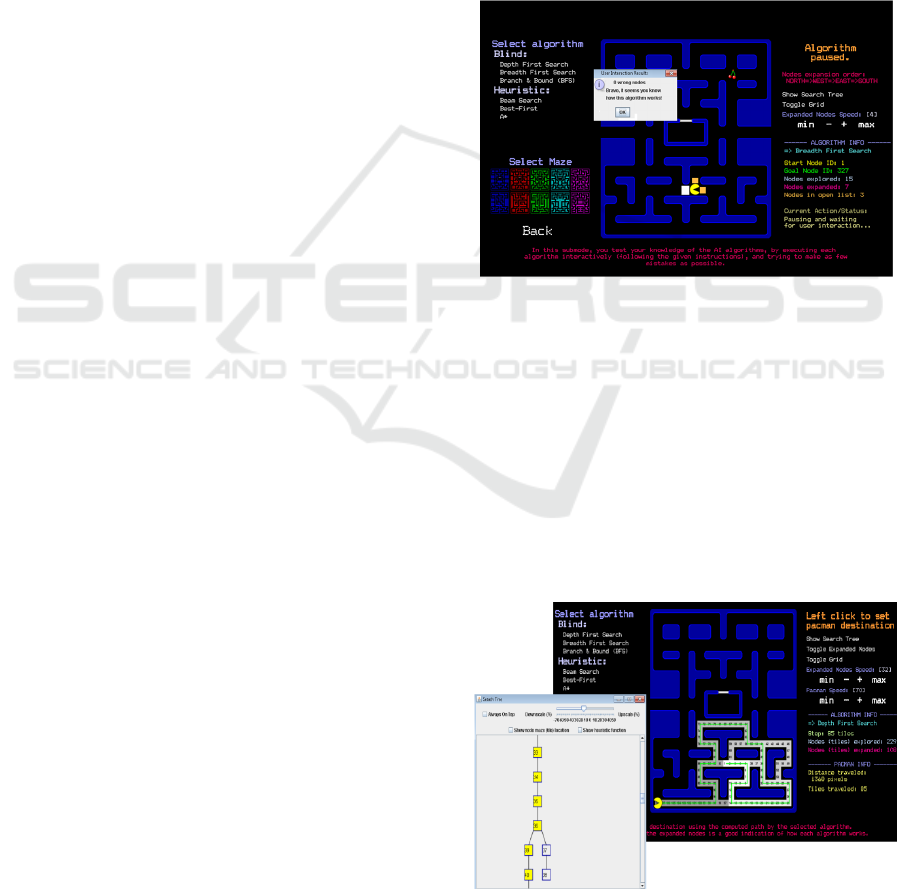
As an example, consider the simple case depicted
in Figure 2 where the visualization demonstrates the
operation of the breadth search algorithm in a case
where the aim is for Pacman to reach the cherries in
the maze starting from the default position. The
visualization has paused just after the first
movement of the algorithm and asks student to
specify the grid to be visited by Pacman based on
the algorithm. The student can either click on the
grid or move the Pacman with the keyboard.
Figure 2: An example visualization.
Additionally, the game provides students the
capability to select the type of algorithm and then to
see the application of it on the maze with the
additional explanations and information at the steps
of the algorithms such as heuristic functions, cost
calculated and other. For example, Figure 3 presents
the application of Depth-First algorithm as
implemented by the Pacman in order to get the
power-up in the bottom-left corner starting from the
default starting position. The corresponding tree
representation is presented in an expletory window.
Figure 3: Depth-First Algorithm in PacMan.
CSEDU 2016 - 8th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
132
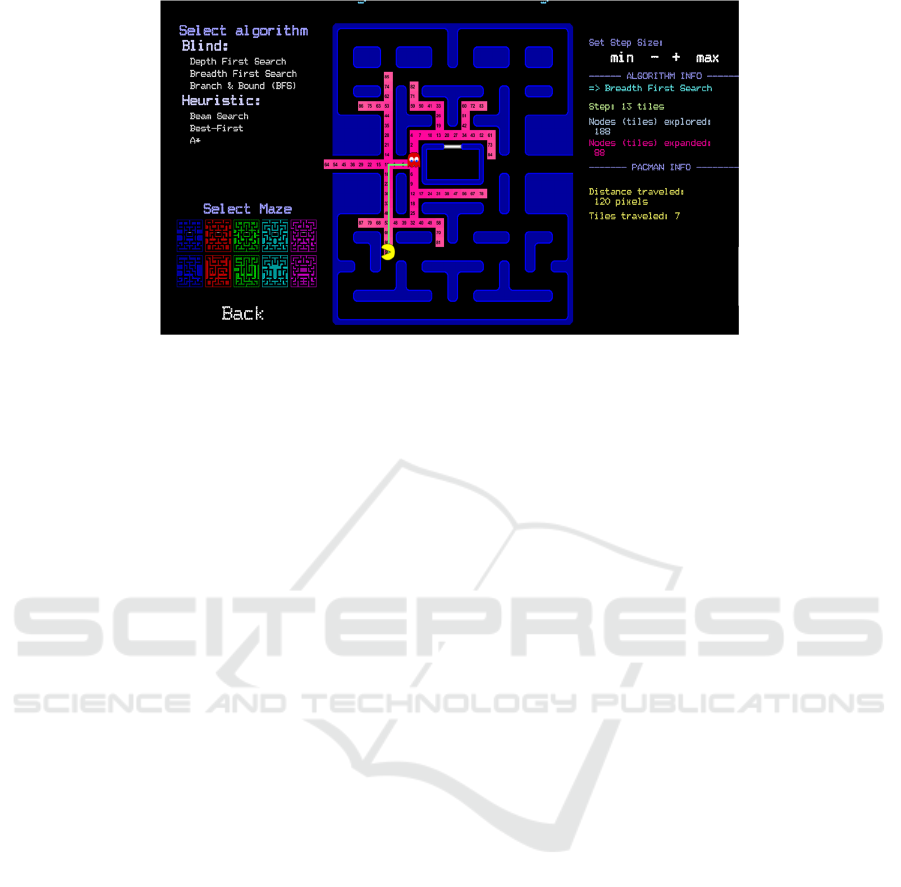
Figure 4: Experimental procedure of the Pacman Game.
The graph represents the maze and the way that
the Pacman moved in it. The nodes of the graph are
the tiles of the maze and the additional information
like heuristic and cost are illustrated on the graph to
help students to understand how movement
decisions were made.
Furthermore, the game provides various
demonstrations of how a ghost agent can move in a
move according to a specific algorithm. Specifically,
the game can highlight aspects of how a ghost
‘operates’ according to a specific algorithm and
moves in the maze. For example, in Figure 4, the
way that a ghost operates and is moving is
illustrated. The ghosts are generally aiming to reach
the Pacman and then the game ends. The student can
move the Pacman in the maze to collect the dots and
evade the ghosts and can observe, while Pacman is
moving, the way that the ghost applies a specific
algorithm and how is examining the maze tiles and it
decides to move. In this spirit, in every state the
maze’s tiles that are expanded and are in the open
list of the algorithm, are highlighted with purple
background. The green line between the Pacman and
the ghost highlights the shortest path between them.
The game illustrates in every state the distance in
tiles between the ghost and the Pacman and also the
number of tiles that the ghost and the algorithm has
explored and has expanded. In the example state
presentend in Figure 4, the ghost has explored 188
tiles, has expanded 88 tiles and the distance between
the Pacman and the ghost is 13 tiles.
The second game mode of the game, as
mentioned above, is the “playing mode”. It is
designed to be more challenging and fun oriented. In
this mode, the student has to solve predetermined
maze levels of Pacman under different conditions
and in a specific amount of time, something that can
make the playing mode more challenging and
motivating. Also, in this mode students can complete
maze levels and proceed to next ones that are more
complex and challenging in a similar manner like in
the original version of the Pacman game. The
various levels are designed in the spirit to necessitate
students to apply a specific search algorithm and
properly move the Pacman in the maze in order to
accomplish the level requirements. The level
requirements in general concern Pacman to reach in
the maze a specific fruit, a power-up and also eat
dots. In this approach, the student is requested in a
maze level, starting from a random position, to reach
the goal (e.g. a cheery or a power-up) by moving
Pacman based on the specific algorithm that the
level specifies. The student using the keyboard can
move the Pacman in the maze and specify the
direction to follow. In case of an incorrect
movement, the ghosts that are in the maze can move
faster towards to Pacman. The only case for the
student to complete the level is to correctly apply the
algorithm and properly move the Pacman in the
maze towards the goal(s). As the student proceeds,
next levels are getting more complex in terms of
maze characteristics, number of ghosts in the maze,
goals to achieve and most of all, the complexity of
the algorithm and its parameters that are requested
from student to apply.
4 EVALUATION
The purpose of the study is to examine the
efficiency, the motivation and the effectiveness of
the educational Pacman game in learning of AI
search algorithms. We conducted an evaluation
study for the educational Pacman game during the
An Educational Game for Teaching Search Algorithms
133
Artificial Intelligence course at our department. The
participants of this study were 38 students (male and
female) from those enrolled in the Artificial
Intelligence course. Initially, all the students were
randomly divided into two groups of 19 students
each, namely experimental group (EG) and control
group (CG). The two groups consist of almost the
same number of girls and boys. Also, we used a pre-
test, a post-test study and a questionnaire survey for
measuring the learning effectiveness, the learning
attitudes and the motivation from using the Pacman
game in the context of Artificial intelligence course
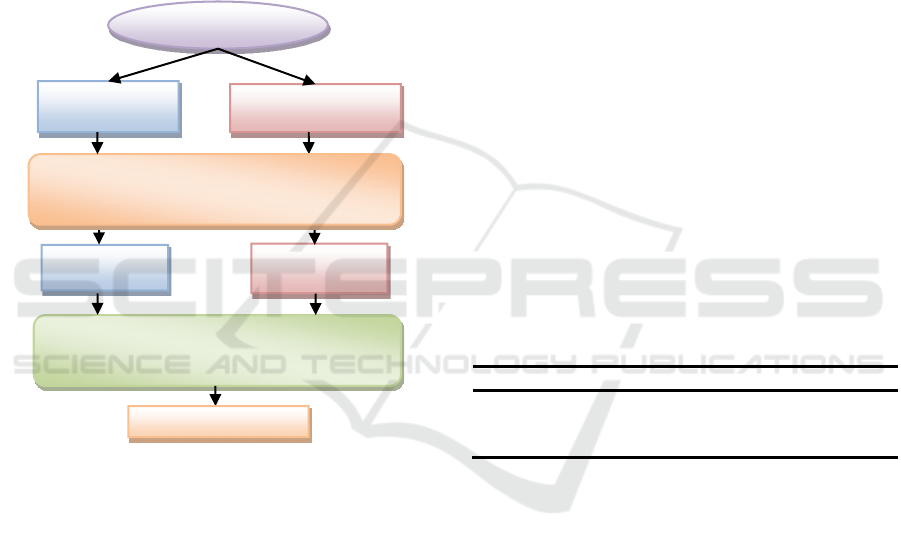
in our department. The experimental procedure used
to evaluate the game is illustrated in Figure 5.
Figure 5: Experimental procedure of the Pacman Game.
All the students took a pre-test to evaluate the
prior knowledge on AI search algorithms. The pre-
test aimed to ensure that the groups had equivalent
prior knowledge on AI search Algorithms. The
pretest consisted of twelve questions on the AI
algorithms and the duration of the pretest was 45
minutes. Then, all the pretests were marked by an
expert-tutor and the score of the test ranged from 0
to 10 points.
After that, the experimental group interacted
with the Pacman game for two weeks and the control
group was selected to study the lectures and discuss
with the teacher. Then, all the students took a post-
test. The purpose of the post-test was to evaluate
the learning performance and achievement of the
students after the participation in the learning
activities. The post-test consisted of twelve exercises
of the same difficulty levels with those in pre-test
and the students were given 45 minutes to complete
the test and submit their answers. After the learning
activities the students were asked to fill in a
questionnaire and express their feelings and opinions
towards the game and assess its learning assistance.
4.1 Evaluation Results
Initially, a one-way Analysis of Variance (ANOVA)
was performed on the pretest. The means of pre-test
for Control Group (CG) and Experimental group
(EG) were 3.63 and 3.72 respectively. The results
showed no significant difference among the students
of the groups (p=0.648> 0.05, F=0.212) so it is
concluded the two groups had equivalent prior
knowledge before using the game. Then, we
conducted an Analysis of Covariance (ANCOVA) to
extract the difference between the two groups using
the pre-test scores as the covariate and the post-test
scores as dependent variables. Table 1 summarizes
the descriptive statistics for the post-test conducted.
The ANCOVA results indicate the differences in
post-test scores are statistically and significantly
different between the two groups (F=83.143
p=0.00<0.05). Finally, the results showed that the
performance of the students of experimental group,
who used the Pacman game, was better than that of
control group.
Table 1: Post test Results.
Groups N Mean SD
Control Group (CG) 19 4.605 0.698
Experimental Group (EG) 19 6.861 0.782
Then, the students of the experimental group
were asked to fill in a questionnaire including
questions for evaluating usability of the game,
stating their experience and their opinions about the
learning impact of the game in teaching search
algorithms. The questionnaire included 15 questions.
The questions Q1-Q12 were based on the Likert
scale (1: not at all, 5: very much). Questions 13-15
were open type questions and concerned strong and
weak points of the game or problems faced and also
improvements that can be made to the game.
After analyzing the students’ responses to the
questionnaire, the reliability of the questionnaire was
checked using the Cronbach’s alpha (Cronbach
1951) metric. The reliability of the scale was good
and the internal consistency coefficient was 0.87.
The questionnaire results indicate that the
students’ feeling about the game was very positive,
as summarized in Table 2. Results point out that the
All students
Control group
(CG)
Experimental group
(EG)
Traditional
Learnin
g
Using Educational
Pacman Game
Post-Test
Evaluating learning achievements
(Duration 45 Minutes)
Q
uestionnaire
Pre-Test
Evaluating prior knowledge
(
Duration 45 Minutes
)
CSEDU 2016 - 8th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
134

Table 2: Questionnaire Results.
Q QUESTIONS
ANSWERS (%)
1 2 3 4 5
1 I enjoyed playing the game 0 0 0 5.3 94.7
2
The interface of the game is easy
to use.
0 0 0 10.5 89.5
3
The game made me more active
in the course
0 0 0 21.0 78.9
4
The game can increase my
motivation
0 0
10.
5
10.5 78.9
5
The game can enhance my
engagement in the course.
0 0 5.3 15.8 78.9
6
The game can enhance my
learning interest.
0 0 5.3 15.8 78.9
7
The using of the game for
learning is more interesting than
other ways of learning.
0 0 0 10.5 89.5
8
The game assisted me in learning
more effectively the search
algorithms.
0 0 0 5.3 94.7
9
The game assisted me in getting
a deeper understanding of the
functionality of the algorithms
after playing.
0 0 5.3 10.5 84.2
10
The interaction with the
visualizations of the algorithms
assisted me in understanding the
algorithm way of function.
0 0 0 10.5 89.5
11
Using the game provides me
with new way of thinking about
AI search algorithms
0 0 0 10.5 89.5
12
Will you recommend the
educational game to other
classmates and be integrated in
the course curriculum?
0 0 5.3 10.5 84.2
majority of the students greatly enjoyed studying
and playing with the game (94.7%) and a
considerable portion of them (89.5%) found the
interface of the game easy to use. Also, (78.9%) of
the students indicated that the game is more
interesting that other educational approaches and
ways of learning (89.5%). In addition, a great
portion of the students stated the game increased
their motivation (78.9%), engagement (78.9%) and
interest (78.9%) and made them more active in the
course (78.9%). Regarding the learning efficiency of
the game, students stated that the game helped them
in learning more effectively (94.7%) and in getting a
deeper understanding of the algorithms (84.2%) after
playing. In addition, the interactions with the game
during the algorithm visualization assisted students
to understand the way an algorithm function (
89.5%).
In general, the results showed that the game assisted
the students to get a deeper understanding of the AI
search algorithms and the way they operate in an
entertaining way. Moreover, approximately (89.5%)
of the students stated that the game can provide them
a new way of thinking about AI search algorithms.
Finally, the majority of students (84.2%) suggested
the game to be integrated in the course curriculum
and be used by the next year students.
5 CONCLUSIONS
The educational games can offer various
possibilities for learning. In this paper we present an
educational computer game based on Pacman that
aims to assist the students to learn the artificial
intelligence search algorithms in an entertaining,
interactive and motivating way. During the game,
students can observe the behaviour of the search
algorithms and graphical annotated depictions of
them, through algorithm visualizations.
Visualizations can demonstrate the operational
functionality of algorithms and are designed in line
with the principles of student’s active learning.
Various learning activities require of students to
apply specific search algorithms in various example
cases with or without the assistance and the
feedback of the game. An extended evaluation study
was conducted in real classroom conditions and
revealed quite promising results. The results indicate
that the educational Pacman game is an effective
way to enhance students’ motivation and help them
to deeper understand AI search algorithms.
As future work, a bigger scale evaluation will be
designed to provide a more complete insight of the
learning efficiency of the game and also evaluate
specific educational capabilities such as the
feedback and assistance offered to learners.
Furthermore, a learning analytics module will be
developed to record students learning actions while
playing and analyse them with the aim to extract
knowledge from them. Exploring this direction is a
key aspect of our future work.
REFERENCES
Anderson, L. W., Krathwohl, D. R., & Bloom, B. S.
(2001). A taxonomy for learning, teaching, and
assessing: A revision of Bloom's taxonomy of
educational objectives. Allyn & Bacon.
Baecker, R. (1998). Sorting out sorting: A case study of
software visualization for teaching computer science.
Software visualization: Programming as a multimedia
experience, 1, 369-381.
An Educational Game for Teaching Search Algorithms
135

Bayliss, J. D. (2007). The effects of games in CS1-3. In
Microsoft Academic Days Conference on Game
Development in Computer Science Education,. 59-63.
Bloom, B.S. (1956). Taxonomy of educational objectives
(Vol. 1). New York: David McKay Company.
Chang, W. C., Chiu, Y. D., & Li, M. F. (2008). Learning
Kruskal’s Algorithm, Prim’s Algorithm and Dijkstra’s
Algorithm by board game. In Advances in Web Based
Learning-ICWL 2008 (pp. 275-284). Springer Berlin
Heidelberg.
Connolly, T. M., Boyle, E. A., MacArthur, E., Hainey, T.,
& Boyle, J. M. (2012). A systematic literature review
of empirical evidence on computer games and serious
games. Computers & Education, 59(2), 661-686.
Cronbach, L. J. (1951). Coefficient alpha and the internal
structure of tests. psychometrika, 16(3), 297-334.
De Gloria, A., Bellotti, F., & Berta, R. (2014). Serious
Games for education and training. International
Journal of Serious Games, 1(1).
DeNero, J., & Klein, D. (2010). Teaching introductory
artificial intelligence with pacman, In Proc. of the
EAAI Symposium.
Eagle, M., & Barnes, T. (2008). Wu's castle: teaching
arrays and loops in a game. In ACM SIGCSE Bulletin
(Vol. 40, No. 3, pp. 245-249). ACM.
Gibson, B., Bell, T. (2013, November). Evaluation of
games for teaching computer science. In Proceedings
of the 8th Workshop in Primary and Secondary
Computing Education (pp. 51-60). ACM.
Hansen, S., Narayanan, N. H., & Hegarty, M. (2002).
Designing educationally effective algorithm
visualizations. Journal of Visual Languages &
Computing, 13(3), 291-317.
Hartness, K. (2004). Robocode: using games to teach
artificial intelligence. Journal of Computing Sciences
in Colleges, 19(4), 287-291.
Hatzilygeroudis, I., Grivokostopoulou, F., & Perikos, I.
(2012). Using game-based learning in teaching CS
algorithms. In Teaching, Assessment and Learning for
Engineering (TALE), 2012 IEEE International
Conference on (pp. H2C-9). IEEE.
Hundhausen, C. D., Douglas, S. A., & Stasko, J. T. (2002).
A meta-study of algorithm visualization effectiveness.
Journal of Visual Languages & Computing, 13(3),
259-290.
Lee, M. H., & Rößling, G. (2010). Integrating categories
of algorithm learning objective into algorithm
visualization design: a proposal. In Proceedings of the
fifteenth annual conference on Innovation and
technology in computer science education (pp. 289-
293). ACM.
Levitin, A., Papalaskari, M. A. (2002). Using puzzles in
teaching algorithms. In ACM SIGCSE Bulletin (Vol.
34, No. 1, pp. 292-296). ACM.
Ma, T., Xiao, X., Wee, W., Han, C. Y., & Zhou, X.
(2014). A 3D Virtual Learning System for STEM
Education.In Virtual, Aug-mented and Mixed Reality.
Applications of Virtual and Augmented Reality (pp.
63-72). Springer International Publishing.
Markov, Z., Russell, I., Neller, T., & Zlatareva, N. (2006,
October). Pedagogical possibilities for the N-puzzle
problem. In Frontiers in Education Conference, 36th
Annual (pp. 1-6). IEEE.
Michael, D. R., & Chen, S. L. (2005). Serious games:
Games that educate, train, and inform. Muska &
Lipman/Premier-Trade.
Mihail, R. P., Goldsmith, J., Jacobs, N., & Jaromczyk, J.
W. (2013, July). Teaching graphics for games using
Microsoft XNA. In Computer Games: AI, Animation,
Mobile, Interactive Multimedia, Educational &
Serious Games (CGAMES), 2013 18th International
Conference on (pp. 36-40). IEEE.
Naps, T. L., Rößling, G., Almstrum, V., Dann, W.,
Fleischer, R., Hundhausen, C., ... & Velázquez-
Iturbide, J. Á. (2002, June). Exploring the role of
visualization and engagement in computer science
education. In ACM SIGCSE Bulletin (Vol. 35, No. 2,
pp. 131-152). ACM.
Papastergiou, M. (2009). Digital game-based learning in
high school computer science education: Impact on
educational effectiveness and student motivation.
Computers & Education, 52(1), 1-12.
Parberry, I., Roden, T., & Kazemzadeh, M. B. (2005).
Experience with an industry-driven capstone course on
game programming. ACM SIGCSE Bulletin, 37(1), 91-
95.
Russell, S. J., & Norvig P. (2003). Artificial Intelligence
A Modern Approach. Second Edition. Prentice Hall,
Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey.
Shabanah, S. S., Chen, J. X., Wechsler, H., Carr, D., &
Wegman, E. (2010). Designing computer games to
teach algorithms. In Information Technology: New
Generations (ITNG), 2010 Seventh International
Conference on (pp. 1119-1126). IEEE.
Sosnowski, S., Ernsberger, T., Cao, F., & Ray, S. (2013).
SEPIA: A Scalable Game Environment for Artificial
Intelligence Teaching and Research. In Fourth AAAI
Symposium on Educational Advances in Artificial
Intelligence.
Sung, H. Y., & Hwang, G. J. (2013). A collaborative
game-based learning approach to improving students'
learning performance in science courses. Computers &
Education, 63, 43-51.
Taylor, M. (2011). Teaching reinforcement learning with
mario: An argument and case study. In Proceedings of
the 2011 AAAI Symposium Educational Advances in
Artificial Intelligence.
Wong, D., Zink, R., and Koenig, S. (2010). Teaching
artificial intelligence and robotics via games. In
Proceedings of the 2010 AAAI Symposium
Educational Advances in Artificial Intelligence.
Wu, W. H., Hsiao, H. C., Wu, P. L., Lin, C. H., & Huang,
S. H. (2012). Investigating the learningtheory
foundations of gamebased learning: a meta
analysis. Journal of Computer Assisted Learning,
28(3), 265-279.
CSEDU 2016 - 8th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
136
