
A Serious Game to Improve Students’ Skills in Global Software
Development
David Valencia
1
, Aurora Vizcaíno
1
, Juan Pablo Soto
2
and Mario Piattini
1
1
Alarcos Research Group, University of Castilla-La Mancha, Ciudad Real, Spain
2
Department of Mathematics, University of Sonora, Hermosillo, Mexico
Keywords: Serious Games, Global Software Development.
Abstract: In recent years, companies have been forced to change their business model, due to the phenomenon of
globalization. Software development companies are no exception, and have attempted to join the global
market so as to be able to hire labor in other countries, seeking to reduce costs, increase productivity and
gain competitive advantages. This is known as Global Software Development (GSD). To perform this
practice, companies require developers who possess knowledge and skills for solving problems that arise
due to geographical, temporal and cultural distance. Traditional methods for teaching students or employees
how to work in GSD environments are usually expensive, and require much effort. This is where serious
games can play a key role, as they are educational games that allow for the acquisition of knowledge and
skills at a low cost. This article presents a serious game with which some of the competencies needed in
GSD can be acquired. The game simulates scenarios that usually occur in the overall development of a
software project, so that the user can become aware of the problems concerning GSD and gain some
experience in solving these problems.
1 INTRODUCTION
Many areas such as defense, education, health,
policy, emergency management, engineering, etc.
require people with proper training, who possess the
knowledge, skills and abilities needed to
successfully perform their job. Traditional teaching
methods are often costly and require a lot of
preparation time, which is why "Serious Games" are
increasingly being introduced. Serious games are
designed in such a way that their main purpose is not
the entertainment of the user, but rather his or her
training in a certain area (Michael and Chen, 2005).
This does not mean that the game cannot be
enjoyable, but the entertainment derived from the
game is designed to educate, so that the learning
experience of the player becomes fun (Guenaga et
al., 2013). Some of the distinctive features of these
kinds of games is that they are oriented towards
skills training, the understanding of complex
processes and the simulation of situations that occur
in real life (Coster, 2013; Marcano, 2008).
In the area of software development,
globalization has led many companies to undertake
the development of their products in a distributed
way, with that process being conducted by different
teams, even from different countries. This new
development paradigm is known as "Global
Software Development" (Herbsleb and Moitra,
2001); it brings with it a lot of additional problems
in comparison to traditional software development.
These include the delocalization of equipment,
which involves problems of communication,
coordination and control, as well as issues arising
from cultural differences between the different
teams (Vízcaino et al., 2014). Those problems often
hinder understanding between project participants,
especially when they must use a common language.
When those taking part are not using their native
language, misunderstandings that affect
communication and coordination of work may
occur; these could pose a risk for the project
(Monasor et al., 2009). Another important aspect is
trust among those involved in GSD. Mutual trust is
necessary for people to be able to cooperate and
work with each other and a lack in this key
commodity can cause the breakdown of coordination
efforts between remote teams. That makes it
necessary for people working in the GSD to possess
competencies over and above those required in
traditional software development.
470
Valencia, D., Vizcaino, A., Soto, J. and Piattini, M.
A Serious Game to Improve Students’ Skills in Global Software Development.
In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Computer Supported Education (CSEDU 2016) - Volume 1, pages 470-475
ISBN: 978-989-758-179-3
Copyright
c
2016 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

In general, it is difficult to find a suitable method
for teaching these skills, given that lectures are
insufficient. Other methods, such as that described in
(Deiters et al., 2011), in which students located in
different countries carry out a software development
project, are costly and complex to coordinate.
To ease the problems that often arise in GSD, a
serious game that allows the user to acquire the
skills required for the GSD area is proposed. By
playing a game, a global software development
project will be simulated, so that students can
become aware of the problems involved in GSD, and
gain some experience when it comes to solving these
issues.
2 SERIOUS GAMES AS A
LEARNING TOOL
The educational paradigm is currently undergoing a
major shift, moving from teacher-centered
knowledge transfer to a new concept that focuses on
the student; one that is based on the acquisition of
certain competencies by the student that are key to
his or her professional development. In recent years,
these competencies are being incorporated into both
compulsory education and higher education
(Guenaga, et al., 2013). This is when the concept of
serious games gains relevance, as it represents a new
way to acquire these skills.
Serious games can be applied to all levels of
education, inside and outside the classroom, from
children to seniors, as well as to a wide variety of
areas. The potential of serious games as a learning
tool has been recognized for its ability to balance the
entertainment, interactivity and replayability of the
typical games with the aim of reaching a given
educational objective. Moreover, the serious games
approach focuses on learning as a difficult, yet
rewarding challenge, aiming thus to increase the
commitment of the players.
According to Dale’s cone of learning (Dale,
1969) (Figure 1), learning outcomes increase from
top to bottom. Learning by simulating a real
experience (bottom part of Dale’s cone) can improve
understanding of what is being learned more than
learning through reading or hearing can (top part of
Dale’s cone). Dale claims that users could remember
90 percent of what they learn by simulation. Thus, in
order to create a highly efficient learning tool, with
controlled risk and budget in actual practice,
simulation with serious games is the most interesting
method.
Figure 1: Dale’s cone of learning (Dale, 1969).
Some serious games developed for very specific
areas (military, health and education) are described
below:
A. Military
The first games created were based on combat and
fighting. For example, board games like Chaturanga
and Hei Wei, both about 4000 years old, were games
designed to develop strategies for battles. It was not
until 1996, with the appearance of the game Marine
Doom, that the potential of games was appreciated.
This game is a modified version of the game Doom
II (Riddell, 1997). Rather than it being kept as a first
person shooting game, more realistic weapons were
introduced; tasks that encouraged the learning of the
proper sequence of attack were included, such as
conservation of ammunition, effective
communication, giving orders and teamwork.
In recent years, the United States Army has been
exploring the use of serious games as a way to treat
post-traumatic stress disorder in its soldiers (Farocki
and Virilio, 2011).
B. Health
When it comes to health, serious games is a growing
field. Such games are based on simulation and are
used for training. For example, in 2008 in
Birmingham, young doctors were allowed to gain
experience in, and be trained for, a variety of
medical scenarios using computerized mannequins
as if they were patients. In (Graafland et al, 2012),
the authors conducted a systematic review of serious
games for teaching surgical skills and medical
knowledge. Their review included 30 serious games,
of which 17 had an educational purpose; 13 were
designed to develop skills necessary for medical
personnel. From this work they concluded that
serious games can be used to develop both technical
and non-technical skills in the surgical field.
A Serious Game to Improve Students’ Skills in Global Software Development
471

Moreover, in (Smith, 2009), the author compared
traditional teaching, for those carrying out
laparoscopic surgery, with training using virtual
reality and tools based on games. He noted that the
latter was less expensive, took less time and resulted
in fewer errors when the surgery was actually
performed. As well as these examples, there are
other games like The Virtual Dental Implant
Training Simulation (Medical College of Georgia,
2009), which was designed to help dental students in
diagnosis, decision making and training protocols.
This technology is also being studied to help in the
rehabilitation of stroke patients, as well as to assess the
cognitive abilities of adults with Alzheimer's.
C. Education
The limited use of serious games in formal
education may be related to the issues around the use
of leisure games. The games are therefore often not
effective for all students. This is due in part to
pedagogy; that is, players learn through repetition
and exploration, which contrasts with the learning of
discrete quantities of information, as can be found in
schools (Squire, 2005).
Another aspect to consider is that the formal
education system has to adhere to the knowledge and
procedures required for external examinations. This
means that games must also address these areas. For
example, some educational serious games that can be
found on the market are: 3D Networks, a serious game
whose aim is to train civil engineering students about
the risks of public works near underground networks;
and NanoMission, a serious game designed to teach
players the concepts of nanoscience through real
world practical applications.
Other interesting serious games are: Quest for oil,
a serious game for oil exploration; Cruise ship, a
game designed to train a cruise crew to respond
appropriately to varying disasters; RescueSim, a
virtual game that prepares security professionals for
real-life accidents; and SimjavaSP (Shaw and
Dermoundy, 2005), a game in which the student plays
the role of project manager and focuses on the
optimization of time, cost and quality of a software
project.
Our research is centered on the software
development process, specifically in GSD. One of
the studies which focused on this area is set out in
(Noll et al, 2014). In this work the researchers
describe a serious game that simulates a GSD
environment. The game’s objective is to provide
students with the necessary expertise to address the
problems that often arise in environments of global
development.
3 A SERIOUS GAME FOR GSD
This section focuses on describing the serious game
tool that we propose. In this game the user will play
the role of a project manager. The game is based on
the planning of a software project, where working
with people from around the world is simulated; the
user has to deal with problems that arise because of
the geographical, cultural and temporal distance that
is present in GSD. Besides being a tool to acquire a
body of knowledge, it combines the essential aspects
of a game, resulting in a more entertaining and
pleasant learning experience for the student.
A. The Game’s Requirements
The system needed to meet a number of
requirements to simulate scenarios that often occur
when working on GSD projects. A scenario consists
of a name, duration, budget, component modules
and the countries involved.
Some of the main capabilities of the game are
now described:
• The game should simulate a series of
unexpected events or problems that could
occur when participating in a GSD project.
For example, a worker is on holiday or sick,
or there is a public holiday in one of the
countries in which part of the development
team is located, or there is a problem with the
server or repository that contains the project,
etc. These events are produced randomly.
• The game should have different scenarios,
which have a variety of levels of difficulty.
The user will start with the simplest,
increasing the level of difficulty as he
progresses. In this way it is intended that
students should acquire skills gradually. In
addition, the application must allow a teacher
to customize scenarios if his intention is for
the student to practice a particular scenario.
• The game will simulate a chat, email and
telephone, so that students have to work with
both synchronous and asynchronous
communication. The application will thus
allow for the random simulation of incoming
emails, telephone calls and chats.
• The user should be able to choose from a list
of solutions whenever an unexpected event
occurs; these solutions receive a higher or
lower score depending on how appropriate
they are for solving the problem in hand.
CSEDU 2016 - 8th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
472

• The game will have a points system, which
will fluctuate depending on the number of
days remaining for the delivery of the software
and on the available budget. A bad decision by
the user when facing an unexpected event will
thus result in a greater budget loss and
reduction in days remaining than if the
decision had been properly selected.
• The user will be able to ask for help when he
is unable to overcome a particular scenario.
• The game will allow the user to modify the
data in his profile, access instructions and use
the game, as well as to see the history of his
or her score achieved at a given time.
• The user will be able to interact with virtual
employees in different scenarios. Employees
are characterized by name, country, role,
salary, email, experience and a photo that
represents them.
B. Tool
The game consists of two main subsystems, one
for students and the other for the teacher responsible
for proposing scenarios and supervising the student.
To access each subsystem both the student and the
teacher must be registered; the system therefore has
an interface for access and another for registration.
Once the student decides to play a game, the
application will show him the main game interface
(Figure 2). As can be seen, the interface is divided
into three columns. The left column contains project
information (name, budget, time remaining, the times
of the countries involved, trust among members
working in the project, etc.). It is also in this column
that students can access the configuration of the
modules that make up the project. Once the modules
are configured, the game can be started. The middle
column contains buttons to access phone, chat and
email; in addition, information related to the action
that is being executed at any one time is shown in this
same column. Finally, the column on the right shows
an image of the calendar, which can be accessed by
clicking on the image; various actions that may be
performed during the game can also be accessed by
clicking on them.
During the execution of the game, problems
which typically arise when working in GSD
environments will appear randomly before the
student; he or she must solve these as the game
progresses. At the end of each game, the system will
show the user the result obtained during the activity
(see Figure 3).
Figure 2: Game interface.
Figure 3: Information containing the outcome of the game.
Moreover, there is a subsystem that only the
teacher can access. In this subsystem the teacher can
create problems, voice calls, chats, projects, see the
results of the student's game, etc. Some of the
interfaces of the subsystem are shown below.
Figure 4: Interface used by the teacher to create a
problema.
A Serious Game to Improve Students’ Skills in Global Software Development
473
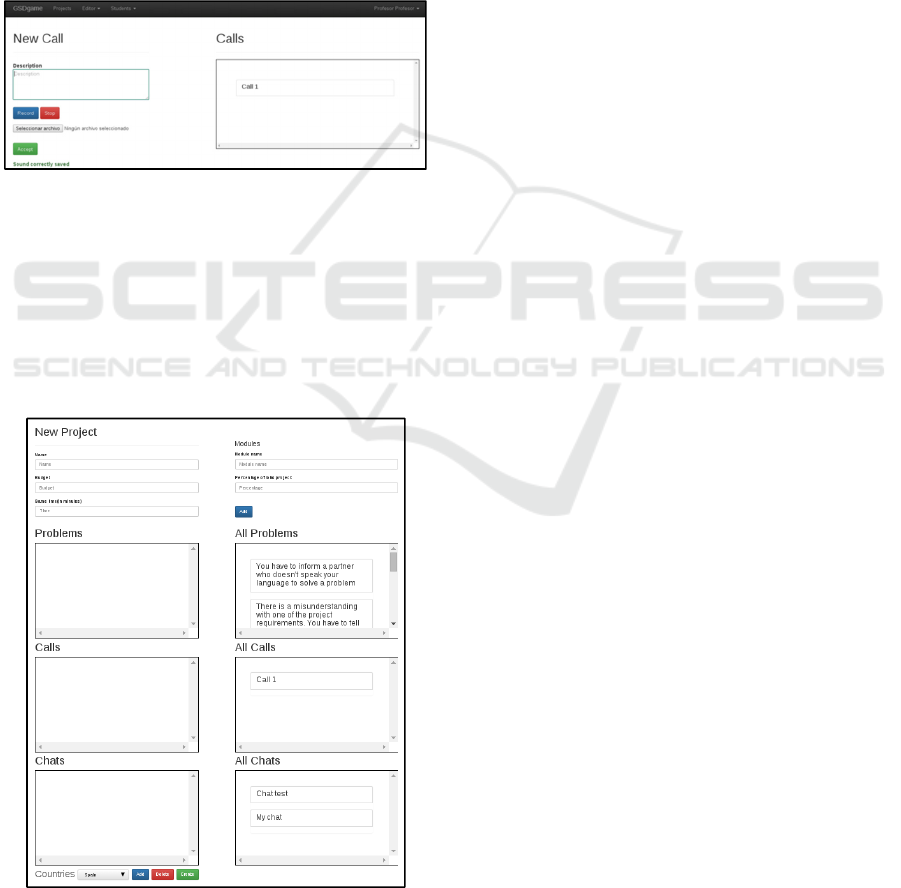
Figure 4 shows the interface used by the teacher
to create a problem. The solutions to the problem are
shown in the Solutions box. To add a solution, the
player should select the one he wants from the box
called All Solutions (bottom panel), which contains
all the available solutions. Furthermore, the
following fields must be captured: Description
(problem description), Difficulty (difficulty level of
the problem) and Type (type of problem, i.e.,
linguistic, cultural, communication or other).
Besides this, the user’s teacher has the option of
creating calls (Figure 5) and creating chats. Both
options allow the teacher to formulate specific
scenarios for each student at their discretion.
Figure 5: Interface used by the teacher to create a phone
call.
Finally, the interface used by the teacher to
create projects is shown (Figure 6). To create a new
project, the teacher must complete the general
project information: name, budget, duration,
component modules, potential problems, phone
calls, chats and countries of the participants in the
development teams.
Figure 6: Interface used by the teacher to create a Project.
4 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
WORK
This article presents a serious game that supports the
acquisition of the knowledge and skills needed in
GSD. Since it is a game, it has the advantage of
being much more affordable and entertaining than
other traditional training methods.
The game is based on the simulation of a
scenario in which a project is developed. The player
must complete all phases that make up each module.
During the development of the game a series of
problems will arise, and the user should be able to
reduce the likelihood of them getting worse, by
choosing certain actions available to him.
The tool is in currently the process of validation
and testing by experts in serious games through a
quality model based on serious games (García-
Mundo et al, 2015), and there are some proposals for
future work. One of these is to adapt the tool to
allow multiple users with different roles to play
between them, offering the possibility of also
training participants in leadership skills.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work is partially supported by GINSENG
(TIN2015-70259), GLOBALIA (PEII-2014-038-P),
Consejería de Educación y Ciencia, Junta de
Comunidades de Castilla-La Mancha and SDGear
(TSI-100104-2014-4), ITEA 2 (Call 7), co-funded
by the“Ministerio de Industria, Energía y
Turismodentro del Plan Nacional de Investigación
Científica, Desarrollo e Innovación Tecnológica”
2013-2016.
REFERENCES
Coster, R., 2013. A theory of fun for game design,
O’Reilly Media, 2
nd
Edition.
Dale, E., 1969. Audiovisual methods in teaching, The
Dryden Press, 3
rd
. Edition.
Deiters, C. et al., 2011. GloSE-Lab: Teaching Global
Software Engineering, International Conference on
Global Software Engineering, p. 156-160.
Farocki, P., Virilio, H., 2011. Serious games: War-Media-
Art, Hatje Cantz Publishers, p. 1705, 2011.
García-Mundo, L., Genero, M., Piattini, M., 2015.
Refinamiento de un modelo de calidad para juegos
serios, Proceeding 2do. Congreso de la Sociedad
Española para las Ciencias del Videojuego, p. 68-79,
Barcelona (Spain).
CSEDU 2016 - 8th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
474

Graafland, M., Schraagen, J., Schijven, M., 2012.
Systematic review of serious games for medical
education and surgical skills training, British Journal
of Surgery, vol. 99(10), p. 1322-1330.
Guenaga, M. et al., 2013. Serious games para el desarrollo
de competencias orientadas al empleo, VAEP-RITA,
vol. 1(1), p. 35-42.
Herbsleb, J., Moitra, D., 2001. Global software
development, IEEE Software, vol. 18(2), p. 16-20.
Noll, J. et al, 2014. GSD Sim: A Global Software
Delevopment Game, 2014 IEEE Interntional
Conference on Global Software Engineering
Workshop, p. 15-20.
Marcano, B., 2008. Juegos serios y entrenamiento en la
sociedad digital, Revista Electrónica Teoría de la
Educación: Educación y Cultura en la Sociedad de la
Información, vol. 9(3), Universidad de Salamanca.
Medical College of Georgia, 2009. Simulation helps
students learn dental implant procedures,
ScienceDaily, June, 2009.
Michael, D., Chen, S., 2005. Serious Games: Games That
Educate, Train, and Inform, Cengage Learning PTR, p.
312.
Monasor, M., Piattini, M., Vizcaíno, A., 2009. Challenges
and improvements in distributed software
development: A systematic review, Advances in
Software Engineering, p. 14.
Riddell, R., 1997. Doom goes to war – the marines are
looking for a few good games, WIRED Magazine.
Shaw K., Dermoudy, J., 2005. Engendering an empathy
for software engineering, Proceedings of the 7th
Australasian Conference on Computing Education,
vol. 42, p. 135-144.
Smith, R., 2009. Investigating the disruptive effect of
computer game technologies on medical education and
training”, Phd thesis, University of Maryland
University College.
Squire, K., 2005. Changing the game: what happens when
video games enter the classrom?, Journal of online
education, Innovate, vol. 1(6).
Vizcaíno, A., García, F., Piattini, M., 2014. Desarrollo
Global de Software, Ra-Ma.
A Serious Game to Improve Students’ Skills in Global Software Development
475
